Patents
Literature
87results about "Angle demodulation by oscillations sampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
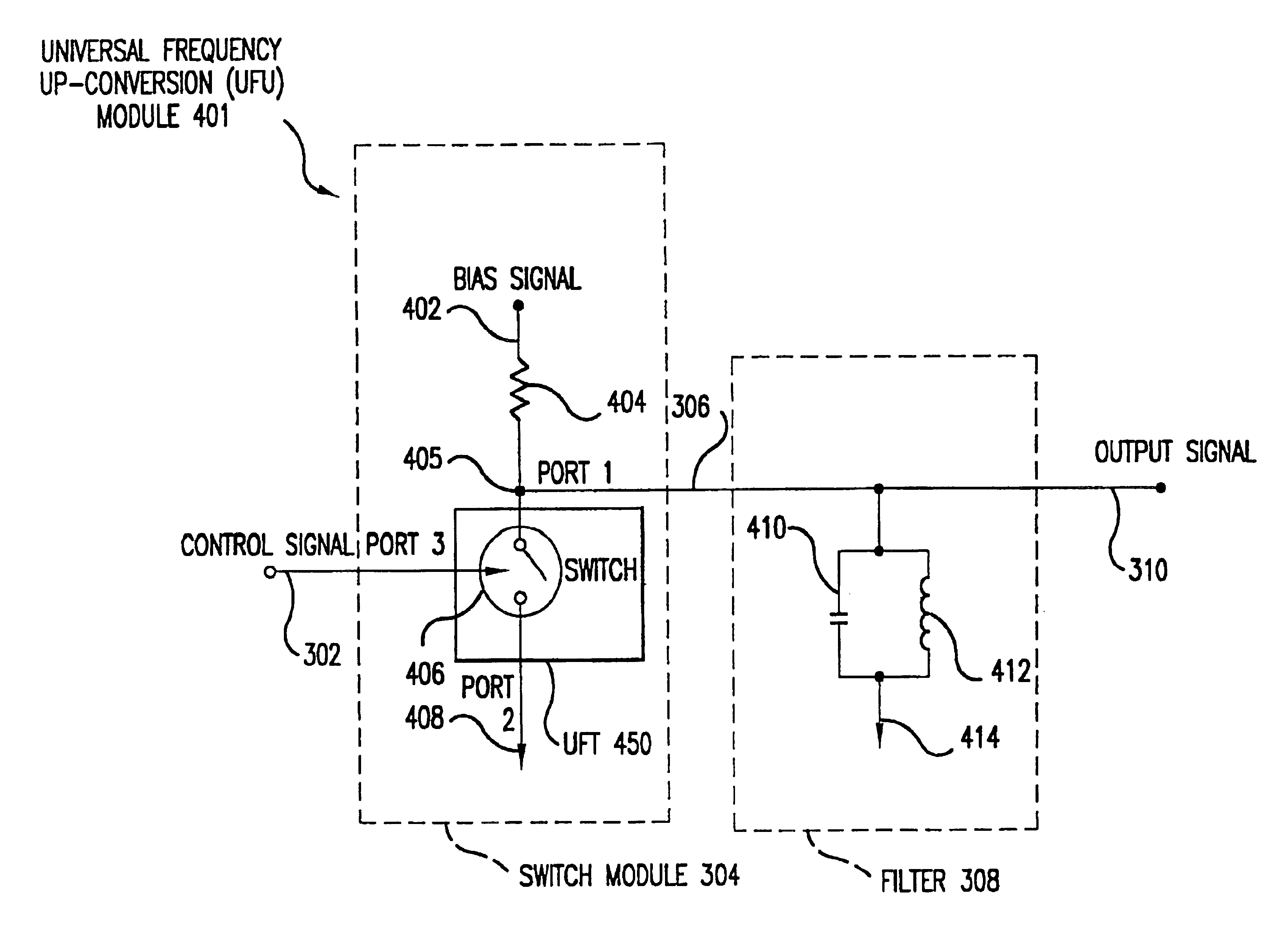
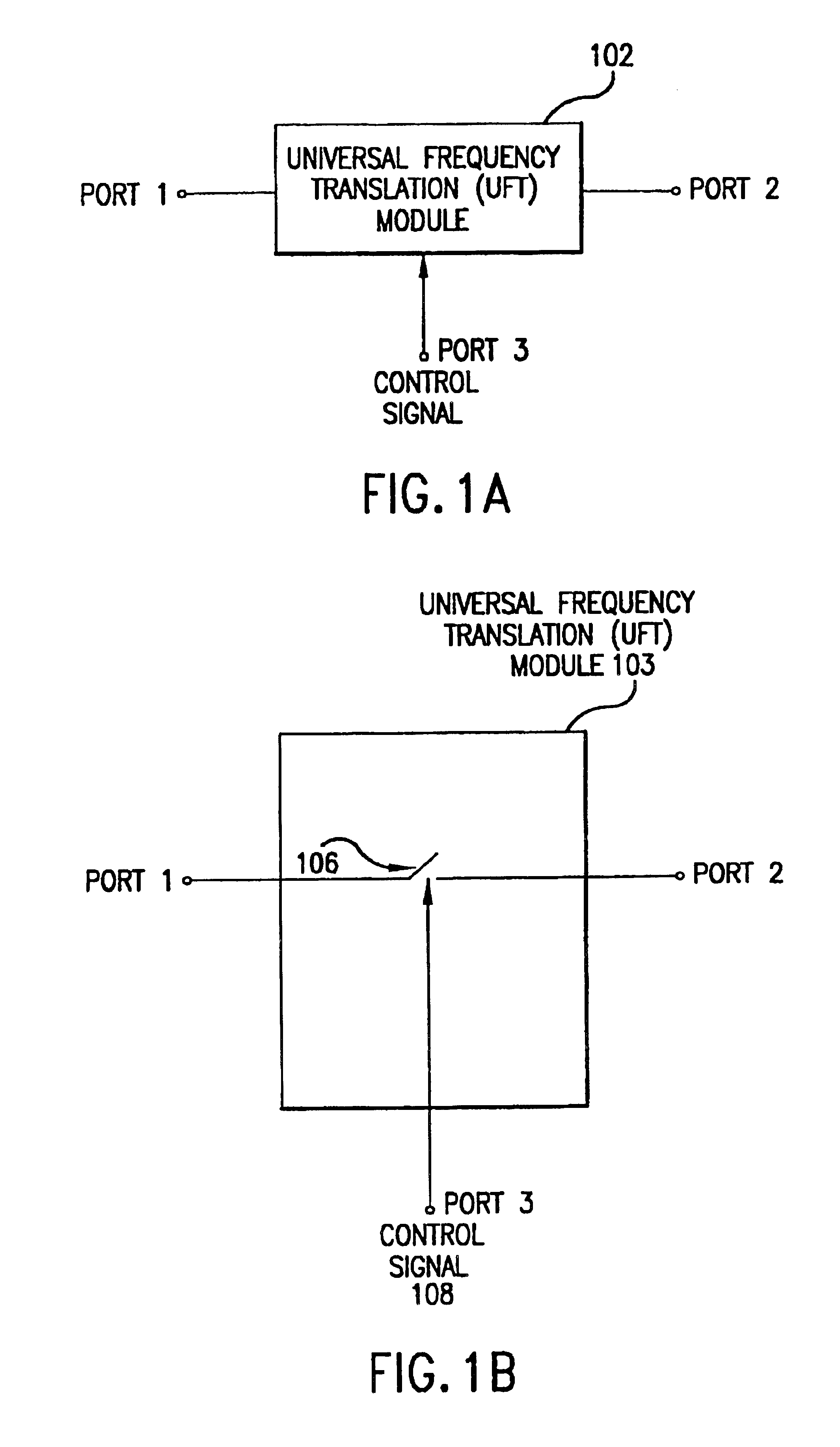
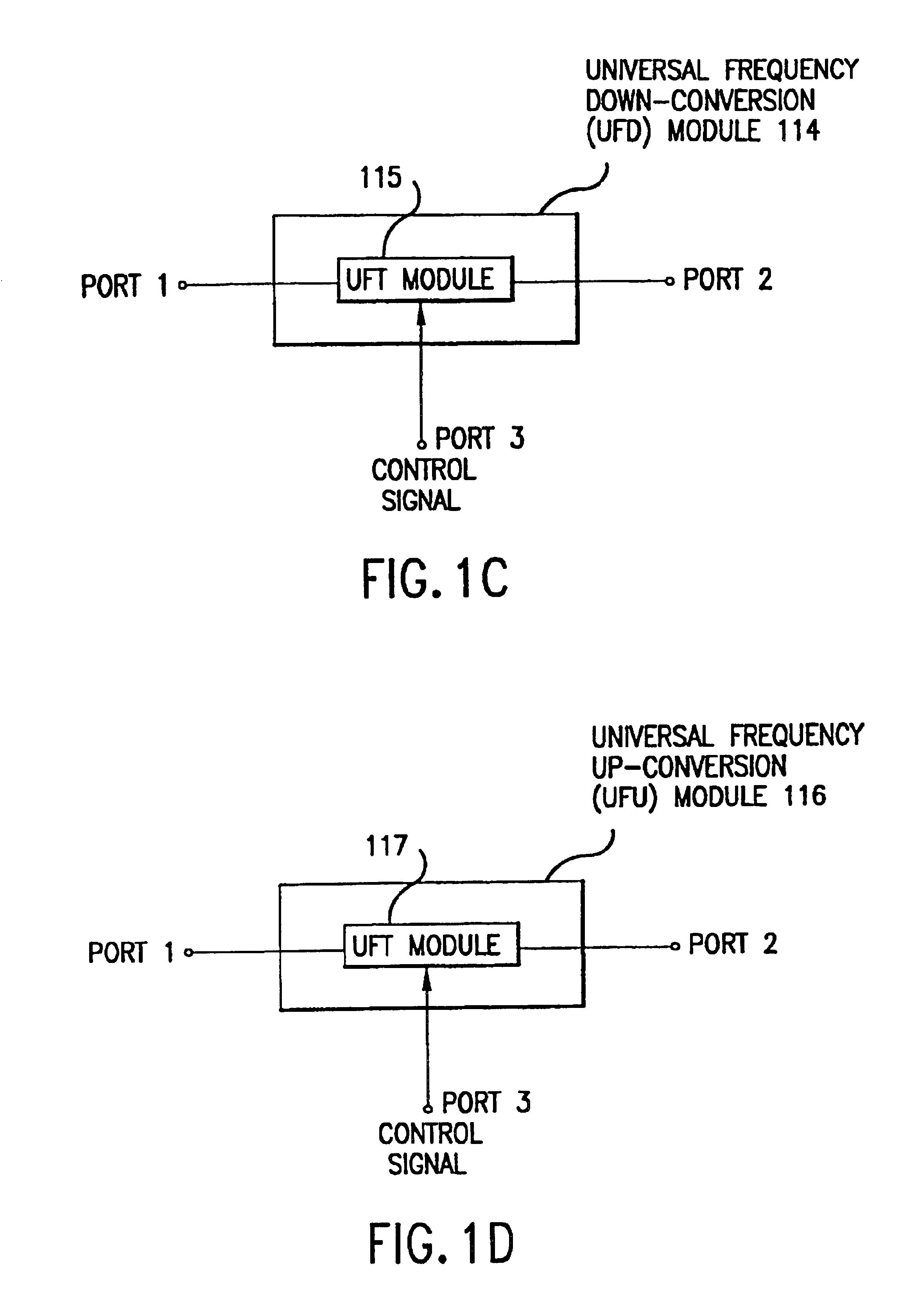
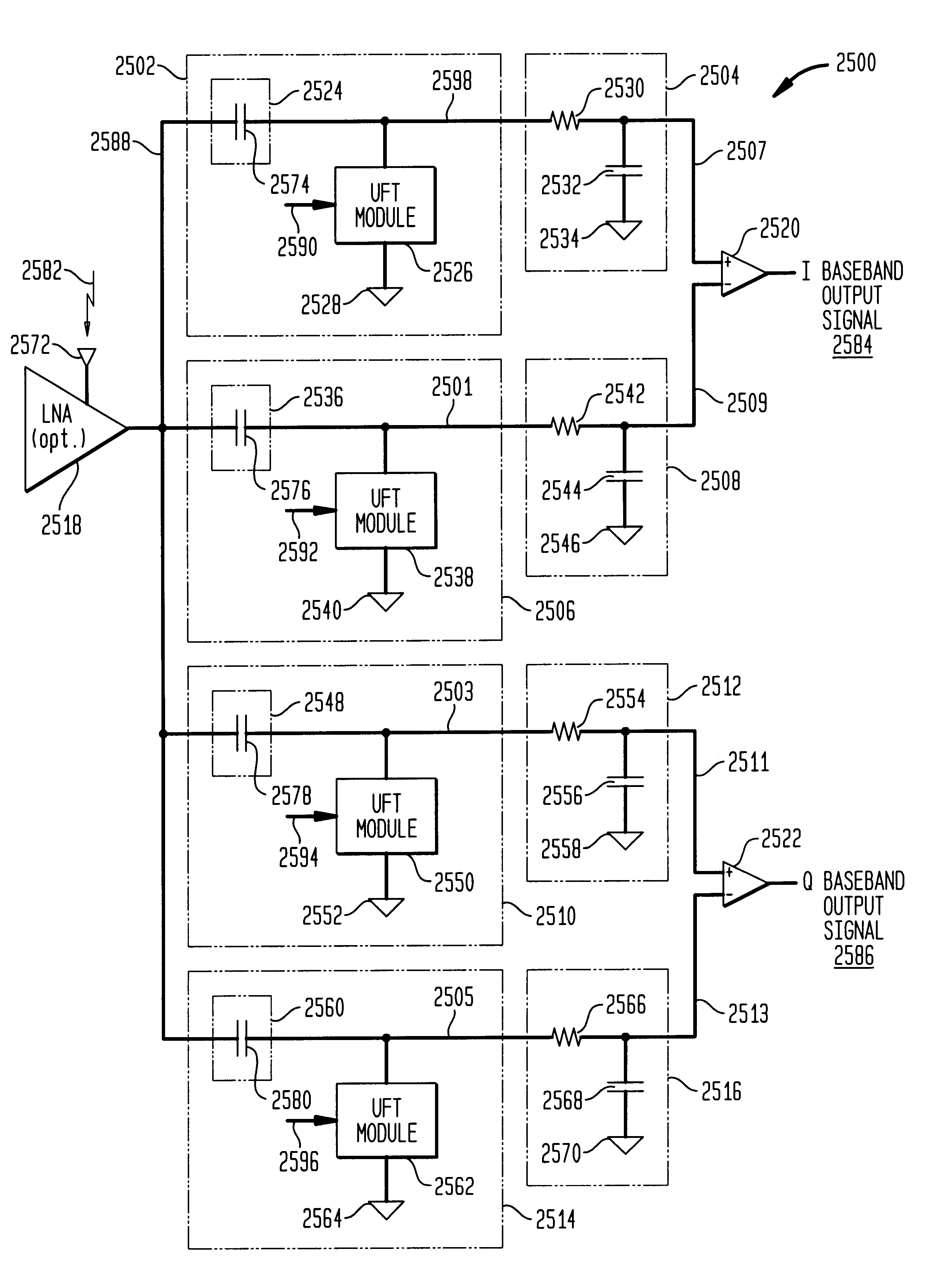
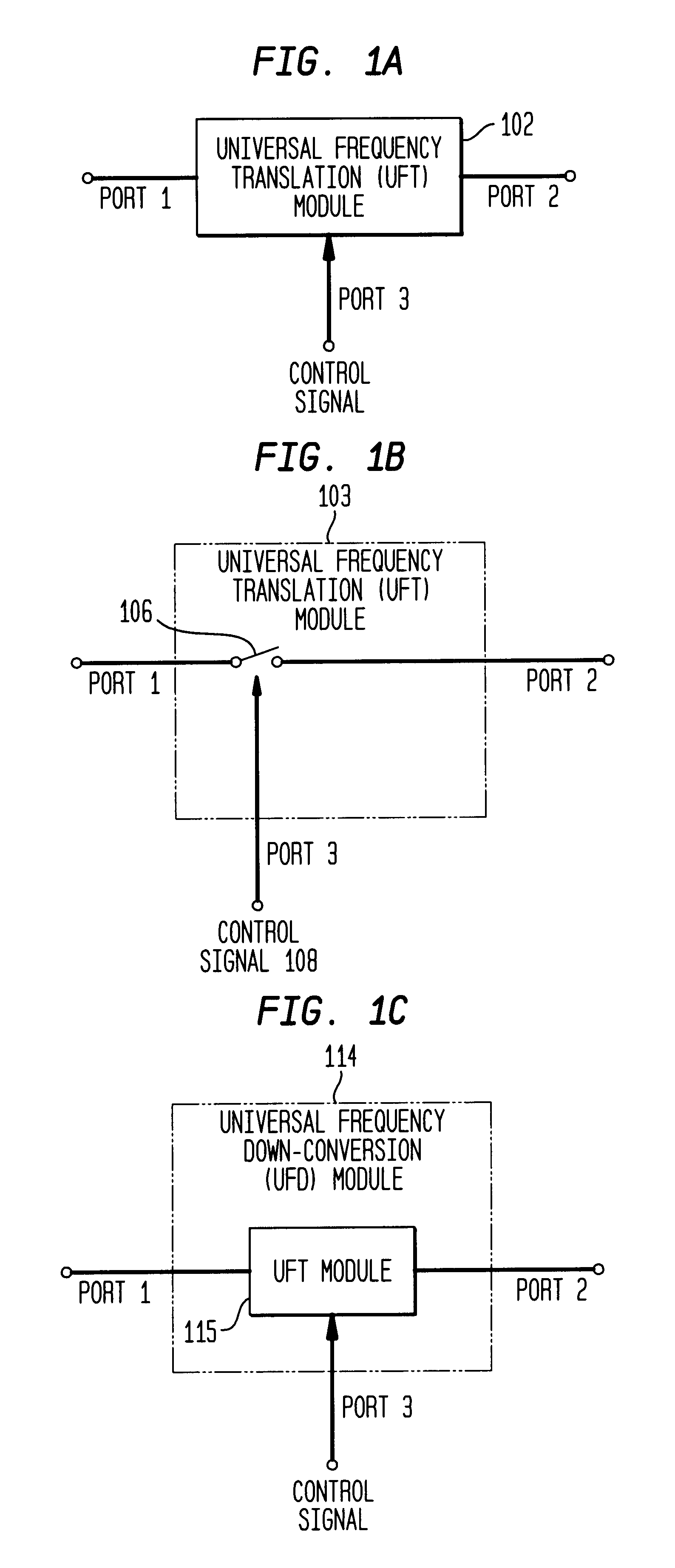
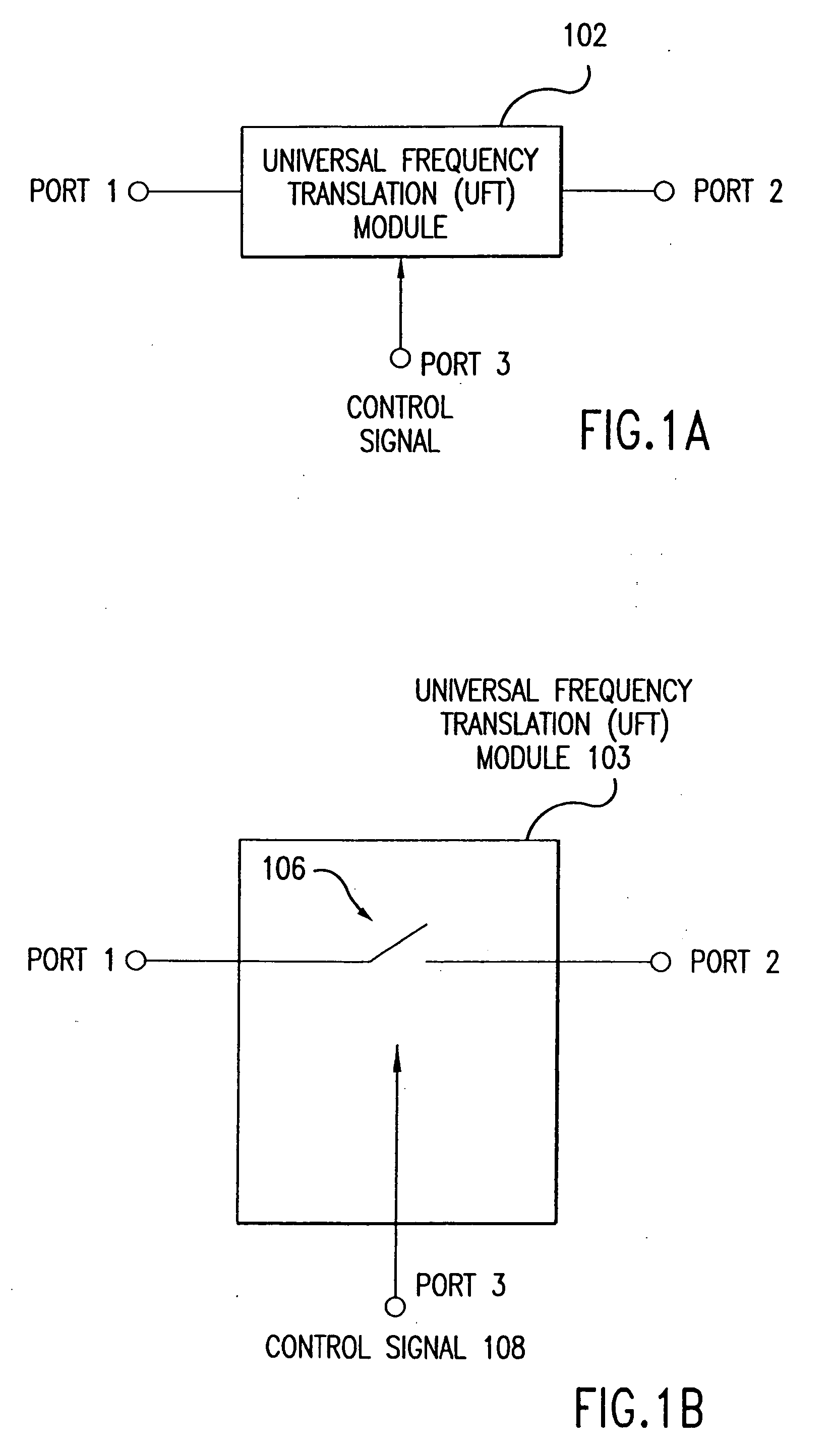
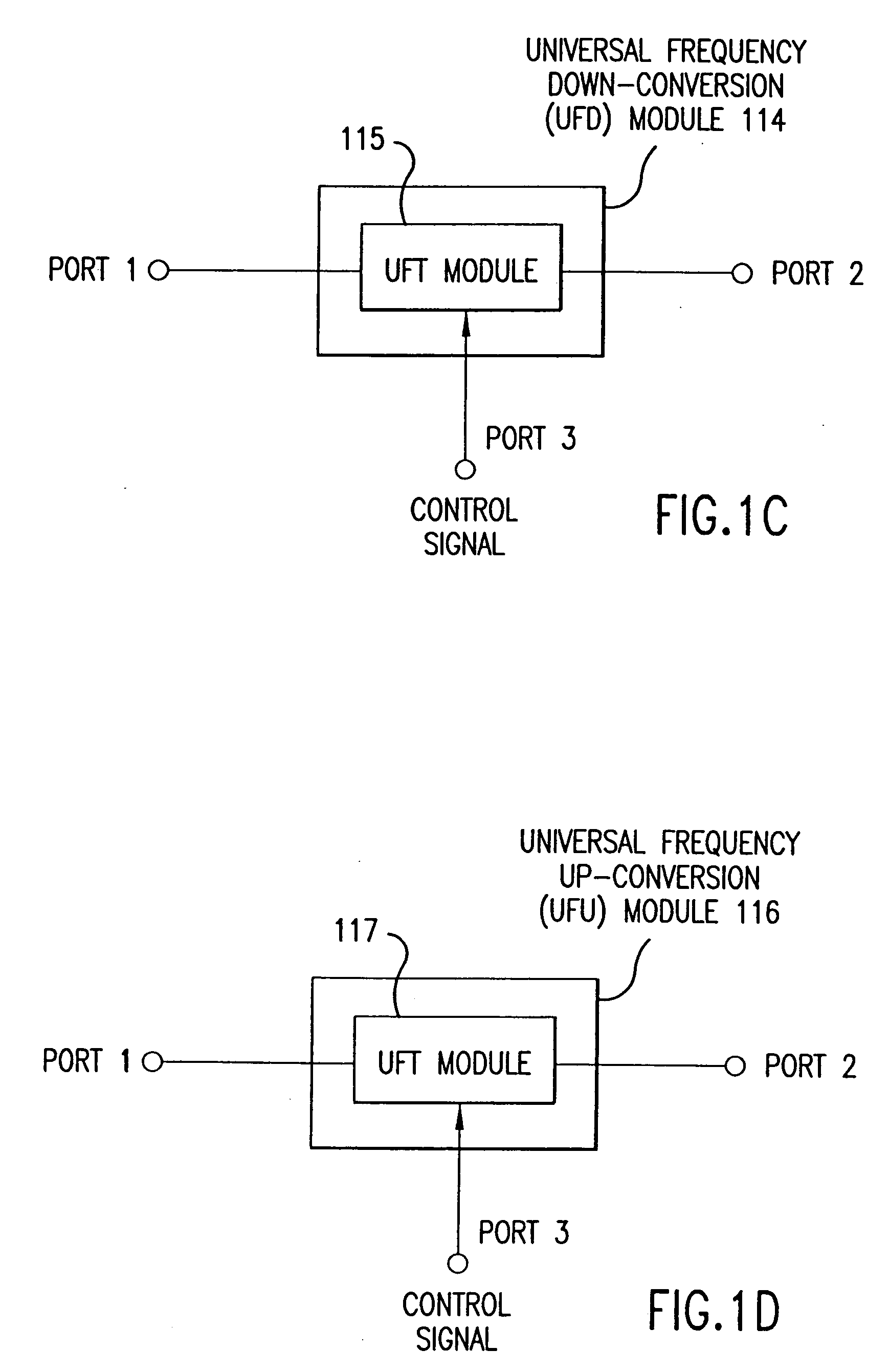
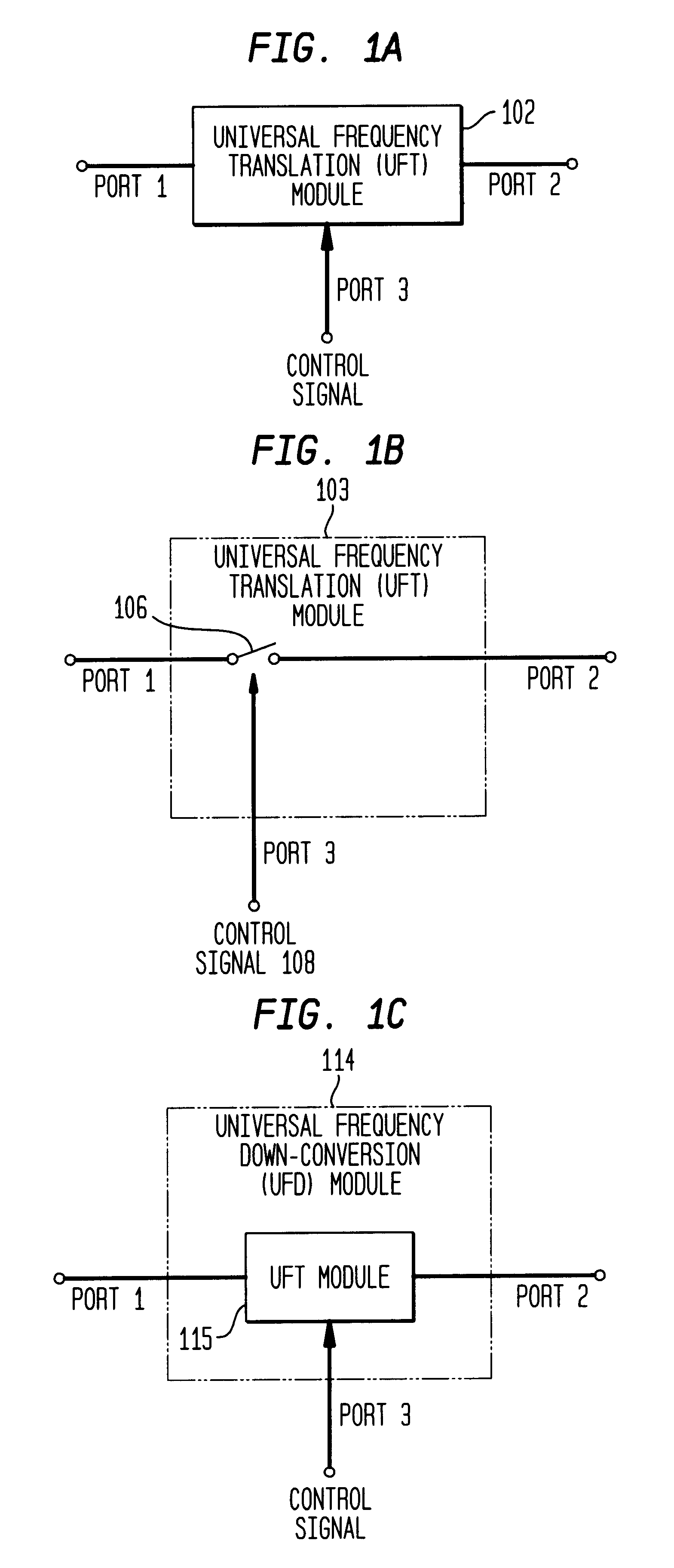
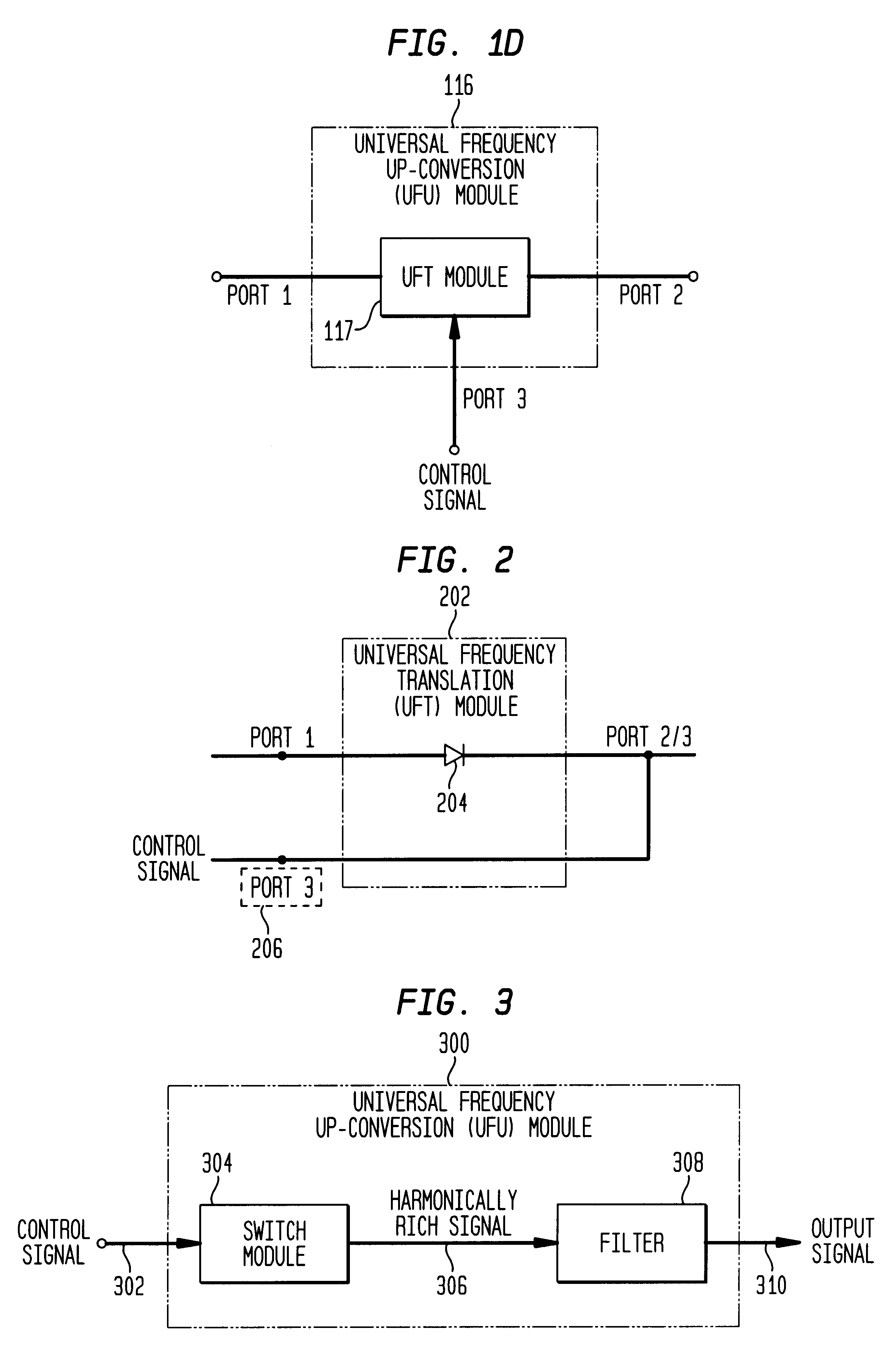
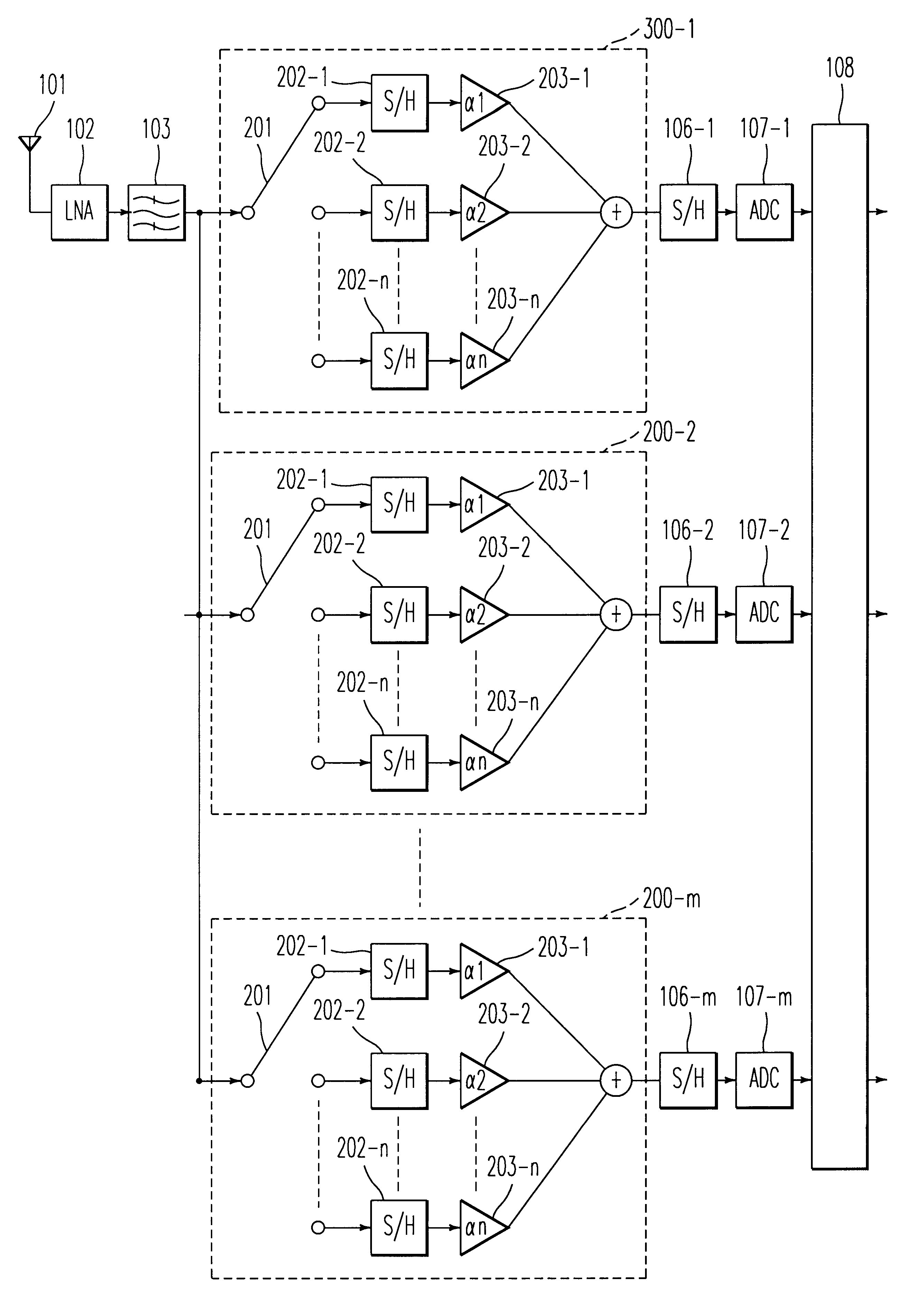
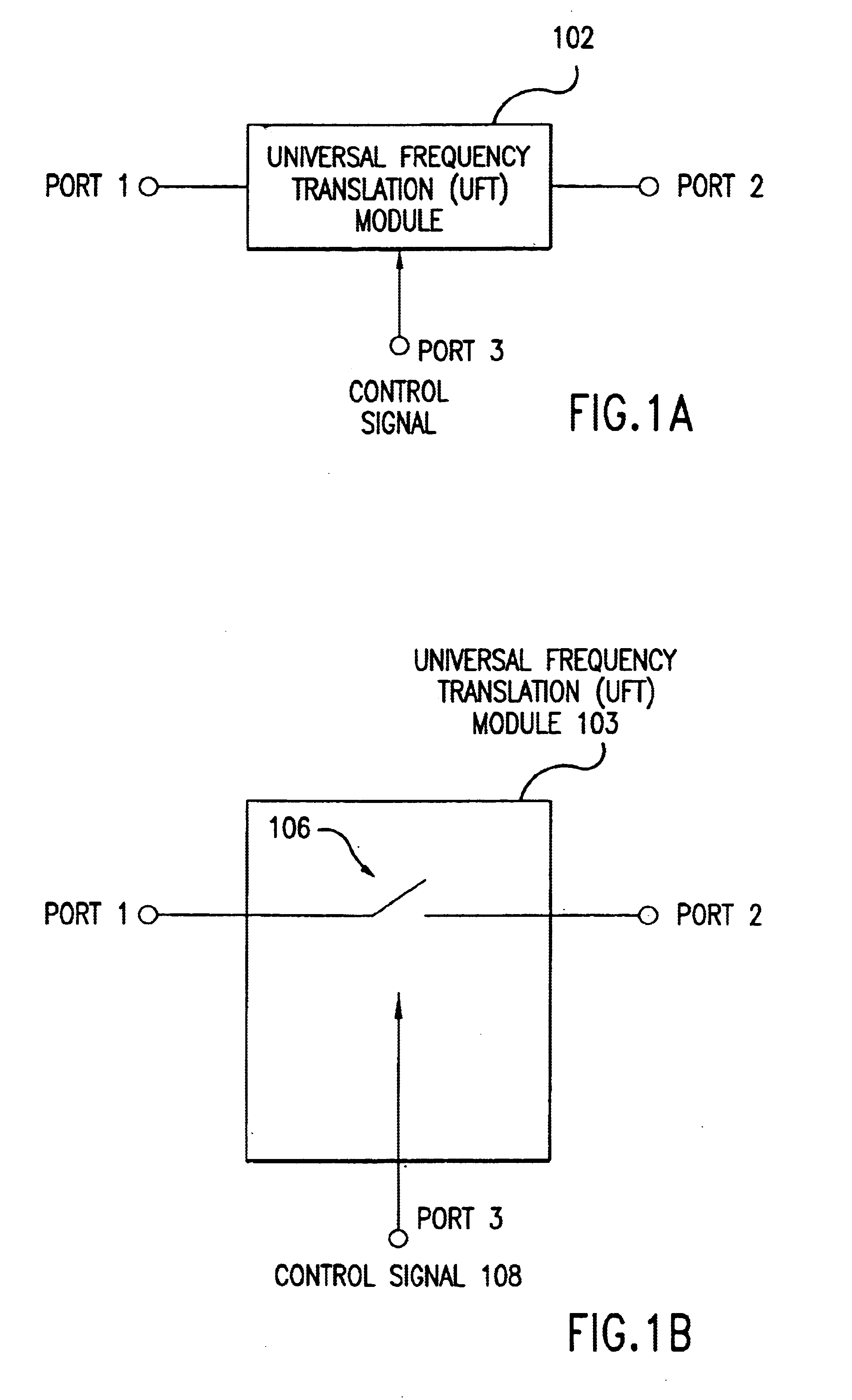
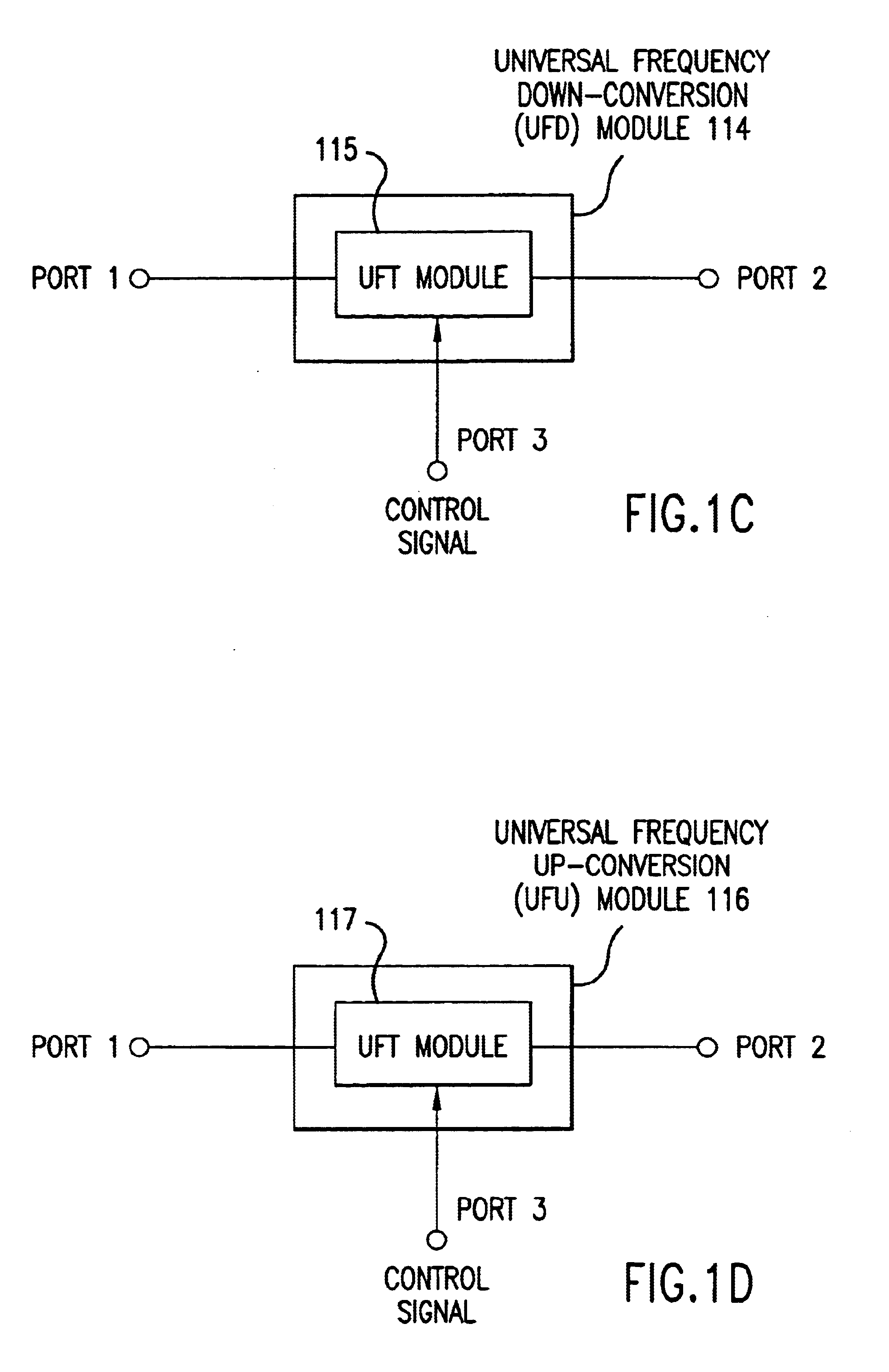
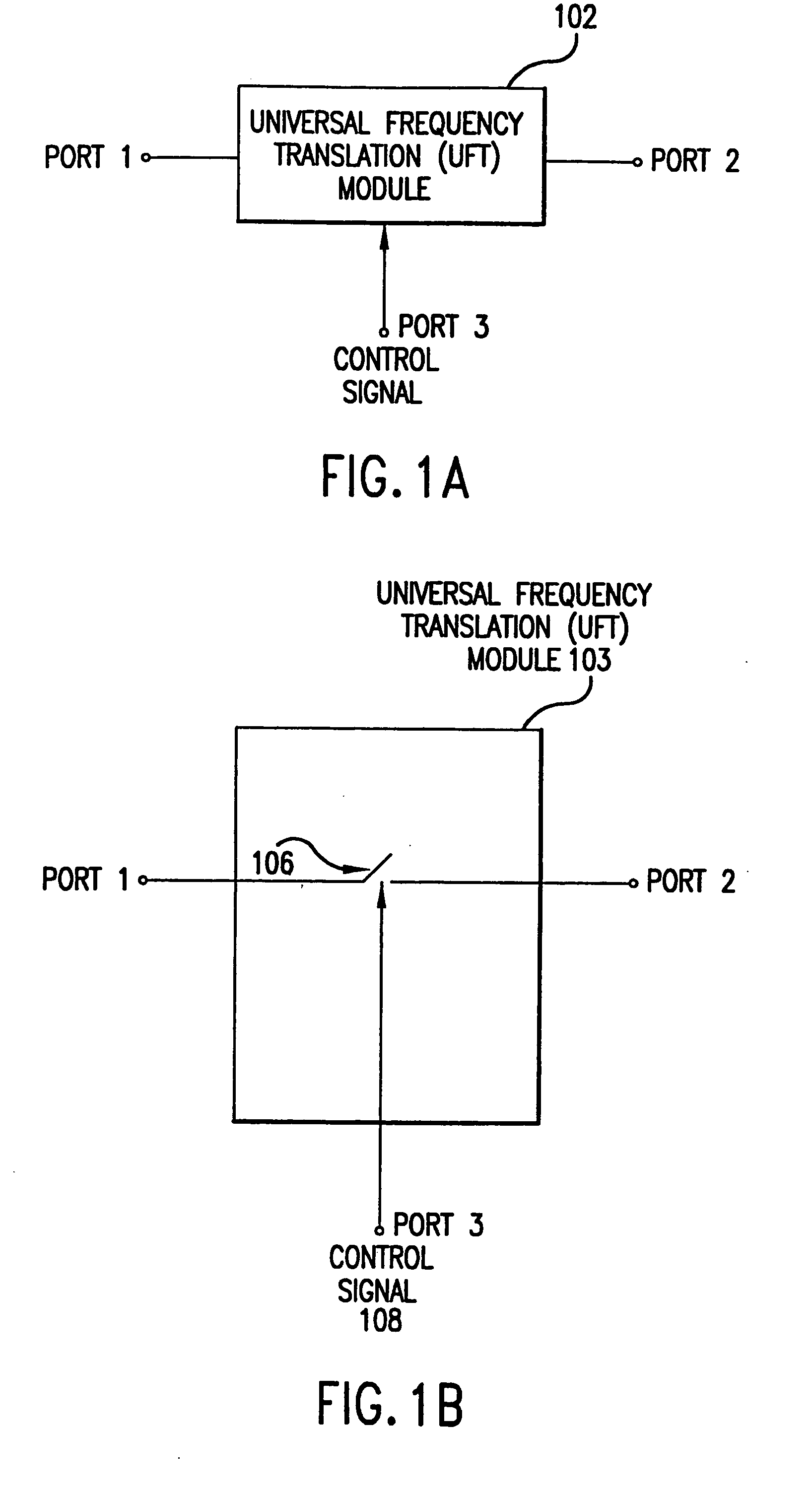
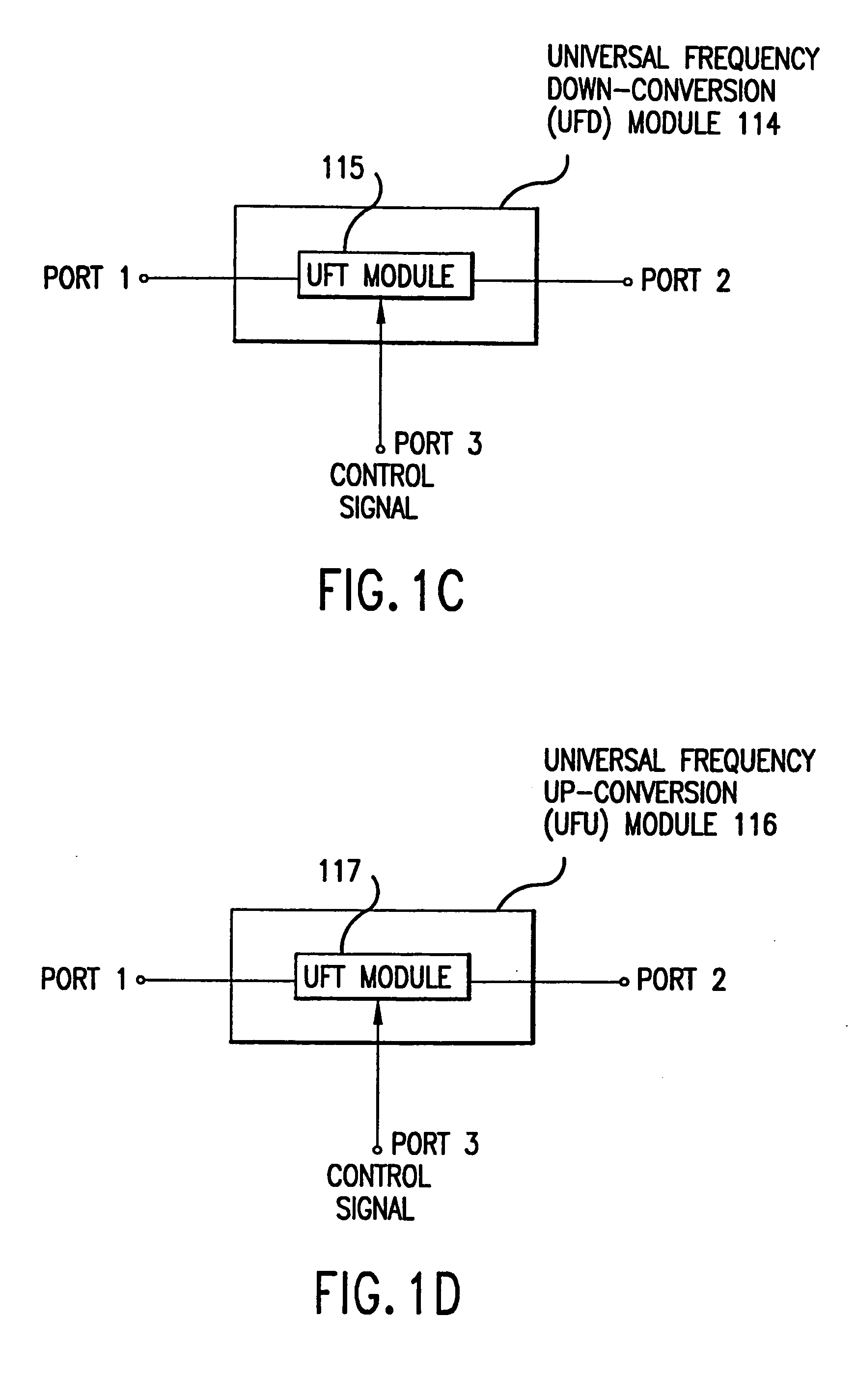
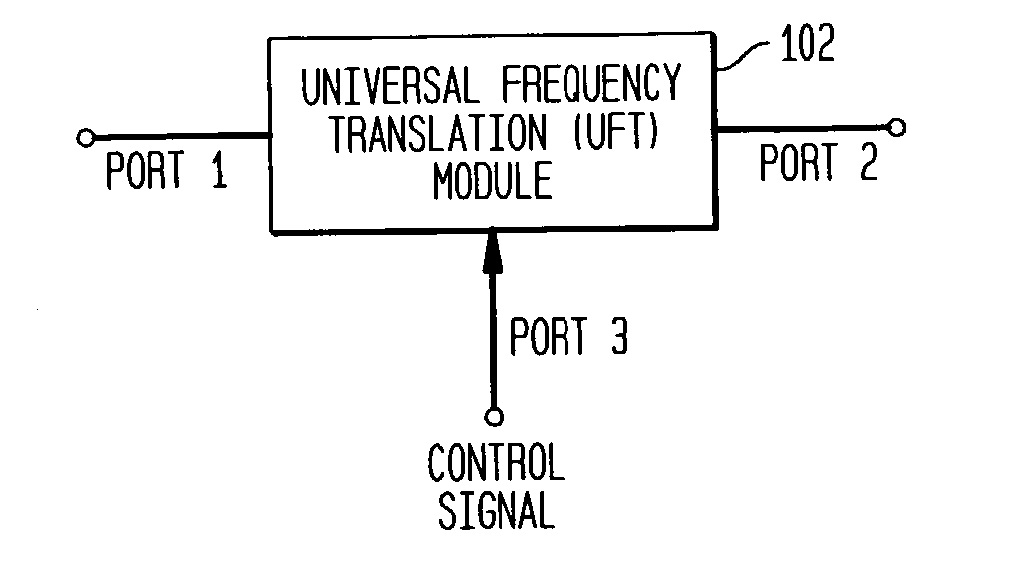
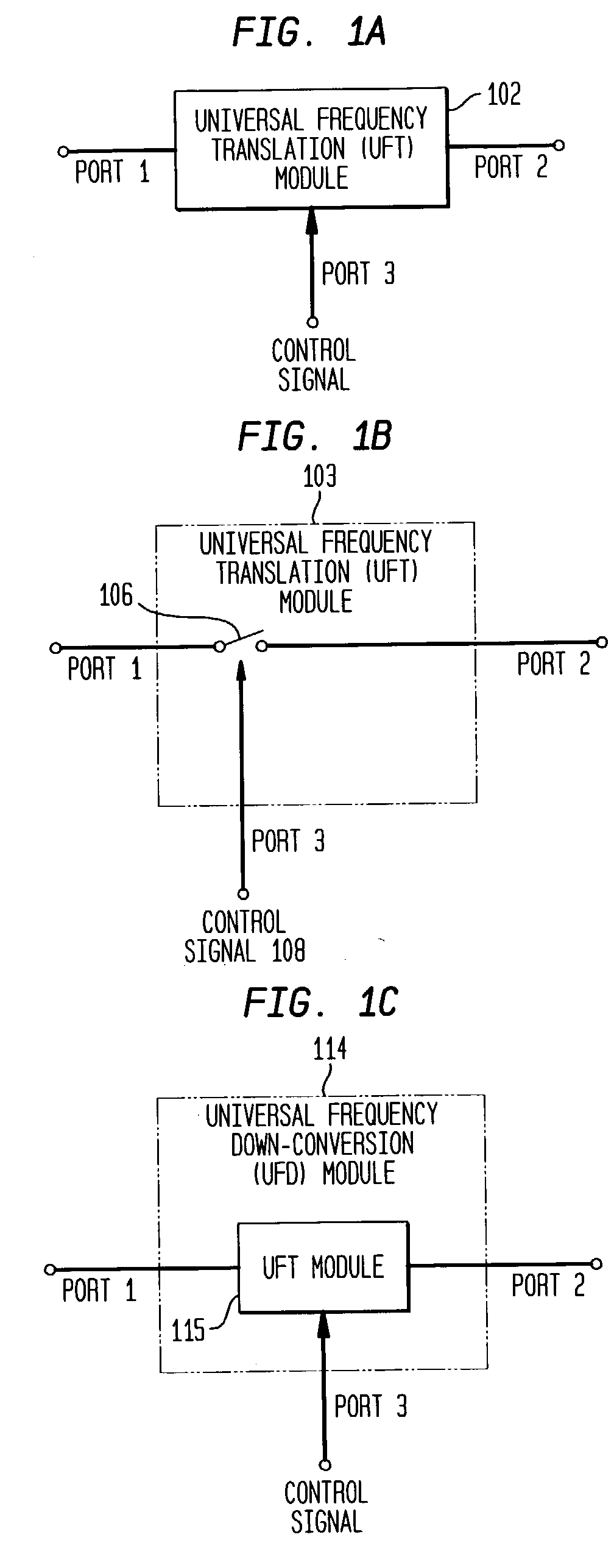
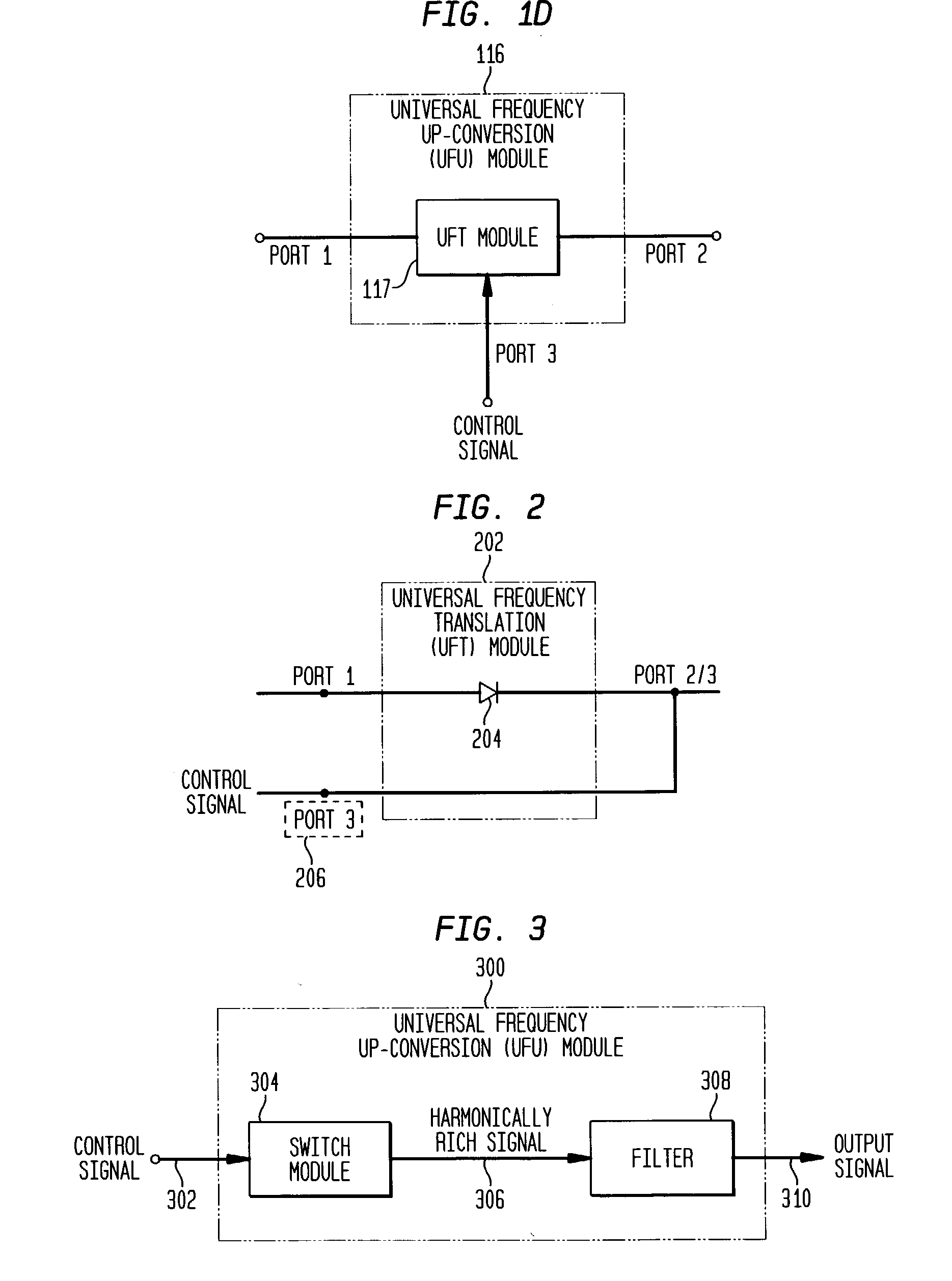
Universal platform module and methods and apparatuses relating thereto enabled by universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6873836B1Modulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionTransceiverCommunications system
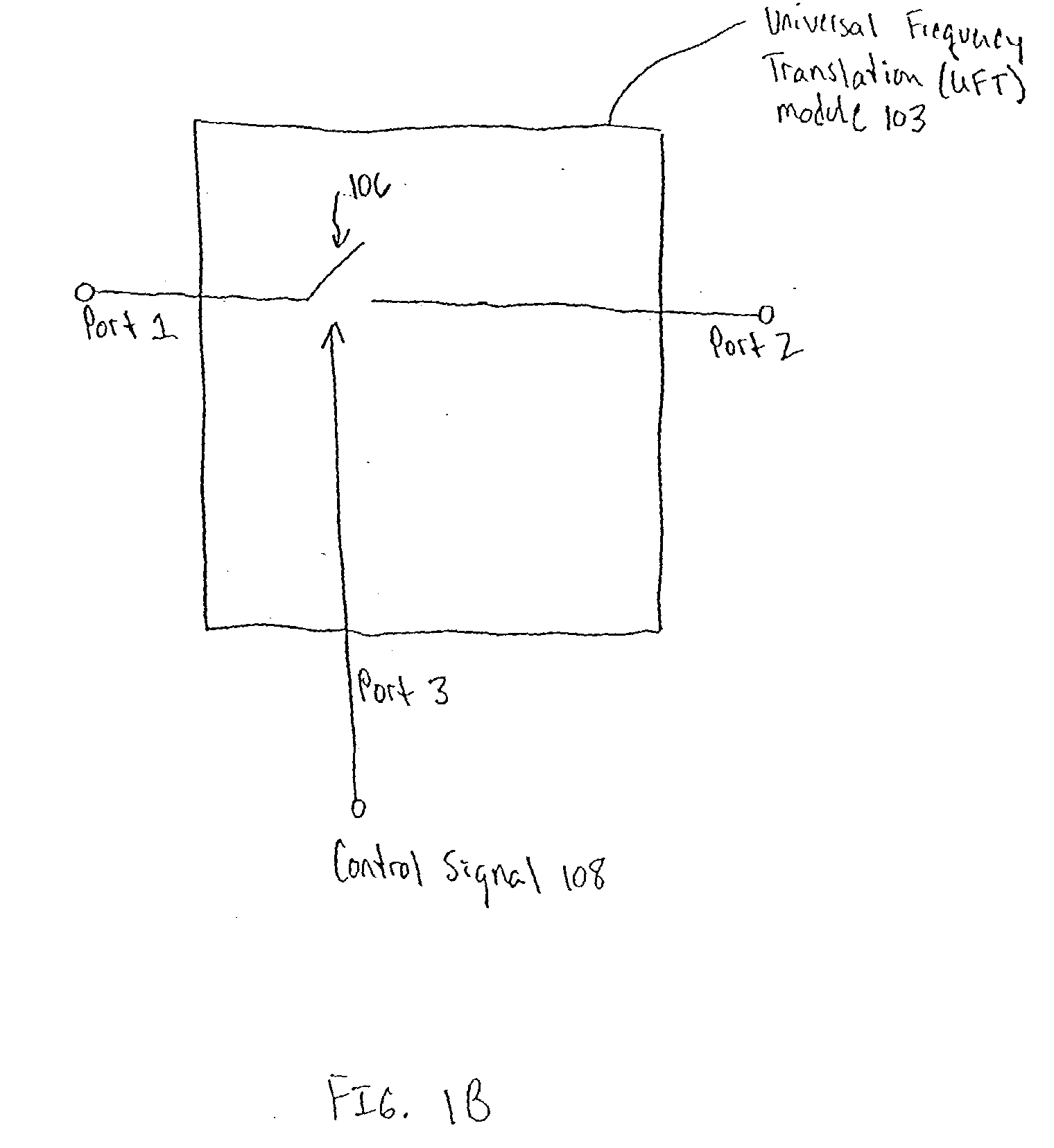
A communication system comprising a multi-protocol, multi-bearer sub-system is described herein. The sub-system is a universal platform module that can transmit and receive one or more information signals in one or more protocols using one or more bearer services. In one embodiment, the sub-system may form a portion of a transceiver that is composed of a transmitter and a receiver, and which is a gateway server between a personal area network (PAN) and the global wireless network.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
DC offset, re-radiation, and I/Q solutions using universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6879817B1Reduce voltageImprove dynamic rangeModulation transferenceTransmission noise suppressionEngineeringDynamic range
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
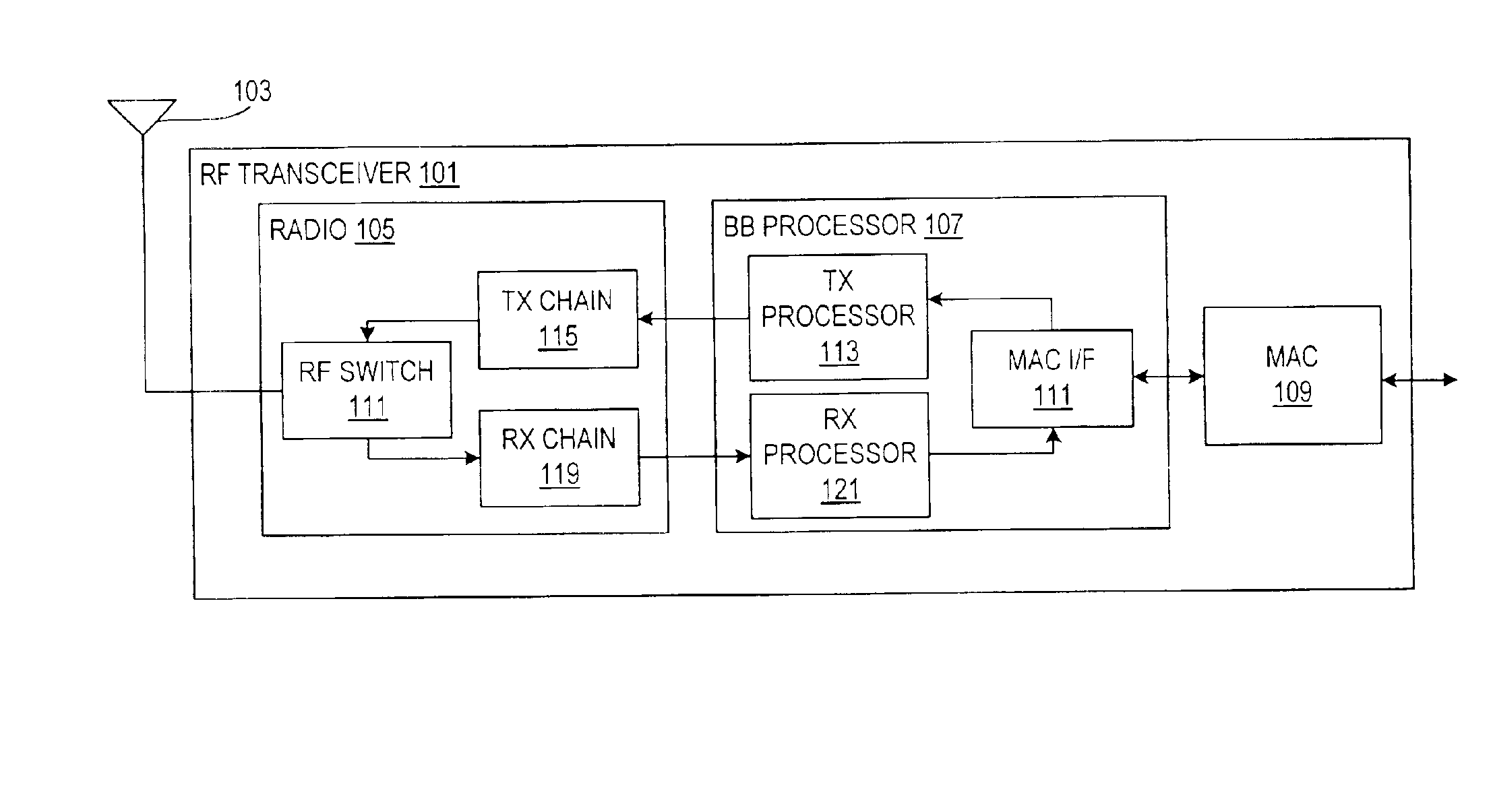
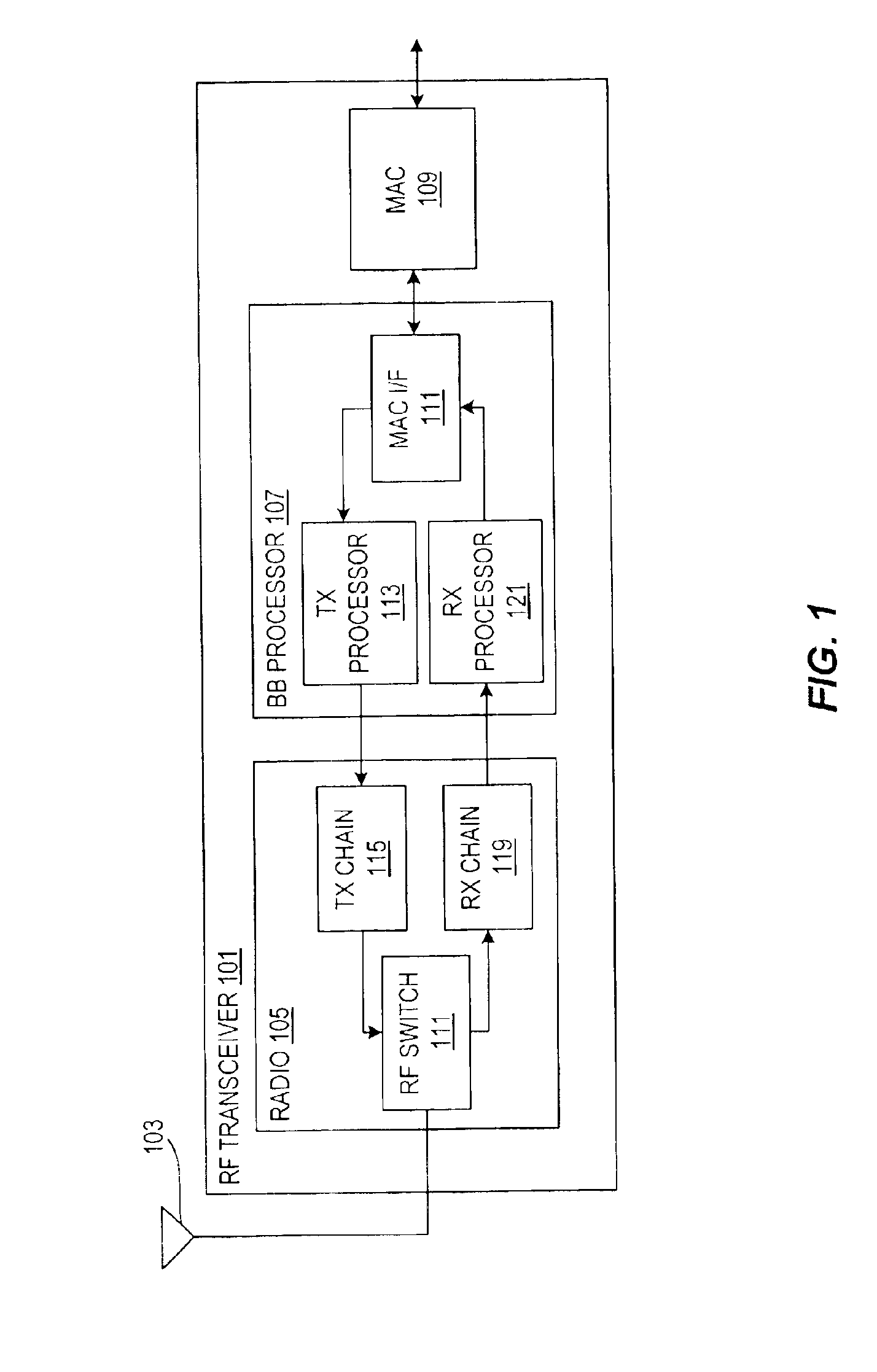
Wireless local area network (WLAN) using universal frequency translation technology including multi-phase embodiments and circuit implementations
InactiveUS20050123025A1Reduce and eliminate re-radiationReduce carrier insertionResonant long antennasNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumModem device
Frequency translation and applications of the same are described herein, including RF modem and wireless local area network (WLAN) applications. In embodiments, the WLAN invention includes an antenna, an LNA / PA module, a receiver, a transmitter, a control signal generator, a demodulation / modulation facilitation module, and a MAC interface. The WLAN receiver includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency down-converts a received EM signal. In embodiments, the UFT based receiver is configured in a multi-phase embodiment to reduce or eliminate re-radiation that is caused by DC offset. The WLAN transmitter includes at least one universal frequency translation module that frequency up-converts a baseband signal in preparation for transmission over the wireless LAN. In embodiments, the UFT based transmitter is configured in a differential and multi-phase embodiment to reduce carrier insertion and spectral growth.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
