Method for testing the severity of an illness
An inspection method and severe disease technology, applied in the direction of disease diagnosis, biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of many measurement items and time-consuming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0059] In order to facilitate the understanding of the present invention, the present invention will be specifically described below with reference examples and examples, but the present invention is of course not limited to the examples.
reference example 1
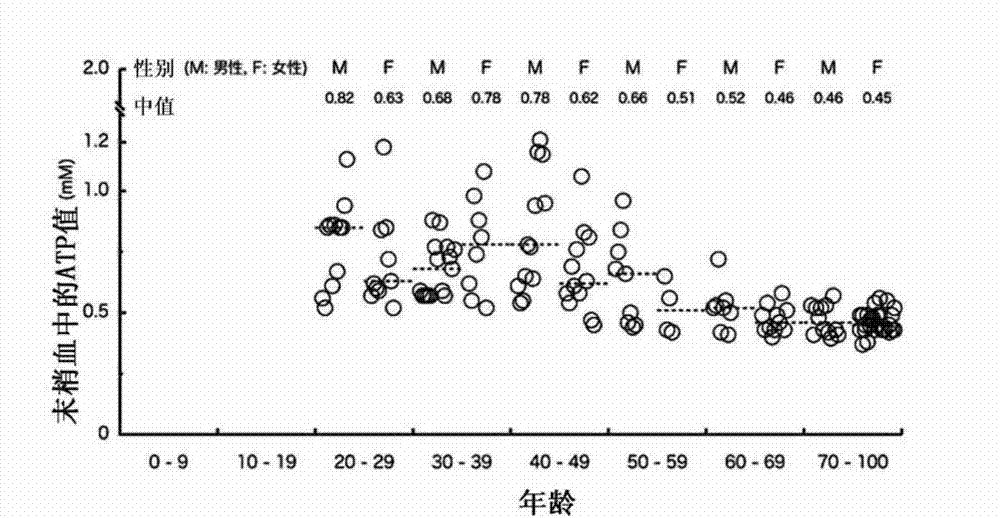
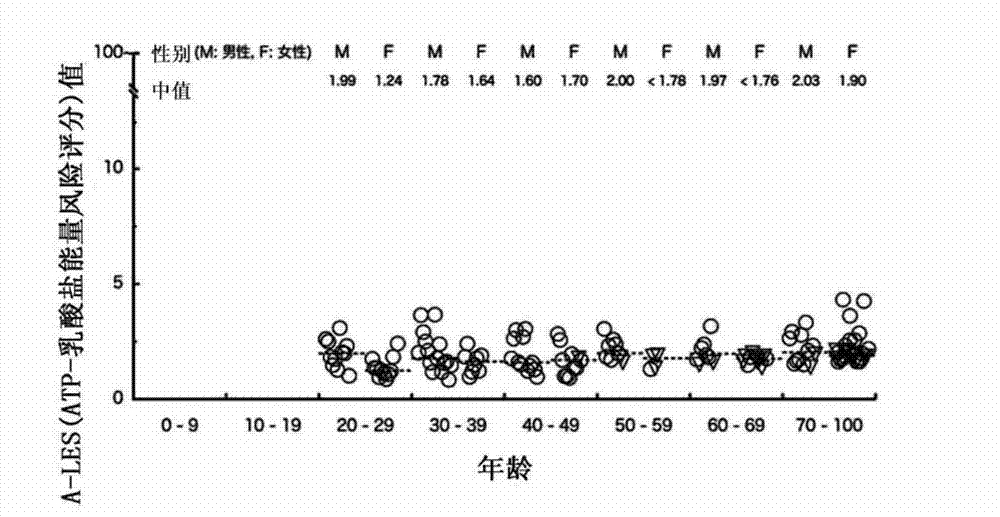
[0060] (Reference Example 1) Study on ATP Amount, Age, and Sex Distribution in Samples Derived from Healthy Persons
[0061] In this reference example, when establishing the method for examining the degree of disease severity of the present invention, in order to grasp the amount of ATP in samples derived from healthy people, a total of 139 samples were collected from 68 males and 71 females aged from their 20s to their 90s. The amount of ATP and lactic acid in the peripheral venous blood of healthy volunteers were measured.
[0062] Using the XL-ATP Kit (manufactured by Aprosyence Co., Ltd.), ATP was extracted from the sample according to the instruction manual, and the amount of ATP was measured. As the reagent for ATP extraction, the extraction reagent A (TE saturated phenol, composition: containing 69% phenol, pH 8.0), extraction reagent B (chloroform, composition: containing 99% chloroform) and sterile ultra- A reagent obtained by mixing pure water at a ratio of 3:5:5. ...
reference example 2
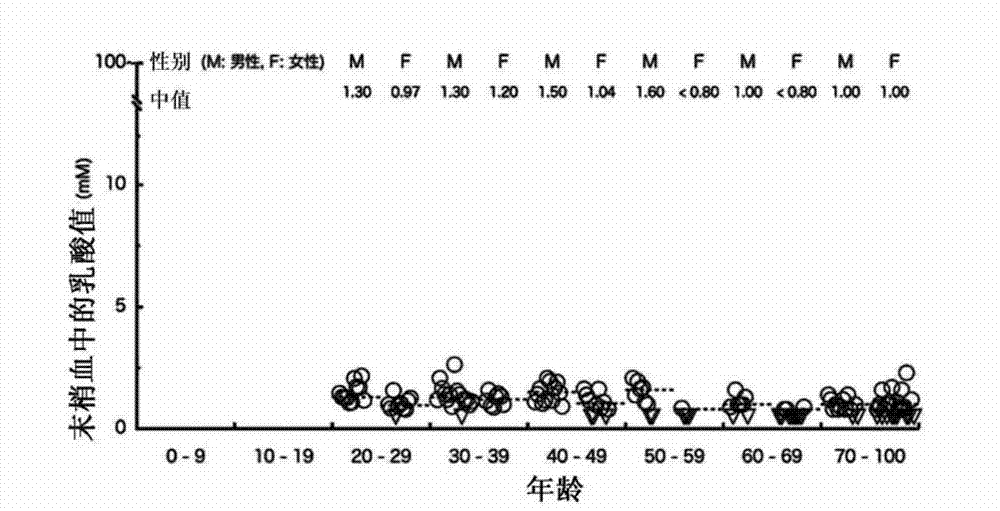
[0068] (Reference Example 2) Study on lactic acid content, age, and sex distribution in samples derived from healthy individuals
[0069] In this reference example, the amount of lactic acid in peripheral venous blood of a total of 139 healthy volunteers shown in Reference Example 1 was measured in order to grasp the amount of lactic acid in samples derived from healthy individuals. In the measurement of the amount of lactic acid, an automatic blood gas measurement device (860COT; Bayer Medical Co., Ltd.) or a simple measurement device (Lactite Pro; ARKRAY Co., Ltd.) was used to measure according to the measurement method recommended by the manufacturer.
[0070] The measured value (mM) of the amount of lactic acid in the sample derived from healthy people shown in Table 1 and Table 2 and its age and sex distribution are shown in figure 2 middle. A total of 139 healthy volunteers had no statistically significant differences in the lactic acid values of peripheral venous bl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com