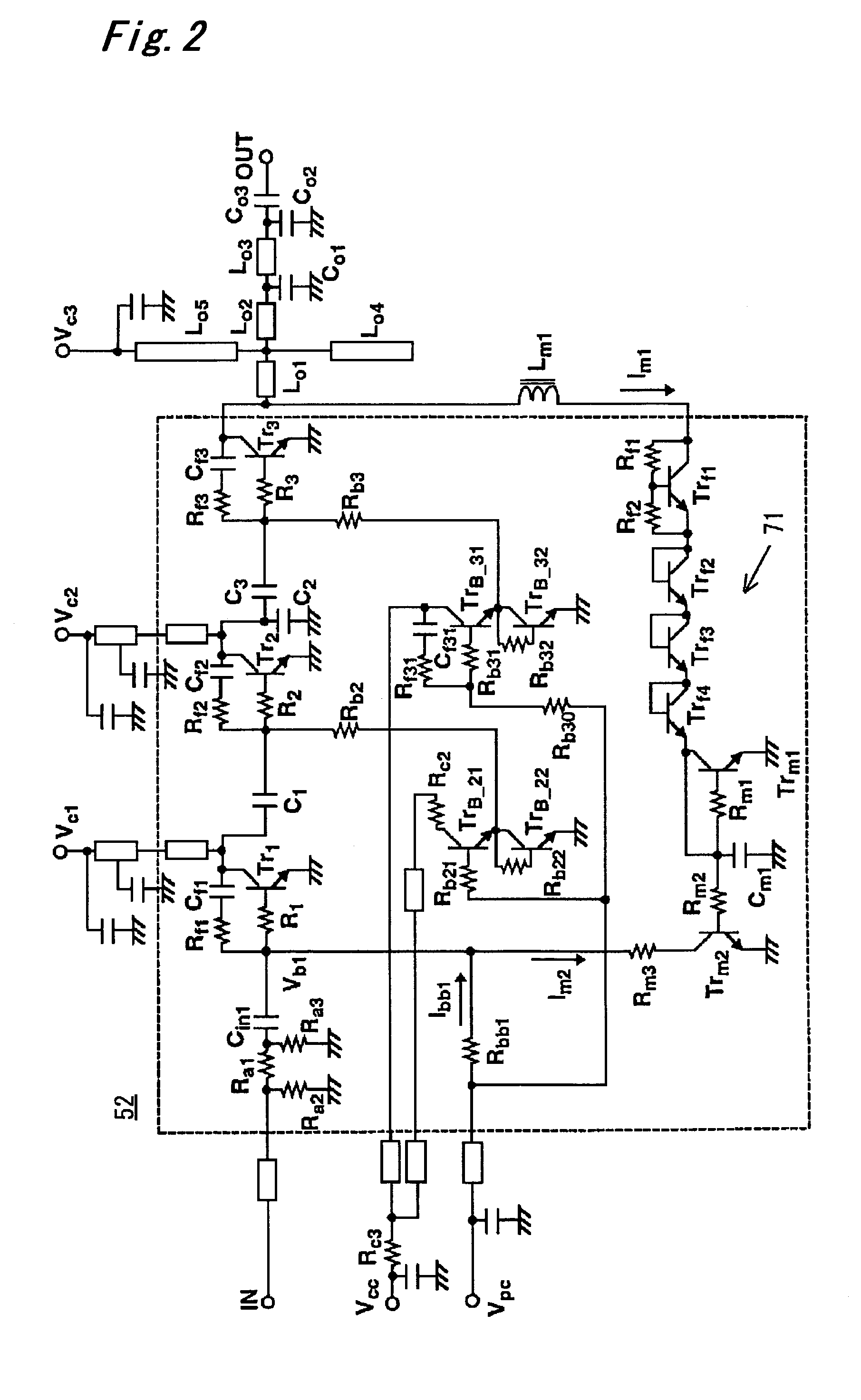
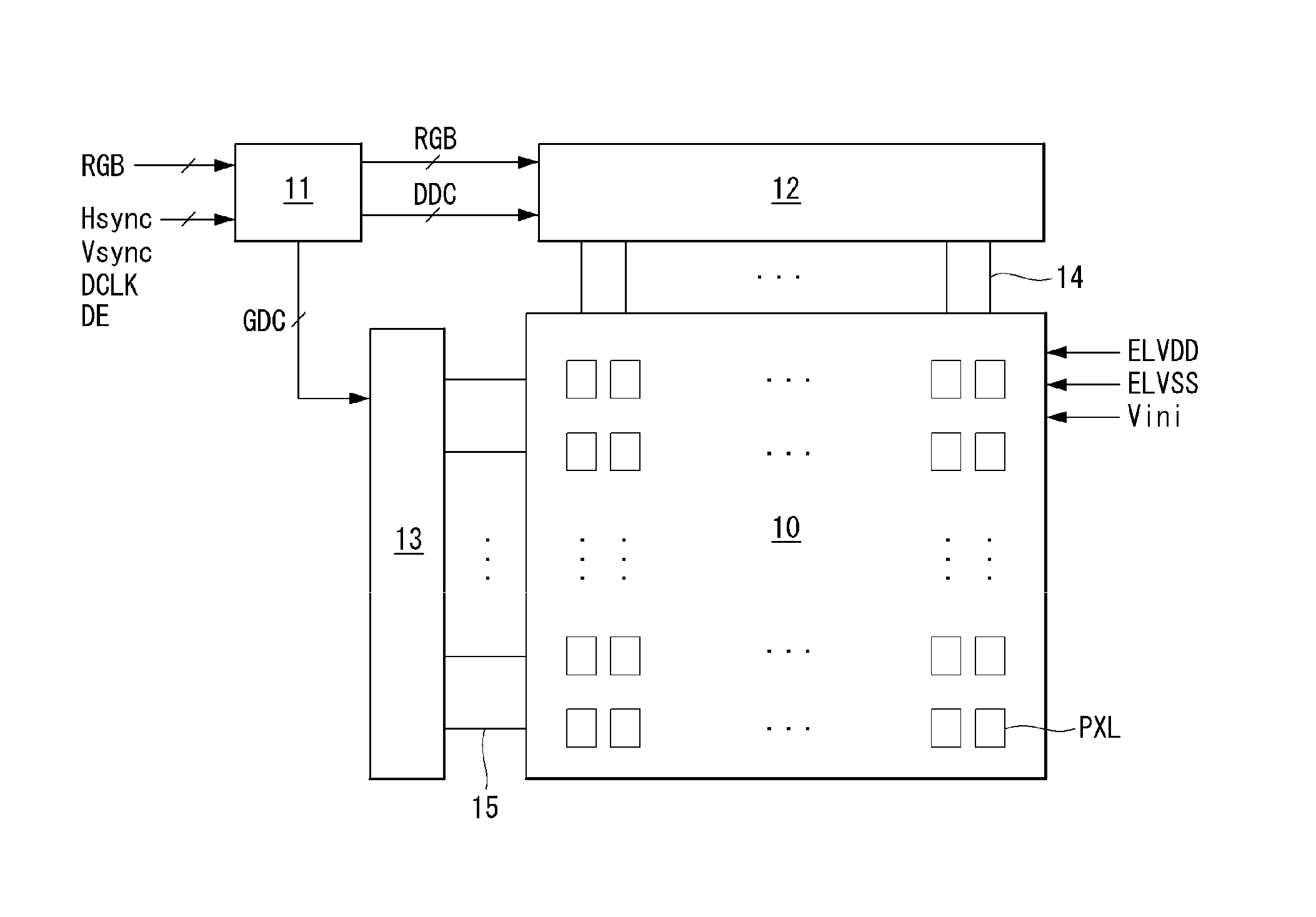
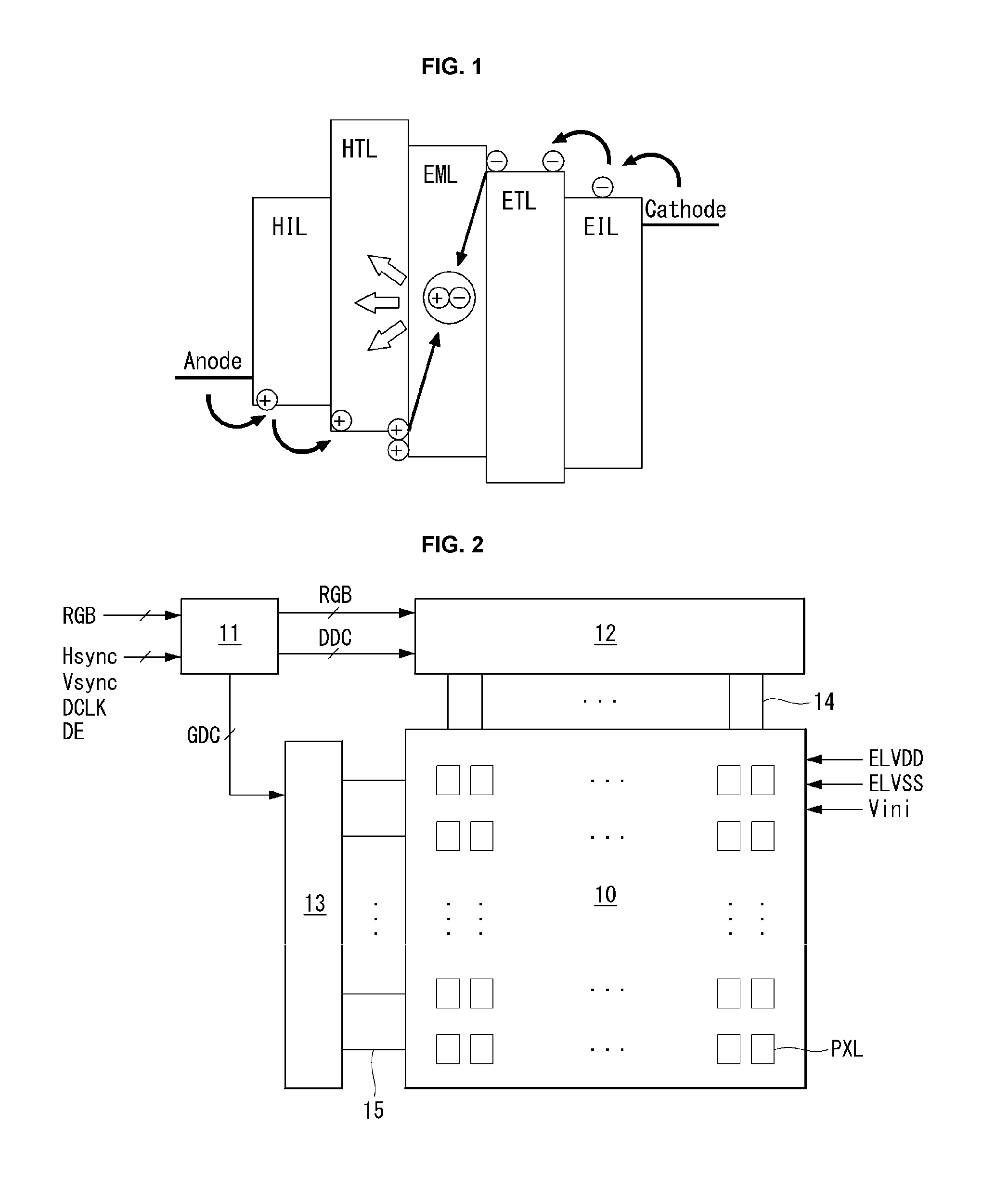
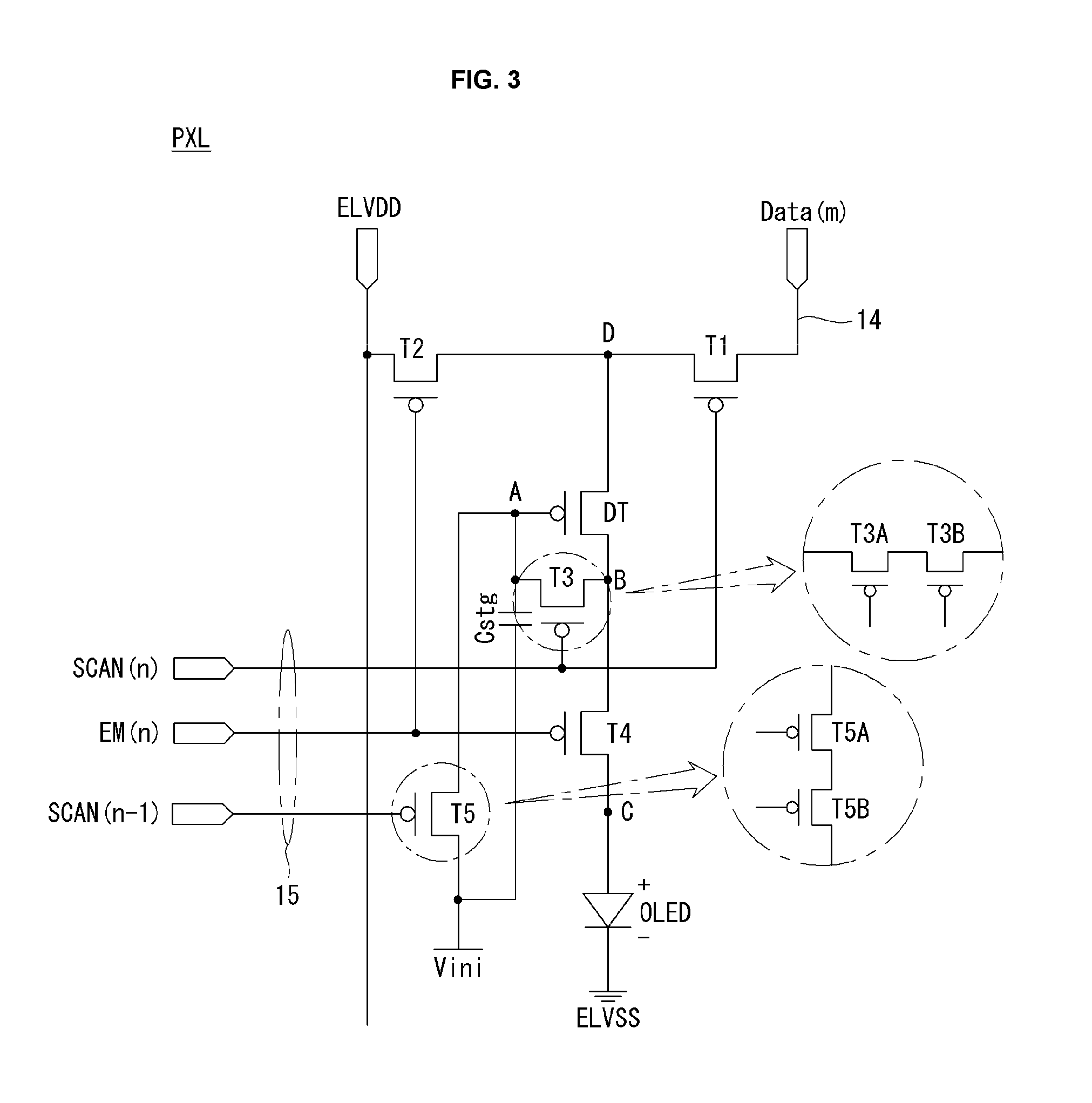
Patents
Literature
401 results about "Optical transistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
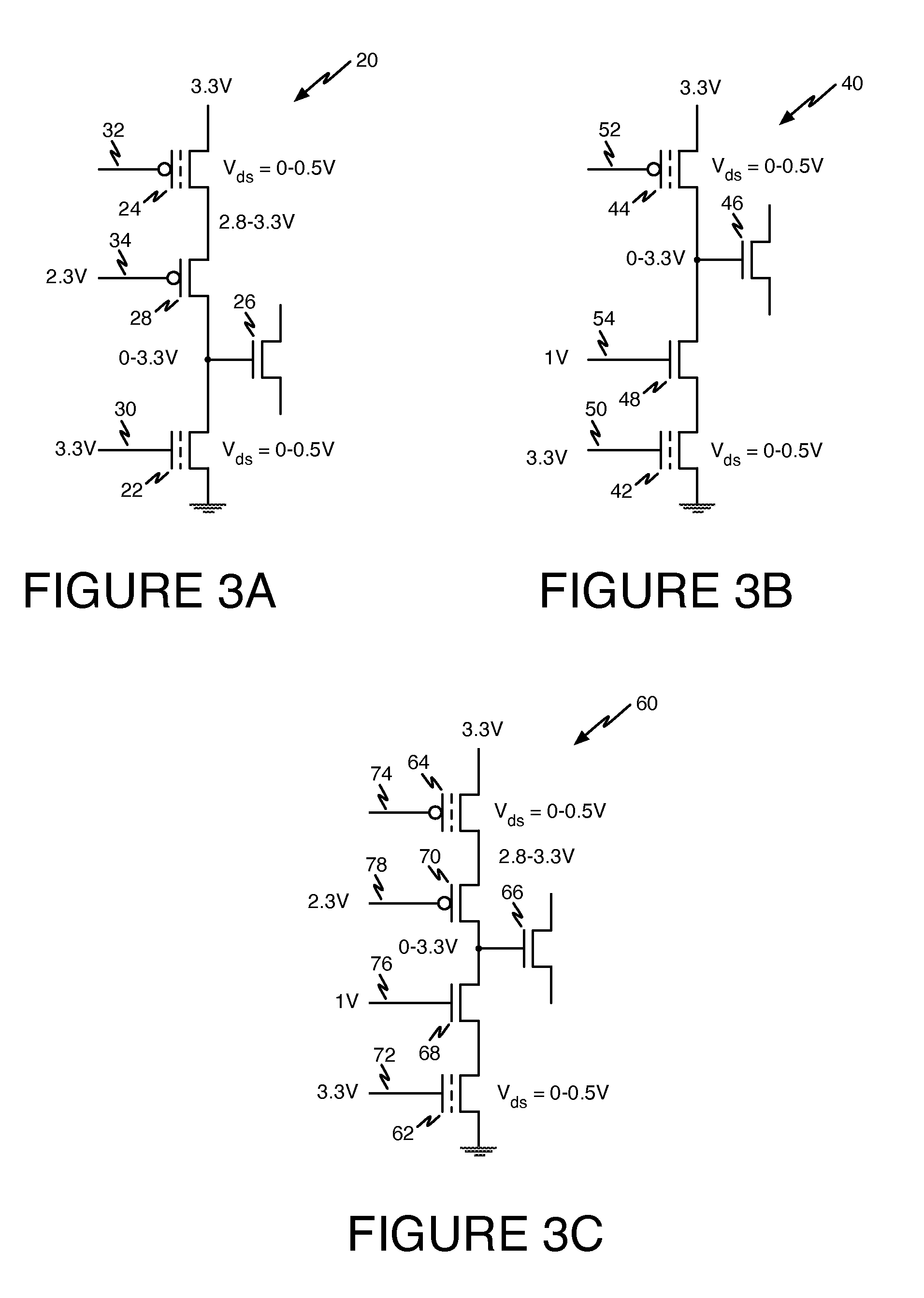
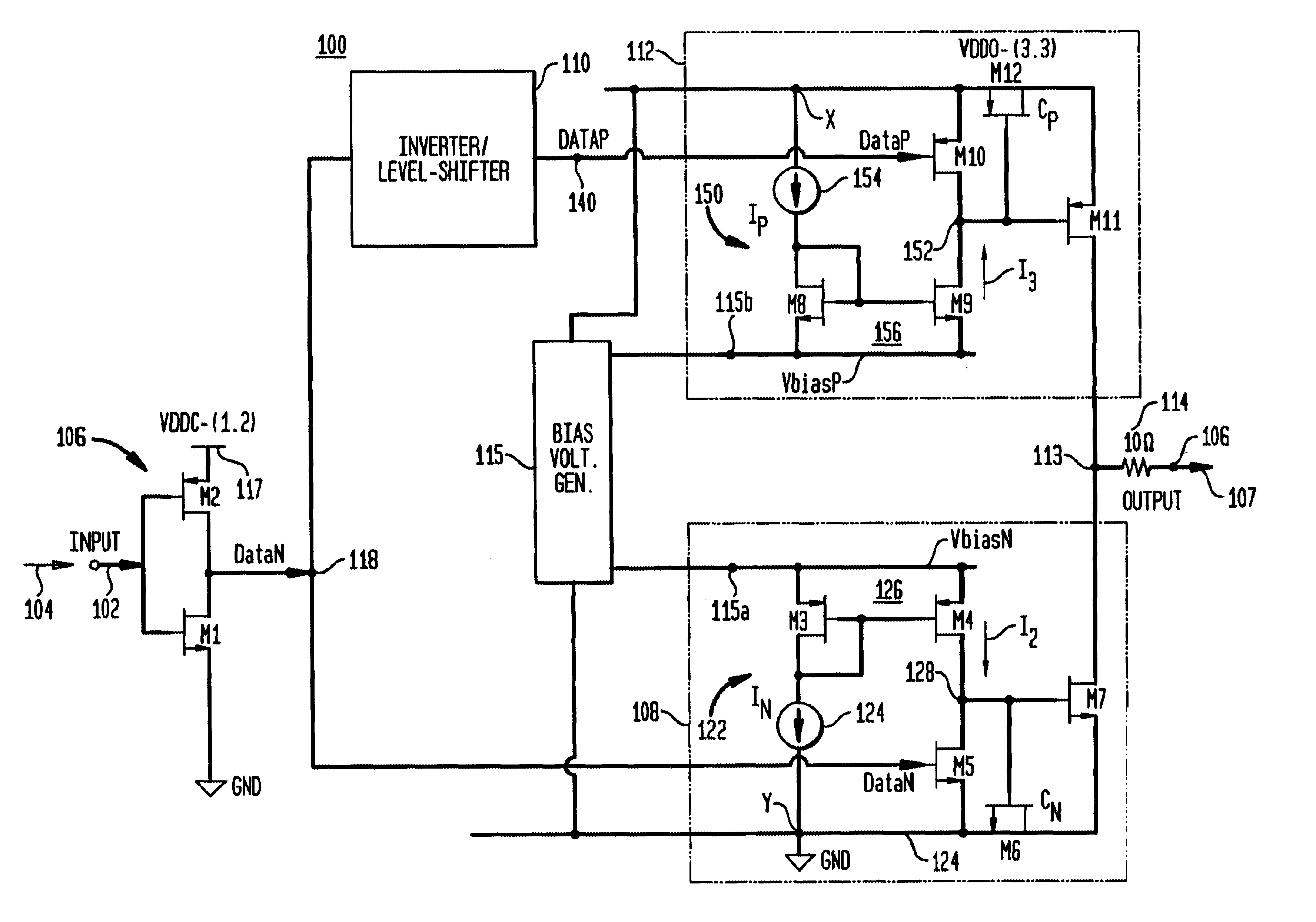
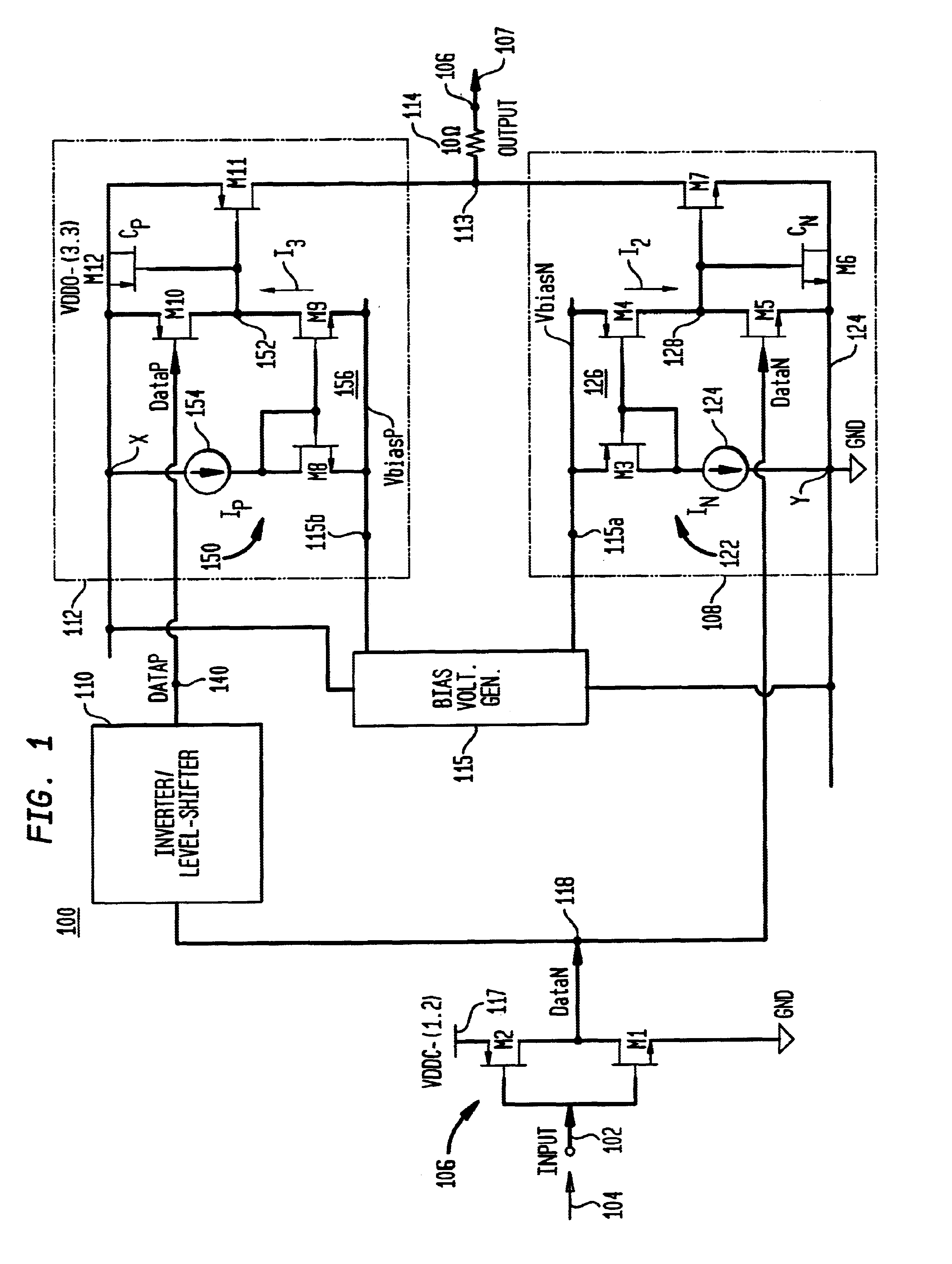
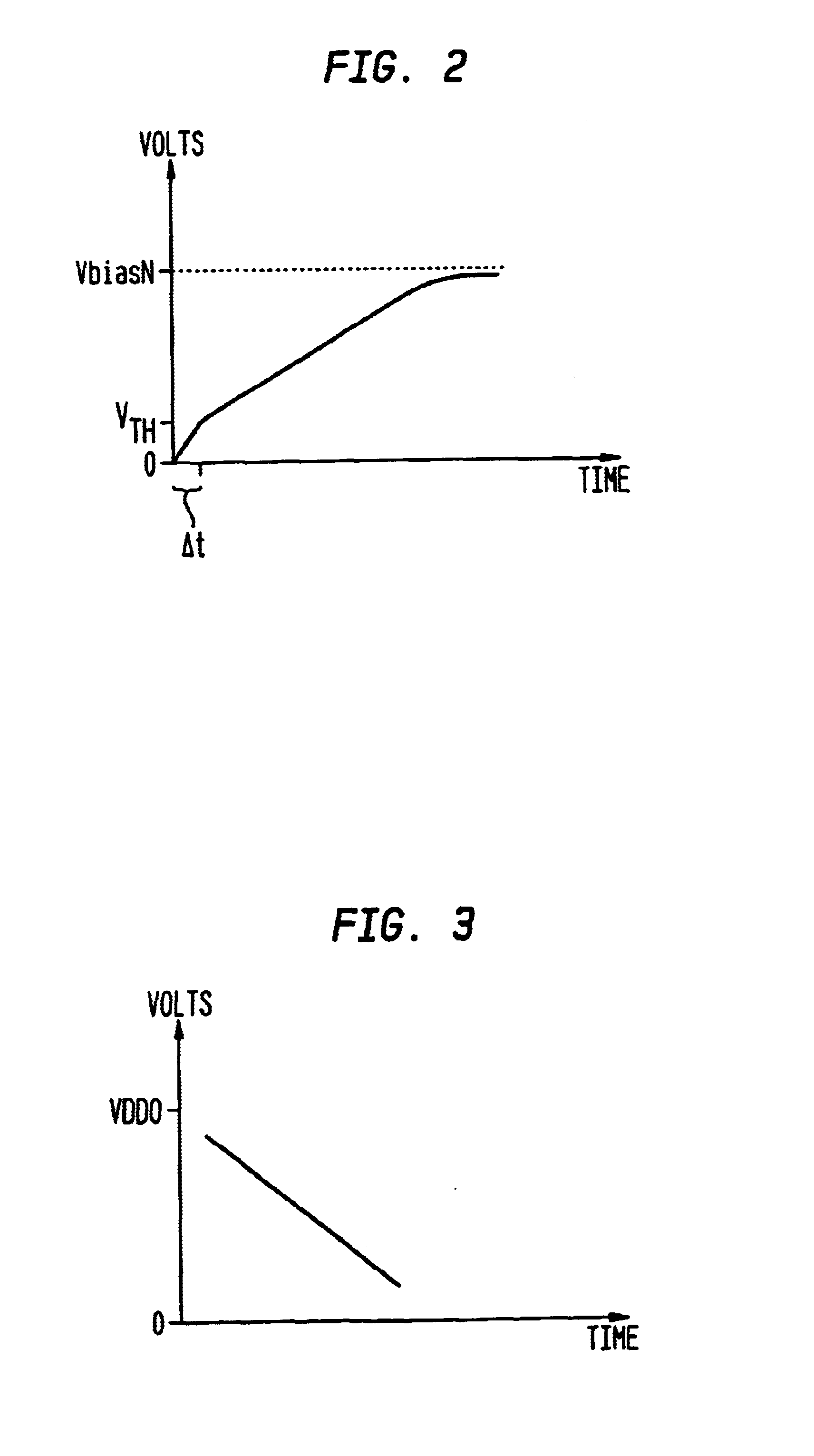
An optical transistor, also known as an optical switch or a light valve, is a device that switches or amplifies optical signals. Light occurring on an optical transistor’s input changes the intensity of light emitted from the transistor’s output while output power is supplied by an additional optical source. Since the input signal intensity may be weaker than that of the source, an optical transistor amplifies the optical signal. The device is the optical analog of the electronic transistor that forms the basis of modern electronic devices. Optical transistors provide a means to control light using only light and has applications in optical computing and fiber-optic communication networks. Such technology has the potential to exceed the speed of electronics, while saving more power.