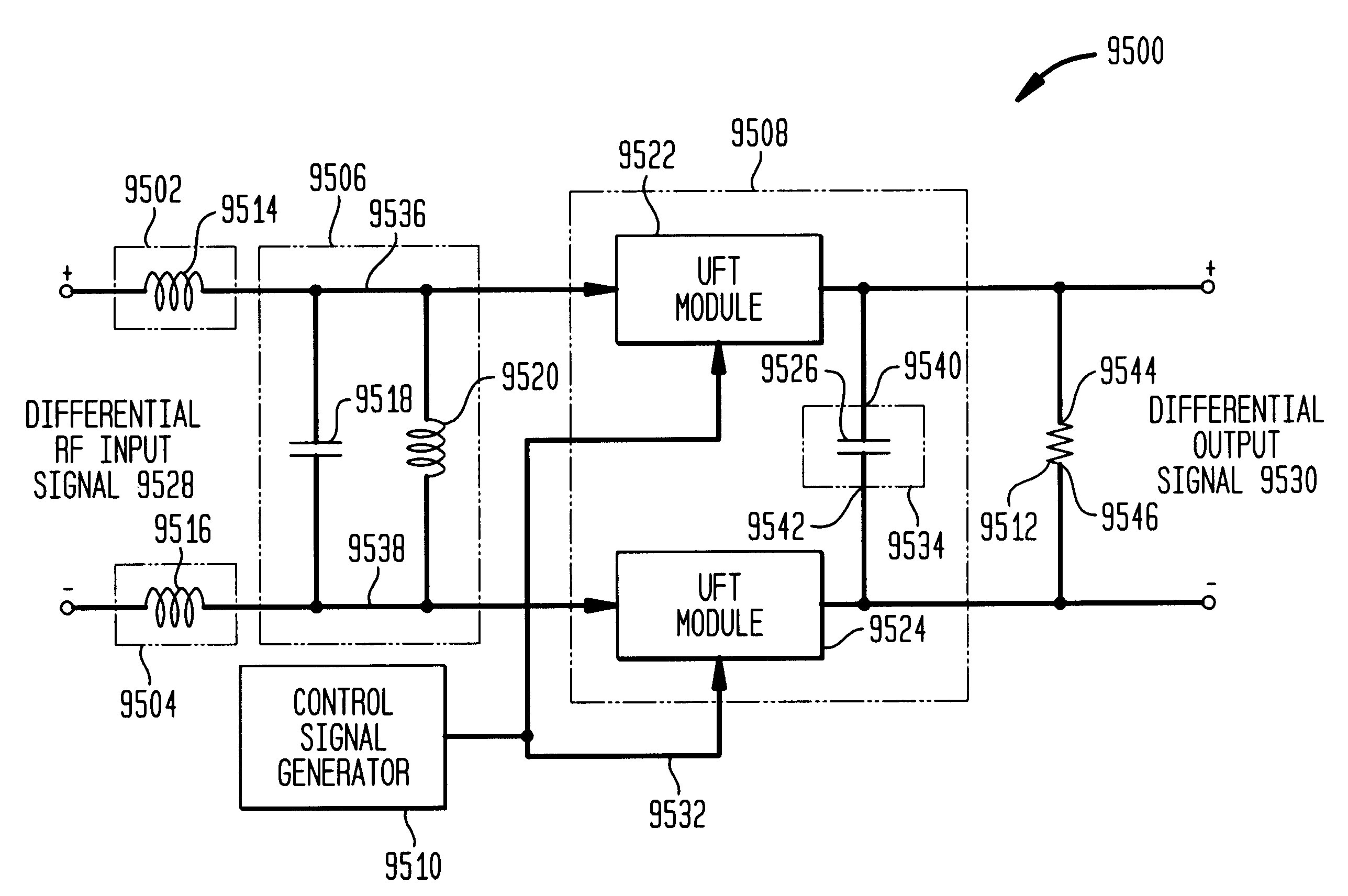
Differential frequency down-conversion using techniques of universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6963734B2Reduce voltageImprove dynamic rangeModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringDynamic range
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
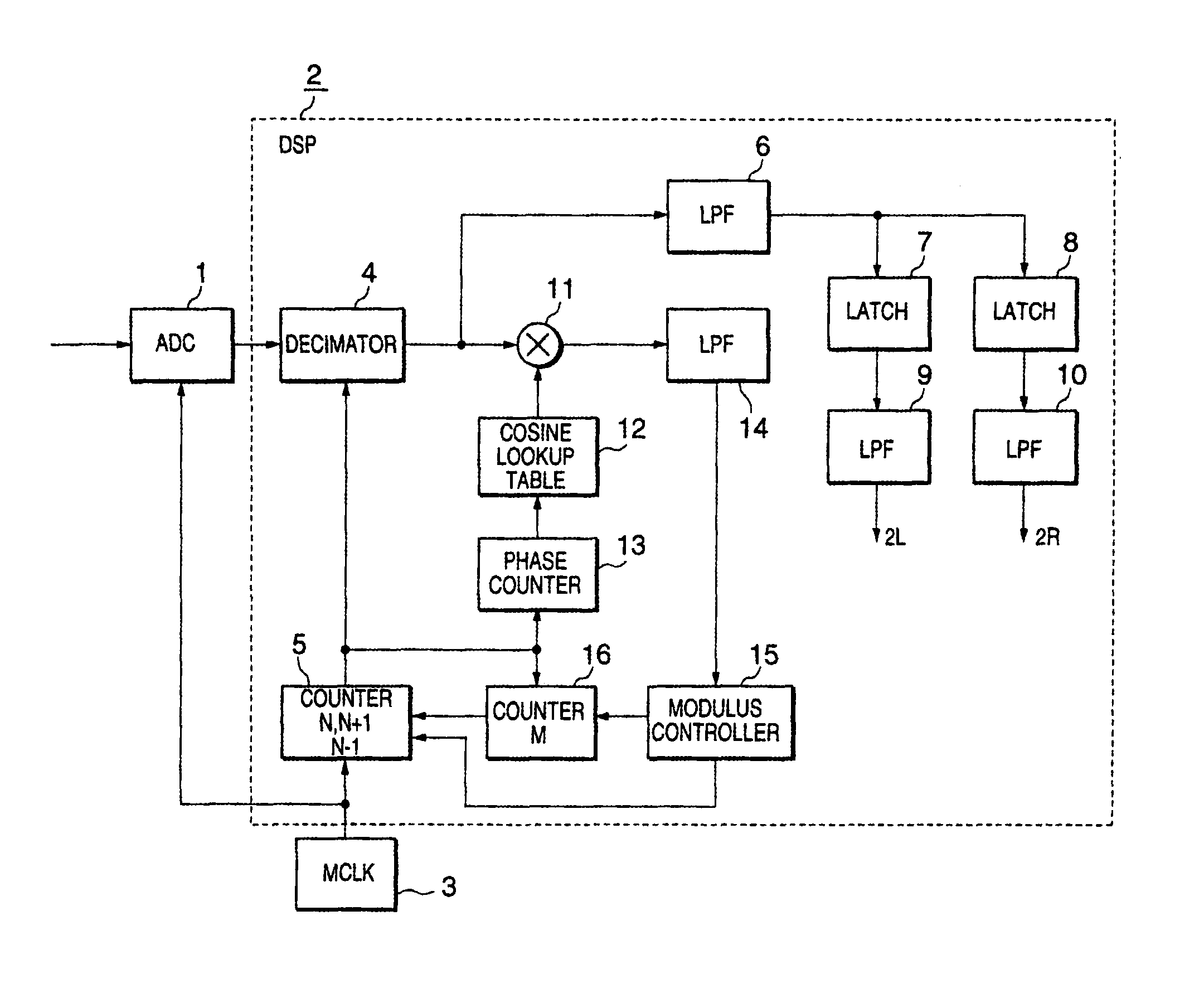
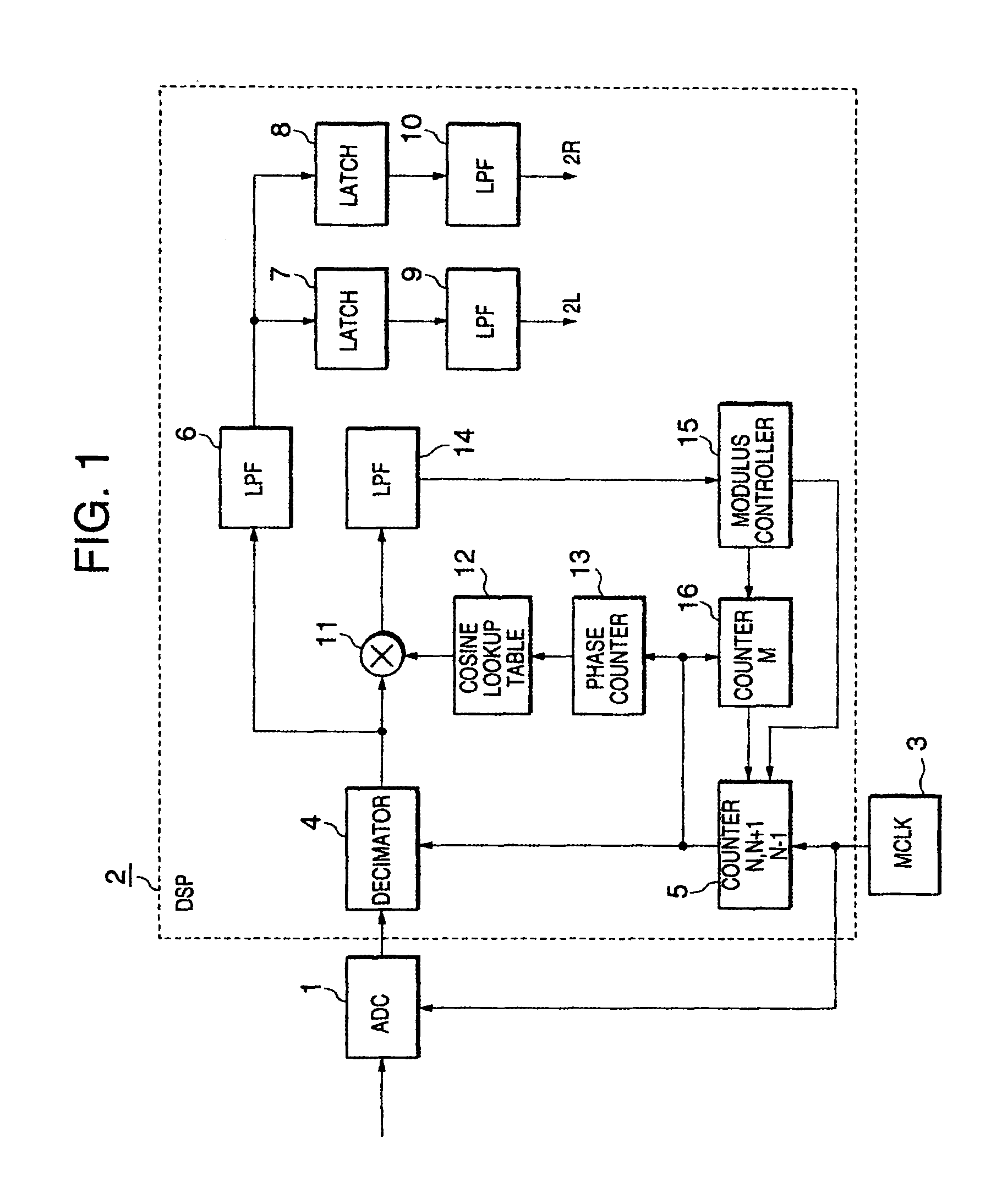
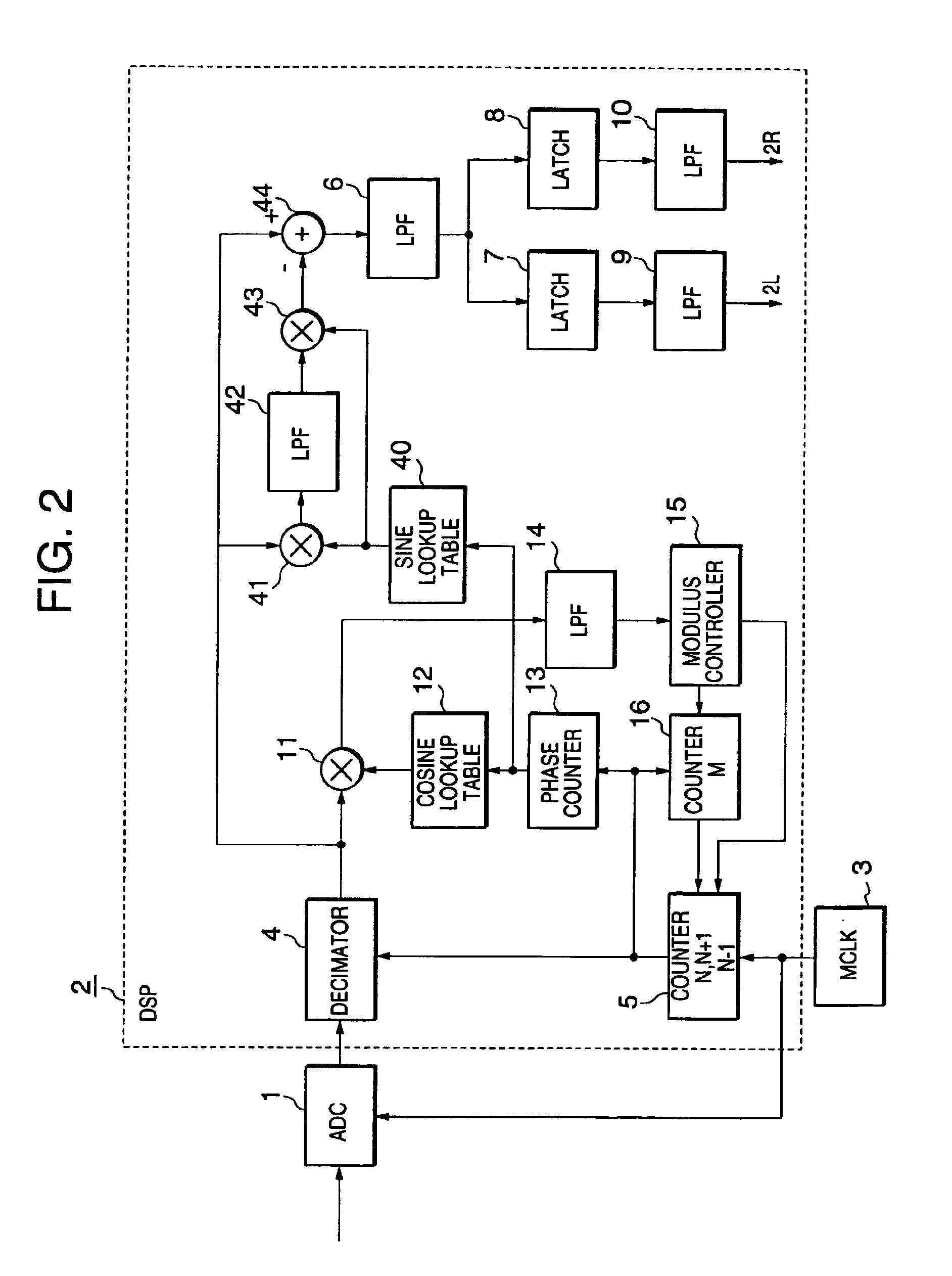
Sampling system
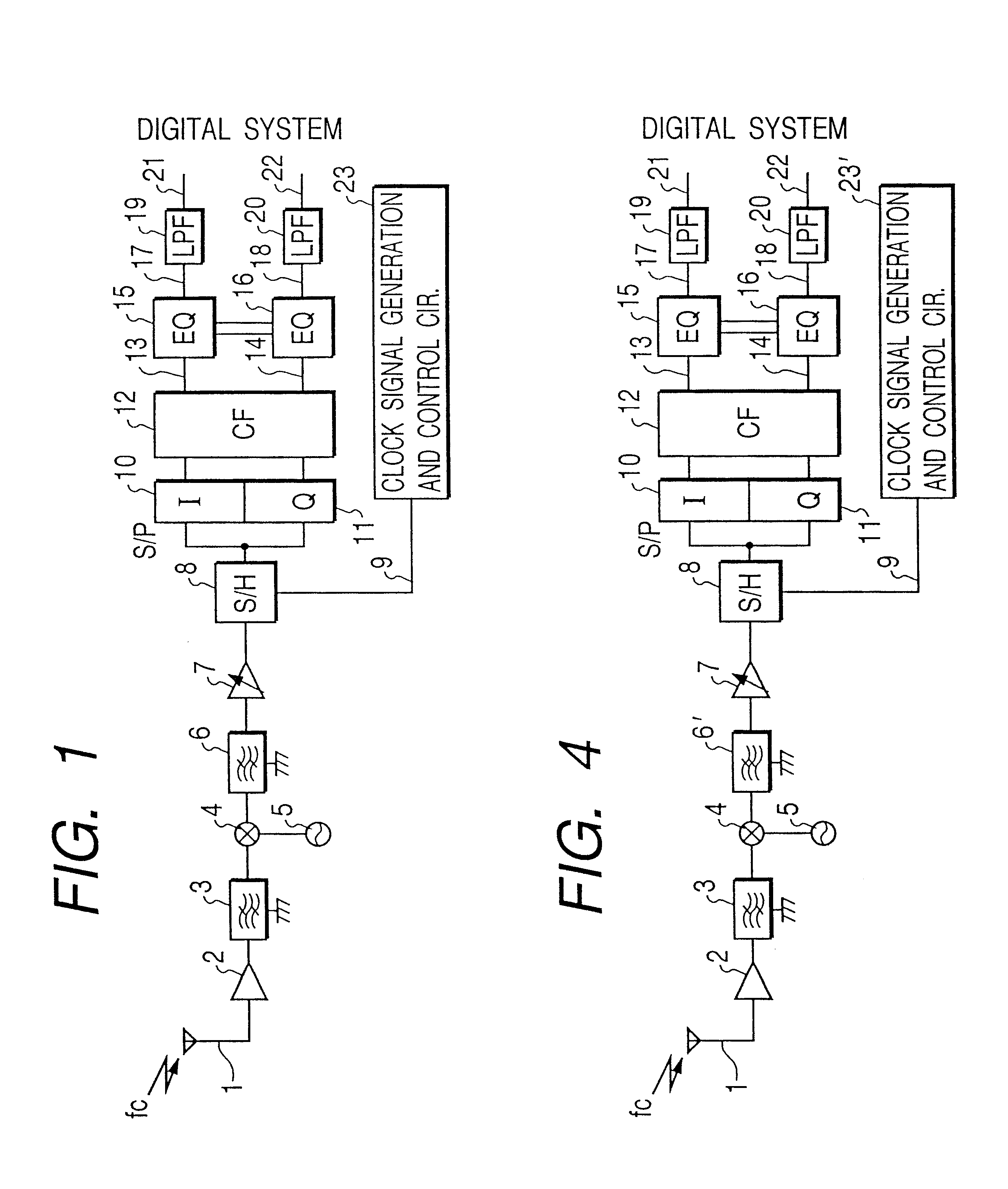
A sampling system arranged such that a modulated signal received by an antenna and input via a low noise amplifier and a band-pass filter is sampled at a sampling frequency higher than the signal band of the modulated signal by a first sample and hold circuit and is input to an analog decimation filter to remove a frequency component which may turn out to be aliasing noise. The output of the analog decimation filter is sampled with a sampling frequency lower than the sampling frequency of the first sample and hold circuit by a second sample and hold circuit and is digitized by an A / D converter to be demodulated by a demodulator. The sampling system which can convert the modulated signal into a low frequency without using the highly precision mixer circuit or a filter having sharp characteristics may be provided by constructing as described above.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Wireless local area network (WLAN) using universal frequency translation technology including multi-phase embodiments and circuit implementations
InactiveUS7110444B1Reduce carrier insertion and spectral growthReduce and eliminate re-radiationModulation transferenceNetwork topologiesModem deviceFrequency spectrum
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
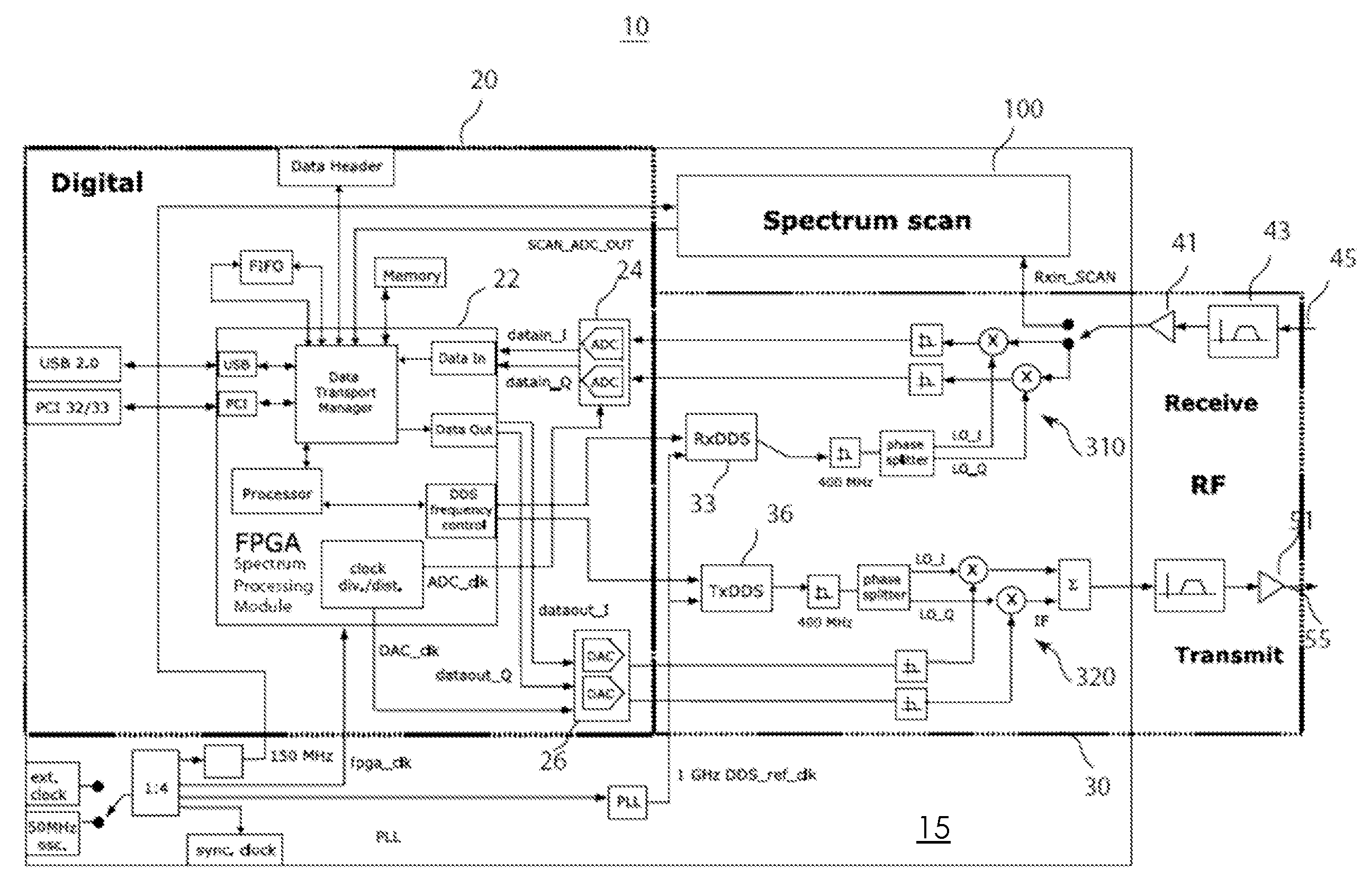
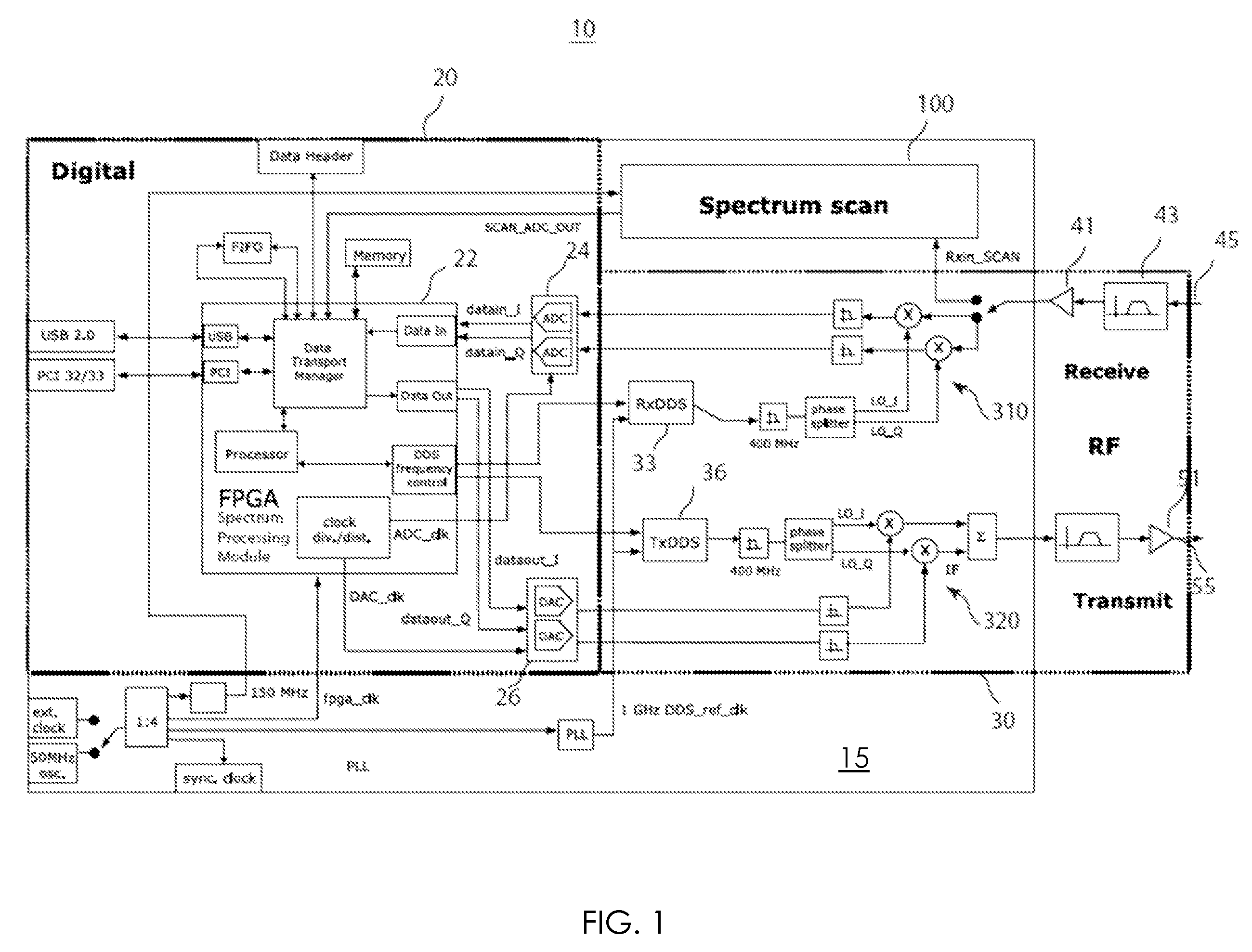
Agile spectrum monitoring in a radio transceiver
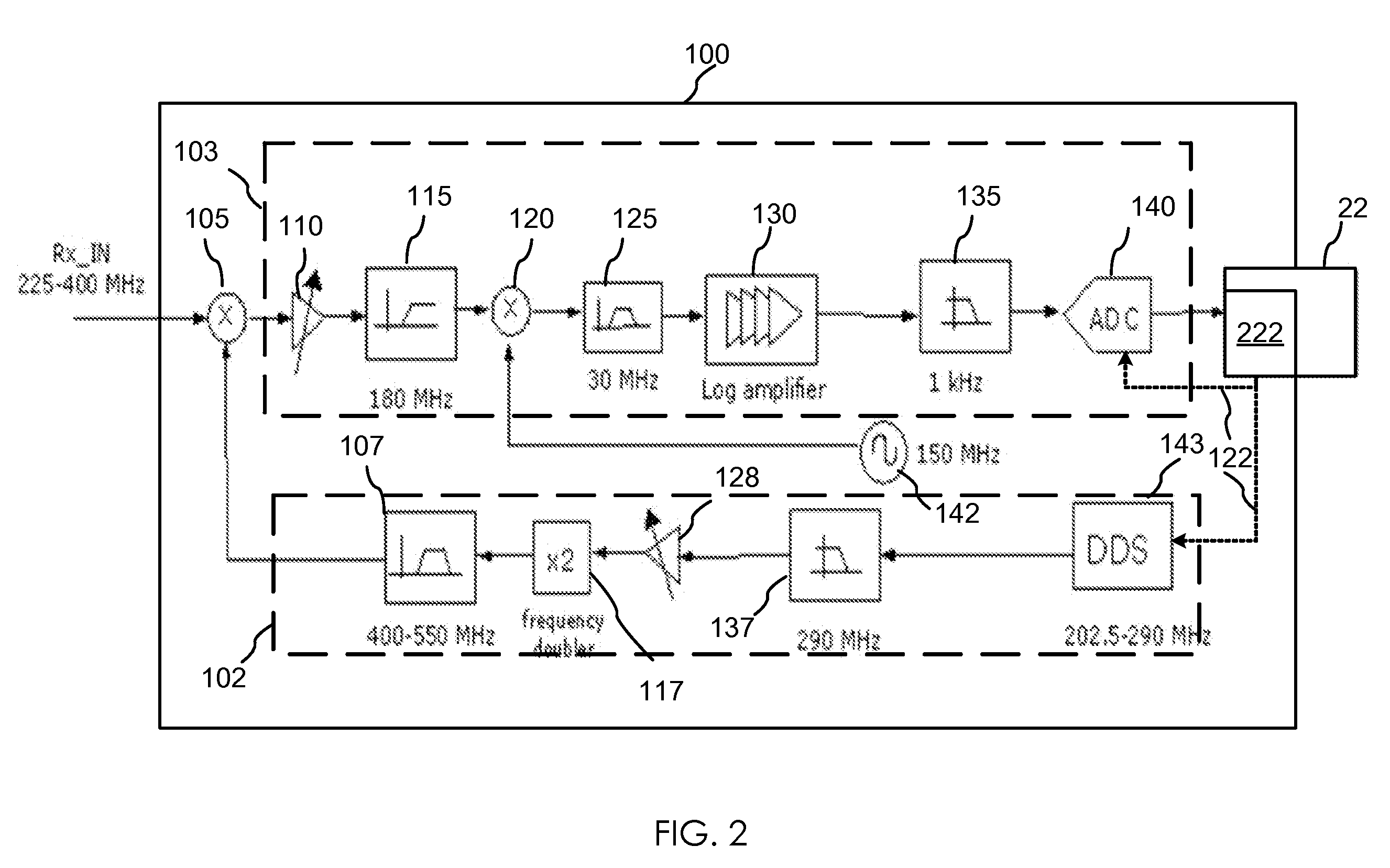
InactiveUS20080291985A1Duplex signal operationAngle demodulation by oscillations samplingFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for agile RF spectrum monitoring in a radio system with dynamic frequency access. It provides a spectrum monitor based on non-coherent heterodyne detection that utilizes a DDS signal generator to digitally generate a reference signal at a variable reference frequency for mixing with an input RF signal received from an RF antenna, a pass-band filter and a log amplifier for obtaining energy estimates at a monitored transmission frequency corresponding to the reference frequency. A processor is provided for adaptively selecting sets of monitored transmission frequencies, for controlling the DDS signal generator, and for processing obtained spectral energy estimates to assess spectral usage data.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
