Optical modulator
A technology of optical modulators and optical couplers, which is applied in optics, instruments, nonlinear optics, etc., and can solve problems that affect the transmission degradation of polarization mode dispersion, affect system realizability, and affect modem characteristic requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0109] [First Embodiment: Basic Concept].
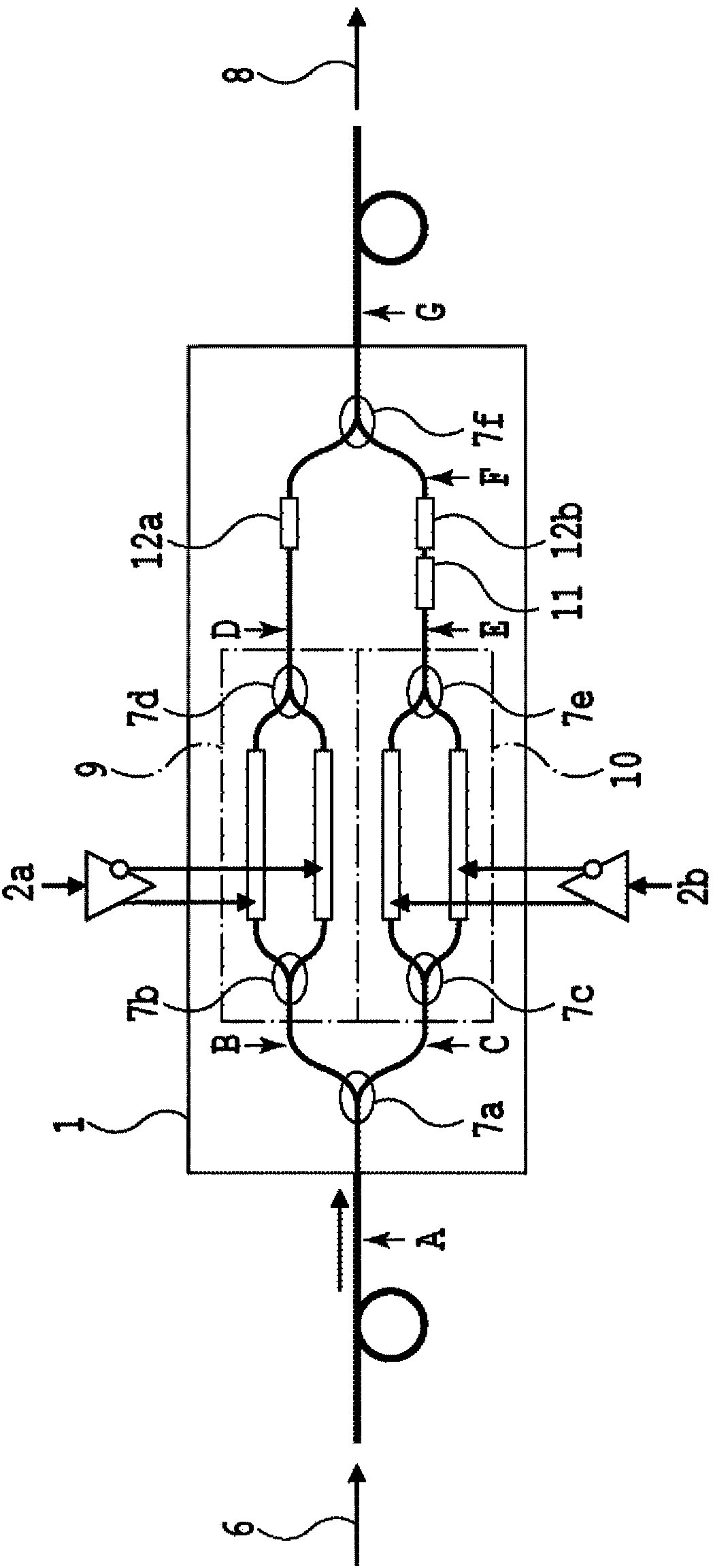
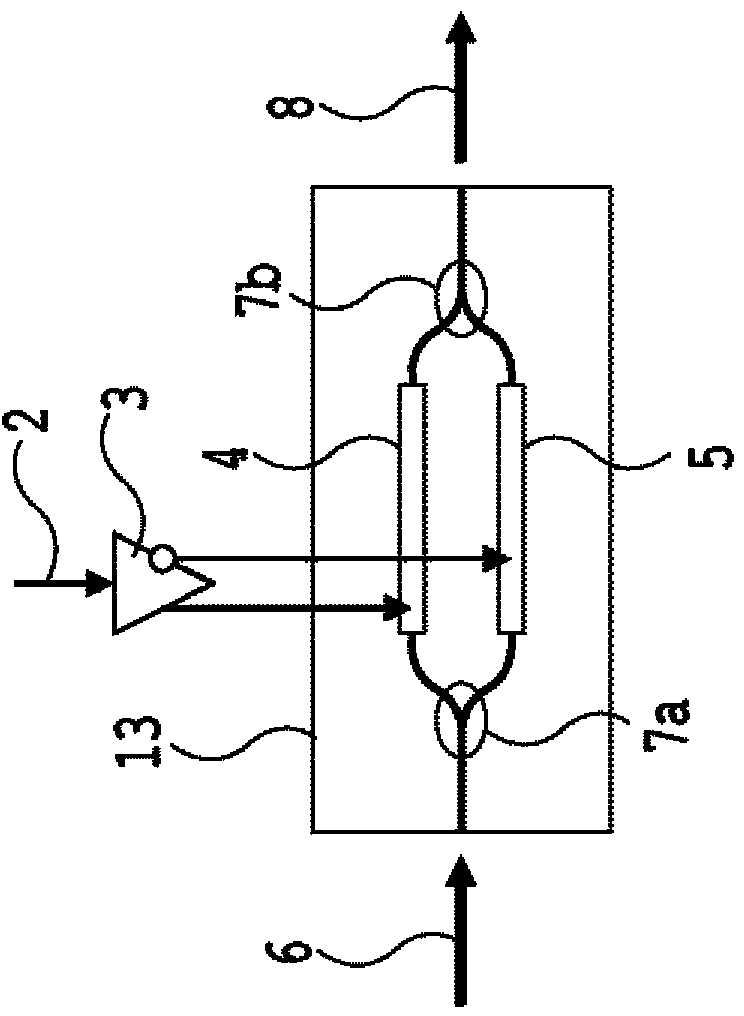
[0110] Figure 7 The structure of the format variable modulator according to the first embodiment of the present invention is shown. The modulator structure of this embodiment consists of a variable 1×M demultiplexing filter 24, M phase modulators (PSK modulators) 13-1~13-4, M / 2 dual-input single-output optical couplers 7a, 7h, and a (M / 2)-input-single-output variable optical coupler 25, wherein the variable 1×M demultiplexing filter 24 is formed by connecting multiple stages of variable 1×2 ILF. Figure 7 An example of M=4 is shown.
