Bevel gear based on conjugate curves and meshing pair thereof
A technology of conjugate curves and bevel gears, which is applied to gear transmissions, belts/chains/gears, components with teeth, etc., and can solve problems such as broken teeth, low load-carrying capacity of gears, and affecting reliability of gear transmission.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
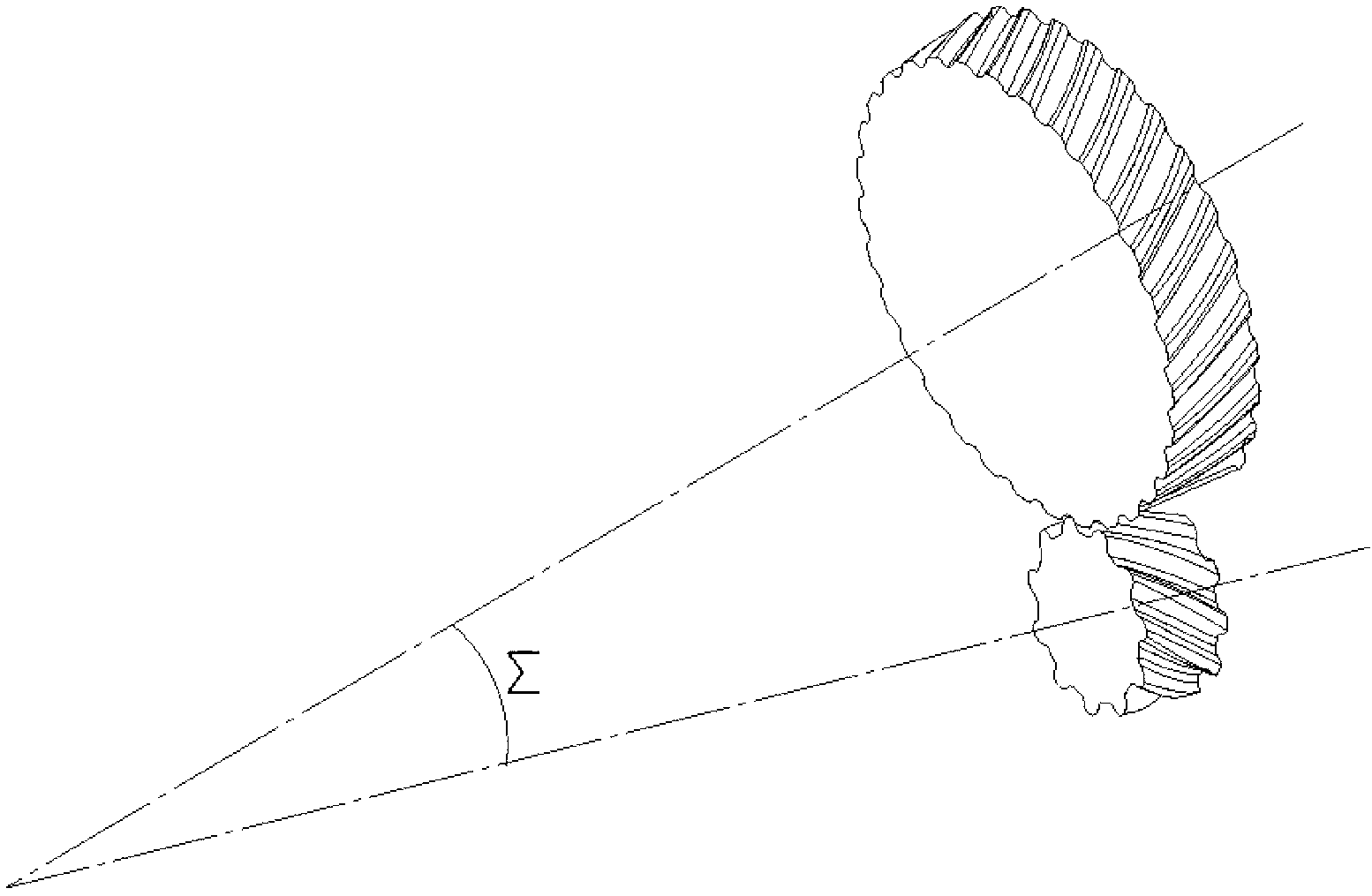
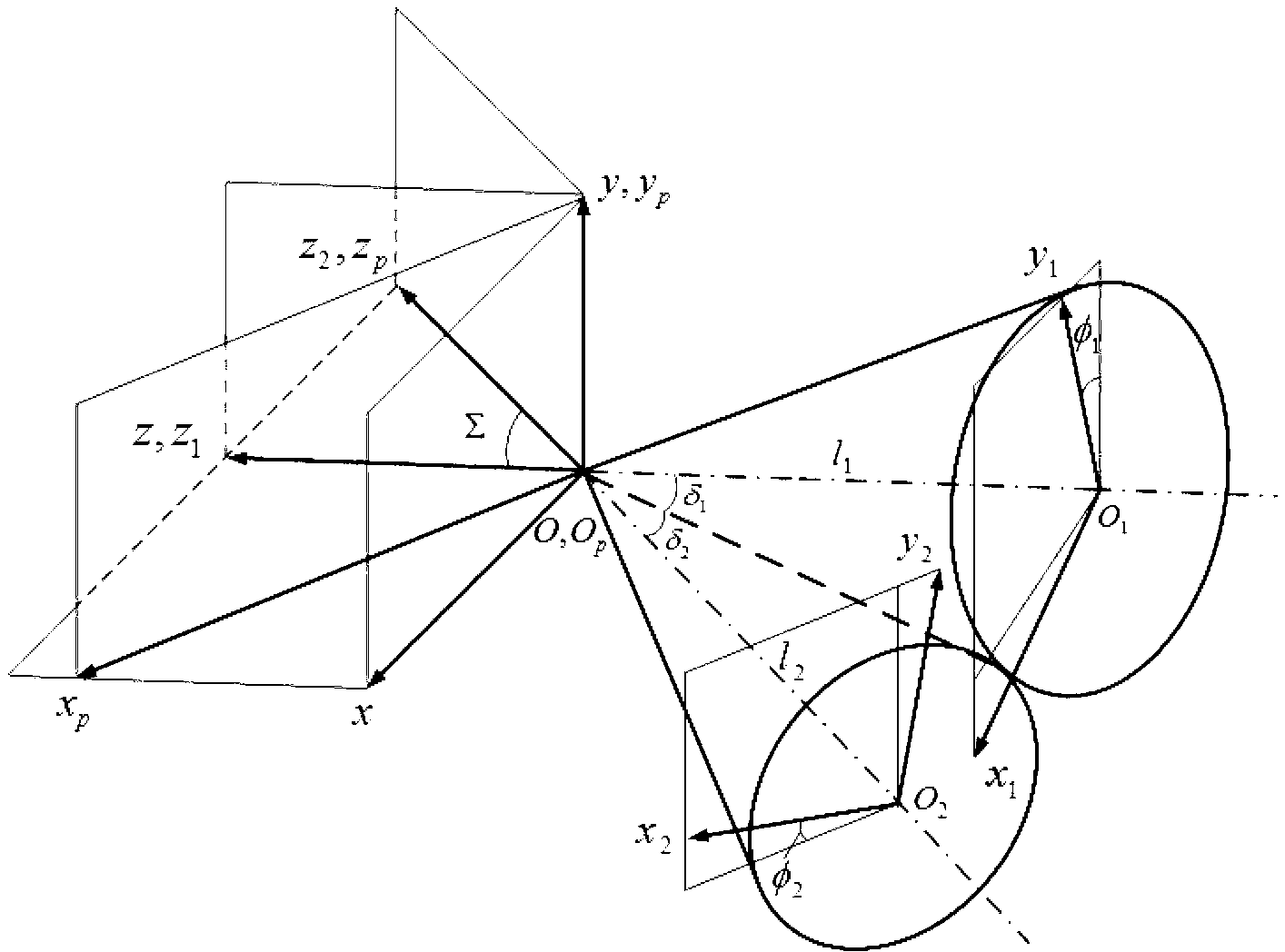
[0070] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a structural schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the bevel gear meshing pair based on the conjugate curve of the present invention. This embodiment is based on the bevel gear meshing pair of conjugate curves, including bevel gear I and bevel gear II that mesh with each other and whose tooth profile curves are all circular arcs, and the shaft angle between bevel gear I and bevel gear II is 0°< ∑≦90°, the angle of intersection between the axes of the bevel gear I and the bevel gear II in this embodiment is 10°, and the axis of the bevel gear I and the axis of the bevel gear II in this embodiment intersect in a plane.
