Patents
Literature
258 results about "Log amplifier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
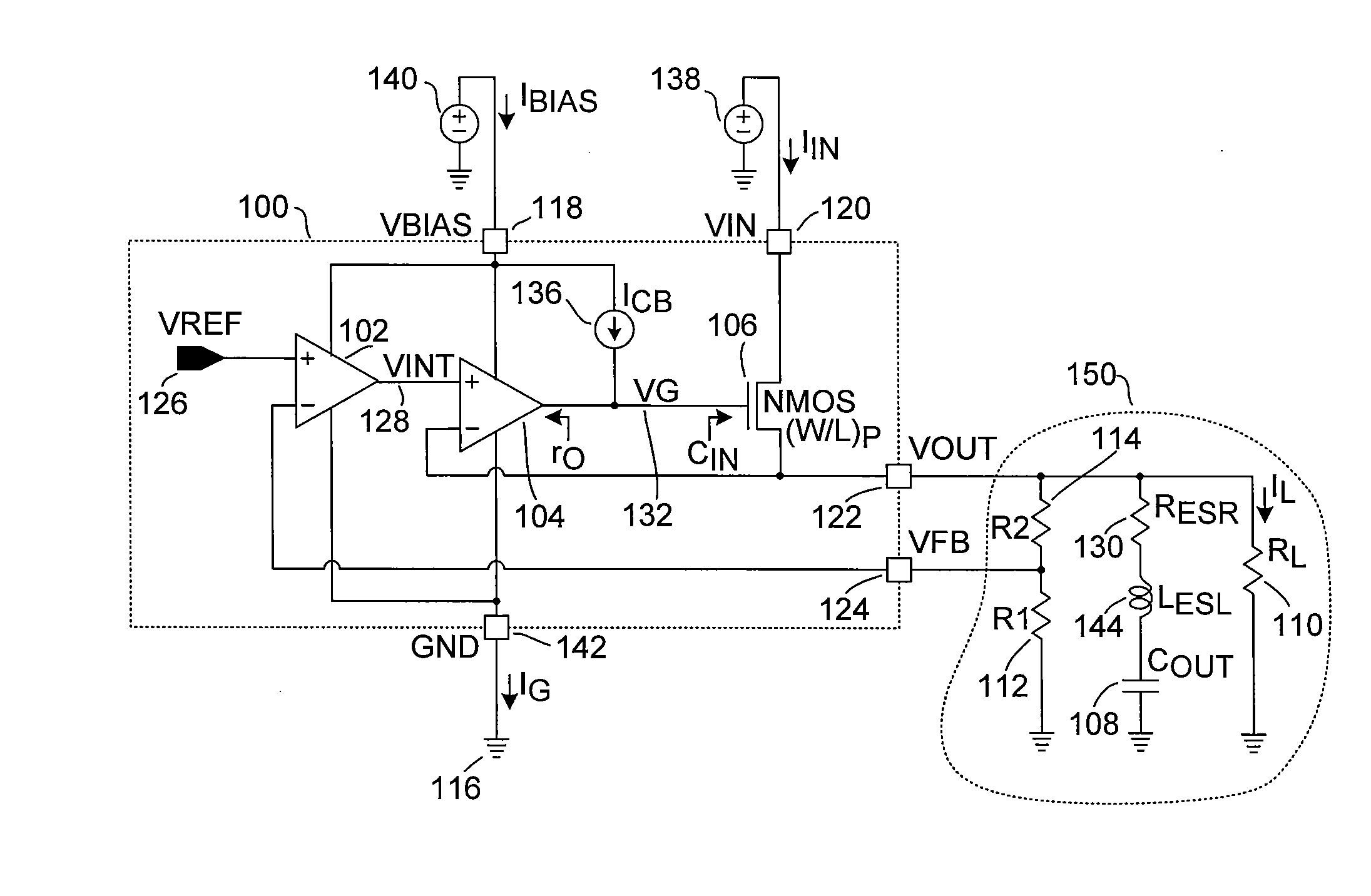
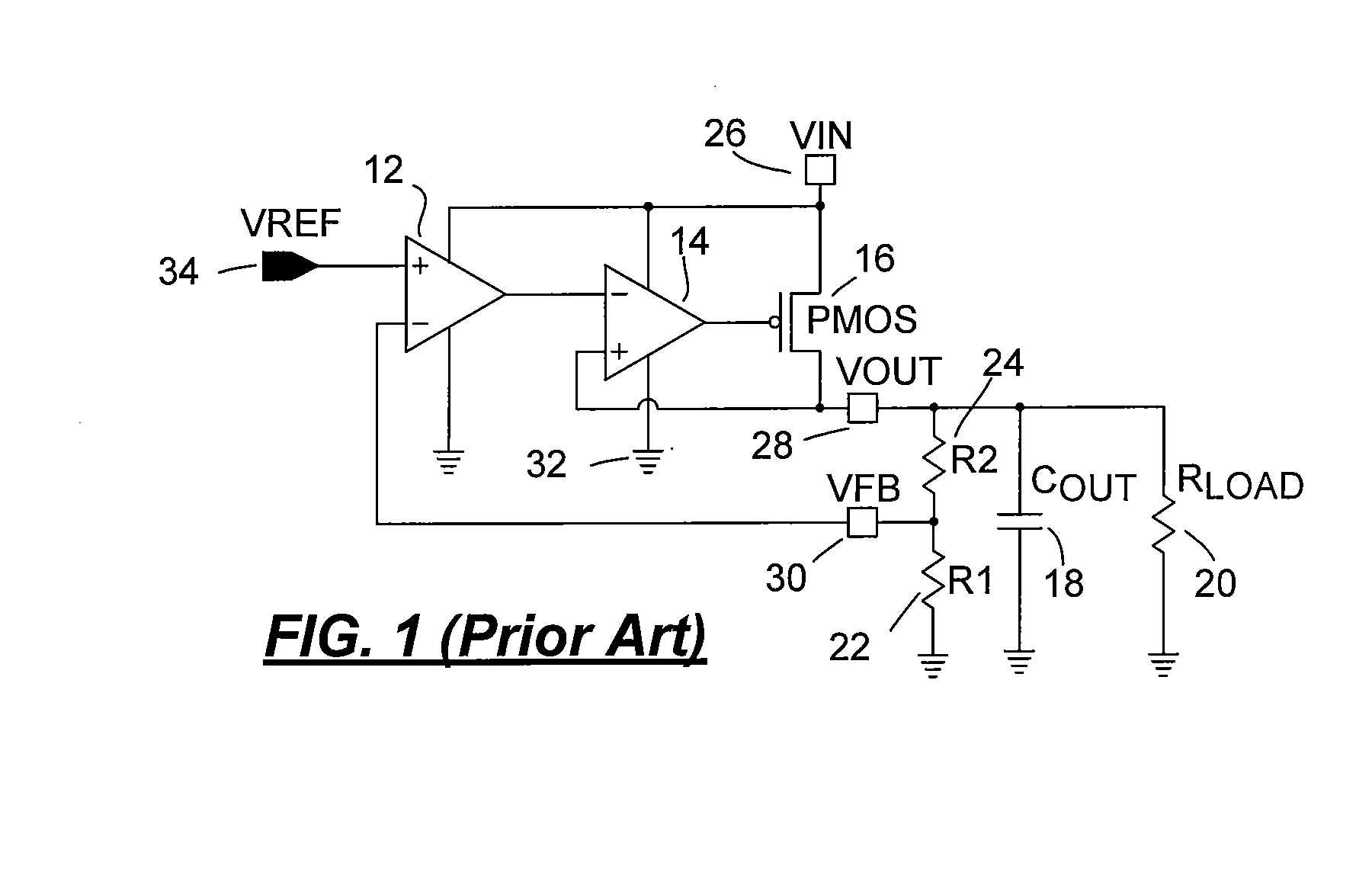
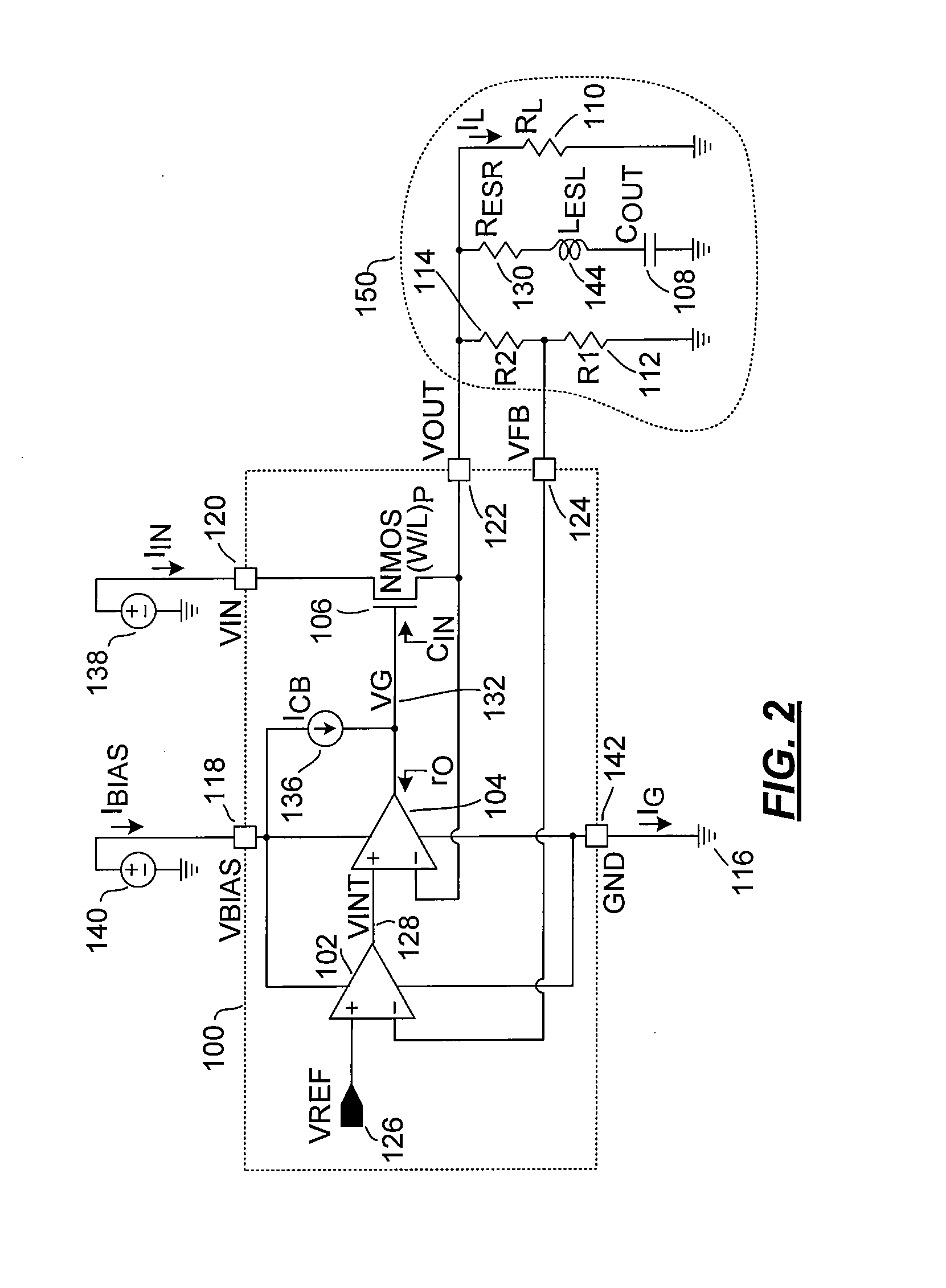
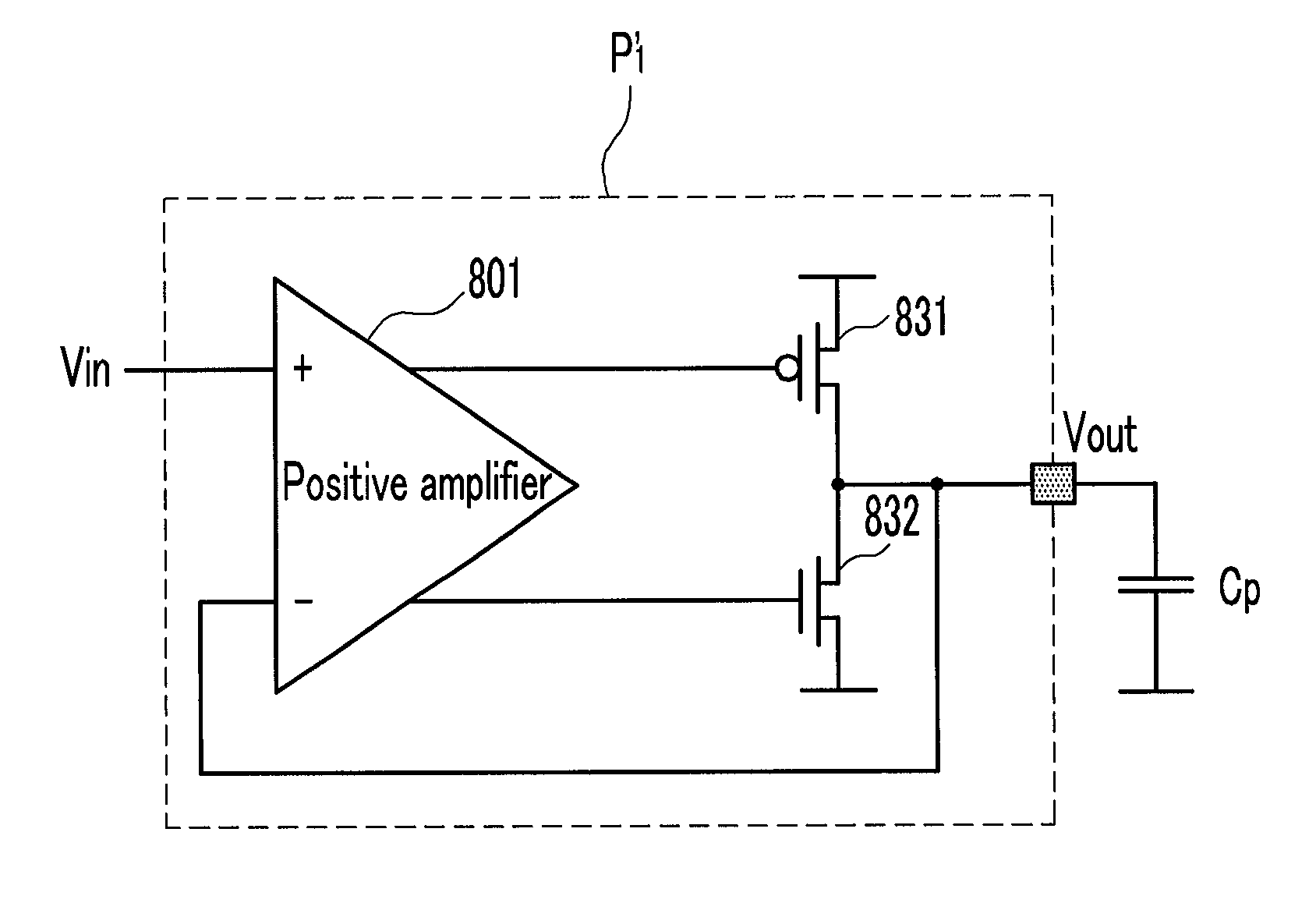
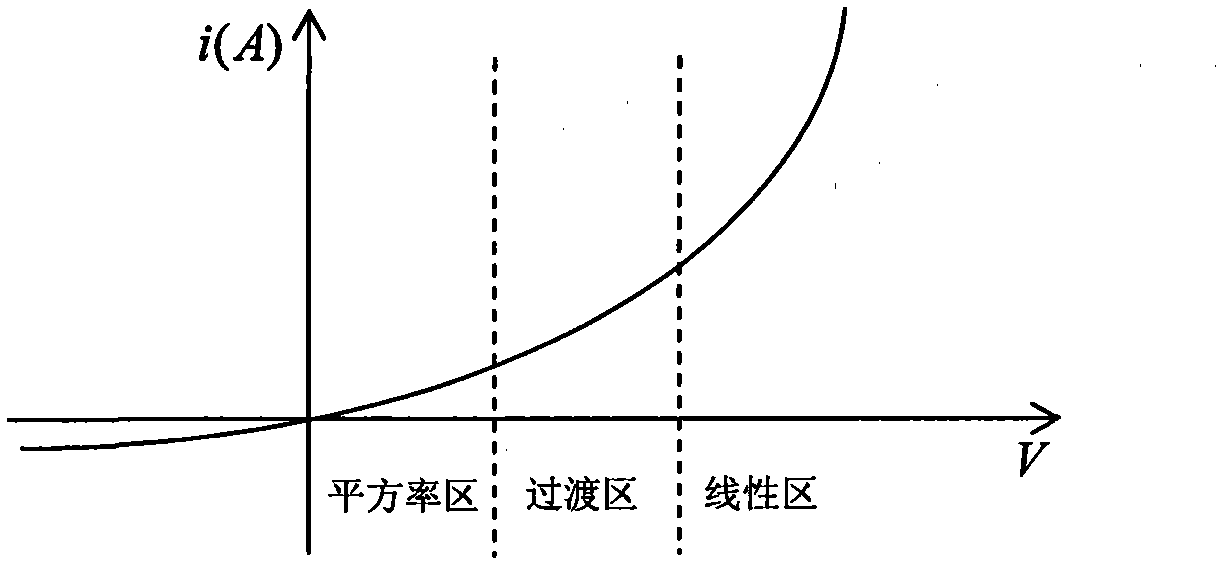
A log amplifier is an amplifier for which the output voltage Vₒᵤₜ is K times the natural log of the input voltage Vᵢₙ. This can be expressed as, Vₒᵤₜ=Kln(Vᵢₙ/Vᵣₑf) where Vref is the normalization constant in volts and K is the scale factor. The logarithm amplifier gives an output voltage which is proportional to the logarithm of applied input voltage. To design a logarithm amplifier circuit, high performance op-amps like LM1458, LM771, LM714 are commonly used and a compensated logarithm amplifier may include more than one.
Electrosurgical generator
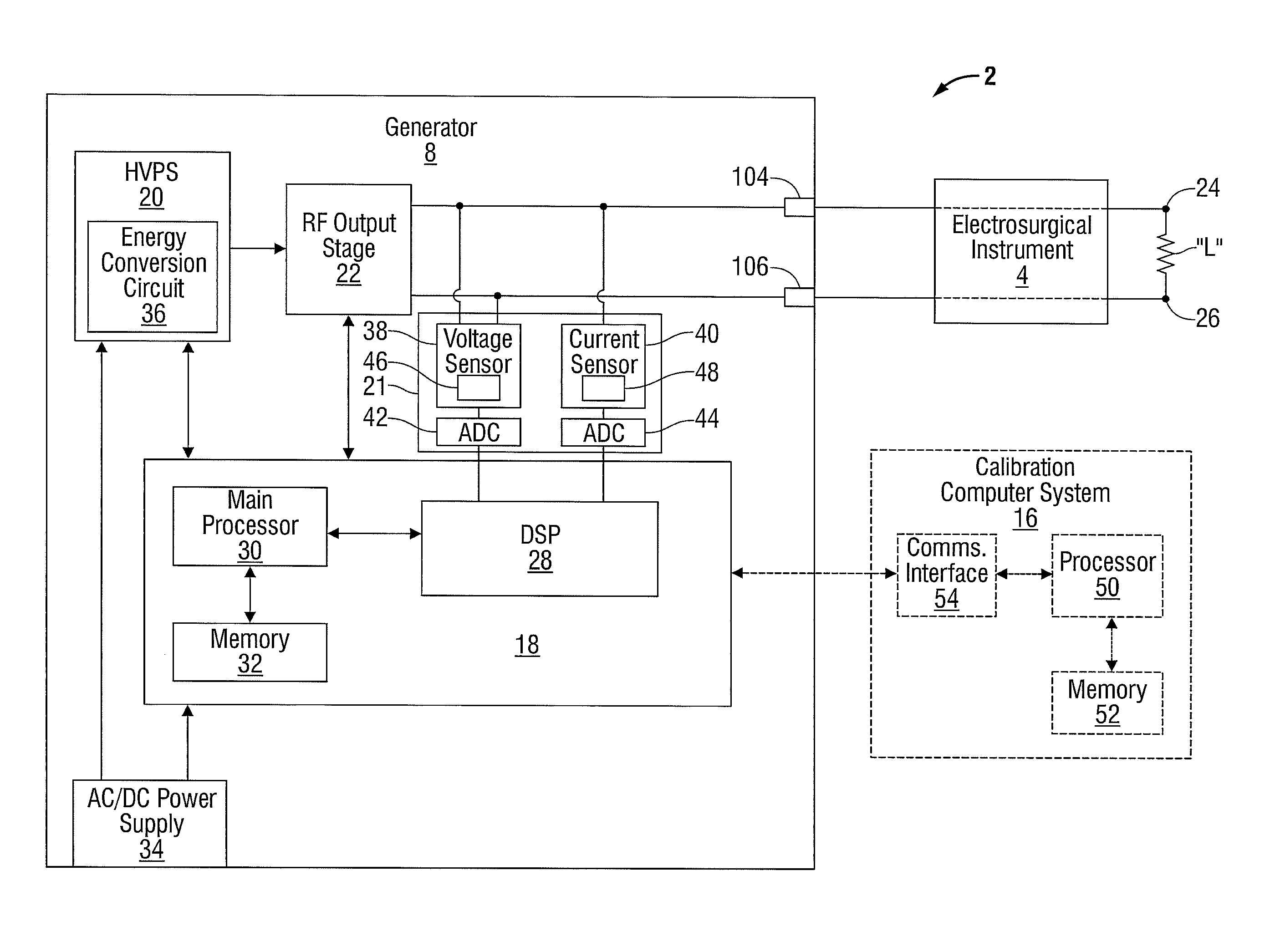
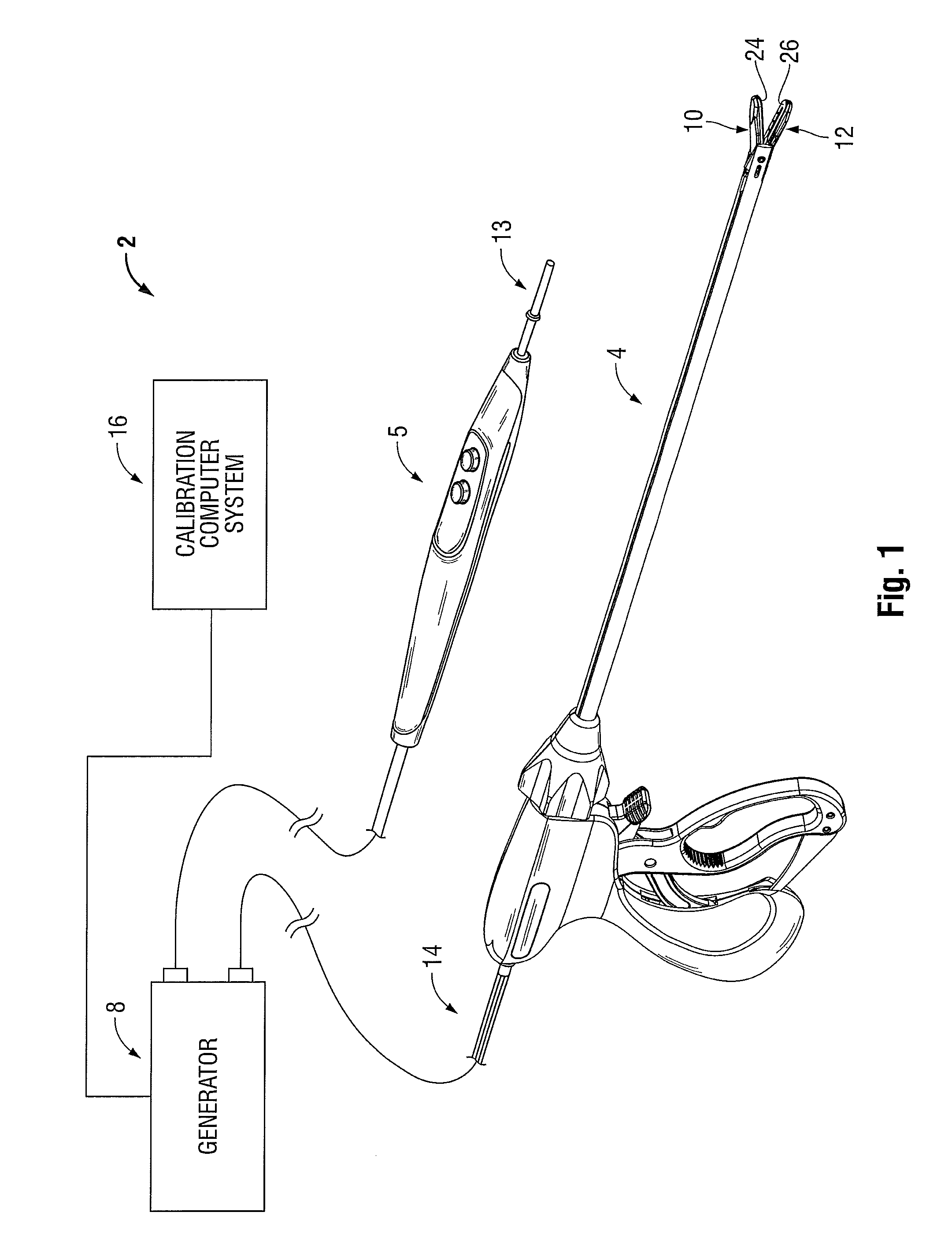
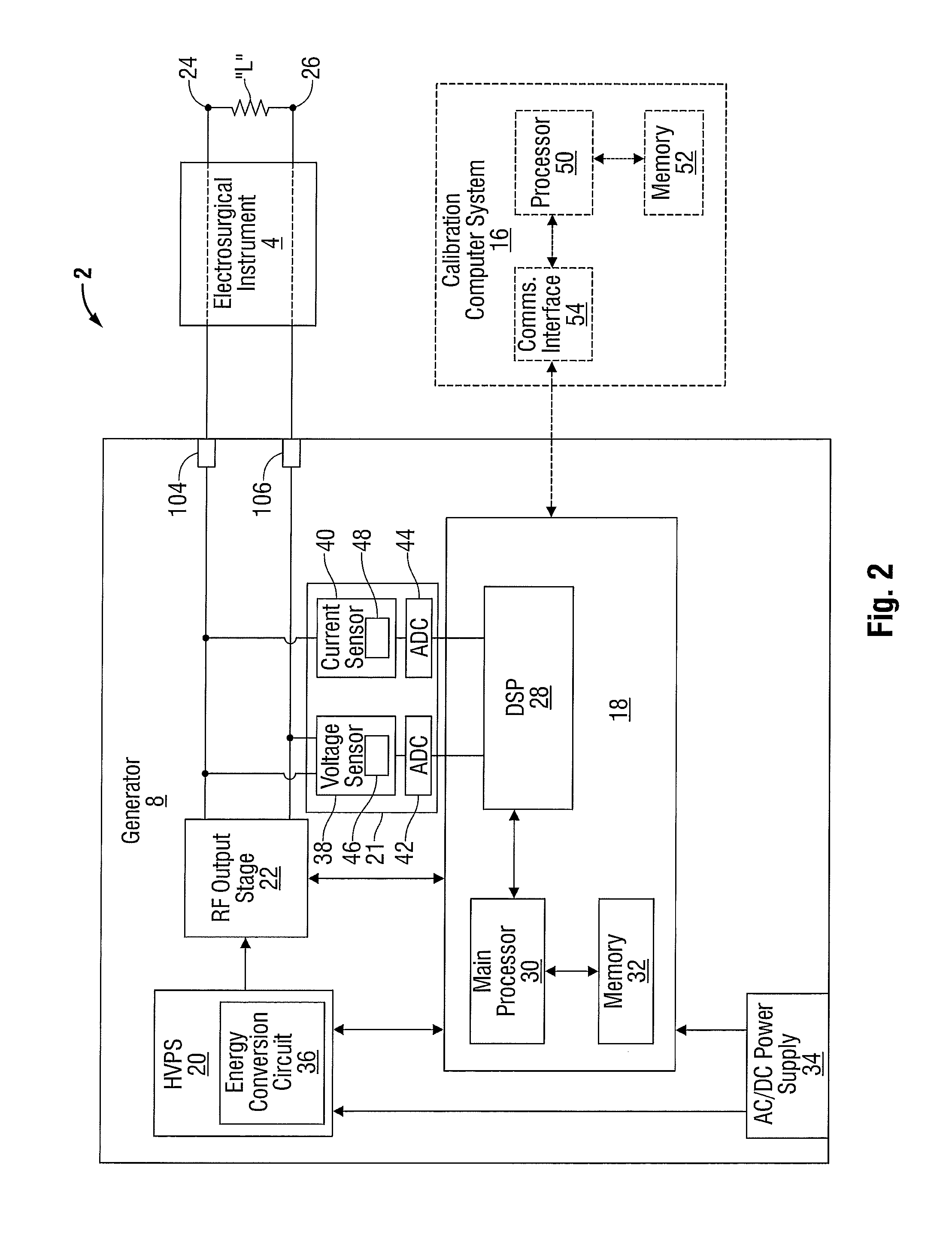
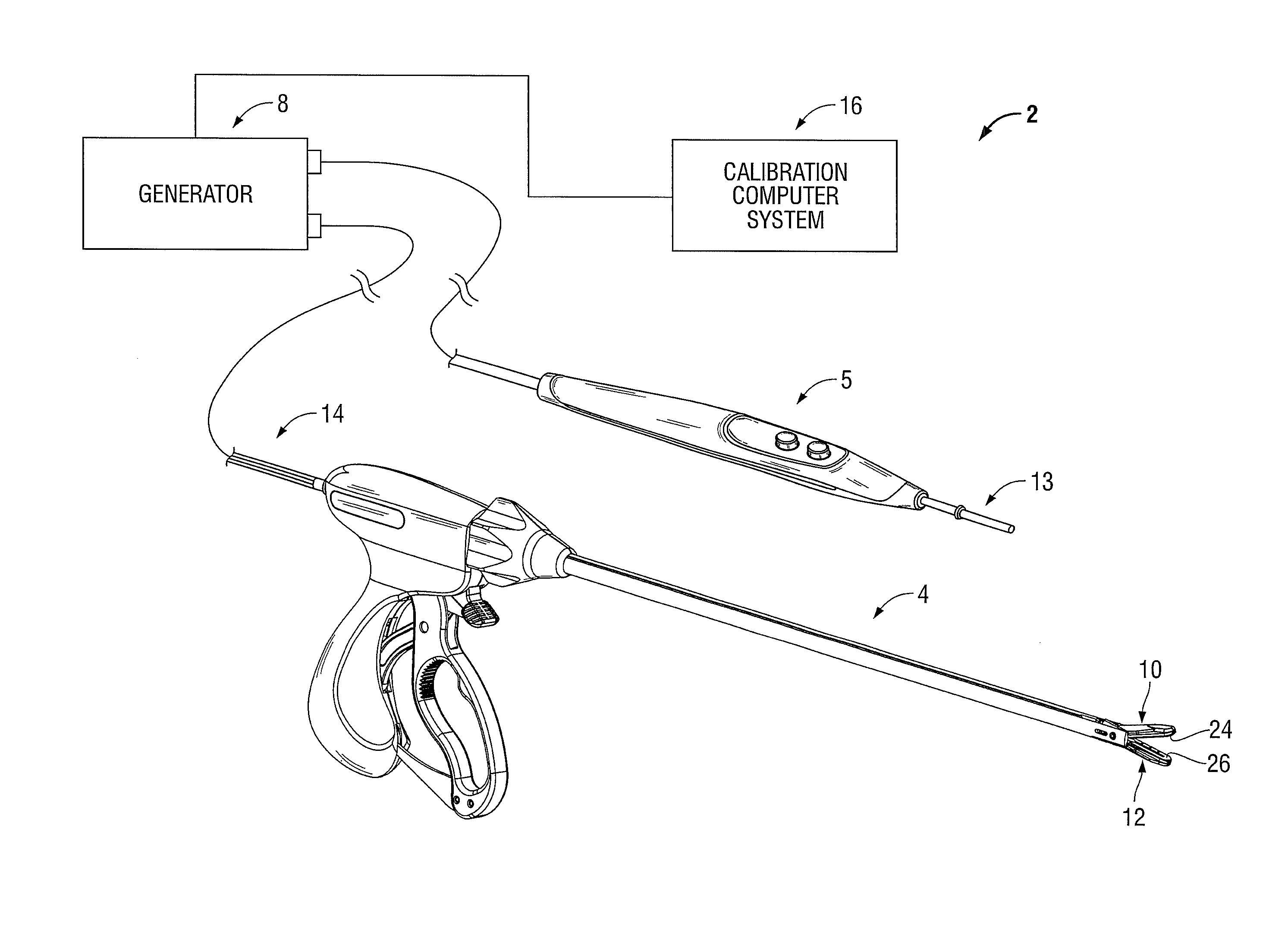
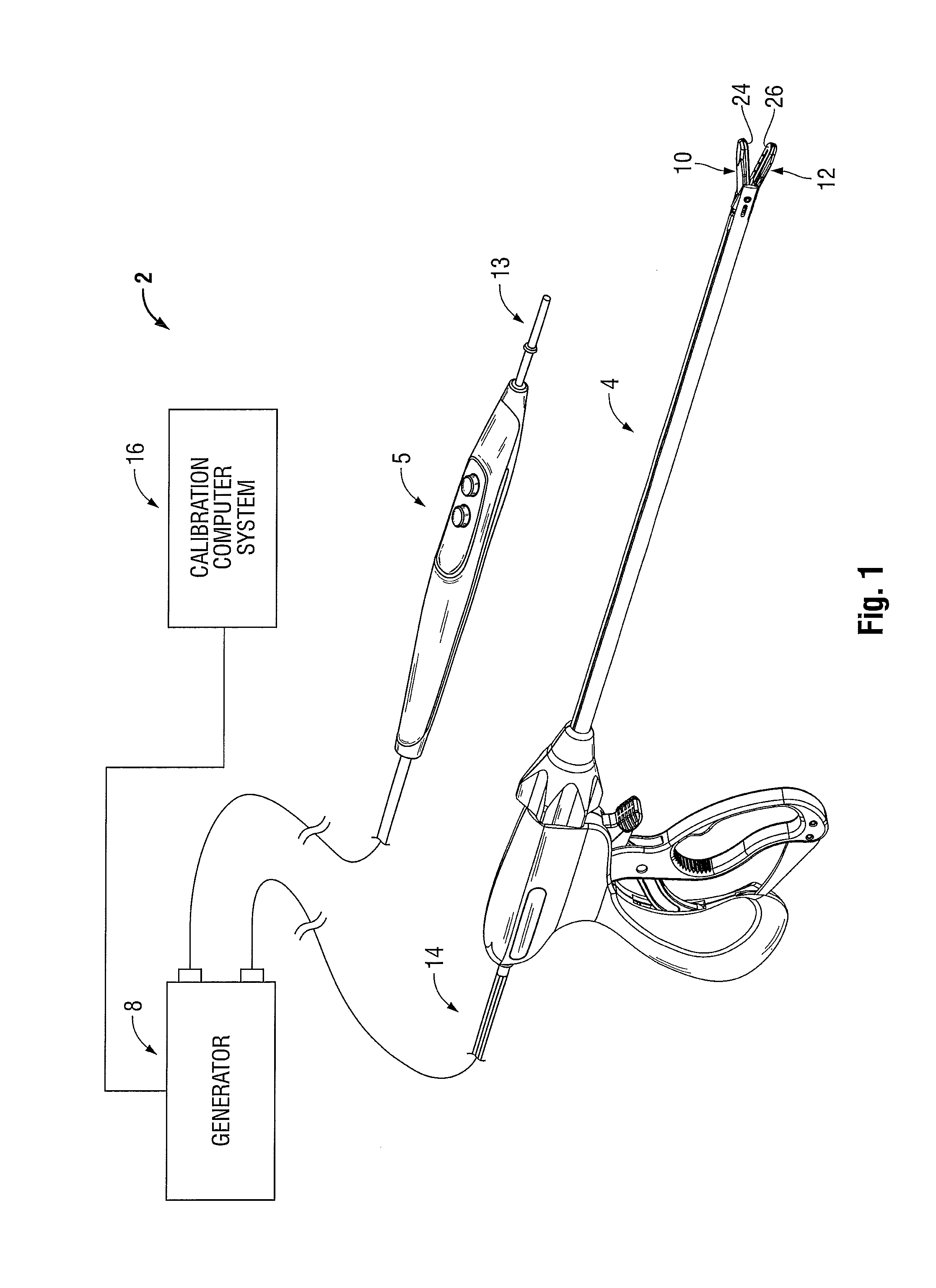
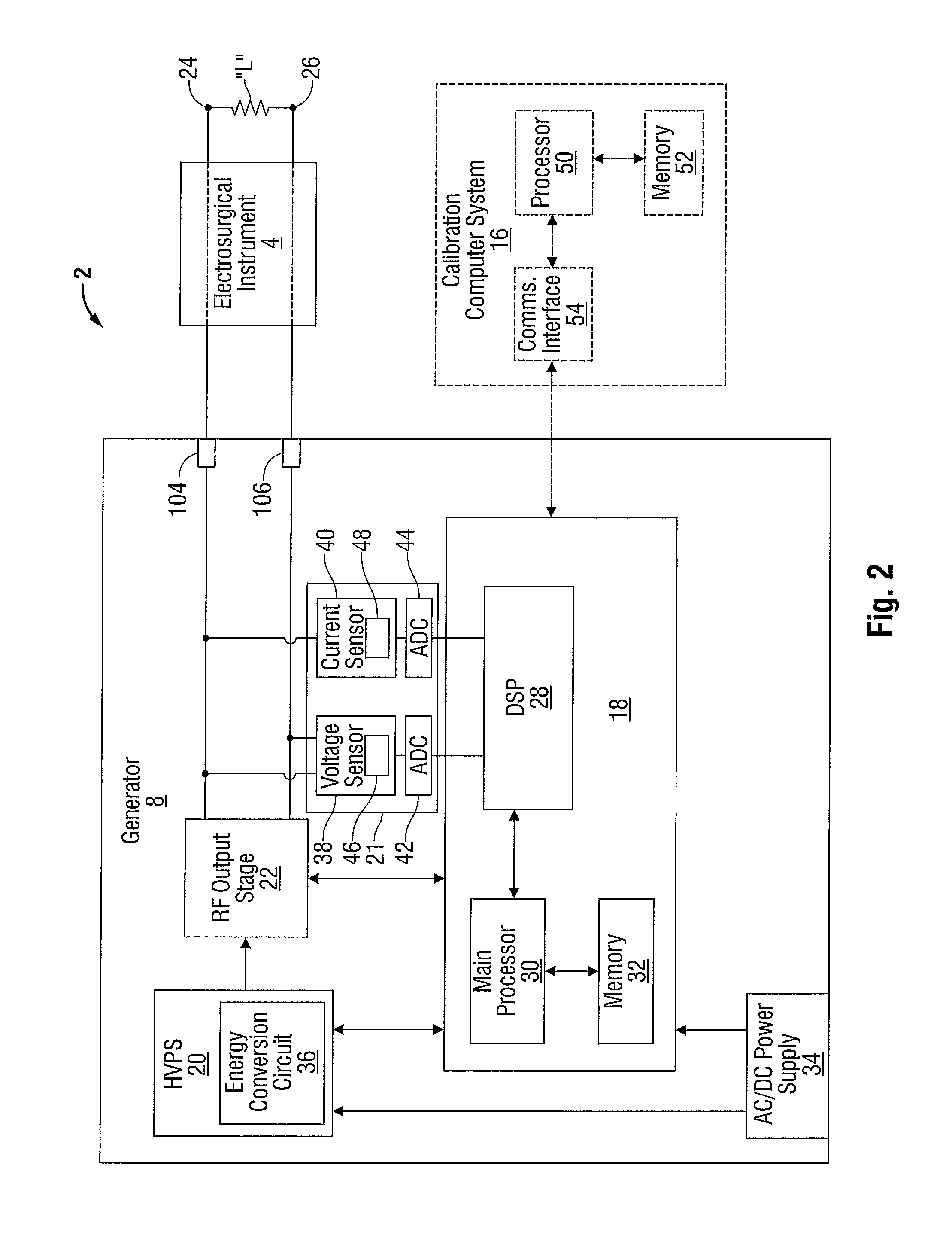
An electrosurgical system for performing an electrosurgical procedure is provided and includes an electrosurgical generator and a calibration computer system. The electrosurgical generator includes one or more processors and a measurement module including one or more log amps that are in operative communication with the processor. The calibration computer system configured to couple to a measurement device and is configured to measure parameters of an output signal generated by the electrosurgical generator. The calibration computer system is configured to compile the measured parameters into one or more data look-up tables and couple to the electrosurgical generator for transferring the data look-up table(s) to memory of the electrosurgical generator. The microprocessor is configured to receive an output from the log amp(s) and access the data look-up table(s) from memory to execute one or more control algorithms for controlling an output of the electrosurgical generator.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Electrosurgical Generator
An electrosurgical system for performing an electrosurgical procedure is provided and includes an electrosurgical generator and a calibration computer system. The electrosurgical generator includes one or more processors and a measurement module including one or more log amps that are in operative communication with the processor. The calibration computer system configured to couple to a measurement device and is configured to measure parameters of an output signal generated by the electrosurgical generator. The calibration computer system is configured to compile the measured parameters into one or more data look-up tables and couple to the electrosurgical generator for transferring the data look-up table(s) to memory of the electrosurgical generator. The microprocessor is configured to receive an output from the log amp(s) and access the data look-up table(s) from memory to execute one or more control algorithms for controlling an output of the electrosurgical generator.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
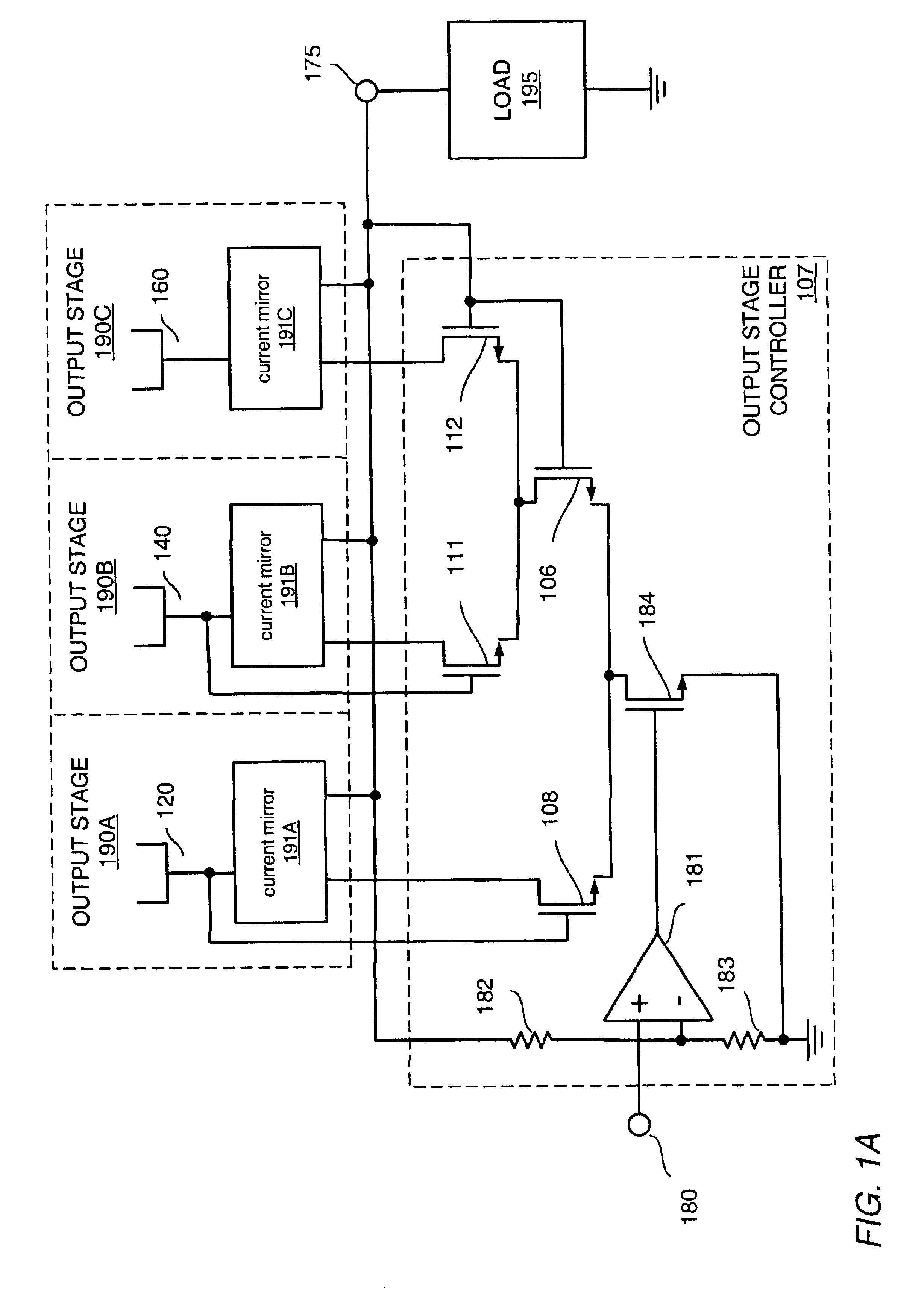
Efficient class-G amplifier with wide output voltage swing
InactiveUS6838942B1Reduce noiseImprove efficiencyGated amplifiersPower amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
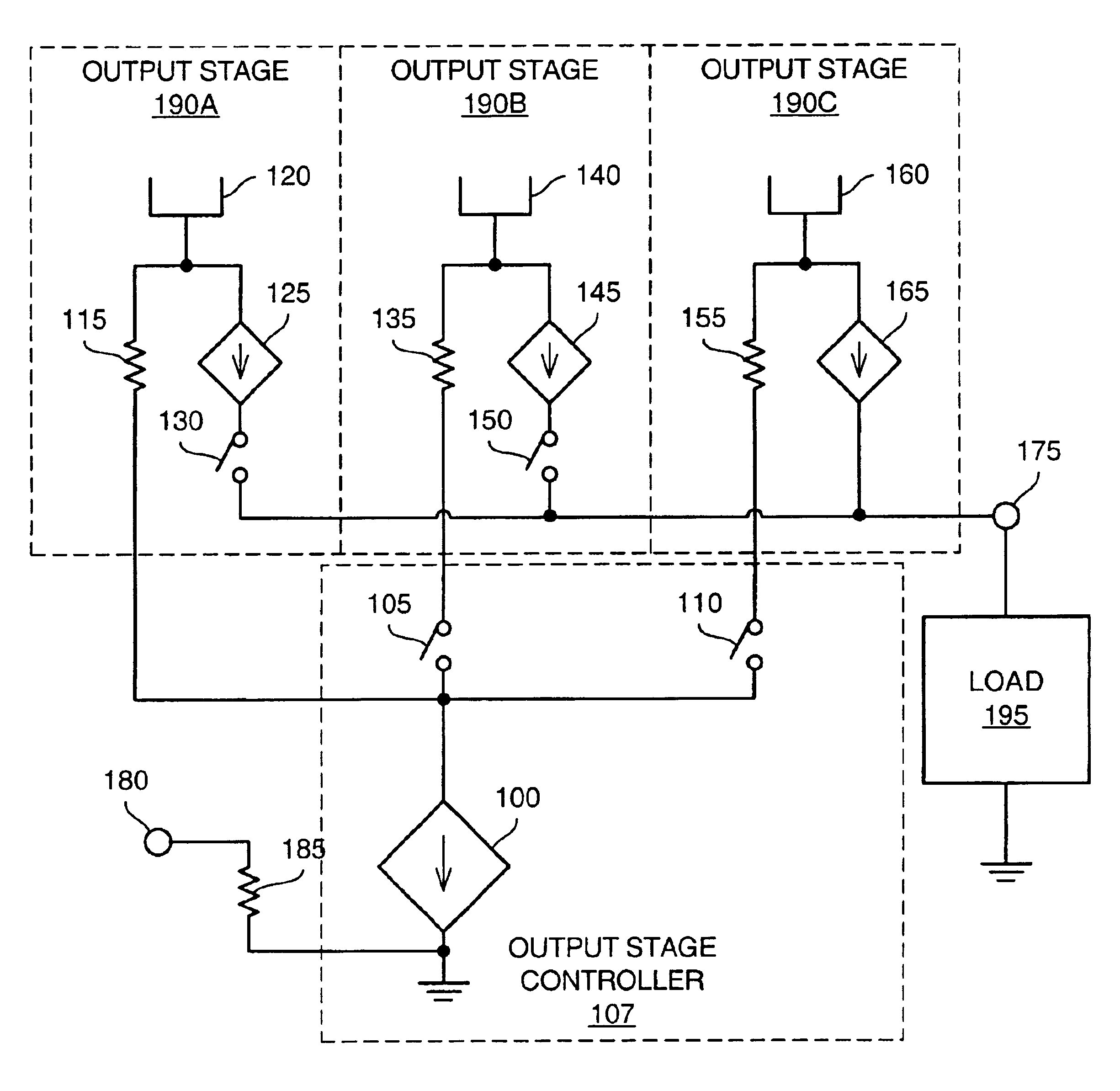
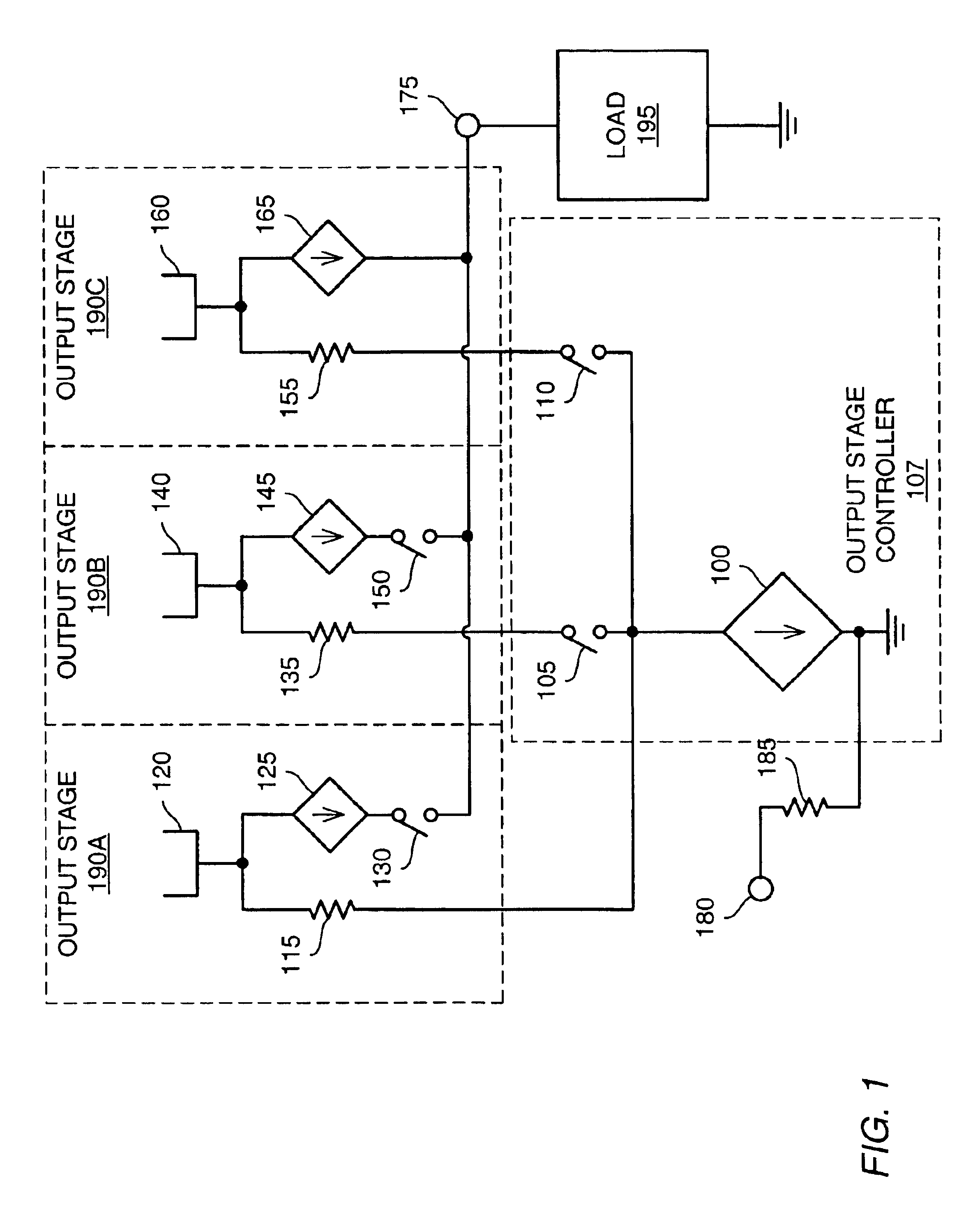
Various embodiments of methods and apparatus for an amplifier with wide output voltage swing are disclosed. The amplifier may include multiple output stages, each associated with a distinct supply voltage. Each output stage may contribute current to the output of the amplifier over a range of amplifier output voltages and these ranges may overlap. Each output stage may contribute current until the amplifier output voltage reaches the supply voltage associated with that output stage. The amplifier output may be as great as the largest supply voltage minus a drop equal to Rdson for an output transistor multiplied by the output current. In a CMOS implementation, this voltage drop may be approximately 0.15V. When the amplifier output voltage is close to the supply voltage associated with an output stage, both that output stage and the output stage associated with the next highest supply voltage may contribute to the amplifier output.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