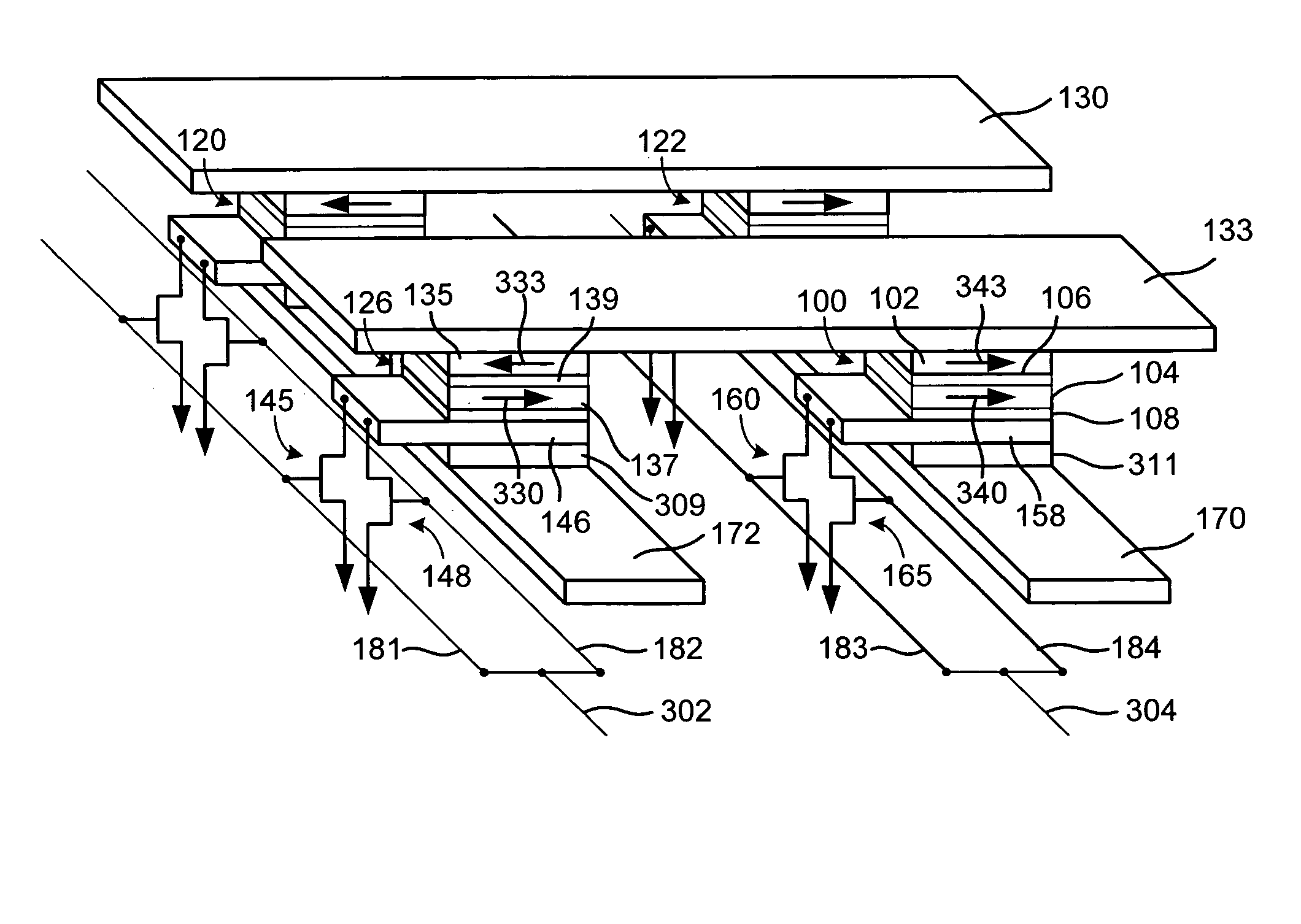
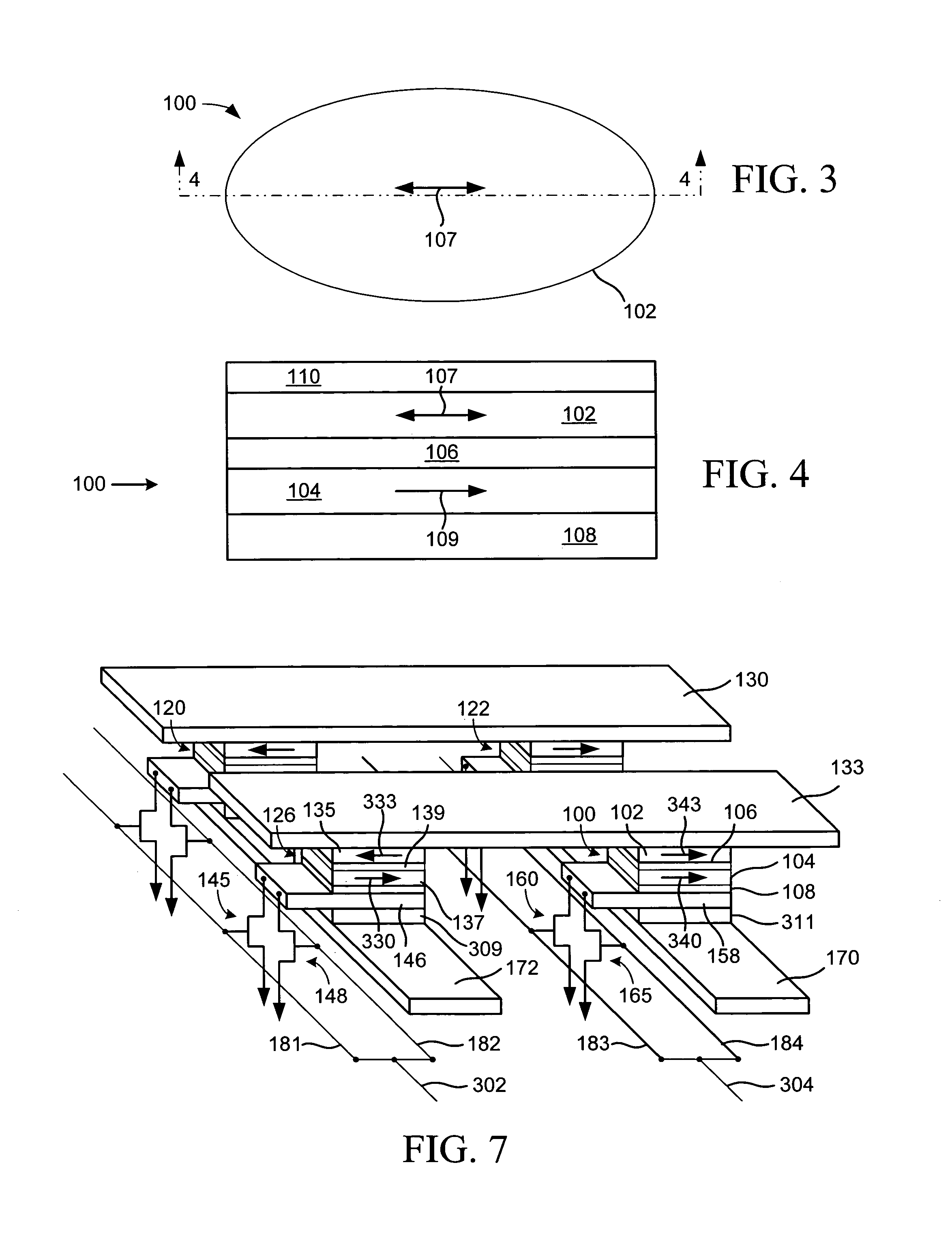
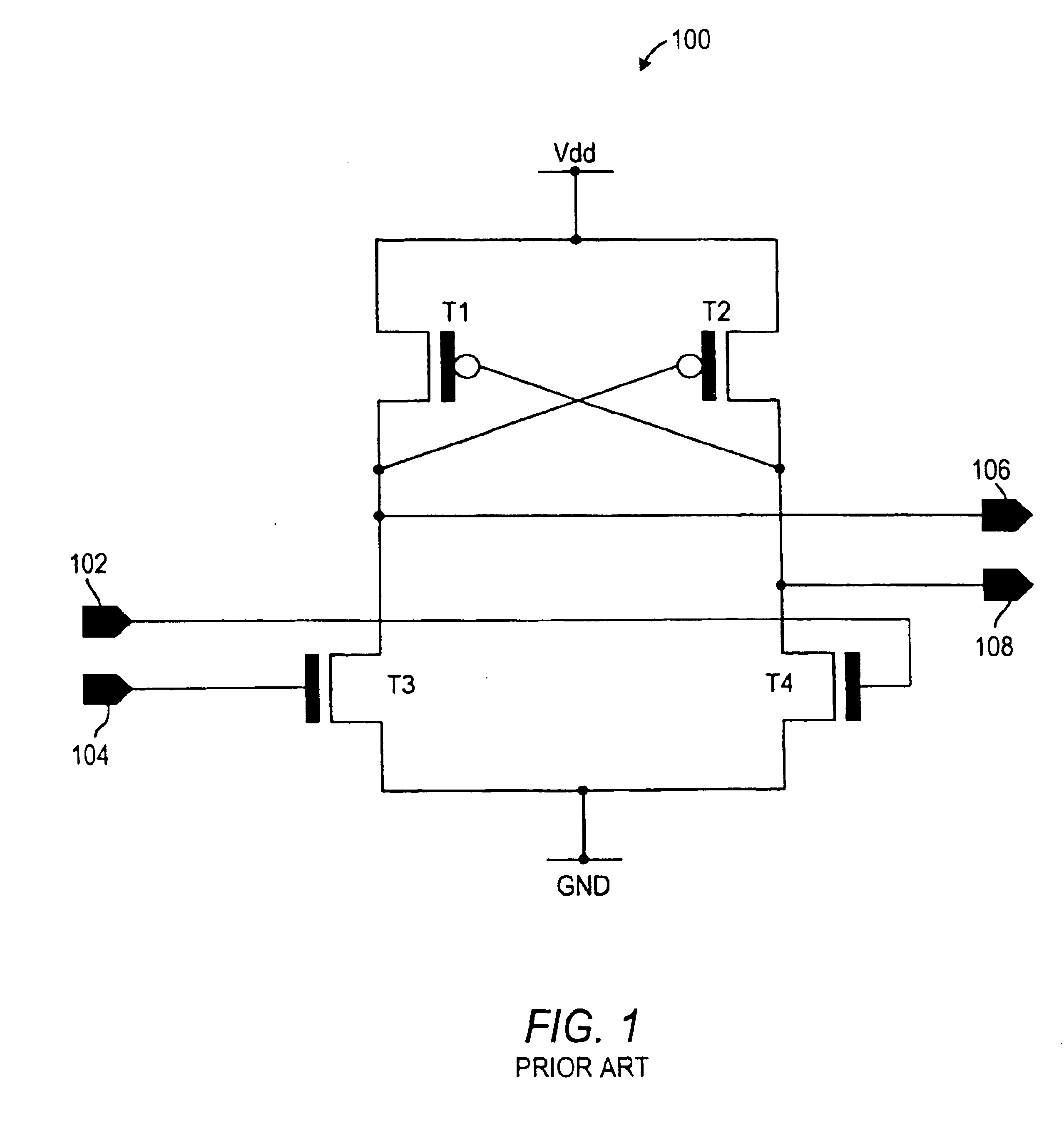
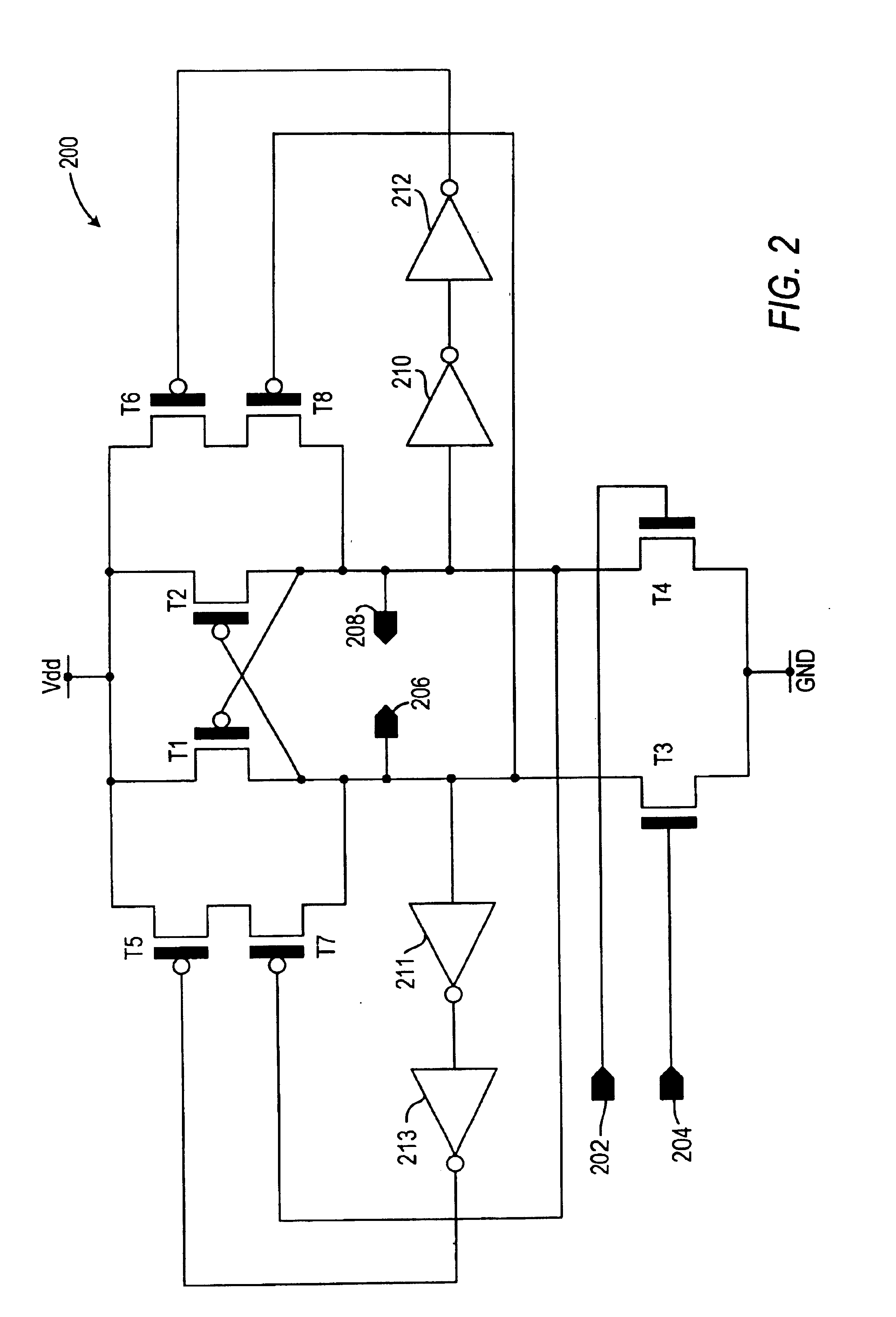
Magnetic memory cell with plural read transistors
A magnetic random access memory (MRAM) device has increased ΔR / R for sensing a state of a pin-dependent tunneling (SDT) device. The MRAM device includes plural transistors connected to a read line for sensing the state of the SDT device. Plural transistors lower an underlying resistance during reading, increasing ΔR / R. The plural transistors can share a source region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC +1
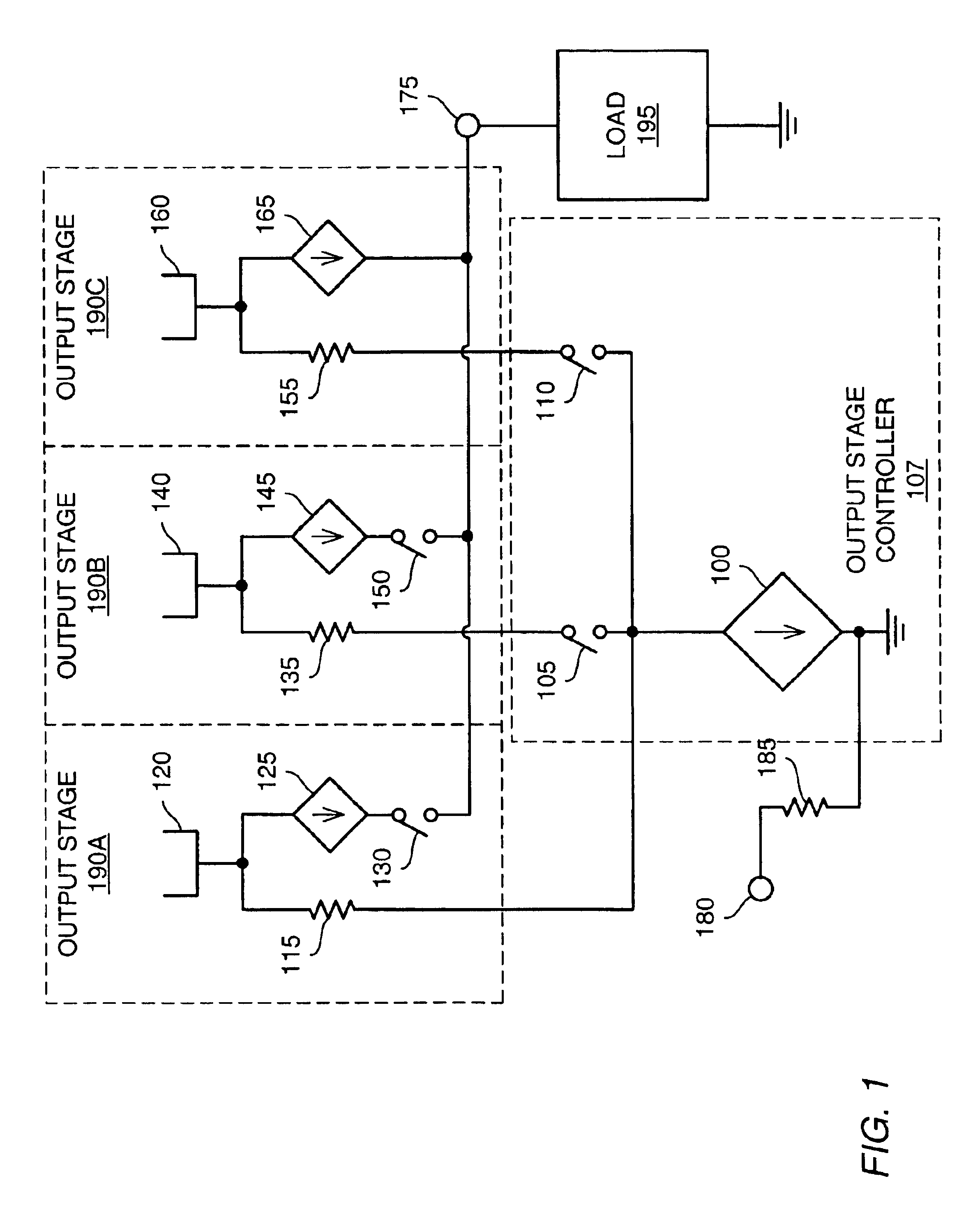
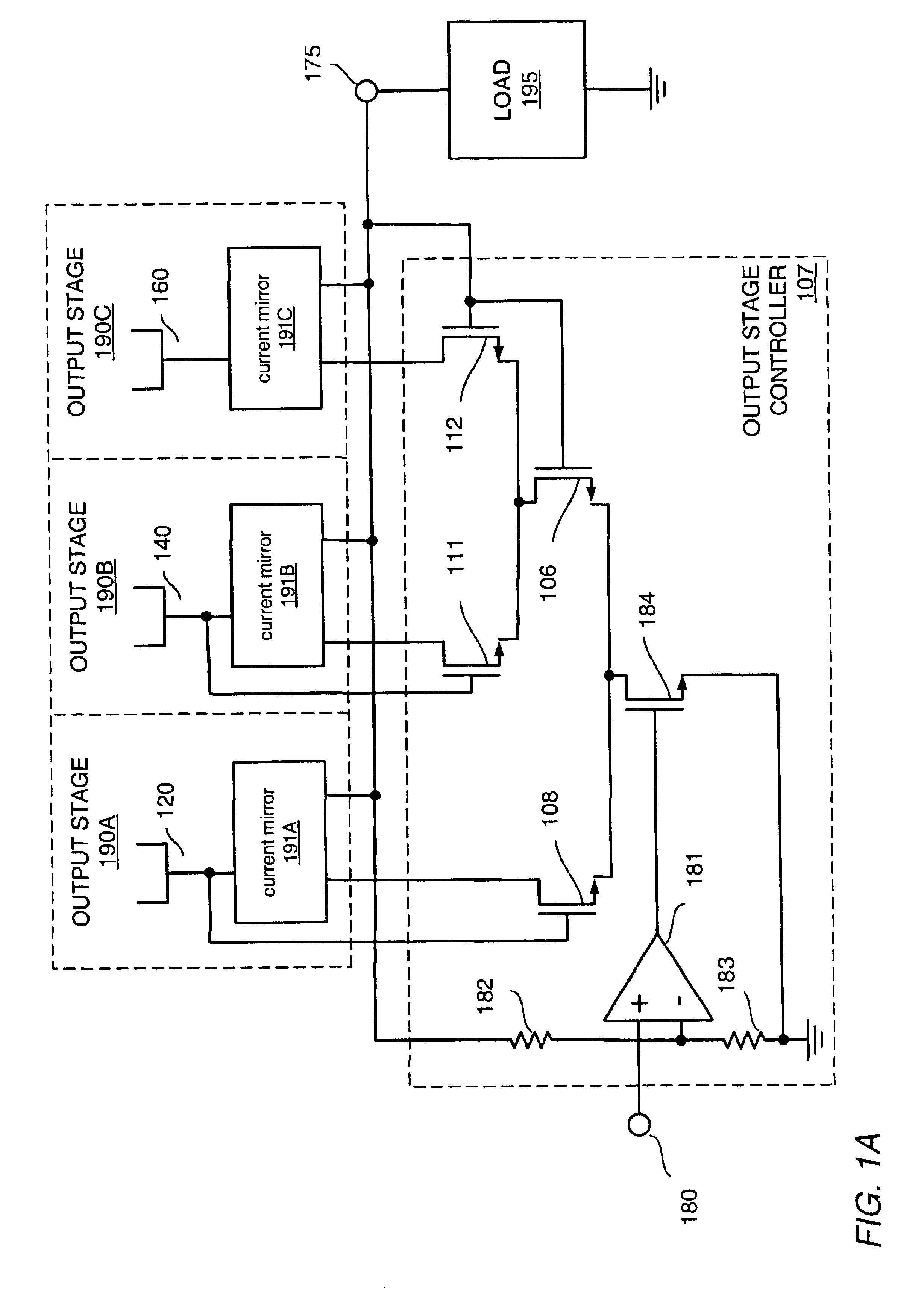
Efficient class-G amplifier with wide output voltage swing
InactiveUS6838942B1Reduce noiseImprove efficiencyGated amplifiersPower amplifiersCMOSAudio power amplifier
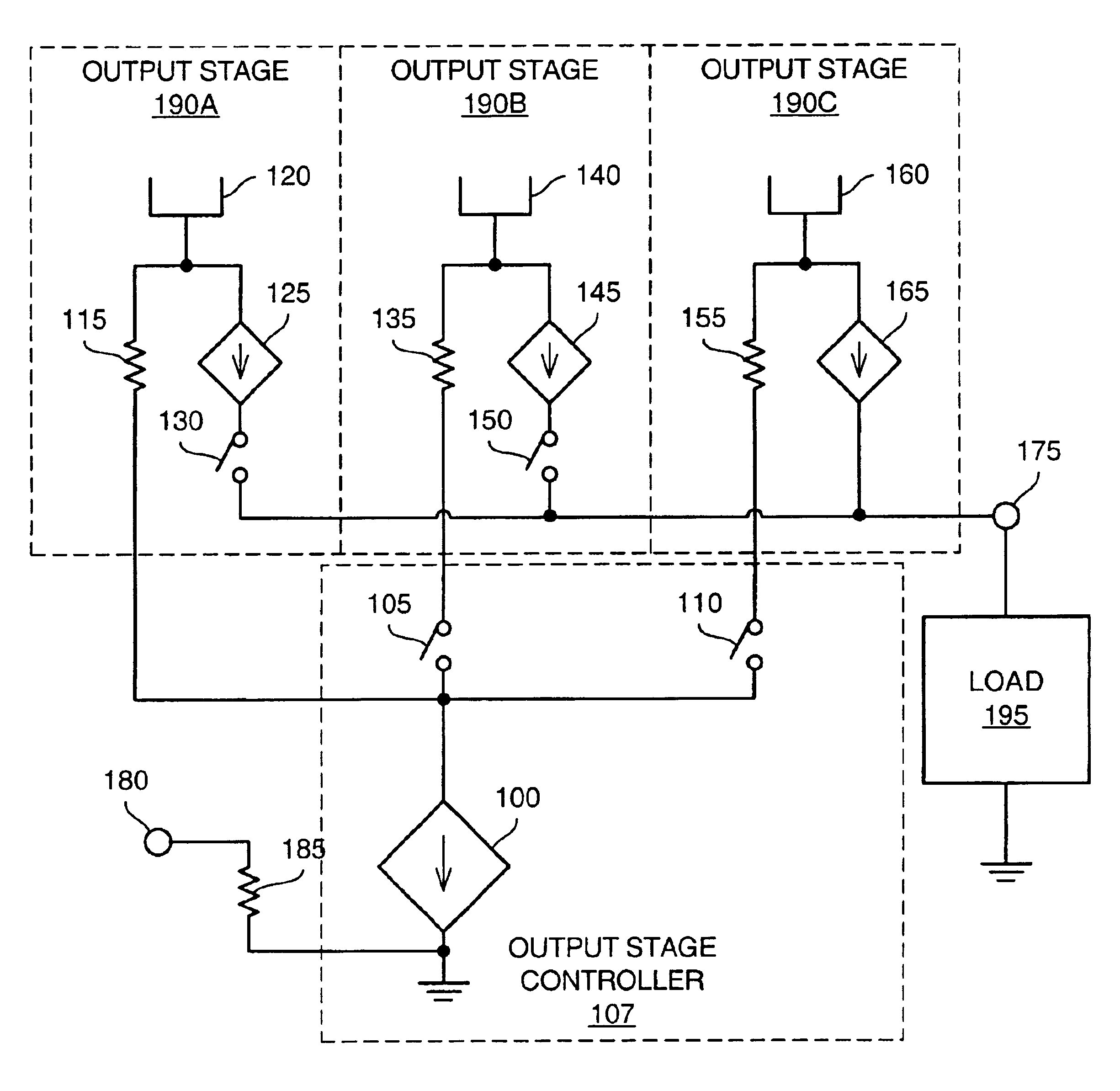
Various embodiments of methods and apparatus for an amplifier with wide output voltage swing are disclosed. The amplifier may include multiple output stages, each associated with a distinct supply voltage. Each output stage may contribute current to the output of the amplifier over a range of amplifier output voltages and these ranges may overlap. Each output stage may contribute current until the amplifier output voltage reaches the supply voltage associated with that output stage. The amplifier output may be as great as the largest supply voltage minus a drop equal to Rdson for an output transistor multiplied by the output current. In a CMOS implementation, this voltage drop may be approximately 0.15V. When the amplifier output voltage is close to the supply voltage associated with an output stage, both that output stage and the output stage associated with the next highest supply voltage may contribute to the amplifier output.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Output overvoltage protection circuit for power amplifier
ActiveUS7145397B2Reduce outputBias of the first-stage transistorPower amplifiersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsOvervoltageAudio power amplifier
Disclosed is an output overvoltage protection circuit for a power amplifier having a plurality of stages, which comprises a monitor circuit for monitoring an output overvoltage of an output transistor in the final stage of the power amplifier and allowing a current to flow therethrough in response to the monitored output overvoltage, and a current mirror circuit for supplying a current proportional to the current from the monitor circuit in such a manner that the base bias of the first-stage transistor of the power amplifier is reduced in response to the current supplied from the current mirror circuit, to reduce the output of the final-stage output transistor.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Organic Light Emitting Display
ActiveUS20160351124A1Guaranteed accuracyEnsure designStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesTransistor arrayScan line
An organic light emitting display comprises a display panel having a plurality of pixels, a gate drive circuit that drives scan lines and emission lines on the display panel, and a data drive circuit that drives data lines on the display panel, (n−1)th and nth pixels arranged in a row, a transistor array having a driving transistor, a sampling transistor, and a first initial transistor, and a capacitor connected between an initial voltage input terminal and the sampling transistor. A gate electrode of the first initial transistor for initializing the driving transistor of the nth pixel is connected to a scan line in the (n−1)th pixel.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
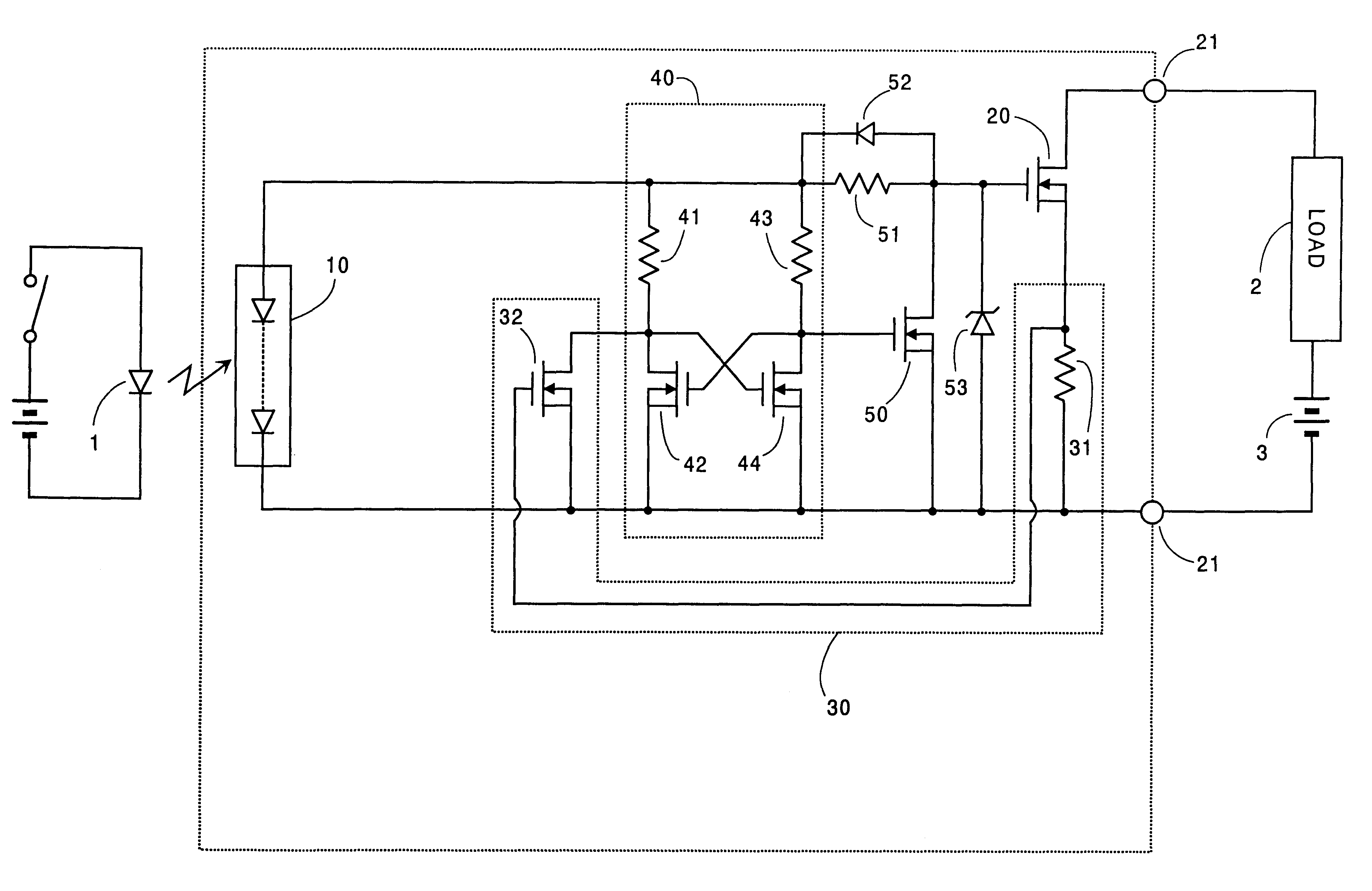
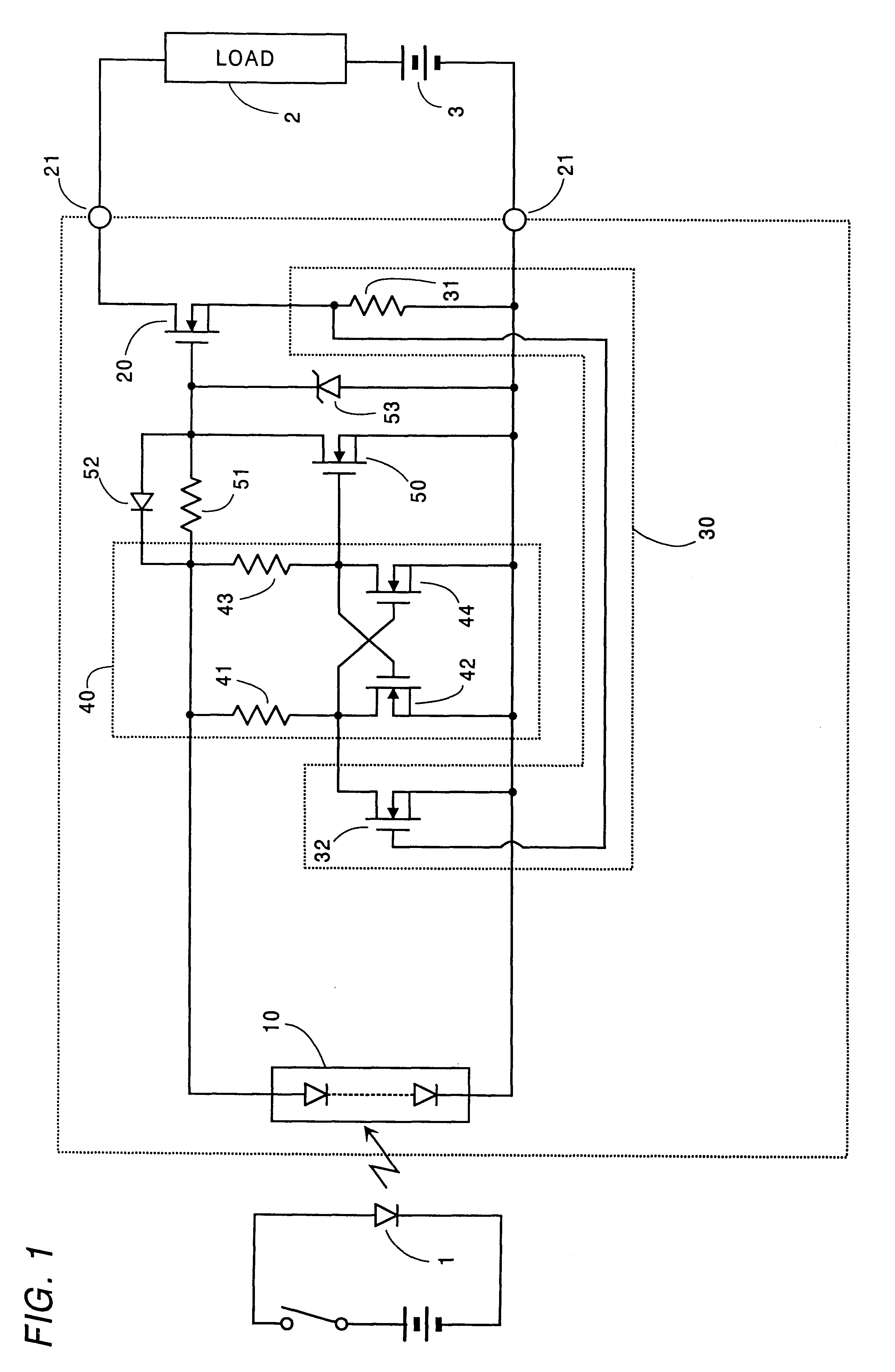
Light responsive semiconductor switch with shorted load protection
InactiveUS6339236B1Low working voltageSuccessful and reliable interruptionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCurrent limitingOvercurrent