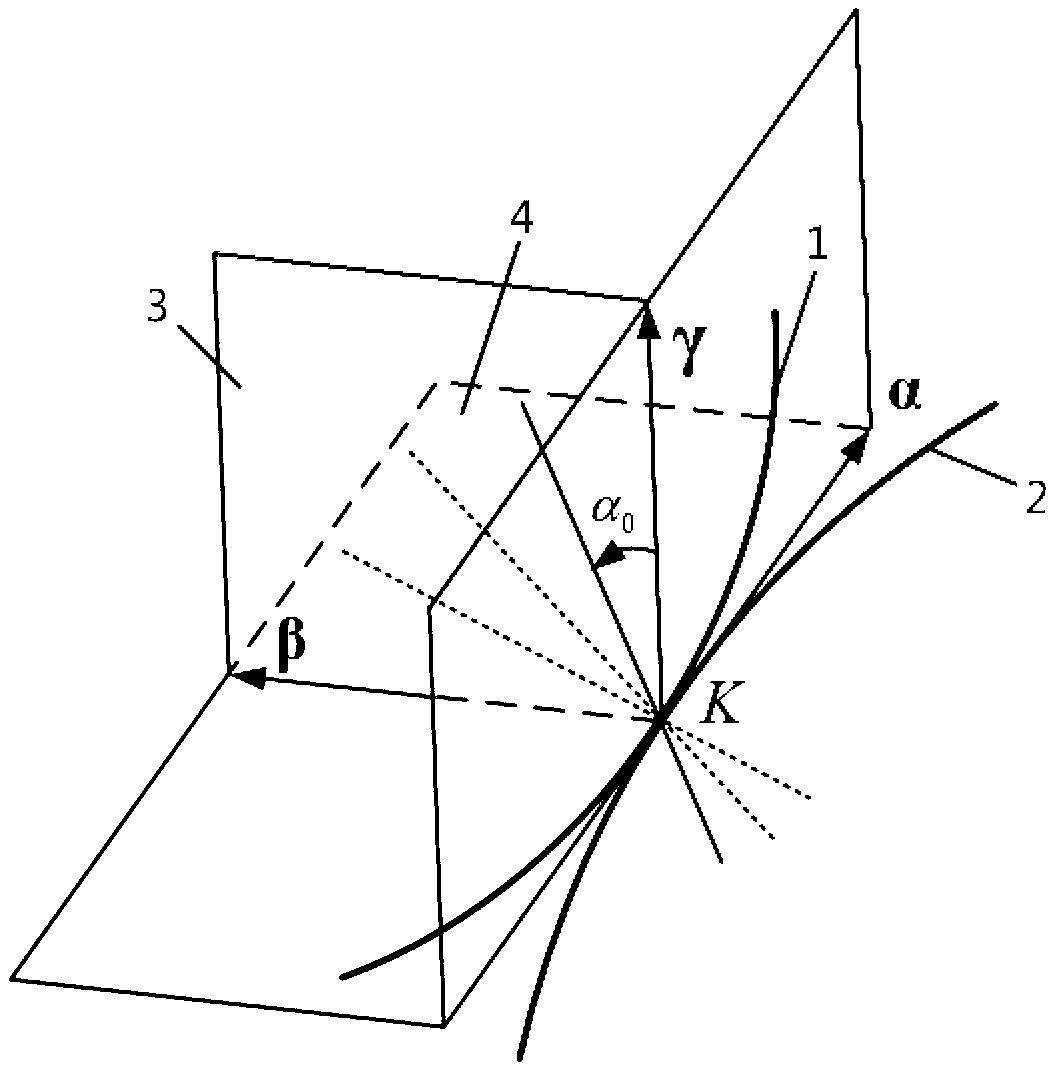
[0071] Further, there is a point contact mesh between the bevel gear I and the bevel gear II, and the tooth profile surface of the bevel gear I 1 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 1 With the tooth profile surface of bevel gear II ∑ 2 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 2 is a conjugat...
no. 2 example
[0106] Such as Figure 7 As shown, it is a structural schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the bevel gear meshing pair based on the conjugate curve of the present invention. The bevel gear meshing pair based on conjugate curves in this embodiment includes bevel gear I and bevel gear II that mesh with each other and whose tooth profile curves are all circular arcs, and the shaft angle between bevel gear I and bevel gear II is 0° <∑≤90°, the angle of intersection between the axes of the bevel gear I and the bevel gear II in this embodiment is 90°, and the axis of the bevel gear I and the axis of the bevel gear II in this embodiment intersect in a plane.
[0107] Further, there is a point contact mesh between the bevel gear I and the bevel gear II, and the tooth profile surface of the bevel gear I 1 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 1 With the tooth profile surface of bevel gear II ∑ 2 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 2 is a conjugate c...
no. 3 example
[0131] Such as Figure 8 As shown, it is a structural schematic diagram of the third embodiment of the bevel gear meshing pair based on the conjugate curve of the present invention. This embodiment is based on the bevel gear meshing pair of conjugate curves, including bevel gear I and bevel gear II that mesh with each other and whose tooth profile curves are all circular arcs, and the shaft angle between bevel gear I and bevel gear II is 0°< Σ≤90°, and the axis of bevel gear I and the axis of bevel gear II in this embodiment are staggered in space.
[0132] Further, there is a point contact mesh between the bevel gear I and the bevel gear II, and the tooth profile surface of the bevel gear I 1 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 1 With the tooth profile surface of bevel gear II ∑ 2 The contact curve Γ formed by the meshing points 2 is a conjugate curve. Preferably, the contact curve Γ 1 with contact curve Γ 2 All are smooth curves to ensure the smooth meshi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com