Braking device for vehicles
A braking device and vehicle technology, applied in the direction of brakes, braking components, vehicle components, etc., can solve problems such as inability to boost pressure, control, and inability to perform servo pressure, so as to avoid excessive control delay, simplify the structure, and suppress excessive control. delayed effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach 〉
[0039] (Structure of vehicle brake system)
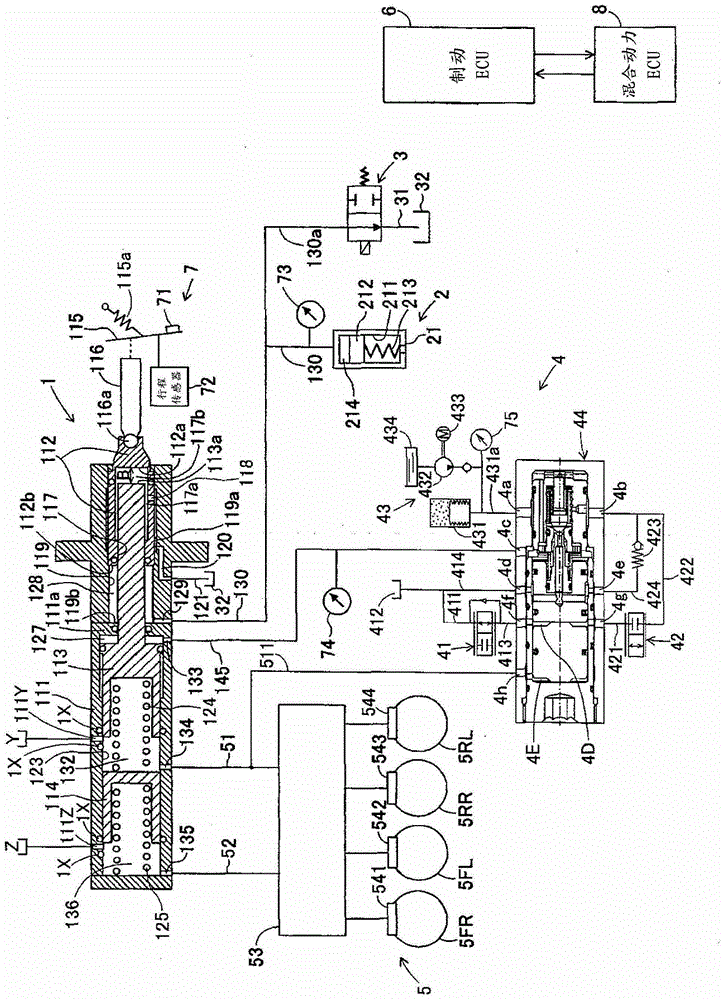
[0040] figure 1 A schematic configuration diagram of a vehicle brake device according to the present embodiment is shown. The brake device for a vehicle according to the present embodiment includes: a master cylinder 1 including master pistons 113, 114 arranged with a distance B in the advancing direction of the input piston 112, and relative to The input piston 112 slides independently along the axial direction; the reaction force generating device 2, the reaction force generating device 2 makes the reaction force chamber 128 generate a reaction pressure corresponding to the movement amount of the input piston 112; the switching valve 3, the switching valve 3 is located at Open path 31, which is branched from the liquid path 130 that communicates the reaction force chamber 128 with the reaction force generating device 2 and communicates with the reservoir 32; booster 4, which is used to generate servo pressure; wheel The brake 5 ...
no. 2 approach 〉
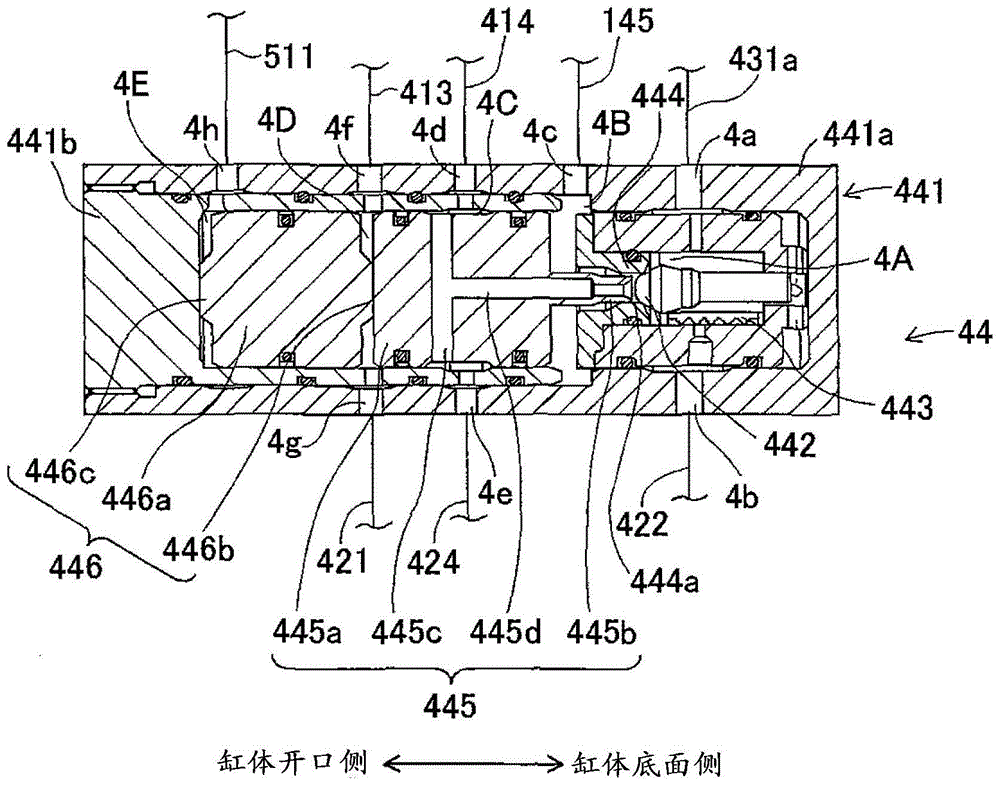
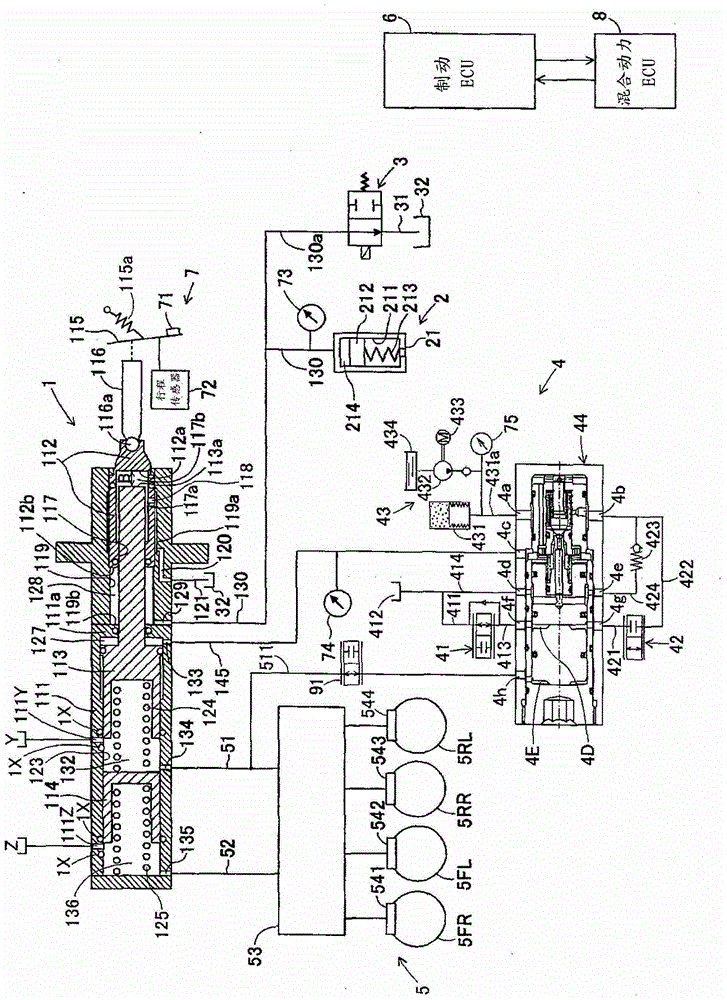
[0093] The vehicle braking device of the second embodiment is as follows: image 3 As shown, in the first embodiment, the restriction valve 91 is arranged on the piping 511 . Therefore, descriptions of other configurations are omitted.