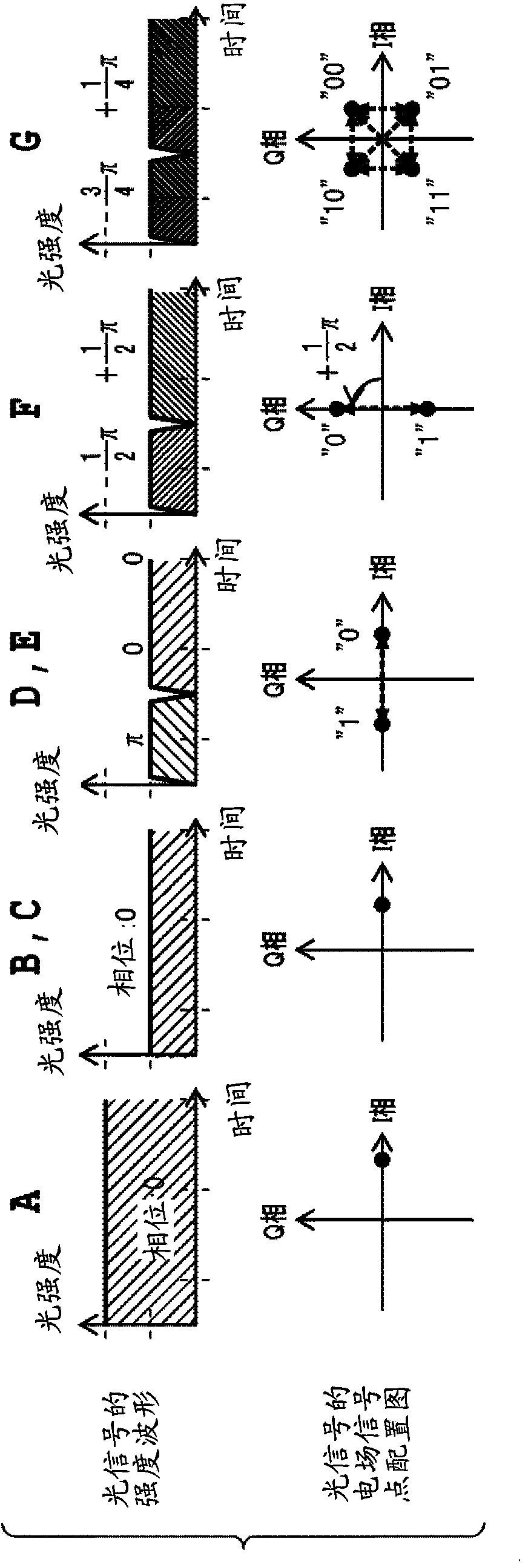
[0111] Variable ILF (Tunable ILF: TILF) 27-1-1 to 27-2-2 The optical path length difference ΔL clamped by two 3dB optical couplers 7a-7f (Here, the optical path length difference is not the waveguide length difference, but Considering the refractive index of the waveguide (the value converted to the length in vacuum) of the delay line and the variable optical phase shifter 12a-12f, according to the ...
no. 2 approach
[0133] [Second embodiment: case where M is a power other than 2]
[0134] Next, Figure 14 The configuration when M is not a power of 2, for example, M=12 is shown. This structure is based on the structure of M=16, omitting some structural elements. Specifically, TILF27-4-1~27-4-4 in the fourth section and VC25-4-1~25-4-4 in the first section are respectively arranged in eight in the structure of M=16, while in this In the structure, TILF27-4-1~27-4-4 in the fourth section and VC25-4-1~25-4-4 in the first section are respectively arranged in four. In addition, the structure of the optical modulator array part is also changed from 16 cut down to 12. By reducing a part of the elements of the structure, the number of corresponding carriers can be reduced. Note that, of course, the basic unit ΔL of the difference in optical path length of each TILF in the figure is a value when M=16 by the above formula. Figure 15A and 15B Specific examples of operating states for generatin...
Embodiment 1
[0209] [Format adjustable modulator]
[0210] Figure 33 The structure of the format-tunable modulator fabricated according to the first embodiment is shown. In this embodiment, it is assumed that M=4 in the above-mentioned embodiment, the structure of the distribution part is the pure MZI type of the distribution part type 1, the structure of the collection part is the variable coupler type of the collection part type 1, and the optical modulator array The part takes the nested MZI type QPSK modulator as the basic structure. Therefore, this modulator can be used in three types of modulators: 4-carrier QPSK modulator, dual-carrier 16QAM modulator, and single-carrier 256QAM modulator.
[0211] The modulator is realized by using the composite integration technology (non-patent document 3) after combining the quartz-like planar lightwave circuit (PLC) and the LN modulation array. Because the EO effect is very small, the PLC waveguide cannot constitute a high-speed modulator al...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com