A detachable wound and neonatal umbilical cord care device
A nursing device, a technology for newborns, applied in abdominal bandages, breast bandages, etc., can solve the problems of catheter wound injury, increased material and labor costs, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., to achieve the effect of tension-free fixation and elimination of skin damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
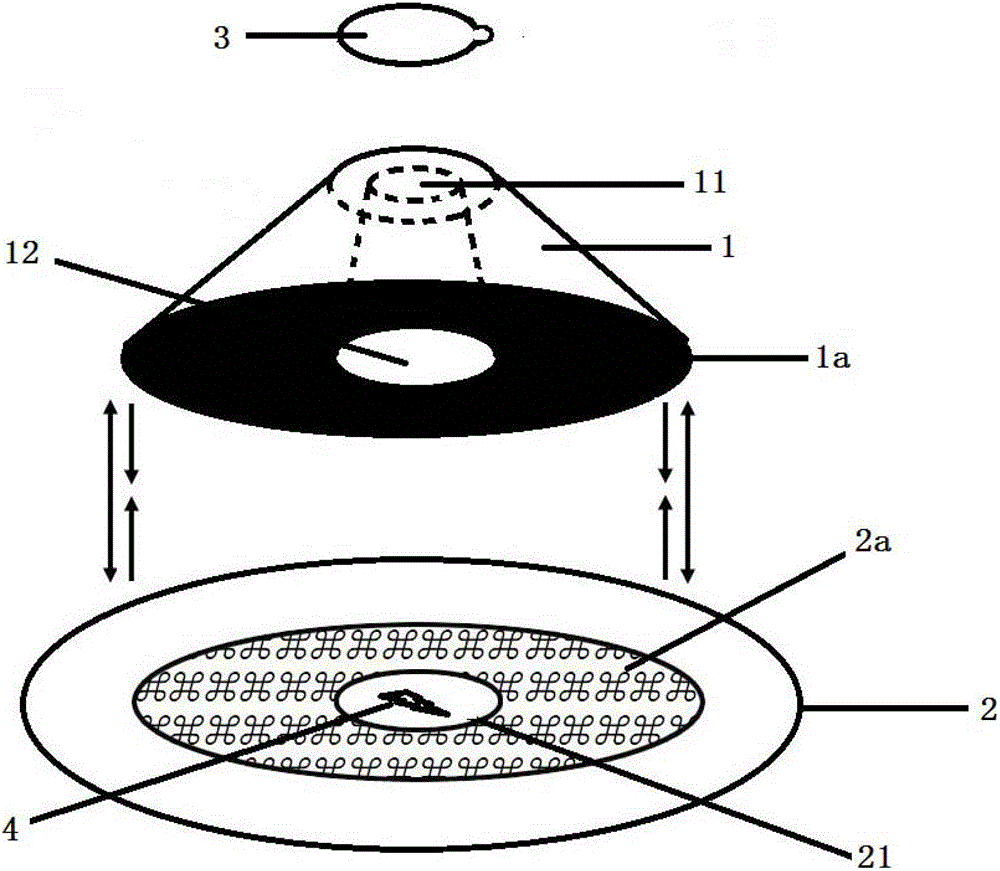
[0054] see Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 , the device for wound and neonatal umbilical cord care in this embodiment includes a protective body 1 and a fixed body 2 , and a cover 3 arranged above the protective body 1 .