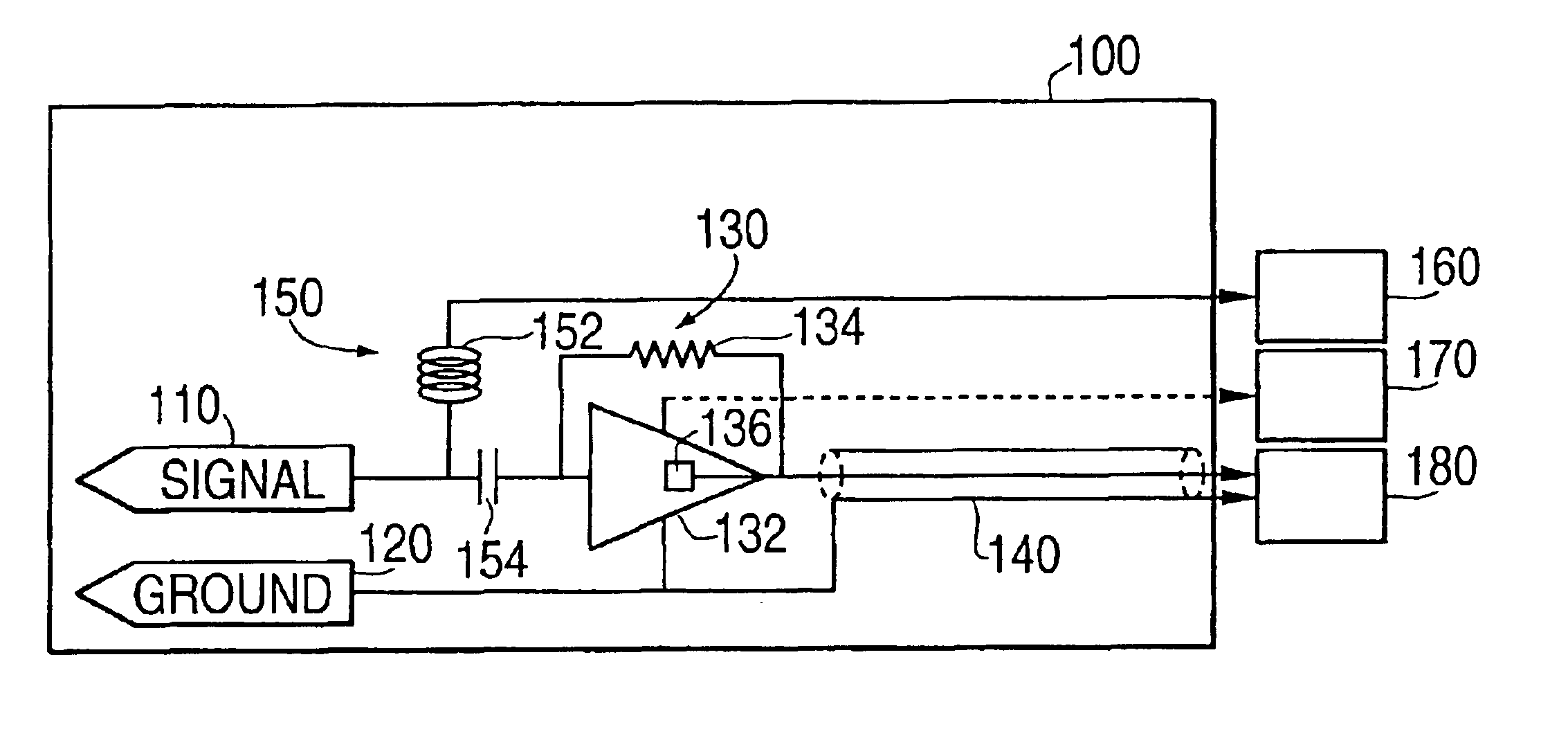
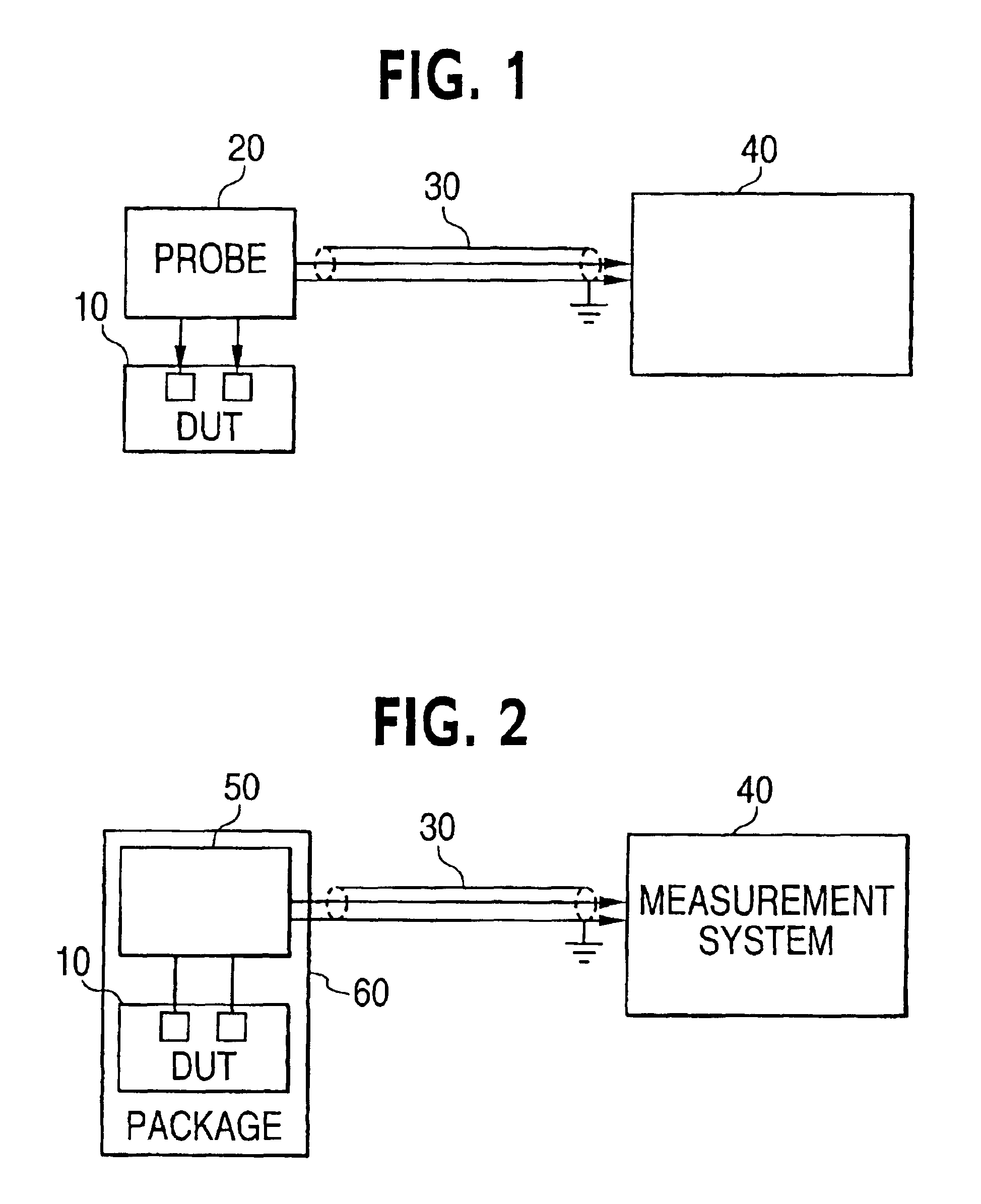
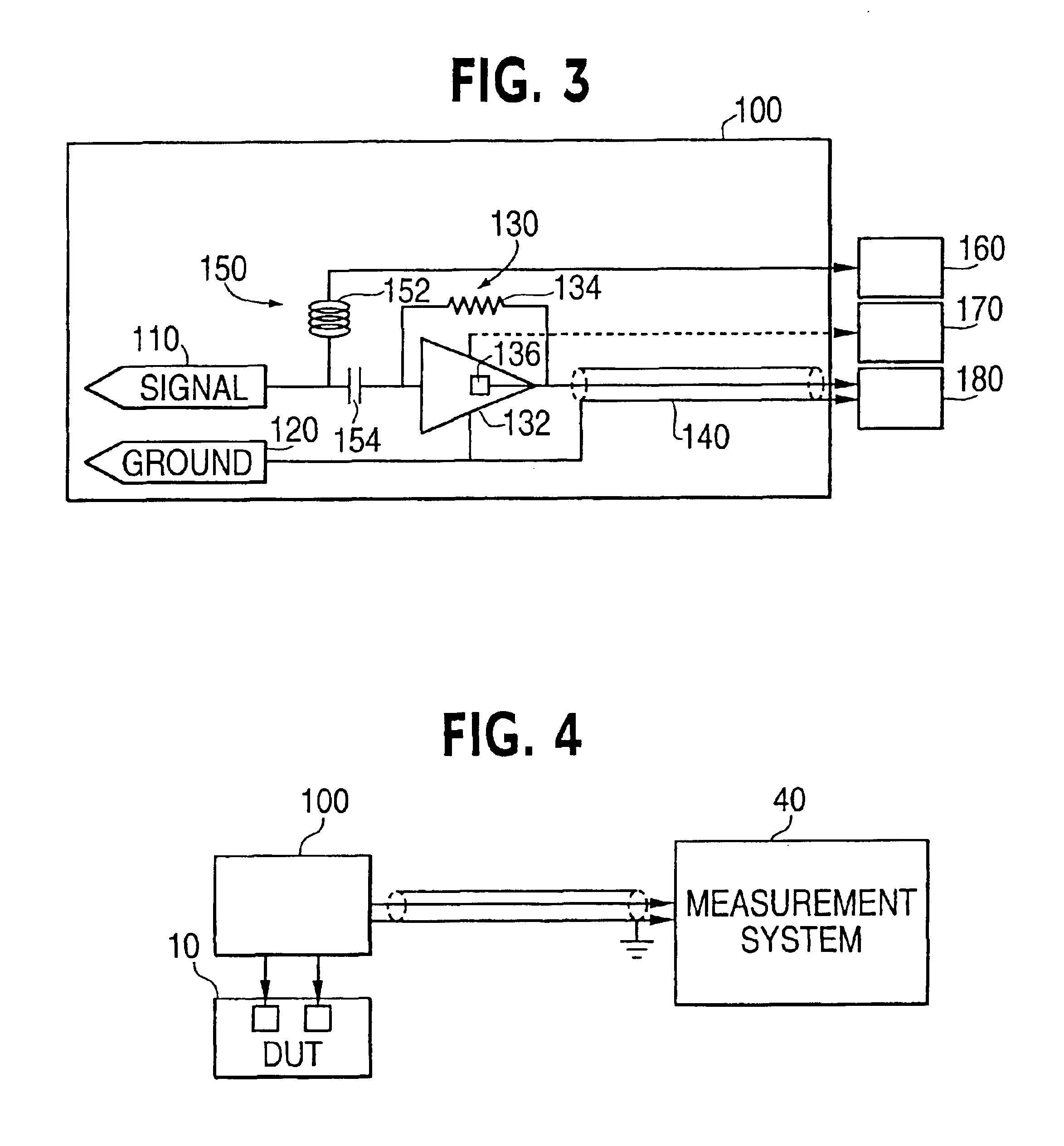
Current probe device having an integrated amplifier
InactiveUS6856129B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsAudio power amplifierIntegrated amplifier
A measurement system is provided that includes a probe device having an integrated amplifier. The integrated amplifier may be a transimpedence amplifier that amplifies input current to an output voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fast low dropout voltage regulator circuit
A voltage regulator includes first and second closed-loop amplifiers and a N-type transistor. The first amplifier receives a first reference voltage and a feedback voltage. The second amplifier is responsive to the first amplifier and to the regulated output voltage of the regulator. Both amplifiers are biased by a biasing voltage. The second amplifier has a bandwidth greater than the bandwidth of the first amplifier and a gain smaller that the gain of the first amplifier. The N-type transistor has a first terminal responsive to the output of the second amplifier, a second terminal that receives the input voltage being regulated, and a third terminal that supplies the regulated output voltage. The feedback voltage is generating by dividing the regulated output voltage. An optional fixed or dynamically biased current source biases the first terminal of the N-type transistor. The voltage regulator optionally includes an overshoot correction circuit.
Owner:DECICON A CALIFORNIA CORP
Voltage amplifier and driving device of display device using the voltage amplifier
InactiveUS8314764B2Negative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCathode-ray tube indicatorsAudio power amplifierDisplay device
An amplifying circuit of a display device including a plurality of pixels includes an input unit, a bias unit, and an output unit. The input unit is coupled between a first power source for supplying a first voltage and a second power source for supplying a second voltage, receives a first input signal and a second input signal, and is controlled by the first and second input signals. The bias unit receives a bias voltage for operating the input unit, and includes a first node and a second node controllable by the input unit. The output unit applies an output voltage to a pixel by using a first output transistor turned on / off by a signal applied to the first node and a second output transistor turned on / off by a signal applied to the second node, and the first output transistor is a different type to the second output transistor. In this instance, the input unit includes a first input transistor having a first terminal coupled to a first power source and being turned on / off by a first input signal and a second input transistor of the same type as the first input transistor, having a first terminal coupled to the first power source, and being turned on / off by a second input signal. The bias unit includes a first transistor controllable by the on / off state of the first input transistor and a second transistor controllable by the on / off state of the second input transistor.
Owner:MC TECH CO LTD
Log-polar signal processing
InactiveUSRE37138E1Improve accuracyLow costComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsDigital data processing detailsAudio power amplifierCommunications system
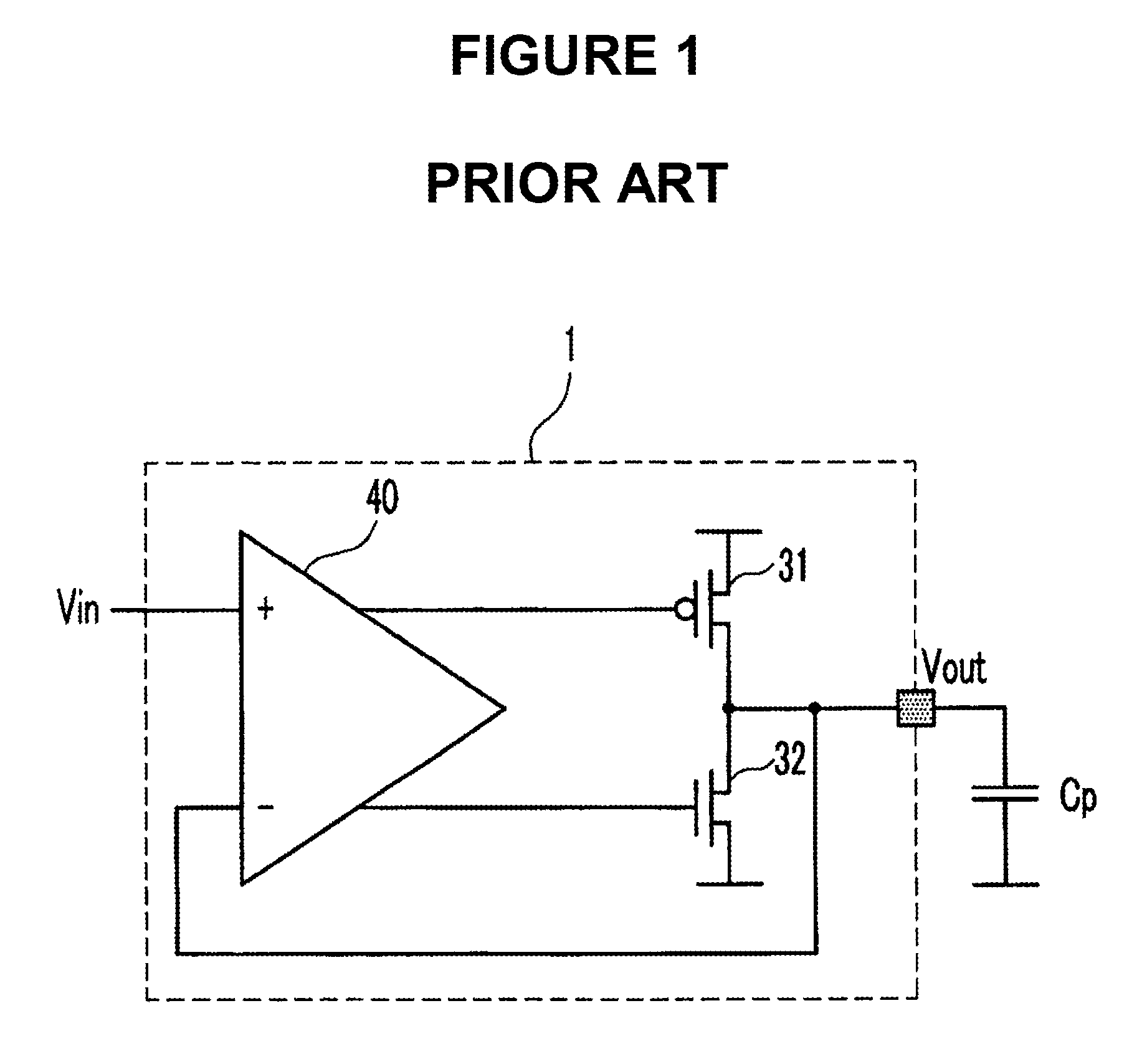
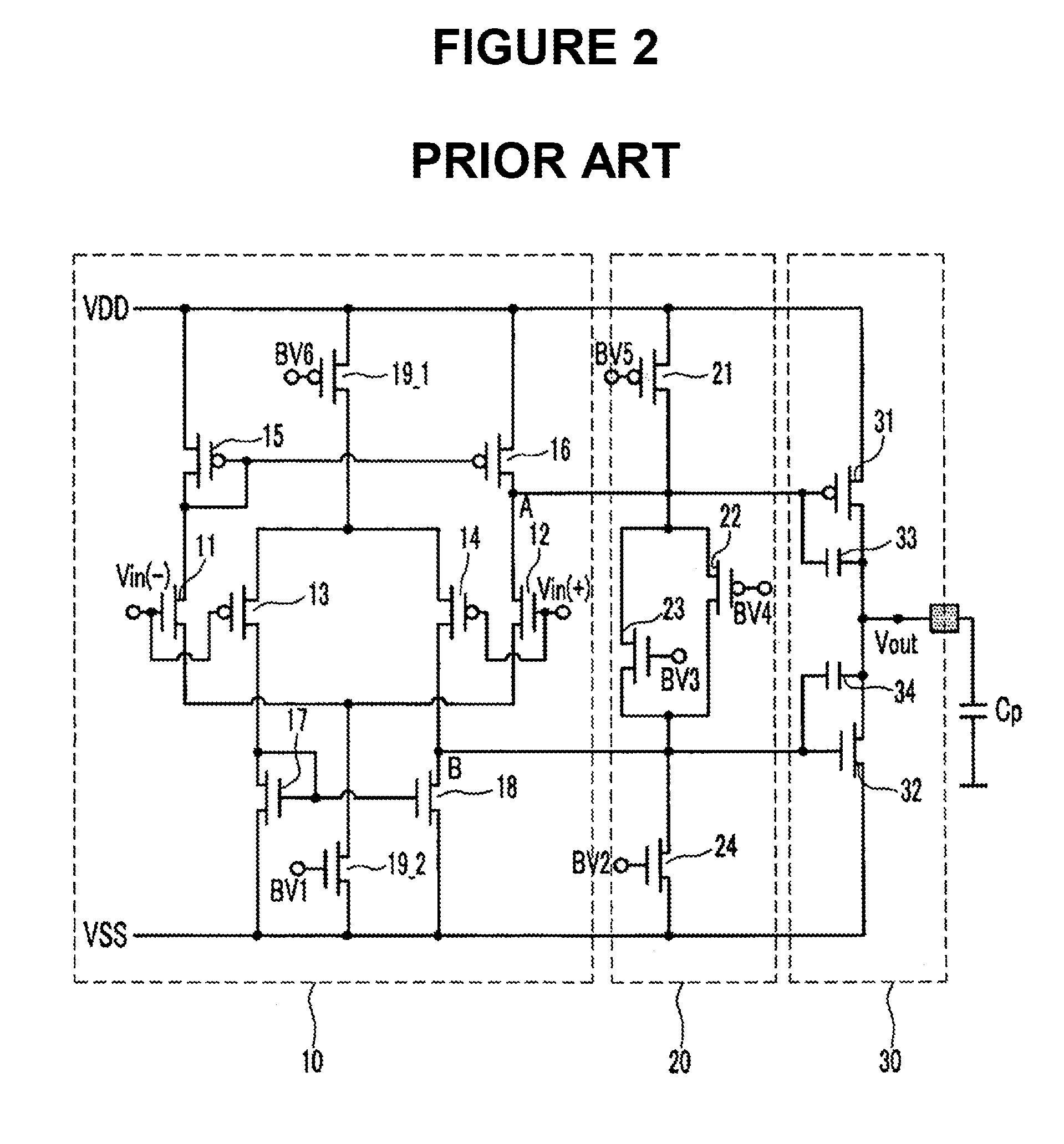
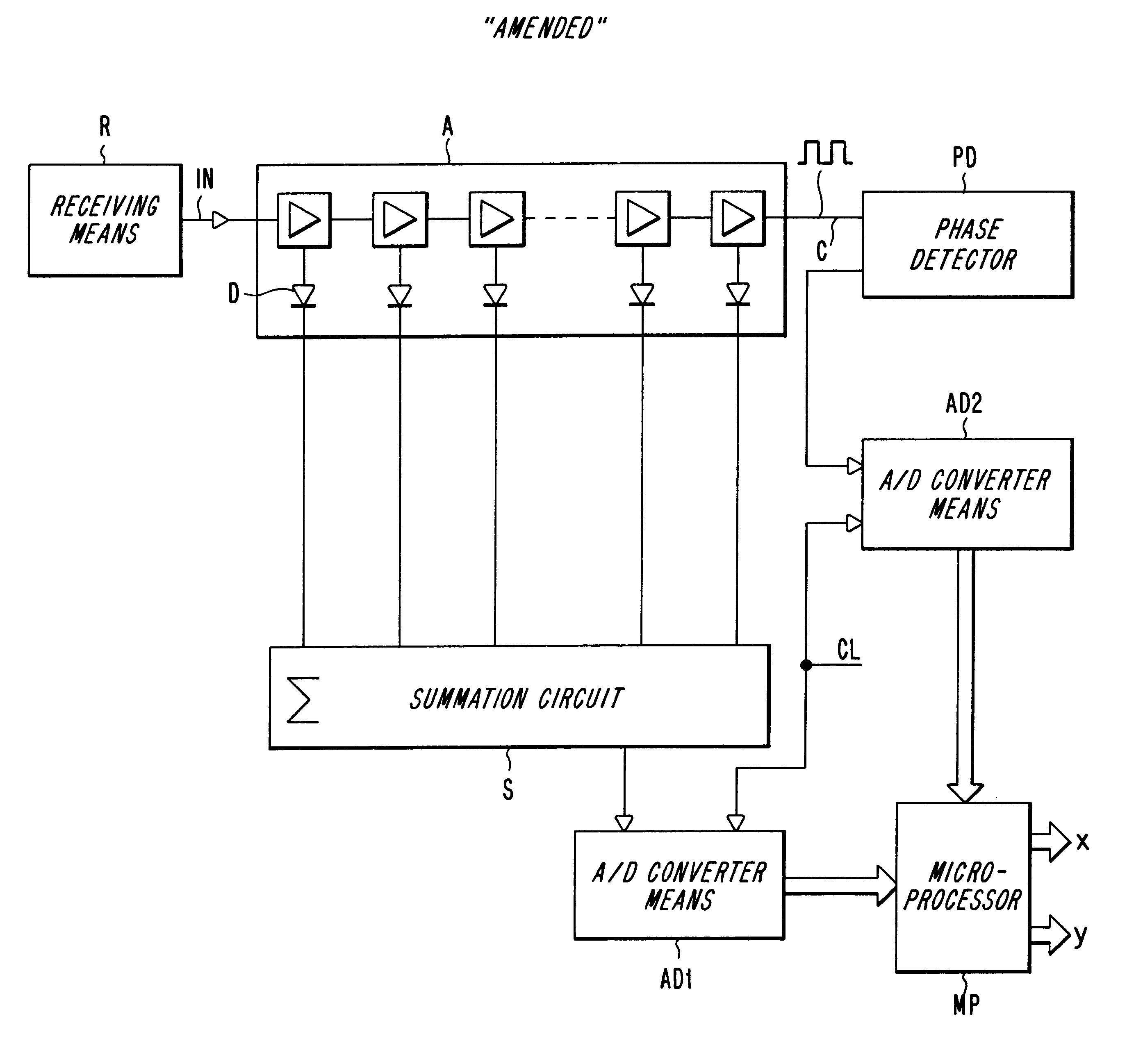
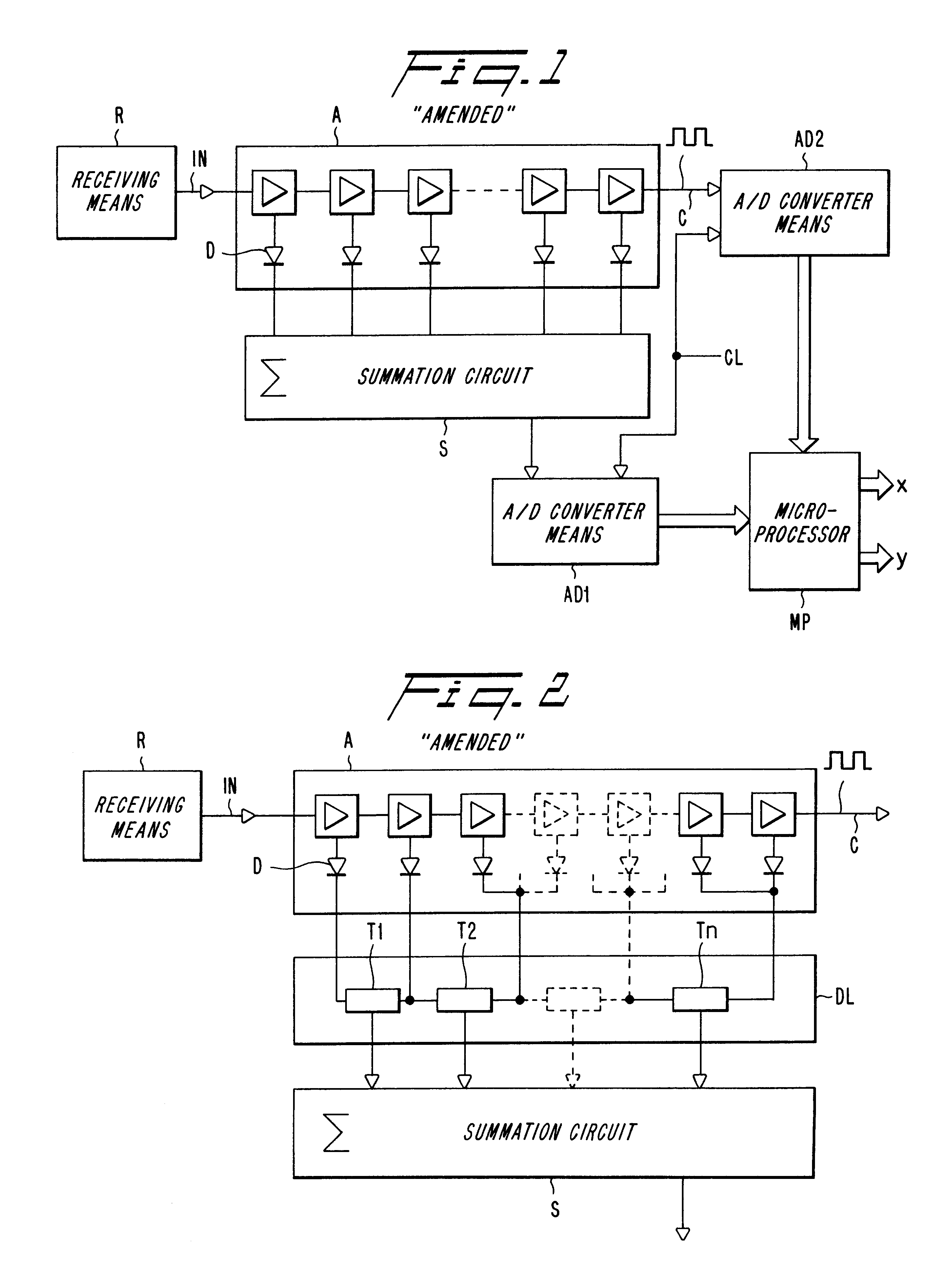
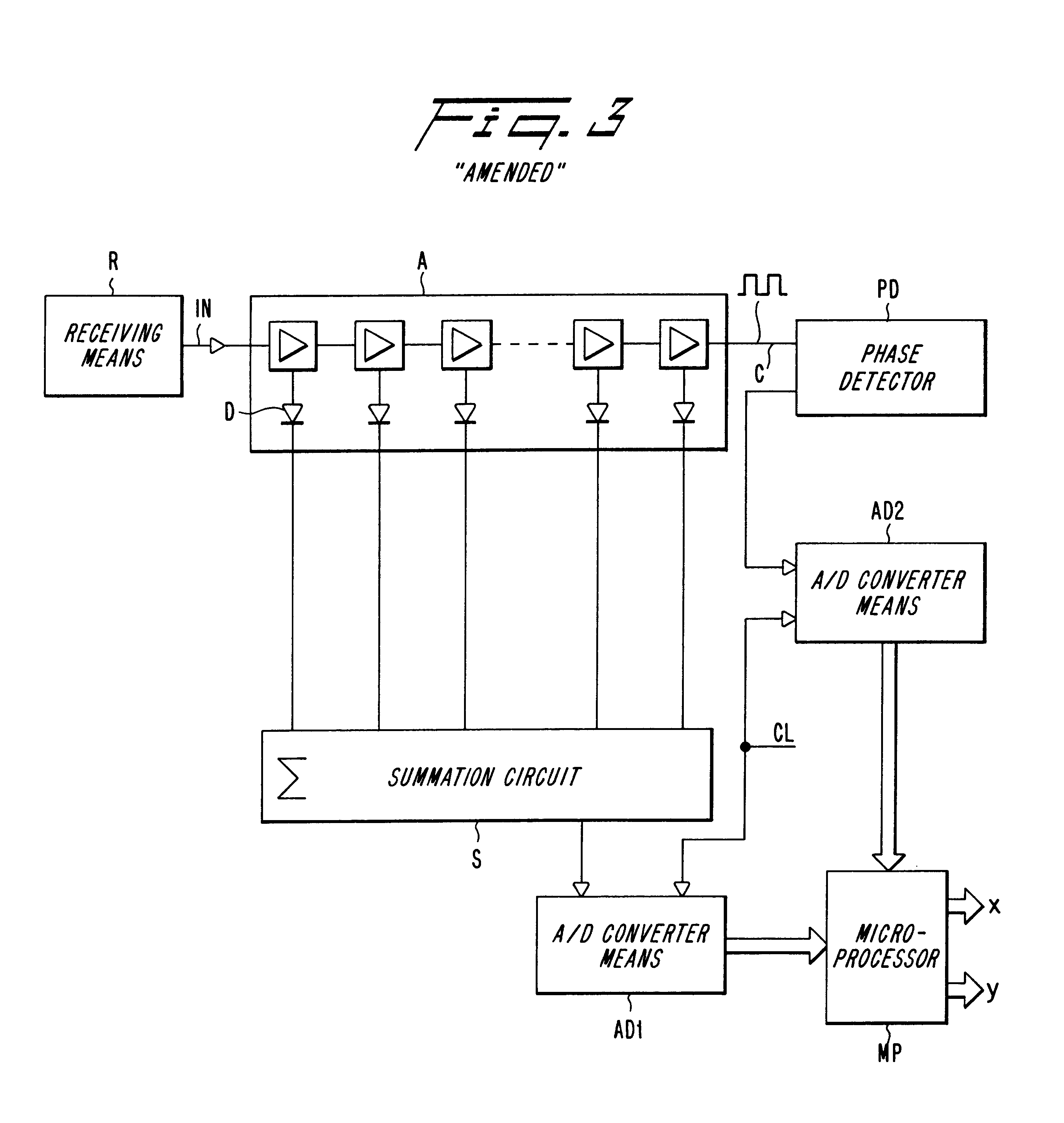