An improved light responsive semiconductor switch with shorted load protection capable of successfully interrupting a load overcurrent. The switch is includes an output transistor which is triggered by a photovoltaic element to connect a load to a power source thereof, and an overcurrent sensor which provides an overcurrent signal upon seeing an overcurrent condition in the load. A shunt transistor is connected in series with a current limiting resistive element across the photovoltaic element to define a shunt path of flowing the current from the photovoltaic element through the current limiting resistive element away from the output transistor. A latch circuit is included to be energized by the photovoltaic element and to provide an interruption signal once the overcurrent signal is received and hold the interruption signal. The interruption signal turns on the shunt transistor so as to flow the current from the photovoltaic element through the shunt path, thereby turning off the output transistor for interruption of the overcurrent. The current limiting resistive element is connected in series with the shunt transistor to limit the current from the photovoltaic element when the shunt transistor is turned on, thereby providing a supply voltage from the photovoltaic element to the latch circuit. Thus, the latch circuit is enabled to keep providing the interruption signal for reliable interruption of the overcurrent.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Efficient charge transferring in CMOS imagers
ActiveUS20070045681A1Improve dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSEngineering
Methods for operating a pixel cell include efficient transferring of photo-charges using multiple pulses to a transistor transfer gate during a charge integration period for an associated photosensor. The pixel cell can be operated with efficient transfer characteristics in either normal or high dynamic range (HDR) mode. The high dynamic range can be realized by either operating an optional HDR transistor or by fluctuating the voltage applied to a reset gate.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
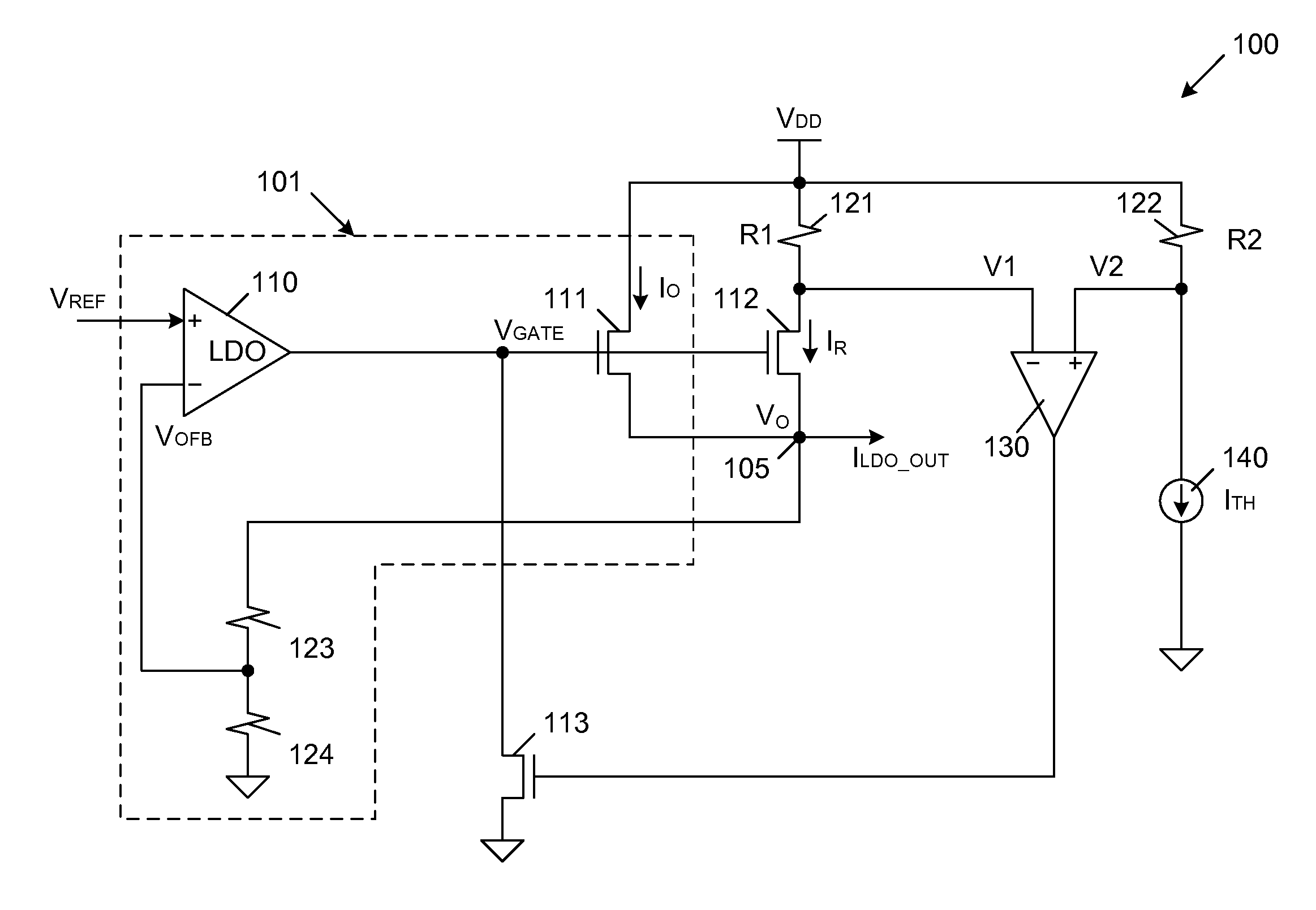
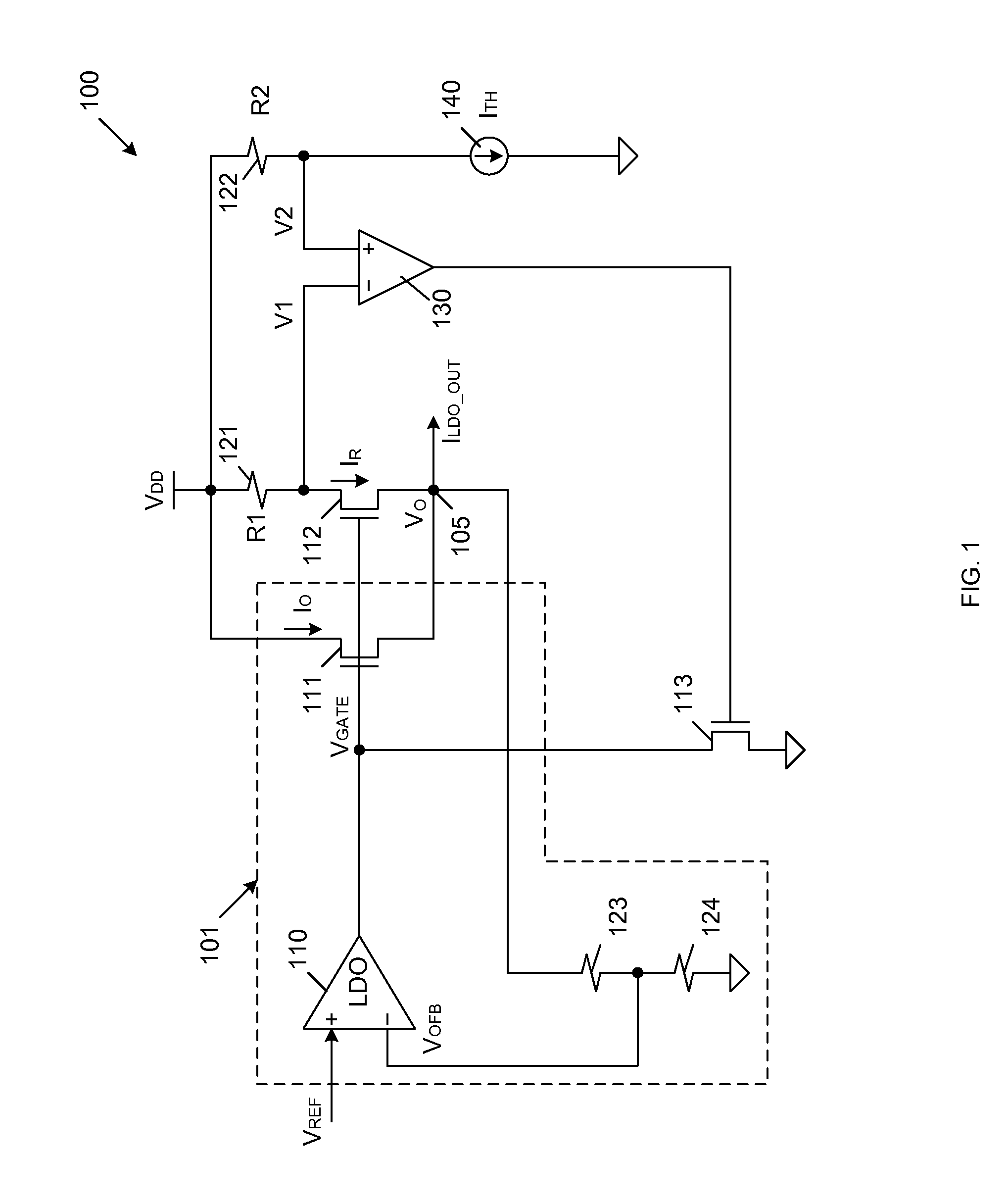
Current Limit Circuit Architecture For Low Drop-Out Voltage Regulators
InactiveUS20130293986A1Reduce output voltageSimple designEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorEngineering
A current limiting circuit for a linear regulator includes an output stage transistor and a replica transistor, which have gates coupled to receive an output voltage from a linear amplifier and sources coupled to load circuitry. A drain of the output stage transistor is coupled to a VDD supply terminal, while a drain of the replica transistor is coupled to the VDD supply terminal through a first resistor. The output stage transistor and replica transistor are operated in saturation, such that proportional currents flow through these transistors. The voltage drop across the first resistor provides a first voltage, which is applied to a second amplifier. A reference voltage is also applied to the second amplifier. When the first voltage becomes less than the reference voltage, a feedback transistor is enabled to pull down the output voltage of the linear amplifier, thereby limiting the output current supplied to the load circuitry.
Owner:TOWER SEMICONDUCTOR
Semiconductor device with multiple power sources
InactiveUS7030681B2Low costTotal current dropPulse automatic controlSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
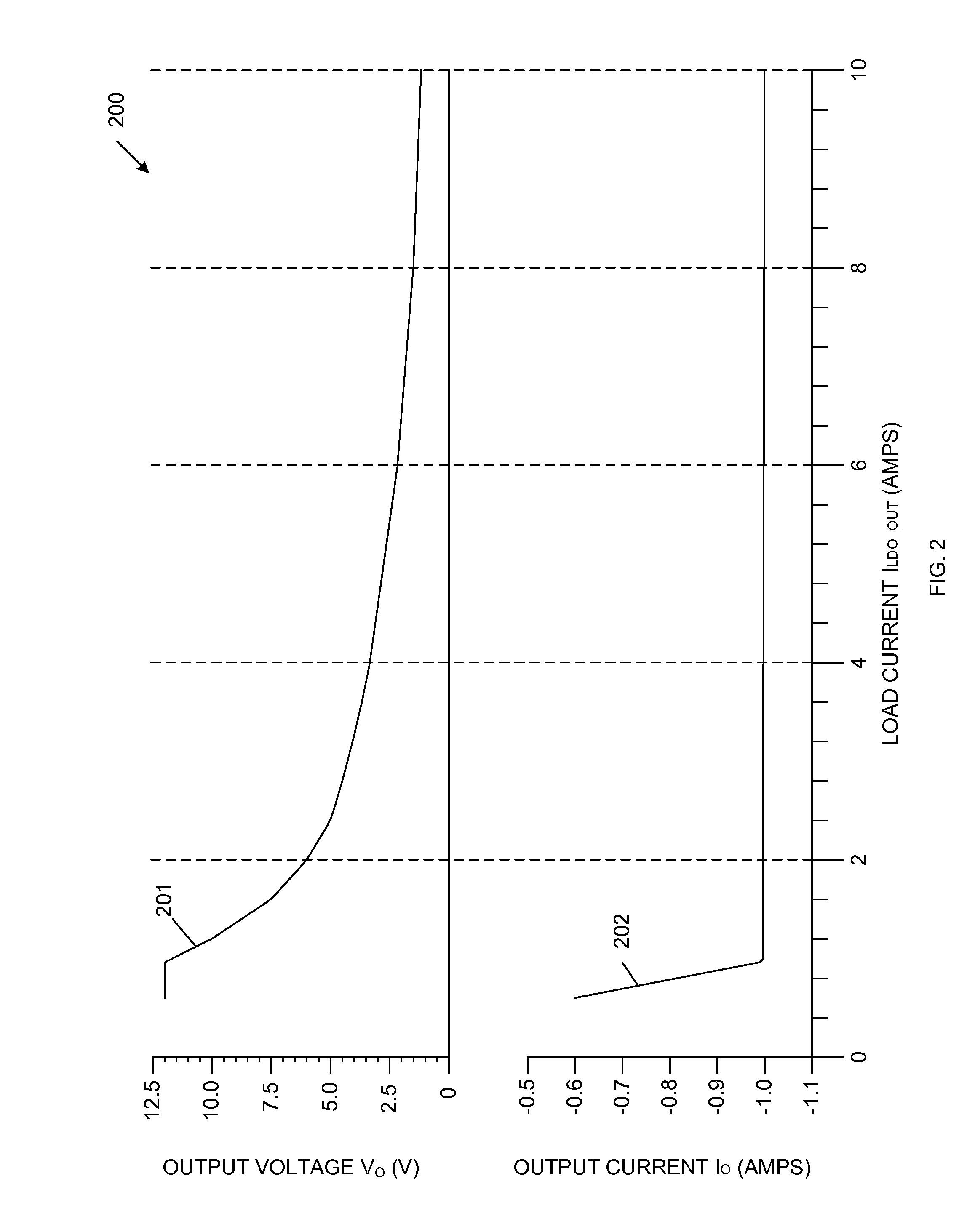
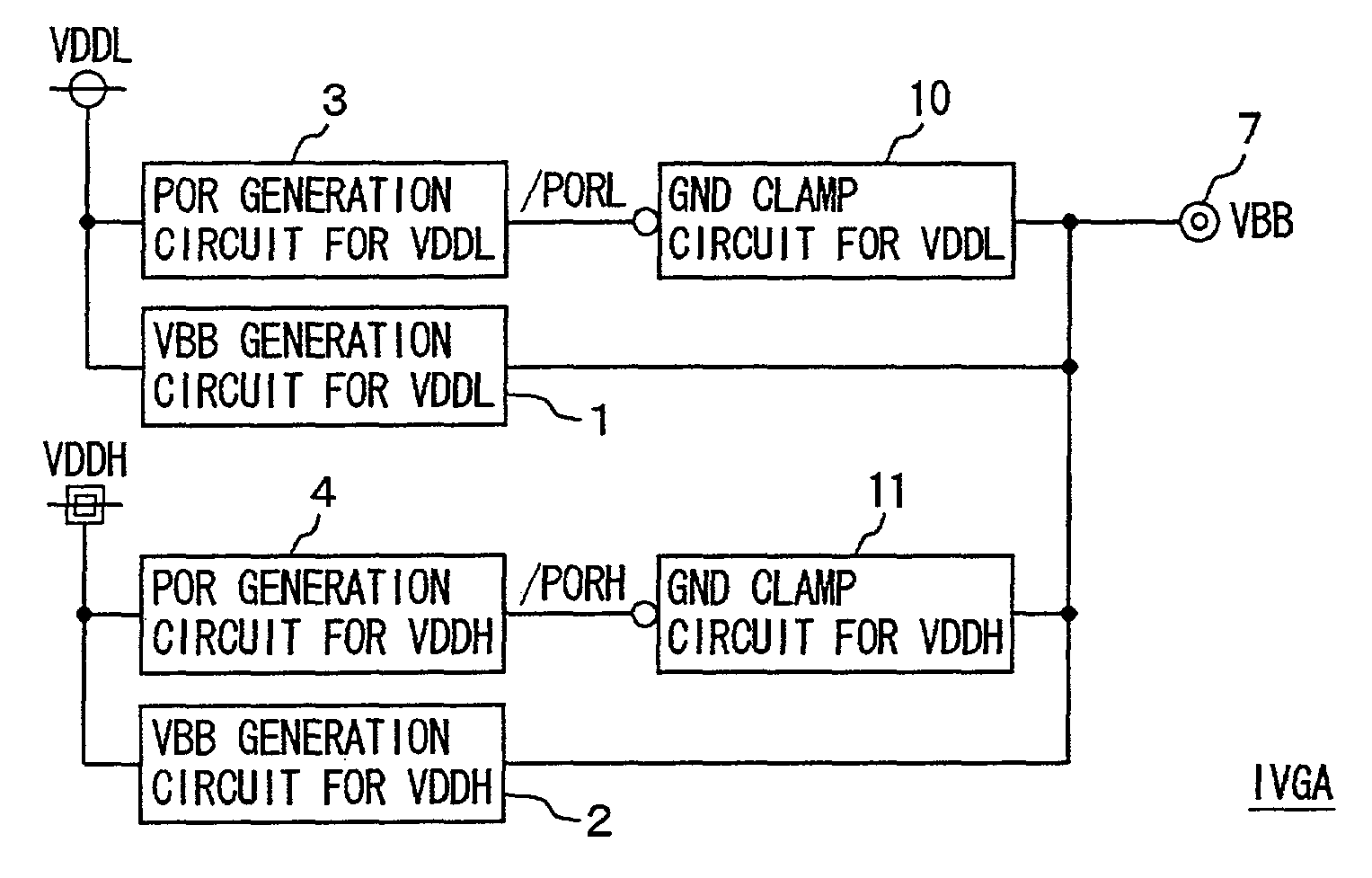
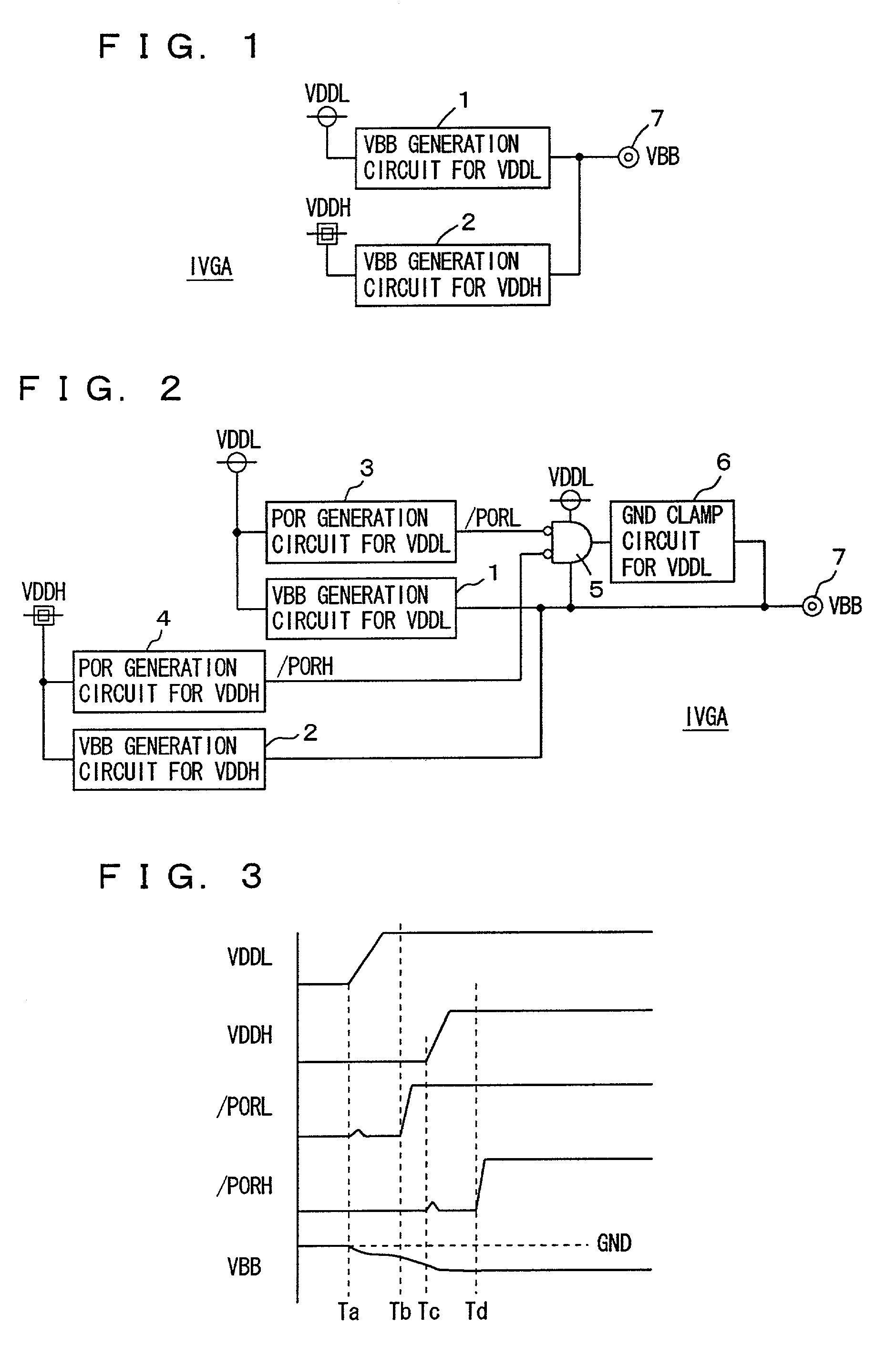
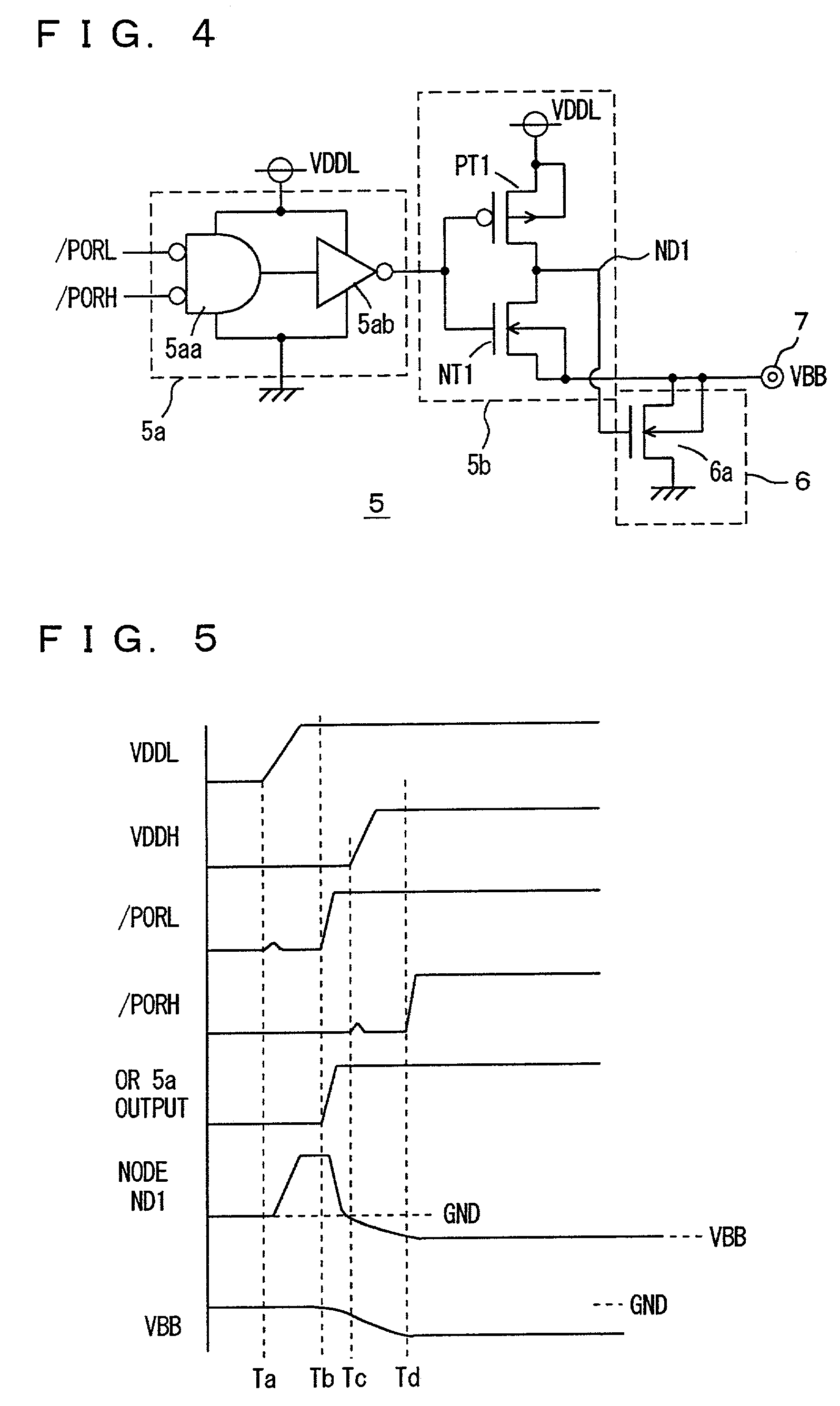
Well bias voltages are generated in accordance with a logic power supply voltage and a memory power supply voltage. The transistor included in a control circuit in a memory core is constituted of a logic transistor manufactured through the same manufacturing steps as those for the transistors of a logic formed on the same semiconductor substrate. Well bias voltages (VBB, VPP) are applied to a back gate of this logic transistor. A memory integrated with a logic on a common semiconductor substrate is provided which allows a transistor of a control circuit therein to be manufactured through the same manufacturing process as that of the logic and allows reduction of current consumption.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Voltage regulator
ActiveUS7142044B2Reduce leakage currentSmall valueElectric variable regulationVoltage regulationEngineering
The present invention provides a voltage regulator capable of causing a large output current to flow during a heavy load operation, and of making a leakage current from output transistors small during a light load operation. The voltage regulator includes a plurality of output transistors and a circuit for changing connection of the output transistors to allow a W / L value of the output transistor to be changed. Moreover, the voltage regulator further includes an output current detection circuit for detecting an output current, and a circuit for changing connection of the output transistors based on the output current to allow a W / L value of the output transistors to be changed based on the output current.