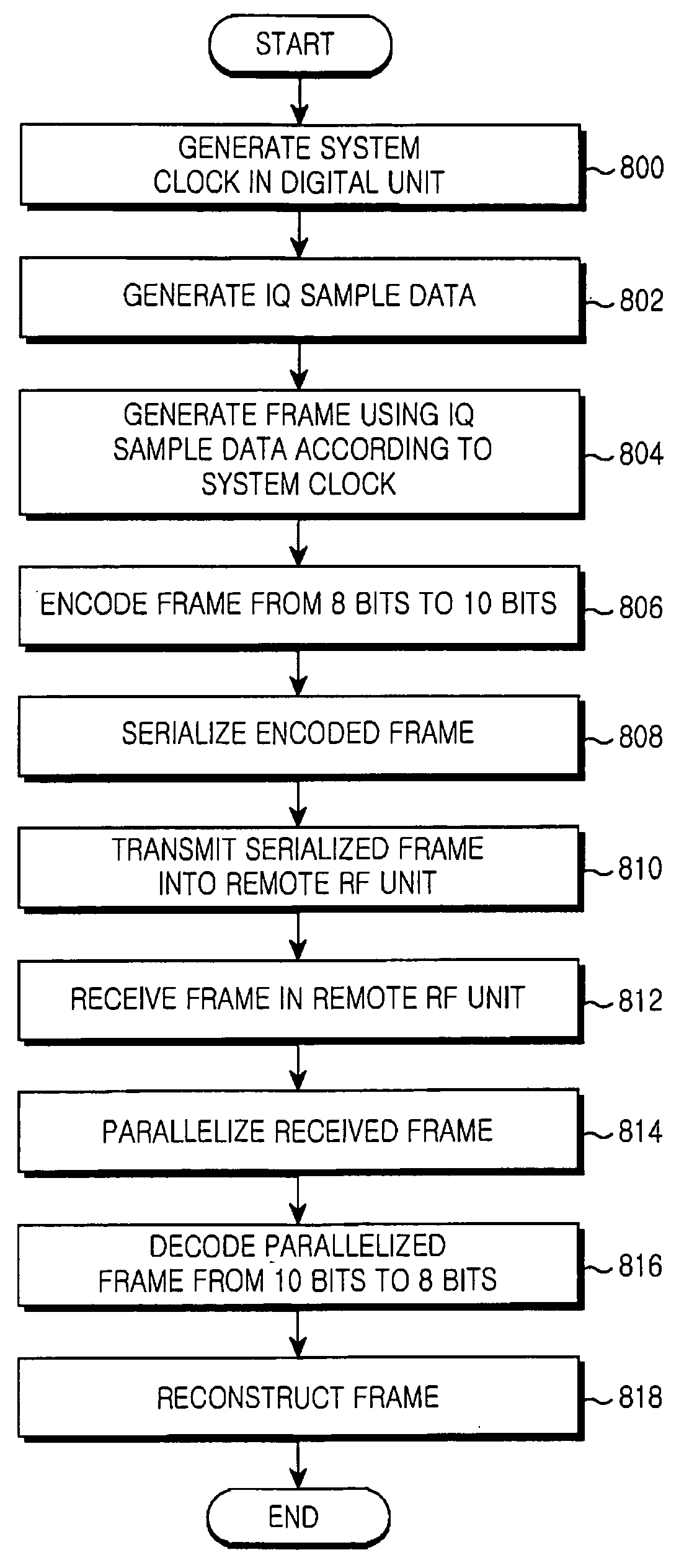
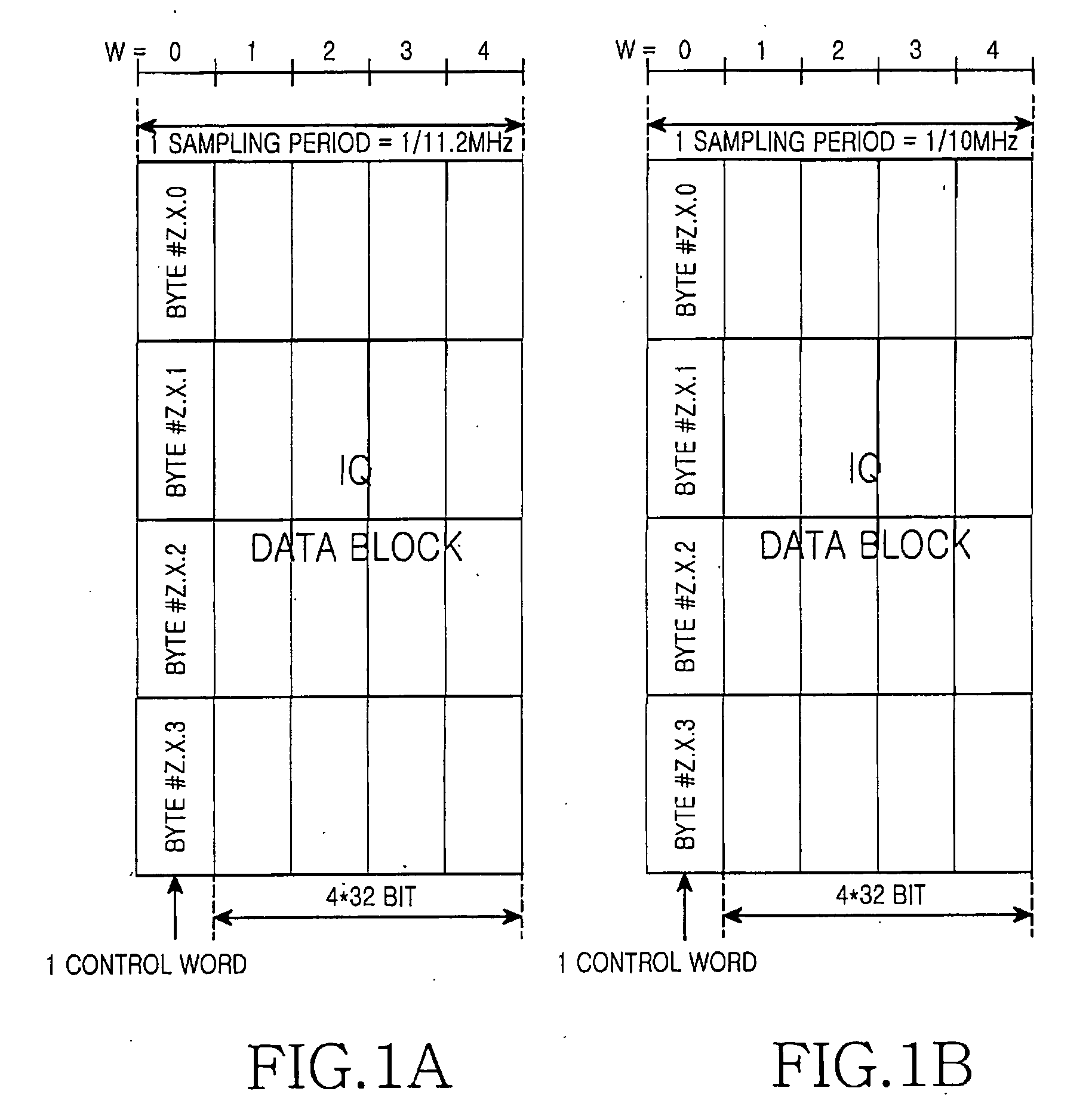
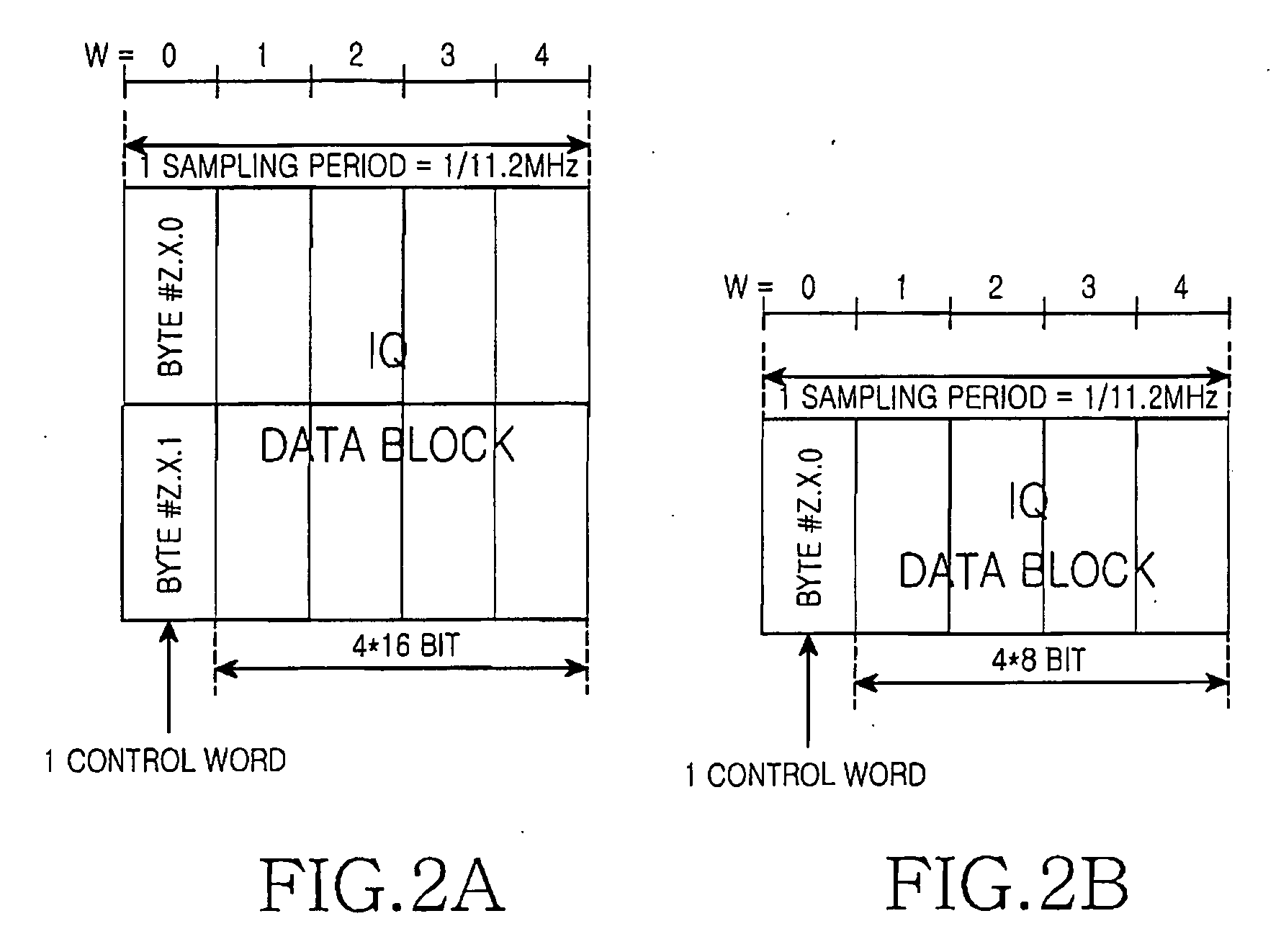
Apparatus and method for communication between a digital unit and a remote RF unit in a broadband wireless communication system
InactiveUS20070147488A1Modulated-carrier systemsRadio transmission for post communicationBroadbandRadio frequency
Provided are an apparatus and method for communication between a digital unit and a remote radio frequency unit in a broadband wireless communication system. A frame structure of Inphase / Quadrature (IQ) sample data based on various channel bandwidths and sampling frequencies is defined, and then the IQ sample data are generated in the frame. The digital unit transmits the IQ sample data into the remote Radio Frequency (RF) unit, and then the remote RF unit reconstructs the frame by using the received IQ sample data from the digital unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
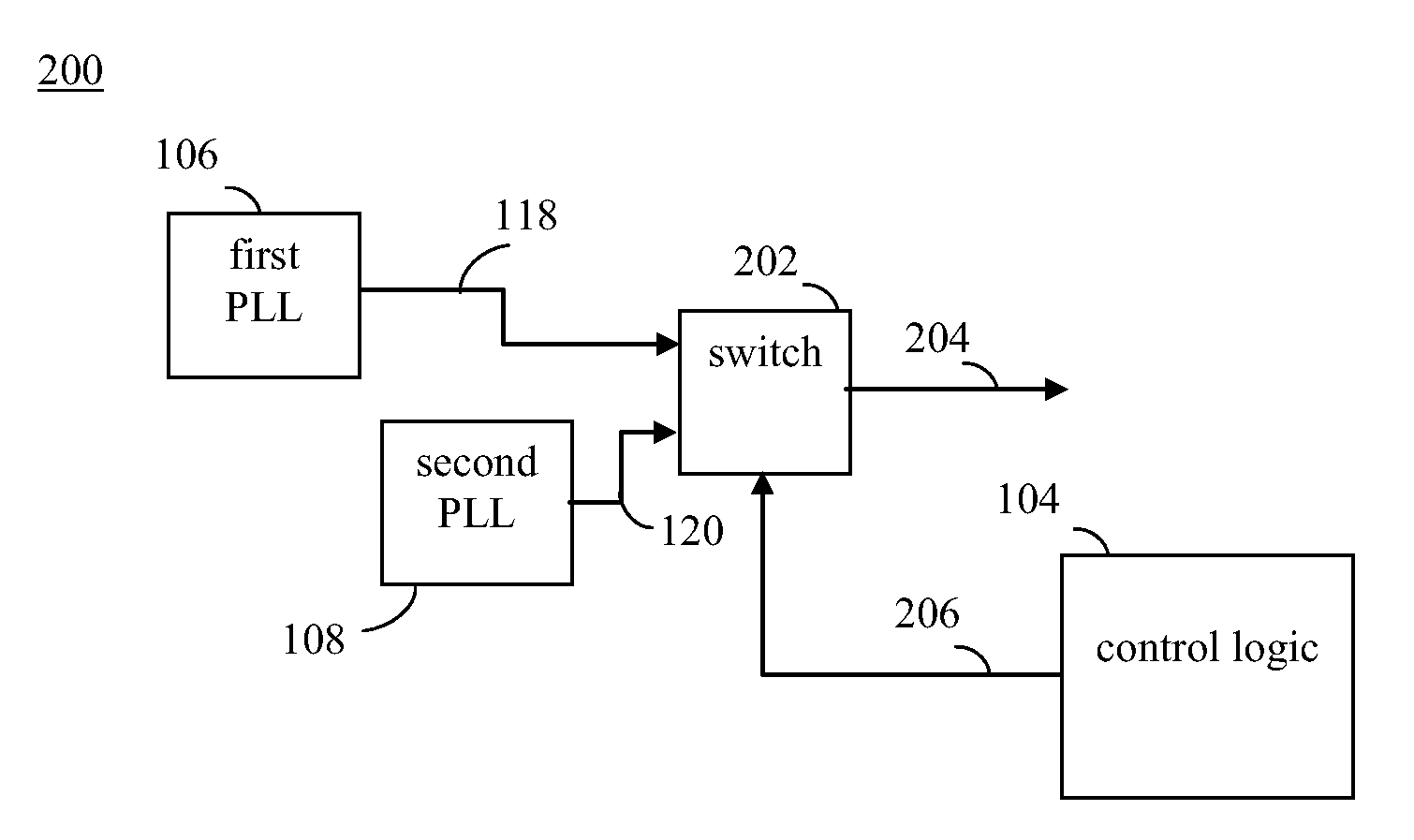
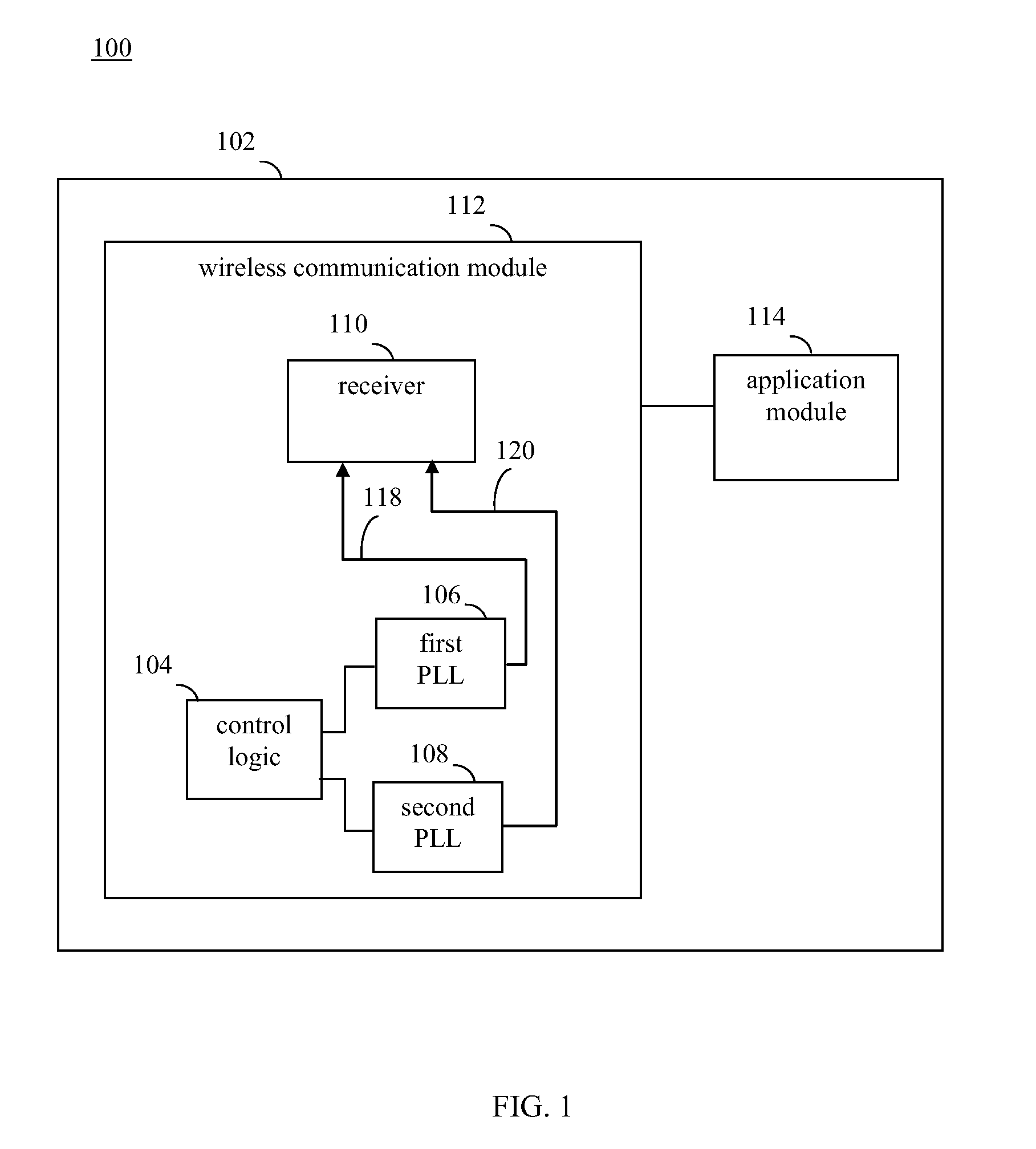
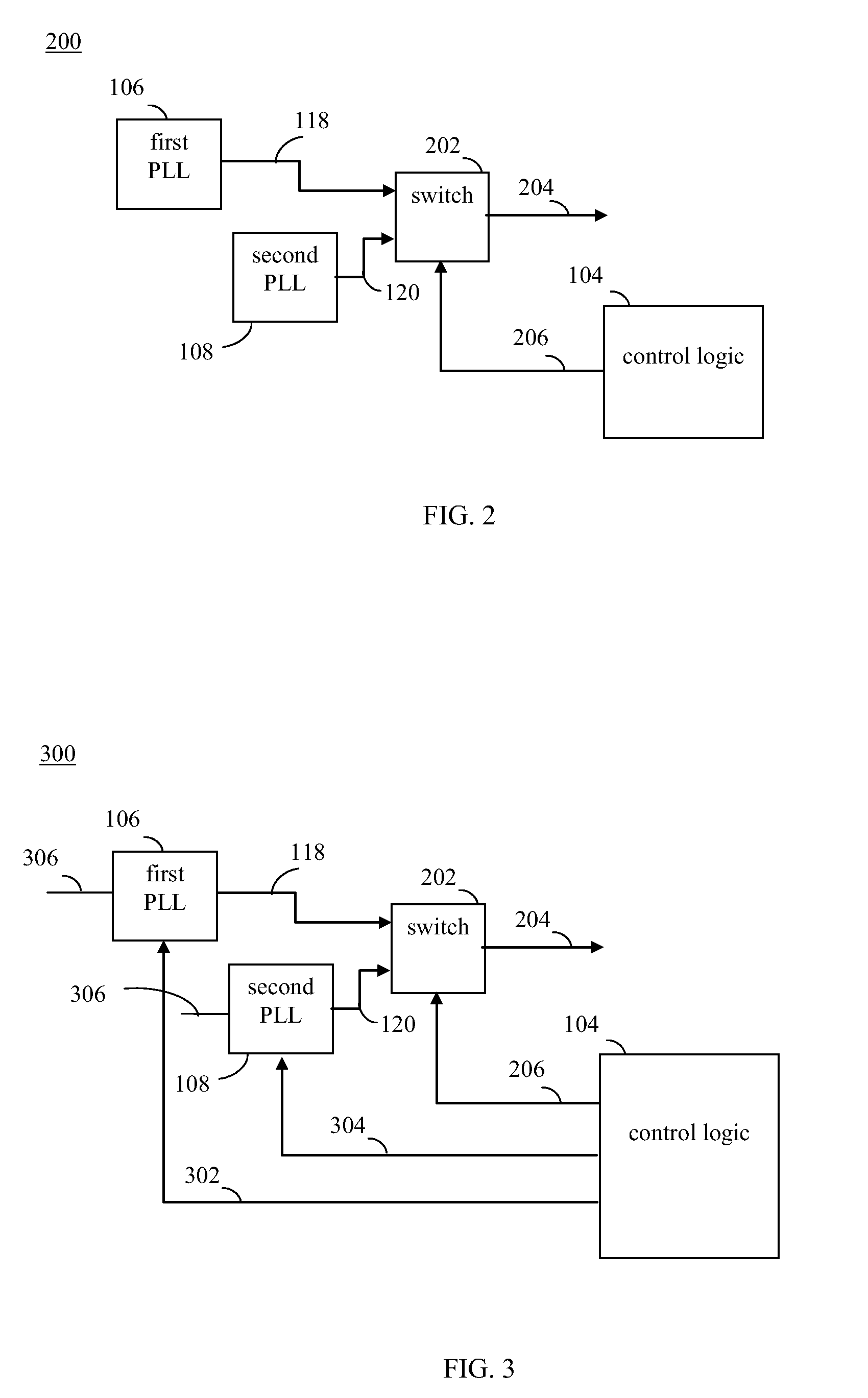
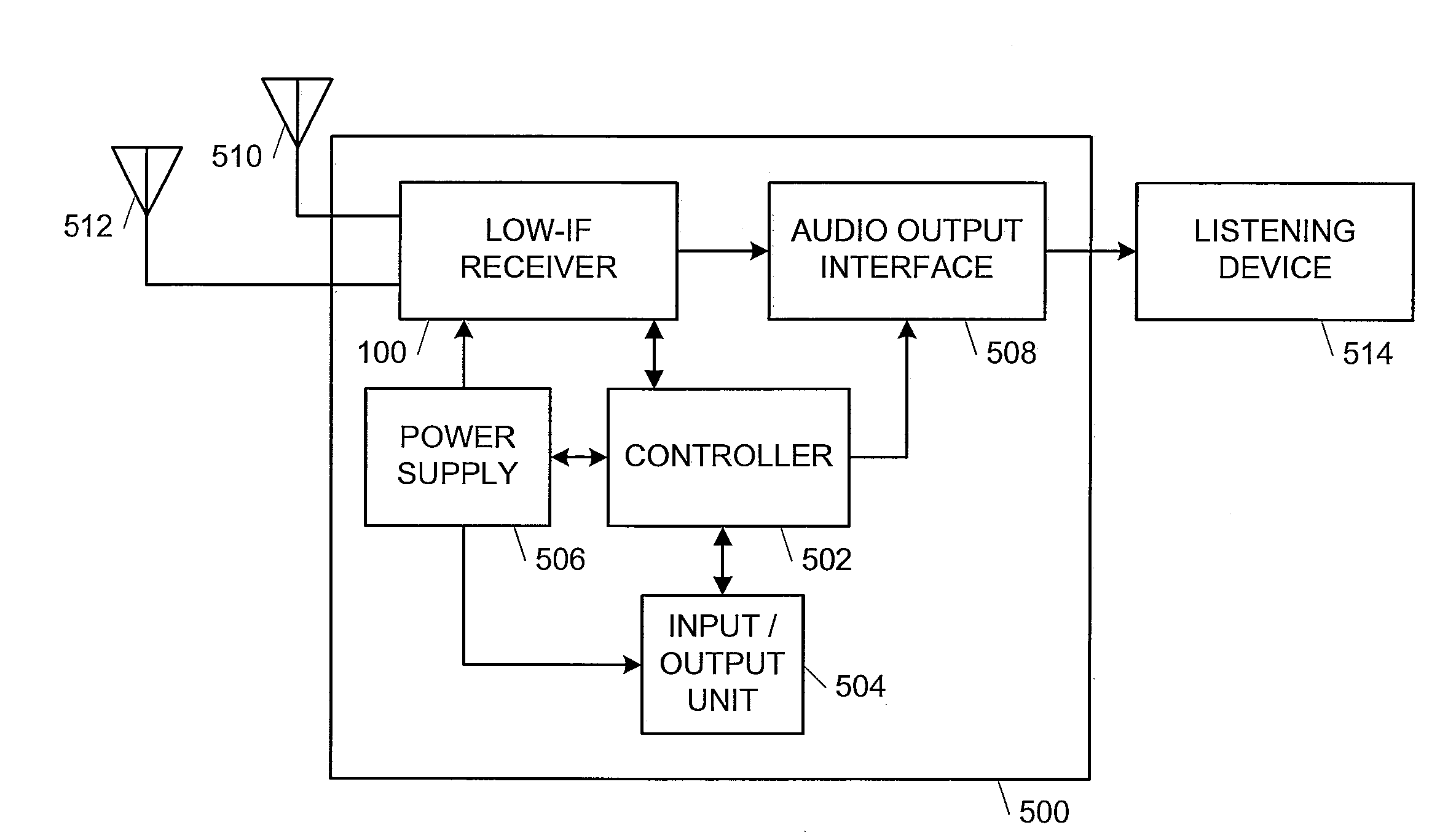
Dual phase locked loop (PLL) architecture for multi-mode operation in communication systems
InactiveUS20080317185A1Reduce adverse effectsImprove accuracyPower managementPulse automatic controlCommunications systemLow jitter
The clock generating portion of a communication system includes a low-power, high-jitter phase locked loop (PLL) and a high-power, low-jitter PLL. Control logic within the chip allows for selective switching between the low-power and high-power PLL for receiving the broadcast signals, such as mobile TV signals. The switching may occur in a manner that is dependent on the conditions of the wireless channel and / or the complexity of the modulation scheme being used. The switching may be used to provide an oscillating signal from one or both of the PLLs to a receiver to be used to receive communication signals. The control logic may power off one of the PLLs to save power when not in use.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
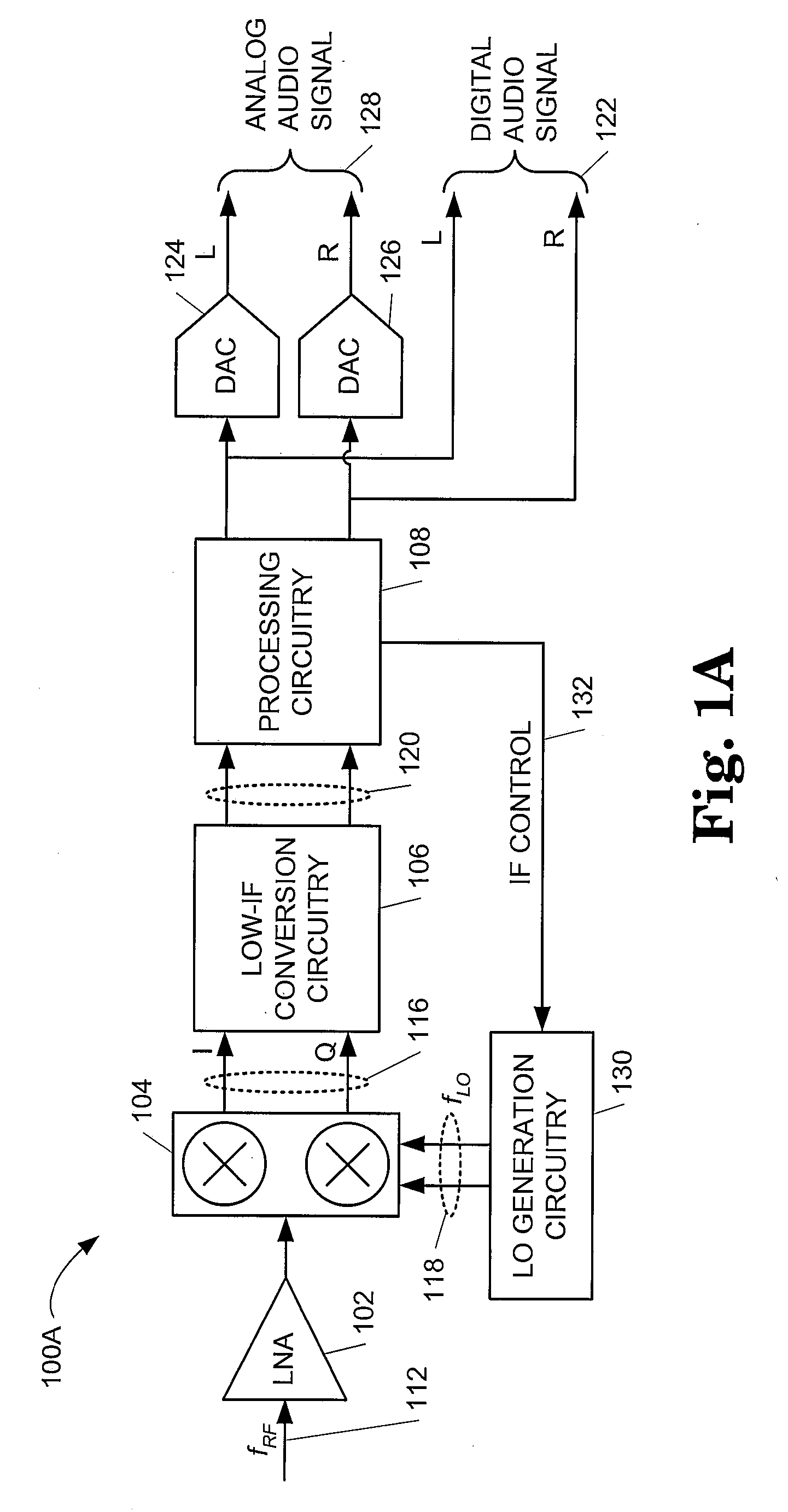
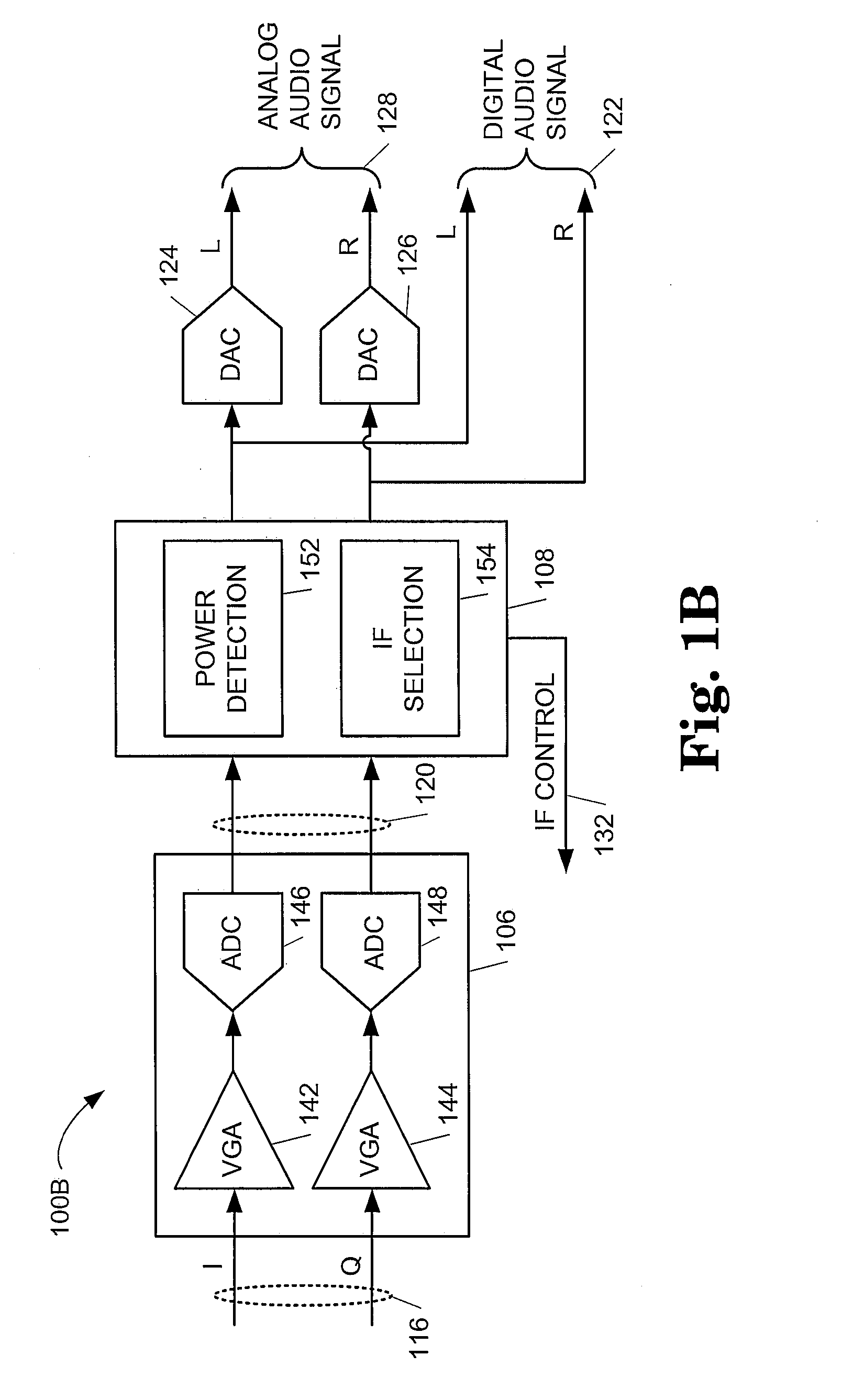
System and method for selecting an intermediate frequency
InactiveUS20080261548A1TransmissionAngle demodulation by oscillations samplingFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
A receiver including a mixer configured to generate a mixed signal at a first intermediate frequency from an input signal and a mixing signal and processing circuitry configured to detect a power level for each of a plurality of possible images in the mixed signal and configured to cause the mixer to generate the mixed signal at a second intermediate frequency that differs from the first intermediate frequency and corresponds to an image frequency of one of the plurality of possible images with a lowest of the power level is provided.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
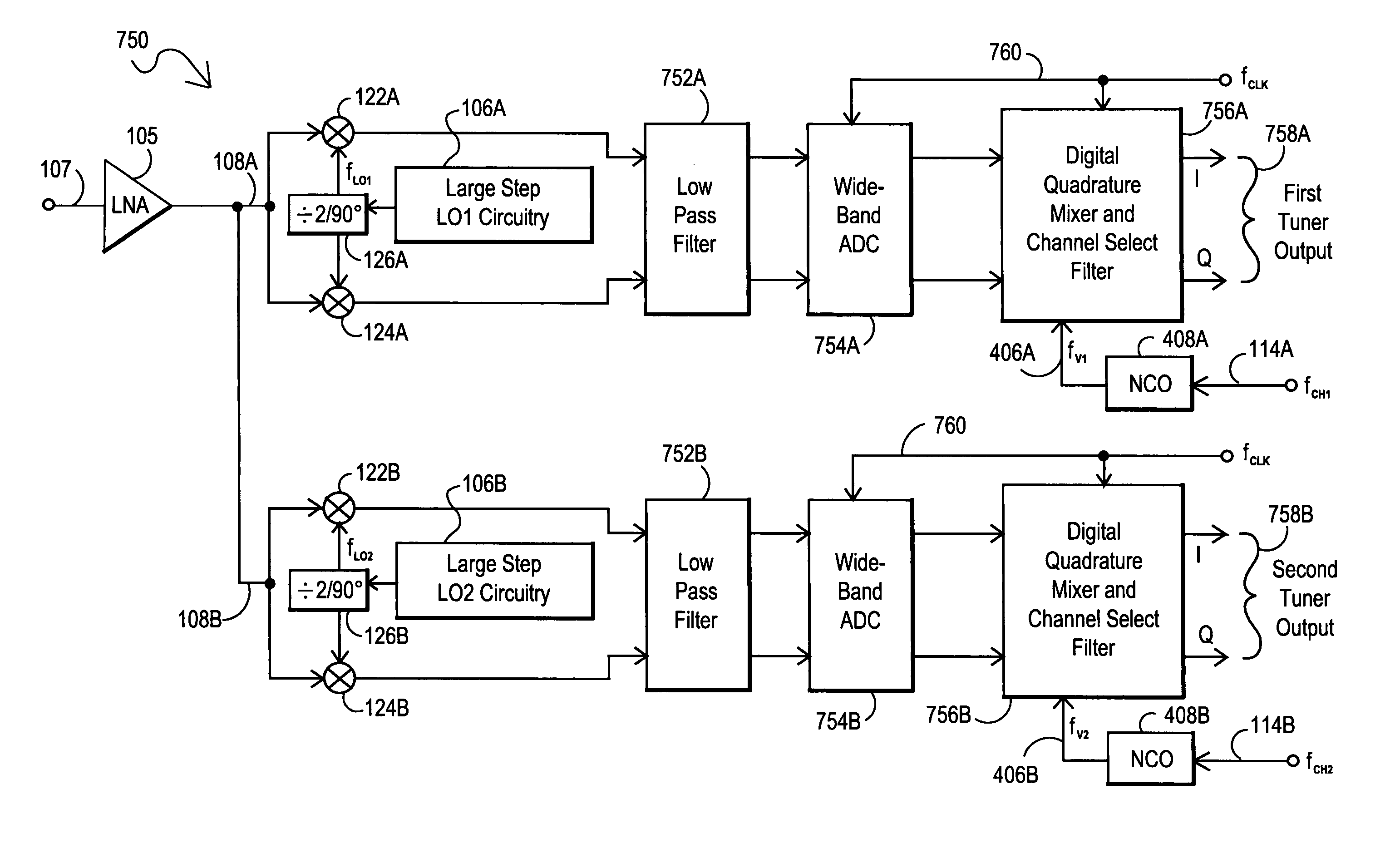
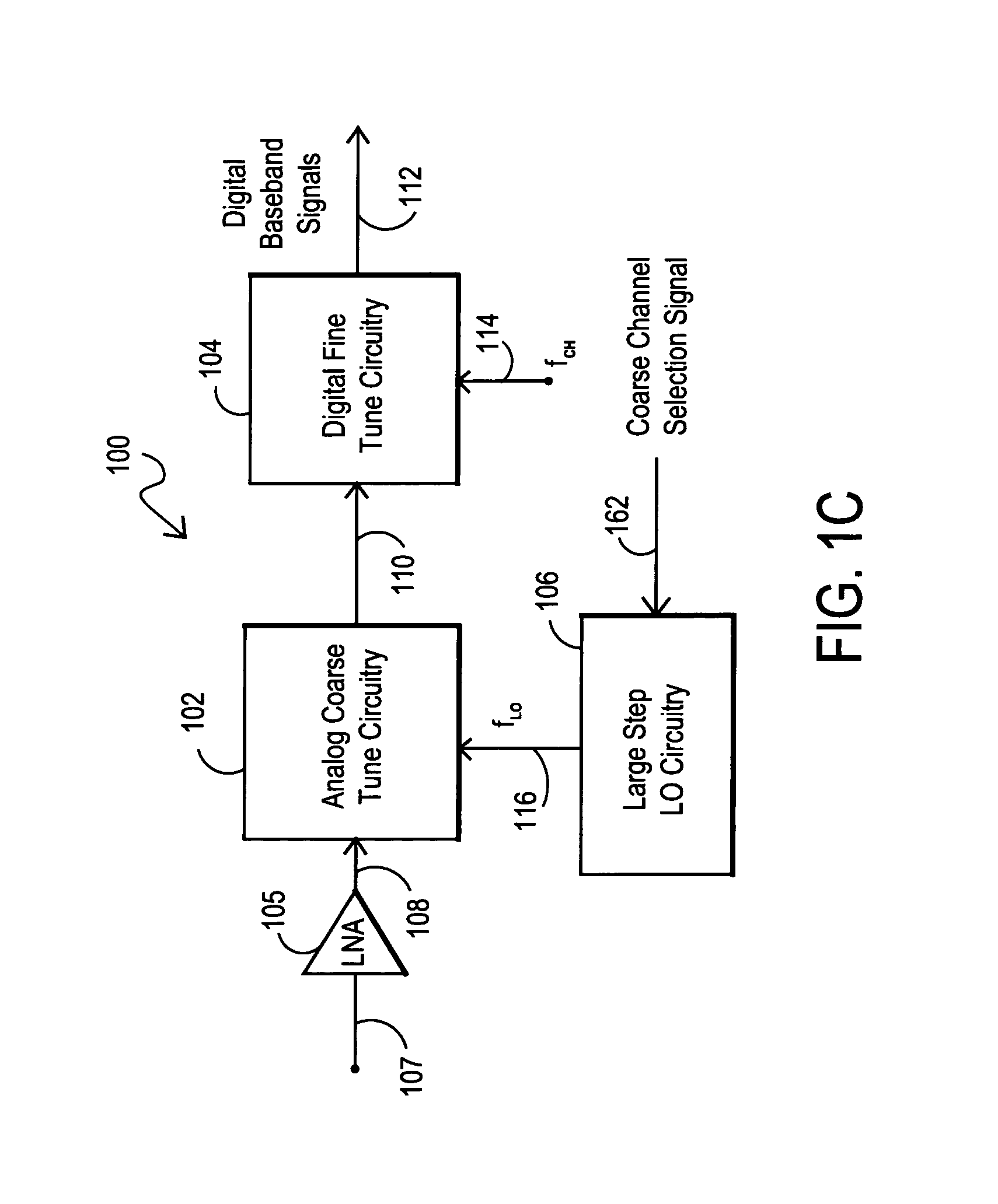