The invention relates to a method and an arrangement intended for radio communication systems and effective in digitalizing and subsequently processing numerically arbitrary radio signals. The signals are represented by composite (complex) vectors which have been subjected to disturbances in the system, such that information in the signals has been lost. This information is restored in its entirety when practising the present invention. For the purpose of solving this problem, the inventive digitalizing arrangement includes a multistage logarithmic amplifier chain (A) in which each stage is connected to a separate detector (D), the output signals of which are added in an adder. The adder output signals are then transmitted to a first A / D-converter (AD1) for digitalizing and converting the amplitude components of the signal. At the same time, the undetected signal from the saturated output stage in the amplifier chain is transmitted to a second A / D-converter for digitalizing and converting the phase components of the signal. The digital values obtained on the outputs of the AD-converters (AD1, AD2) are applied to different inputs of a digital signal processor (MP) for numerical processing of the pairwise received digital values in a manner such as to restore the complete vector characteristic of the signal.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
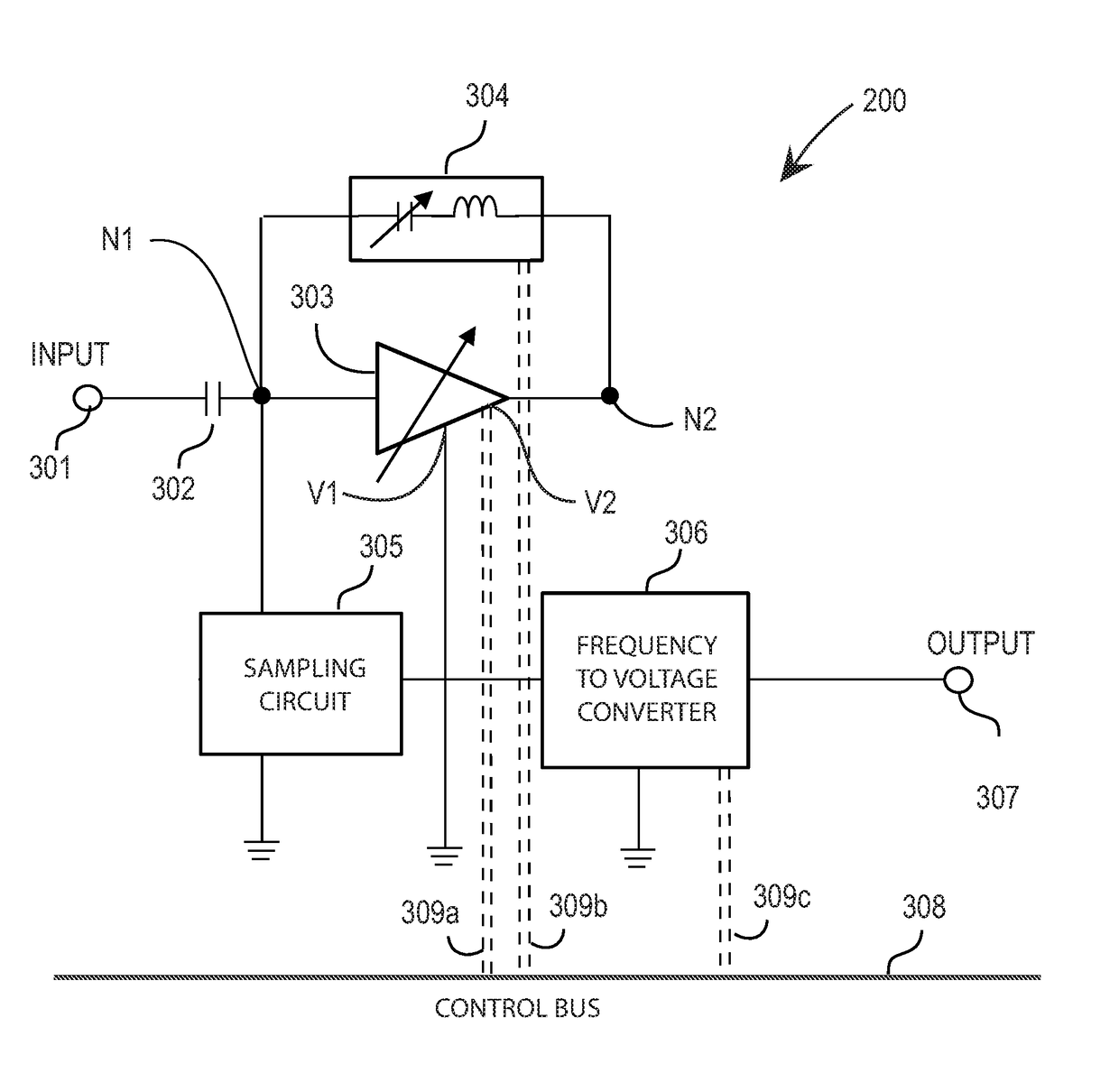
Tunable logarithmic amplifier
ActiveUS9755580B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePower amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:KYOCERA AVX COMPONENTS (SAN DIEGO) INC
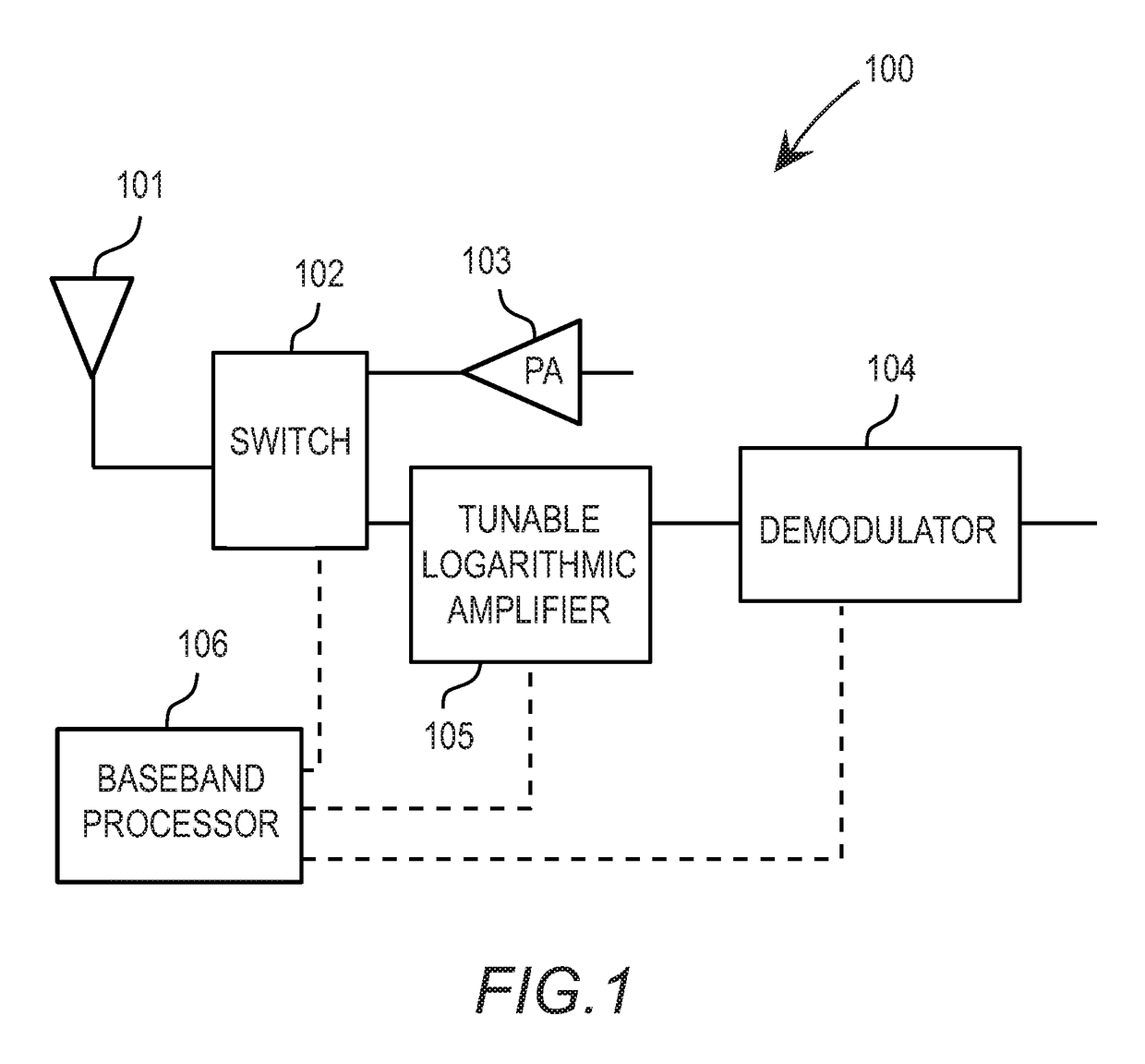
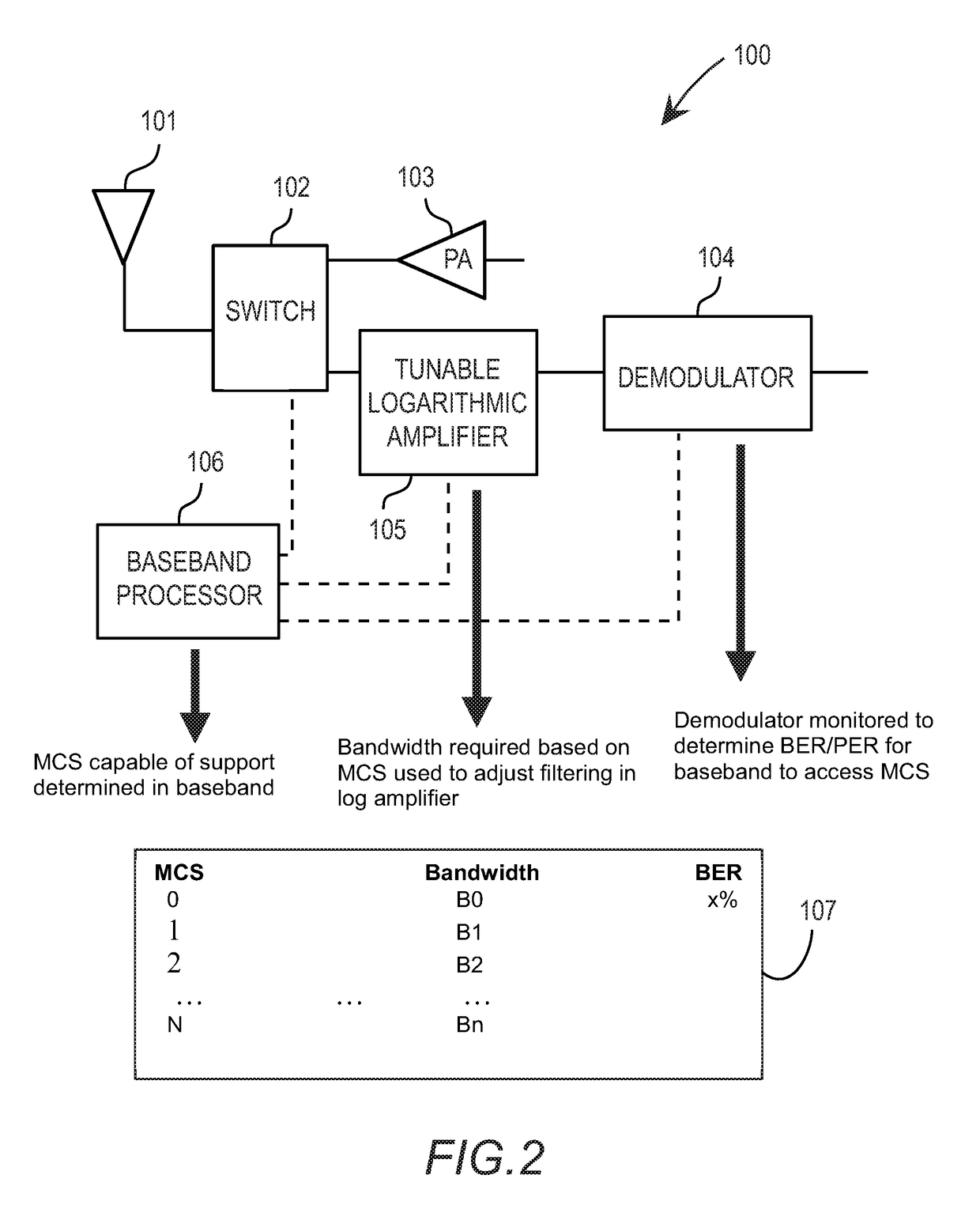
Agile spectrum monitoring in a radio transceiver
InactiveUS20080291985A1Duplex signal operationAngle demodulation by oscillations samplingFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
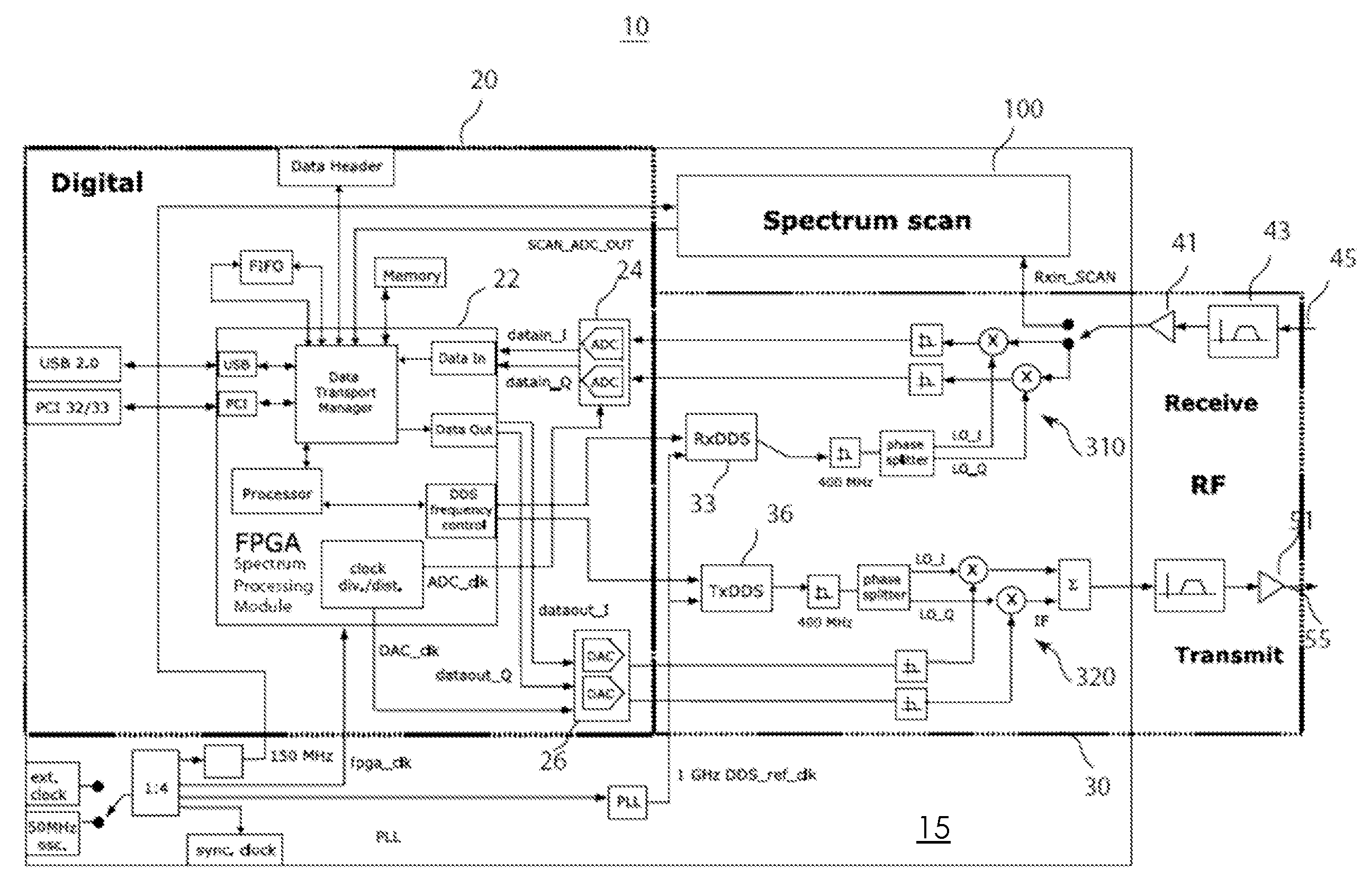
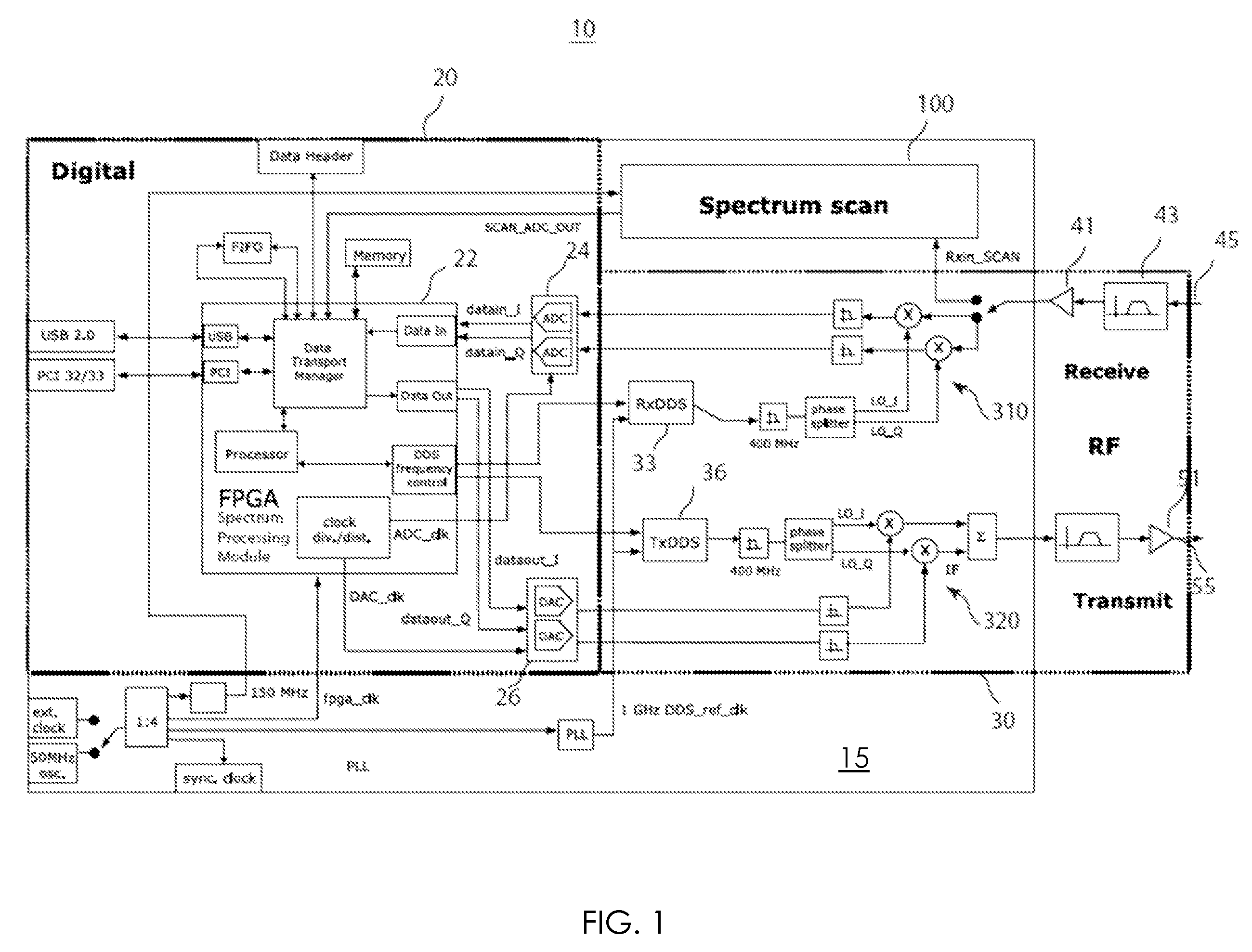
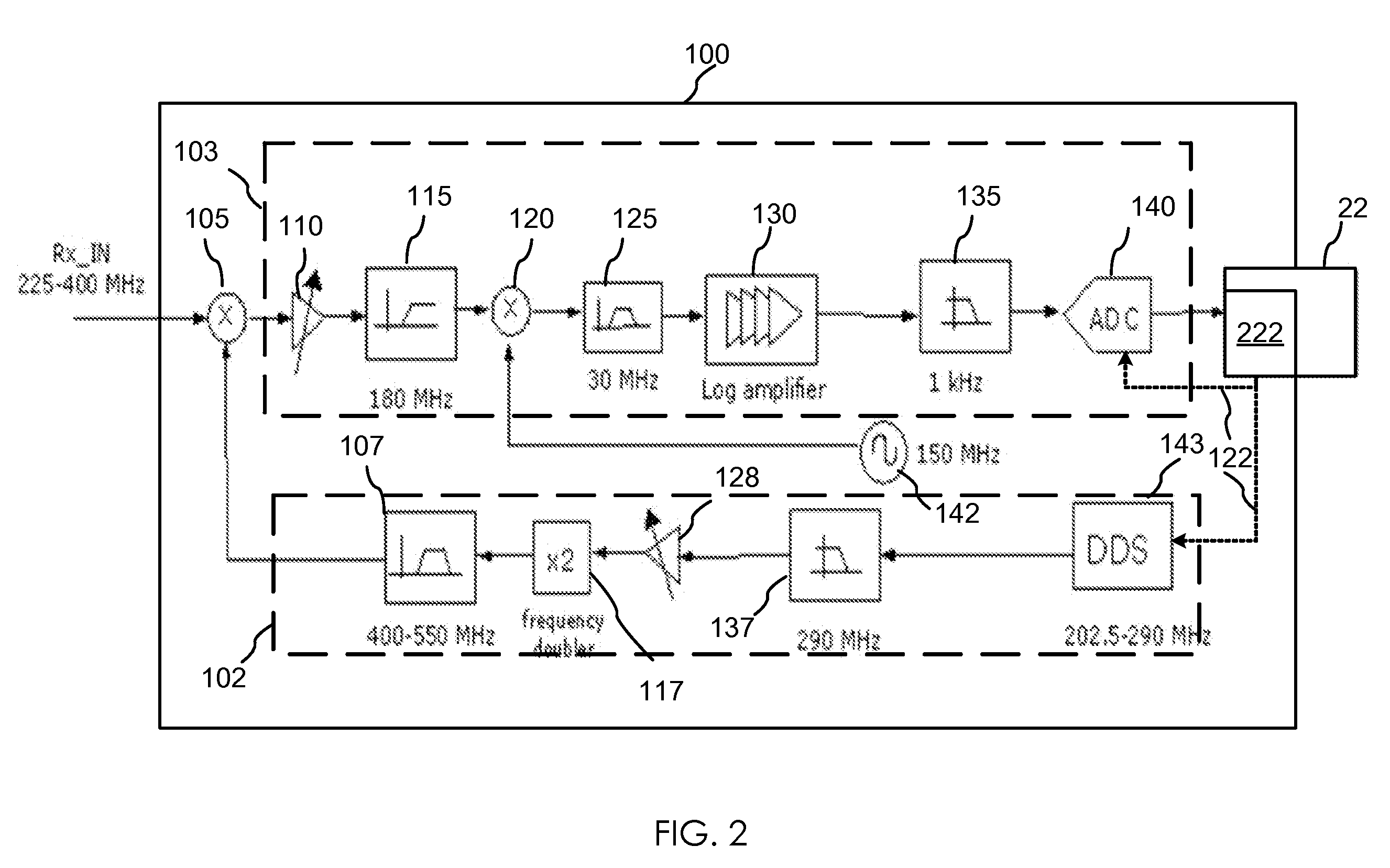
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for agile RF spectrum monitoring in a radio system with dynamic frequency access. It provides a spectrum monitor based on non-coherent heterodyne detection that utilizes a DDS signal generator to digitally generate a reference signal at a variable reference frequency for mixing with an input RF signal received from an RF antenna, a pass-band filter and a log amplifier for obtaining energy estimates at a monitored transmission frequency corresponding to the reference frequency. A processor is provided for adaptively selecting sets of monitored transmission frequencies, for controlling the DDS signal generator, and for processing obtained spectral energy estimates to assess spectral usage data.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Method and system for RF front-end calibration scheme using fractional-N frequency synthesized signals and RSSI
ActiveUS20070207759A1Spatial transmit diversityReceivers monitoringAudio power amplifierRF front end
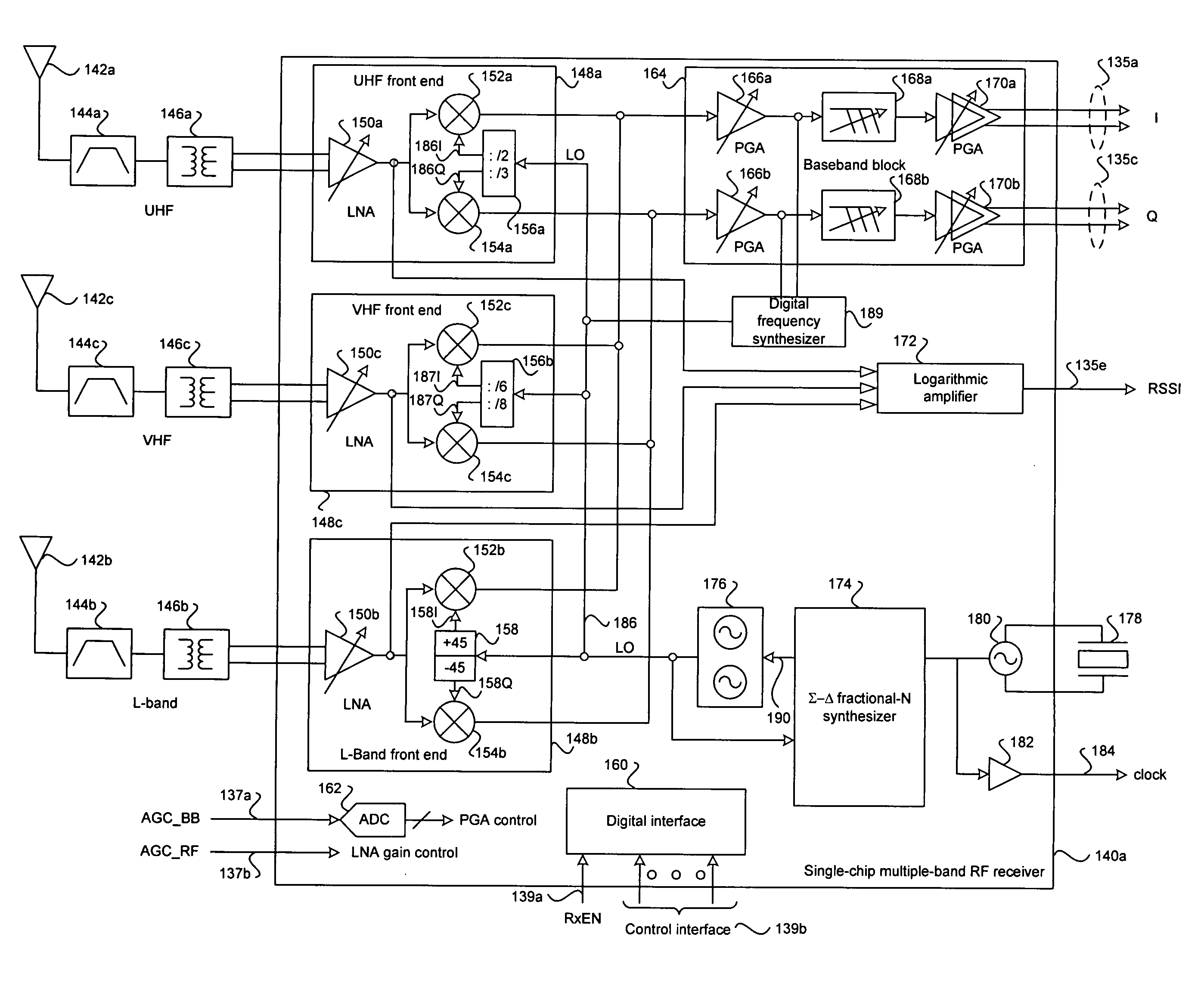
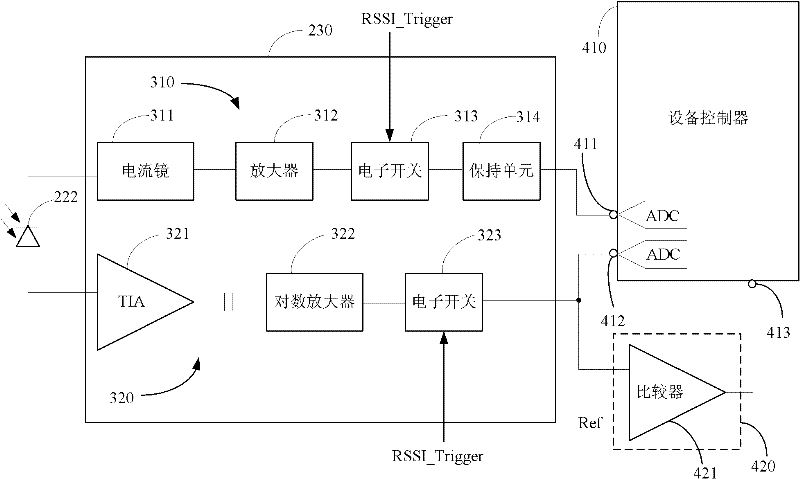
Aspects of a method and system for an RF front-end calibration scheme using signals from a fractional-N frequency synthesized and received signal strength indicator (RSSI) are provided. A frequency synthesizer within a wireless receiver may generate a signal for dynamically modifying a gain in an integrated low-noise amplifier (LNA) for each selected receiver channel. The frequency-synthesized signals may be applied to at least one tunable load communicatively coupled to the LNA. The tunable load may be an input load or an output load. The signal generated by the frequency synthesizer may be sequentially applied to the input load and the output load. A logarithmic amplifier may generate an RSSI signal from the LNA output during the calibration process. The RSSI signal may be utilized for controlling a tunable load coupled to the LNA and optimize the tuning of the LNA in a desired channel by adjusting the tunable load.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and device for detecting optical power of passive optical network (PON) and PON system
InactiveCN102130720AAvoid misjudgmentGuaranteed receiving optical power measurement accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsLuminous intensityAudio power amplifier
