Efficient blood oxygen saturation detection circuit
A detection circuit and saturation technology, applied in the electronic field, can solve the problems of low blood oxygen saturation accuracy, increased measurement cost, limited range, etc., and achieve the effects of high sensitivity, simple circuit, and easy integration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
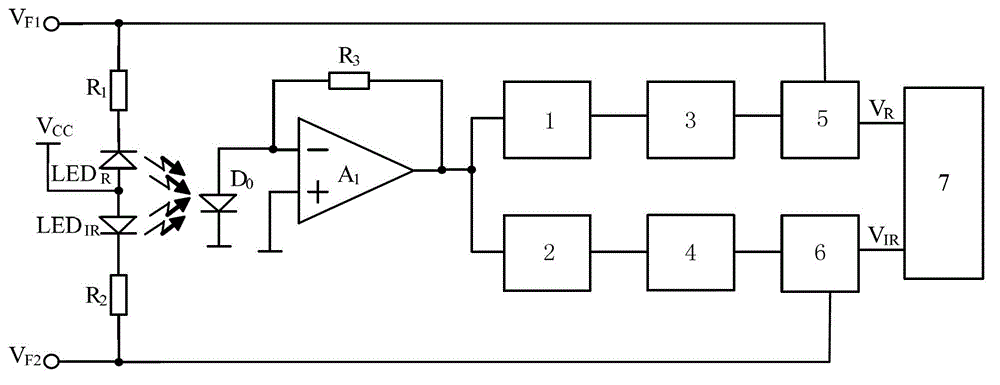
[0059] see figure 1 , a high-efficiency blood oxygen saturation detection circuit, including: a first resistor R 1 , the second resistor R 2 and photodiode D 0 ,
[0060] The first resistor R 1 One end of the input first sinusoidal signal V F1 , the first resistor R 1 The other ends are respectively connected to the first light-emitting diode LED R The cathode and the first frequency converter 5, the first light-emitting diode LED R The anode is connected to the power supply Vcc; the second resistor R 2 One end of the input second sinusoidal signal V F2 , the second resistor R 2 The other ends are respectively connected to the second light-emitting diode LED IR The cathode and the second frequency divider 6, the second light-emitting diode LED IR The anode of the power supply Vcc;
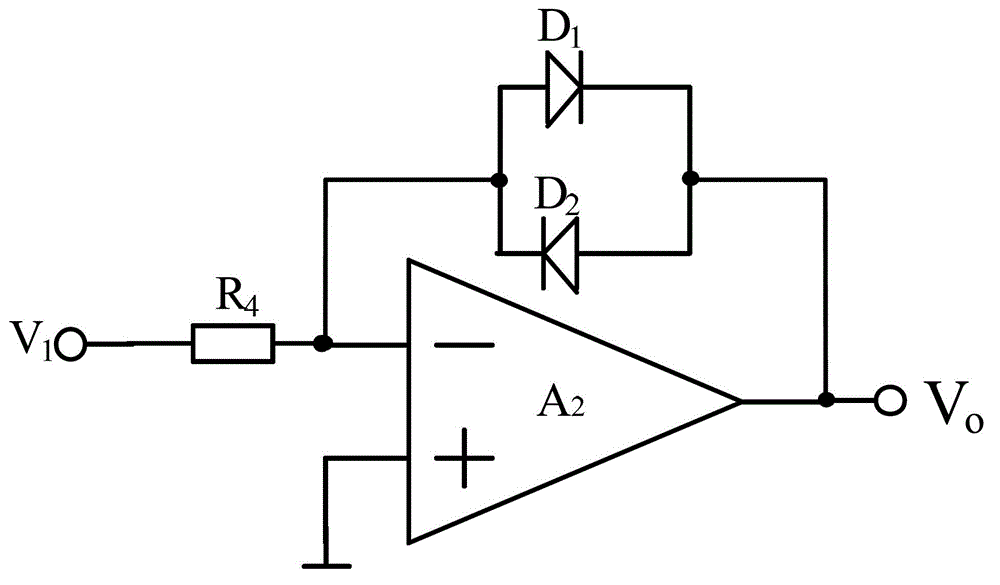
[0061] Photodiode D 0 The cathode is grounded, and the anode is respectively connected to the third resistor R 3 and the first operational amplifier A 1 The negative terminal of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0119] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is only the specific structure of the frequency difference device, see Figure 6 , the frequency differencer includes: a fifth resistor R 5 and the sixth resistor R 6 ,
[0120] Fifth resistor R 5 One end of the input second signal source V 2 , the fifth resistor R 5 The other ends are respectively connected to the third diode D 3 anode of the fourth diode D 4 cathode of the third diode D 3 cathode and fourth diode D 4 The anode is connected to the third operational amplifier A at the same time 3 The output of V 0 , output photoplethysmography; the third diode D 3 Parallel capacitance C;
[0121] Sixth resistor R 6 One end of the input third signal source V 3 , the sixth resistor R 6 The other ends are respectively connected to the third diode D 3 The anode of the fourth diode D 4 cathode and the third op amp A 3 The negative polarity input terminal; the third operational amplifier A 3 The positiv...
Embodiment 3
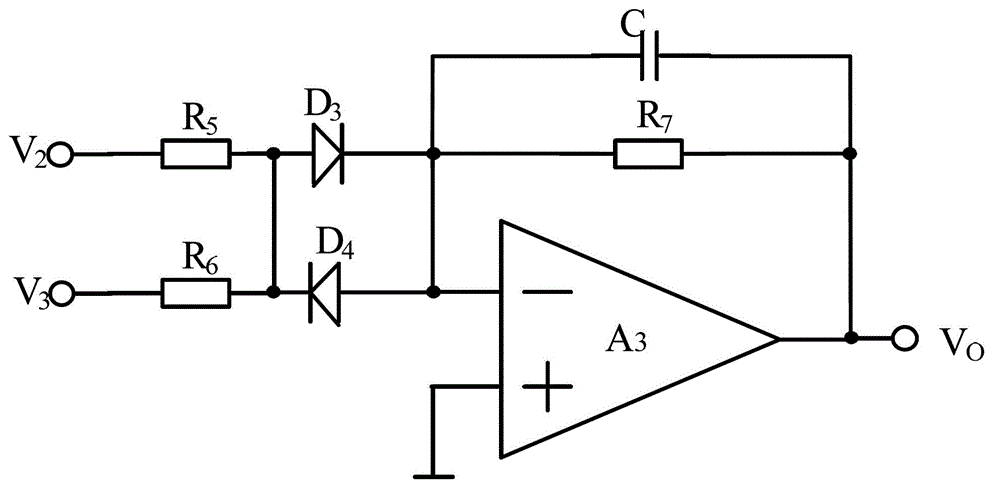
[0151] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is only the specific structure of the frequency difference device, see Figure 7 , the frequency differencer includes: including: a fifth resistor R 5 and the sixth resistor R 6 ,
[0152] Fifth resistor R 5 One end of the input second signal source V 2 , the fifth resistor R 5 The other end of the seventh resistor R 7 One end of the seventh resistor R 7 The other end of the third operational amplifier A 3 The output of V 0 , output photoplethysmography;
[0153] Sixth resistor R 6 One end of the input third signal source V 3 , the sixth resistor R 6 The other ends are connected to the seventh resistor R 7 One end and the third operational amplifier A 3 The negative polarity input terminal; the third operational amplifier A 3 The positive polarity input terminal is grounded.
[0154] by right Figure 7 The analysis shows that the frequency difference device is an inverting operational amplifier type...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com