Decision-making method of spectrum sensing interval in cognitive radio network
A cognitive radio and spectrum sensing technology, applied in the decision-making field of spectrum sensing interval, can solve the problems of energy consumption, system throughput reduction, and the inability of secondary users to transmit data, and achieve the effect of reducing energy consumption and high throughput.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
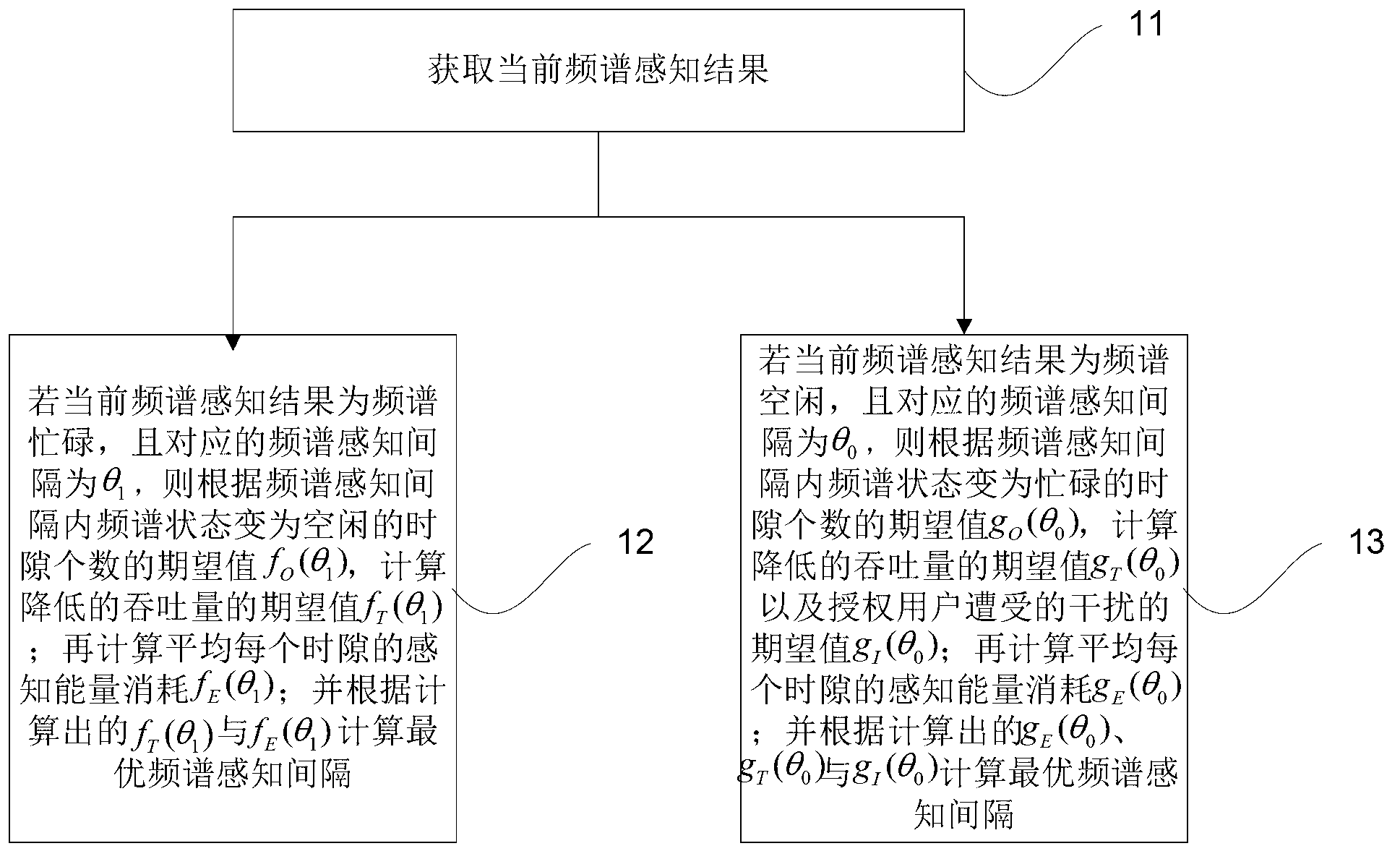
[0018] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a decision method for a spectrum sensing interval in a cognitive radio network provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the method mainly includes the following steps:
[0019] Step 11. Obtain the current spectrum sensing result. If the current spectrum sensing result is spectrum busy, go to step 12; otherwise, go to step 13.