Owner:ABLIC INC
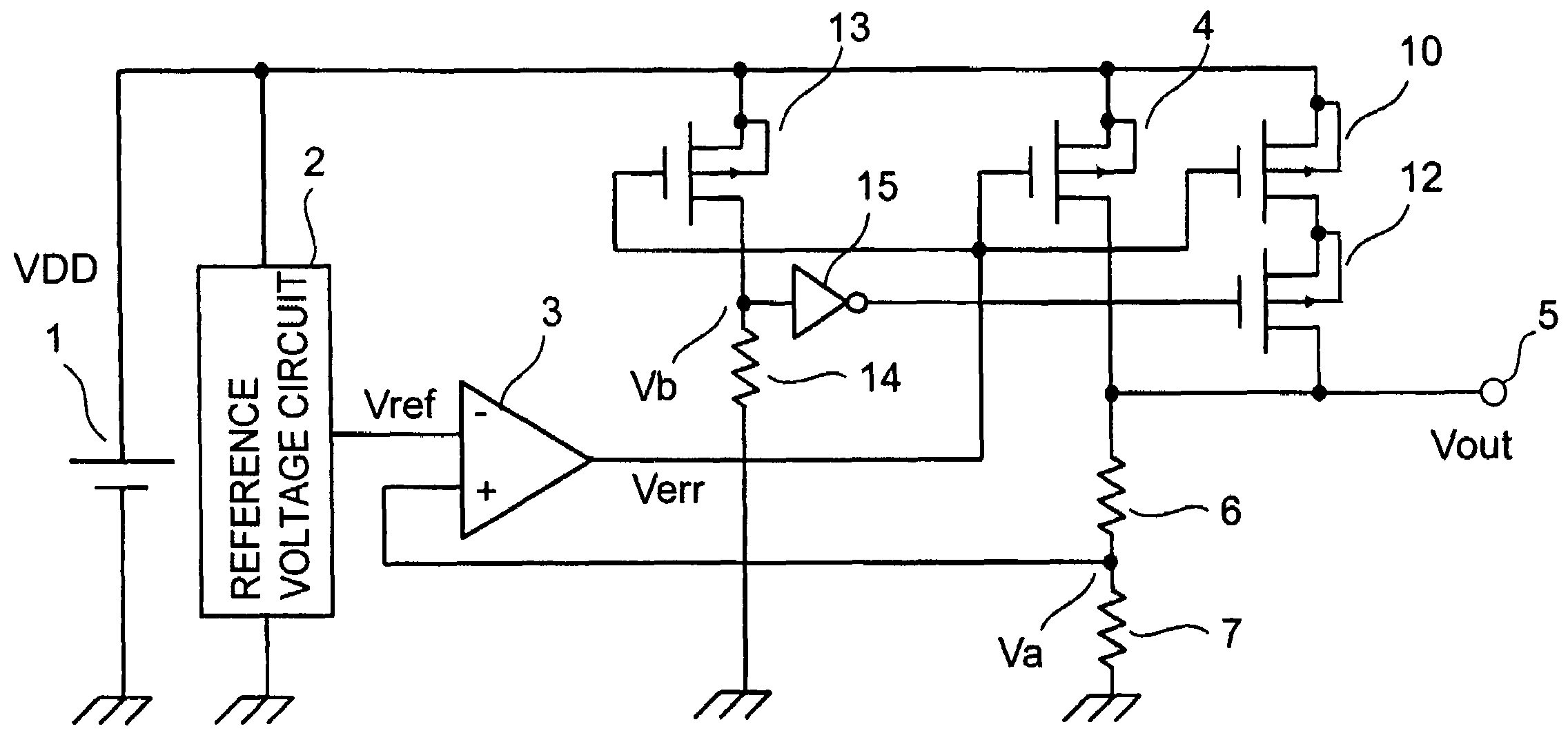
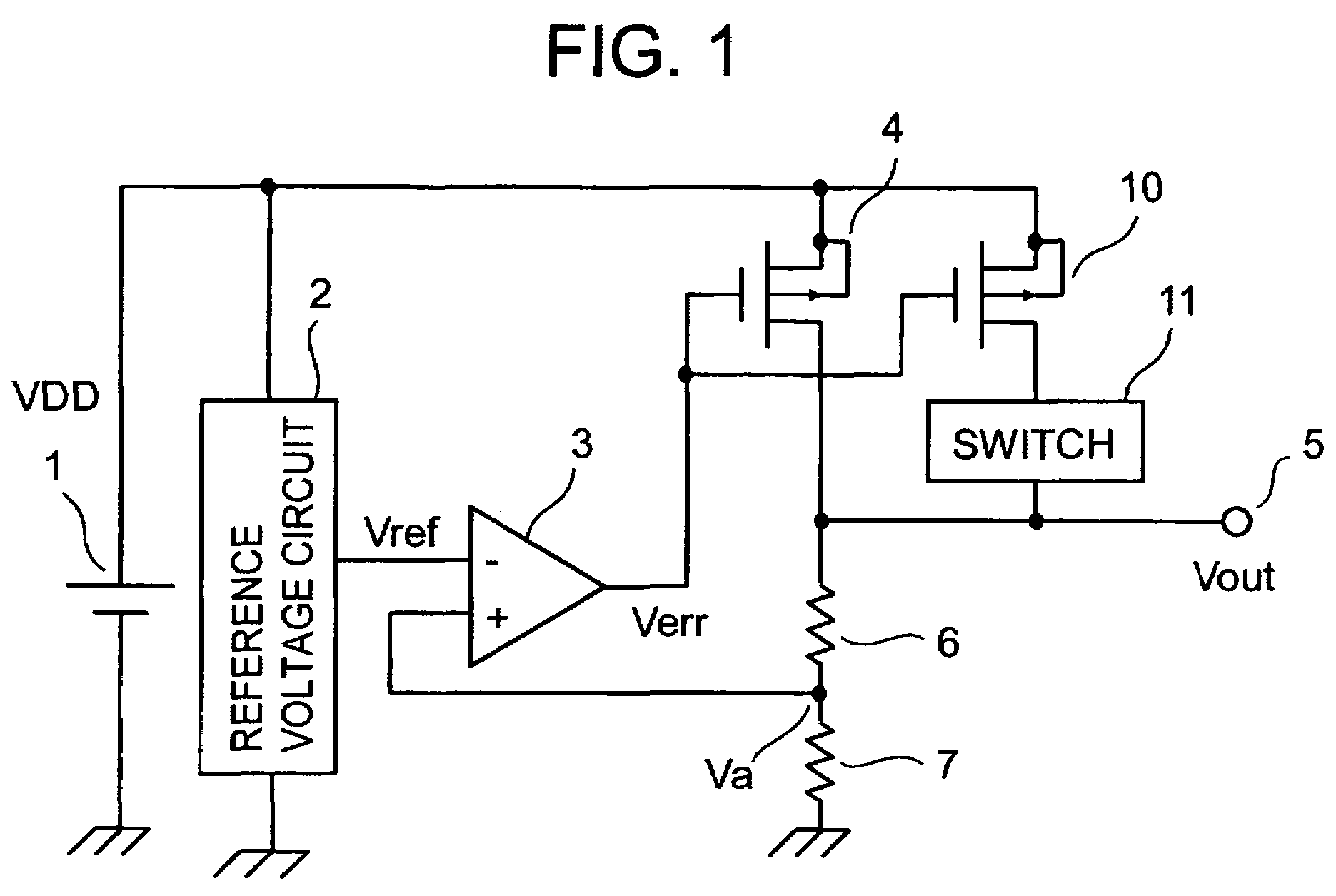
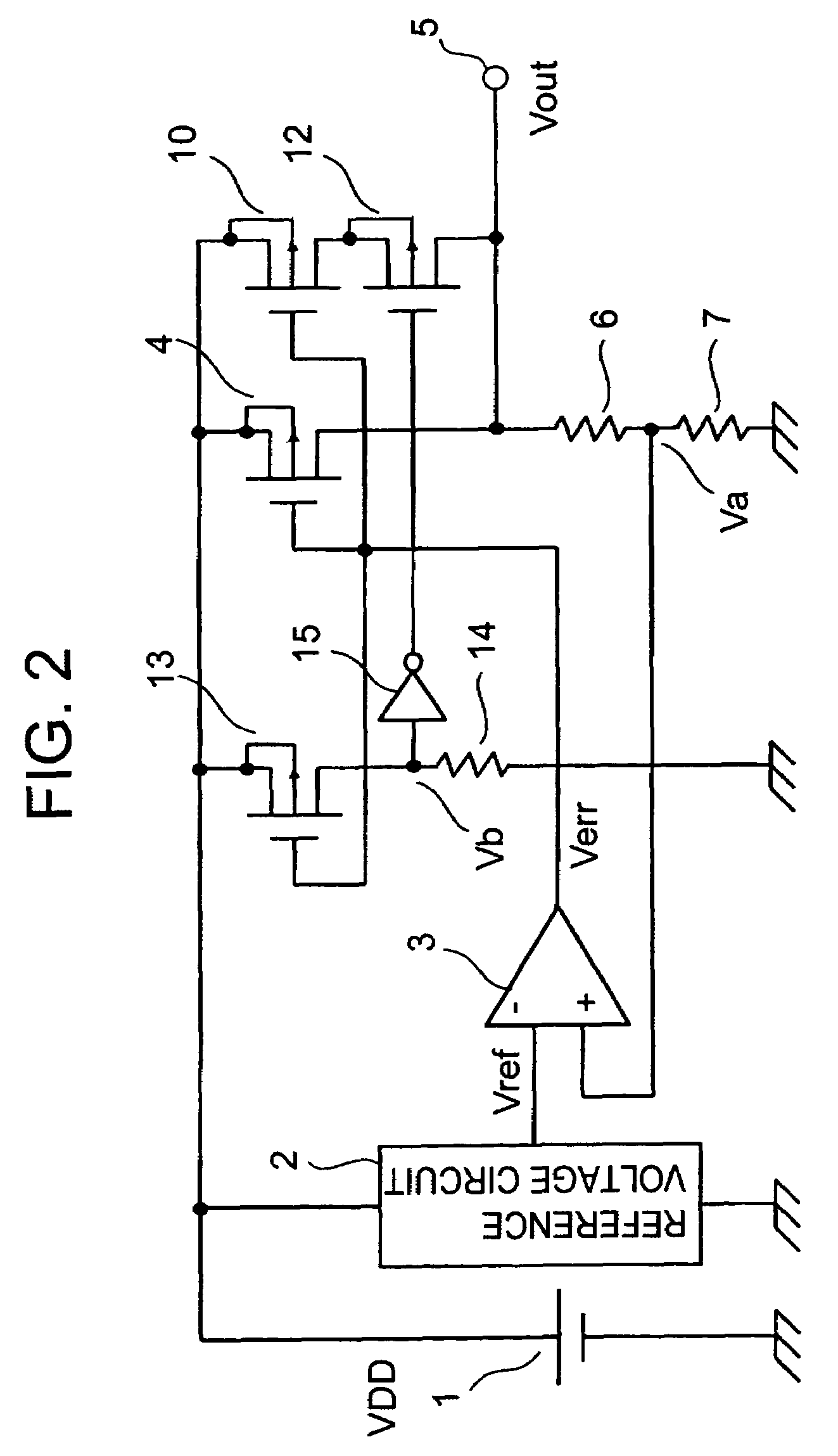
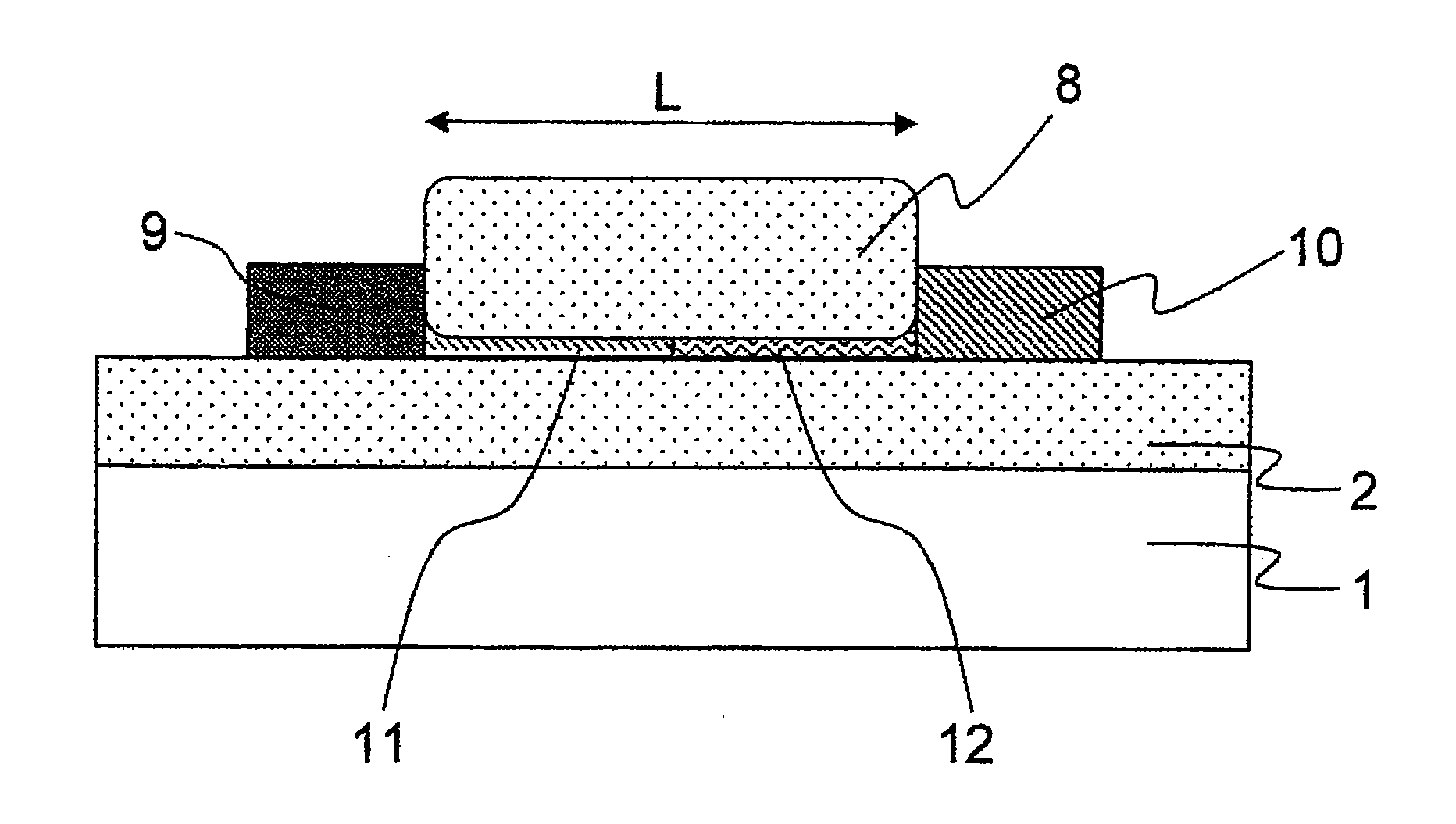
Silicon light emitting diode, silicon optical transistor, silicon laser and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20080128713A1Easy to makeImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPlane orientationLight emitting device
A light-emitting device according to the present invention includes a first electrode unit 9 for injecting an electron, a second electrode unit 10 for injecting a hole, and light-emitting units 11 and 12 electrically connected to the first electrode unit 9 and the second electrode unit 10 respectively, wherein the light-emitting units 11 and 12 are formed of single-crystal silicon, the light-emitting units 11 and 12 having a first surface (topside surface) and a second surface (underside surface) opposed to the first surface, plane orientation of the first and second surfaces being set to a (100) plane, thicknesses of the light-emitting units 11 and 12 in a direction orthogonal to the first and second surfaces being made extremely thin.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
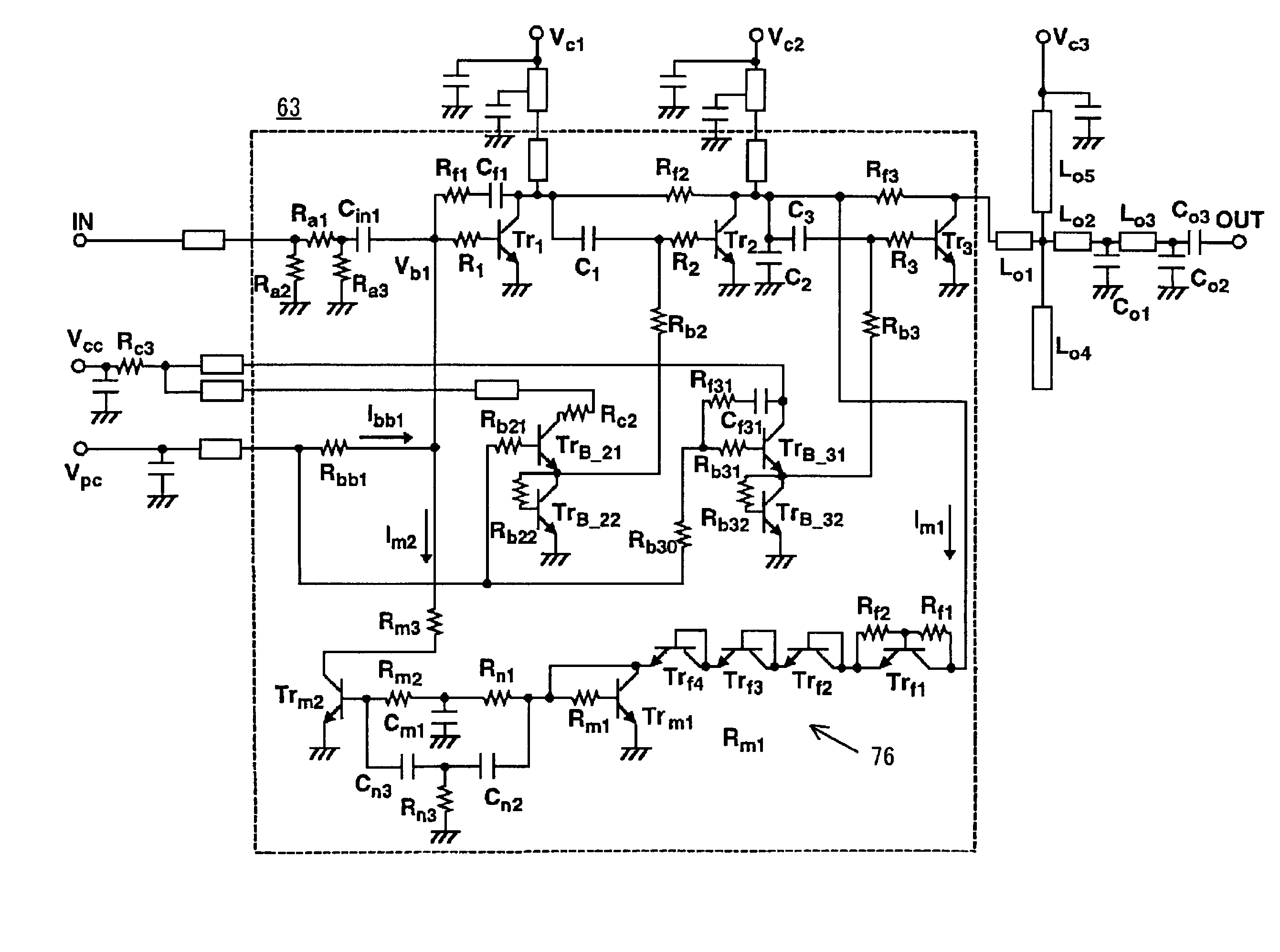
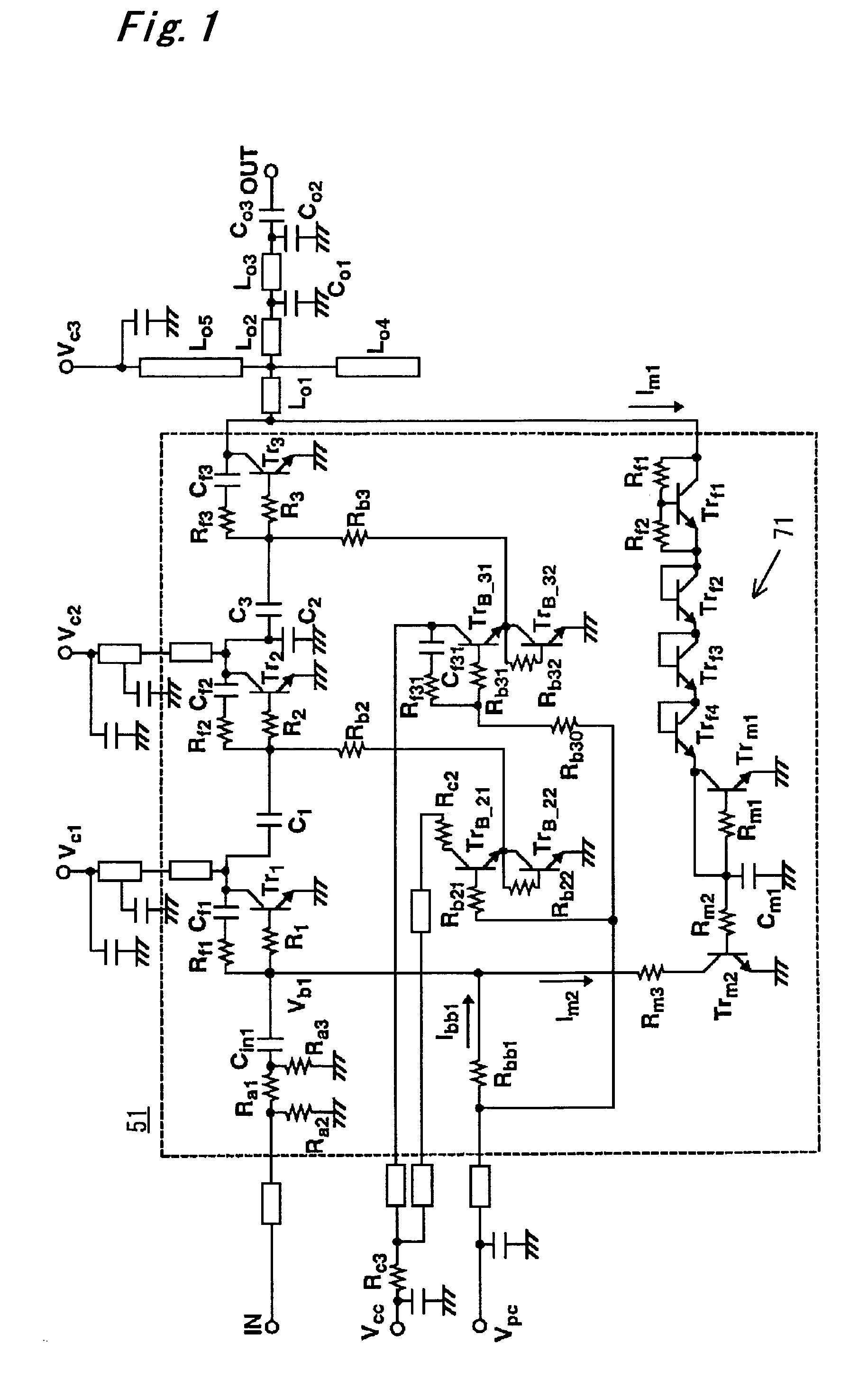
Power amplifier
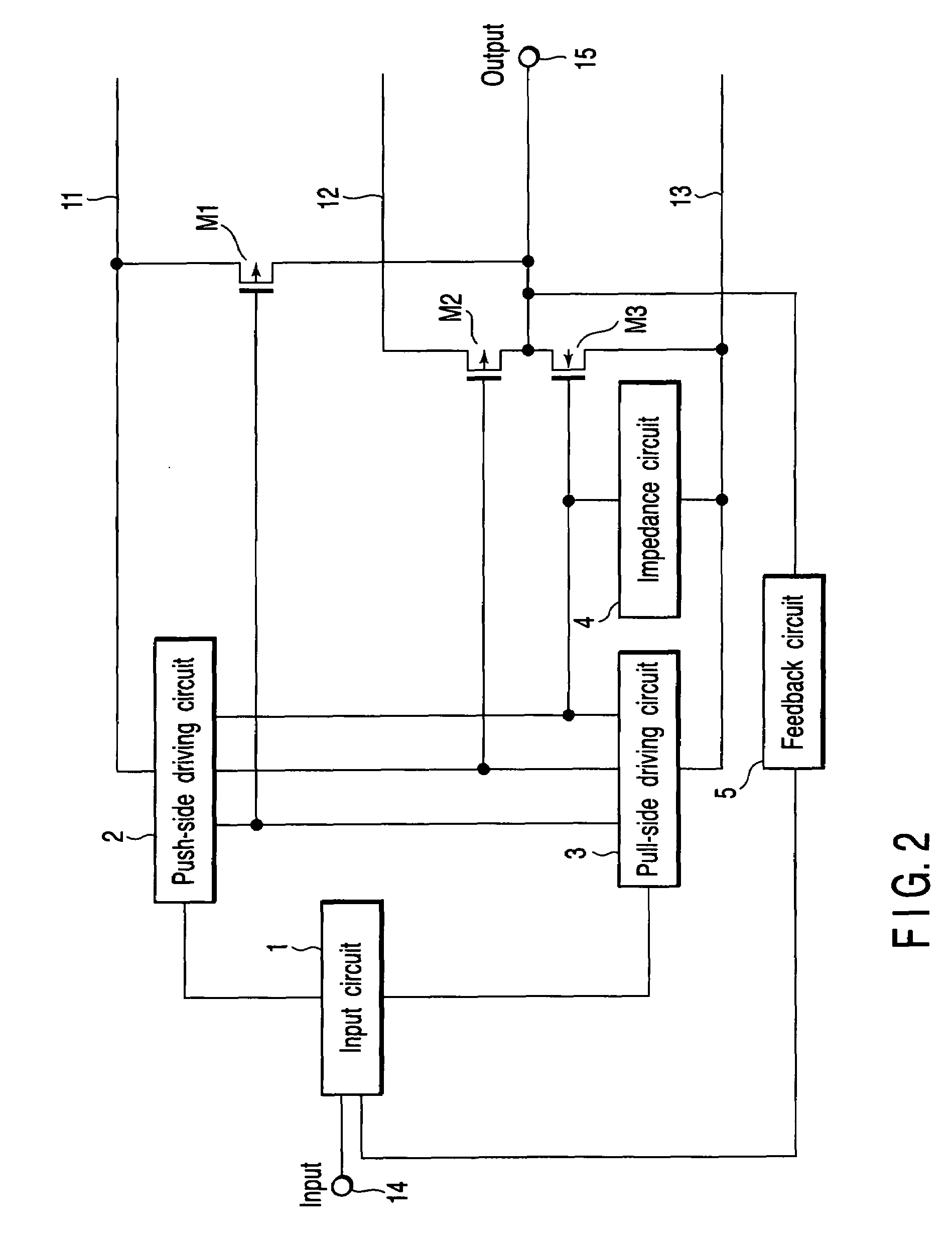
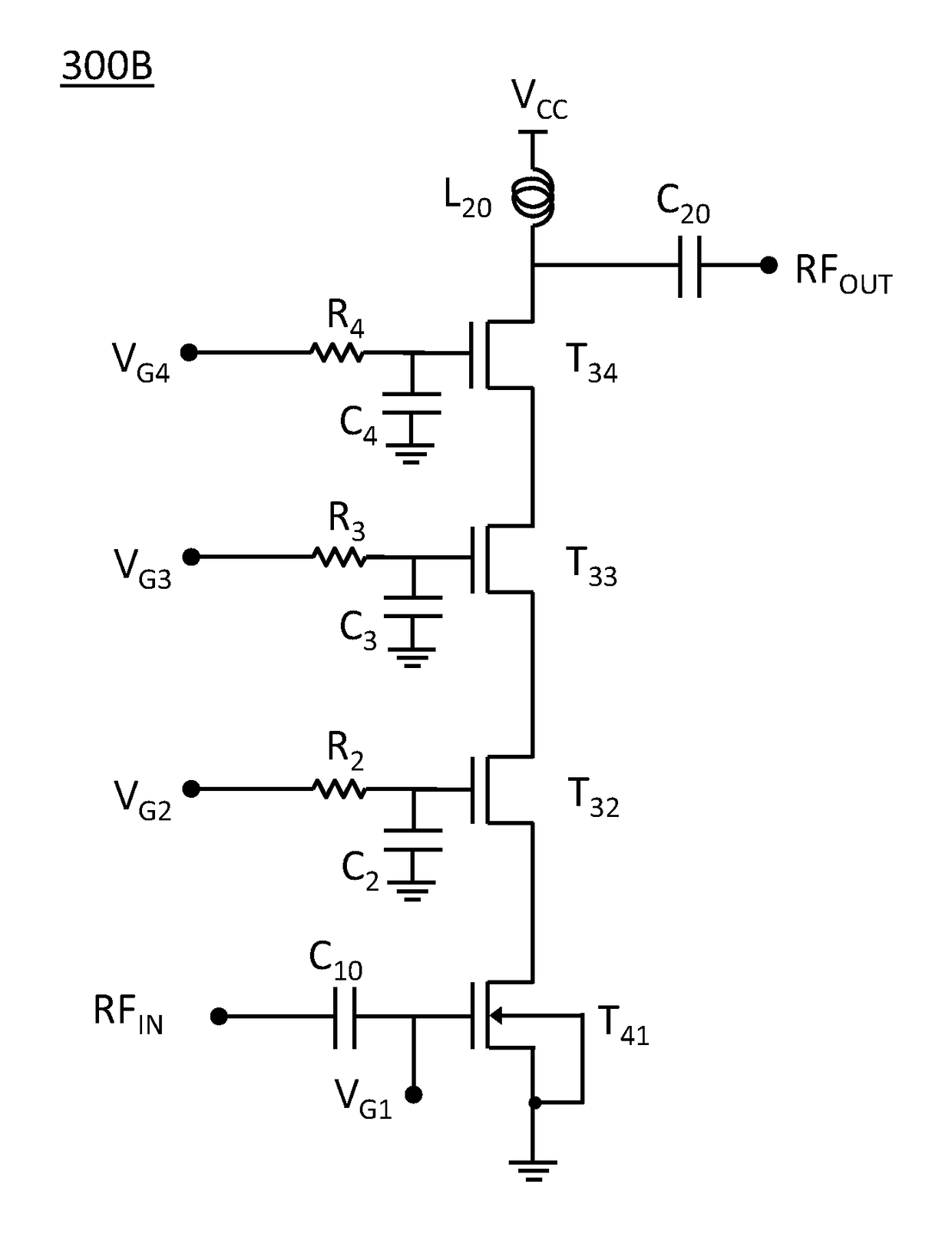
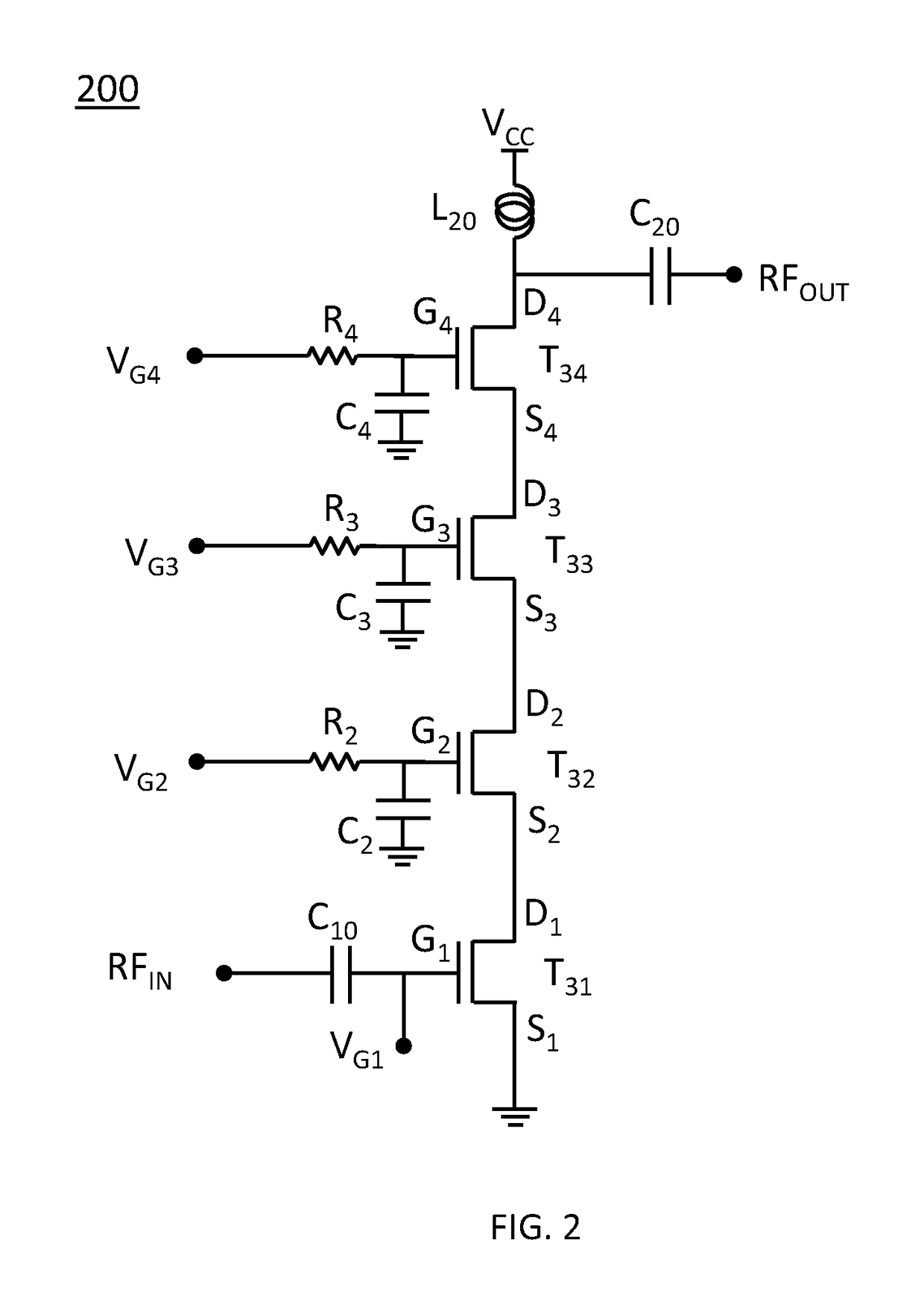
A power amplifier includes an input circuit, three power supply lines with voltages successively decreasing in an order of first, second and third power supply lines, a push-side driving circuit and a pull-side driving circuit which receive control signals from the input circuit, three driving signal lines which are led out of the driving circuits, three output transistors which have current paths connected at one ends to the first, second and third power supply lines, and have gates connected to the three driving signal lines, respectively, an output terminal which is commonly connected to the other ends of the current paths of the output transistors, an impedance circuit which adjusts a gate impedance of the output transistor connected to the third power supply line, and a feedback circuit connected between the output terminal and the input circuit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
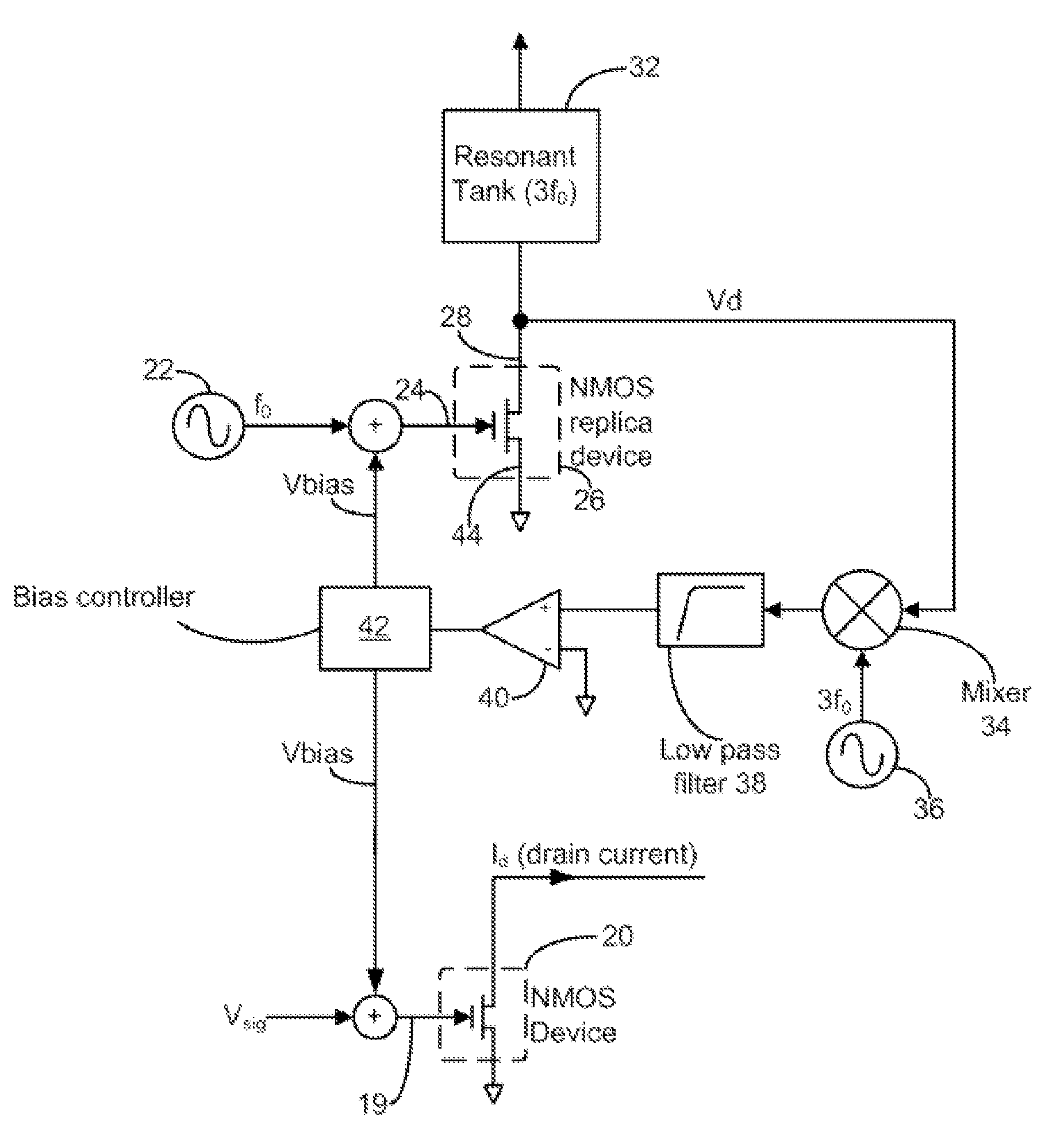
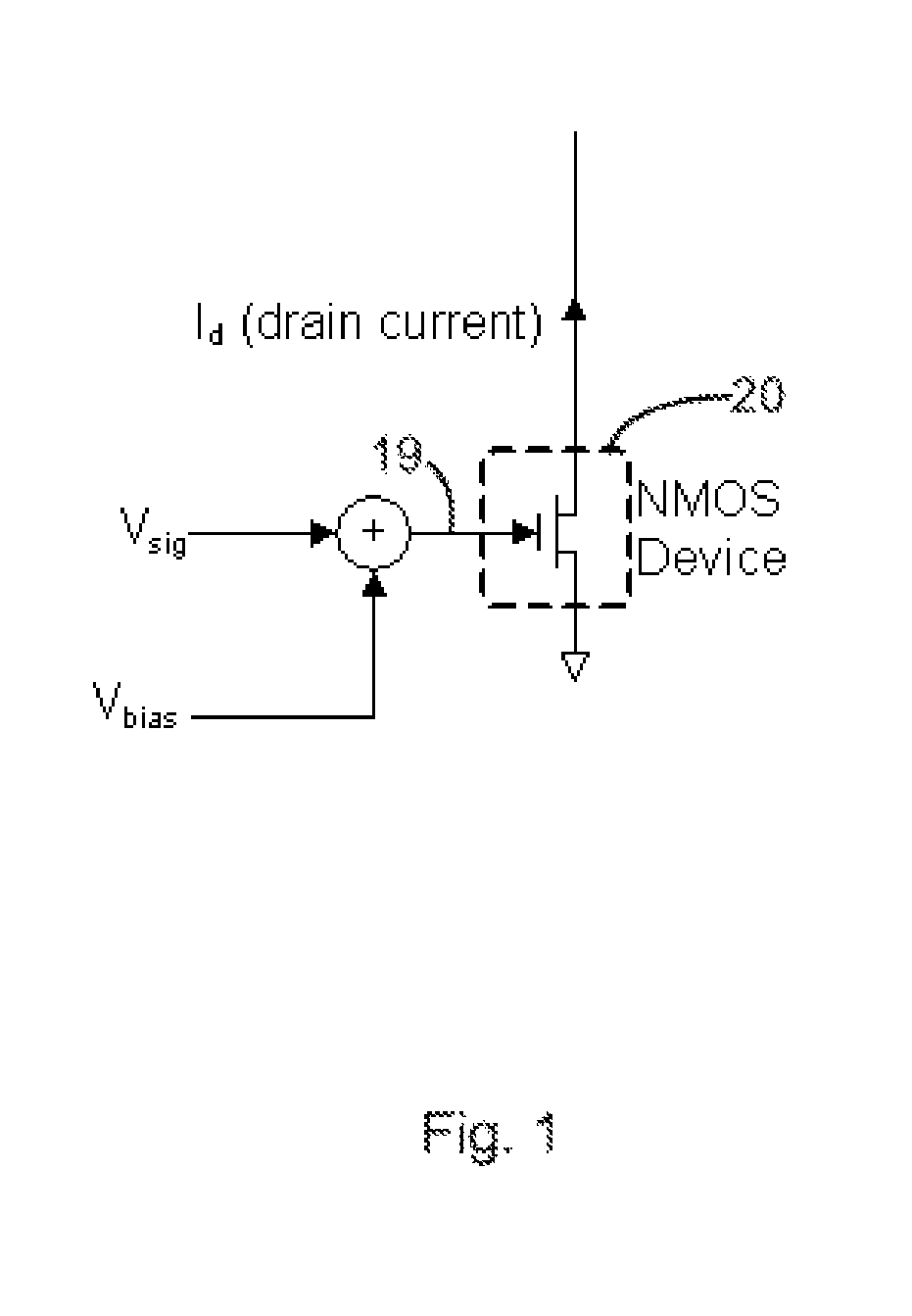
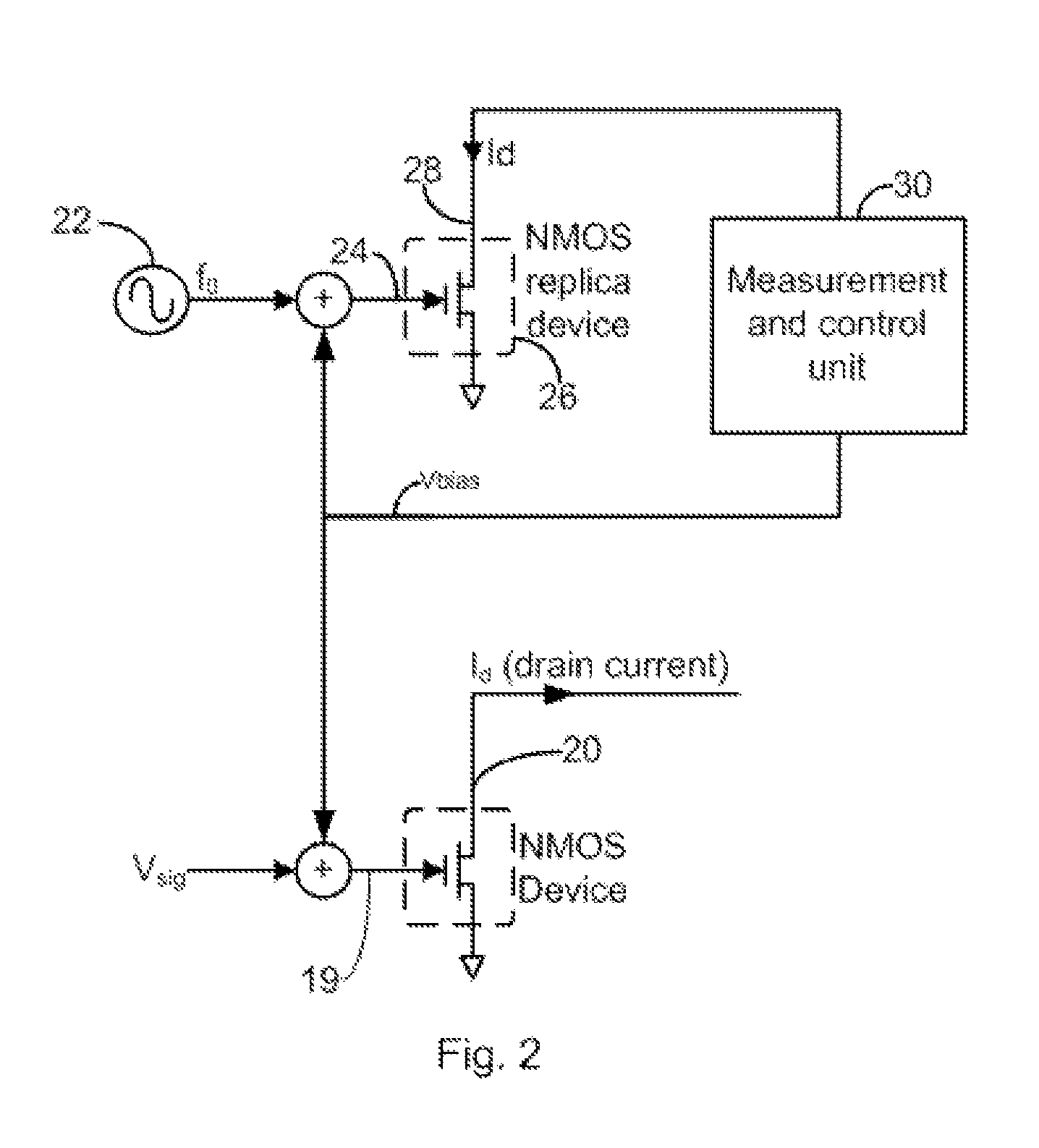
Continuous wave based bias method and apparatus for minimizing MOS transistor distortion
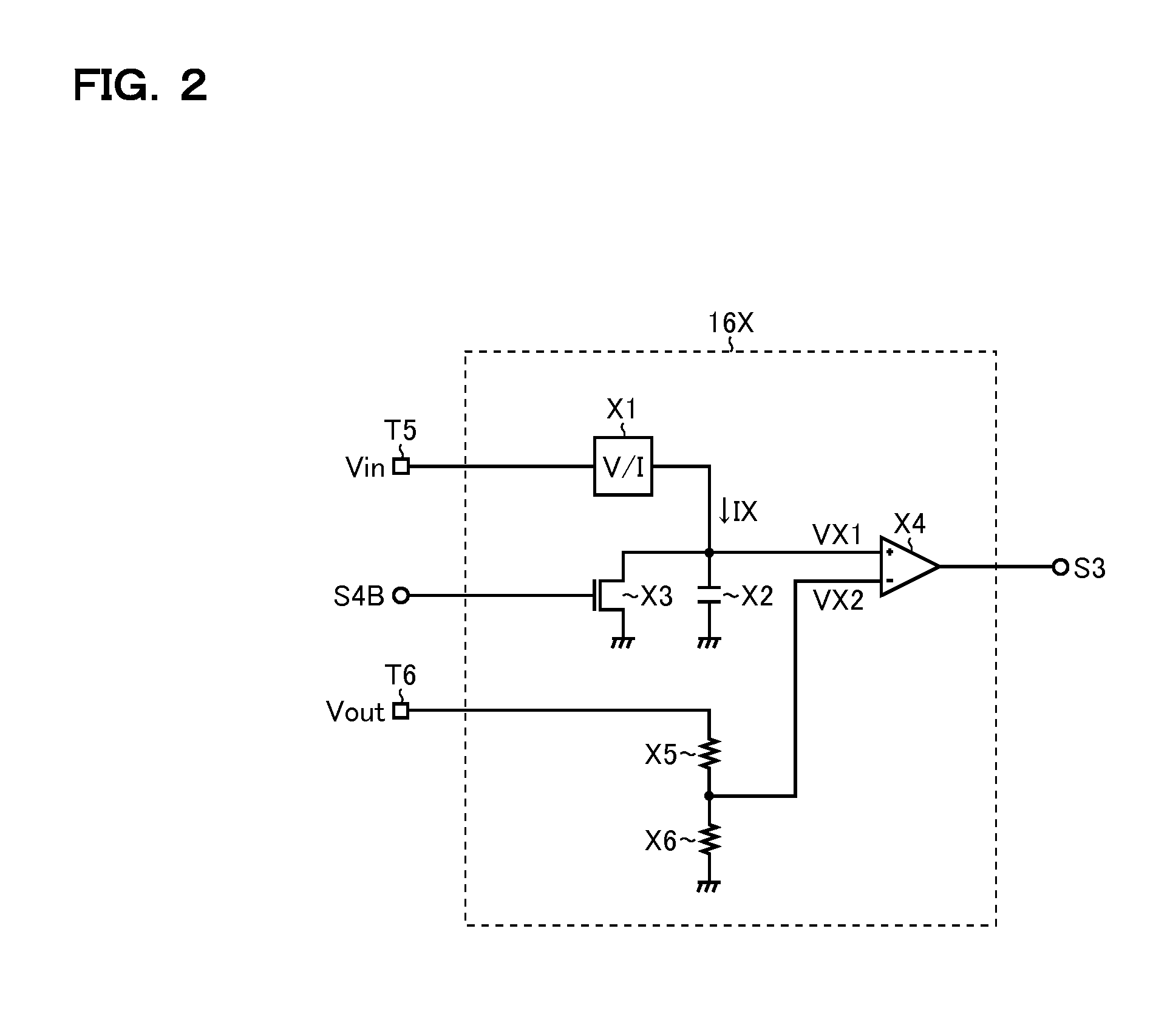
ActiveUS7679448B1Minimize distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationOptical transistorDistortion minimization
A biasing circuit and method for minimizing distortion in a MOS transistor. A first CW source provides a first CW signal at the input of a replica transistor to obtain an output signal at the output of the replica transistor. The output signal is mixed with another CW signal having a frequency equal to N times that of the first CW signal, N being an integer greater than one, to obtain a mixed signal having a DC component with an intensity proportional to the Nth-order distortion present in the output signal. A bias voltage to minimize this distortion is then applied to the input of the original transistor on which the replica transistor is based, the bias voltage determined in accordance with the intensity of the DC component.
Owner:MAXLINEAR ASIA SINGAPORE PTE LTD
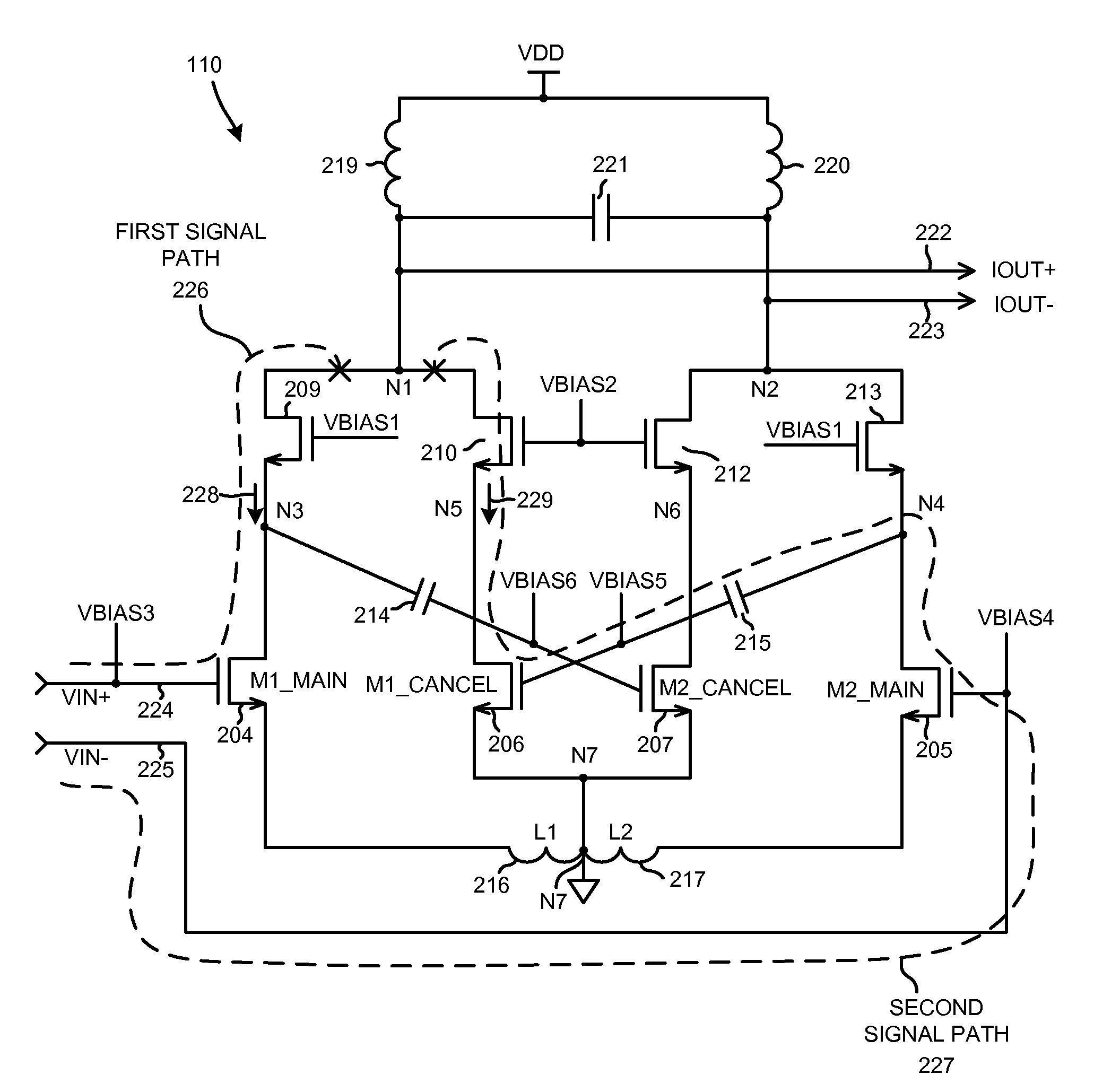
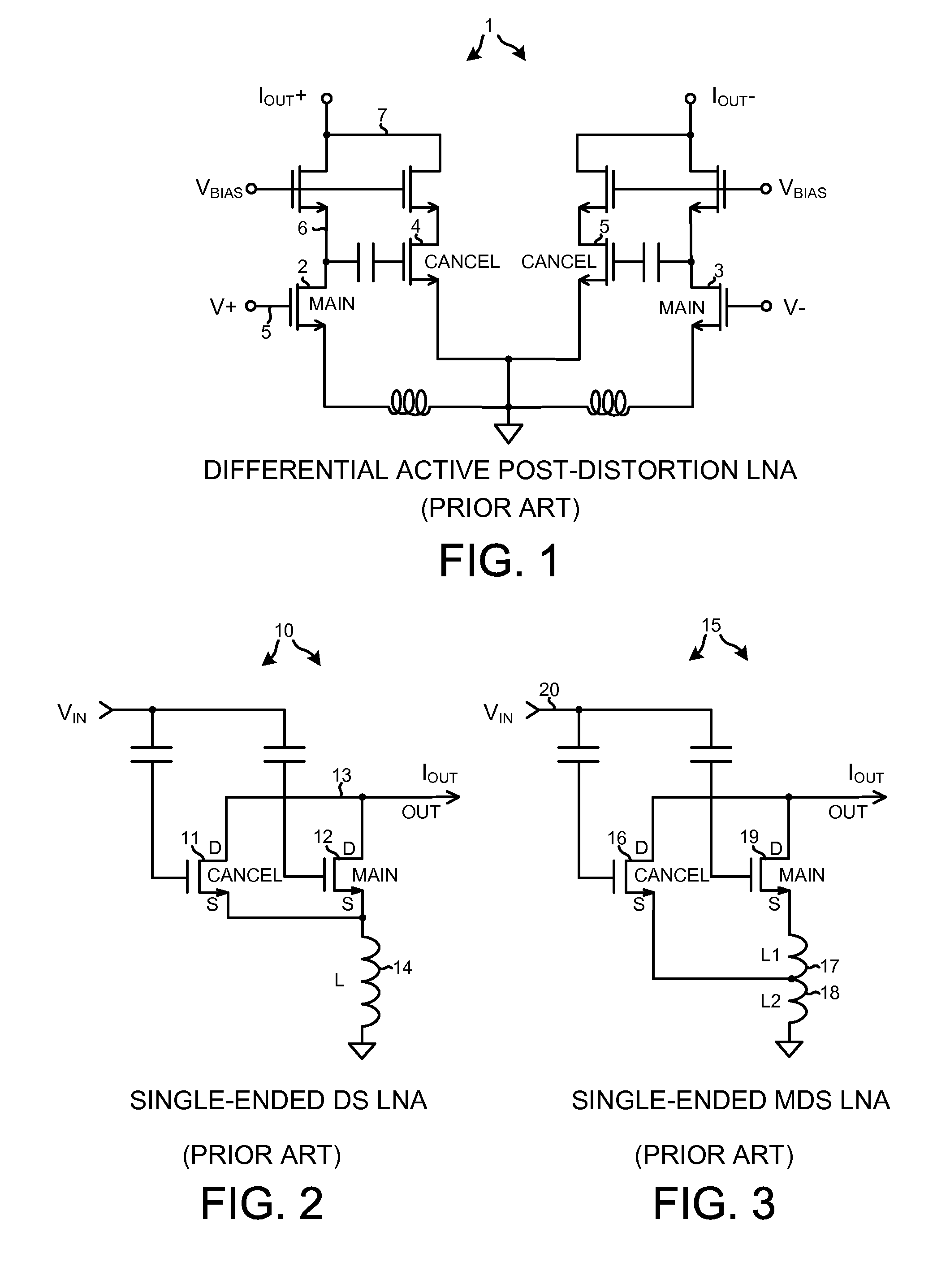
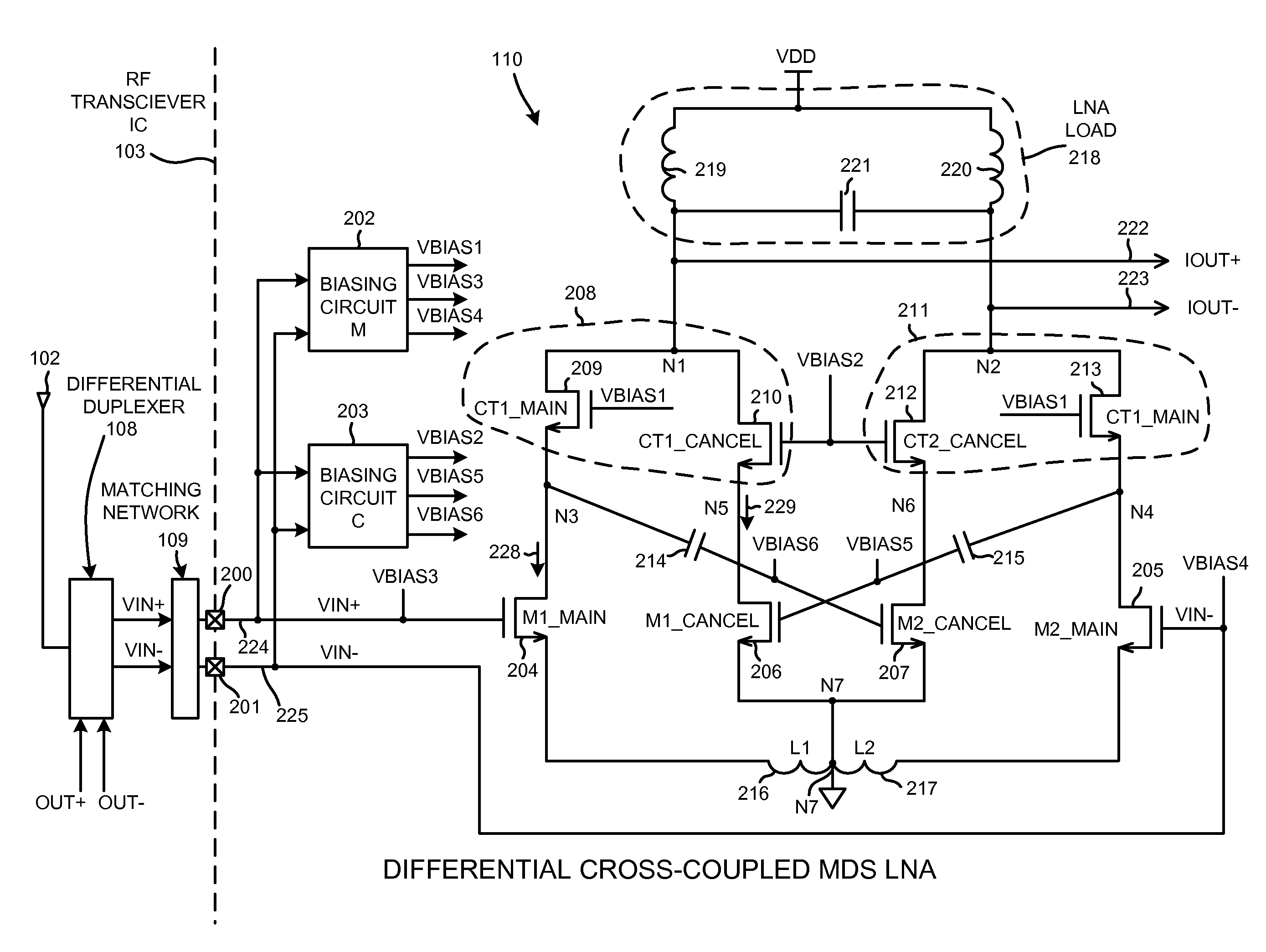
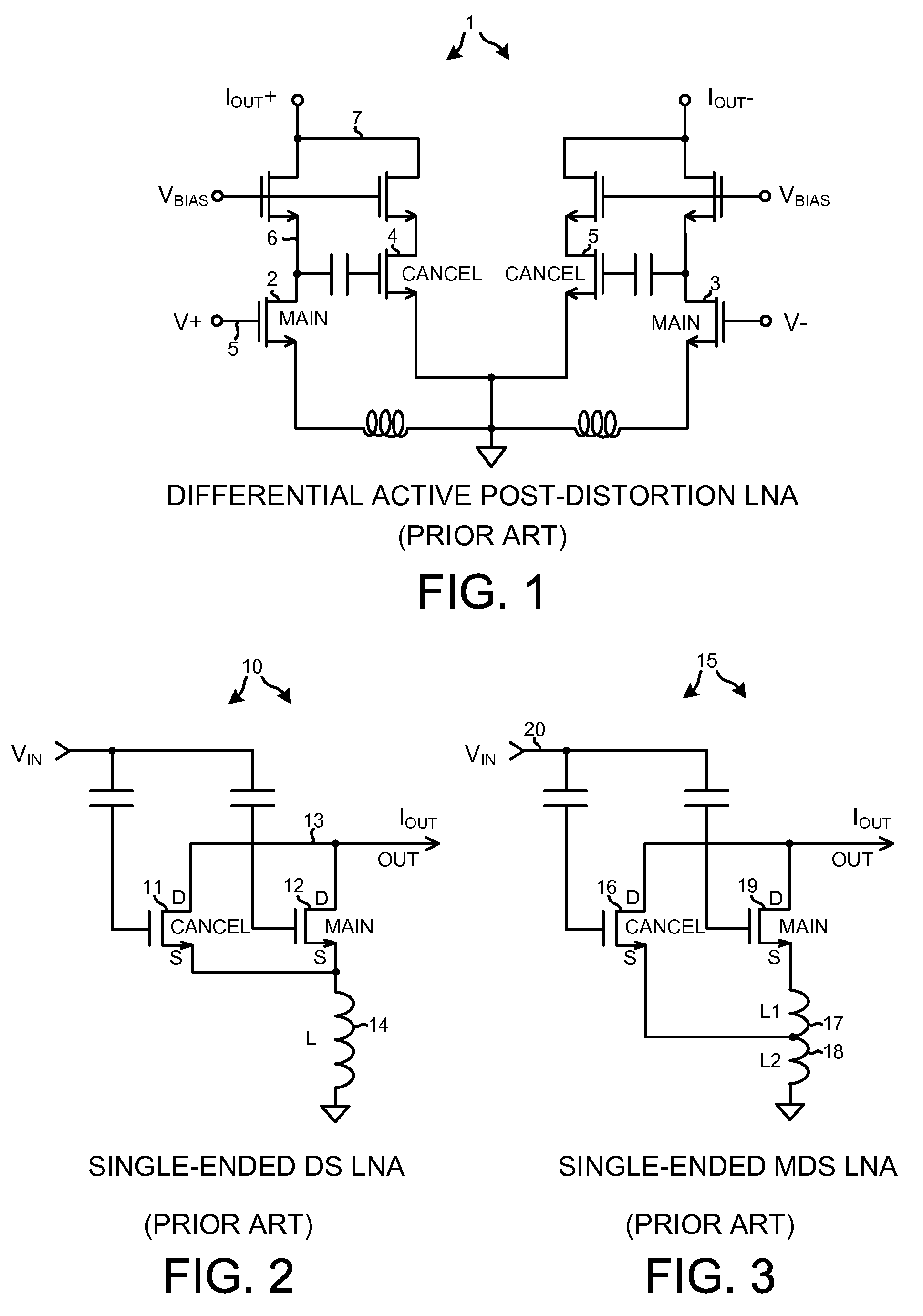
Low noise and low input capacitance differential mds lna
ActiveUS20090153244A1Reduce input capacitanceReduce noise contributionGain controlDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceLow noise
A differential low noise amplifier (LNA) involves two main amplifying transistors biased in saturation, and two cancel transistors biased in sub-threshold. In one example, the gates of the cancel transistors are coupled to the drains of main transistors, in a symmetrical and cross-coupled fashion. The main transistors are source degenerated. Because the gates of cancel transistors are not coupled to the differential input leads of the LNA, the input capacitance of the LNA is reduced. Noise introduced into the LNA output due to the cancel transistors being biased in the sub-threshold region is reduced because there are two stages. The first stage involves the main transistors, and the second stage involves the cancel transistors. By increasing the gain of the first stage and decreasing the gain of the second stage, overall LNA gain is maintained while reducing the noise that the sub-threshold biased transistors contribute to the LNA output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Output buffer with programmable voltage swing
InactiveUS6300802B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
