Catalyst and method for performing carboxyl reaction on C6 of bacterial cellulose
A bacterial cellulose and catalyst technology, applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, organic compounds/hydrides/coordination complex catalysts, etc., can solve the problems of poor experimental repeatability, poor controllability, and cellulose oxidation. Overshoot and other problems, to achieve the effects of high controllability and repeatability, increased yield, and easy storage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0050] When 1 gram of dry bacterial cellulose is used as the reaction raw material: TEMPO / NaClO 2 / NaClO system
[0051] 1) Add 1 g of lyophilized BC and 300 ml of phosphate buffer solution (0.05 mol / L, pH=6.5) into a three-necked flask, and stir well.
[0052] 2) During stirring, add 0.012g TEMPO and 1.2g NaClO in sequence 2 .
[0053] 3) Take 1ml of analytically pure NaClO solution (relative density (water=1): 1.10g / ml, 10% available chlorine), and add it to 1mL of deionized water. After mixing evenly, add to the above system.
[0054] 4) The above-mentioned system is sealed, stirred, and heated to 60°C.
[0055] 5) After 24 hours, stop heating and pour 65ml of ethanol. Centrifuge at 10,000r / min for 15 minutes to obtain a sol-like product, and put it in a -78°C refrigerator for 24 hours.
[0056] 6) Freeze drying. Cold trap temperature -50°C, vacuum degree 0.05atm, 3 days. A fibrous dry material is obtained.
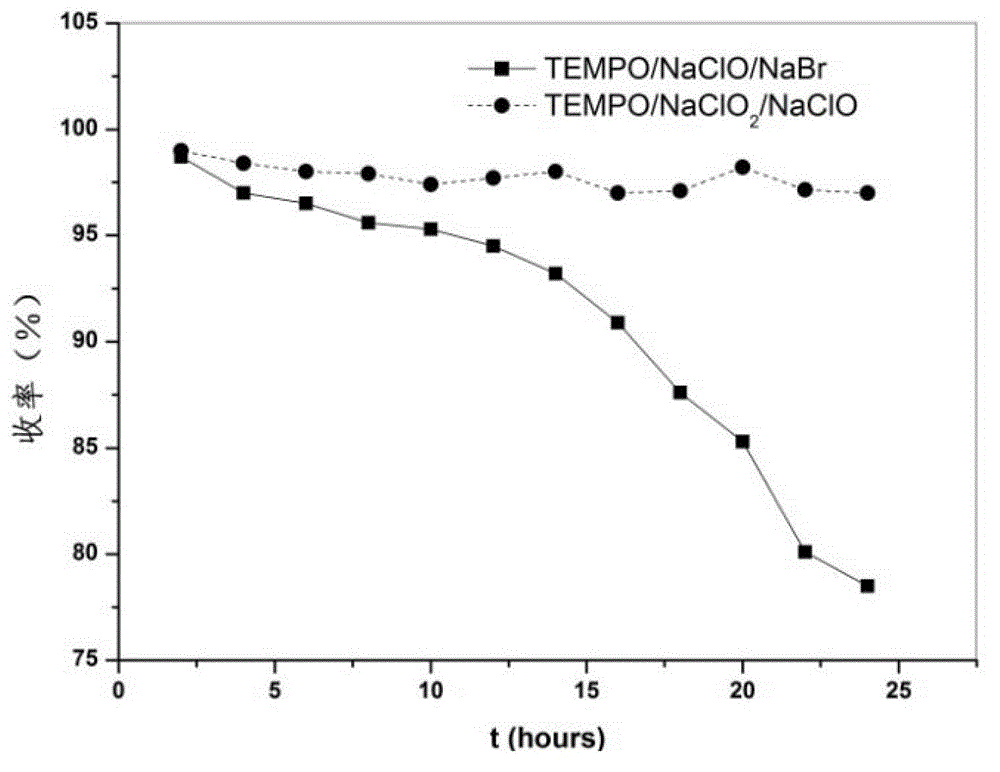
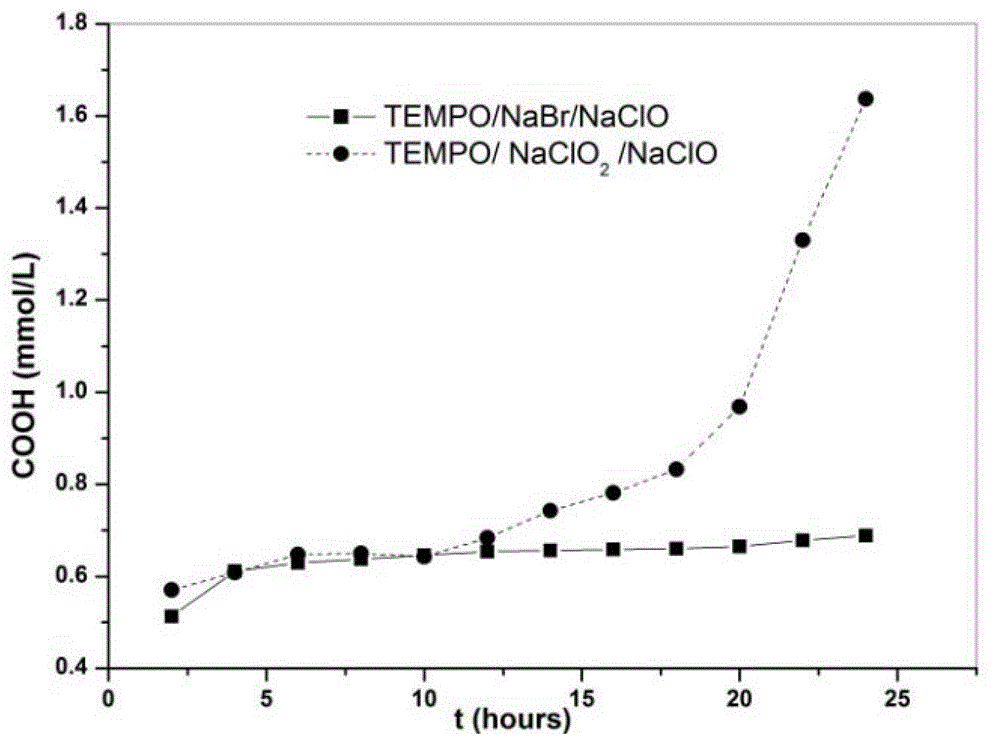
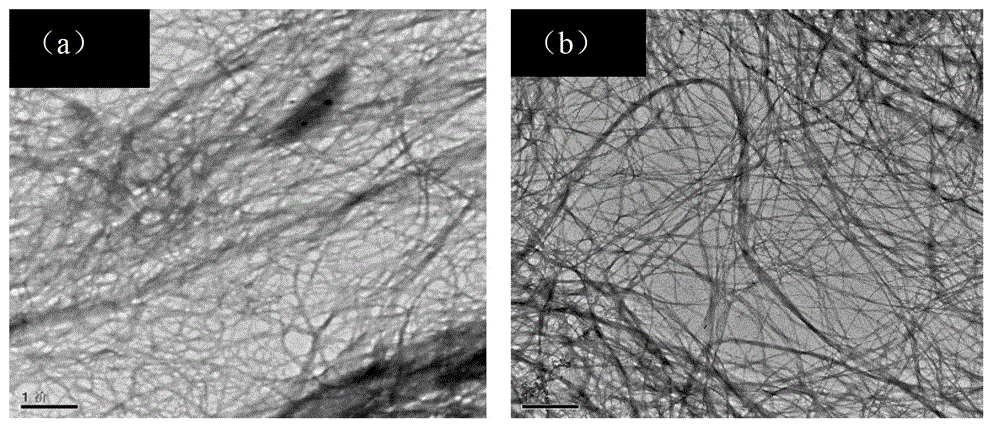
[0057] Compare the resulting products above:
[0058] 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com