Fault line selection method based on time domain waveform correlation analysis of three-phase current breaking variable
A technology of time-domain waveform and three-phase current, which is applied in the direction of the fault location, etc., can solve the problems of inconsistency in the transmission characteristics of three-phase current transformers and the reliability of fault line selection methods that affect zero-sequence currents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
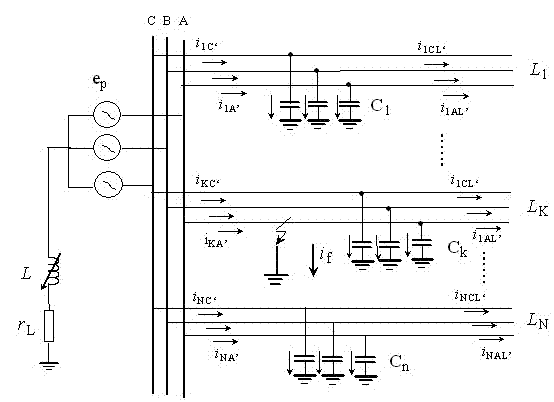
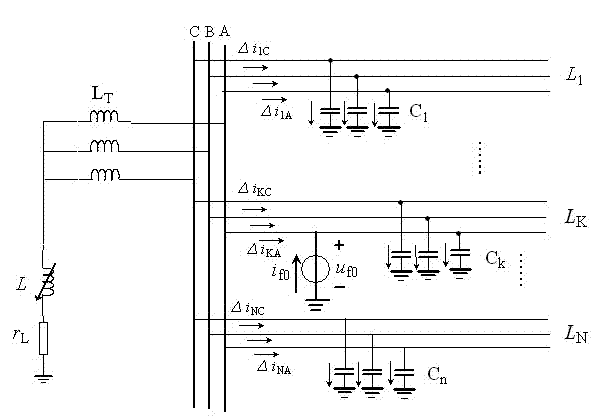
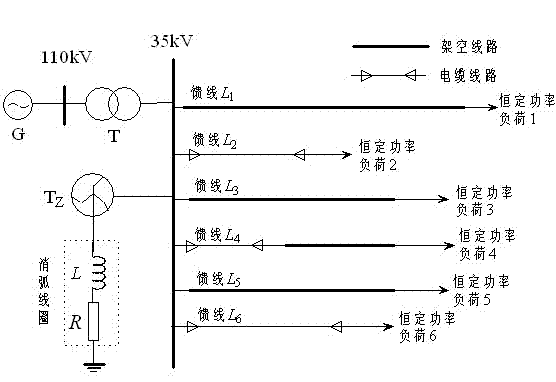
[0071] Embodiment 1: as Figure 4 The single-phase ground fault simulation model of the 110kV / 35kV distribution network shown has 6 feeders, and the neutral point of the Z-shaped transformer is grounded through the arc-suppression coil series resistance. overhead feeder =15km, =18km, =30km, wire-cable hybrid feeder =17km, the overhead feeder is 12km, the cable is 5km, and the cable feeder =6km, =8km. Among them, the overhead feeder is JS1 rod type, LGJ-70 type conductor, the span is 80m, and the cable feeder is YJV23-35 / 95 type cable. G in the power grid is an infinite power source; T is the main transformer with a transformation ratio of 110 kV / 35kV, and the connection group is / d11; Is a zigzag transformer; L is the arc suppression coil; R is the damping resistance of the arc suppression coil. The feeder adopts three types of lines: overhead line, overhead line-cable hybrid line and cable line. The load uses a constant power load model. hypothetical feeder...
Embodiment 2
[0078] Embodiment 2: as Figure 4 The parameters of the single-phase-to-ground fault simulation model of the 110kV / 35kV distribution network shown in the example have been described in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here. Now assume the feeder A single-phase ground fault occurs in phase A 4 kilometers away from the beginning, the ground resistance is 60Ω, the fault angle is 30°, and the sampling frequency is 10kHz. The data of the 5 ms time window after the fault in the time domain waveform of the three-phase current mutation of each feeder collected by the three-phase current transformer is used to calculate the phase-to-phase correlation coefficient and the comprehensive correlation coefficient. The calculation results are shown in Table 2.
[0079] It can be seen from Table 2 that the correlation coefficient between the faulty phase and the healthy phase is small, and the correlation coefficient between the healthy phase and the healthy phase is large; the compre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com