A long-term durable and stable road yard pavement structure layer and its construction method
A technology of structural layer and stable layer, which is applied to cohesive pavement paved on site, roads, roads, etc., can solve problems such as poor coordination deformation ability, large differential settlement of soil foundation, and aggravated crack width, so as to reduce maintenance costs, Ease of construction and reduction of adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
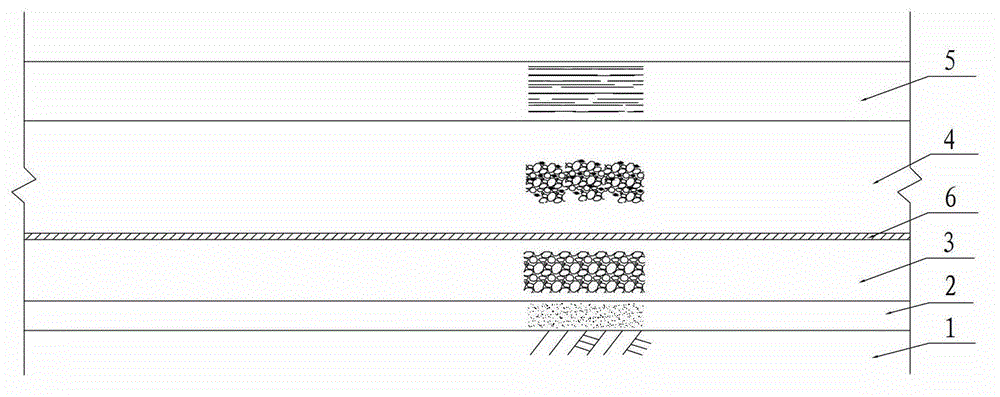
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, follow the steps below to implement:
[0028] (1) To level the site, if necessary, general tamping should be used to compact the ground surface during the process of leveling the site.
[0029] (2) Lay a layer of sand cushion 2 with a thickness of about 10cm on the soil foundation 1, and the sand cushion 2 is medium-fine sand.
[0030] (3) Lay a graded crushed stone layer 3 on the sand cushion layer 2 as the subbase.
[0031] (4) Set the flexible structural layer 6 on the flat subbase. The flexible structural layer 6 adopts geogrid. When laying, the geogrid is arranged parallel to the axis of the embankment, that is, the laying direction of the geogrid is parallel to the center line of the subgrade. When paving, it should be straightened and smooth, and it should be close to the underlying layer without twisting, folding or overlapping. Geogrids are spliced along the longitudinal direction using the lap joint method, each lap width (longi...
Embodiment 2
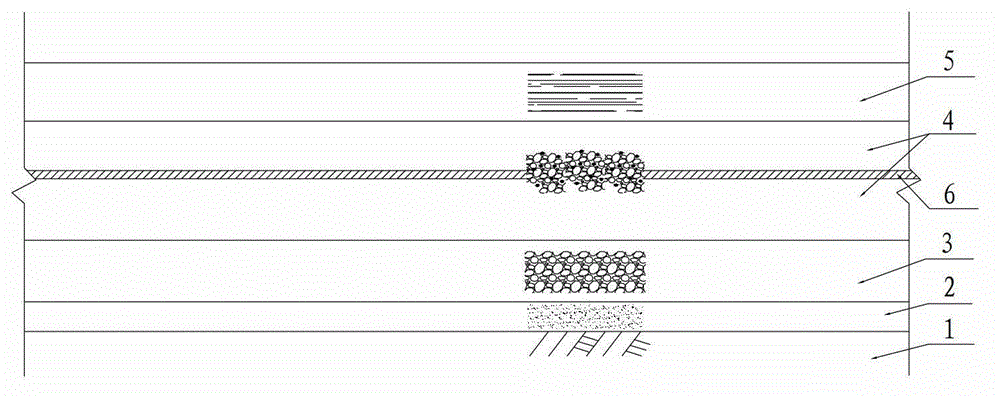
[0034] Such as figure 2 As shown, follow the steps below to implement:
[0035] (1) To level the site, if necessary, general tamping should be used to compact the ground surface during the process of leveling the site.
[0036] (2) Lay a layer of sand cushion 2 with a thickness of about 10cm on the soil foundation 1, and the sand cushion 2 is medium-fine sand.
[0037] (3) Lay a graded crushed stone layer 3 on the sand cushion layer 2 as the subbase.
[0038] (4) Lay a cement stabilization layer with a certain thickness (generally 20cm) on the subbase. Then set a flexible structural layer 6 above the paved cement stabilization layer. The flexible structural layer adopts steel mesh. When laying, the steel mesh is arranged parallel to the axis of the embankment, that is, the laying direction is parallel to the center line of the subgrade, and it should be straightened when paving. , smooth, close to the underlying layer, without twisting, wrinkling, or overlapping. The long...
Embodiment 3
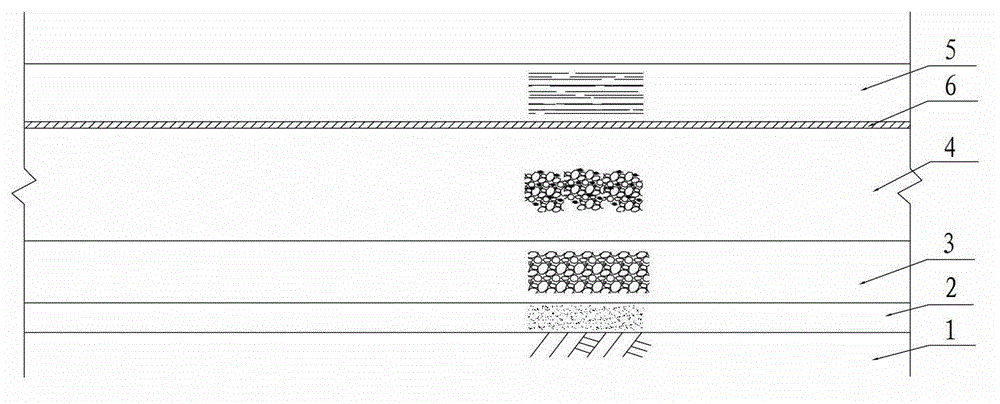
[0041] Such as image 3 As shown, follow the steps below to implement:
[0042] (1) To level the site, if necessary, general tamping should be used to compact the ground surface during the process of leveling the site. .
[0043] (2) Lay a layer of sand cushion 2 with a thickness of about 10cm on the soil foundation 1, and the sand cushion 2 is medium-fine sand.
[0044] (3) Lay a graded crushed stone layer 3 on the sand cushion layer 2 as the subbase.
[0045] (4) Lay a cement stabilization layer on the subbase.
[0046] A flexible structural layer 6 is arranged above the cement stabilization layer. The flexible structural layer adopts geotextile and geogrid. When laying, the geotextile and geogrid are arranged parallel to the axis of the embankment, that is, the laying direction is parallel to the center line of the subgrade. When paving, it should be straightened and smooth, and it should be close to the underlying layer. , without twisting, wrinkling, or overlapping. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com