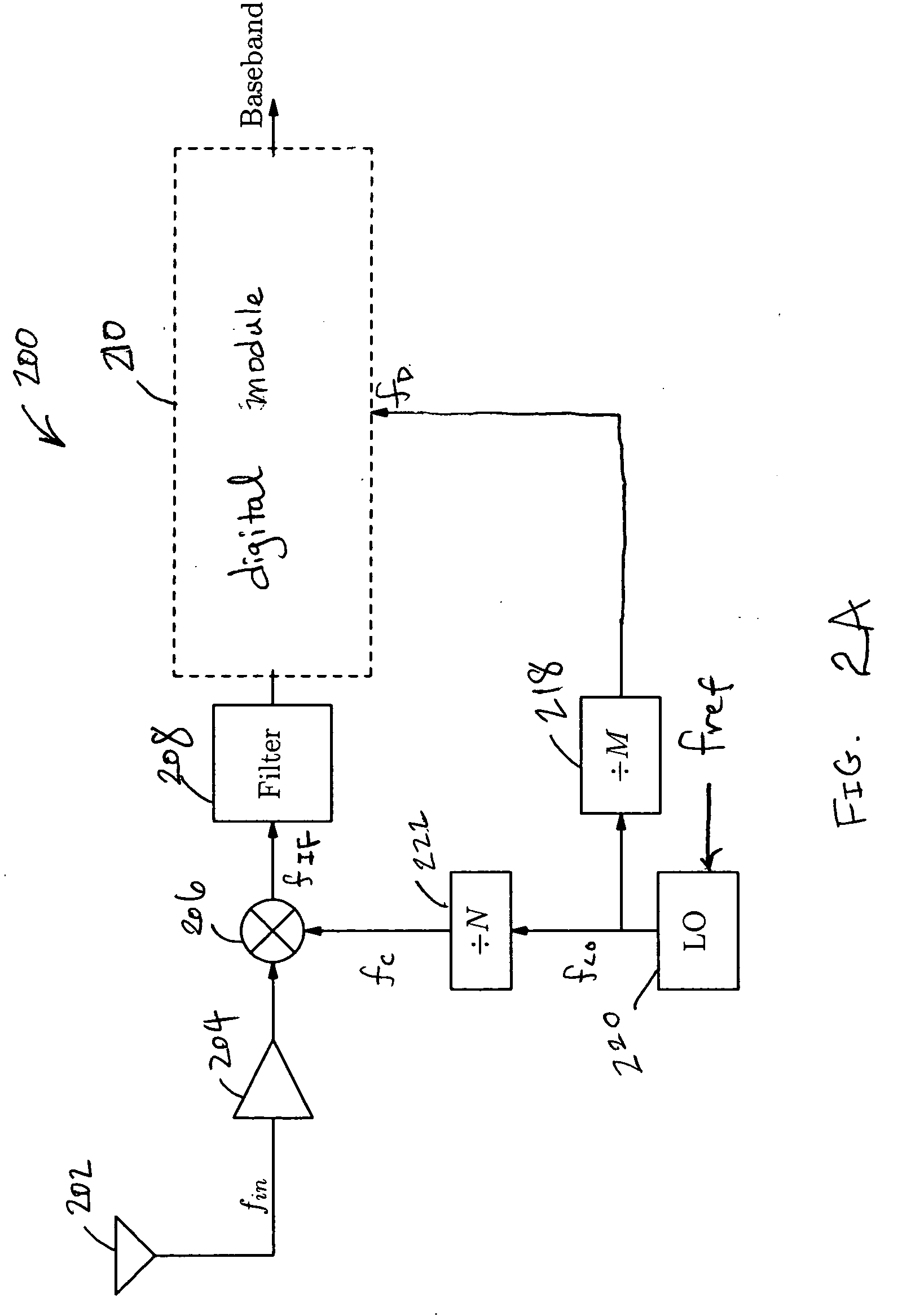
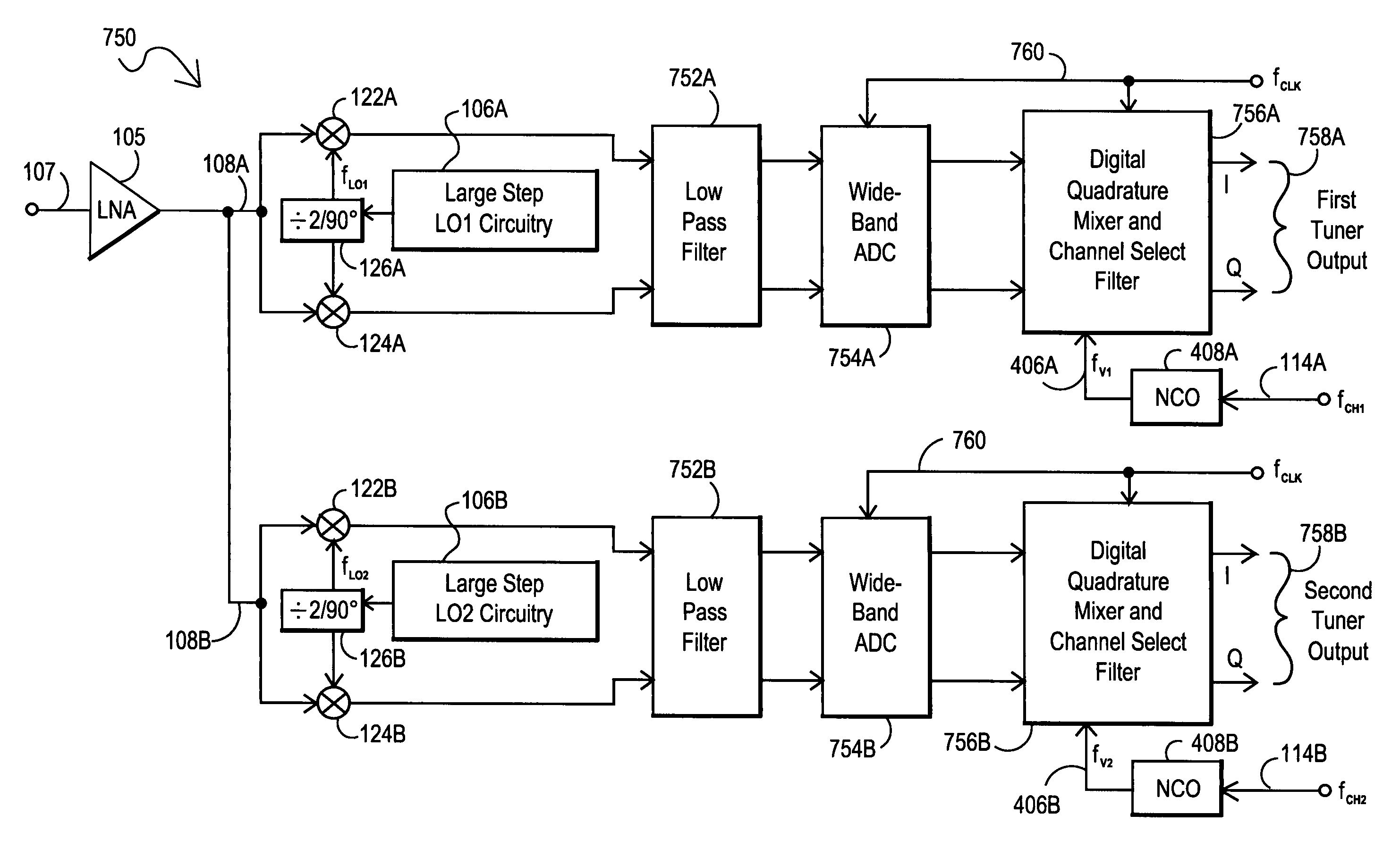
Integrated multi-tuner satellite receiver architecture and associated method
InactiveUS7167694B2Avoid interferenceAvoid noise problemsTelevision system detailsSatellite broadcast receivingFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Multi-tuner receiver architectures and associated methods are disclosed that provide initial analog coarse tuning of desired channels within a received signal spectrum, such as transponder channels within a set-top box signal spectrum for satellite communications. These multi-tuner satellite receiver architectures provide significant advantages over prior direct down-conversion (DDC) architectures and low intermediate-frequency (IF) architectures, particularly where two tuners are desired on the same integrated circuit. Rather than using a low-IF frequency or directly converting the desired channel frequency to DC, initial coarse tuning provided by analog coarse tuning circuitry allows for a conversion to a frequency range around DC. This coarse tuning circuitry can be implemented, for example, using a large-step local oscillator (LO) that provides a coarse tune analog mixing signal. Once mixed down, the desired channel may then be fine-tuned through digital processing, such as through the use of a wide-band analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a narrow-band tunable bandpass ADC.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
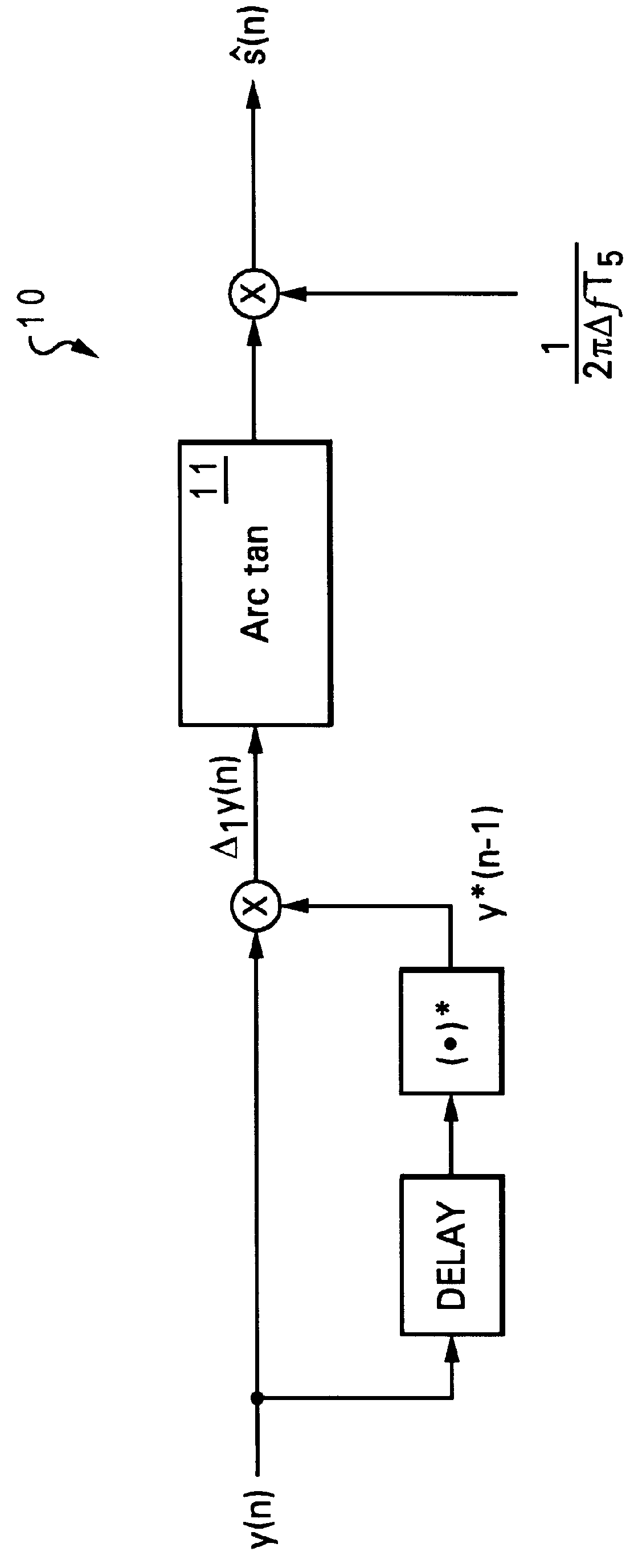
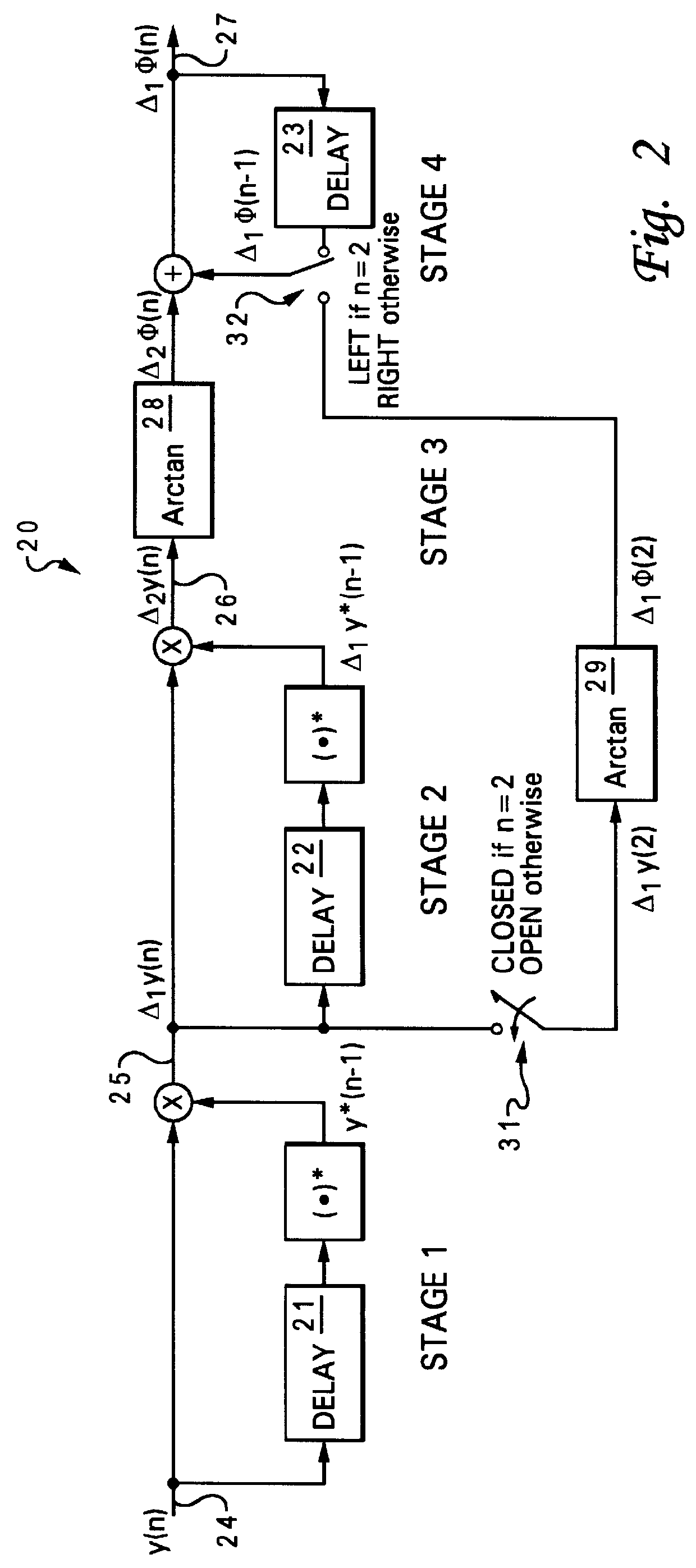
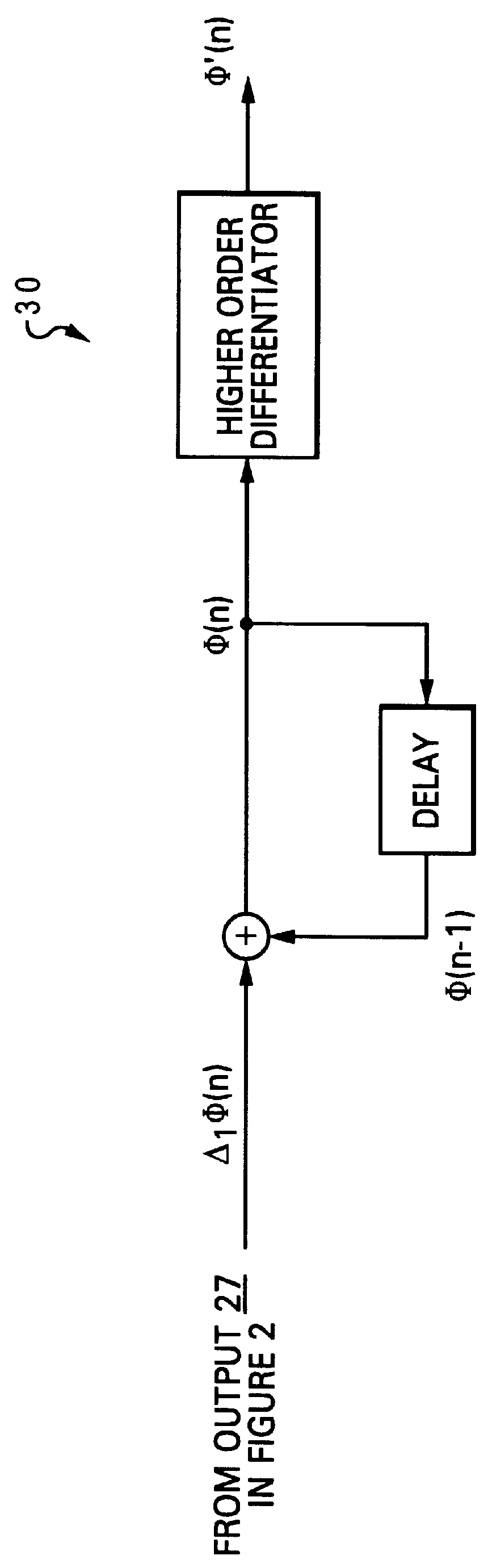
Method and apparatus for demodulating digital frequency modulation (FM) signals
InactiveUS6031418AFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsComplex valuedPulse-frequency modulation
A method for demodulating digital frequency modulation (FM) signals is disclosed. A group of complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is initially received. A corresponding first complex product for each of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is computed, and a corresponding second complex product for each of the first complex values of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples is computed. Subsequently, an inverse tangent of the second complex products are computed to yield an angle for each of the second complex values, wherein each of the angles represents a second-order difference of a phase of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples. Finally, a digital integration is performed to obtain a first-order difference of the phase of the complex-valued discrete-time FM signal samples.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Radio receiving apparatus for receiving communication signals of different bandwidths
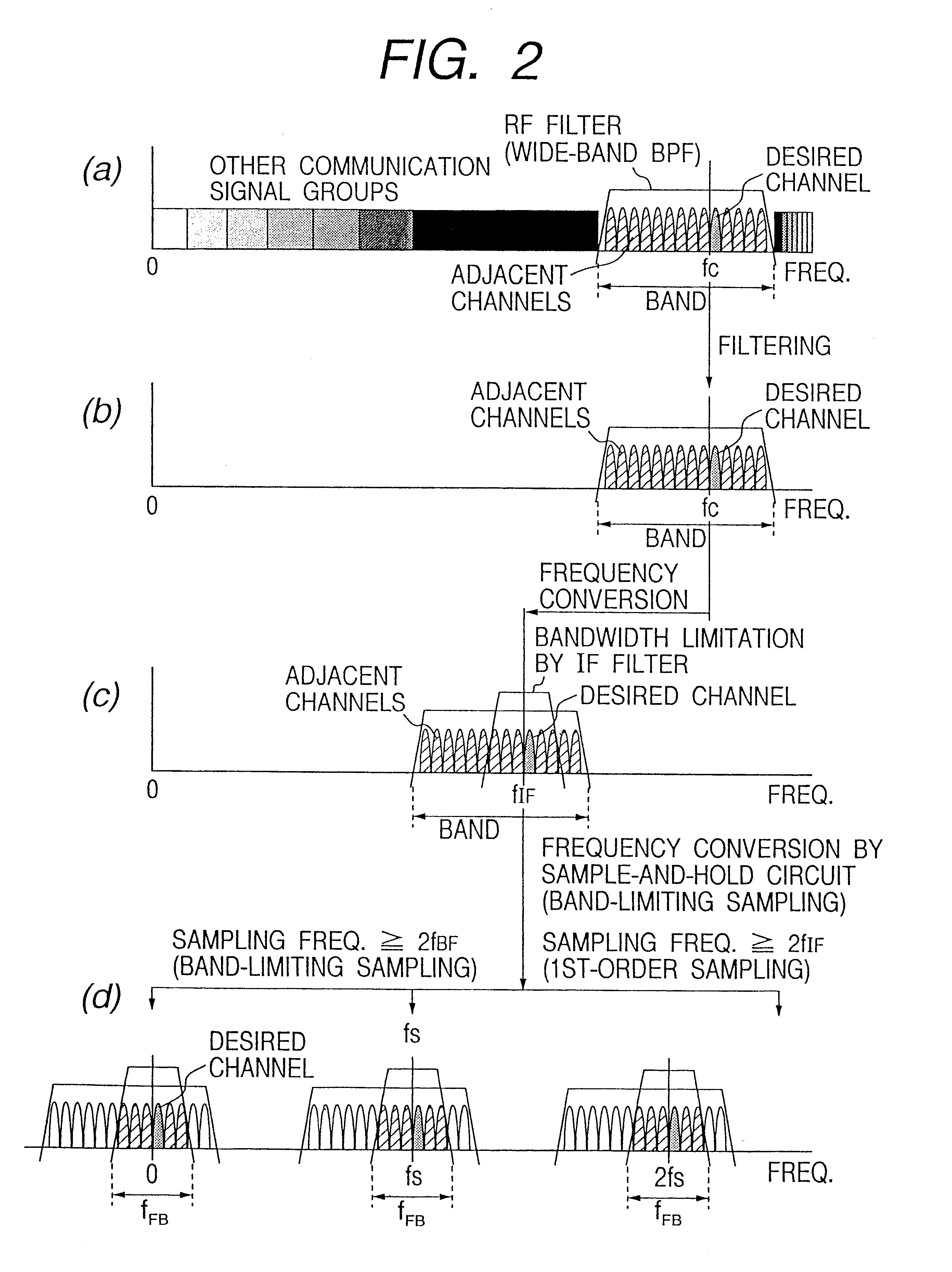
InactiveUS6307897B1Small sizeLow powerPhase-modulated carrier systemsPulse demodulatorBandpass filteringCommunications system
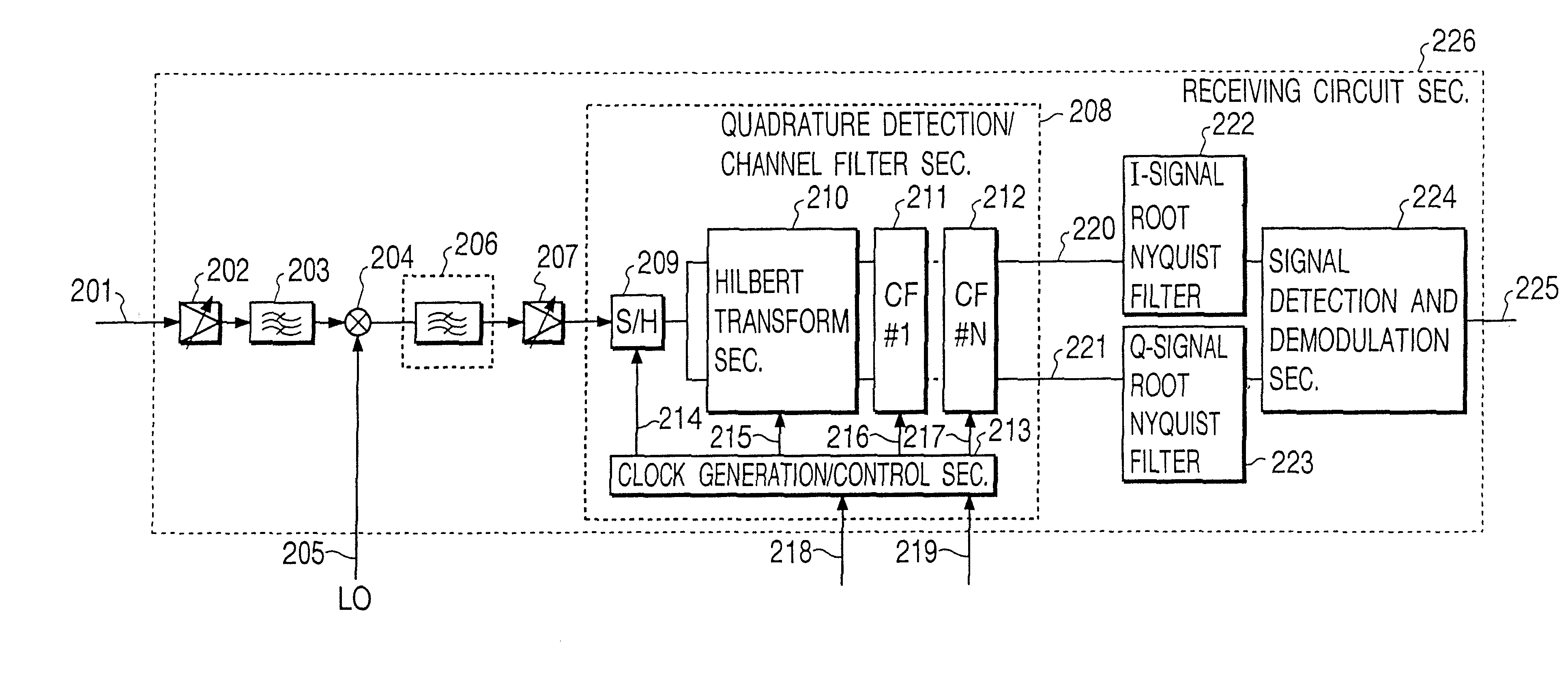
