Enterobacter 638 and its application method
An Enterobacteriaceae, plant-based technology that can be used in applications related to plant growth and development to address issues affecting agricultural productivity, rainfall patterns, and temperature increases
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] Example 1: Isolation and Identification of Enterobacter 638
[0079] Root and shoot samples were collected from a 10-year-old hybrid poplar H11-11 (Trichocarpa Populus americana). Additionally, native willow (Salixgooddingii) material was collected from 5-year-old native plants grown in the presence of trichlorethylene (18ppm) and carbon tetrachloride (12ppm). Cuttings were cut from plants using scissors, which were cleaned with alcohol during cutting, and placed in acetone-rinsed volatile organic analytical vials, which were placed on ice for shipment from the site. Roots and shoots were treated separately. Fresh root and shoot samples were washed vigorously in distilled water for 5 min and surface sterilized in a solution containing 1% (w / v) active chloride (as a sodium hypochlorite [NaOCl] solution) plus 1 drop of Tween 80 per 100 ml of solution 5 min and rinsed three times in sterile distilled water. A 100 μl water sample from the third rinse was plated on 869 m...
Embodiment 2
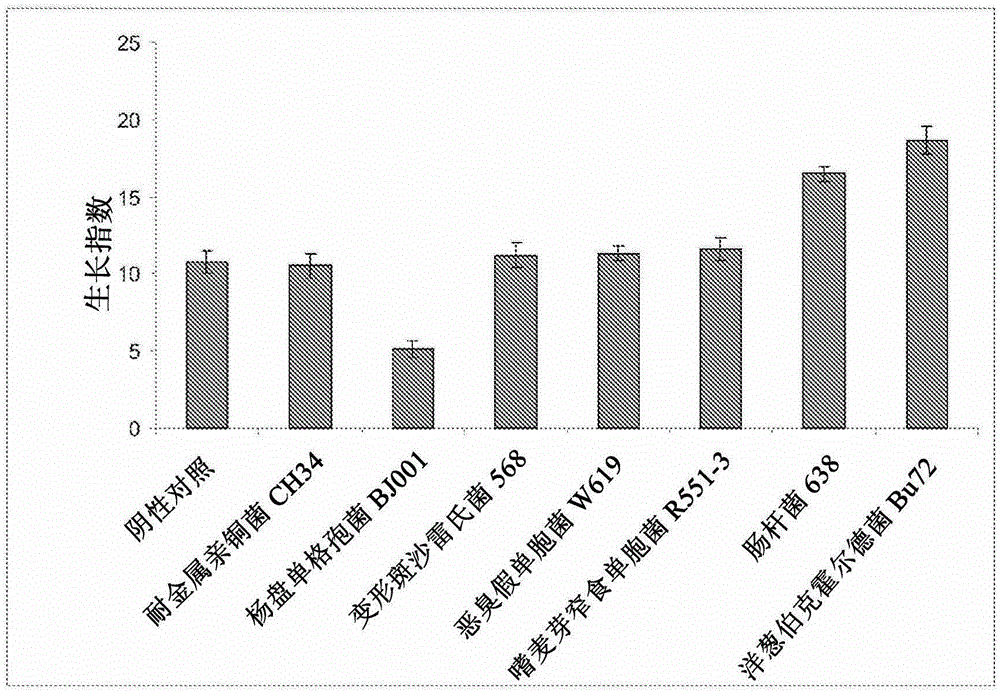
[0081] Example 2: Screening of endophytic bacteria for plant growth promoting properties of poplar
[0082] Prepare an inoculum (250 ml culture) with endophytic bacteria grown on 1 / 10 strength 869 medium (25) on a rotary shaker at 30°C until the cell concentration reaches 10 9 CFU / ml (1 optical density at 660nm [OD660]). Cells were collected by centrifugation, and 10 mM MgS0 4 Rinse it twice, then suspend it in 1 / 10 of the original volume (in 10mM MgSO 4 in), thus obtaining a cell concentration of 10 10 CFU / ml of inoculum. To test each microbial strain, seven cuttings approximately 30 cm from poplar (Pulus nigra × Pulpus nigra) DN-34 were weighed and placed in 0.5 L half-strength sterile Hoagland nutrient solution (5) In the 1L beaker, the nutrient solution was renewed every 3 days. Cuttings develop roots after about 4 weeks of rooting. Subsequently, a final concentration of 10 in half-strength Hoagland nutrient solution 8 Add bacterial inoculum to each cup at CFU / ml. ...