The embodiment of the invention discloses a device for detecting optical power of a passive optical network (PON). The device comprises a receiving module, a detection module and a controller, wherein the receiving module is used for receiving optical signals sent by an optical network unit (ONU); the detection module comprises a current mirror received signal strength indication (RSSI) detection branch and a logarithmic amplifier RSSI detection branch; the current mirror RSSI detection branch and the logarithmic amplifier RSSI detection branch are respectively coupled with the receiving module and used for carrying out RSSI measurement on the optical signals received by the receiving module in accordance with received RSSI function trigger signals; and the controller is coupled with the detection module and used for outputting the RSSI function trigger signals to the detection module, selectively receiving RSSI measurement results which are output by the RSSI detection branch and correspond to the luminous intensity of the optical signals sent by the ONU according to the selection control signals provided by a selection control signal generating module, and calculating the optical power information of the optical signals in accordance with the RSSI measurement results. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a method for detecting optical power of a PON and a PON system.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Successive approximation A/D converter provided with a sample-hold amplifier
ActiveUS7199745B2Increase speedElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersControl signalĆuk converter
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Superhigh frequency rediofrequency identical label reader
InactiveCN1815487AHigh sensitivitySafe and reliable workModulated-carrier systemsSensing record carriersAutomatic controlLow-pass filter
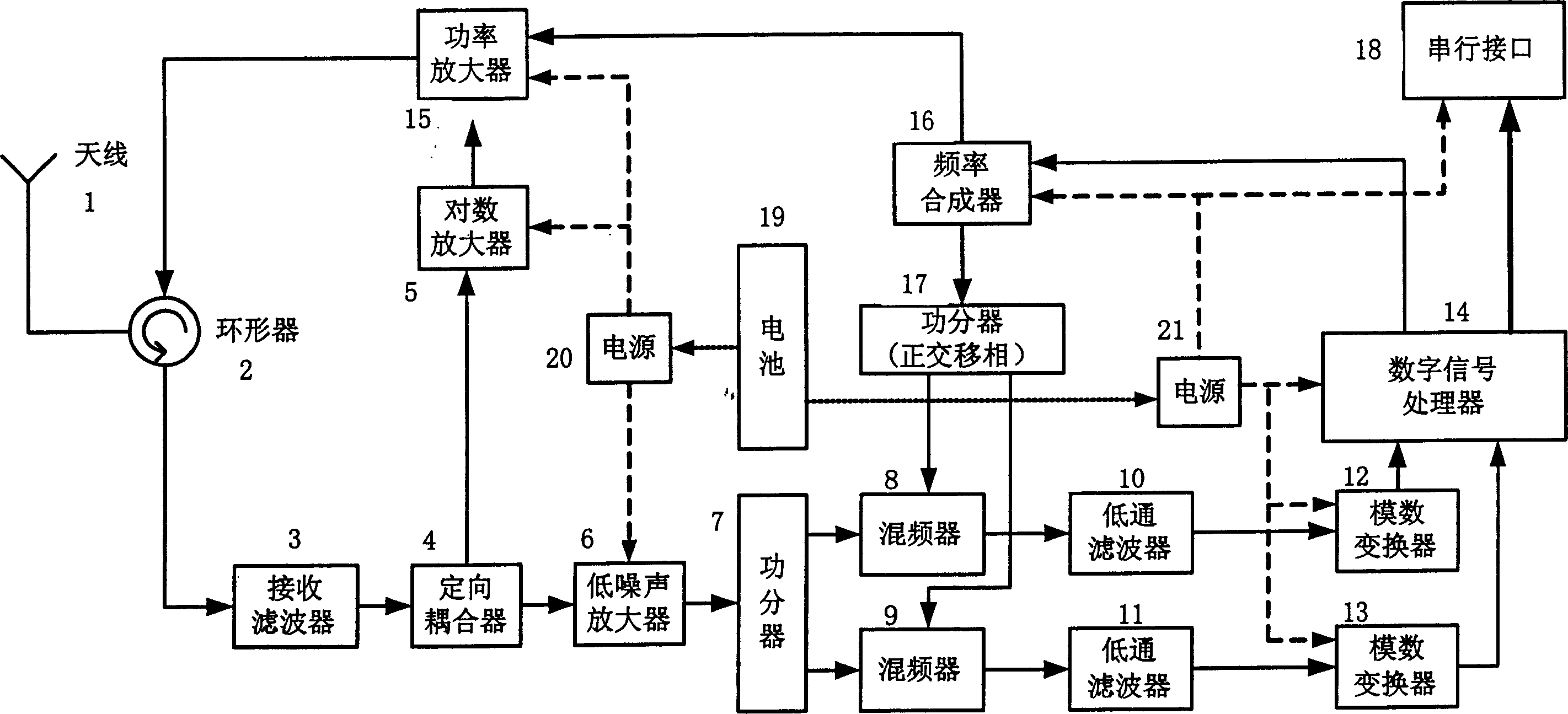
The disclosed reader is composed of antenna, directional coupler, logarithmic amplifier, two pieces of A / D converter, digital signal processor, power amplifier, frequency synthesizer, and serial interface etc. using orthogonal non coherent demodulation technique, the reader receives and detects data information (amplitude modulation or phase modulation) carried by backscattering electromagnetic wave of ID label in radio frequency. Thus, the invention omits complex phase-lock circuit of local oscillation of receiver as well as realizes higher sensitivity of receiver, and longer distance for reading card. Using directional coupler and logarithmic amplifier, the power amplifier carries out automatic power control. Comparing with traditional ID label reader in UHF, the disclosed reader possesses advantages of simple structure, stable performance, and low price.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
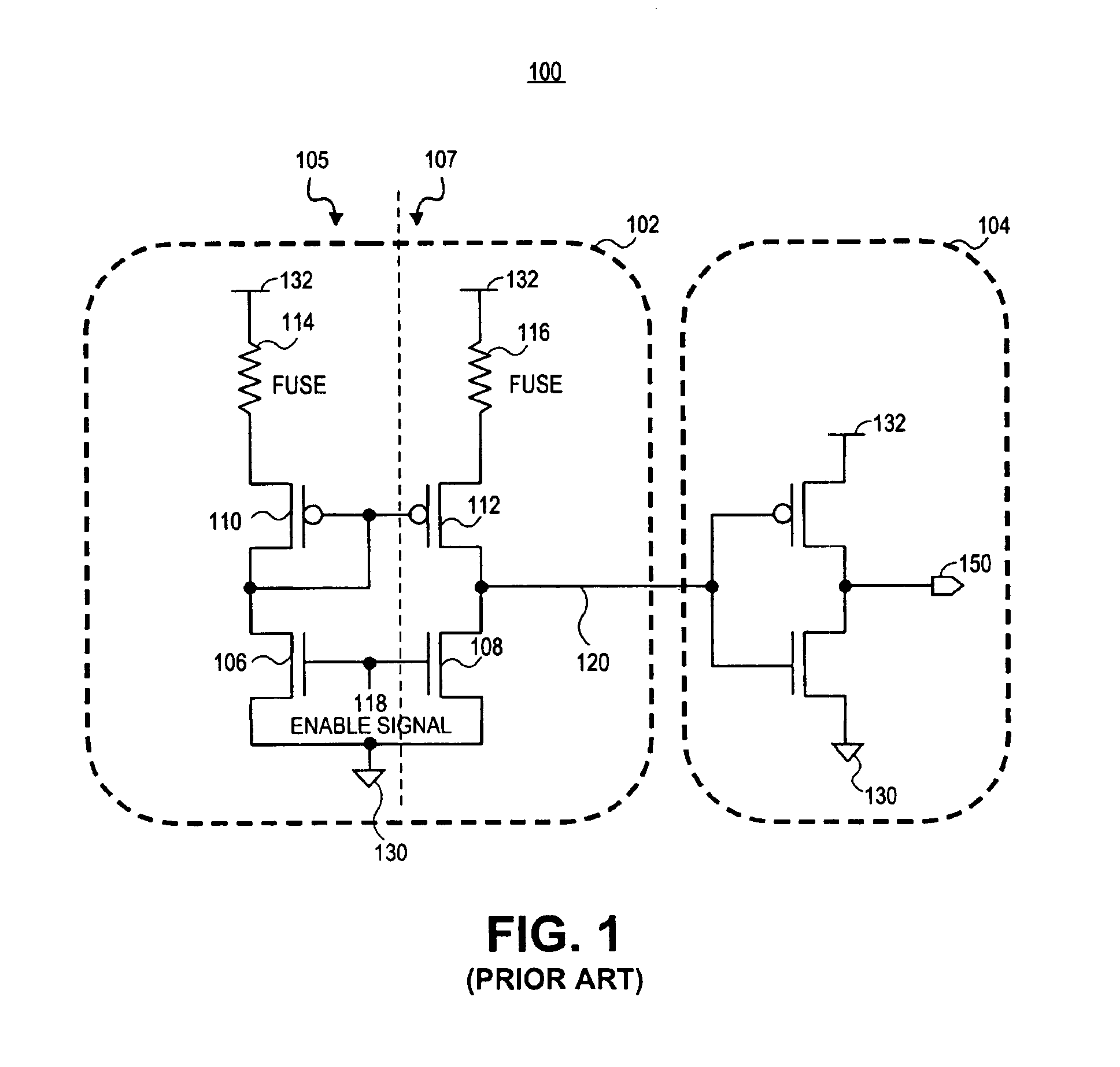
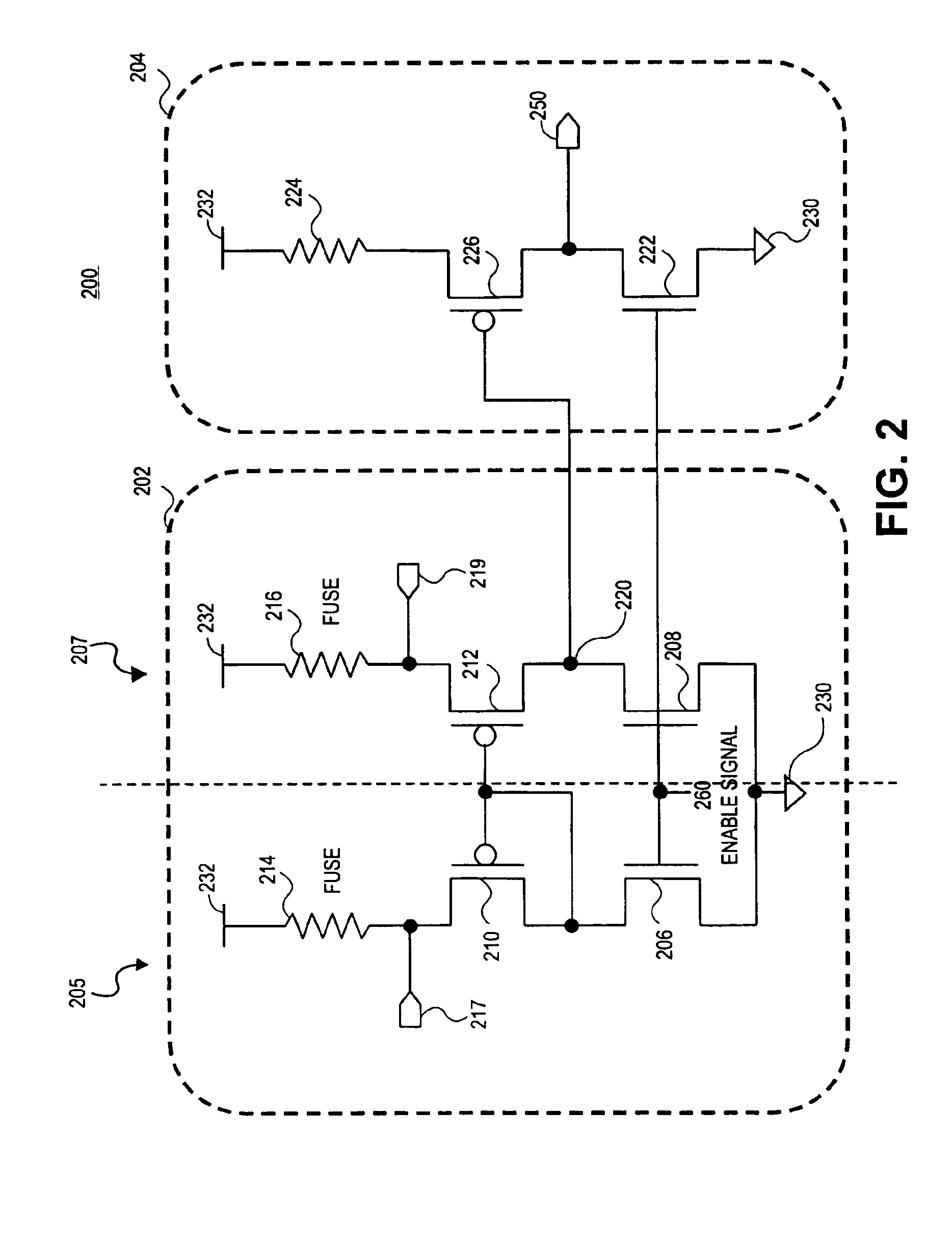
Fuse sense circuit
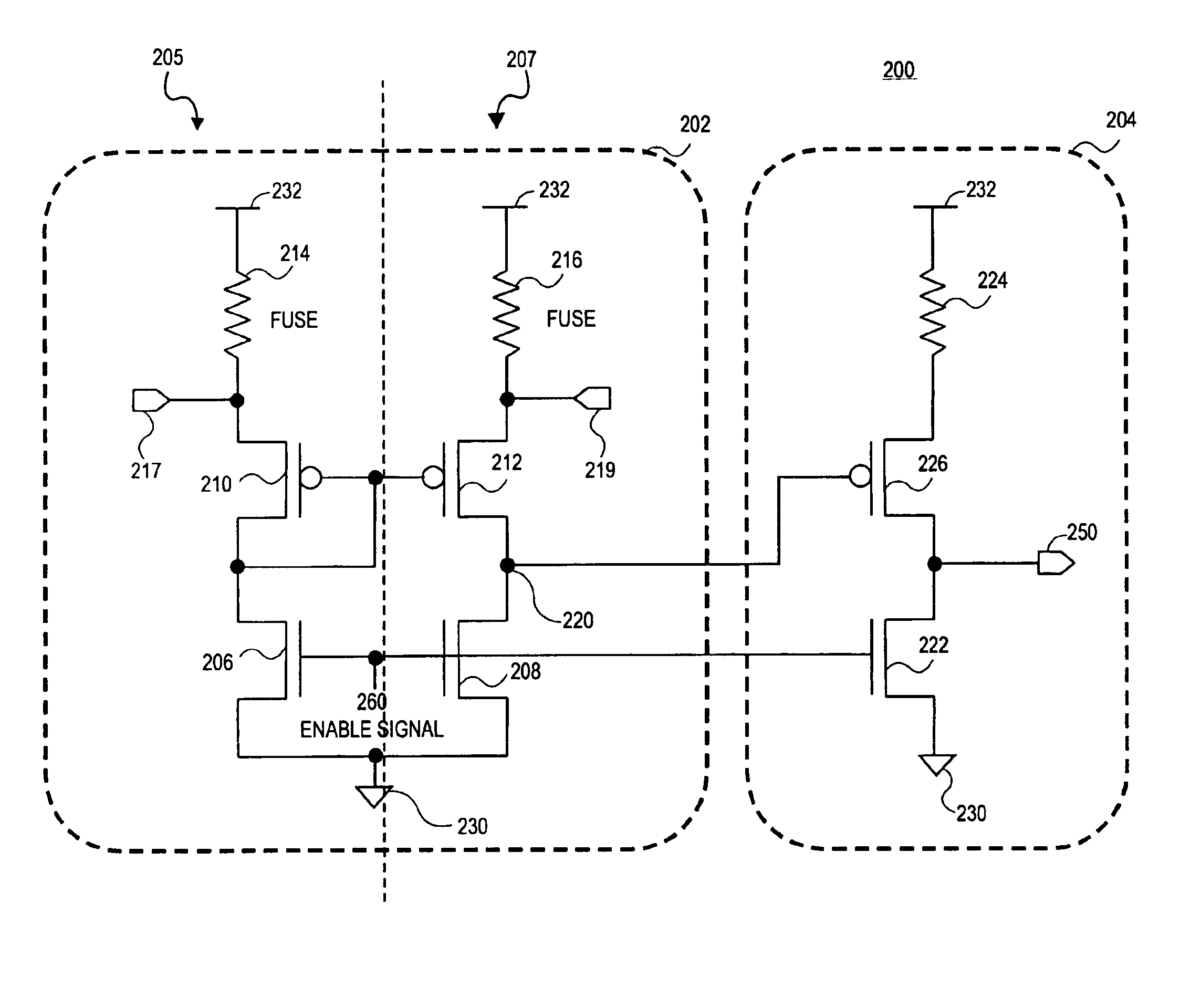
A fuse sense circuit has a sense amplifier and a post amplifier (gain stage). The sense amplifier has a reference branch and one or more sense (or fuse) branches. The fuse sense circuit determines the state of the fuses using safe currents and provides much higher gain than prior art. The post amplifier is a scaled replica of the reference branch or one of the sense branches in that the devices in the post amplifier maintain the same ratio as similar devices in the reference branch, and components in the post amplifier each matches components in the reference branch. The sense amplifier output is interpreted by the post amplifier's matched gain stage and has a trip point that sufficiently tracks the reference voltage. The result is reduced process and voltage sensitivity, which allows lower differential fuse resistance to be accurately detected with a non-ideal sense amplifier. Multiple gain stages may be added to multiple sense branches for redundancy and single-ended sensing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Digital logarithm gamma energy spectrometer
InactiveCN101799554AGuaranteed Energy ResolutionHigh count pass rateX-ray spectral distribution measurementAnti-aliasingProgrammable logic device