An integrated circuit device in which the magnitude of the output voltage swings of outputs in a circuit having emitter coupled output transistors is programmable includes a variable bias generator that produces a bias voltage. The bias voltage is connected to the base of a current source transistor in order to program the magnitude of the output voltage swings. An electrical connection area of the integrated circuit device is connected to the bias voltage generator. An external programming circuit can be connected to the electrical connection area in order to set the bias voltage, to thereby program the desired magnitude of the output voltage swings. The external programming circuit typically can be a resistance or an external voltage source. The variable bias generator can be any of a number of circuits that produce a bias voltage that is dependent upon the external programming circuit connected to the electrical connection area, and that produce a default bias voltage if no external programming circuit is connected to the electrical connection area. Another aspect of the invention is a method for programming the magnitude of the output voltage swings in an integrated circuit device having emitter coupled output transistors. The invention provides the ability to program the magnitude of the output voltage swings of the outputs to increase the magnitude of the output voltage swings, or alternatively, to decrease the magnitude of the output voltage swings thereby advantageously saving power and preventing unnecessary heat generation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Switching power supply device
InactiveUS20160028311A1Avoid misuseSuppress overshootEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringControl circuit
A power control IC has a switching control circuit of a fixed on-period type which generates an output voltage from an input voltage by driving a coil by turning on and off an output transistor according to a result of comparison between a feedback voltage and a reference voltage, and a quieting circuit which forcibly turns on the output transistor by ignoring the result of comparison when, after an on-timing of the output transistor, a predetermined threshold time elapses without the next on-timing coming.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Body tie optimization for stacked transistor amplifier
ActiveUS9882531B1Improve RF performanceImprove performancePower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierTransistor stacking
A transistor stack can include a combination of floating and body tied devices. Improved performance of the RF amplifier can be obtained by using a single body tied device as the input transistor of the stack, or as the output transistor of the stack, while other transistors of the stack are floating transistors. Transient response of the RF amplifier can be improved by using all body tied devices in the stack.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Low noise and low input capacitance differential MDS LNA
ActiveUS7944298B2Weakening rangeReduce input capacitanceGain controlDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceLow noise
A differential low noise amplifier (LNA) involves two main amplifying transistors biased in saturation, and two cancel transistors biased in sub-threshold. In one example, the gates of the cancel transistors are coupled to the drains of main transistors, in a symmetrical and cross-coupled fashion. The main transistors are source degenerated. Because the gates of cancel transistors are not coupled to the differential input leads of the LNA, the input capacitance of the LNA is reduced. Noise introduced into the LNA output due to the cancel transistors being biased in the sub-threshold region is reduced because there are two stages. The first stage involves the main transistors, and the second stage involves the cancel transistors. By increasing the gain of the first stage and decreasing the gain of the second stage, overall LNA gain is maintained while reducing the noise that the sub-threshold biased transistors contribute to the LNA output.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
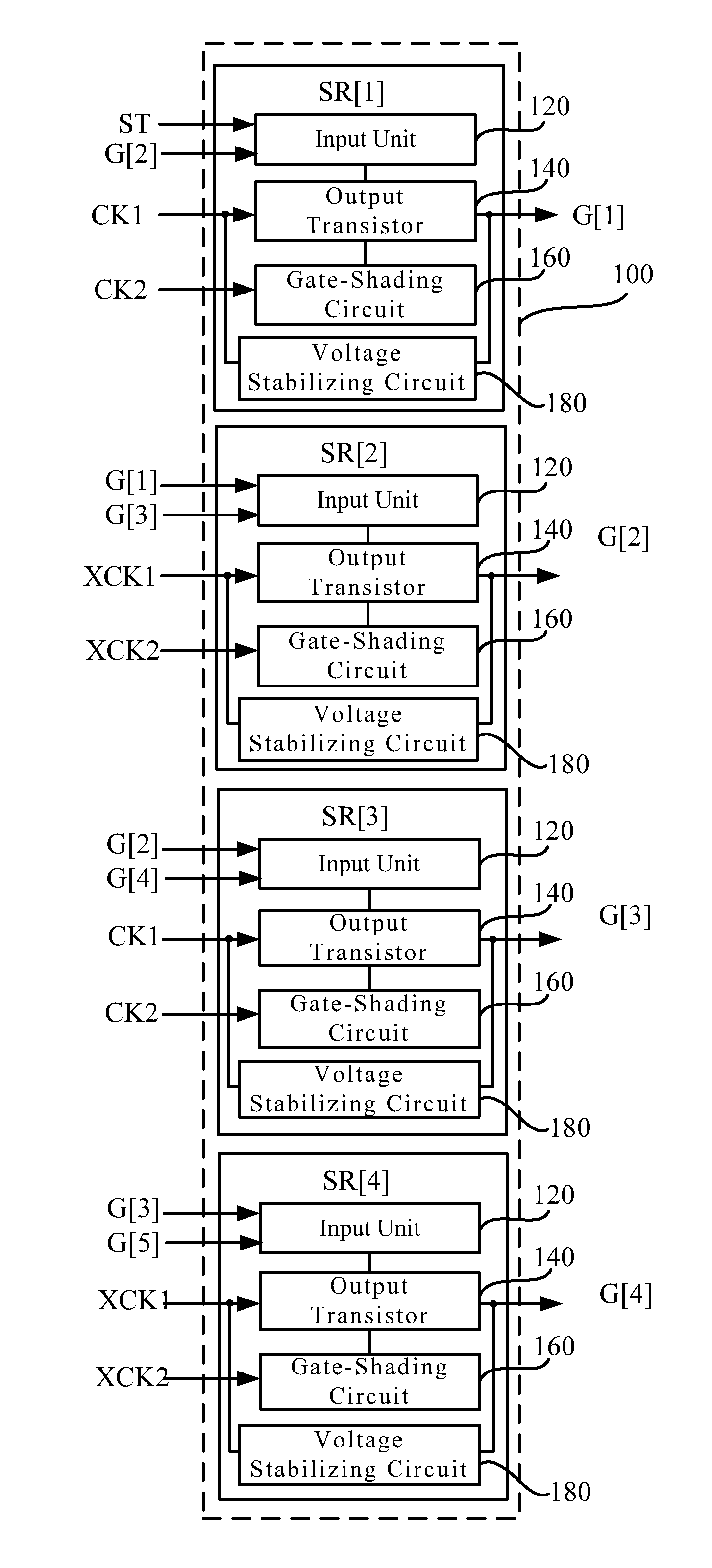
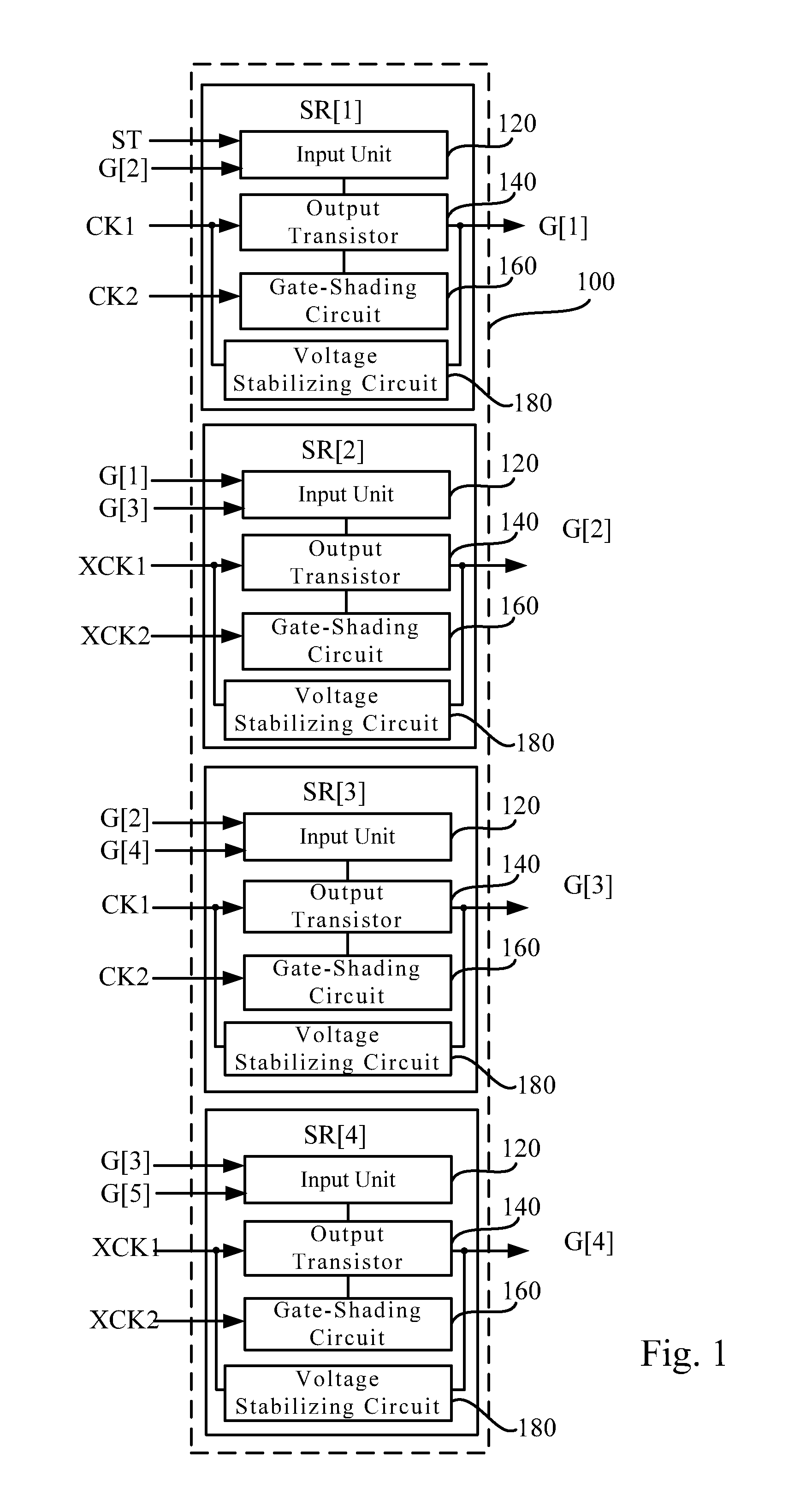
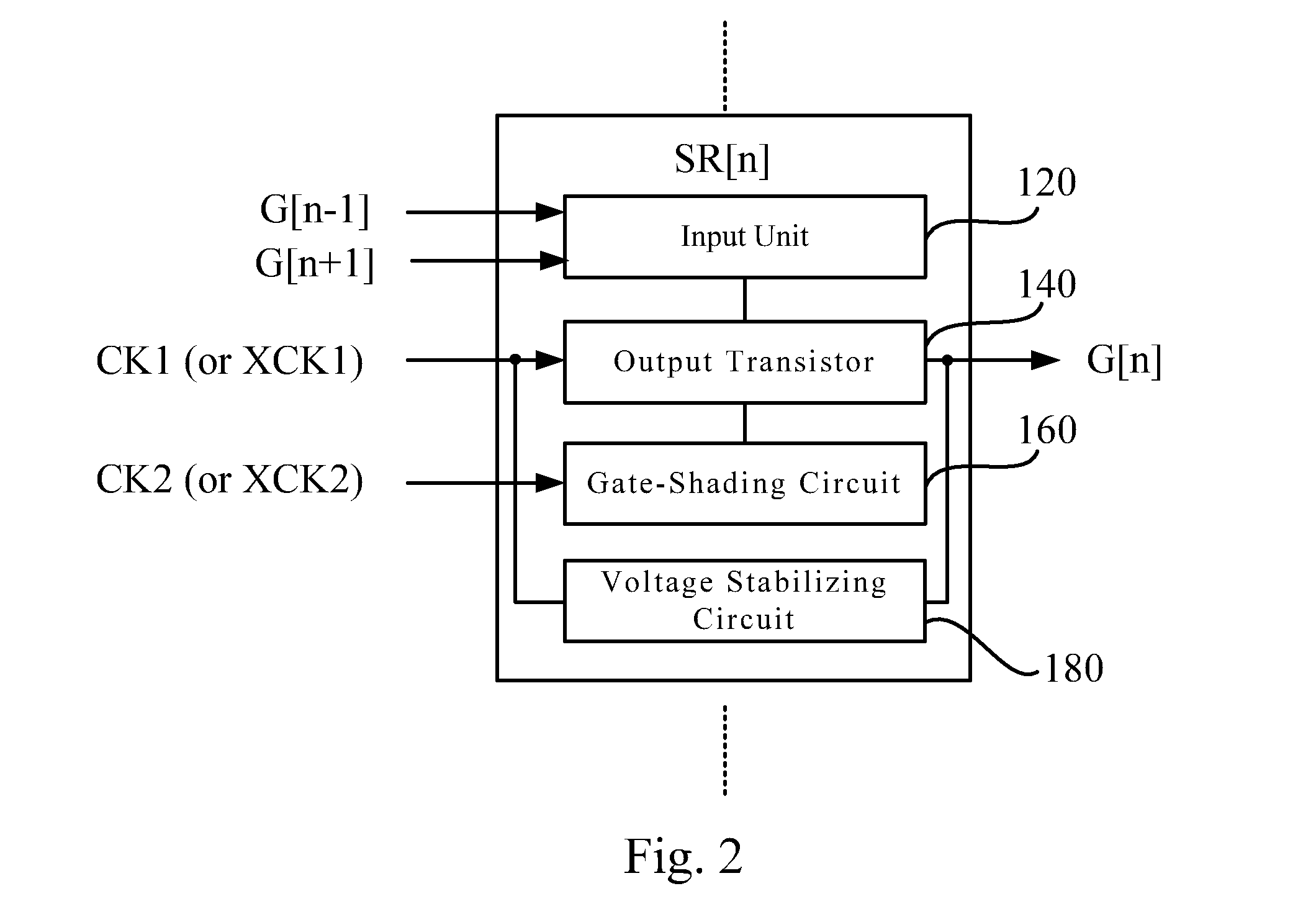
Shift register circuit and shading waveform generating method
ActiveUS20140219412A1Efficiently formedEffective shieldingStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerProcessor register