A received signal obtained from an antenna is subjected to high-frequency amplification. The amplified signal is supplied to a first bandpass filter, which extracts only signals of all the channels of a communications system concerned while filtering out other radio signals. The extracted signals are frequency-converted by using a local oscillation frequency, and only a desired wave is passed by a second bandpass filter. The desired wave is supplied to a sample-and-hold circuit, which performs sampling according to the bandwidth-limiting sampling theorem. A resulting discrete signal is supplied to an I-axis-component and Q-axis-component separating circuits, where the polarity of sample values is inverted for every other clock pulse with respect to each of the I and Q axes to thereby effect Hilbert transform. Resulting two orthogonal components on a phase plane are supplied to a complex coefficient filter.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
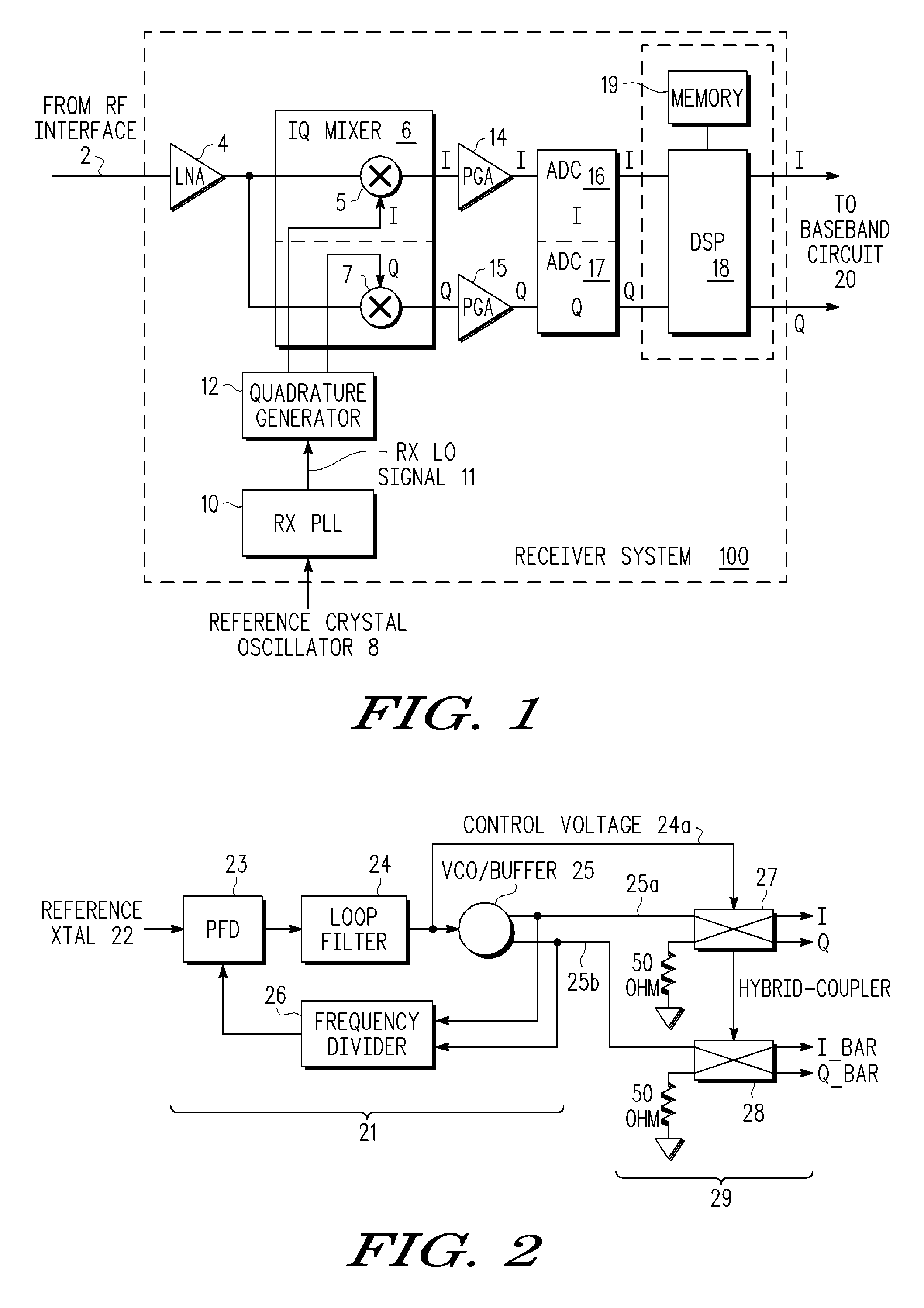
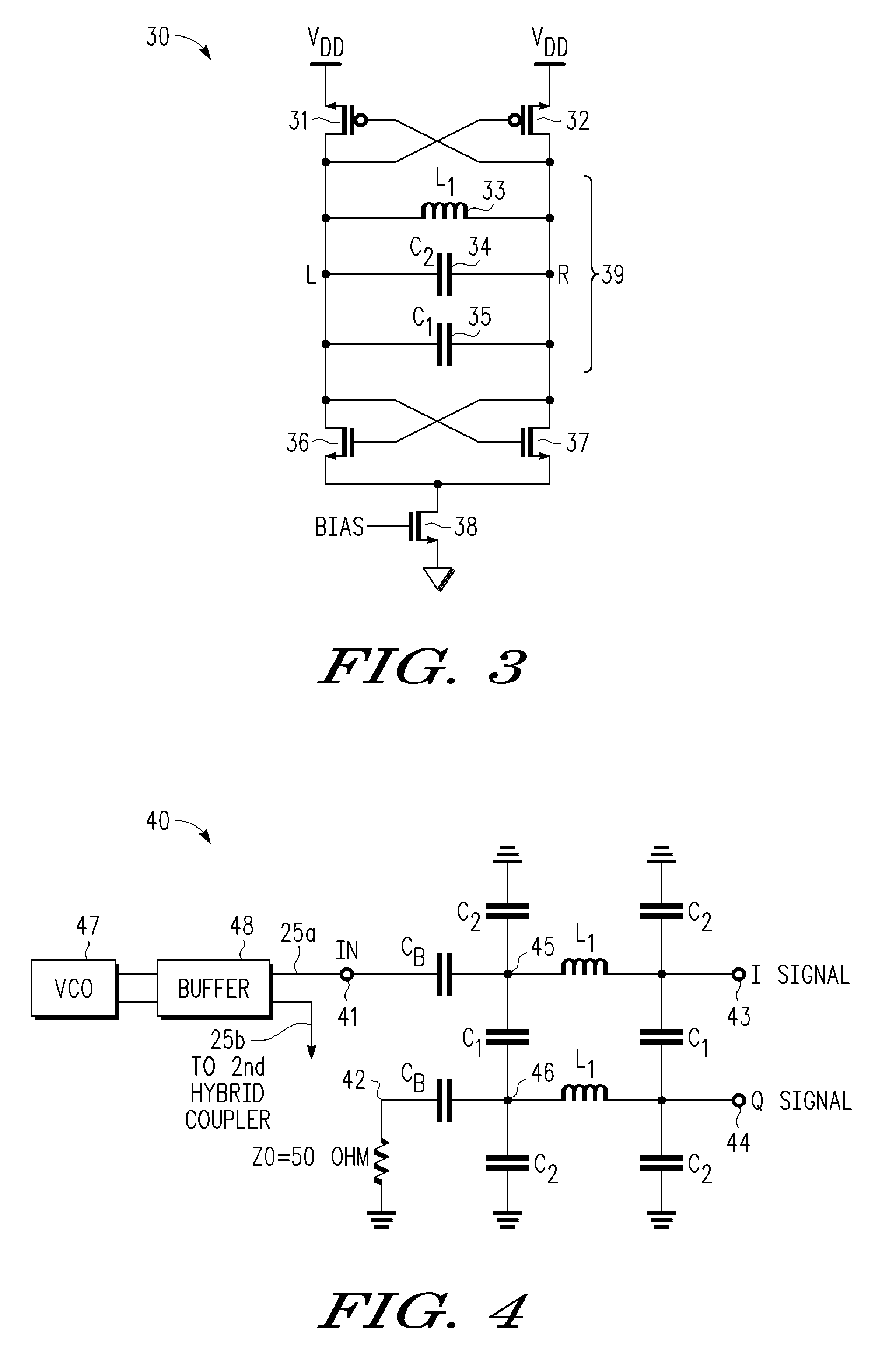
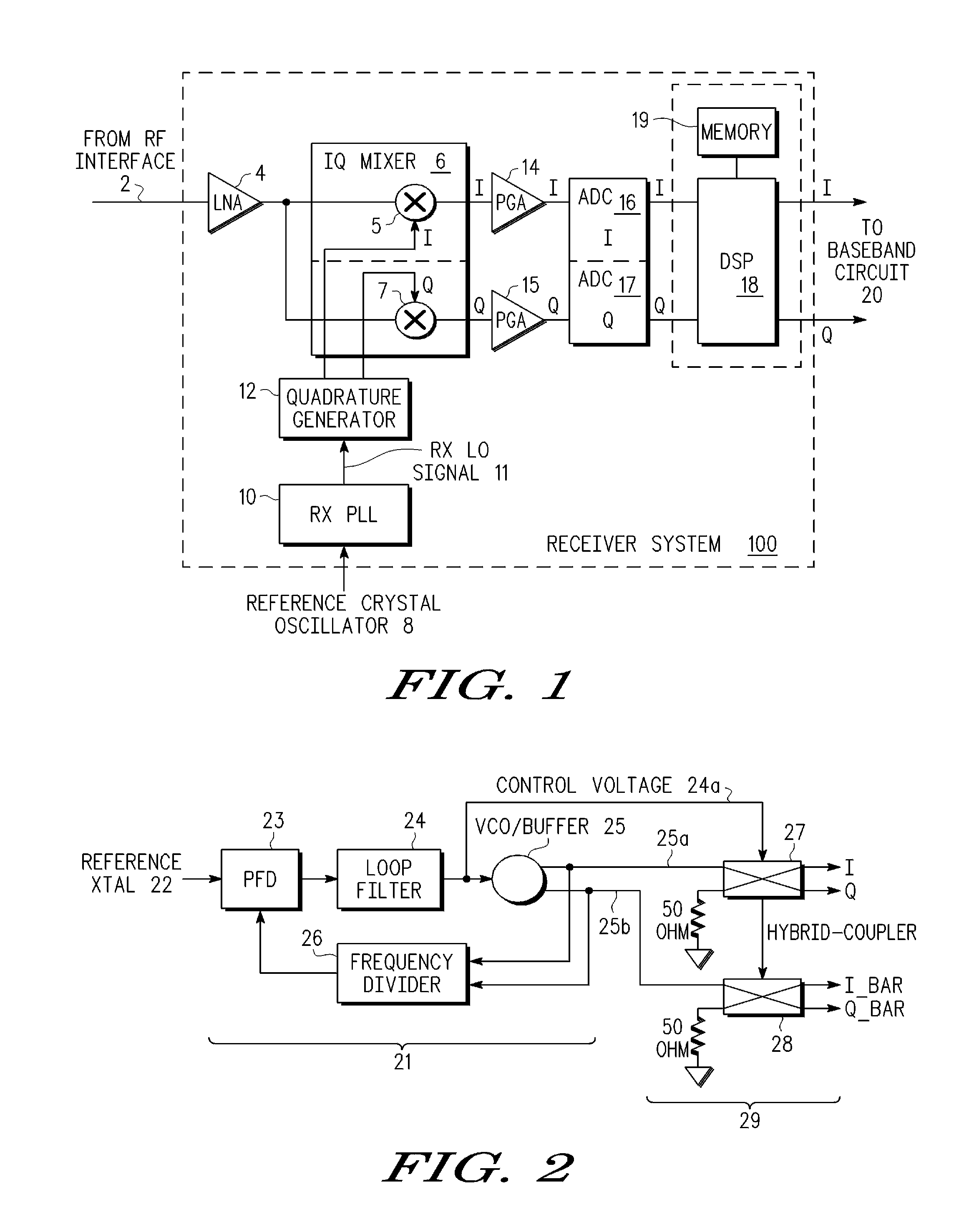
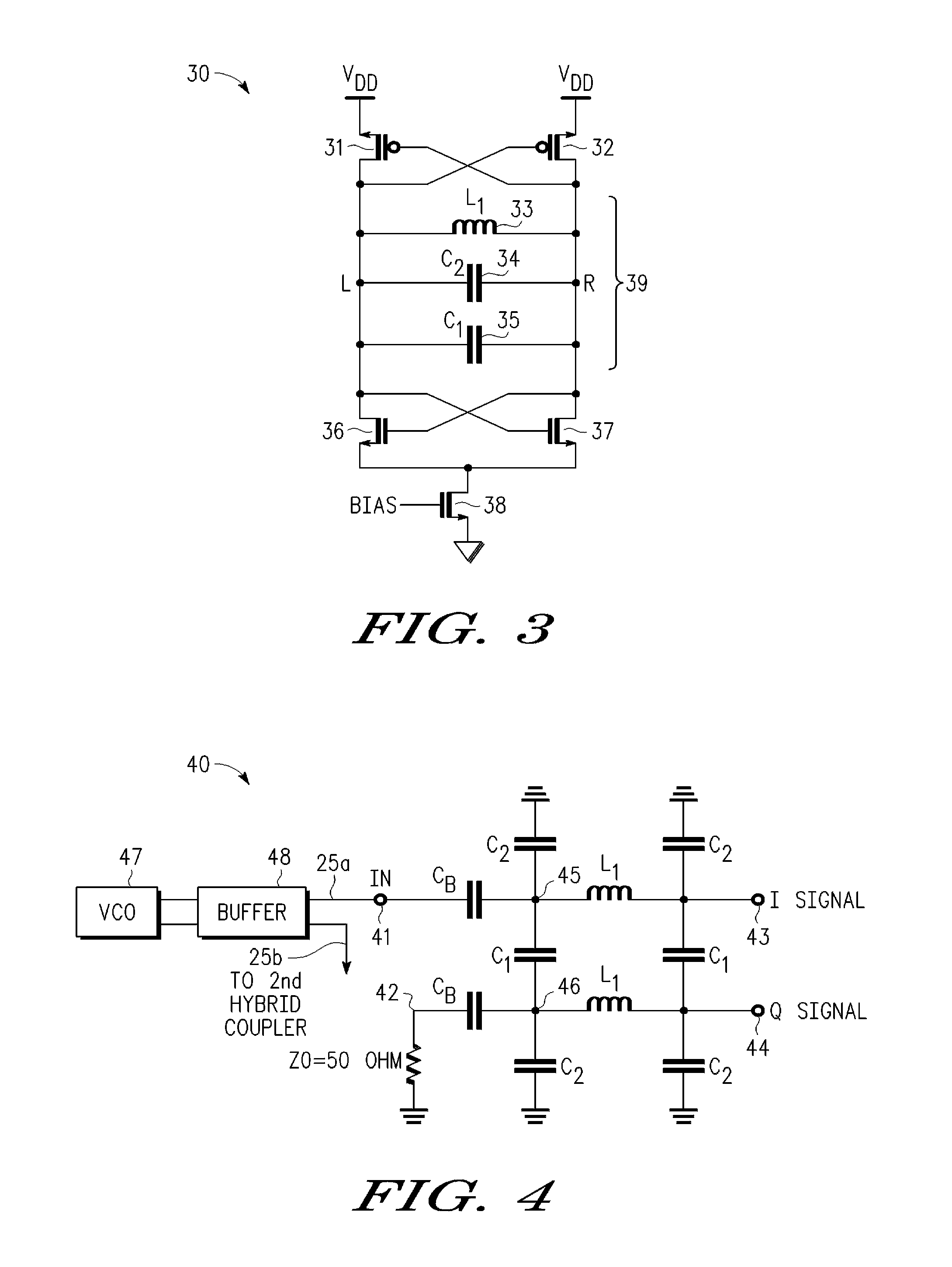
Calibrated Quadrature Generation for Multi-GHZ Receiver
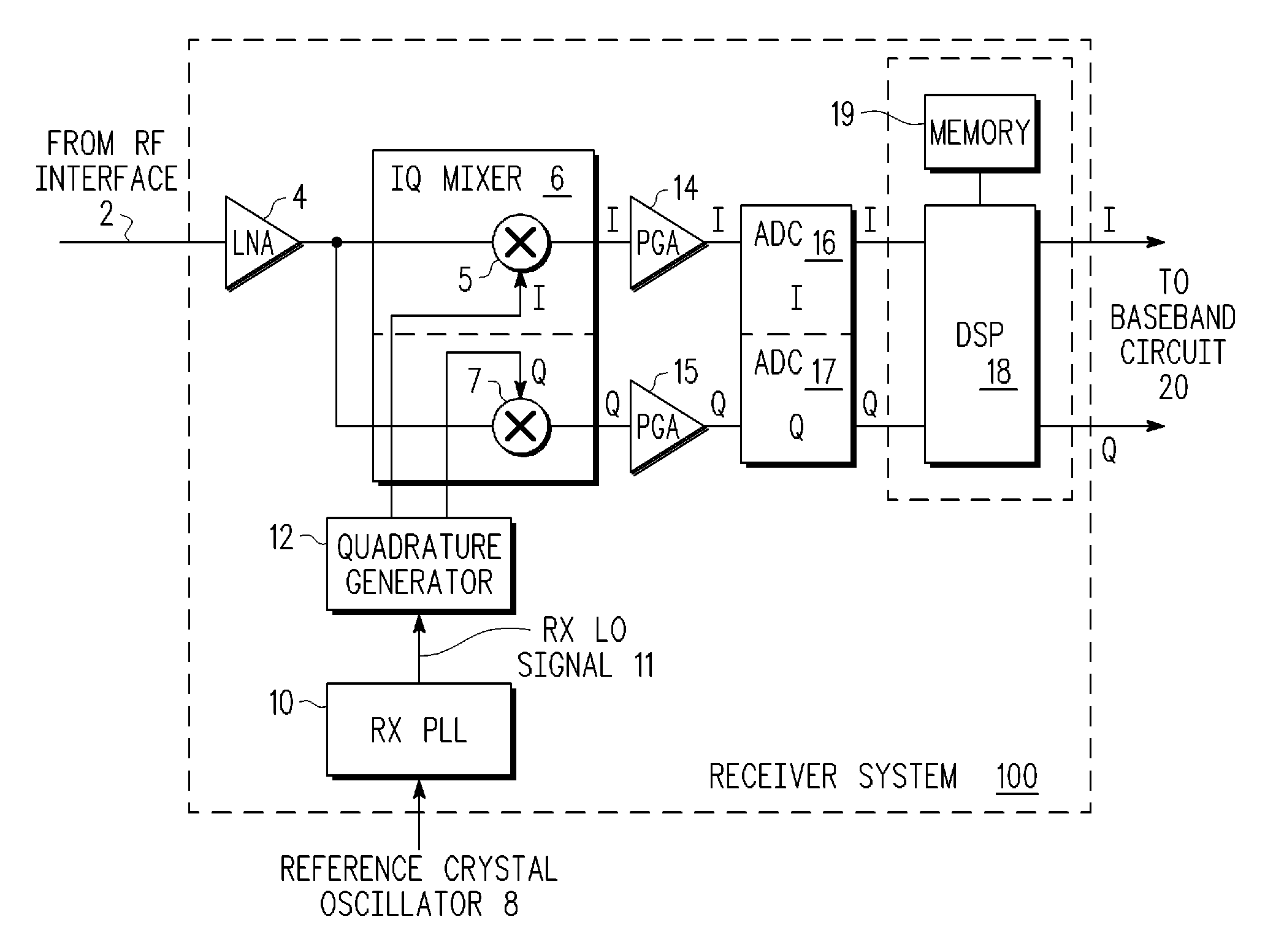
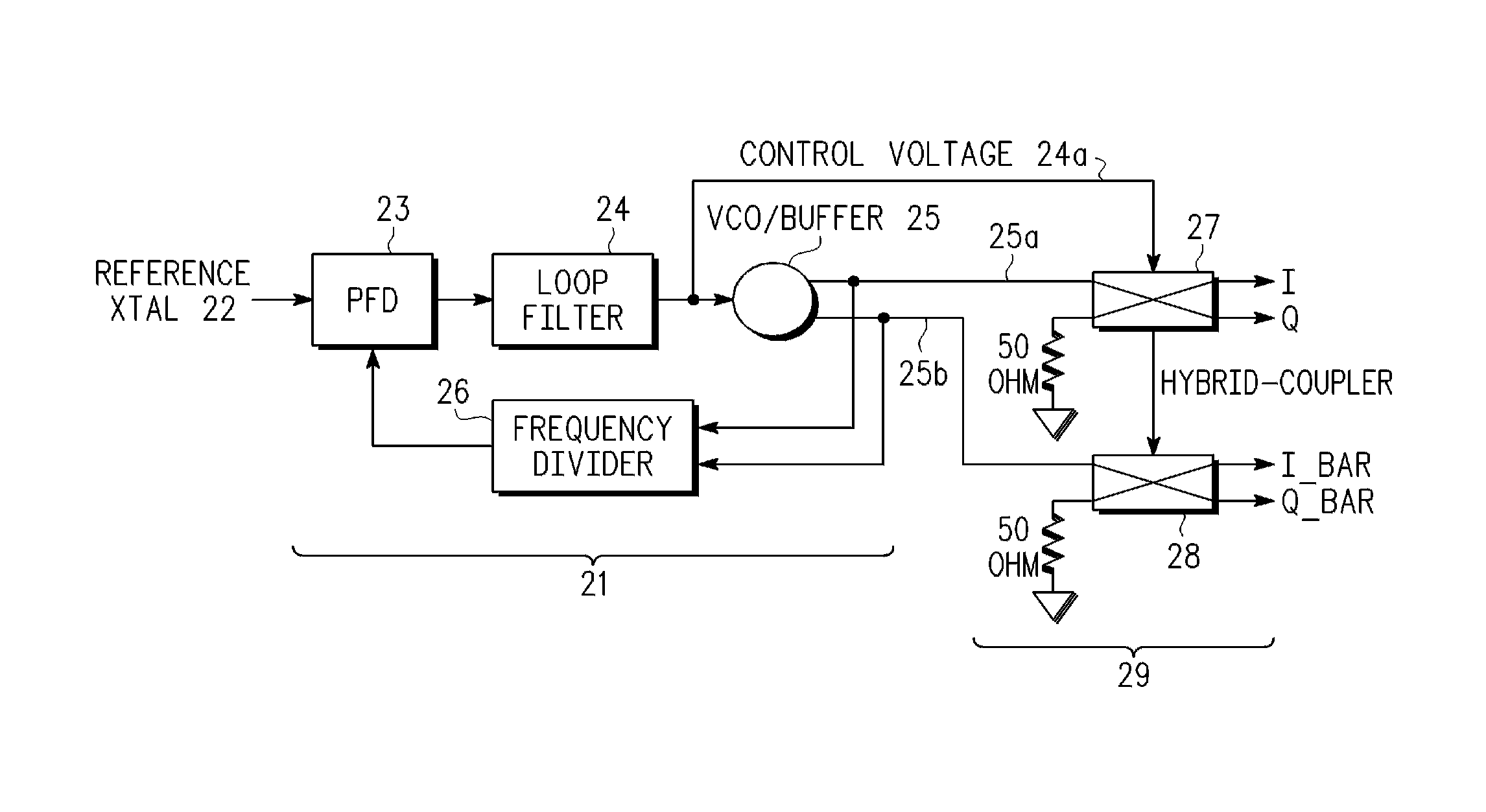
InactiveUS20090279642A1Impedence matching networksBalance-unbalance networksPhase locked loop circuitEngineering
An integrated receiver circuit includes aphase locked loop circuit (21) with a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) (25) and a quadrature generator circuit (29) which uses hybrid-branch line coupler circuits (27, 28) coupled to buffered VCO outputs, where the hybrid-branch line coupler circuits (27, 28) are tuned by same control voltage (25a) that controls the VCO (25). By replicating the VCO core circuitry in each hybrid-branch line coupler circuit (27, 28) under common control of a control voltage, calibrated quadrature signals are generated that have the same frequency as the phase locked loop circuit (21).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Digital noise coupling reduction and variable intermediate frequency generation in mixed signal circuits
InactiveUS20050265483A1Modulated-carrier systemsAmplitude demodulation detailsCommunications systemIntermediate frequency
A communications system comprises a local oscillator configured to generate a local oscillator output and a signal processing component coupled to the local oscillator. The signal processing component is configured to receive a clock signal and the clock signal is derived from the local oscillator output. A method of demodulating an input signal comprises deriving a conversion signal from a local oscillator output, deriving a clock signal from the local oscillator output, mixing the input signal with the conversion signal to generate an intermediate frequency signal, and processing the intermediate frequency signal using a signal processing component driven by the clock signal. A method of modulating an input signal comprise deriving a conversion signal from a local oscillator output, deriving a clock signal from the local oscillator output, processing the input signal using a signal processing component driven by the clock signal to generate an intermediate frequency signal and mixing the intermediate frequency signal with the conversion signal to generate a modulated signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
