Method for detecting human amniotic epithelial cell molecular mechanism for in vitro immune regulation of lymphocyte
A technology of amniotic membrane epithelial cells and molecular mechanisms, applied in the field of detection of molecular mechanisms of human AECS in vitro immunosuppression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
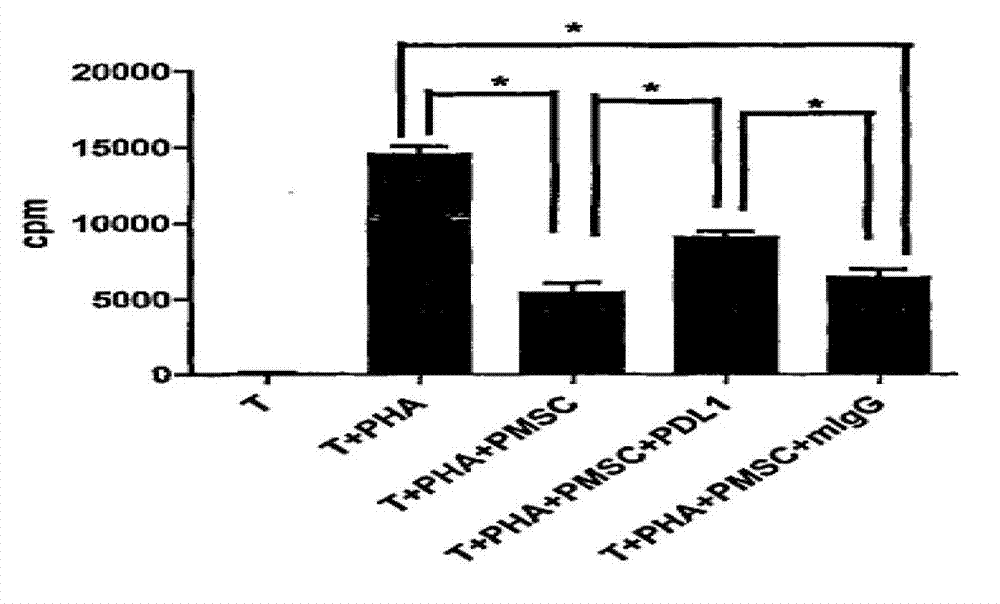
[0023] A detection method of the molecular mechanism of human AECS in vitro immunosuppressive action of the present invention, the research purpose of which is to further understand the immune regulation ability of human amnion cells and its possible effect mechanism, so as to provide the final clinical application of this technology and expand its clinical application indications Provide a theoretical basis.
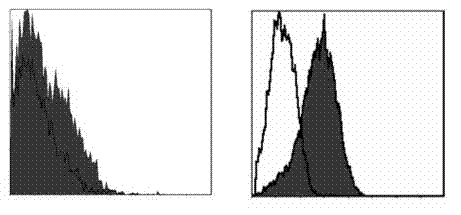
[0024] The materials and equipment used in this experiment include an inverted phase contrast microscope (Olympus, Japan), a C02 incubator (Jouan, France), a constant temperature centrifuge (Jouan, France), a flow cytometer (Beckman. Coulter, USA), culture flasks and Culture plate (Cotingcostar, USA), β liquid scintillation counter (Pharmac ia, Uppsala, Sweden), LG-DMEM medium (Hyclone), fetal bovine serum (Hyclone), trypsin (Sigma), DMEM (Gibco company), mouse anti-human PD1, CD80, CD83, CD86, CD4, CD69 cloned antibody (eBioscienee company), mouse anti-human B7H3mAb, P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com