A shift register circuit and a shading waveform generating method are disclosed. The shift register circuit includes plural stages of shift registers. Each stage of the shift register includes an output transistor, an input unit and a gate-shading circuit. The output transistor is configured for generating an output signal of the stage of the shift register. The input unit is configured for controlling a voltage level on a gate terminal of the output transistor. The gate-shading circuit includes a first switch, a second switch and a third switch. The first switch is configured for outputting a control signal. The second switch is configured for pulling down the voltage level on the gate terminal of the output transistor according to the control signal. The third switch is configured for pulling down a level on an output terminal of the output transistor according to the control signal.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Push-pull programmable logic device cell
ActiveUS20110002167A1Relieve pressureSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesProgrammable logic devicePush pull
A memory cell includes a non-volatile p-channel transistor having a source coupled to a first potential, a drain, and a gate. A non-volatile n-channel transistor has a source coupled to a second potential, a drain, and a gate. A switch transistor has a gate coupled to a switch node, a source, and a drain. A stress transistor has a source and drain coupled between the drain of the non-volatile p-channel transistor and the drain of the non-volatile n-channel transistor, the stress transistor having a gate coupled to a gate bias circuit. Where one of the first or second potentials is a bit line, an isolation transistor is coupled between the other of the second potentials and one of the non-volatile transistors.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Slew rate controlled output buffer
InactiveUS6903588B2Control rateReduce degradationElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceCharge current
An output buffer includes first and second circuit portions coupled between input and output terminals. Each circuit portion includes a capacitive element; an output transistor having a gate coupled to the capacitive element, and a drain that drives a voltage at the output terminal; and a current generator configured to generate a charging current that is directed to the capacitive element responsive to a logic transition at the input terminal, wherein the charging current causes a substantially linear ramp voltage to form at the gate of the output transistor, whereby the ramp voltage controls a slew rate of the output terminal voltage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Buffer amplifier
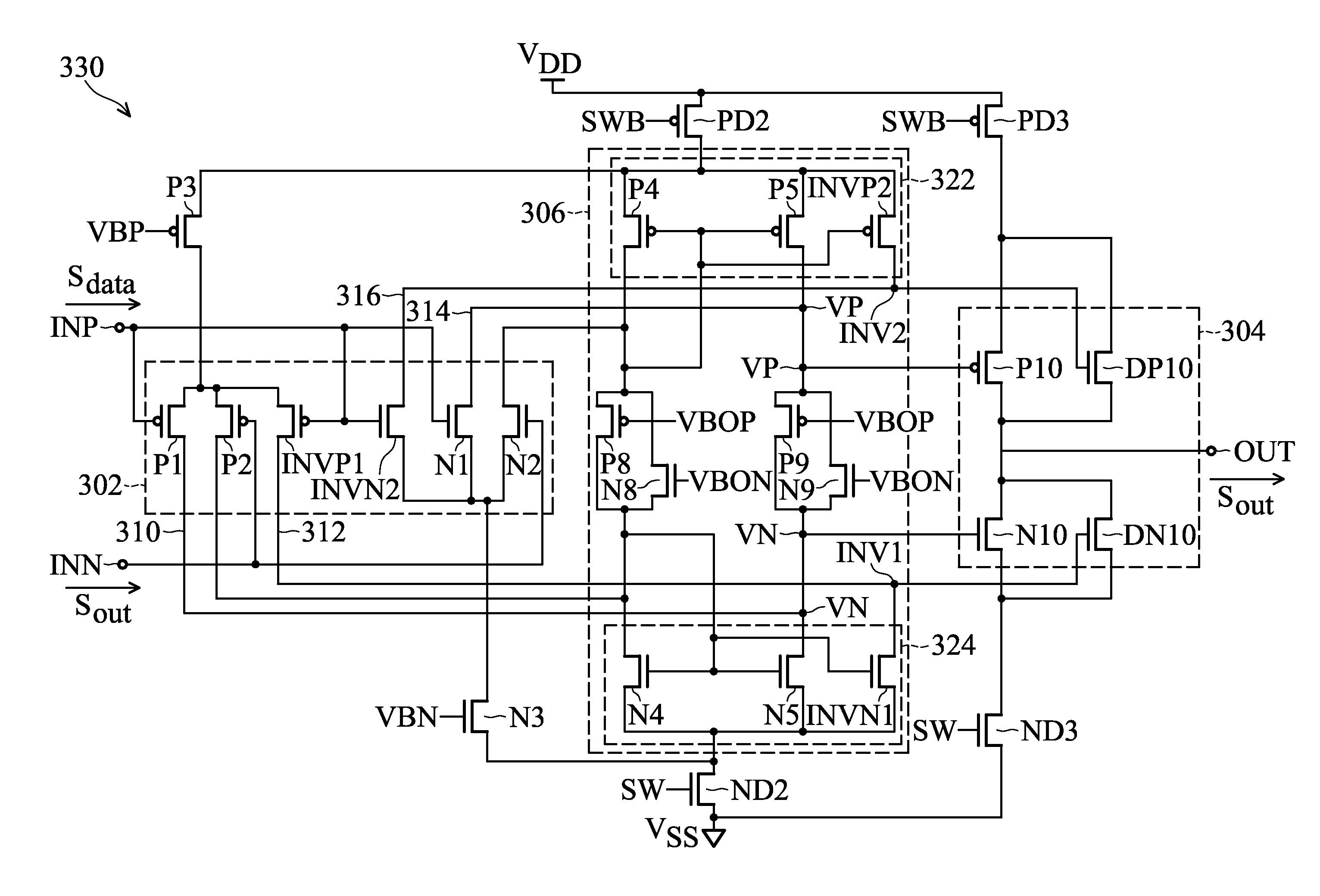
A buffer amplifier includes an input stage circuit, an output stage circuit and a bias circuit, providing a buffered output signal at an output terminal according to an input signal applied to a first input terminal. The input stage circuit generates four control signals in response to the input signal when the logic level of the buffered output signal is opposite to that of the input signal. The output stage circuit includes four output transistors, wherein the first and second output transistor of a first type are provided for discharge in response to a first control signal and a second control signal, and the third and fourth output transistor of a second type are provided for charge in response to a third control signal and a fourth control signal. The bias circuit is used for determining the first, second, third and fourth control signal.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD
Level shift circuit
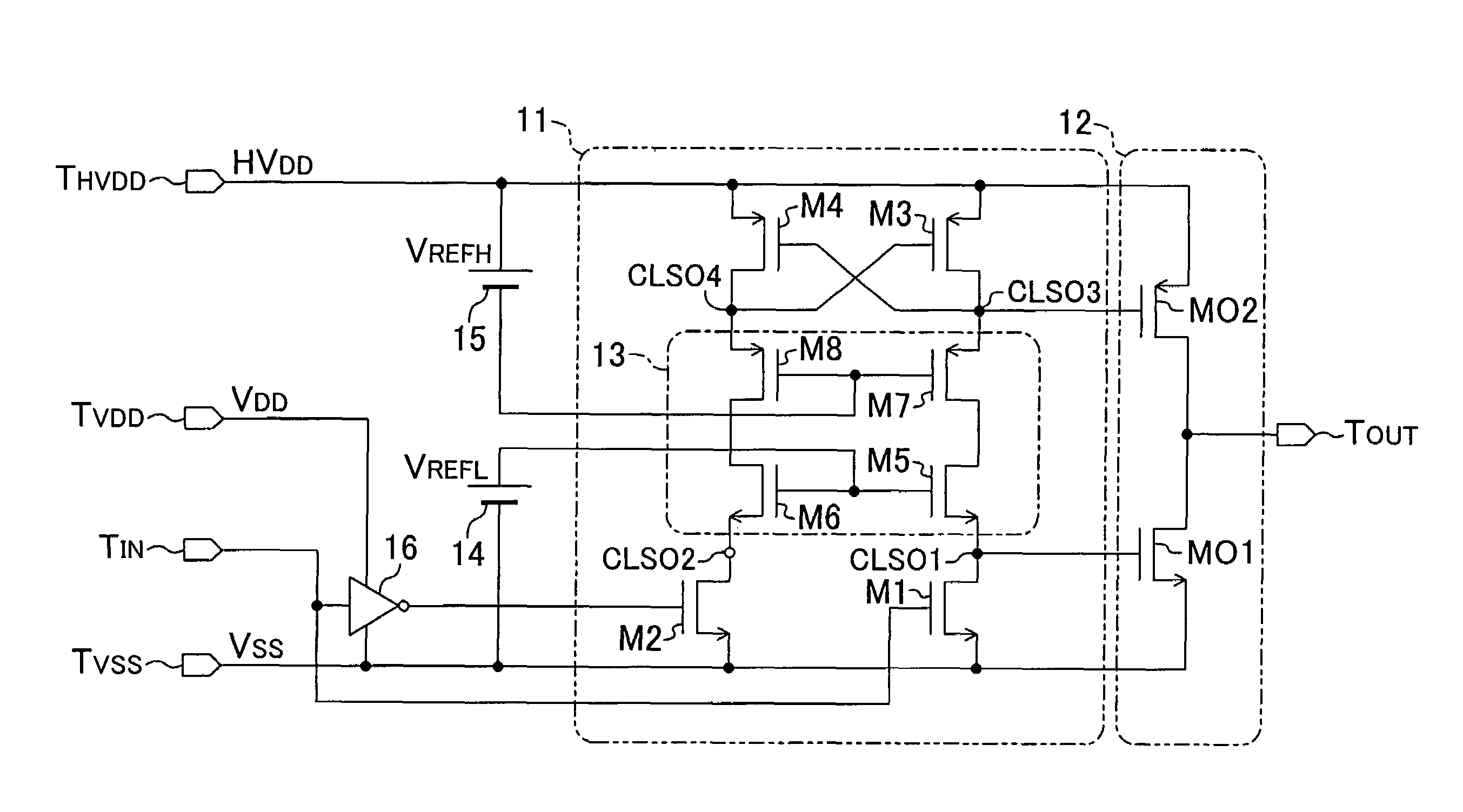
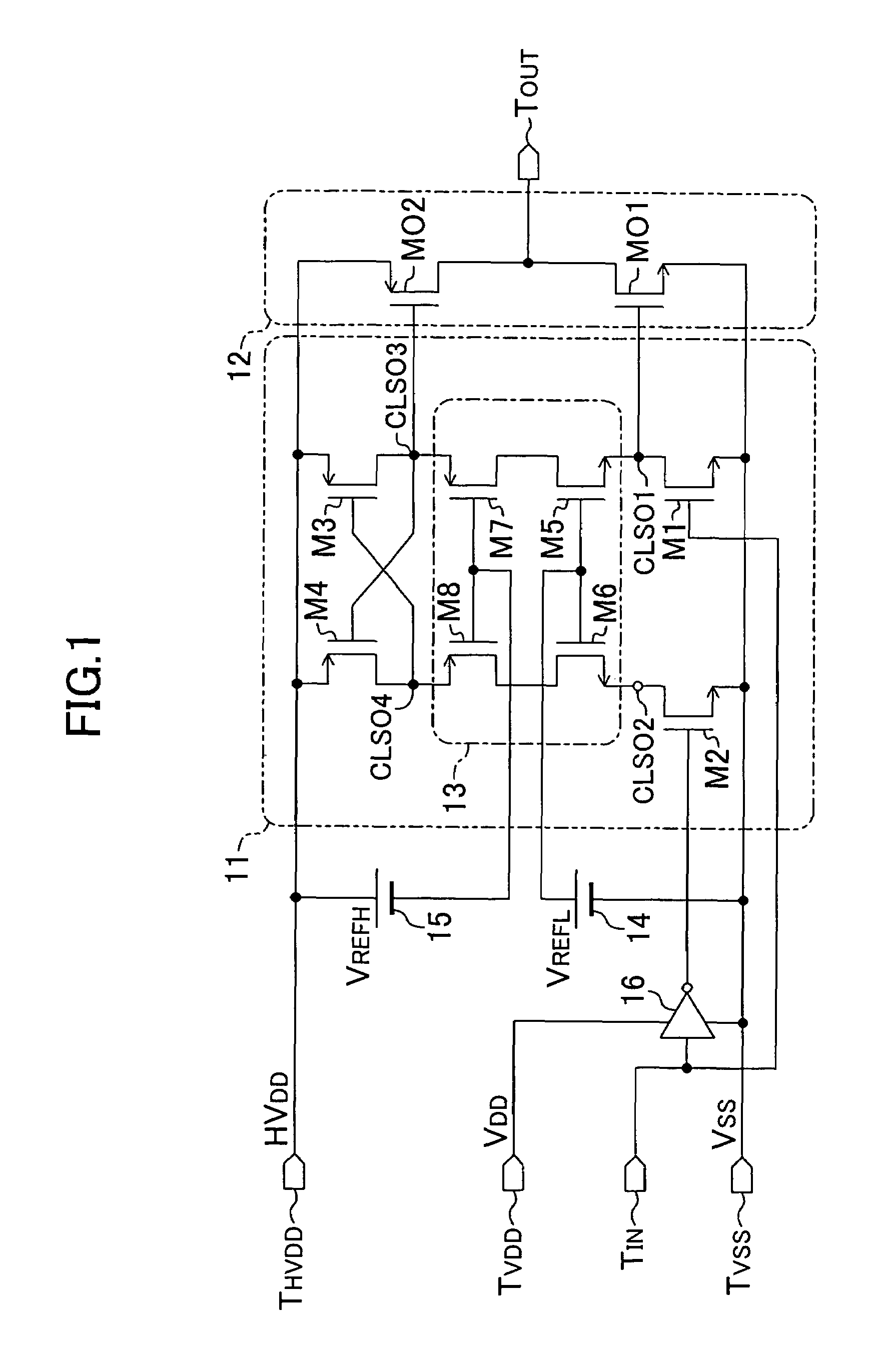
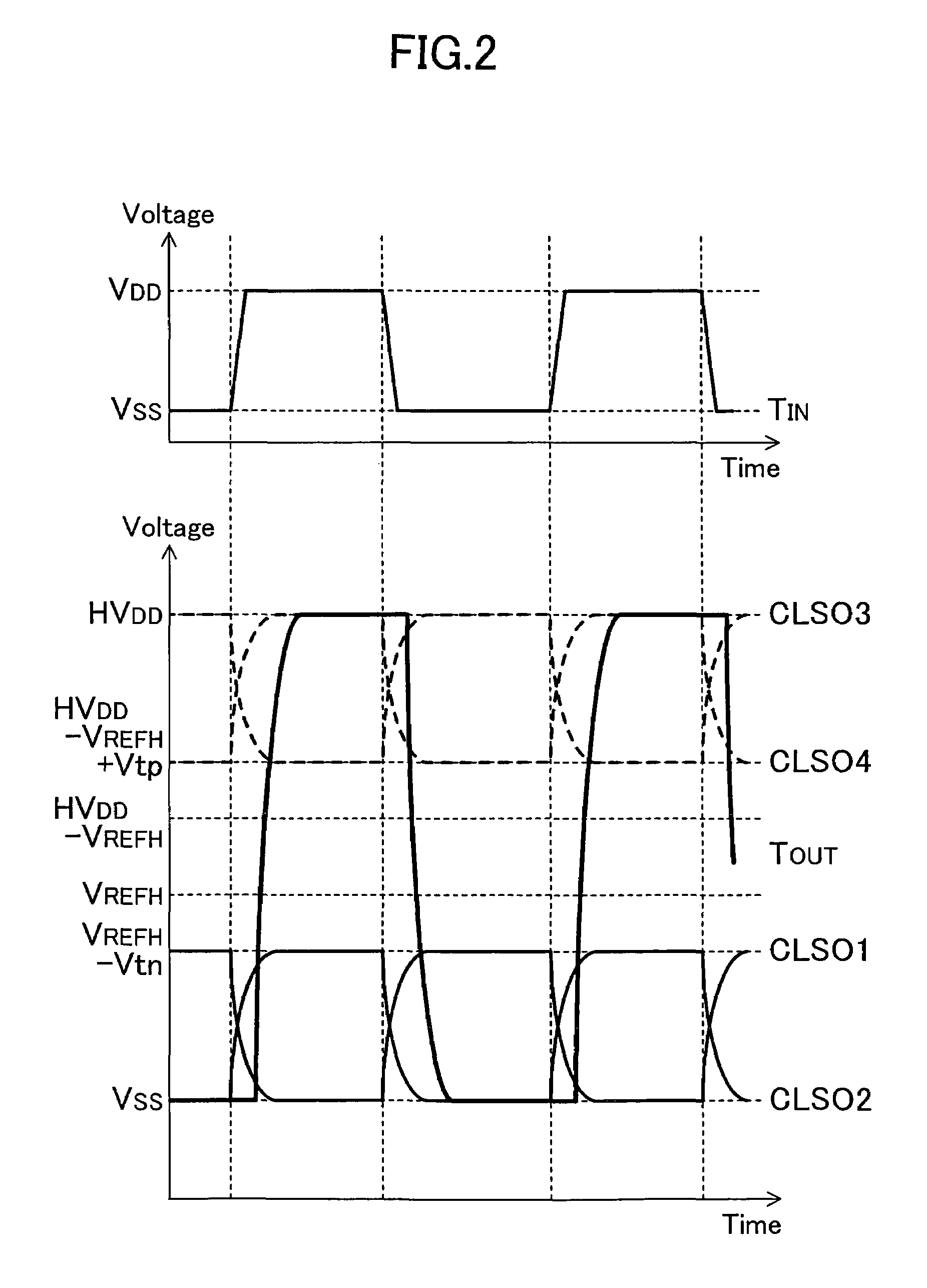
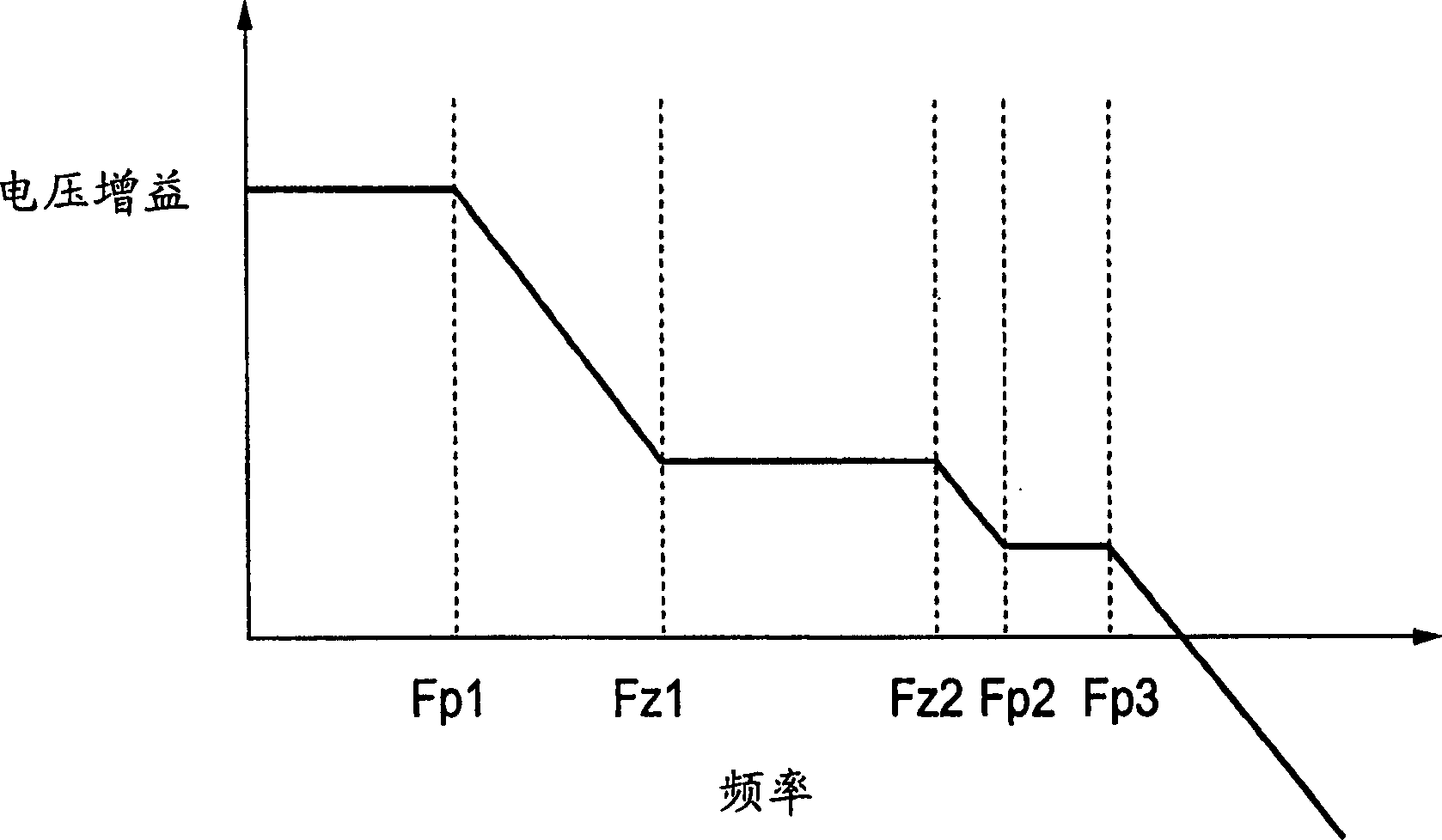
InactiveUS7348800B2Simple designEasy to makePulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorDriver circuitOptical transistor
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electric voltage regulator
InactiveCN1487384AImprove response characteristicsStable jobAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationCapacitanceEngineering
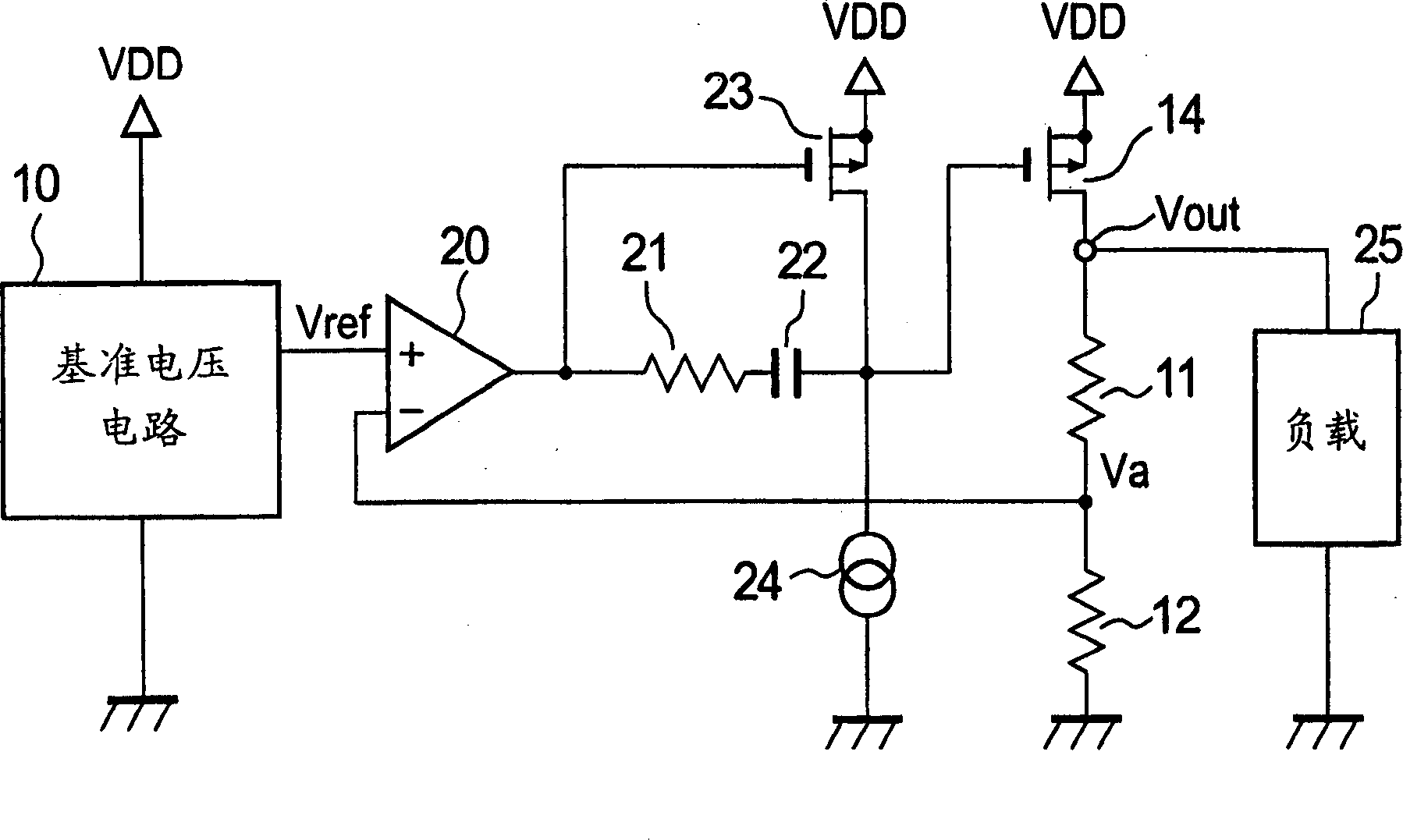
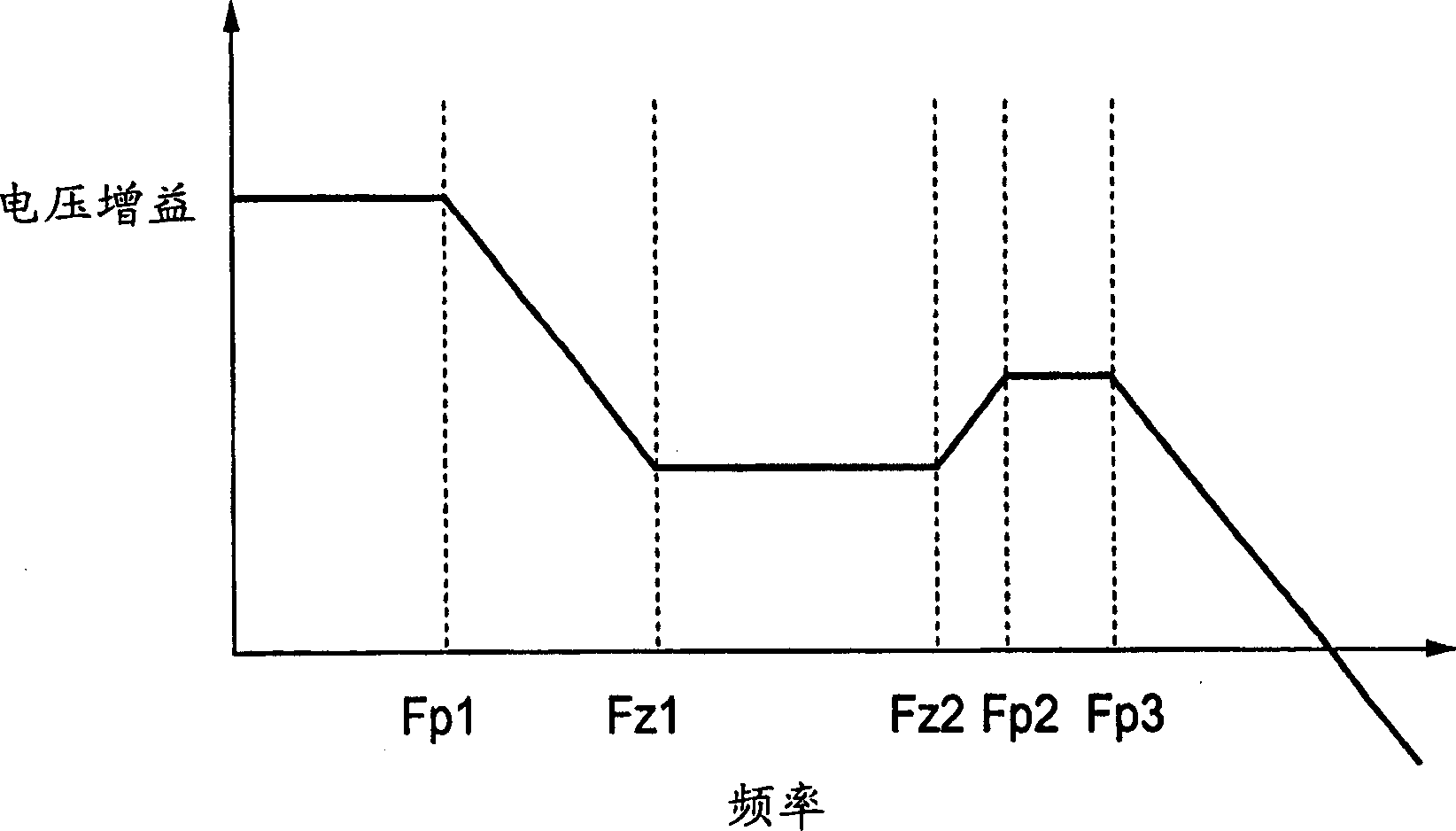
Provided is a voltage regulator which has a high speed response property in a low consumption current and is stably operable in a low output capacitance. The voltage regulator has: a differential amplifier for comparing an output of a reference voltage circuit with an output of a voltage dividing circuit and outputting a first signal; a phase compensating circuit in which a resistor and a capacitor are connected in series; a MOS transistor in which an output of the differential amplifier is inputted to a gate electrode, which is connected between a power supply and the phase compensating circuit, and in which a source is grounded; a constant current circuit connected between the MOS transistor and a ground; and an output transistor in which a second signal output from a connection point between the MOS transistor and the phase compensating circuit is inputted to a gate electrode and which is connected between the power supply and the voltage dividing circuit. A resistor side of the phase compensating circuit is connected with an output terminal of the differential amplifier and a capacitor side of the phase compensating circuit is connected with a drain electrode of the MOS transistor.
