Method for preparing protein nanoparticles for in vivo delivery of pharmacologically active substances
A pharmacologically active and nanoparticle technology, which is applied in the direction of drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, organic active ingredients, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to deliver in vivo, loss of protein activity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] Example 1. Preparation of paclitaxel-albumin nanoparticles
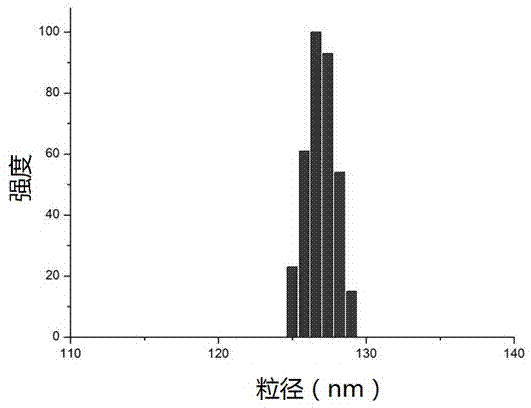
[0077] 100 mg HSA was dissolved in 10 mL pH6 phosphate buffer containing 0.5 mg / mL EDTA and 0.05 M mercaptoethanol, and the reaction was continued at 55°C for two hours. After the end, the protein was precipitated and washed with 5% trichloroacetic acid, and 1.6 mL of 10 mg / mL paclitaxel (dissolved in ethanol) solution into the pellet, mix for 2 minutes, add 50 mL of 0.08 M phosphate buffer and stir to dissolve the mixture. The obtained suspension is transparent, and the average particle size of the drug-loaded particles is 80-200 nm (BIC 90plus Particle Size Analyzer). The encapsulation efficiency of paclitaxel was determined by a reversed-phase C18 column, the mobile phase was acetonitrile: water (60:40), and the detection wavelength was 227 nm. HPLC analysis showed that the encapsulation efficiency of paclitaxel in this experiment was over 90%.
[0078] In the experiment, TCA can also be replaced by ot...
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2. Preparation of paclitaxel-albumin nanoparticles
[0080] 100 mg HSA was dissolved in 50 mL pH7.4 TRIS buffer, in a 37°C water bath, 350 μL 2-mercaptoethanol was added, the reaction lasted for 10 minutes, and 2 mL 10 mg / mL paclitaxel (dissolved in ethanol) was added. After 30 min, samples were dialyzed against pH 7.4 TRIS buffer for 24 h and the resulting samples were lyophilized for 48 h. The resulting lyophilized block sample can be easily redissolved into the original solution with water or saline, and the particle size of the nanoparticles remains unchanged. After lyophilization, the particle size mainly distributed in the range of 80-200 nm (BIC 90plus Particle Size Analyzer). HPLC analysis showed that the encapsulation efficiency of paclitaxel in this experiment was over 90%.
Embodiment 3
[0081] Example 3. Preparation of paclitaxel-albumin nanoparticles
[0082] 100 mg of paclitaxel was dissolved in 10 mL of pH 4.8 buffer solution, placed in an ice-water bath for 30 minutes, then 7.5 mL of 0°C pre-cooled acetone was added dropwise, and the ice bath was continued for 1 hour. Centrifuge to collect the precipitate, add 1 mL of 10 mg / mL paclitaxel (dissolved in acetone) to the precipitate, ultrasonically mix, add 50 mL of normal saline, and stir magnetically to form a suspension. Particle size analysis was carried out with BIC 90plus Particle Size Analyzer, and the result was 150-220 nm. The freeze-dried sample could be reconstituted, and the drug loading was 8.34% according to HPLC analysis.
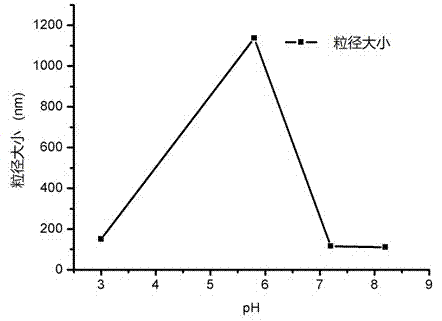
[0083] Additional experiments show that glycine, mannitol, lactose and trehalose can all be used as lyoprotectant, and the particle size obtained by using lactose as lyoprotectant is the smallest.
[0084] During the preparation, we investigated different buffers (water,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com