Test method for achieving electromagnetic transient real-time simulation of electrical power system based on CUDA (compute unified device architecture) parallel computing
An electromagnetic transient simulation and electromagnetic transient technology, which is applied in the direction of concurrent instruction execution and machine execution devices, can solve the problems of expensive prices and achieve the effects of model simplification, performance improvement, and simulation speed improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
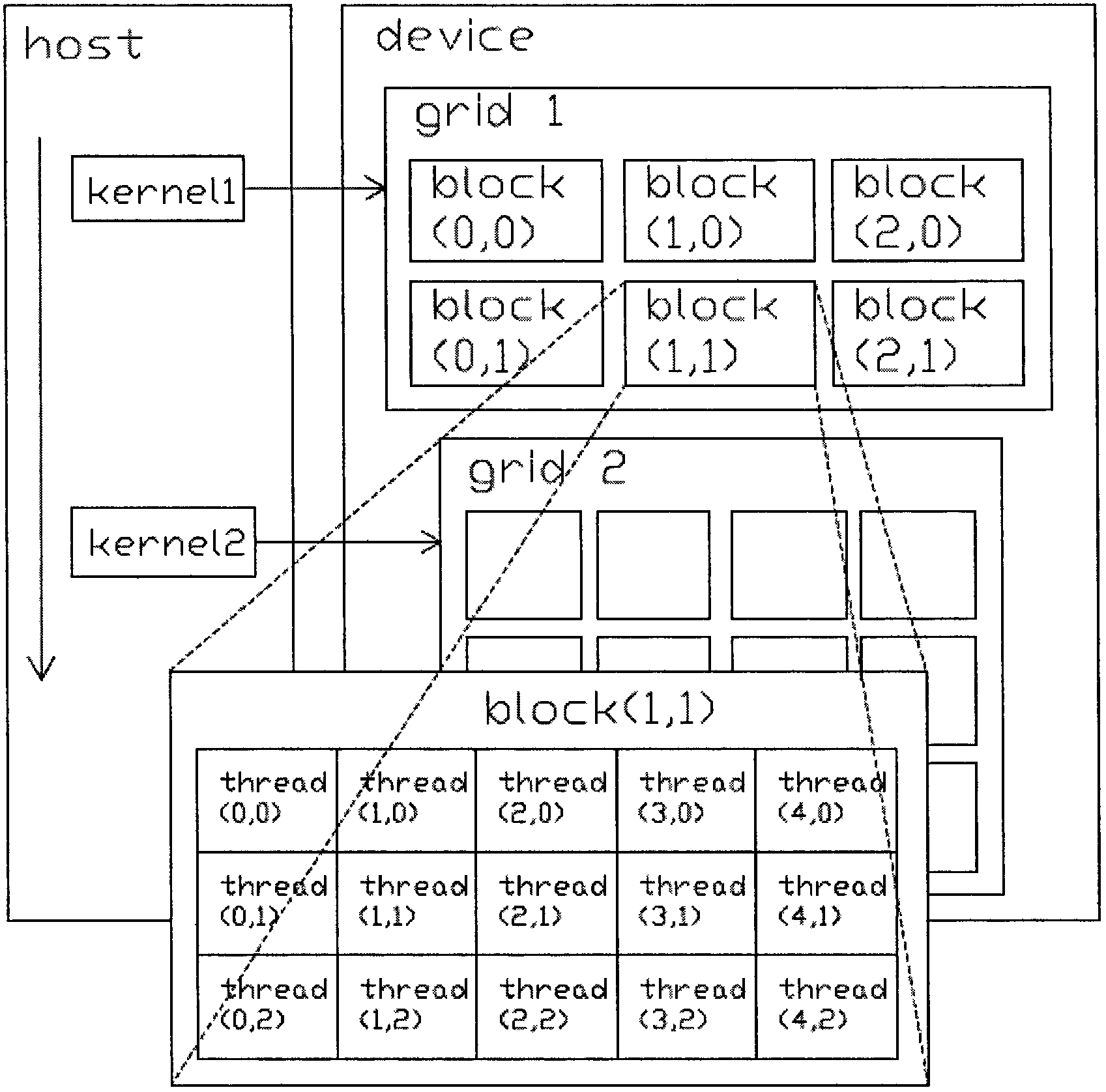
[0029] figure 1 As shown, CUDA decomposes the calculation into thread kernels one by one: kernel_1, kernel_2...kernel_M, each thread kernel is handed over to each grid Grid to complete, and the grid grid divides the task into blocks. Here, the blocks managed by each grid Grid are limited. The Block layer directly manages each thread Thread. When performing real-time simulation of electromagnetic transients in the power system, 2k calculations are allocated to different threads Thread. Go, because the number of CUDA computing cores is very large, when 2k is less than this number, the calculation can be decomposed into more parallel calculations in each 2k calculation, by developing an algorithm suitable for the CUDA program execution model, and setting Block reasonably And the number of Threads can make full use of the powerful parallel processing capabilities of the GPU to solve the problem of processing electromagnetic transient massive data.