Owner:SEIKO INSTR INC
Power switching circuit
InactiveUS20090219661A1Accurately avoidedPrevent overcurrentTransistorElectronic switchingPower switchingEngineering
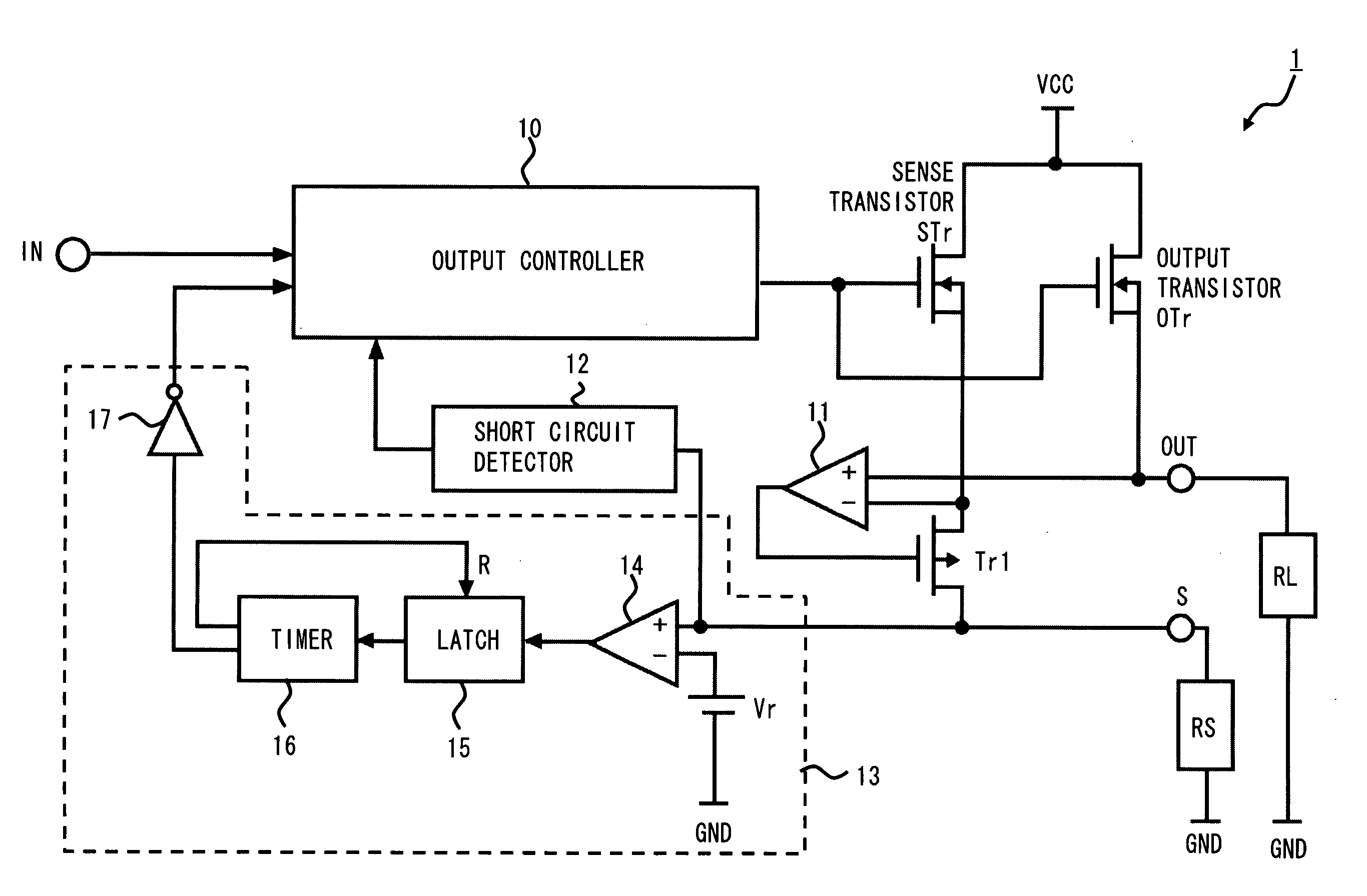
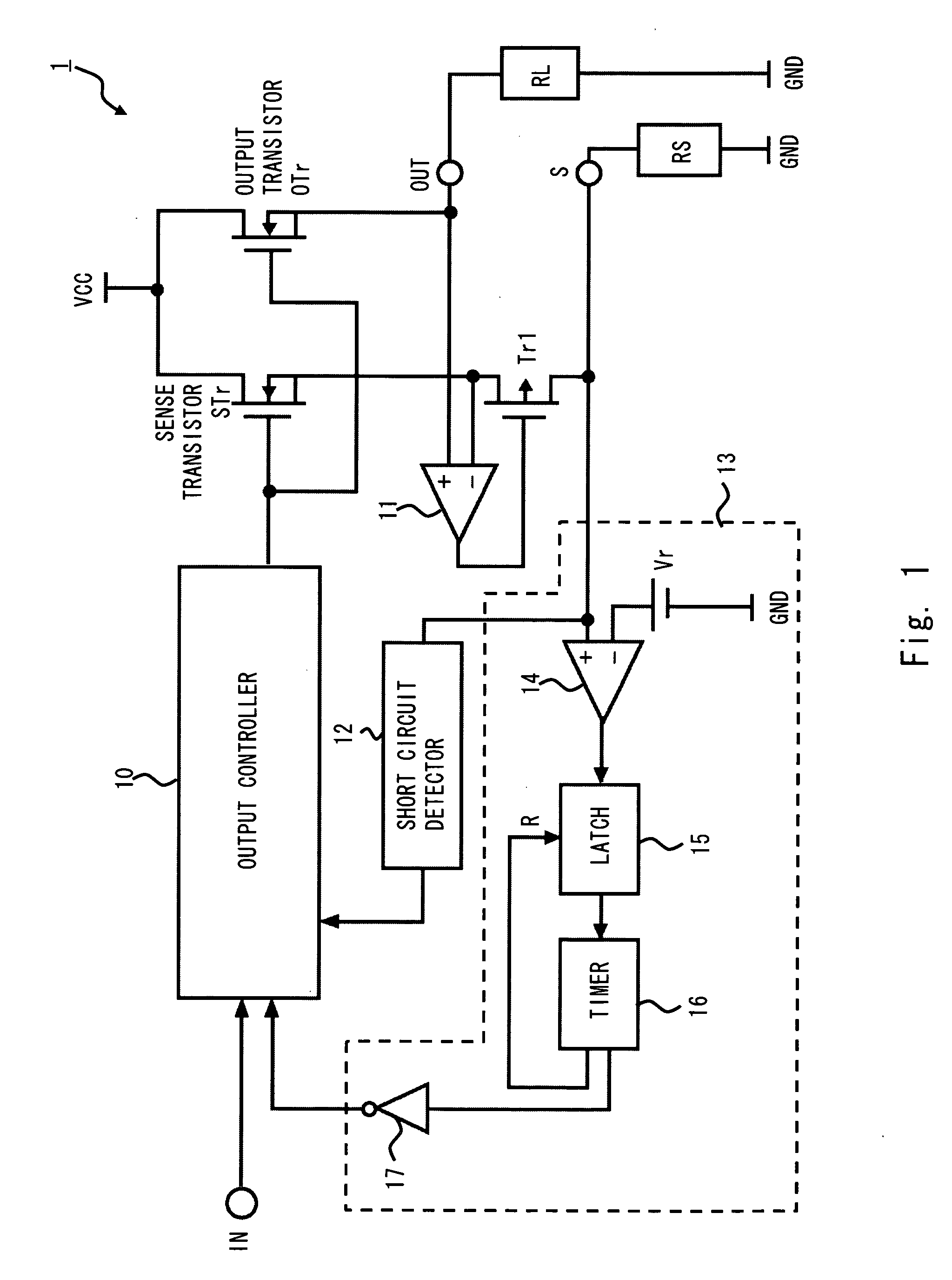
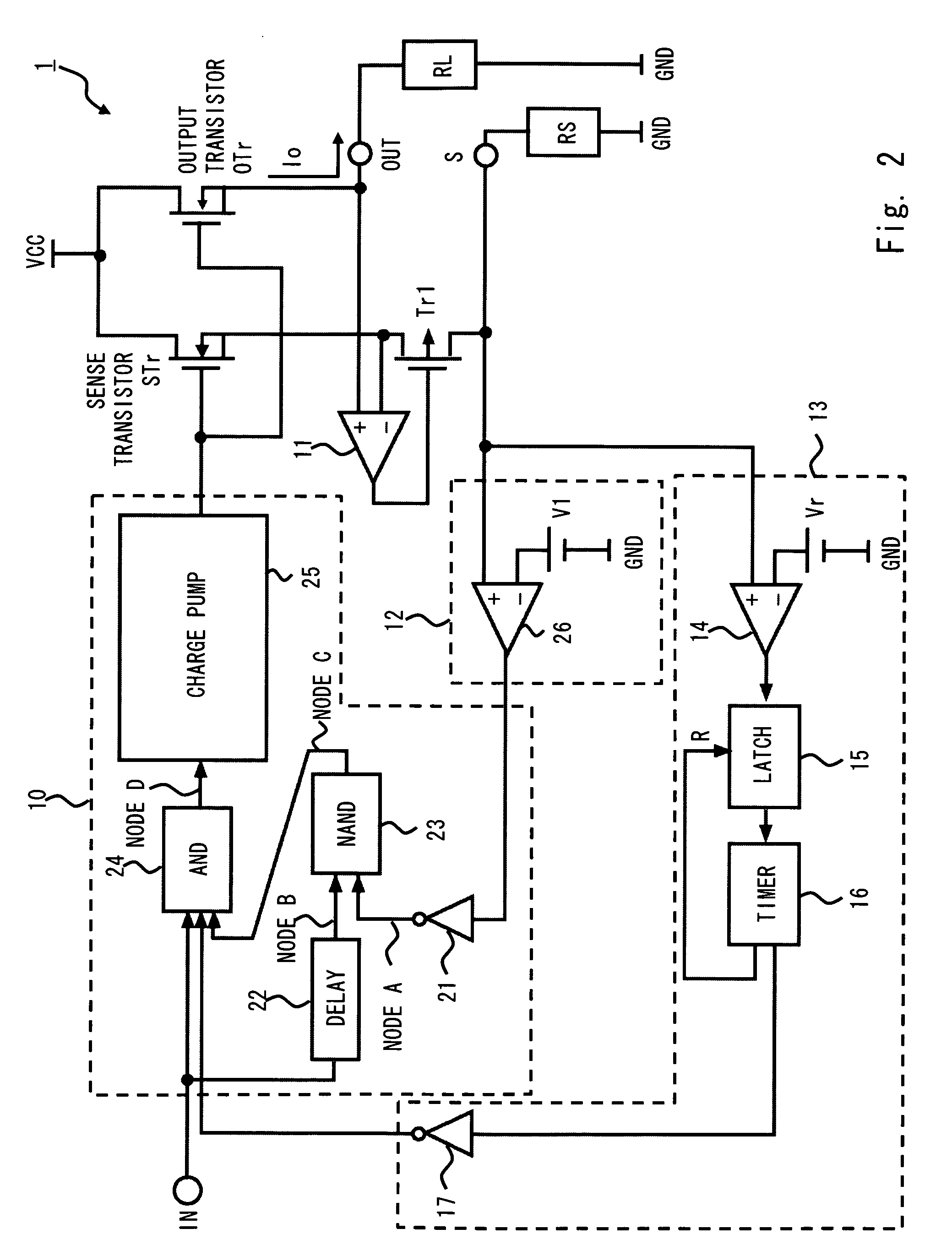
A power switching circuit according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention includes an output transistor connected between a power supply terminal VCC and an output terminal OUT, an output controller which controls a conducting state of the output transistor according to an input signal, a sense transistor having a gate commonly connected with the output transistor, which detects an output current flowing into the output transistor, an output current detection terminal in which a detection voltage is generated according to the output current detected by the sense transistor and a short circuit detector which detects a short circuit condition of the output current detection terminal according to the detection voltage and stops the output transistor or limits the output current.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
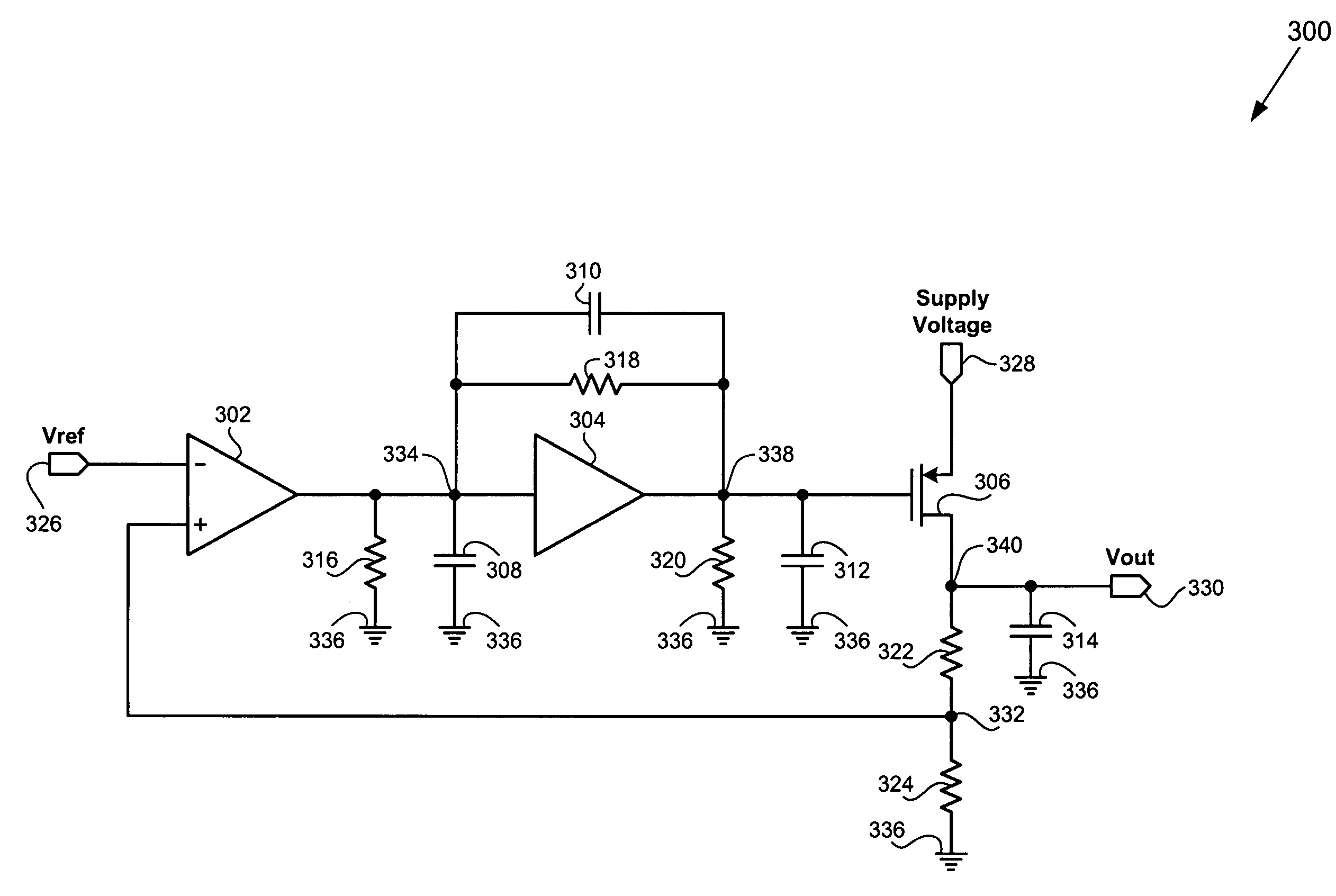
Bias circuit with increased power supply rejection
InactiveUS7622994B2Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
According to one exemplary embodiment, a power supply rejection bias circuit includes a first amplifier coupled to a second amplifier, where the first amplifier receives a reference voltage, and a feedback voltage of the bias circuit. The bias circuit further includes an output transistor driven by the output of the second amplifier, where the output transistor provides the output of the bias circuit and the feedback voltage. The bias circuit further includes a feedback resistor coupled between an input and an output of the second amplifier. According to this embodiment, the output of the second amplifier forms a non-dominant pole of the bias circuit and the output of the bias circuit forms a dominant pole of the bias circuit, thereby increasing power supply rejection of the bias circuit.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Voltage level shifting circuit with improved switching speed
InactiveUS6888394B2Increase conversion rateIncrease speedPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorLevel shiftingLow voltage
Voltage level shifting circuits are provided in which circuit devices are placed across sourcing output transistors to improve the switching speed of the low voltage to high voltage output transition. These circuit devices permit sourcing and sinking output transistors to be sized for optimal switching speed of the high voltage to low voltage output transition.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Radio frequency amplifier circuit
ActiveUS20130106519A1Improve efficiencyImprove stabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHarmonicRadio frequency signal
A radio frequency amplifier circuit includes: low-output transistors, each of which includes an input terminal, an output terminal, and a ground terminal, and amplifies a radio frequency signal; a harmonic processing circuit provided for each of the low-output transistors to be connected to the output terminal of the low-output transistor, and processing a secondary harmonic included in an amplified radio frequency signal, and a resistor connected to the output terminal of each of the low-output transistors. The input terminal of each of the low-output transistors is connected to an input terminal of the radio frequency amplifier circuit via an inductor, and the output terminal of each of the low-output transistors is connected to the other output terminal via the resistance and is further connected to an output terminal of the radio frequency amplifier circuit via an inductor.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Display device
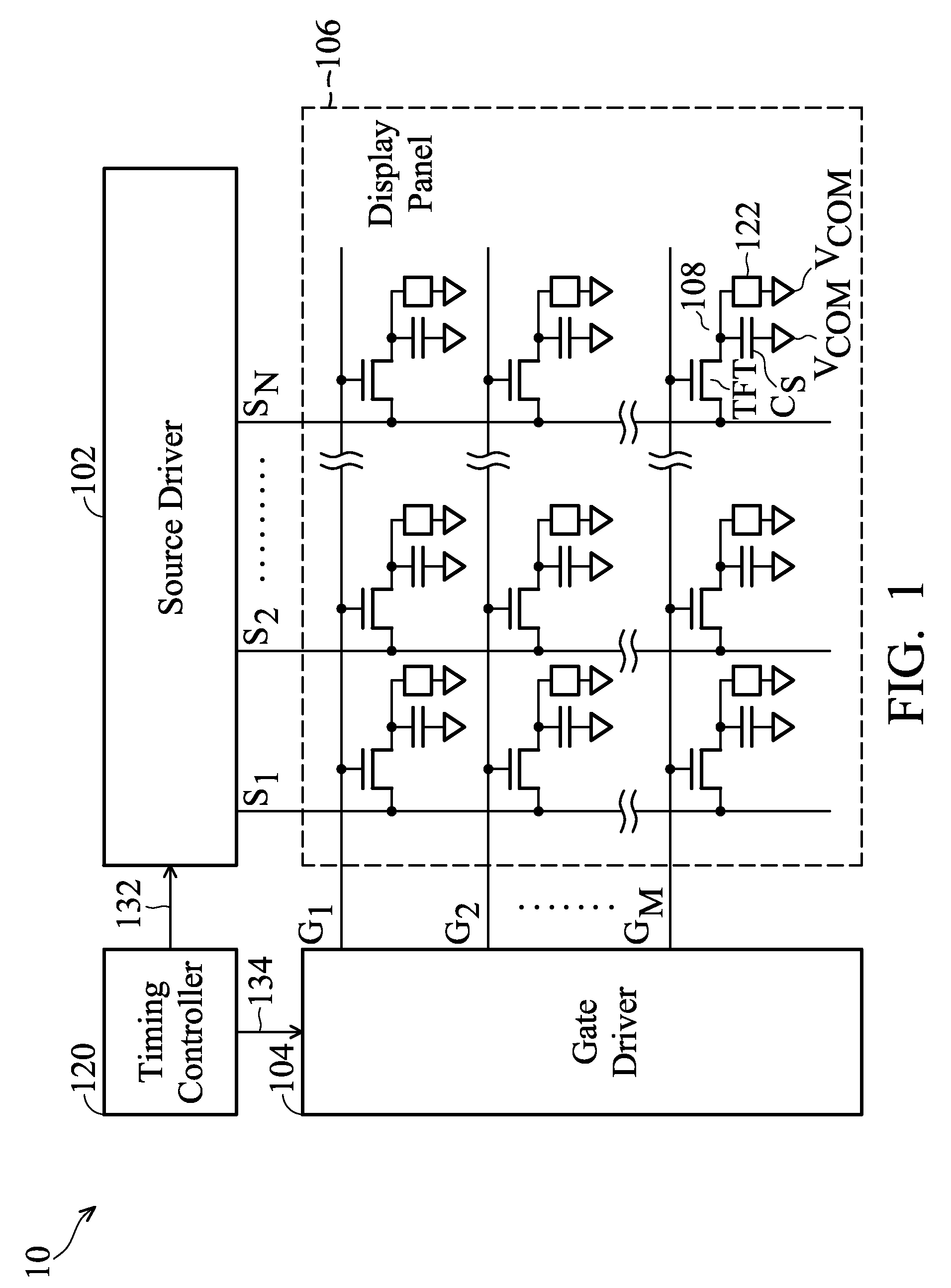
InactiveUS7242376B2Transistor configuring the first switch can be suppressedUniform currentServomotorsSolid-state devicesCurrent sampleDisplay device
A display device able to hold a drain potential of an output transistor functioning as a constant current source constant even in a sampling period of another circuit, able to suppress a change due to leakage of a gate potential of the output transistor, able to obtain a uniform current source free from variation in current value of an output stage, and able to display a high quality image without occurrence of uneven luminance toward a scanning end part, wherein for example a current sample and hold circuit finishing a sampling and holding operation during a period where the sampling and holding operation of its own stage is ended and another stage is performing a sampling and holding operation is configured so as to carry a constant current corresponding to a sampled current by a thin film transistor through a node by operating a leakage elimination circuit.