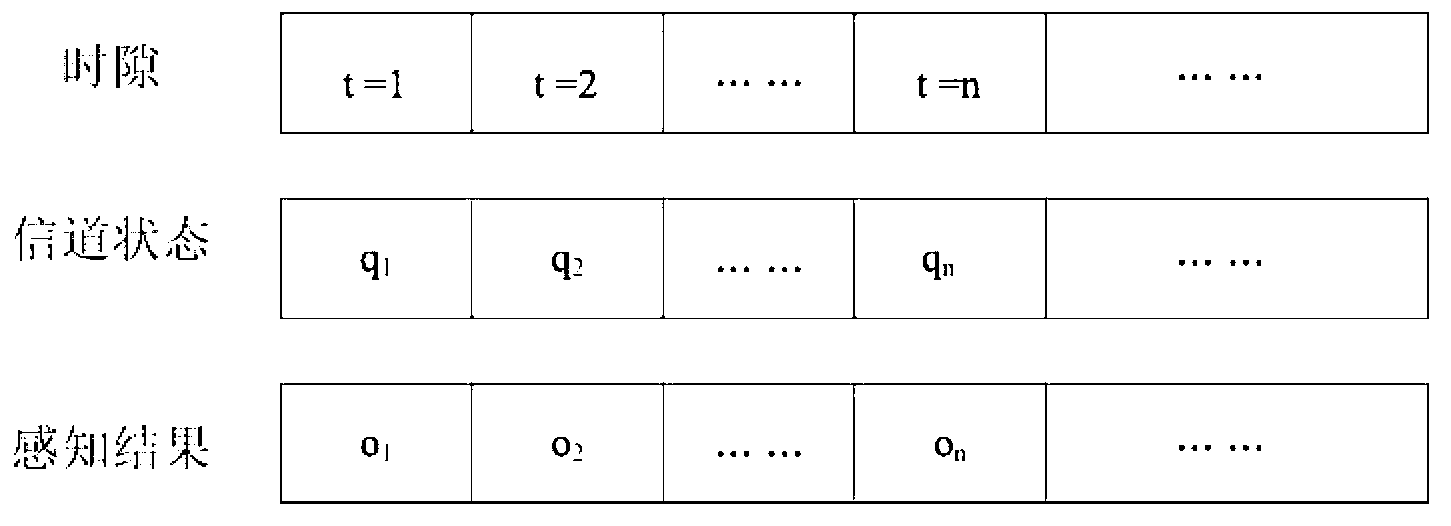
[0020] In the embodiment of the present invention, the current spectrum sensing results include spectrum busy and spectrum idle; the specific spectrum sensing process can be found in figure 2 , mainly including the following steps:
[0021] 1) Establish a spectrum sensing model. In this embodiment, the spectrum sensing process is established as a hidden Markov model;
[0022] where, taking the real state of the spectrum ( figure 2 The channel state q in 1 ,q 2 ,...,q n ) constitutes the hidden state of the hidden Markov model, with X={x 0 ,x 1} represents the hidden s...