The invention discloses a digital logarithm gamma energy spectrometer, which comprises a NaI crystal, a photomultiplier, a high-voltage power supply module, a preamplifier, a logarithmic amplifier, a gain-programmed amplifier, an anti-aliasing active filter, a high-speed analog-digital converter (ADC) and a CPLD programmable logic device, wherein the logarithmic amplifier performs logarithmic operation on received nuclear pulse signals to acquire a high energy section spectral line and a low energy section spectral line; the high-speed analog-digital converter (ADC) performs analog-digital conversion on filtered signals; and the CPLD programmable logic device realizes pulse amplitude analysis, baseline restoration and filtering de-noising to digital signals, and obtains information on corresponding nuclear pulse peak values. The logarithmic amplifier performs logarithmic compression on the nuclear pulse signals to ensure the resolution of the high energy spectral line and the low energy spectral line; and the high-speed analog-digital converter and the CPLD programmable logic device are adopted to realize a digital energy spectrometer and ensure the high counting pass rate and the energy resolution of the energy spectrometer.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
High fidelity, high power switched amplifier
ActiveUS7116166B2Push-pull amplifiersNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAudio power amplifierCoupling
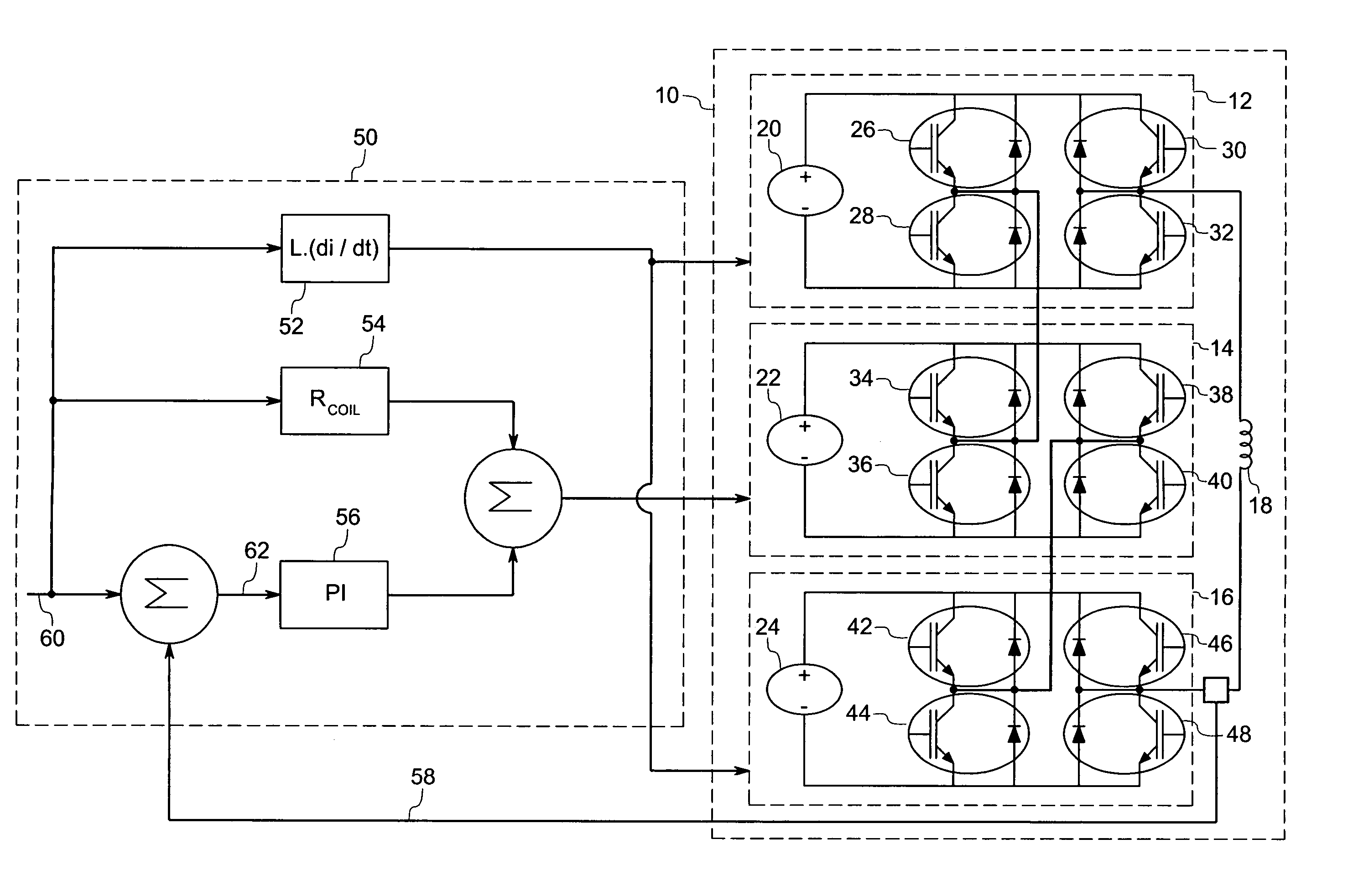
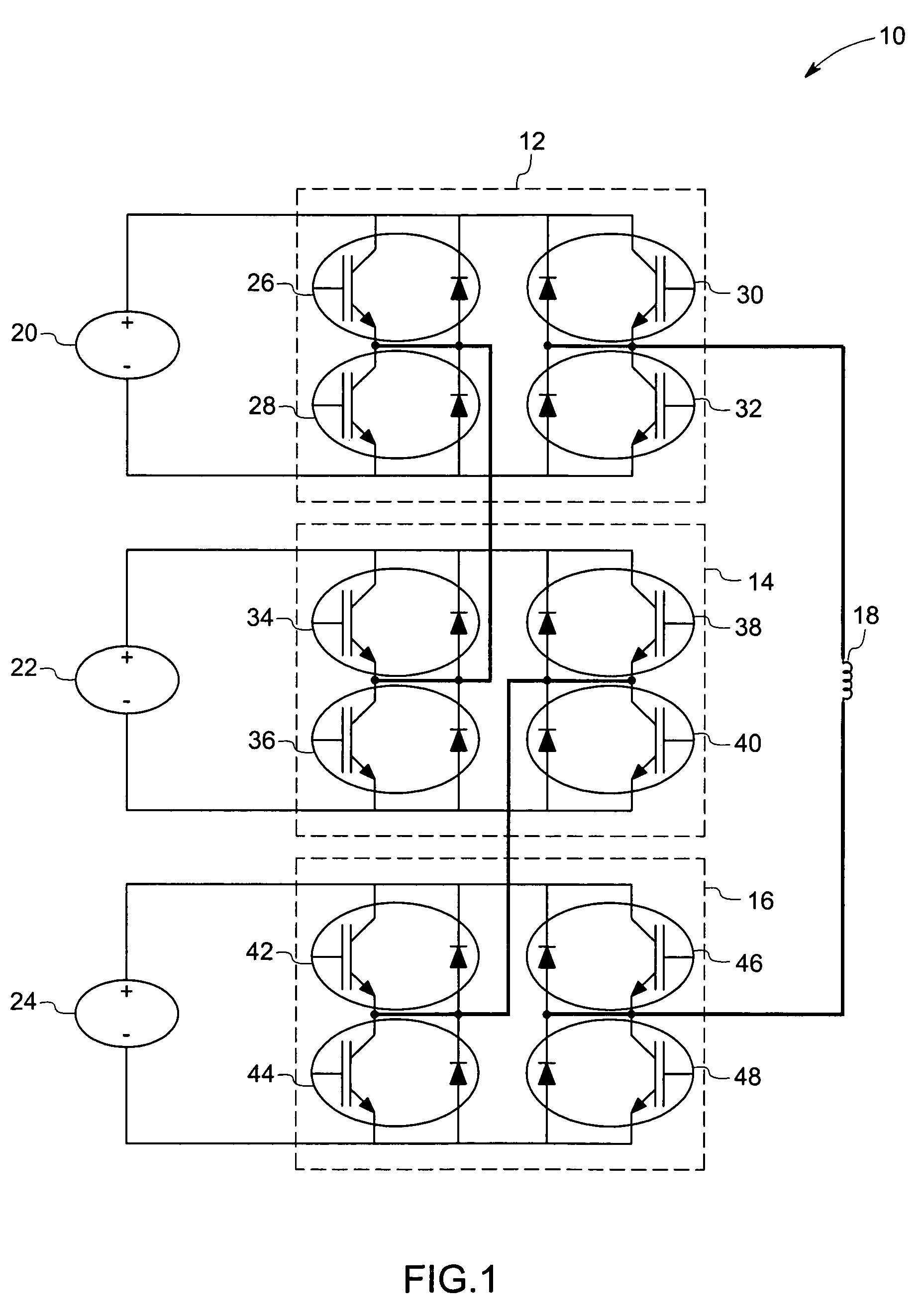
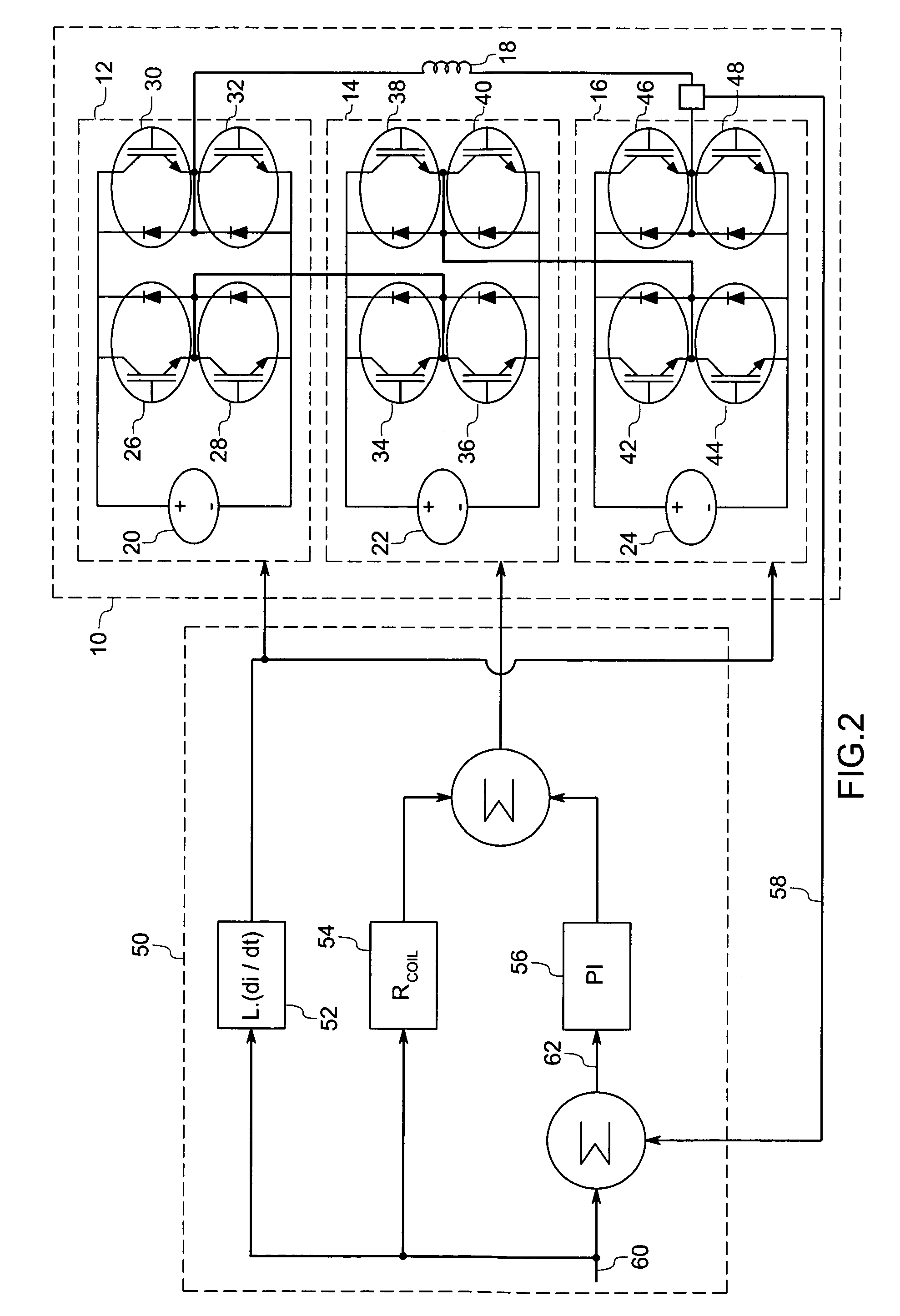
A gradient amplifier arrangement is described that comprises a gradient amplifier power stage. The device may be employed to provide a current to a gradient coil, as in a MRI system. The circuitry disclosed includes a series coupling of a first bridge amplifier operating at a first voltage, a second bridge amplifier operating at a second voltage, a third bridge amplifier operating at a third voltage, and a gradient amplifier control stage. The amplifiers may provide output voltages at different levels, and may be switched at different times and frequencies to provide a range of output voltage and current levels.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Fast low dropout voltage regulator circuit
A voltage regulator includes first and second closed-loop amplifiers and a N-type transistor. The first amplifier receives a first reference voltage and a feedback voltage. The second amplifier is responsive to the first amplifier and to the regulated output voltage of the regulator. Both amplifiers are biased by a biasing voltage. The second amplifier has a bandwidth greater than the bandwidth of the first amplifier and a gain smaller that the gain of the first amplifier. The N-type transistor has a first terminal responsive to the output of the second amplifier, a second terminal that receives the input voltage being regulated, and a third terminal that supplies the regulated output voltage. The feedback voltage is generating by dividing the regulated output voltage. An optional fixed or dynamically biased current source biases the first terminal of the N-type transistor. The voltage regulator optionally includes an overshoot correction circuit.
Owner:DECICON A CALIFORNIA CORP
Method for accurately measuring narrow pulse modulation parameter
InactiveCN102508045AModulation depth measurementsTransmission monitoringAnalog-to-digital converterField-programmable gate array
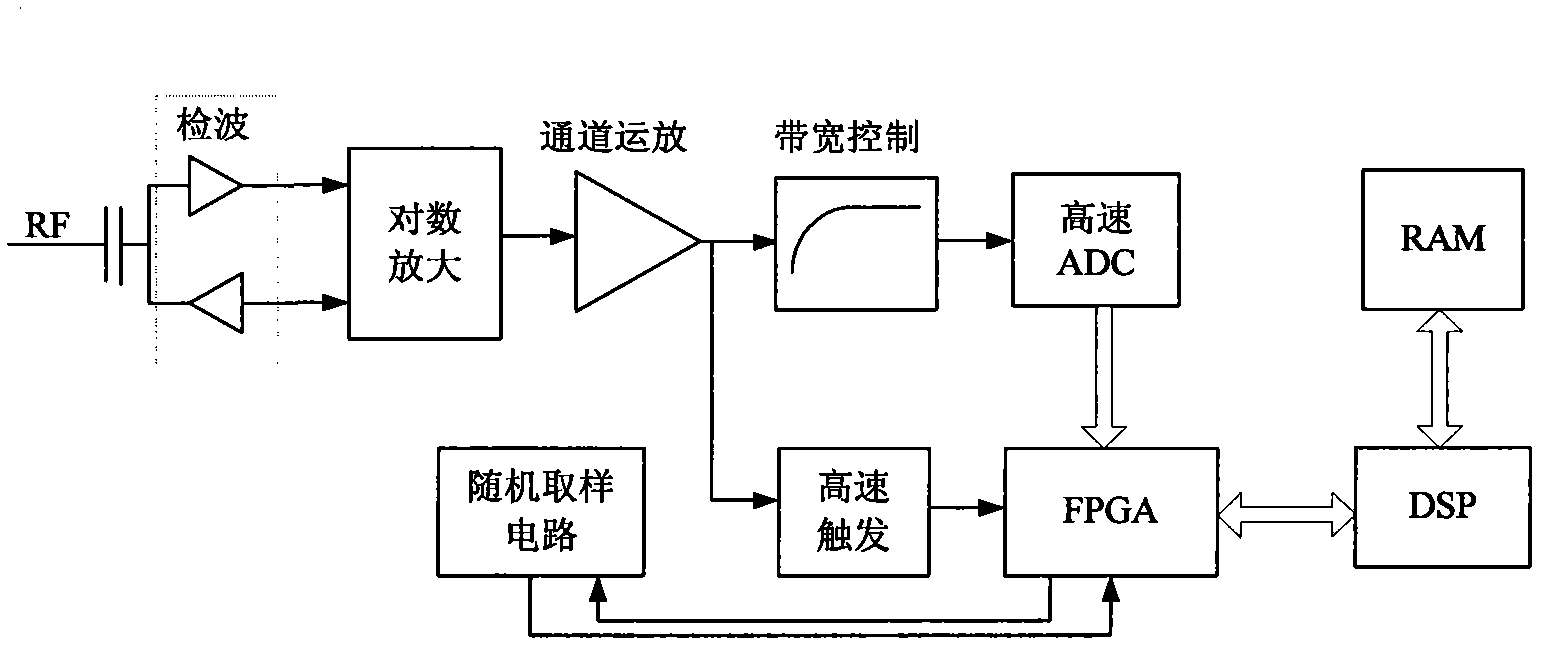
The invention relates to a method for accurately measuring a narrow pulse modulation parameter. According to the method, a narrow pulse modulation signal RF passes through a double-diode detector, a logarithmic amplifier and a channel operational amplifier unit in sequence and is divided into two paths of signals, one path of signal is fed into a high-speed analog-to-digital converter (ADC) module for analog-to-digital (A / D) conversion by a bandwidth control unit, the other path of signal is fed into a high-speed trigger circuit, the high-speed ADC module triggers A / D conversion according to a pulse signal generated by the high-speed trigger circuit, and effective ADC data is acquired, fed into a field programmable gate array (FPGA) and stored in the FPGA according to a trigger signal generated by the high-speed trigger circuit; and a digital signal processor (DSP) unit reads the effective ADC data from the FPGA, processes the data and stores an operation result in a high capacity random access memory (RAM). By the method for accurately measuring the narrow pulse modulation parameter, the narrow pulse modulation parameter with the minimal pulse width of 30ns and the dynamic range of -27 to +20dBm can be measured, and both the time parameter and the amplitude parameter of the narrow pulse modulation signal can be measured.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