Owner:JOLED INC
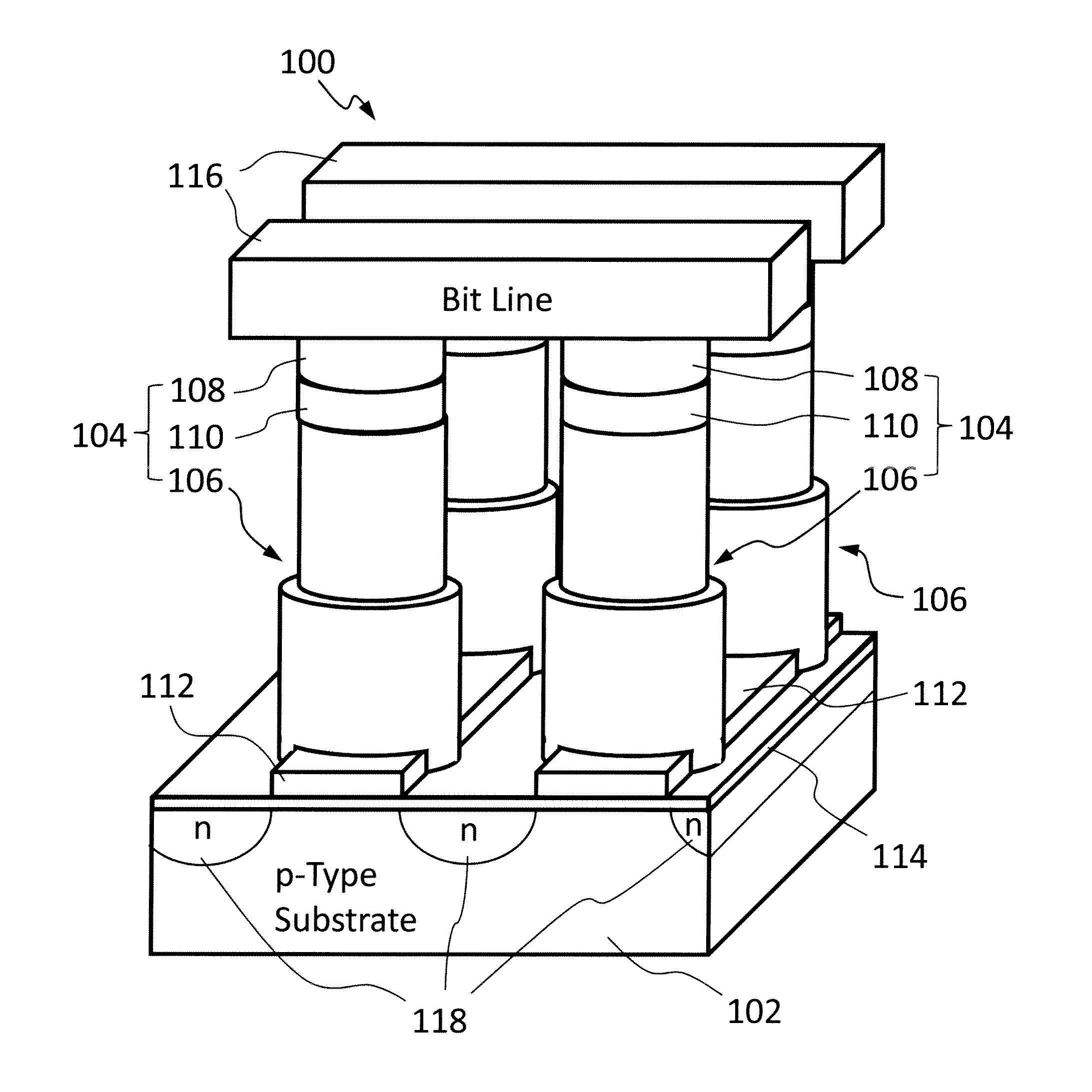
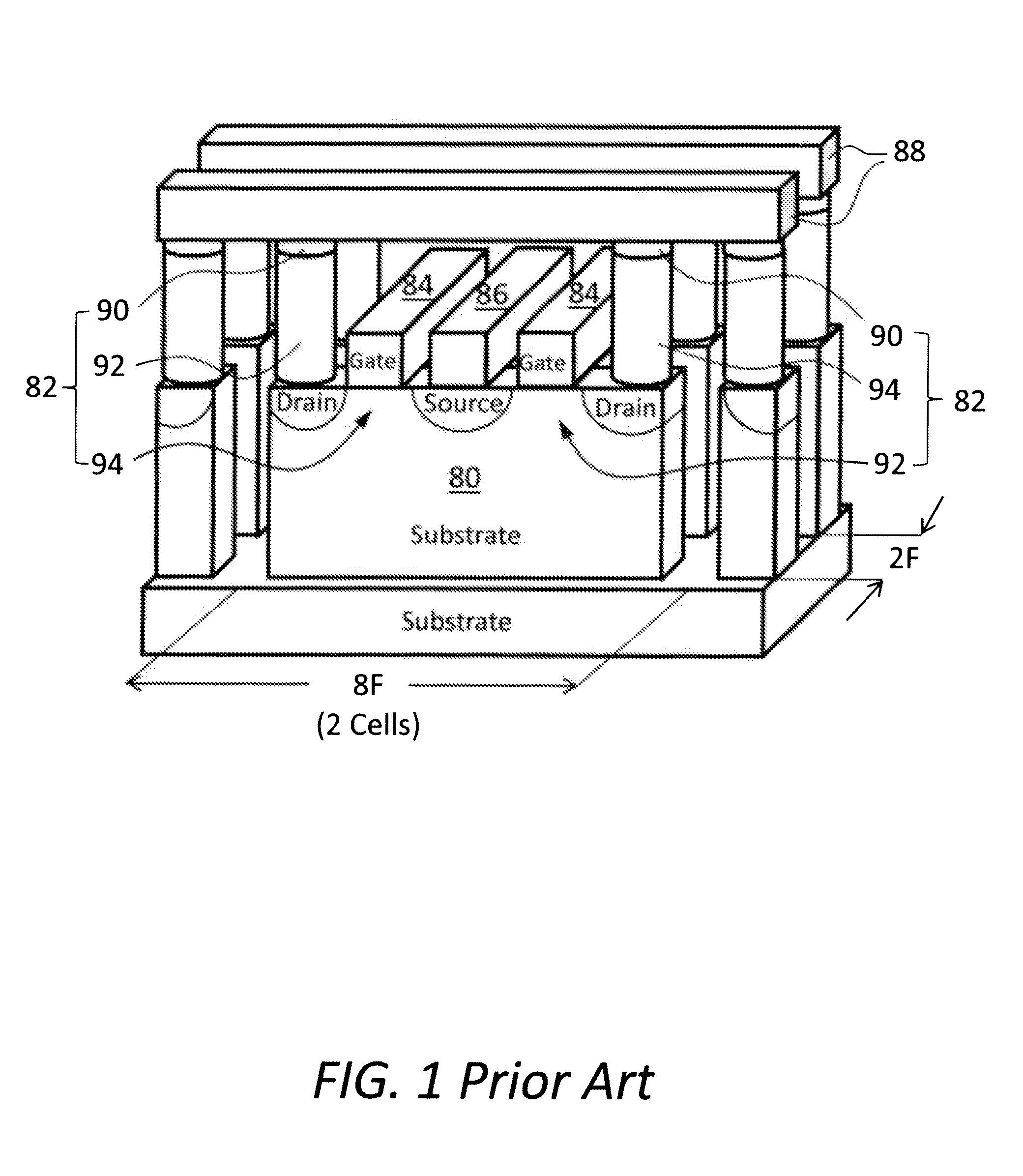
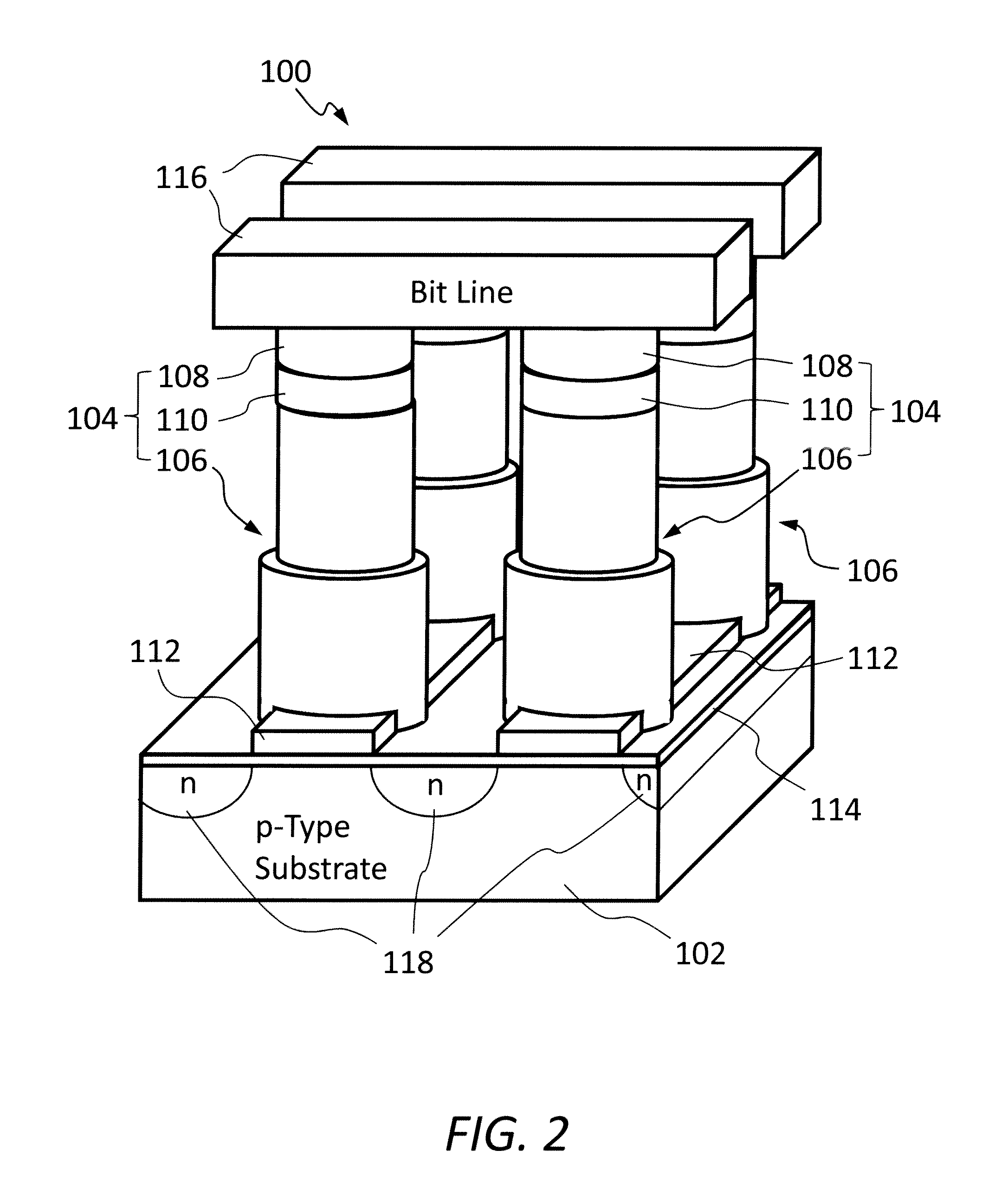
Resistive memory device having vertical transistors and method for making the same
ActiveUS8575584B2Overcomes current drivabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
The present invention relates to resistive memory devices incorporating therein vertical selection transistors and methods for making the same. A resistive memory device comprises a semiconductor substrate having a first type conductivity; a plurality of vertical selection transistors formed on the semiconductor substrate in an array, each of the plurality of vertical selection transistors including a semiconductor pillar protruded from the semiconductor substrate, top region of the semiconductor pillar having a second type conductivity opposite to the first type conductivity provided in the semiconductor substrate; and a gate electrode surrounding the semiconductor pillar with a gate dielectric layer interposed therebetween, the gate electrode being lower in height than the semiconductor pillar; a plurality of contact studs disposed on top of the vertical selection transistors; a plurality of resistive memory elements disposed on top of the contact studs; a plurality of parallel word lines connecting the vertical selection transistors by way of respective gate electrodes, the parallel word lines extending along a first direction; a plurality of parallel bit lines connecting the resistive memory elements, the parallel bit lines extending along a second direction different from the first direction provided in the parallel word lines; and a plurality of parallel source lines with the second type conductivity formed in top regions of the semiconductor substrate in between rows of the semiconductor pillars, wherein the source lines and the top regions of the semiconductor pillars function as source and drain, respectively.
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
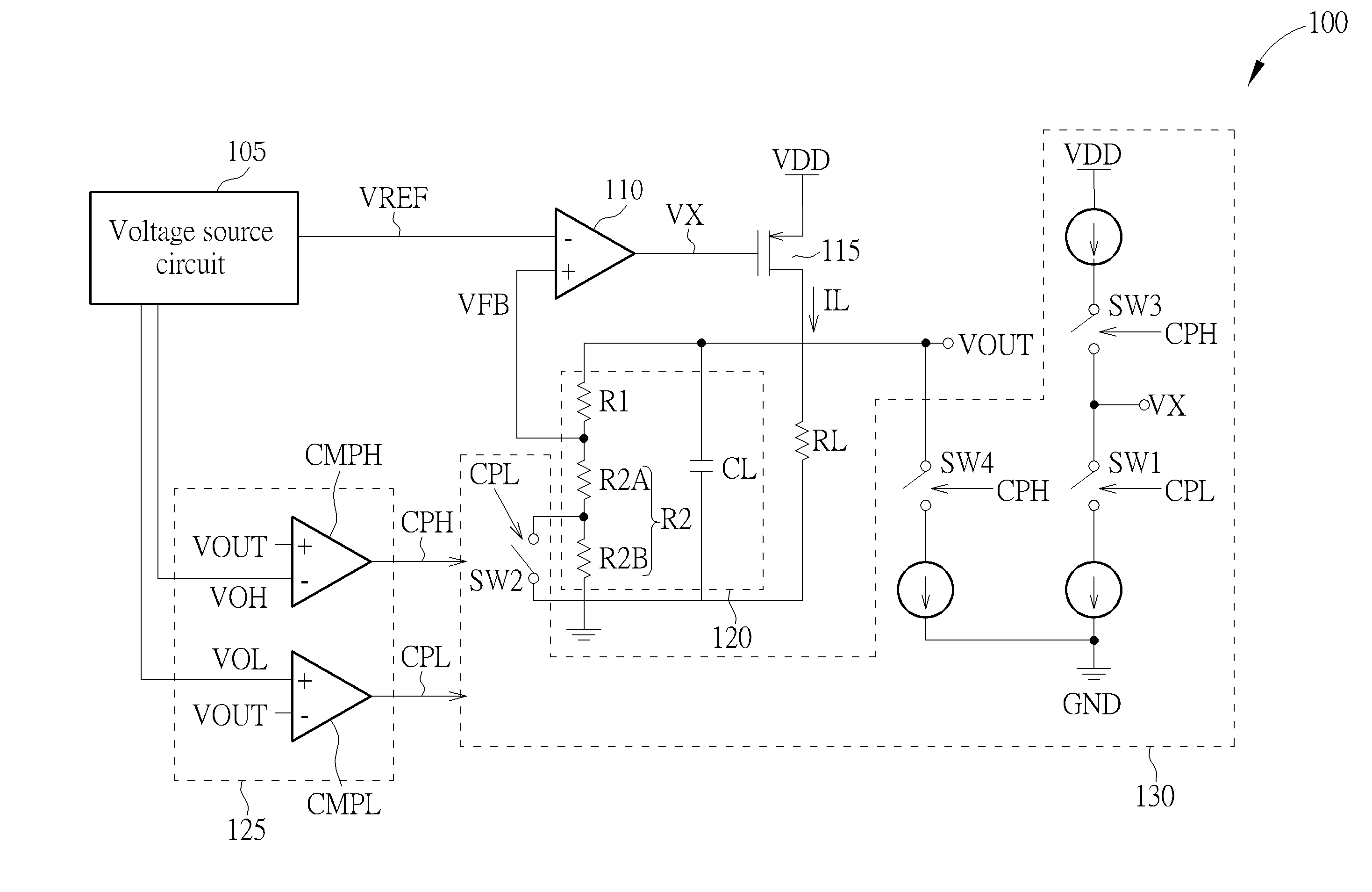
Low-dropout voltage regulator apparatus capable of adaptively adjusting current passing through output transistor to reduce transient response time and related method thereof
ActiveUS20140285165A1Reduce dramatic voltage change of output voltageDecrease in transient response timeElectric variable regulationControl signalDropout voltage
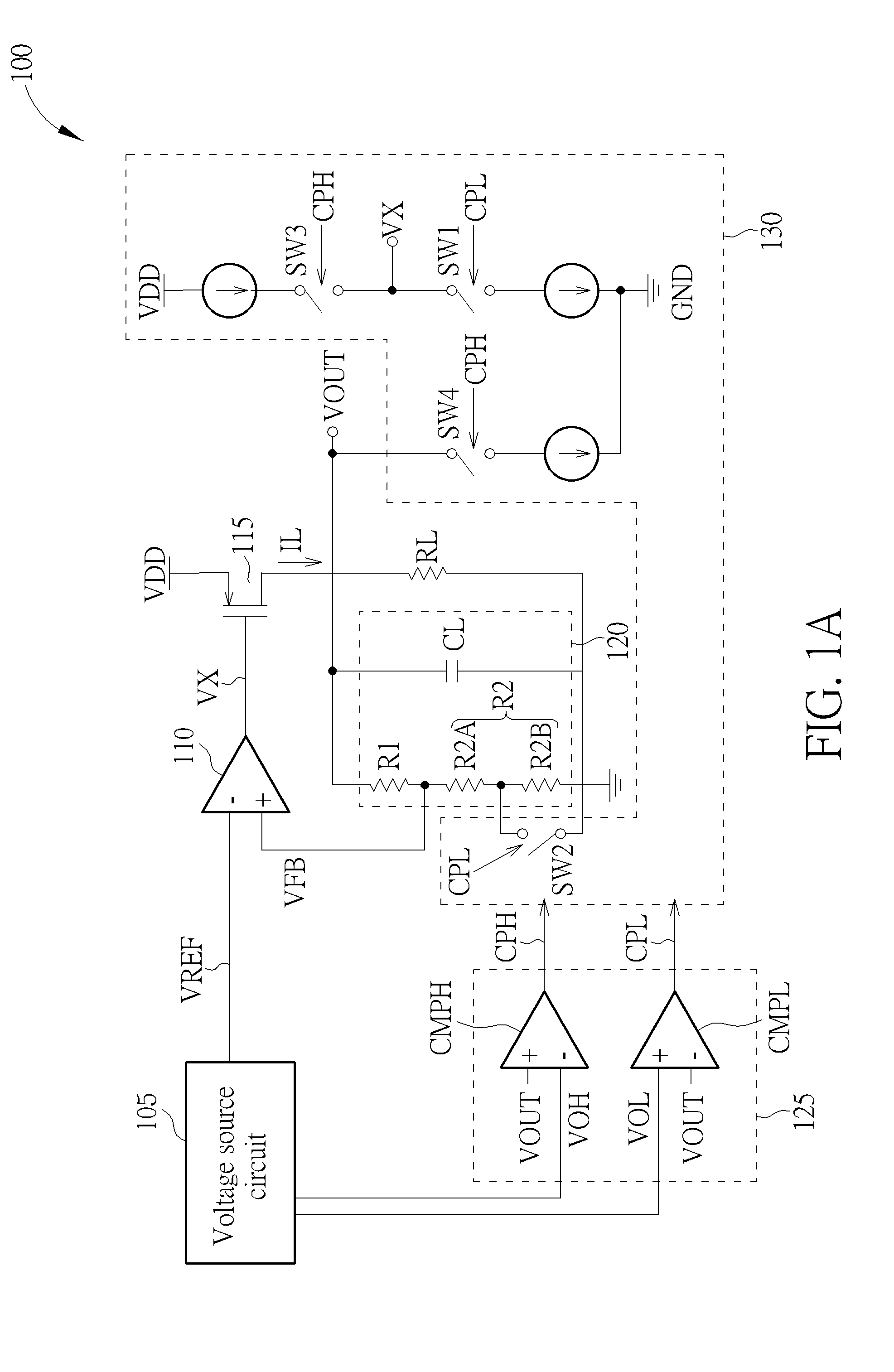
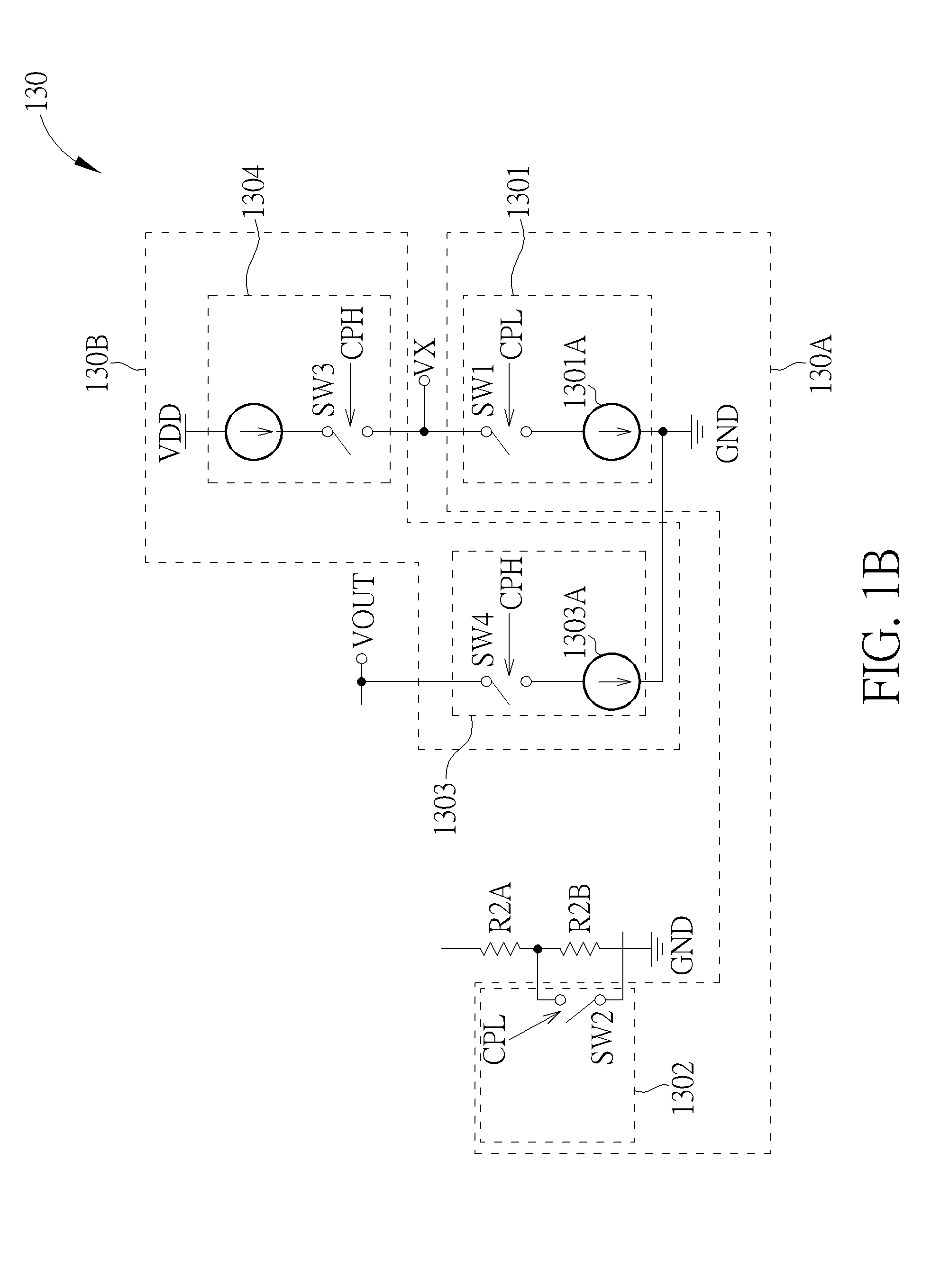
A low-dropout voltage regulator apparatus includes a voltage source circuit, an error amplifier, an output transistor, a resistor-capacitor circuit, a detection circuit, and a current adjusting circuit. The voltage source circuit generates a reference voltage signal and at least one threshold voltage signal. The error amplifier receives the reference voltage signal and a feedback voltage signal to generate an output control signal. The output transistor provides an output current for the output terminal according to the output control signal. The resistor-capacitor circuit generates the feedback voltage signal using voltage dividing according to a voltage corresponding to the output current. The detection circuit compares at least one threshold voltage signal with the output voltage to generate at least one control voltage signal. The current adjusting circuit adaptively adjusts the current passing though the output transistor to decrease the transient response time according to the at least one control voltage signal.
Owner:SILICON MOTION INC (TW)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com