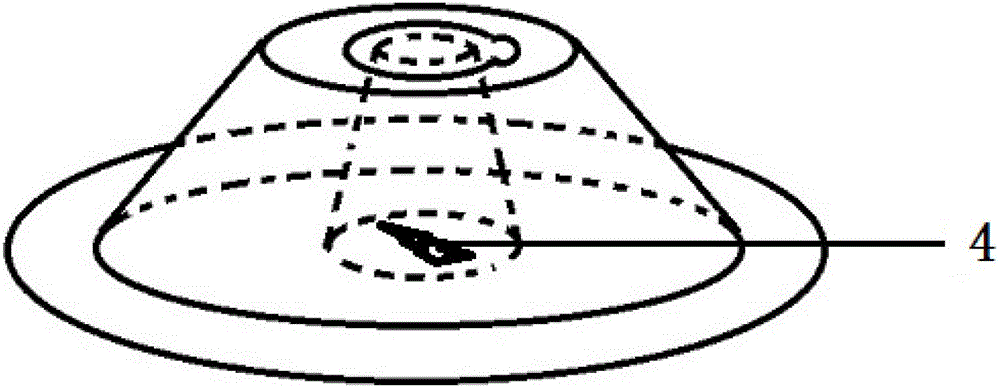
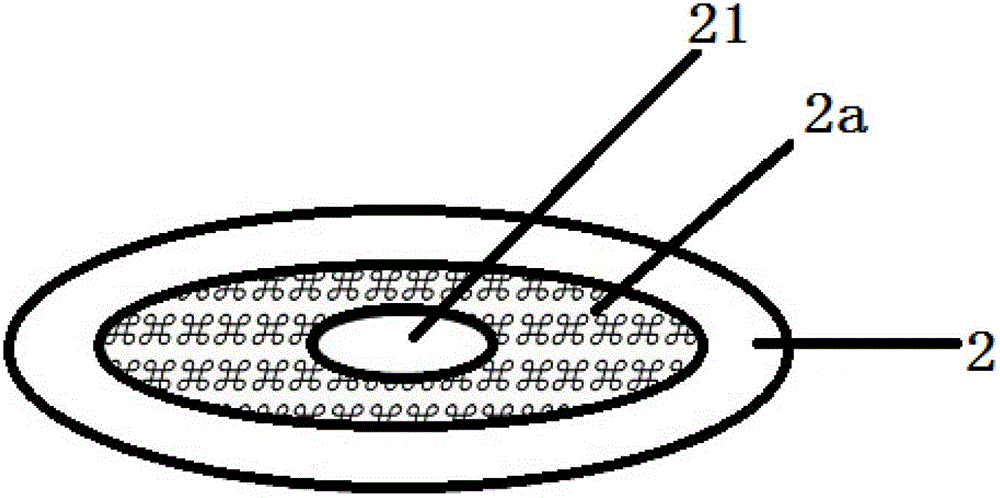
[0055] Wherein, the protective body 1 is an open cavity protective body, which is in the shape of a circular frustum, and is provided with through holes running through its upper and lower surfaces, so that its upper surface and lower surface are all provided with openings 11 and 12; the lower surface of the protective body 1 is provided with There is a detachable bonding surface, which is an adhesive bonding surface 1a, located around the opening 12 on the lower surface of the protective body; Openings 21 on the upper and lower surfaces, the upper surface of the fixed body is provided with a detachable bonding surface, the detachable bonding surface is a fluffy surface bonding surface 2a, located around the opening 21 on the upper surface of the fixed body; the fixed ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Referring to 12 and 13, the detachable wound and neonatal umbilical cord care device in this embodiment includes a protective body 1 and a fixed body 2. The lower surface of the protective body 1 has a villi surface bonding surface 1b, and the upper surface of the fixed body 2 The surface is provided with a hook and loop surface bonding surface 2b containing an adhesive; the pile surface bonding surface 1b and the hook and loop surface bonding surface 2b containing an adhesive can be firmly connected or separated in a detachable manner. The protective body 1 in this embodiment is a belt-shaped opening cavity protective body, which is thick in the middle and thin at both ends, and has the same structure as Figure 7 The structure of the protective body shown is the same, and the different side surfaces of the two ends along the length direction have hook and loop fasteners 14; wherein, the structure of the fixed body 2 is still disc-shaped, and its upper surface is provid...
Embodiment 3
[0074] see Figure 14 , Figure 15 , Figure 16 The detachable wound and neonatal umbilical cord care device in this embodiment includes a protective body 1 and a fixed body 2. The structure of the protective body 1 is a flat square body-shaped protective sticker. The protective sticker is not provided with openings, and its lower surface is provided with There is a pile surface bonding surface 1b containing an adhesive, an opening 1c is formed in the middle of the pile surface bonding surface 1b, and the fixed body is in the shape of a square plate, which is provided with an opening 21, and its upper surface does not contain a separable bonding surface . The fixed body 2 is bonded and fixed on the wound or the skin around the umbilical cord through the adhesive on the back, and its opening 21 surrounds the wound 4 or the umbilical cord. The upper surface of 2 is firmly bonded, so that the protective body 1 can not only cover the wound 4 or the umbilical cord, absorb the ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com