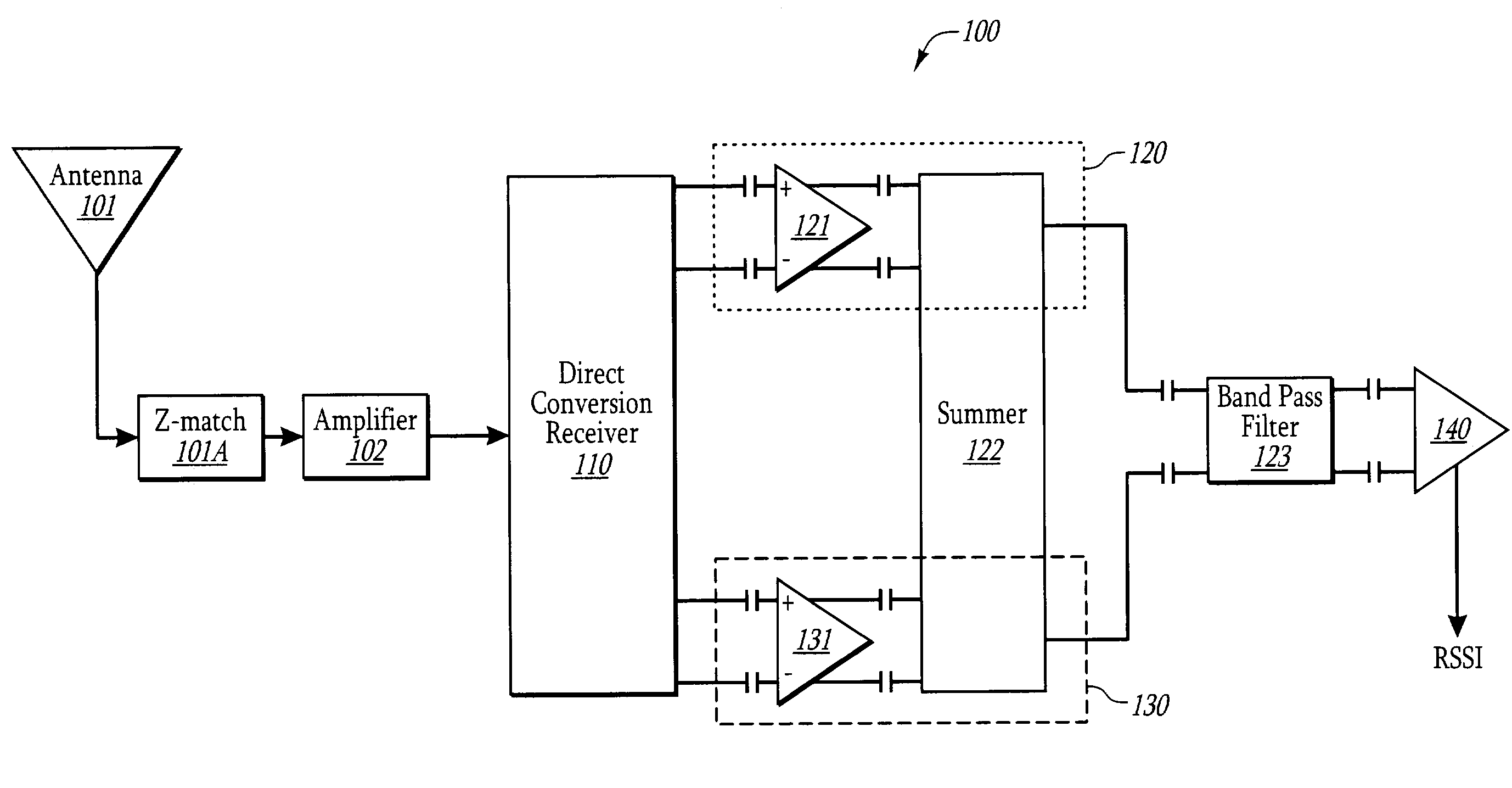
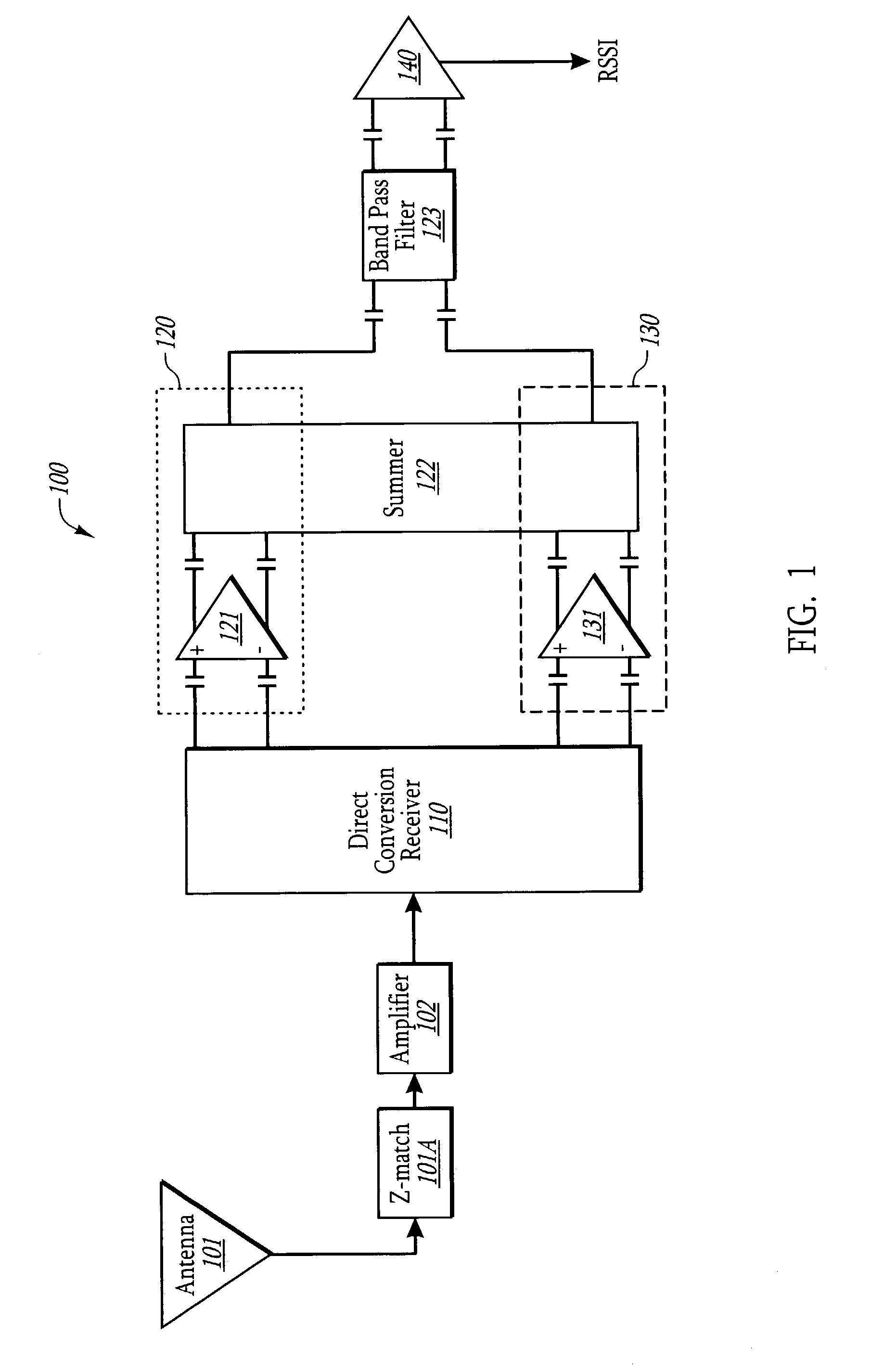
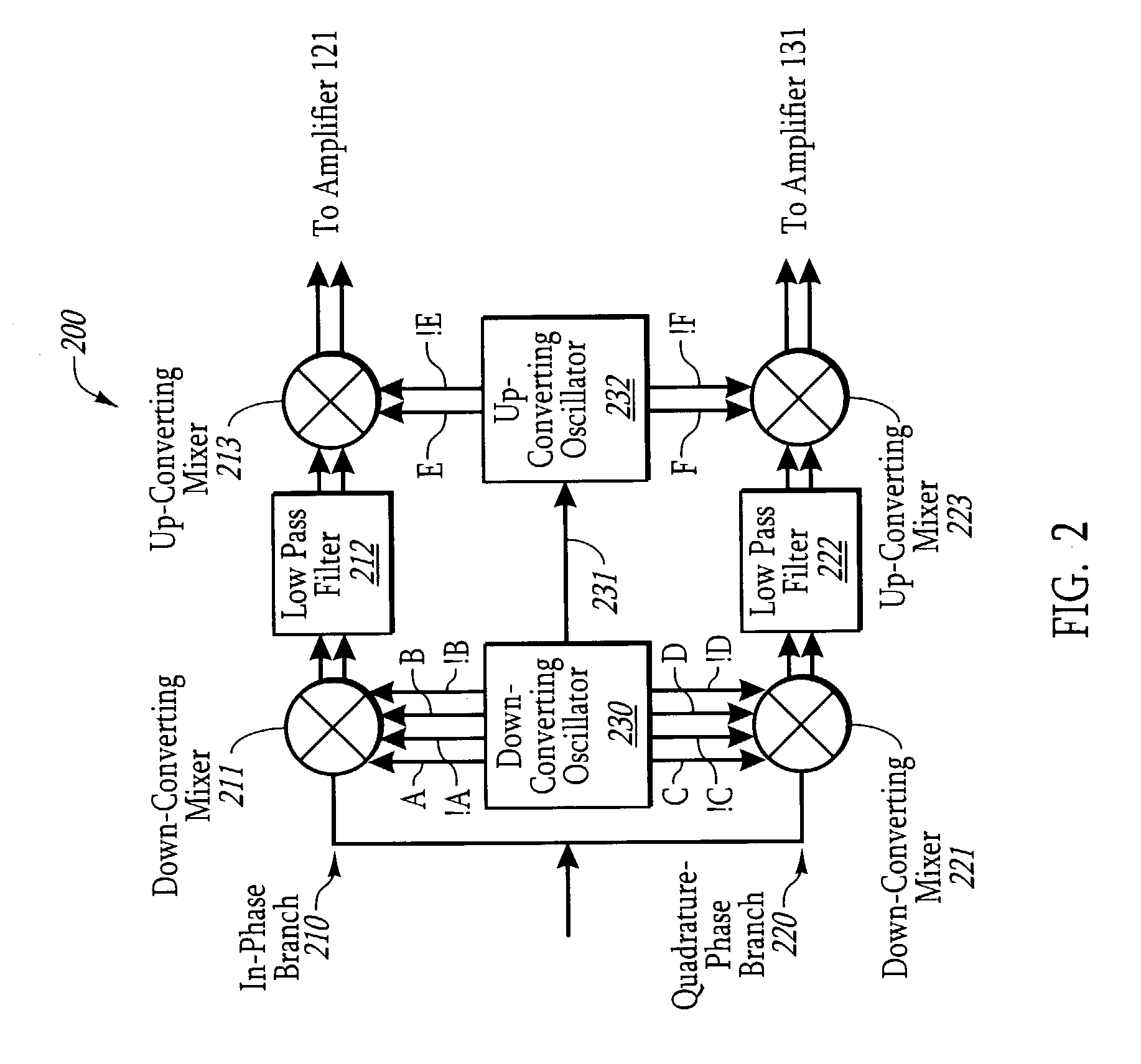
Direct conversion receiver for amplitude modulated signals using linear/log filtering
InactiveUS7113760B1Easy to useConsumes less powerRadio transmissionAmplitude demodulationAudio power amplifierDifferential signaling
A receiver circuit that includes a direct conversion receiver that receives a modulated signal, and generates an in-phase differential signal and a quadrature-phase differential signal. The receiver circuit includes an in-phase branch that processes the in-phase differential signal, and a quadrature-phase branch that processes the quadrature-phase differential signal. Each branch includes an amplifier and a summer. The amplifier is configured to receive and amplify the respective in-phase or quadrature-phase differential signal. The summer receives the resulting amplified differential signal and sums the signals to generate a single signal. A log amplifier receives the summed in-phase and quadrature-phase signal, and generates an RSSI signal that is proportional to the log of the difference between the two summed signals. The data may then be extracted based on the amplitude of the RSSI signal.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
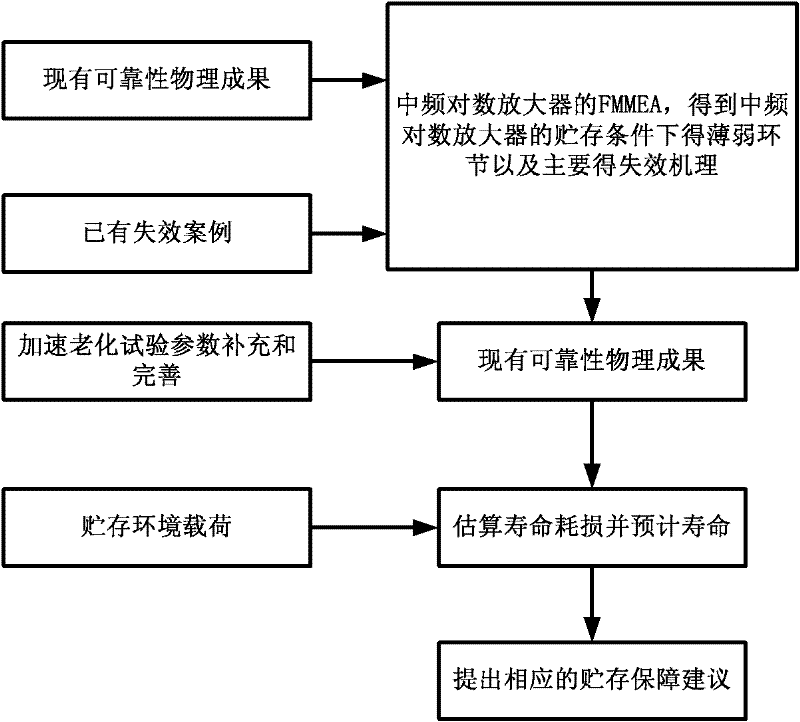
Method for forecasting service life of intermediate frequency log amplifier based on failure physics
The invention relates to a method for forecasting the service life of an intermediate frequency log amplifier based on failure physics. The method comprises the following six steps of: 1) analyzing failure information of a failure mode of intermediate frequency log amplifier electronic products and component information of a product structure technology, and confirming a potential failure mechanism and a failure physical model thereof; 2) confirming an environmental stress influencing the failure mechanism; 3) correcting related parameters in the deduced failure physical model by performing an accelerated ageing test; 4) utilizing an environmental stress sensor to monitor and record the environmental stress in the life cycle of the products; 5) utilizing the confirmed failure physical model to calculate a forecasted time to failure, namely, TTF, under different stress levels, and respectively calculating the life expenditure of the products caused by different failure mechanisms under each stress level according to an expenditure definition; and 6) forecasting the remained life of the products under different failure mechanisms, analyzing the reliability of the intermediate frequency log amplifier and obtaining the failure rate and reliability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
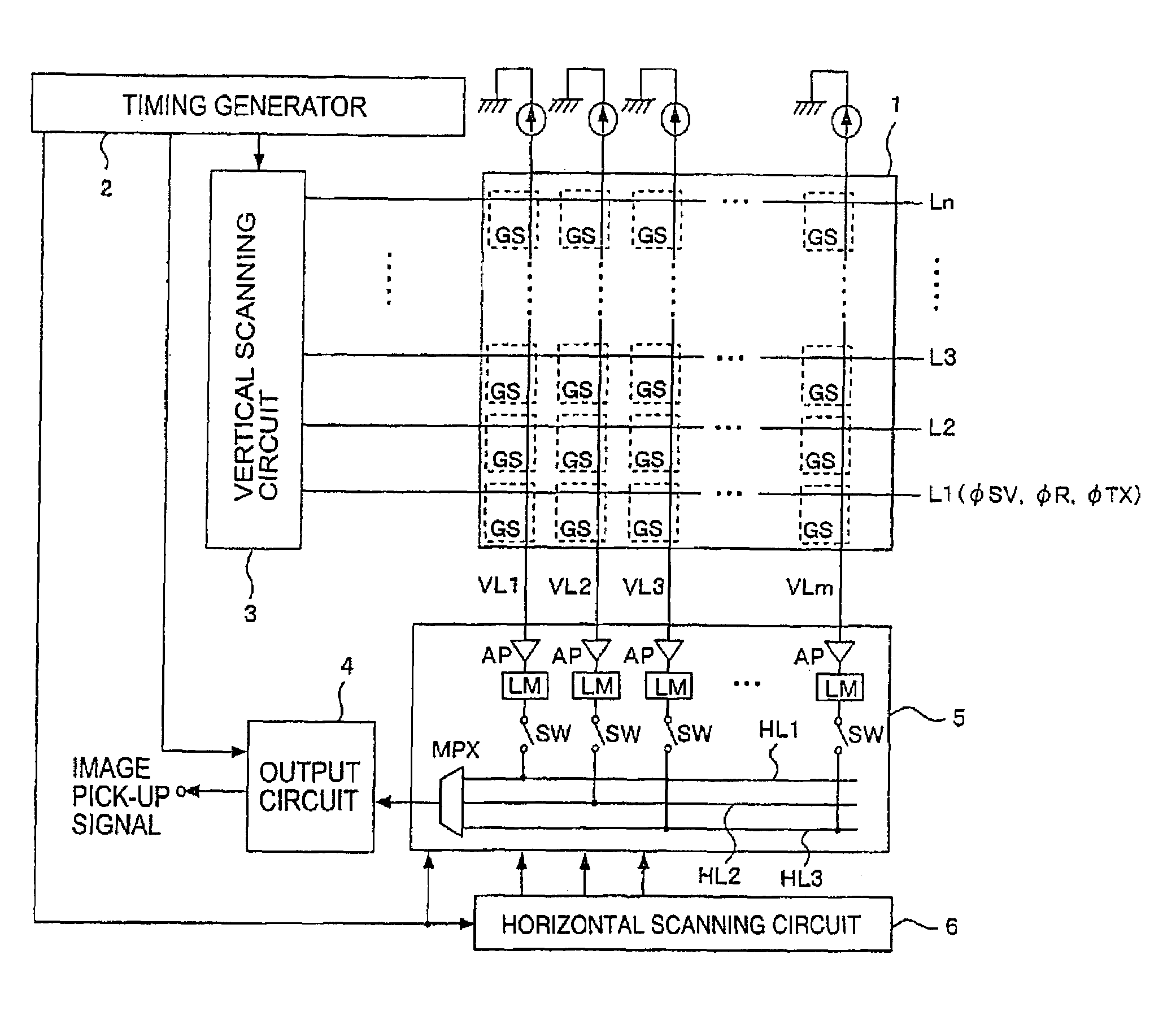
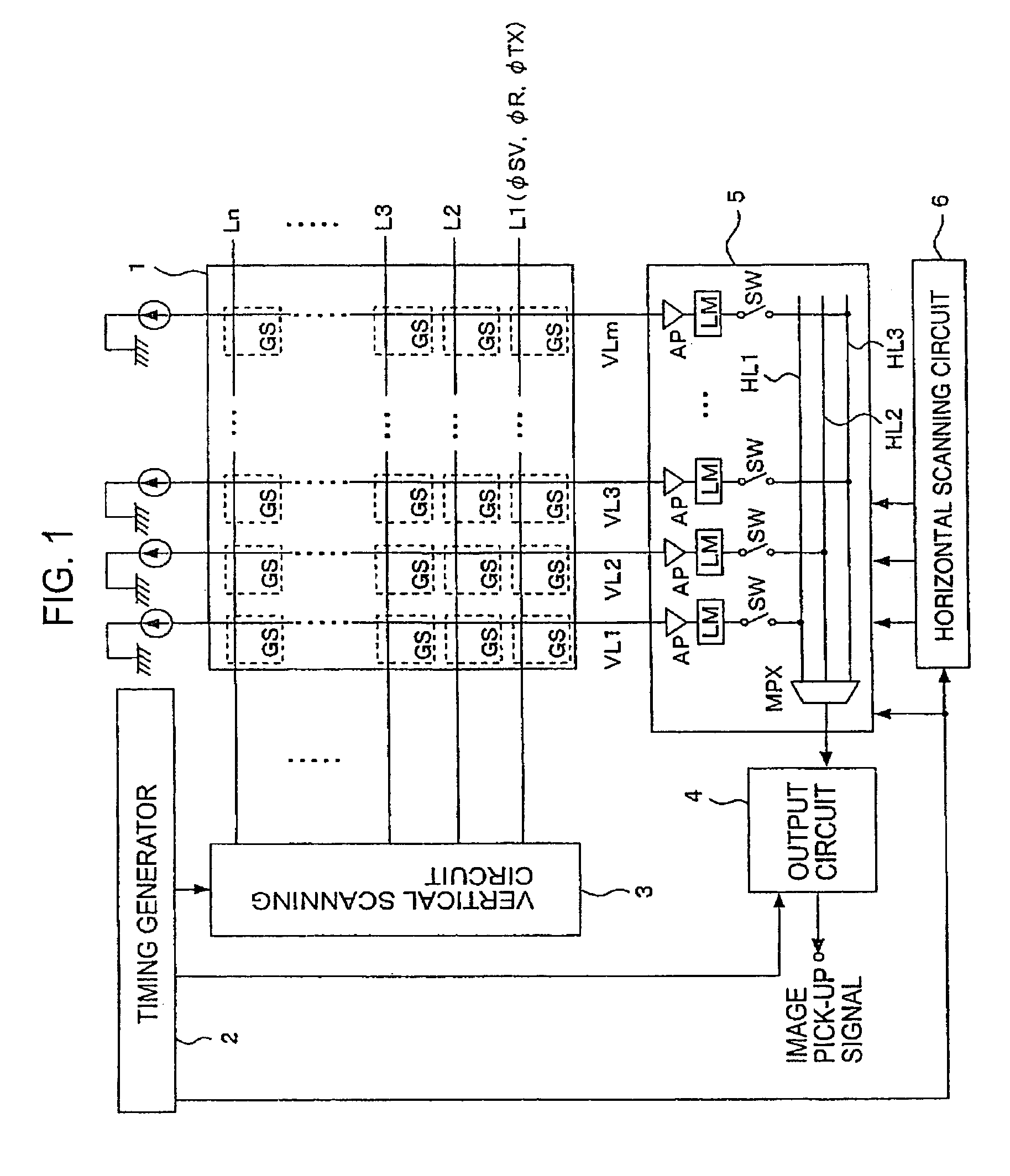
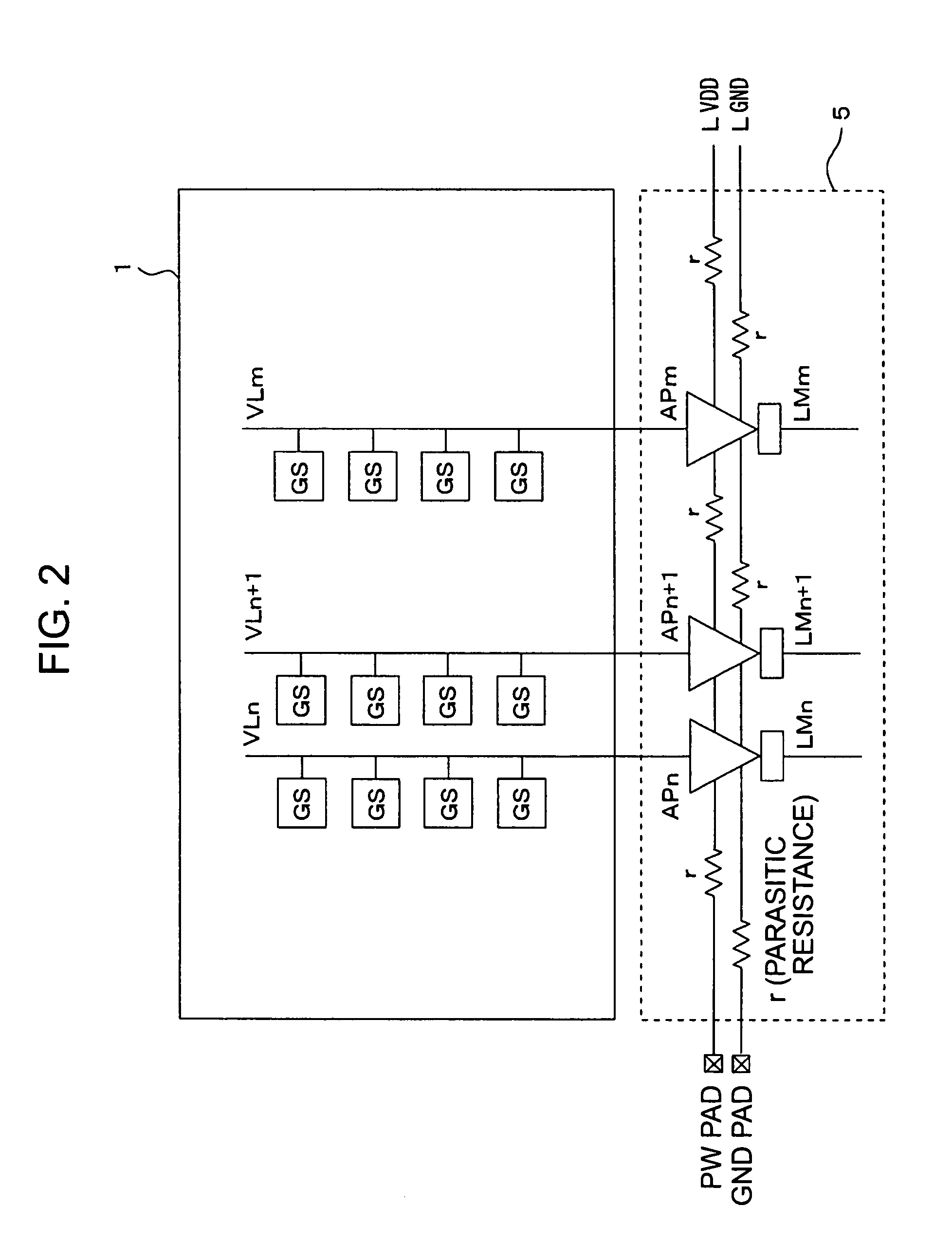
Solid-state image-pickup device with column-line amplifiers and limiters
ActiveUS7141775B2Reduce current consumptionInhibit outputTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierTuned amplifier
The levels of the power supply and the ground are kept constant against a parasitic resistance by keeping the constant current of an amplifier irrespective of the size of a pixel signal and the gain of the amplifier in this case in an image signal reading circuit system having the amplifier arranged to each column. The amplifier has a limiter at an output terminal thereof which limits an output voltage of the amplifier to a range for keeping the constant consumption-current.
Owner:SONY CORP
High-precision remote optical path switch method and system
InactiveCN101789827AHigh precisionImprove the attenuation effectFault recovery arrangementsTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsAudio power amplifierOptical power
