Carbon Reduction Method for Coal-fired Power Plant Tail Gas Emission Reduction
A coal-fired power plant, exhaust gas technology, applied in the direction of separation methods, chemical instruments and methods, air quality improvement, etc., to achieve the effects of reducing environmental protection costs, saving natural gas, and saving environmental protection costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
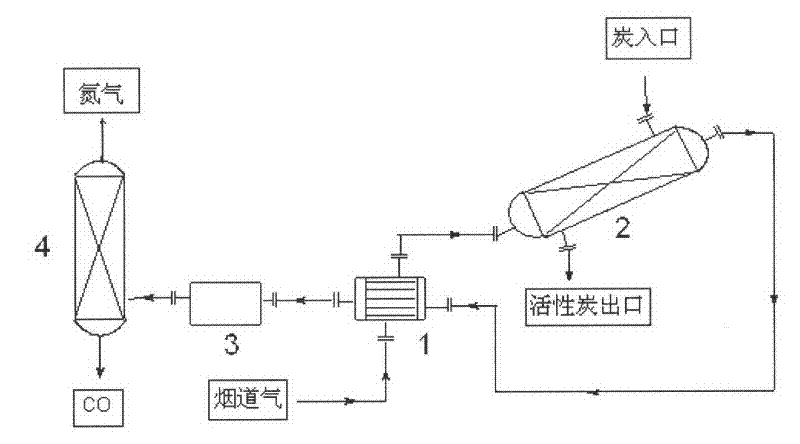
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
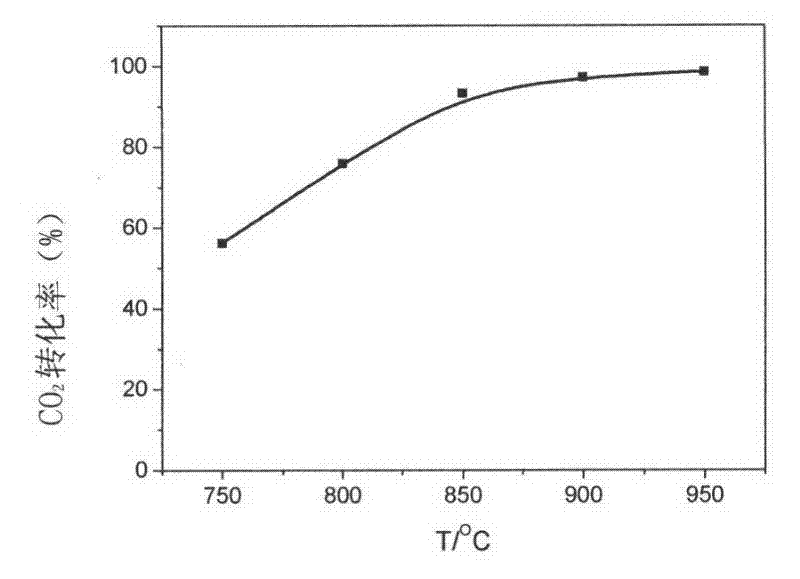
[0035] Using corn cob charcoal as raw material, simulated laboratory flue gas (CO 2 Content 10.13%, SO 2 Content 1500ppm, NO content 360ppm, the rest is N 2 ) for carbon reduction experiments. figure 2 CO in flue gas was simulated for corncob charcoal reduction reaction at different temperatures (750°C, 800°C, 850°C and 950°C). 2 The conversion rate of CO at 950°C 2 The conversion rate can reach 99%, and almost all of them are converted into CO.
[0036] 1. Gas heating up
[0037] The 500°C power plant tail gas enters the heat exchanger to exchange heat with the reactor outlet gas, and then enters the preheating section of the reactor to raise the temperature to 950°C required for the carbon reduction reaction.
[0038] 2. Reduction reaction
[0039] The carbon dioxide in the tail gas fully reacts with the charcoal filled in the reactor to generate carbon monoxide, and a small amount of SO in the tail gas is also reduced in the reactor 2 and NOx. During the reaction p...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Using coconut shell charcoal as raw material, simulated laboratory flue gas (CO 2 Content 10.13%, SO 2 Content 1500ppm, NO content 360ppm, the rest is N 2 ) to carry out the charcoal reduction experiment, and the operation steps are the same as in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Using coke as raw material, simulated laboratory flue gas (CO 2 Content 10.13%, SO 2 Content 1500ppm, NO content 360ppm, the rest is N 2 ) to carry out the charcoal reduction experiment, and the operation steps are the same as in Example 1.
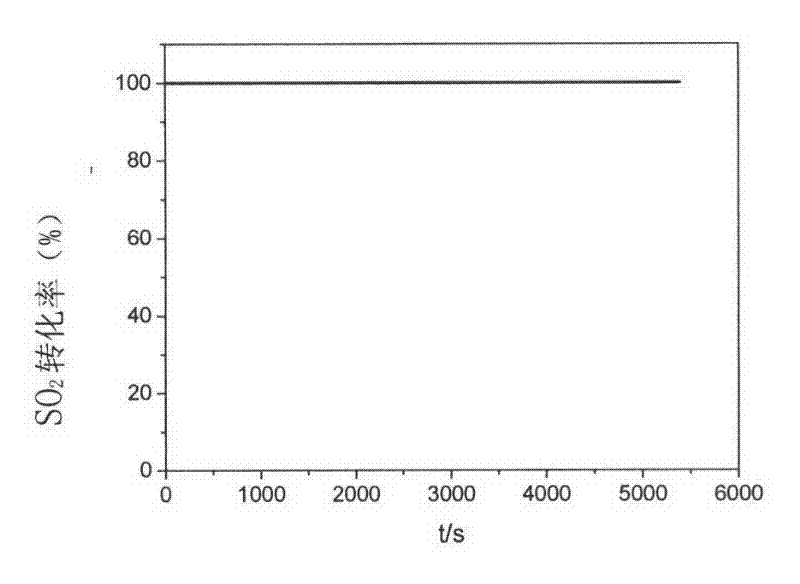
[0049] image 3 and Figure 4 shows that at 950°C SO 2 and NO are completely converted. Figure 5 Simulated CO in flue gas when coconut shell charcoal was subjected to carbon reduction reaction at different temperatures (750°C, 800°C, 850°C and 950°C). 2 The conversion rate of CO at 950°C 2 The conversion rate can reach 98.1%. Similarly, at this temperature, SO 2 and NO conversions are 100%, with image 3 and Figure 4 The results are exactly the same.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com