Embodiment 2
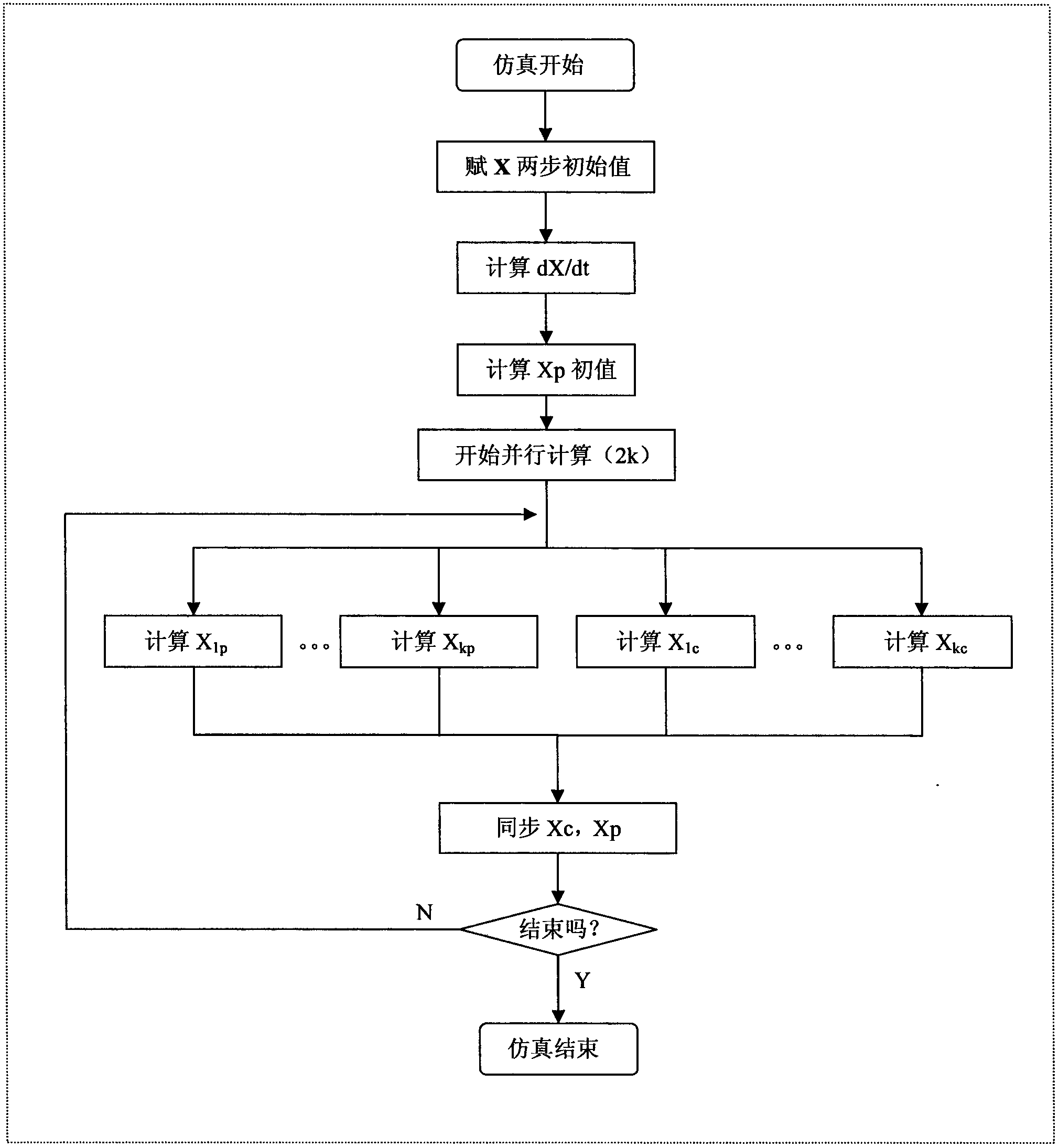
[0031] figure 2 As shown in the figure, the electromagnetic transient simulation of the power system needs to consider the electromagnetic transient process of the stator winding and the line of the generator, which needs to be described by differential equations. This is a system of linear ordinary differential equations that, after simple transformation, can be written in the following form:
[0032] dX / dt=F(X)+G(U) (1)
[0033] X is the system state variable matrix
[0034] Using the two-point Euler method (the principle of other methods is the same), that is
[0035] X i n+1 =X i n-1 +(2h)(dX i n / dt) (2)
[0036] Substituting (1) into (2), we get
[0037] X i n+1 =X i n-1 +(2h)(F i (X n )+G i (U n )) (3)
[0038]In order to ensure the numerical stability of the calculation method, the equation system (3) is solved by the prediction-correction method, and the formula (4) is obtained. Here, X ip n+1 predicted value, X ic n+1 is the correction value ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com