The invention discloses a high-precision remote optical path switch scheme and a system, belonging to the technical filed of optical networking communication. An on-line monitoring and switching unit exchanges information with a remote console by Ethernet or a GPRS mode, a main optical-fibre circuit and an auxiliary optical-fibre circuit are utilized to transmit optical signals, and optical signal power is monitored and compared with a set switching threshold to determine whether the optical path switching is gated; the system comprises the on-line monitoring and switching unit, a communication control unit and the like; the on-line monitoring and switching unit is composed of an optical splitter, a photodiode, a logarithm amplifier, an A / D converter, an optical switch and a control chip; and by introducing the logarithm amplifier, the accuracy of the optical power acquisition value of the traditional fibre is effectively improved, and the problem that the precision is difficult to be accurately measured due to larger attenuate generated after long distance transmission of an optical fibre trunk network is improved, thereby ensuring more accurate and reliable optical path switch in traditional optical path protection. In addition, after the communication control unit is introduced, remote centralized management on an optical path protection module is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Radio frequency power control method of mobile terminal
InactiveCN101309099ALow costEnergy efficient ICTTransmission control/equalisingAudio power amplifierPower detector
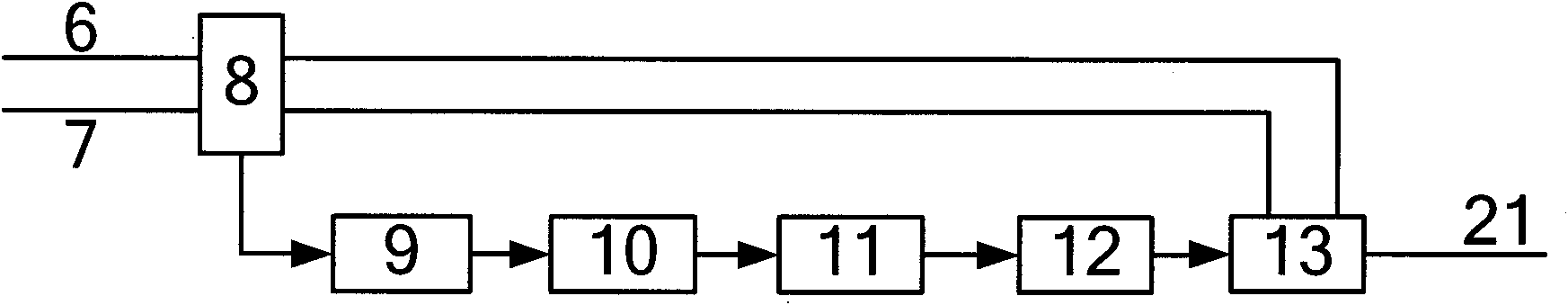
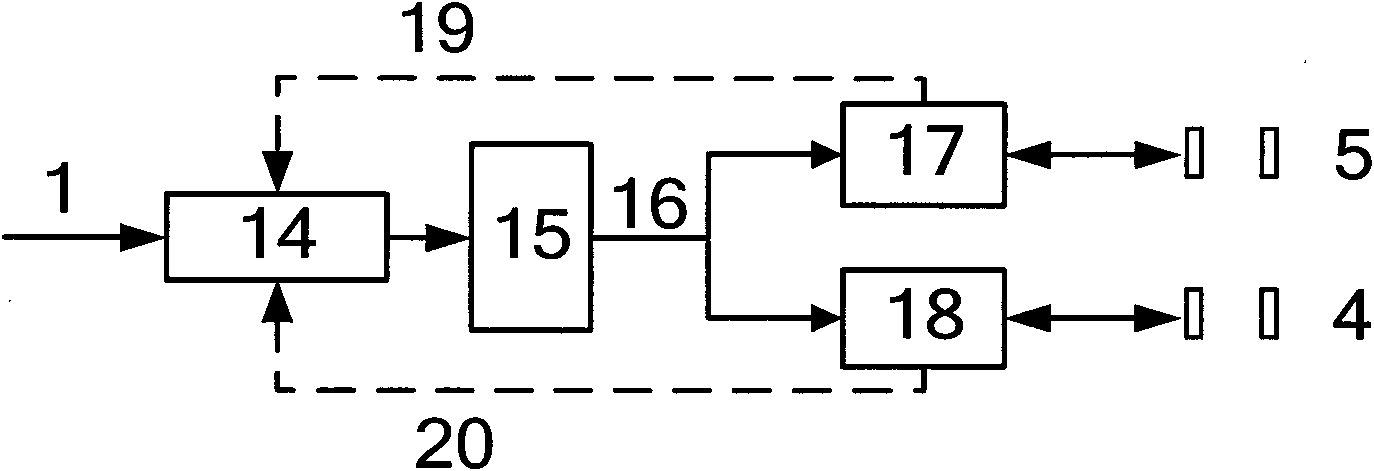
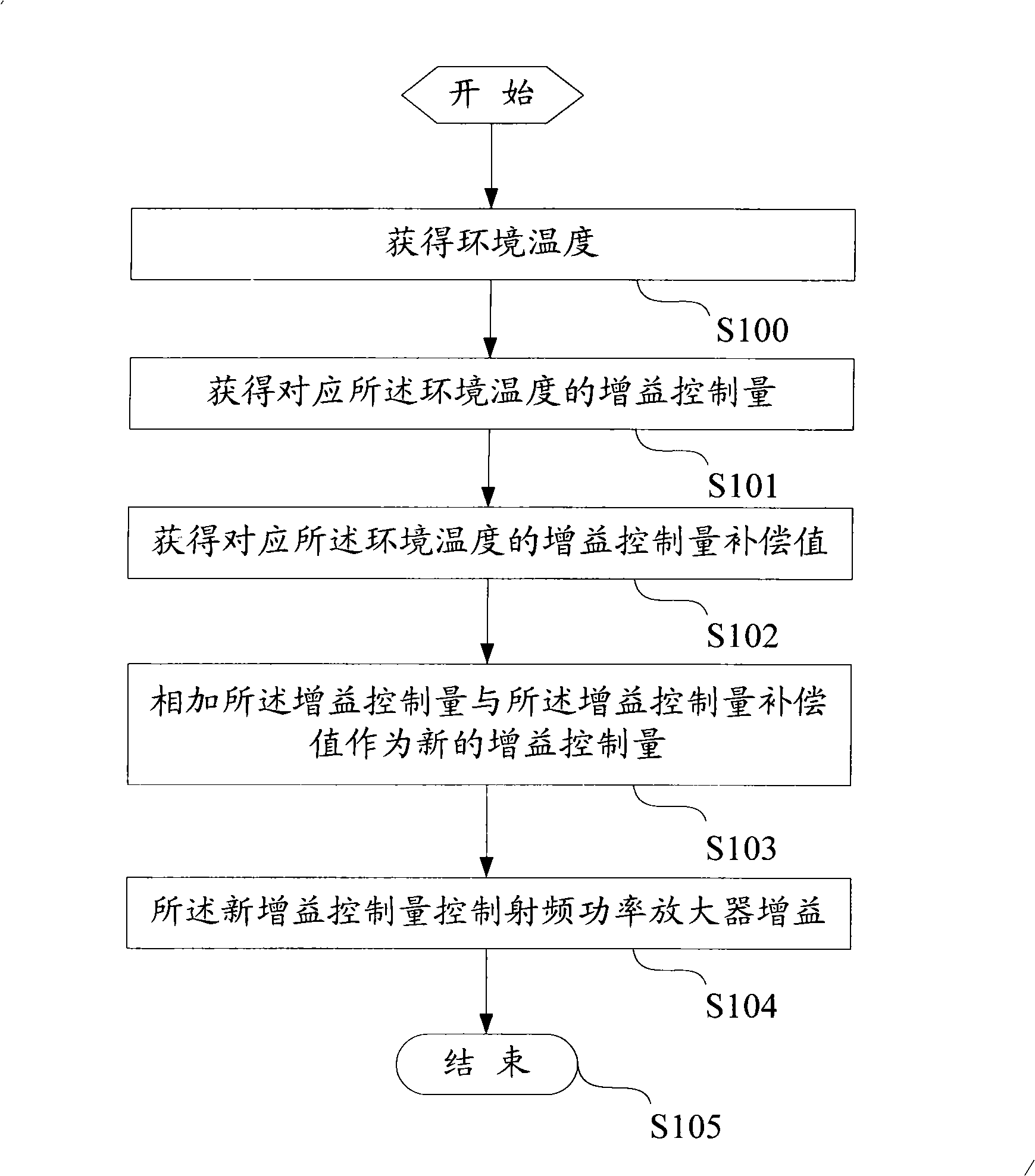
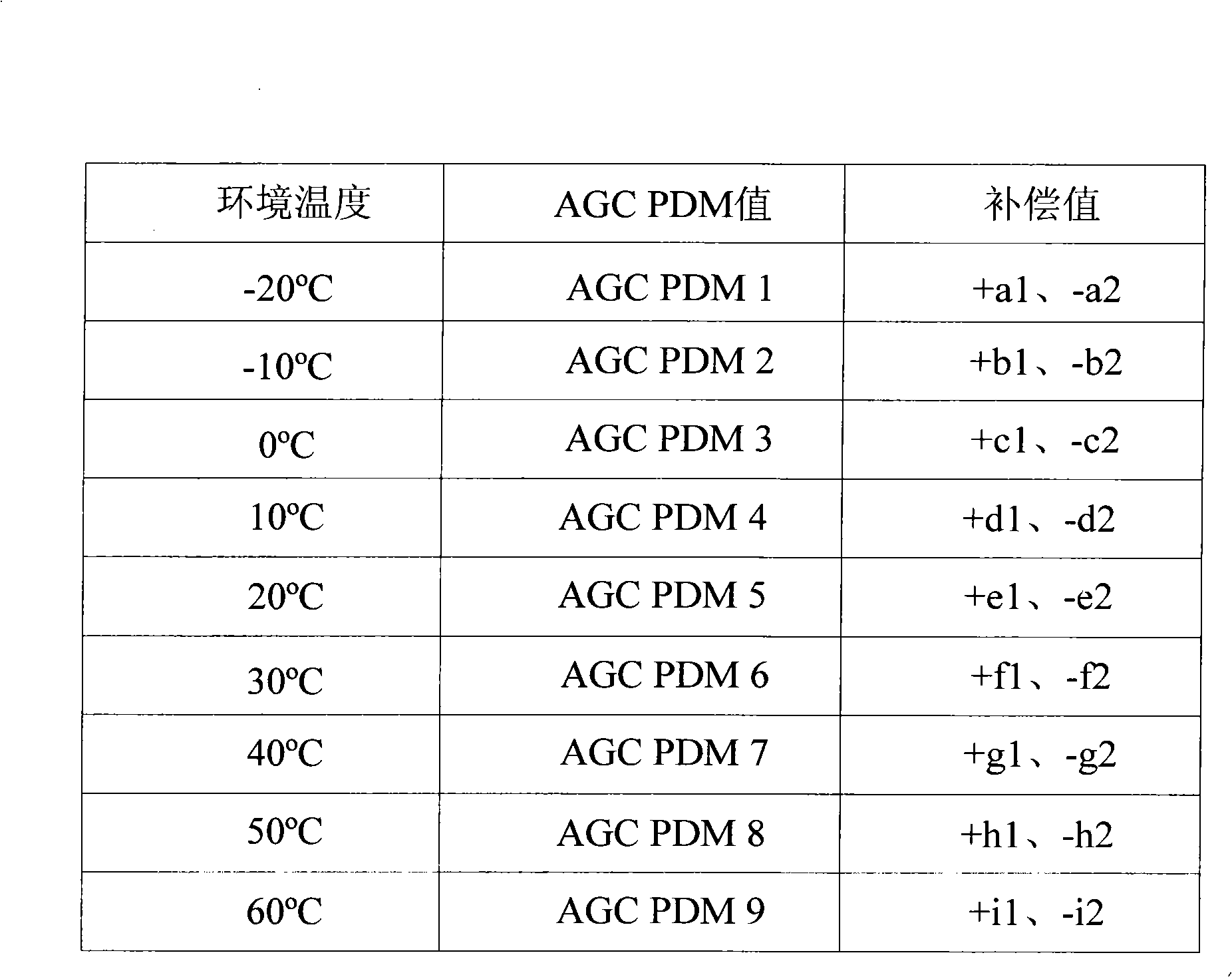
The invention discloses a radio frequency power control method for a mobile terminal, which is characterized in that the method includes the following steps: a), obtain environment temperature; b), obtain the gain control volume corresponding to the environment temperature; c), the gain control value controls the gain of a radio frequency amplifier. The radio frequency power control method of the invention controls the radio frequency power through the detection of the environment temperature, thus saves the HDET circuit or the linear gain logarithmic amplifier power detector circuit, and reduce the cost.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
F-P/ fiber Bragg grating (FBG) fiber sensor demodulation system
PendingCN107024236AHighly integratedImprove performanceConverting sensor output opticallyBeam splitterFourier transform on finite groups
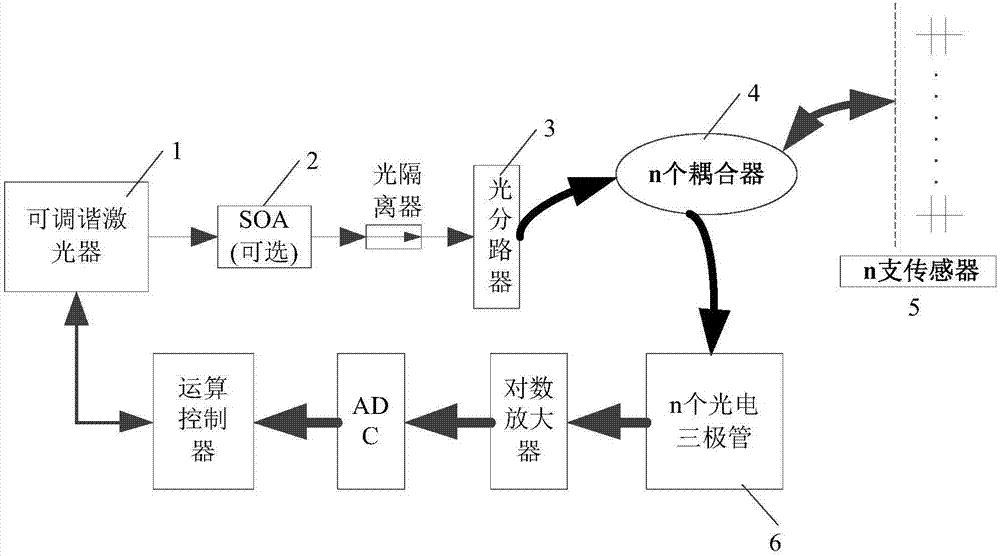
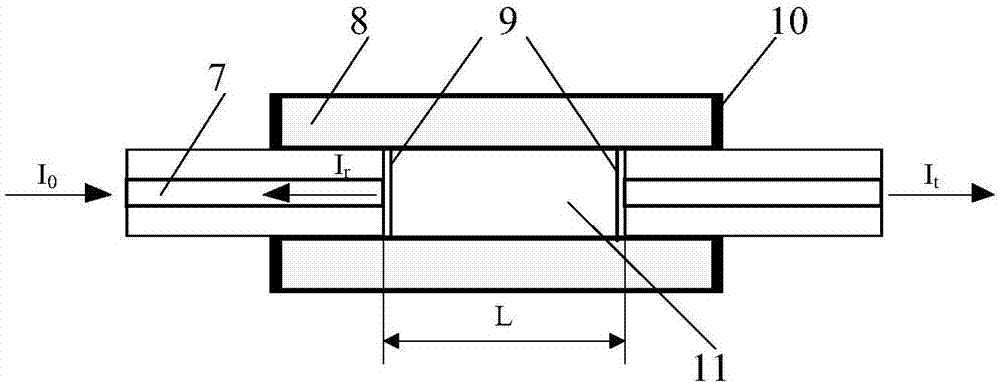
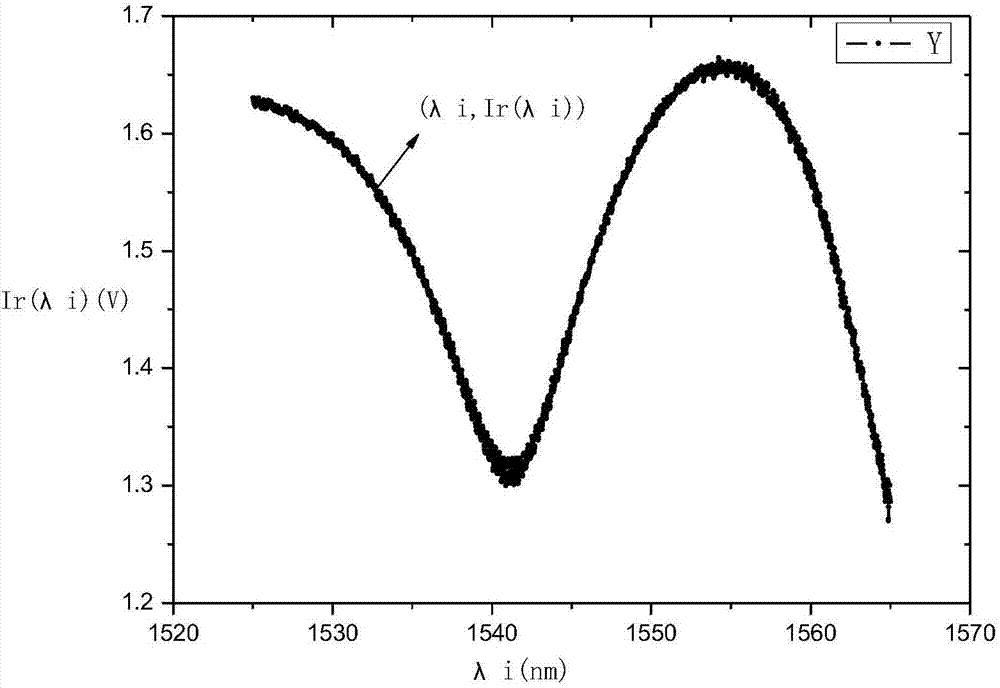
The present invention discloses an F-P and FBG fiber sensor demodulation system, and aims to provide an F-P / FBG demodulation system which is high in wavelength resolution, and enables the demodulation precision to be improved. The F-P / FBG fiber sensor demodulation system of the present invention is realized by the following technical scheme that under the control of an operation control unit, a tunable laser emits out a beam of C-wave band laser of a constant wavelength, by an optical amplifier SOA and / or an optical isolator, and by being divided equally via a beam splitter, the incident light respectively irradiates to n F-P / FBG sensors in one-to-one correspondence, the light reflected by the F-P / FBG sensors is coupled to n phototriodes in one-to-one correspondence by n optical couplers, the optical power is converted into an optical current, the optical current is converted into an optical voltage entering an analog-digital converter by a logarithmic amplifier, the wavelength-reflection optical voltage digital quantity acquired in a time-sharing manner is stored in a memorizer of the operation control unit, the operation control unit carries out the fast Fourier transform on a sampled spectrum, the types of the F-P / FBG sensors are distinguished, and a peak searching demodulation algorithm is carried out to obtain a gradient value containing the cavity length information.