Embodiment 3
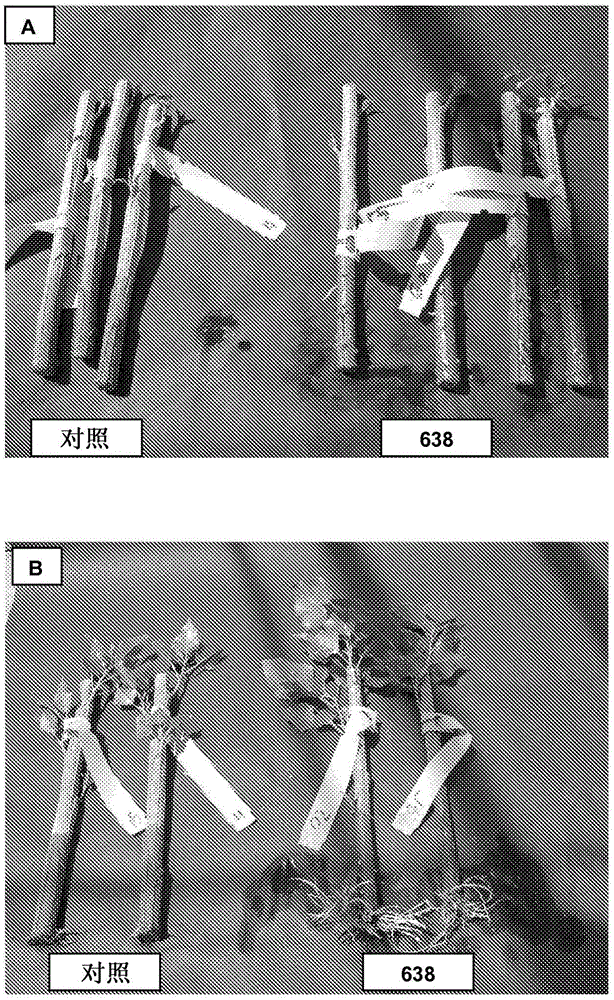
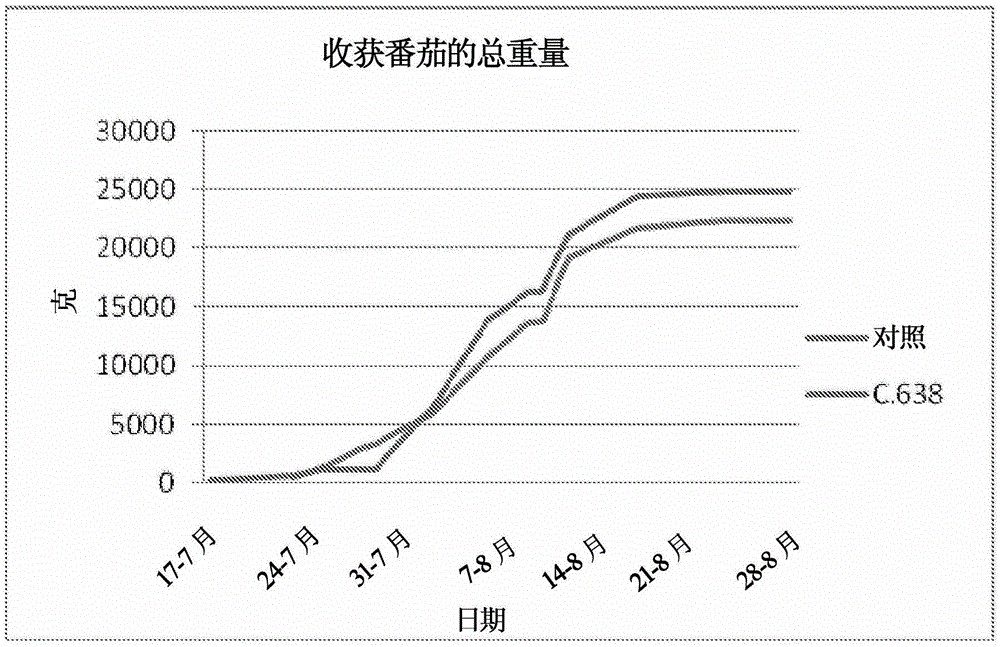
[0087] Example 3: Screening of endophytic bacteria in tobacco for plant growth promoting properties
[0088] Although the tobacco species is not used for field applications, it can be used in this study because it is commonly used in the laboratory as a large plant model for transformation and metabolite studies. Nicotianaxanthi seedlings were planted in a soilless growth medium and moved to a hydroponic solution when first leaves emerged. After one week, the plants were placed on a soil containing 10 8 CFU Enterobacter 638 in solution. After three days the inoculum was renewed and after another three days the plants were placed in pots in the greenhouse.
[0089] Plant growth was monitored weekly and the time of flowering onset was recorded. Plants reached full size faster than non-inoculated plants and most plants flowered one month earlier than the same number of non-inoculated plants.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com