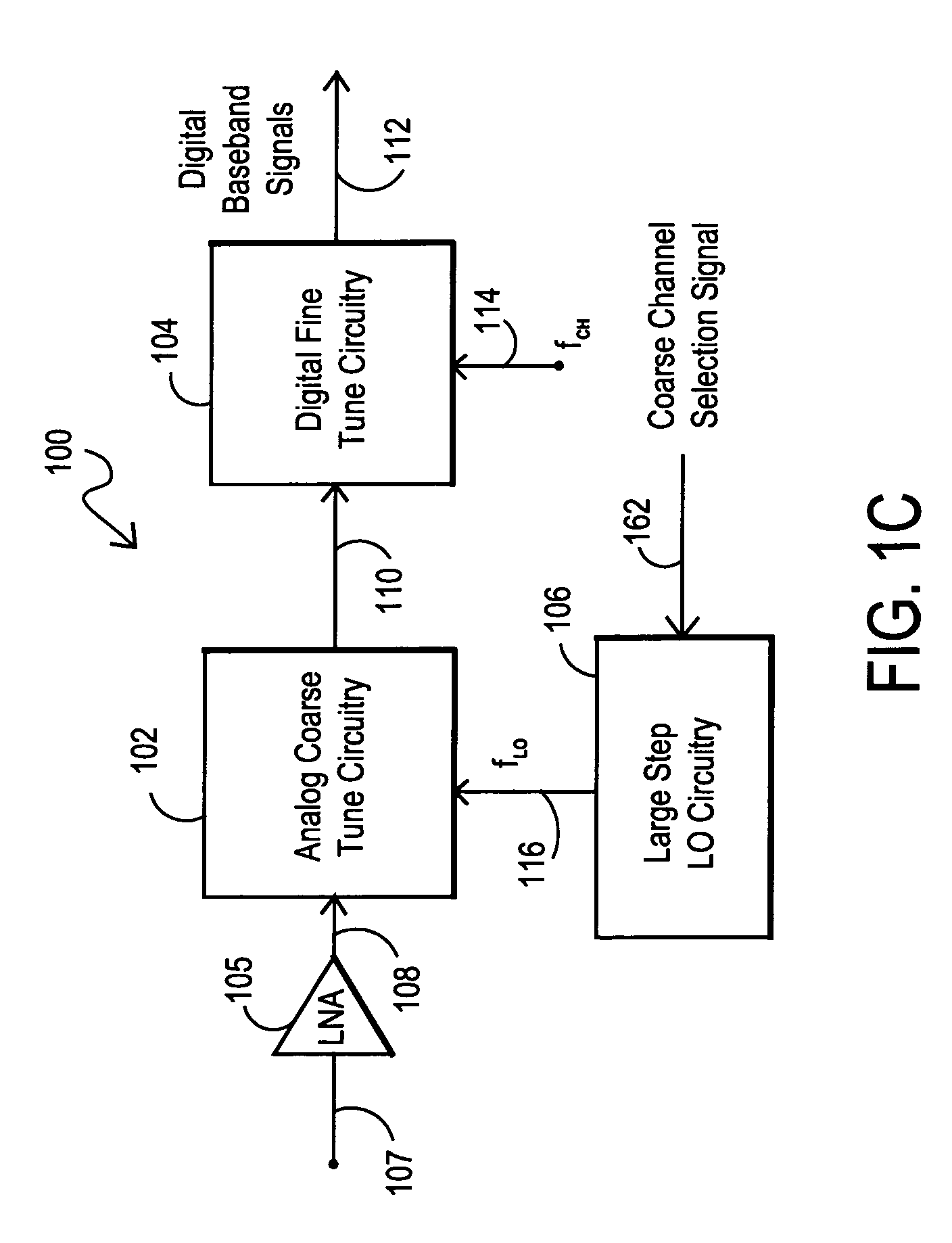
Receiver architectures utilizing coarse analog tuning and associated methods
ActiveUS7340230B2Avoiding interference and noise problemEasy to useTelevision system detailsSatellite broadcast receivingFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Receiver architectures and associated methods are disclosed that provide initial analog coarse tuning of desired channels within a received signal spectrum, such as a set-top box signal spectrum for satellite communications. These architectures provide significant advantages over prior direct down-conversion (DDC) architectures and low intermediate-frequency (IF) architectures, particularly where two tuners are desired on the same integrated circuit. Rather than using a low-IF frequency or directly converting the desired channel frequency to DC, initial coarse tuning provided by analog coarse tuning circuitry allows for a conversion to a frequency range around DC. This coarse tuning circuitry can be implemented, for example, using a large-step local oscillator (LO) that provides a coarse tune analog mixing signal. Once mixed down, the desired channel may then be fine-tuned through digital processing, such as through the use of a wide-band analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a narrow-band tunable bandpass ADC.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
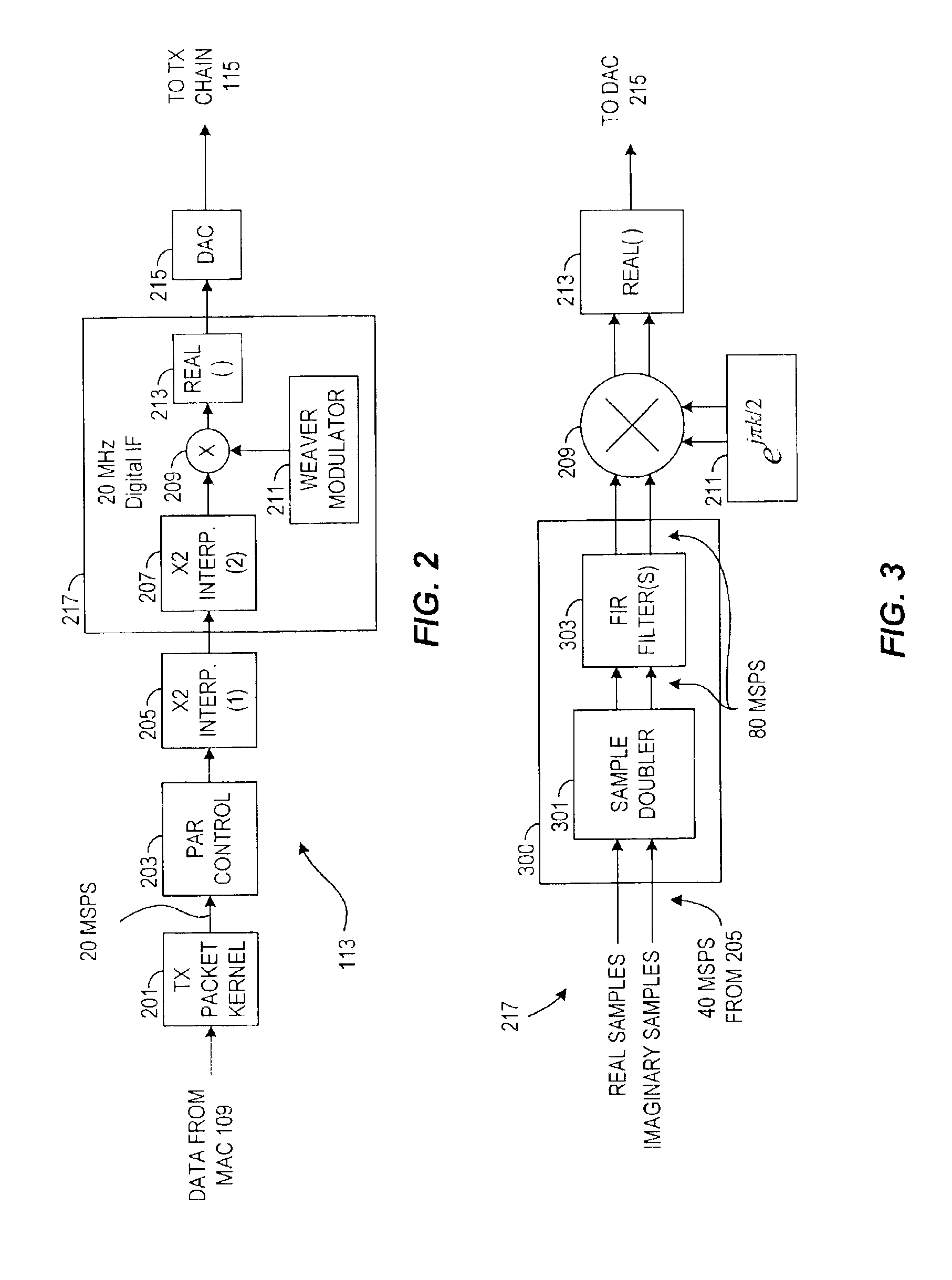
Integrated modulator and demodulator configuration
InactiveUS6876319B2Reduce circuit areaLow costDigital technique networkAnalogue conversionMultiplexerEngineering
An integrated demodulator and decimator circuit including a selective digital sign inverter and a decimator. The sign inverter negates selected digital samples based on Weaver demodulation and outputs demodulated digital samples at a sample rate. The decimator is a symmetric half-band FIR filter, where the demodulated digital samples are sequentially shifted through filter taps at the sample rate. The decimator outputs real output values based on digital samples shifted into alternate taps and imaginary output values based on digital samples shifted into the center tap. An integrated modulator and interpolator circuit includes a symmetric half-band FIR filter interpolator and a digital sign inverter. The interpolator includes two polyphase filters and a multiplexer. A first polyphase filter filters real digital samples and a second filters imaginary digital samples. The multiplexer provides interpolated digital samples at four times the sample rate. The digital sign inverter negates selected digital samples according to Weaver modulation.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
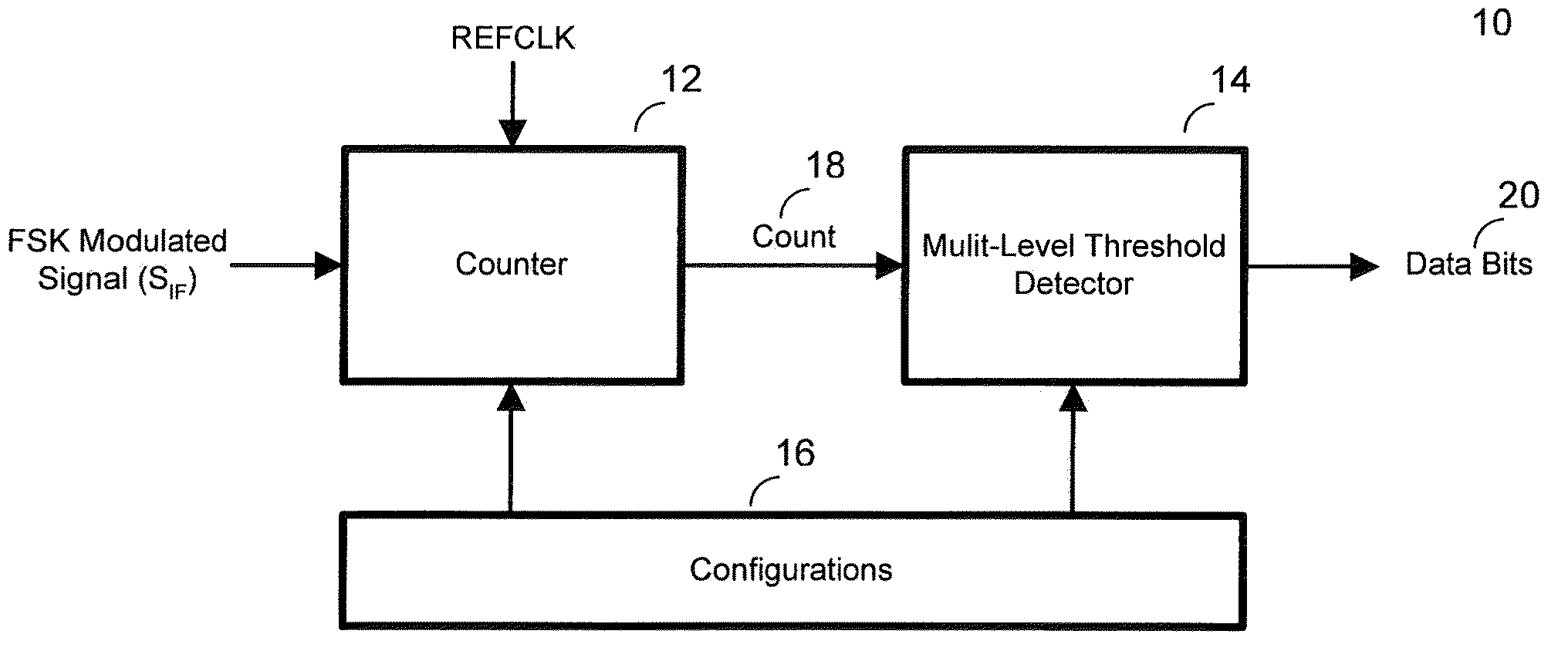
Configurable demodulator and demodulation method