Owner:CHENGDU KAITIAN ELECTRONICS
Programmable logarithmic gain adjustment for open-loop amplifiers
InactiveUS6570447B2Computations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Transconductance-based variable gain amplifiers amplify an input voltage by converting the voltage difference to a current and then amplifying the result. At least one resistor network is adjusted depending on the magnitude of the input voltage difference and the output desired. A network of MOS transistor switches with a small footprint adjusts the resistance of the input voltage circuit in a way to insure consistent resistance and low stray capacitance.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Programmable logarithmic gain adjustment for open-loop amplifiers
InactiveUS20020175758A1Decreasing and increasing input resistanceComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for logarithmic/exponential functionsCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
Transconductance-based variable gain amplifiers amplify an input voltage by converting the voltage difference to a current and then amplifying the result. At least one resistor network is adjusted depending on the magnitude of the input voltage difference and the output desired. A network of MOS transistor switches with a small footprint adjusts the resistance of the input voltage circuit in a way to insure consistent resistance and low stray capacitance.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
High dynamic range RF power monitor
A device with at least one channel for measuring high dynamic range, radio frequency (RF) power levels over broad-ranging duty cycles includes a power sensor circuit comprising at least one logarithmic amplifier; at least one directional RF coupler electrically connected to the at least one power sensor; at least one RF attenuator electrically connected to the at least one RF coupler; and at least one sampling circuit electrically connected to the at least one RF attenuator and the at least one RF coupler. The at least one sampling circuit performs analog-to-digital conversion of electrical signals received to provide digitals signals for measuring the RF power level in the at least one channel.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
High-speed-digital-demodulation-based power control system and method of vector network analyzer
ActiveCN104536339ASimple designImprove signal-to-noise ratioProgramme controlComputer controlDigital signal processingIntermediate frequency
The invention provides a high-speed-digital-demodulation-based power control system and method of a vector network analyzer. On the basis of the digital demodulation and processing way, nearly all digital filters with any random bandwidths can be designed by using a digital signal processing technology, thereby improving the signal to noise ratio of demodulation and achieving an objective of enlarging a power scanning range. The digital demodulation link of the vector network analyzer has high linearity, so that the power control accuracy is improved. With the power control method for digital demodulation and processing, the designs of circuits of microwave detector and a log amplifier and the like are not needed, thereby simplifying the loop hardware design. Because demodulation is carried out on the intermediate frequency without limitation of a signal source frequency range, the same set of amplitude stabilization system can be applied to power control of the vector network analyzer in different power ranges as long as the intermediate frequency is not changed.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Method for measuring parameters of secondary radar echo pulses
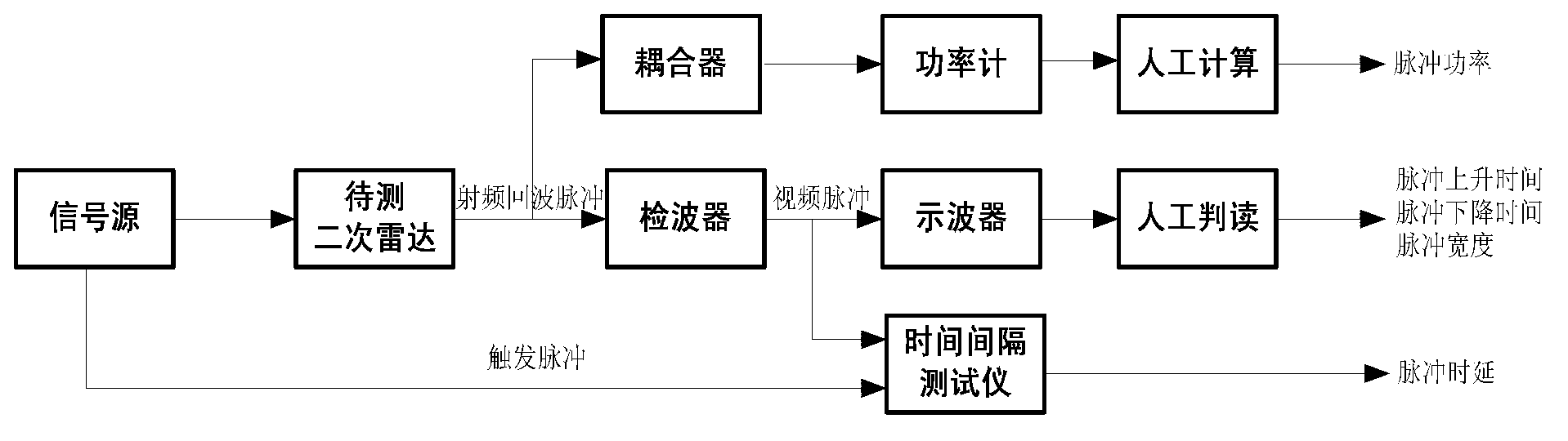
ActiveCN102798846AReduce usageSimple configurationWave based measurement systemsPulse characteristics measurementsHuman–machine interfaceDifferential signaling
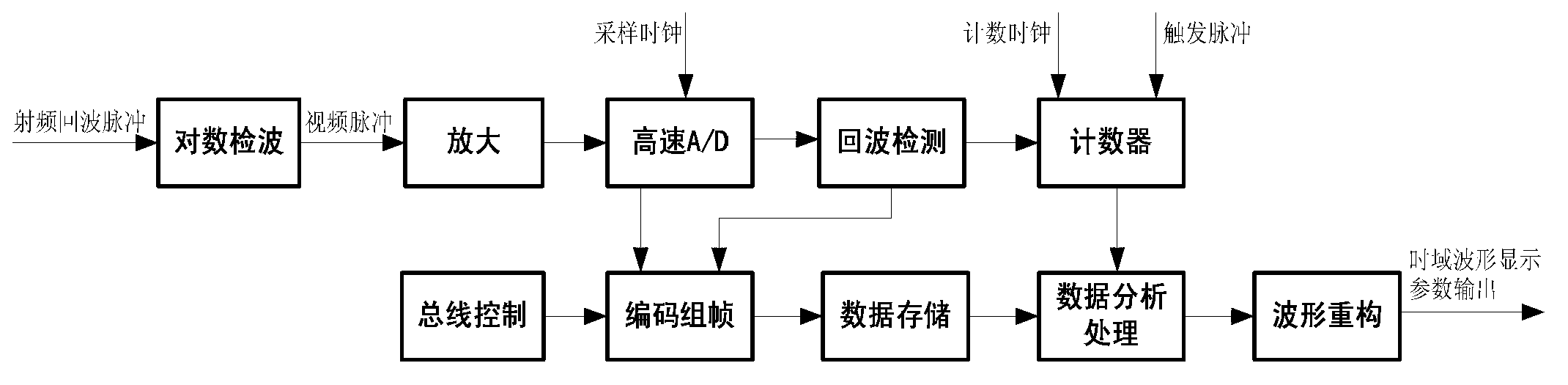
The invention provides a method for measuring parameters of secondary radar echo pulses, which is simple, convenient and reliable in operation and accurate in measurement, is independent of universal instruments, and can be used for accurately measuring the secondary radar echo pulses. According to the technical scheme, the method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: firstly, detecting the secondary radar echo pulses by a log amplifier to obtain video pulse signals; converting the video pulse signals into differential signals, and then carrying out A / D (Analog / Digital) sampling after the differential signals enter an A / D converter; detecting trigger pulse synchronization signals after putting A / D sampling data into an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array); computing the number of clocks by a counter in the FPGA to obtain aircraft distance parameters; submitting the sampling data to computer analysis processing software after being subjected to coding and framing; resolving pulse power and the aircraft distance parameters to obtain the various parameters of the secondary radar echo pulses; and reconstructing measured time domain waveform to a human-computer interface and displaying parameter output. According to the invention, the universal instruments such as an oscilloscope, a power meter and the like are reduced and the complicated test process is simplified.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
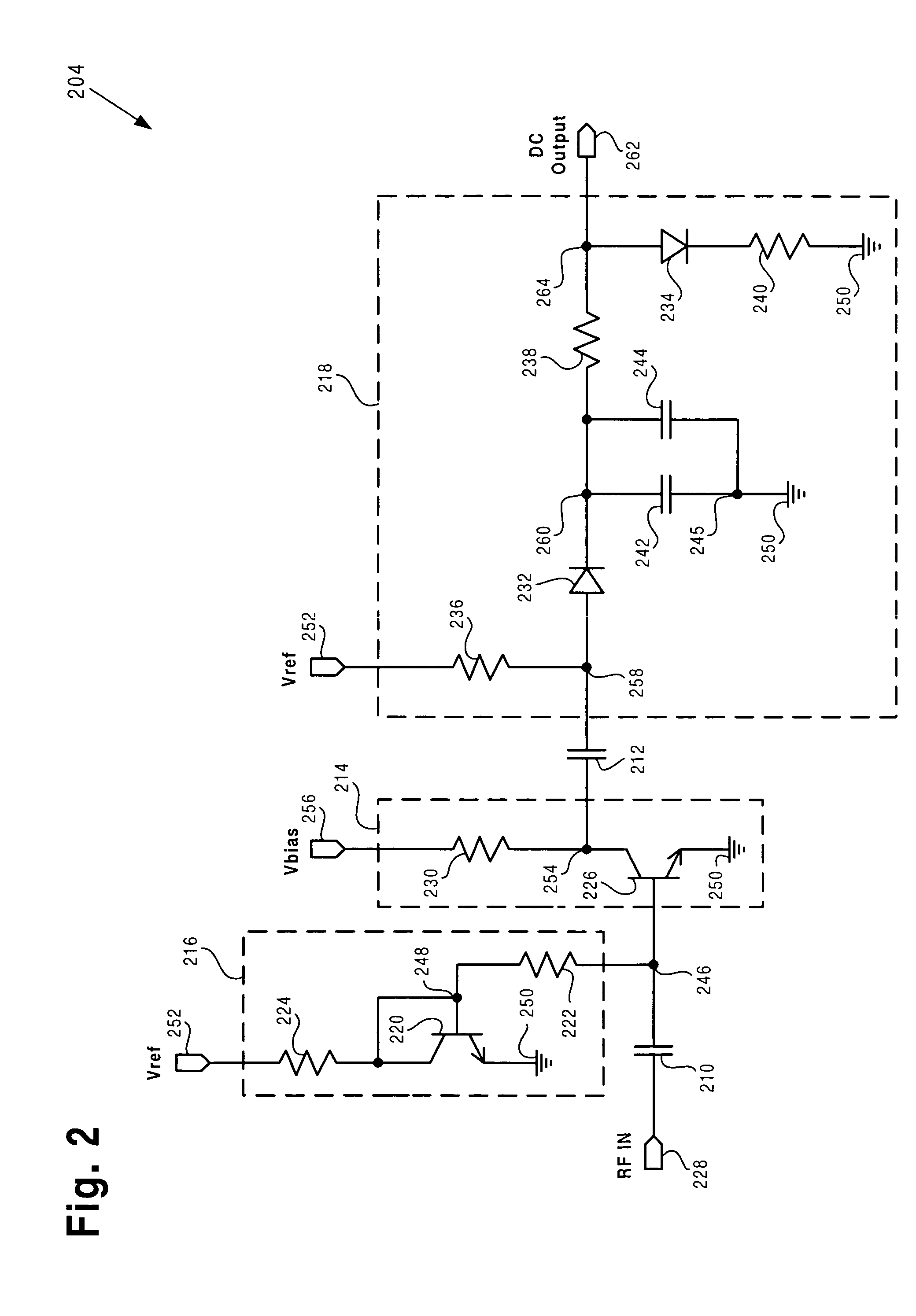
Quiescent current control circuit for power amplifiers
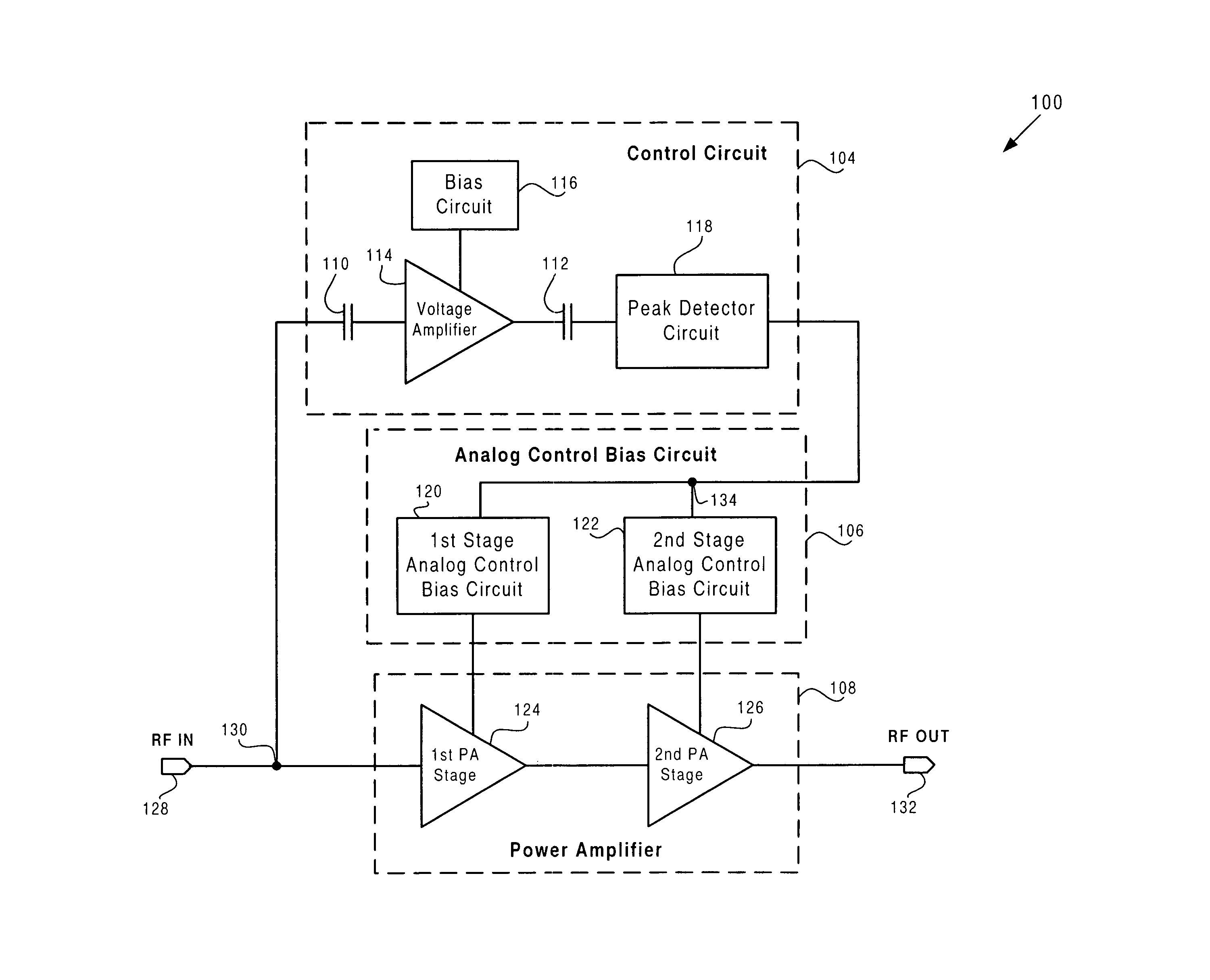
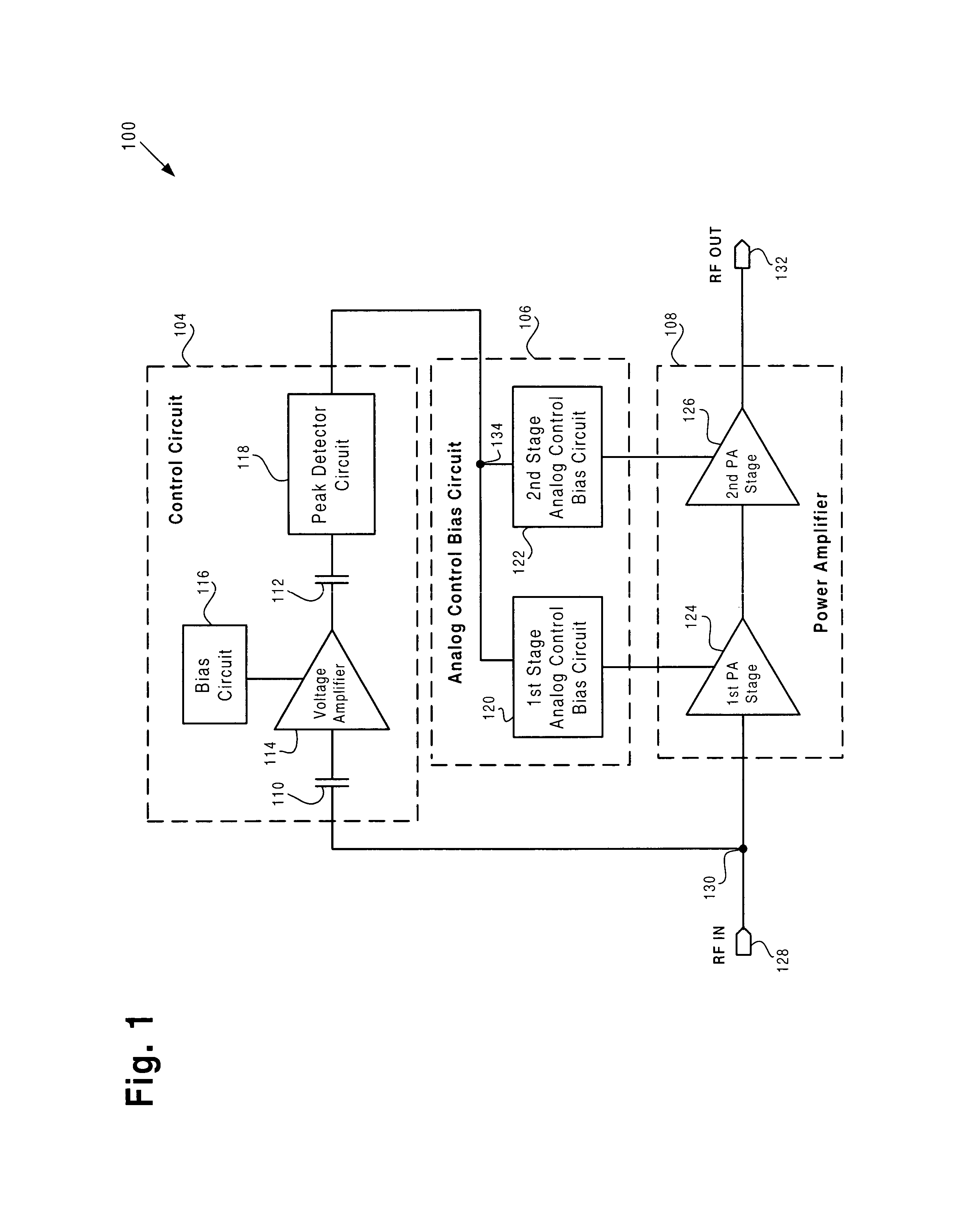
ActiveUS7046087B1Reducing quiescent currentReadily apparentVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesGain controlDetector circuitsAudio power amplifier
According to one exemplary embodiment, a circuit arrangement includes a power amplifier configured to receive an RF input signal. The circuit arrangement further includes a control circuit configured to receive and convert the RF input signal to an output DC voltage. The control circuit includes a voltage amplifier coupled to a peak detector circuit, where the peak detector circuit outputs the output DC voltage. The circuit arrangement further includes an analog control bias circuit coupling the output DC voltage to a bias input of the power amplifier. The output DC voltage causes the power amplifier to have a quiescent current that increases in a way that is substantially logarithmic with respect to the amplitude of the RF input signal. An increase in the RF input power can cause a substantially linear increase in the output DC voltage, where the RF input power is measured in dBm.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com