Embodiment 2
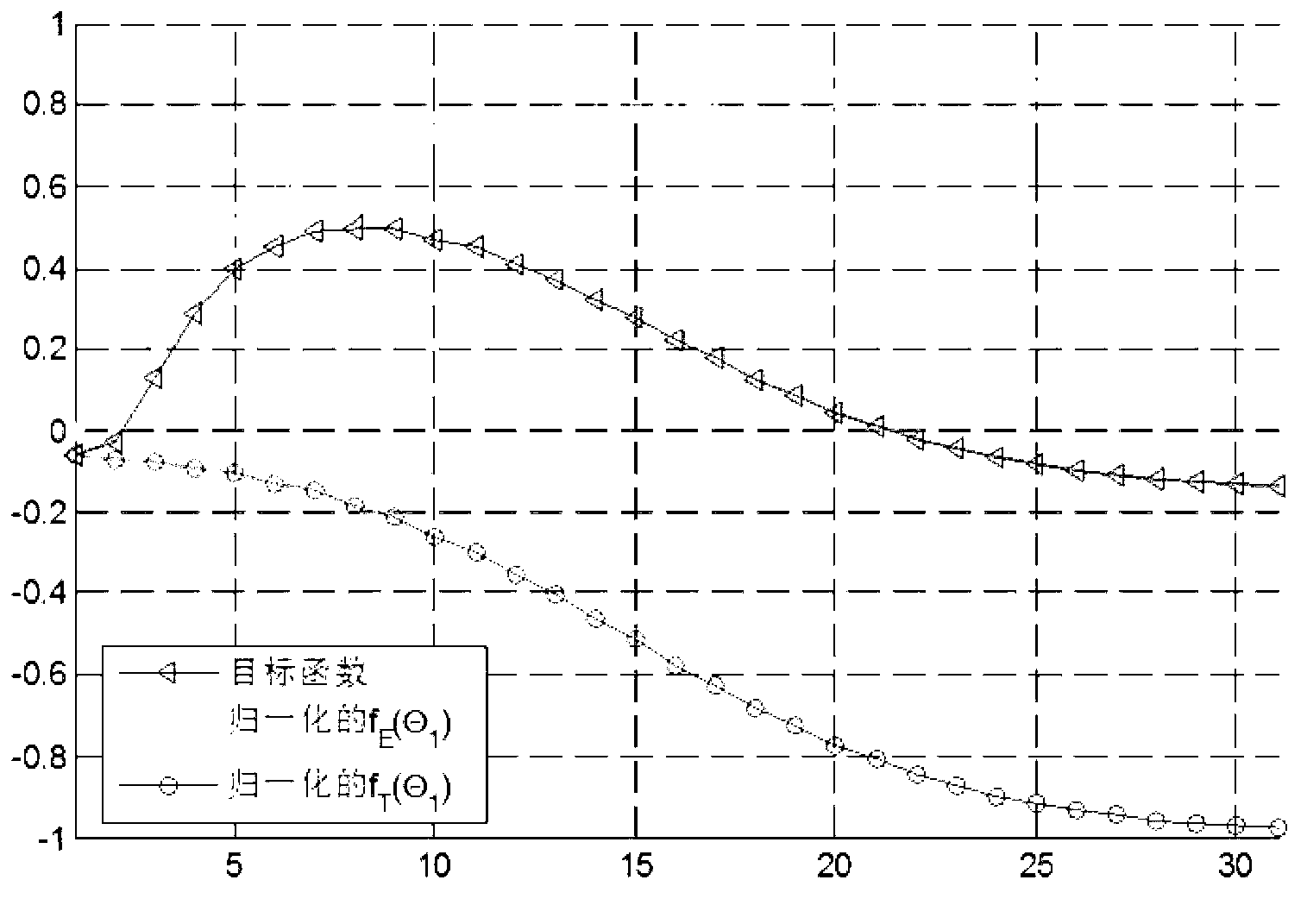
[0063] In order to facilitate understanding of the present invention, below in conjunction with Figure 3-4 The current spectrum sensing results are further explained as spectrum busy and idle respectively.
example 1
[0065]If the current spectrum sensing result is that the spectrum is busy, and the length of a time slot in the system is 0.0794s, the time required for a secondary user to perform a spectrum sensing is 0.0224s, and the required energy is 10mJ; the spectrum bandwidth is W=10kHz , the path loss constant in the system is κ=1, the path loss exponent is μ=3, and the variance of Gaussian white noise is N 0 =-87dBm, the transmitting power of the secondary user is 10mW, the distance between the transmitting end of the secondary user and the receiving end is 50m, and the distance between the transmitting end of the secondary user and the receiving end of the authorized user is 150m.
[0066] Then calculate according to the method of step 12 among the embodiment one, concrete steps are as follows:
[0067] 1) The secondary user calculates the expected value f of the number of time slots where the spectrum state becomes idle within the spectrum sensing interval O (θ 1 ), where θ 1 =0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com