ActiveUS20090096519A1Angle modulationFrequency-modulated carrier systemsFrequency shiftComputer science
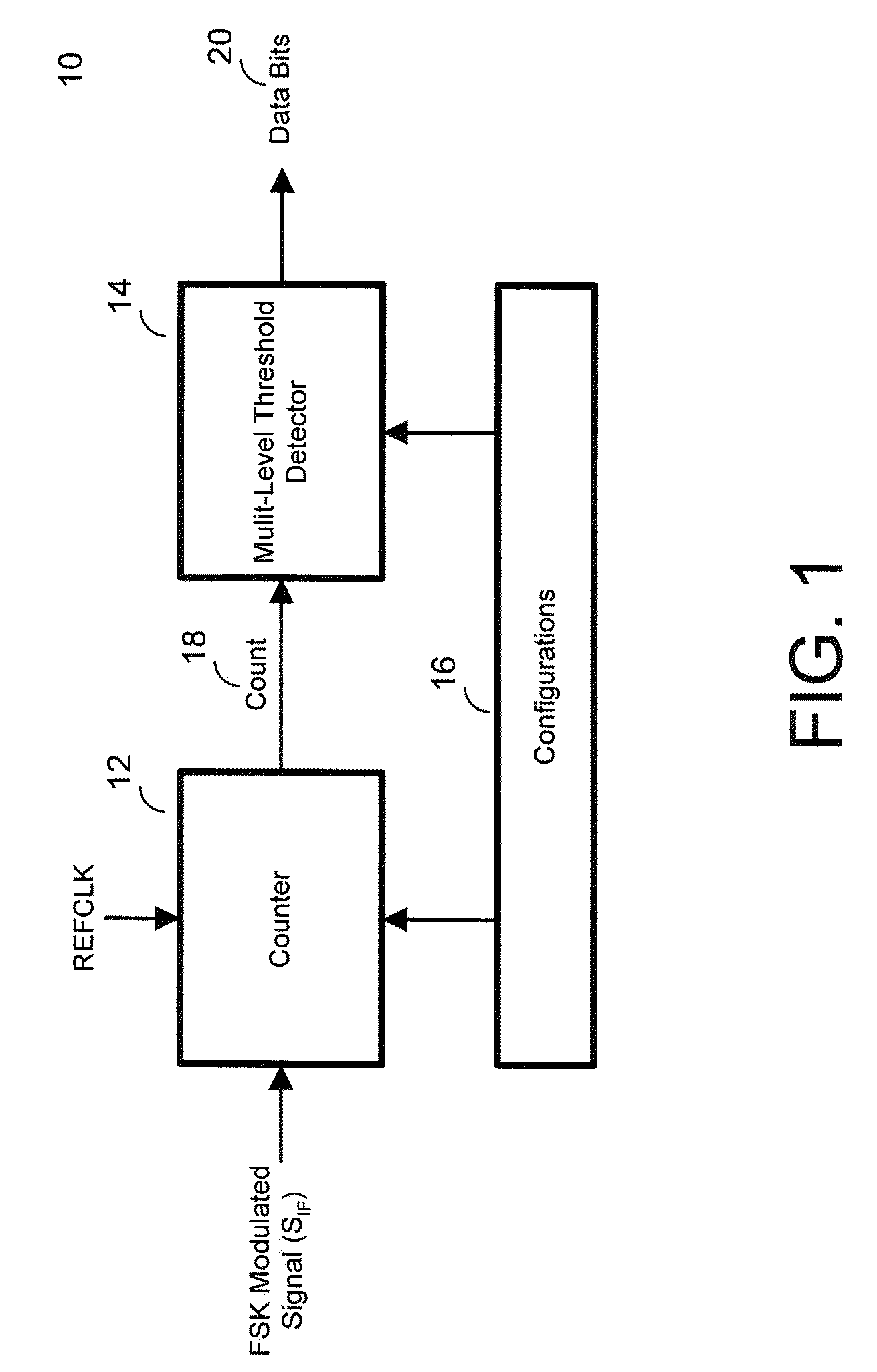
A method and system for a frequency shift key demodulation is provided. The system includes a counting block for counting a reference clock within a window defined by a modulated signal, a detector for comparing a count value output from the counting block with digital multi-level thresholds and outputting baseband data based on the comparison, and a configurations block for configuring at least one of the counting block and the detector. The method includes counting a reference clock within a window defined by the FSK modulated signal and outputting a count value as a result of the counting, and comparing the count value with multi-level thresholds to output baseband data based on the comparison.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Transceiver including a high latency communication channel and a low latency communication channel
ActiveUS20140126613A1Lower latencyAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionSynchronising arrangementTransceiverDelay-locked loop
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are described for reducing the latency in a transceiver. A transceiver includes a high latency communication channel and a low latency communication channel that is configured to be a bypass channel for the high latency communication channel. The low latency communication channel may be utilized when implementing the transceiver is used in low latency applications. By bypassing the high latency communication channel, the high latency that is introduced therein (due to the many stages of de-serialization used to reduce the data rate for digital processing) can be avoided. An increase in data rate is realized when the low latency communication channel is used to pass data. A delay-locked loop (DLL) may be used to phase align the transmitter clock of the transceiver with the receiver clock of the transceiver to compensate for a limited tolerance of phase offset between these clocks.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
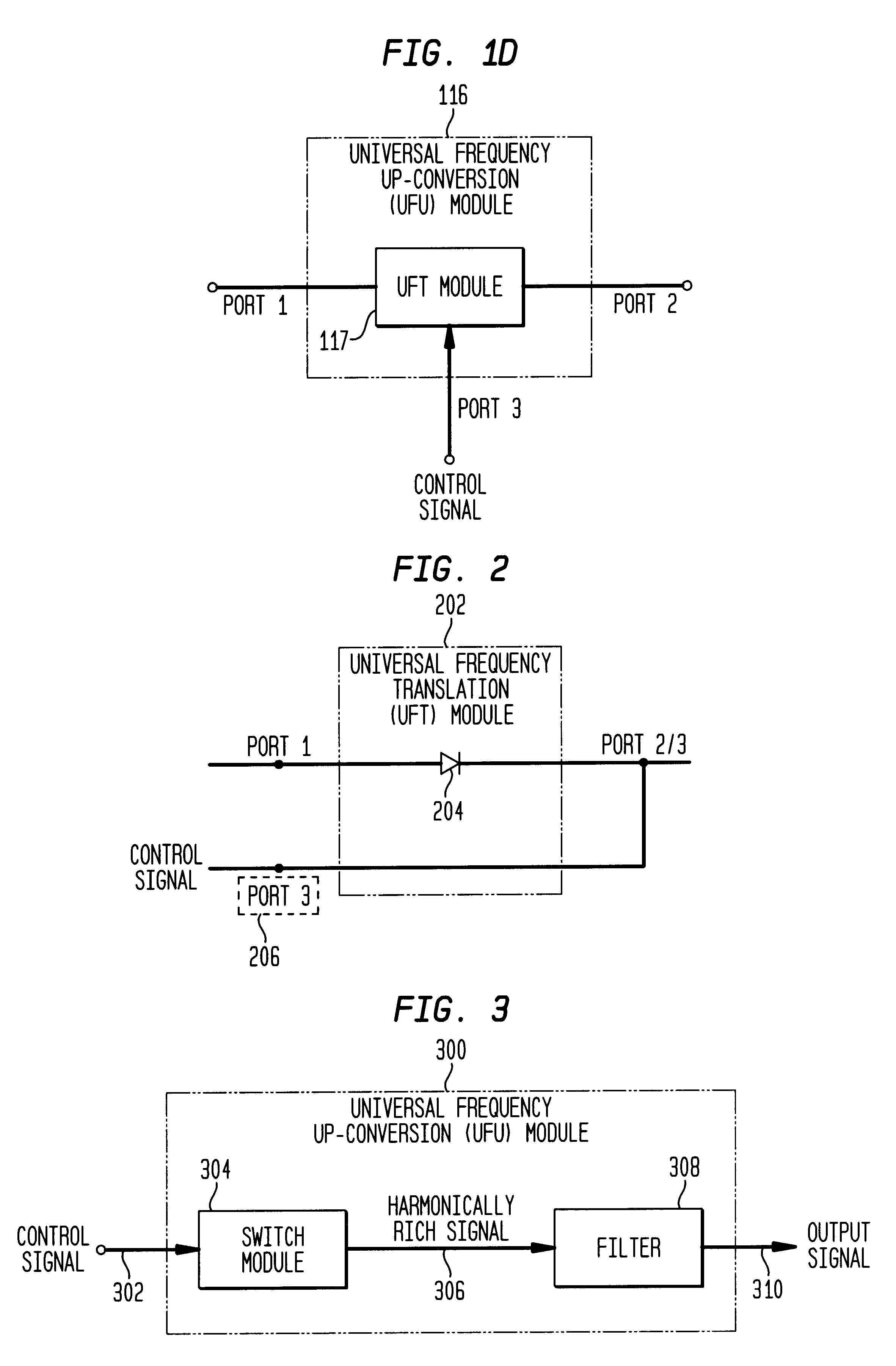
Reducing DC offsets using spectral spreading
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Calibrated quadrature generation for multi-GHz receiver
InactiveUS8243855B2Impedence matching networksBalance-unbalance networksPhase locked loop circuitEngineering
An integrated receiver circuit includes a phase locked loop circuit (21) with a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) (25) and a quadrature generator circuit (29) which uses hybrid-branch line coupler circuits (27, 28) coupled to buffered VCO outputs, where the hybrid-branch line coupler circuits (27, 28) are tuned by same control voltage (25a) that controls the VCO (25). By replicating the VCO core circuitry in each hybrid-branch line coupler circuit (27, 28) under common control of a control voltage, calibrated quadrature signals are generated that have the same frequency as the phase locked loop circuit (21).