[0094] The restriction valve 91 (corresponding to the “restriction portion”) is a normally open solenoid valve and is disposed on the piping 511 . The limit valve 91 is opened and closed according to a command from the brake ECU 6 . In the linear mode, when the pressure of the second pilot chamber 4E is too high compared with the pressure of the first pilot chamber 4D by the pressure supply unit 43 , the brake ECU 6 issues a closing command to the limit valve 91 .
[0095] In the linear mode, it is conceivable that the pressure of the second pilot chamber 4E is too high compared with the pressure of the first pilot chamber 4D. For example, the pressure of the first pilot chamber 4D suddenly drops due to control, and the pressure of the first...
no. 3 approach 〉
[0100] The vehicle braking device of the third embodiment is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, in the first embodiment, an orifice (orifice) 92 is disposed on the pipe 511 . Therefore, descriptions of other configurations are omitted.
[0101] The orifice 92 (corresponding to a “restriction portion”) is arranged on the pipe 511 and restricts the flow of the brake fluid in the pipe 511 . The orifice 92 suppresses a sudden flow of the brake fluid in the pipe 511 by making it difficult for the brake fluid to leak all at once. Specifically, the orifice 92 slows down the depressurization speed of the second pilot chamber 4E due to the pressurization operation of the ABS 53 . By preventing the sudden drop in pressure of the second pilot chamber 4E, it is possible to allow time margin for the pressure control of the first pilot chamber 4D with respect to the drop in pressure of the second pilot chamber 4E. For example, in the control to increase the pressure of the first pilot chamb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com