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
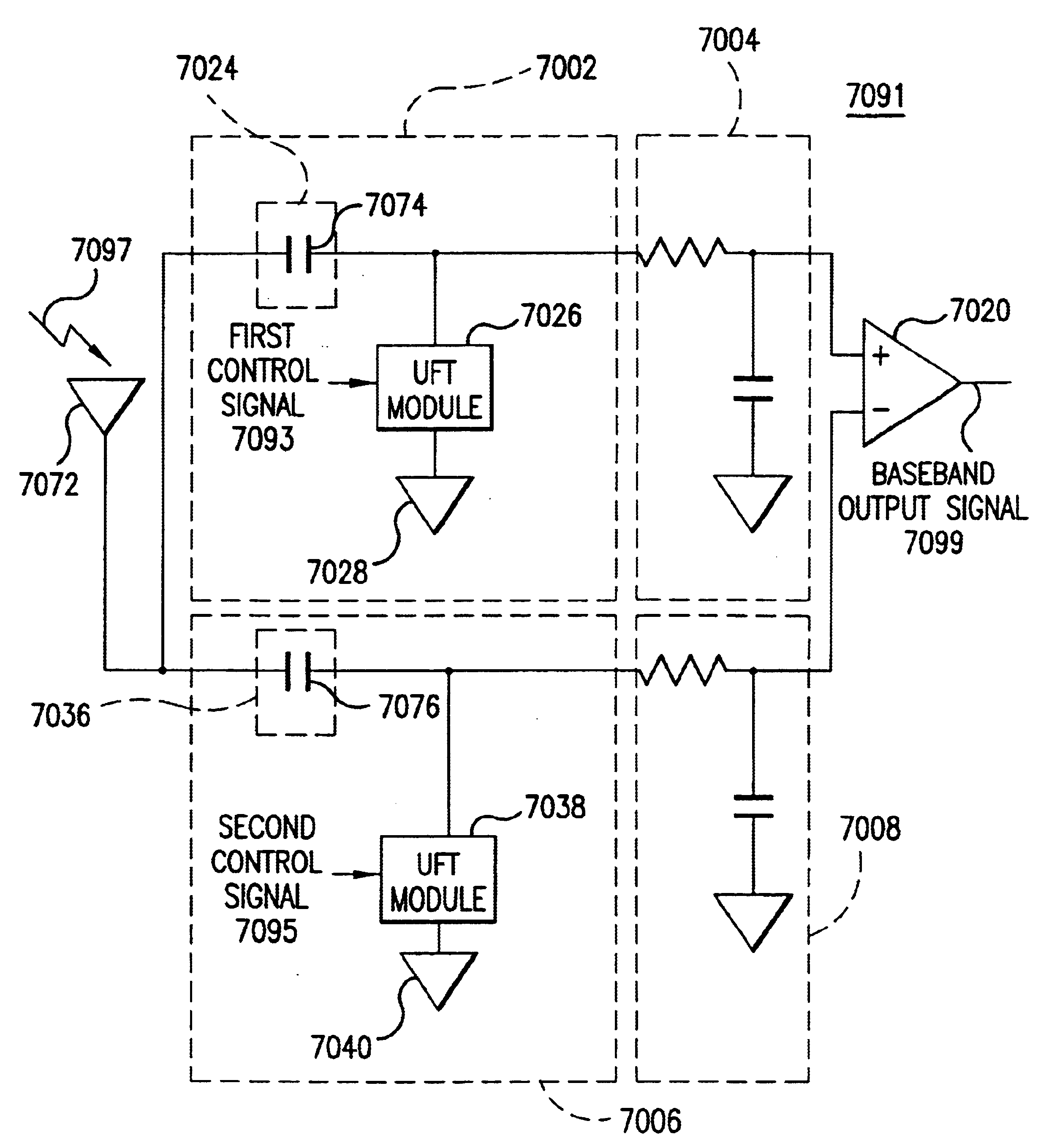
Method and apparatus for reducing re-radiation using techniques of universal frequency translation technology
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Method and apparatus for reducing DC offsets in communication systems using universal frequency translation technology
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
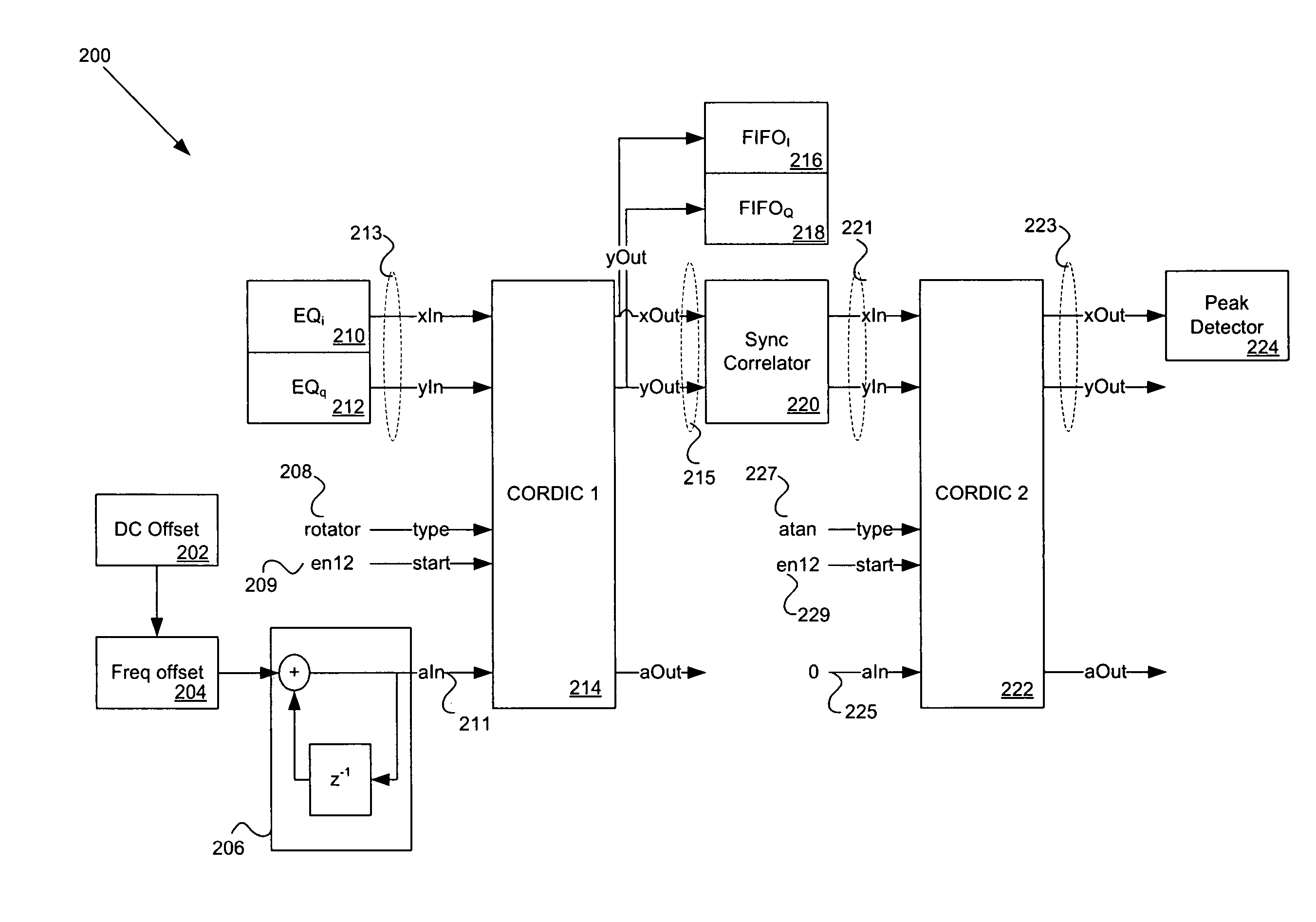
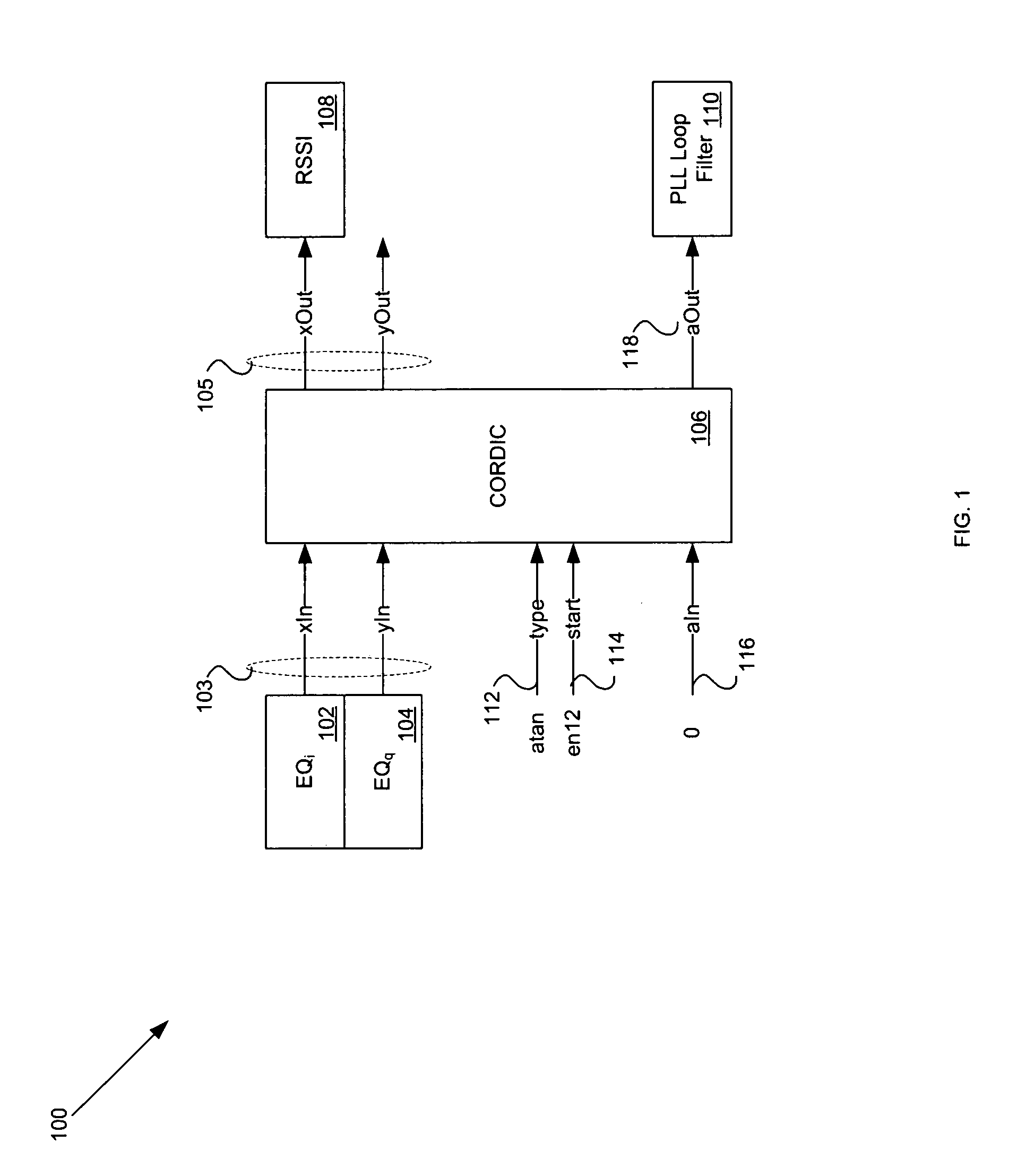
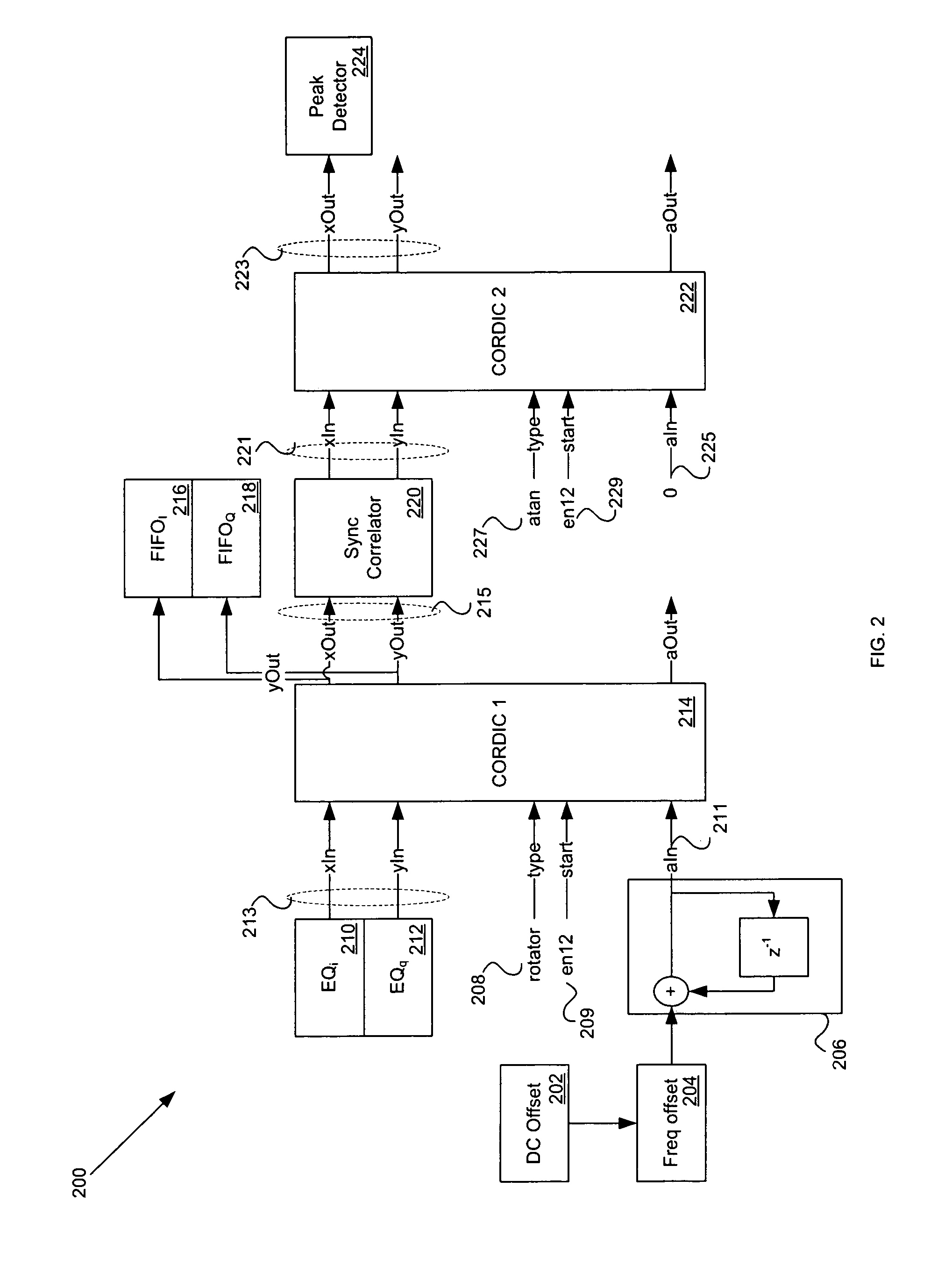
Method and system for reuse of CORDIC in an RF transceiver by reconfiguration in real time
InactiveUS20060093070A1Frequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransceiverMegabit
Methods and systems for processing an RF signal are disclosed herein. Aspects of the method may comprise utilizing a single input CORDIC and a single output CORDIC for synchronizing and demodulating a received signal, wherein the received signal may comprise one or more bit rates. The received signal may comprise a one megabit per second (Mbps) signal. The single input CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and the single output CORDIC may be configured to operate in a rotating mode and / or an arctangent (ARCTAN) mode. A rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be correlated with a phase shift keying (PSK) synchronization (sync) word and a portion of the correlated rotated output of the single input CORDIC may be buffered.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Universal platform module and methods and apparatuses relating thereto enabled by universal frequency translation technology
A communication system comprising a multi-protocol, multi-bearer sub-system is described herein. The sub-system is a universal platform module that can transmit and receive one or more information signals in one or more protocols using one or more bearer services. In one embodiment, the sub-system may form a portion of a transceiver that is composed of a transmitter and a receiver, and which is a gateway server between a personal area network (PAN) and the global wireless network.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
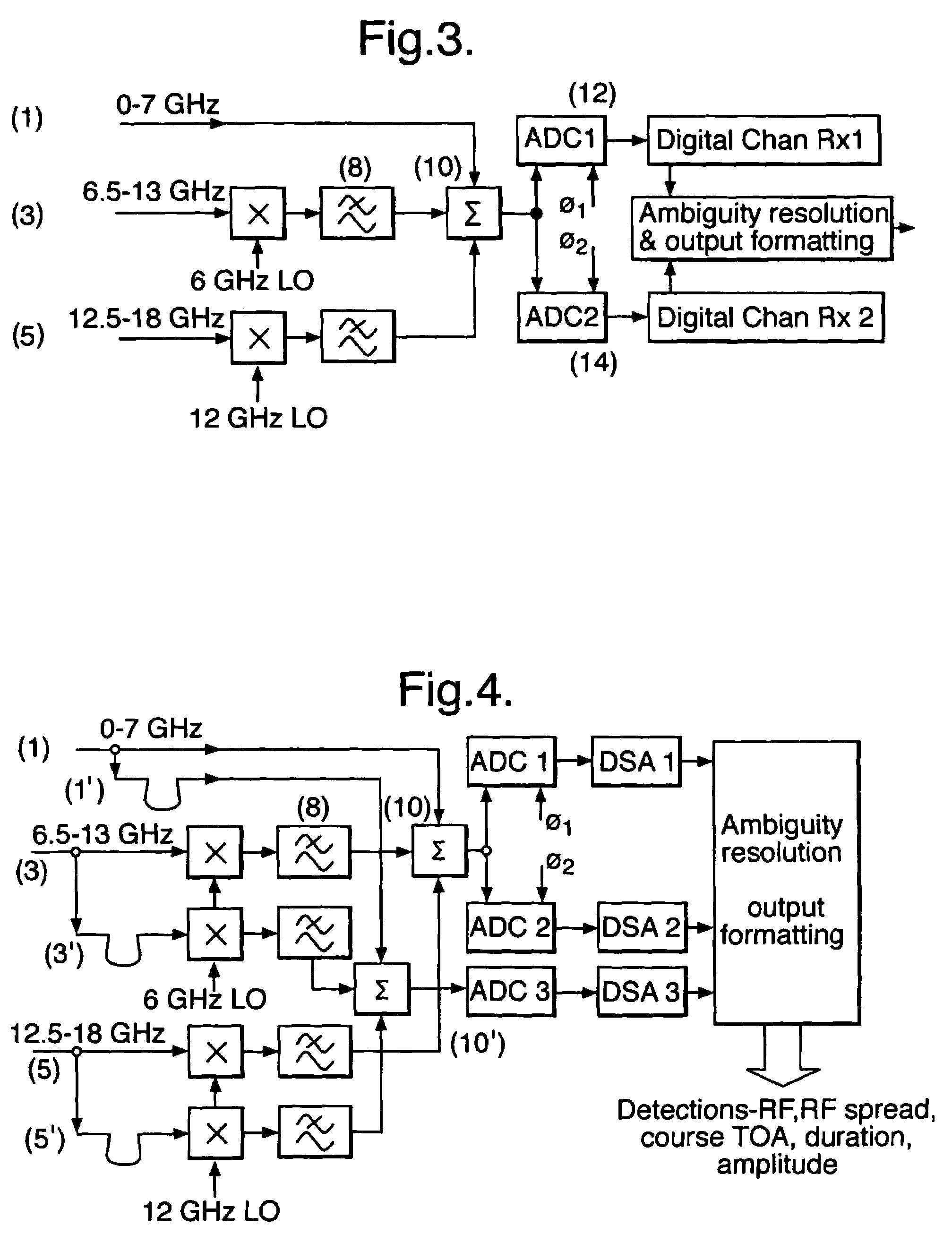
Digital electronic support measures
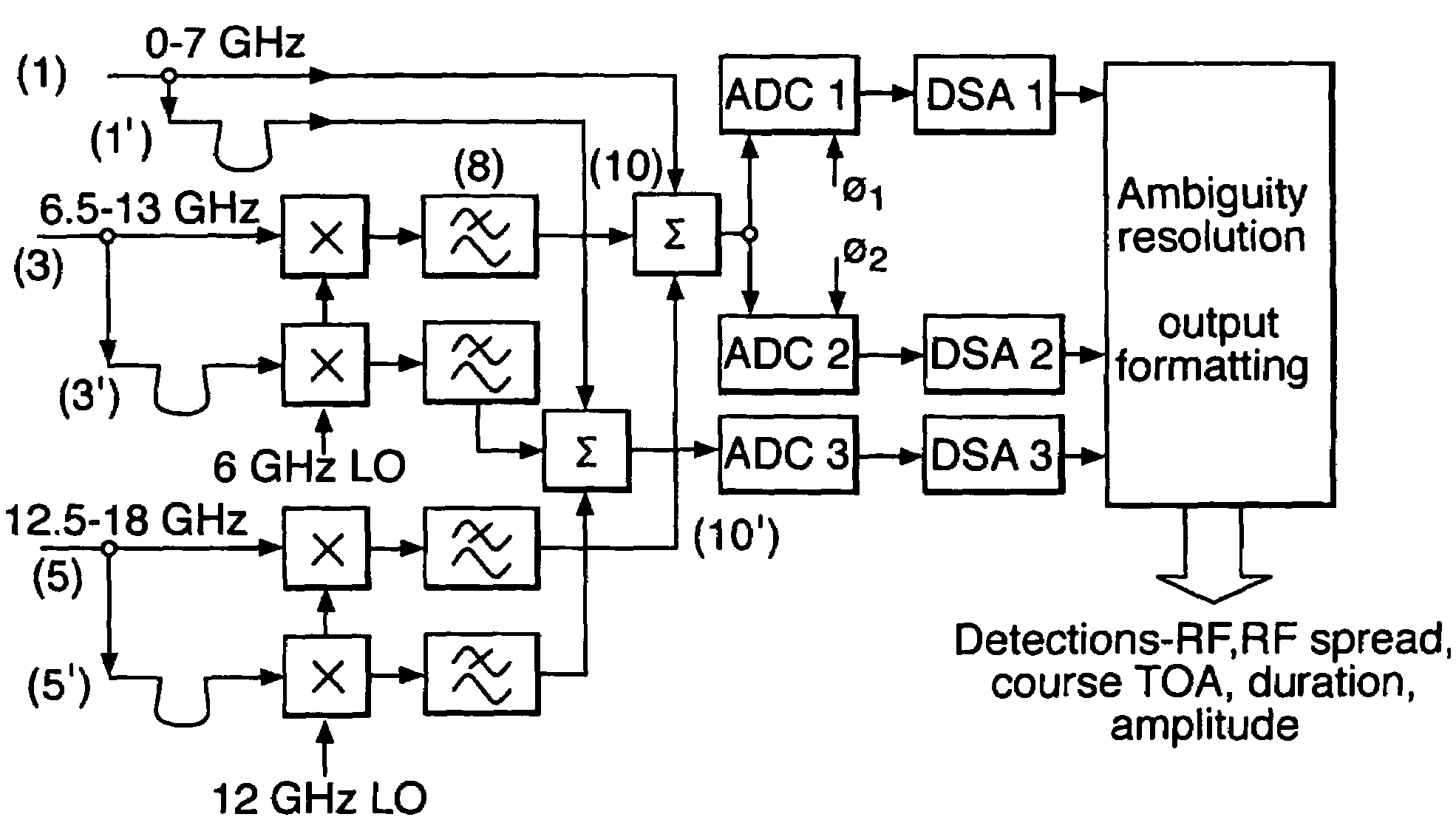
ActiveUS7482967B2Reduce ambiguityGreat freedomCommunication jammingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClock rateAmbiguity
An apparatus for characterising an input signal within abroad frequency band by comparing the same input signal in a plurality of channels, in order to operate digital Electronic Support Measures (ESM) which require a broad bandwidth to function. The apparatus comprises one or more signal input bands spread across the broad frequency band, a means of splitting the input signal in each input band into a plurality of separate channels, and a means of sampling each channel, wherein the sampling means in each channel runs at a different clock rate from sampling means in each of the other channels within the input bands, so as to remove the ambiguities inherent in frequency aliasing.
Owner:THE SEC OF STATE FOR DEFENCE IN HER BRITANNIC MAJESTYS GOVERNMENT OF THE UK OF GREAT BRITAIN & NORTHERN IRELAND
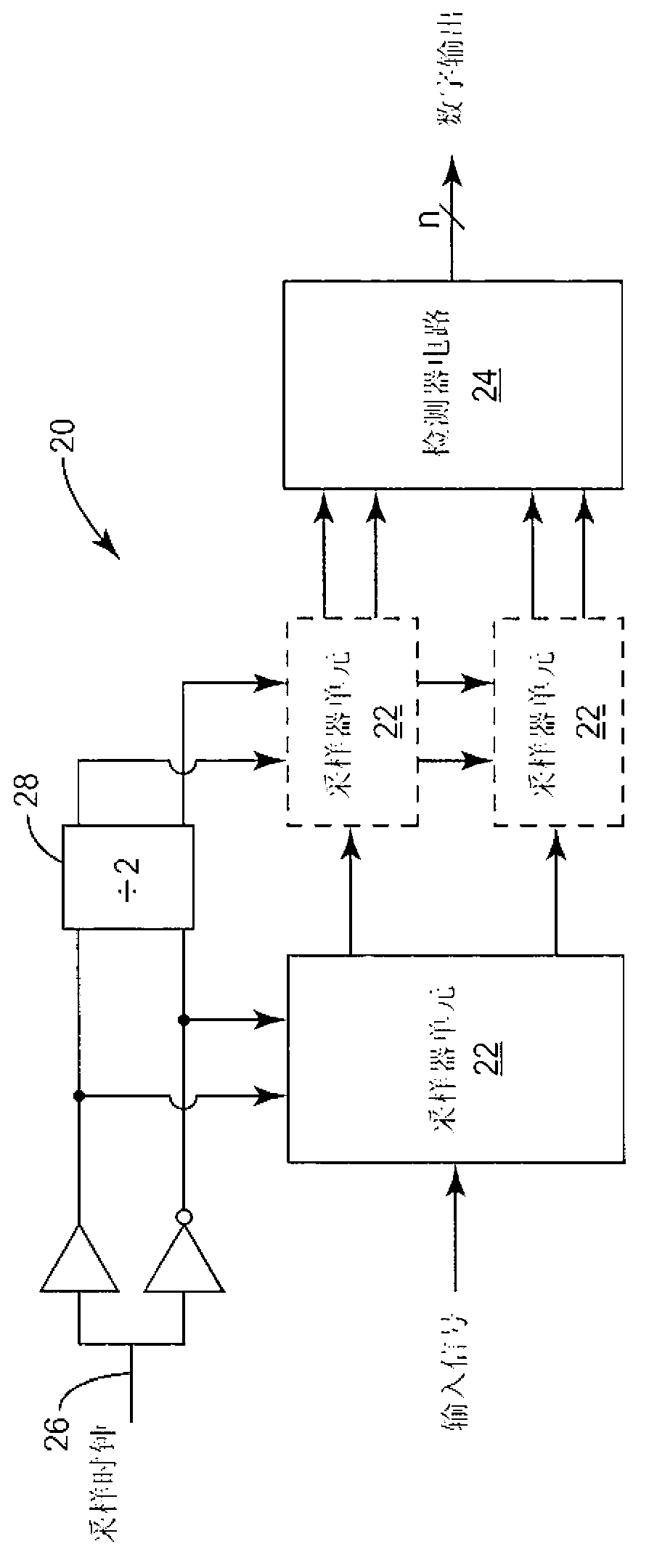
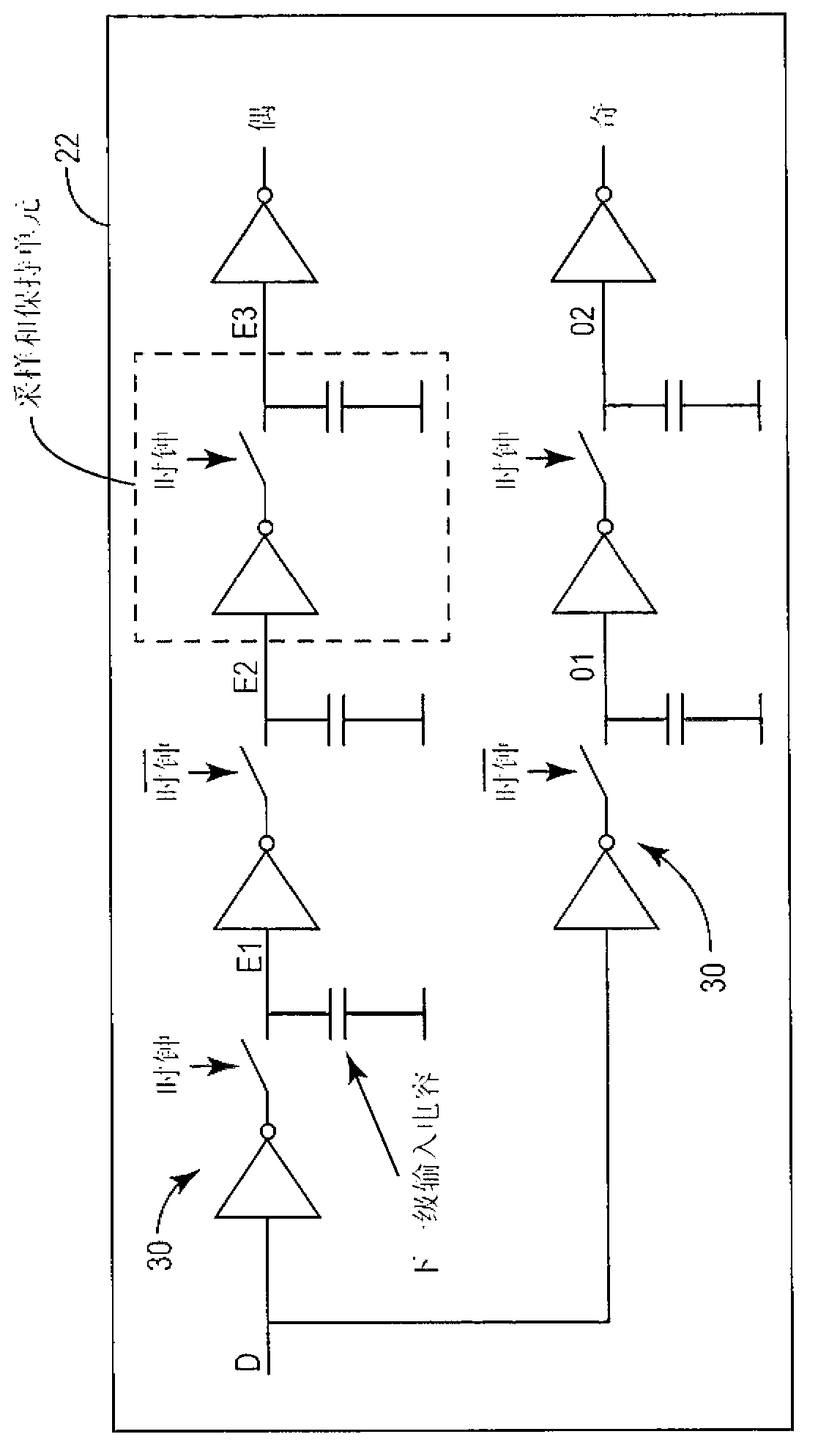
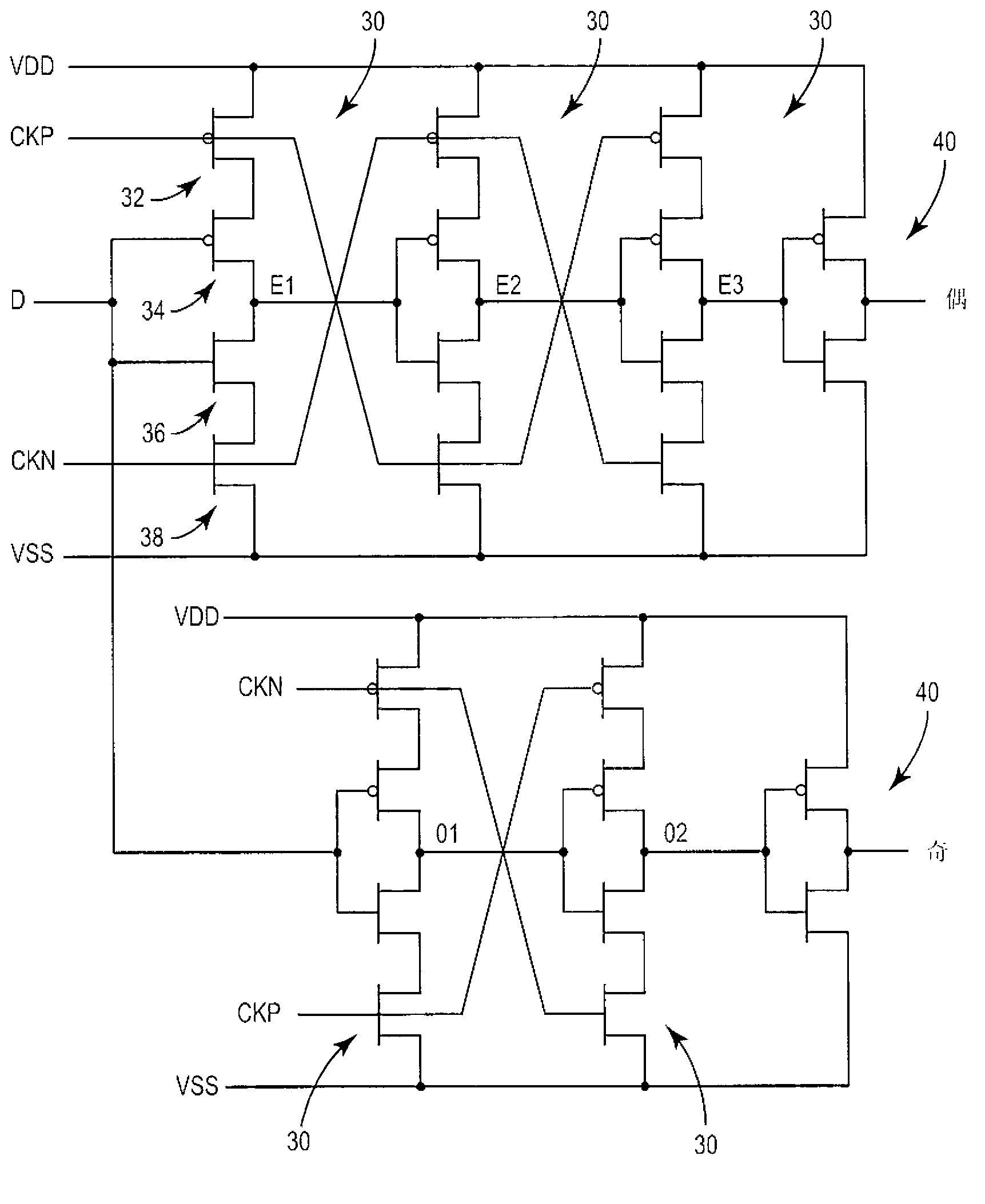
Sampler circuit
ActiveCN103141029APulse automatic controlOscillations comparator circuitsDetector circuitsLow power dissipation
A sampler circuit comprises a plurality of series-connected sampler cells and a detector circuit. Each successive stage comprises twice the number of sampler cells, in parallel, as the previous stage, and is clocked at half the sampling frequency of the previous stage. Each sampler cell comprises two parallel branches of series-connected clocked inverters. A clocked inverter is operative to invert an applied signal during one phase of an applied sampling clock, and to render a high impedance output during the other sampling clock phase. Successive clocked inverters are clocked with opposite (i.e., positive / negative) versions of the sampling clock. The detector circuit examines the outputs of the last stage of sampler cells, and may for example comprise an OR function to detect a state transition in an applied input signal. The sampler circuit exhibits immunity to metastability and low power consumption.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
All-digital FM stereo demodulator and demodulation method
InactiveUS6901146B1Easy to implementPerformance requirementBroadcast circuit arrangementsTransmissionAudio frequencyComputer science
A stereo composite signal including a pilot signal is demodulated by processing input samples to obtain internal samples having variable sampling timings, synchronizing these sampling timings with the pilot signal, and digitally processing the internal samples to obtain stereo audio data. The internal samples may be obtained from the input samples by decimation or interpolation. Since the sampling frequency and sampling timing of the input samples do not have to be precisely controlled, no voltage-controlled oscillator is needed, and the demodulator can easily be incorporated into a monolithic integrated circuit.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Method and apparatus for improving dynamic range in a communication system
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
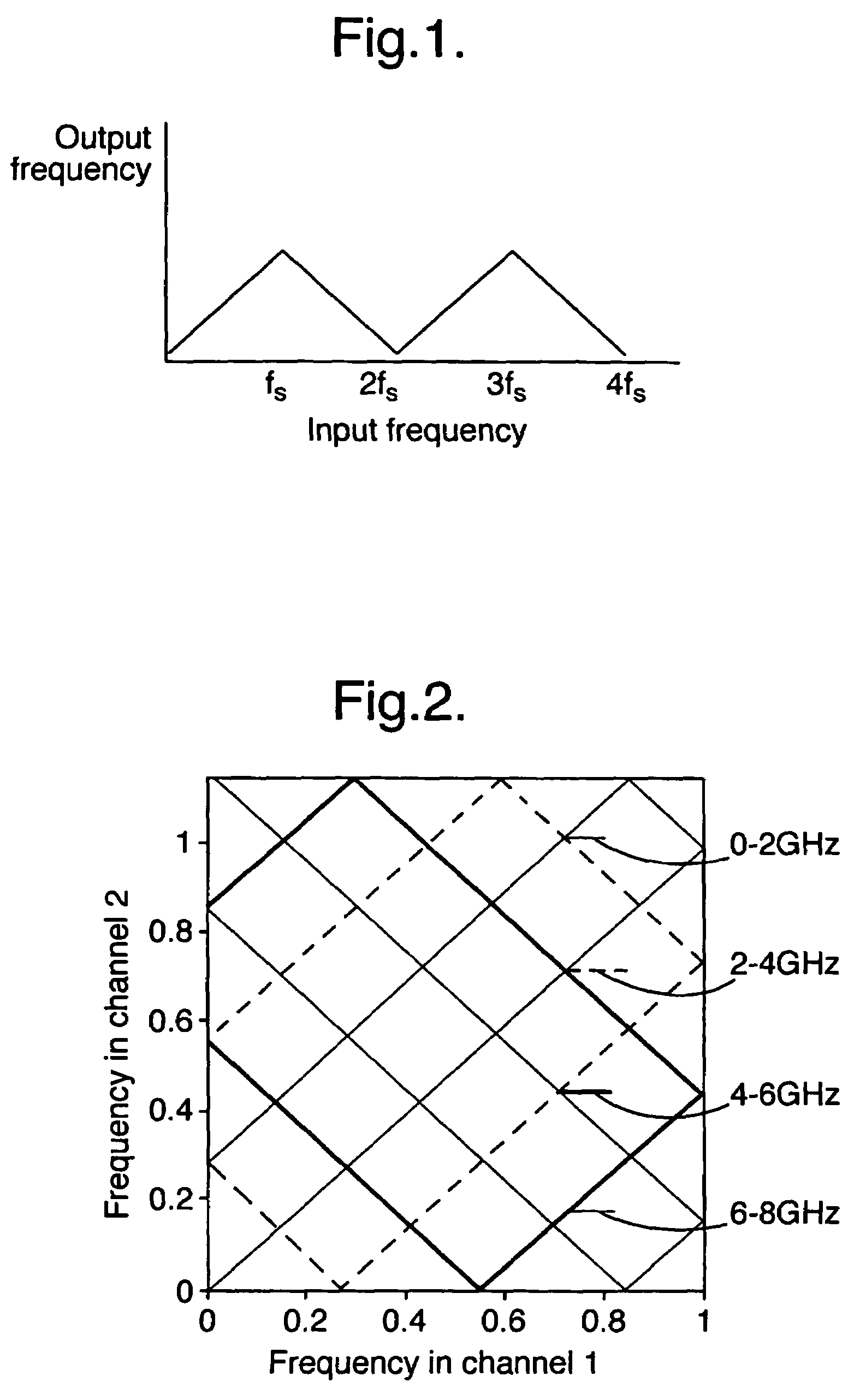
Digital signal processing circuit and method comprising band selection
ActiveUS20100174768A1Reduce the amount of calculationReduce in quantityDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsDigital signal processingFrequency spectrum
A digital signal processing circuit comprises a band selector (14) for selecting at least one sub-band from a frequency spectrum of a digital sampled input signal. The band selector (14) comprises a plurality of processing branches corresponding to respective phases and an adder (28a, 28b) for adding branch signals from the branches. Each branch comprises a subsampler (20a,b) for sub-sampling sample values of the input signal at the phase corresponding to the branch, a filter (24a,b) with a first FIR filter (32, 34), applied alternatingly to sets of even and to sets of odd samples from the subsampler (20a,b) and a second FIR filter (36, 38) applied to further sets of odd and even samples from the subsampler (20a,b) when the first FIR filter is applied to the even and odd sets respectively. Output samples from the first and second FIR filter (24a,b) are combined to form the branch signals of the branch, according to a changing combination pattern that changes cyclically as a function of sample position and depends on a phase for which the branch is used.
Owner:NXP BV
Popular searches
Amplitude to angle modulation conversion Home automation networks Data switching by path configuration Multi-frequency-changing modulation transference Computing operations for multiplication/division Oscillations generators Delay line applications Time-varying network Transmission monitoring Data switching networks
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com