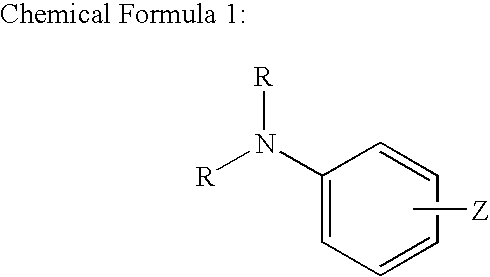
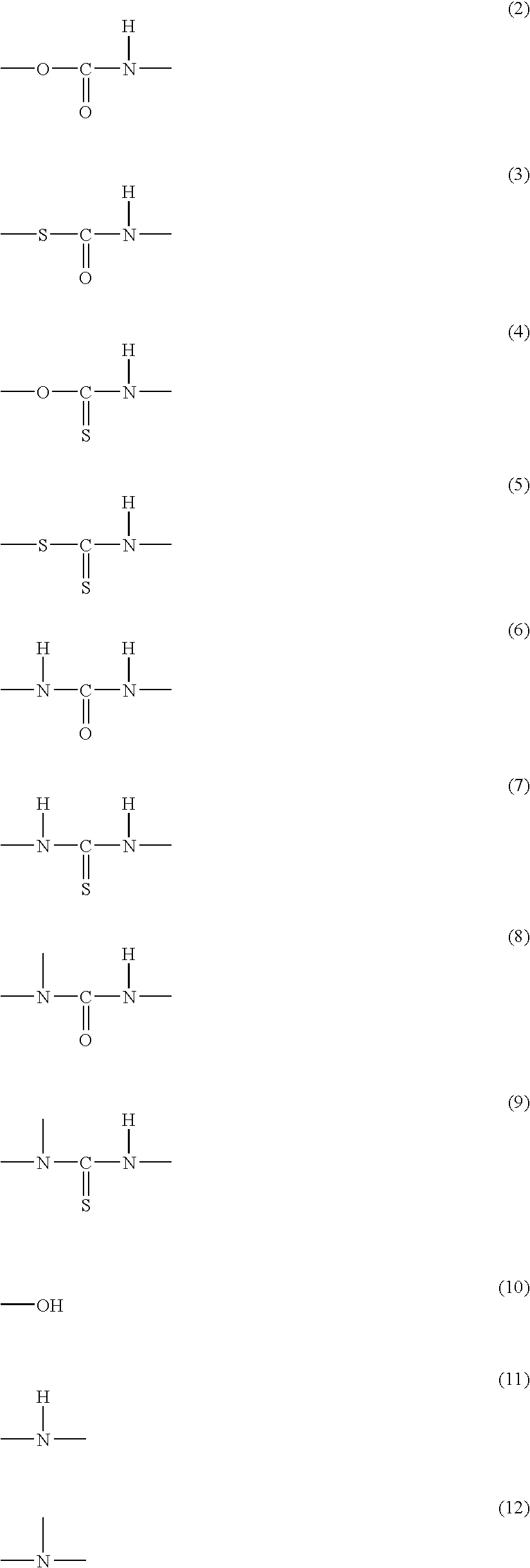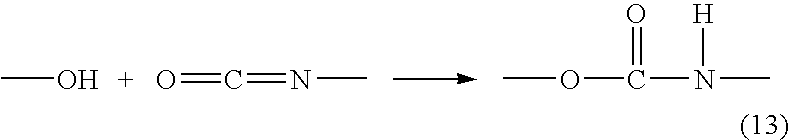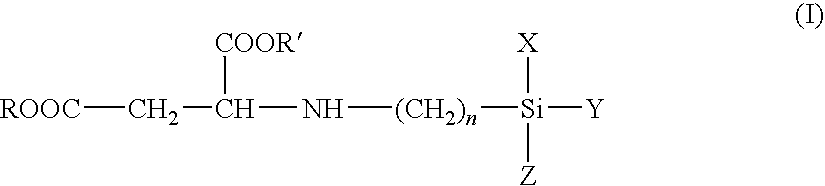Patents
Literature
215 results about "Part type" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
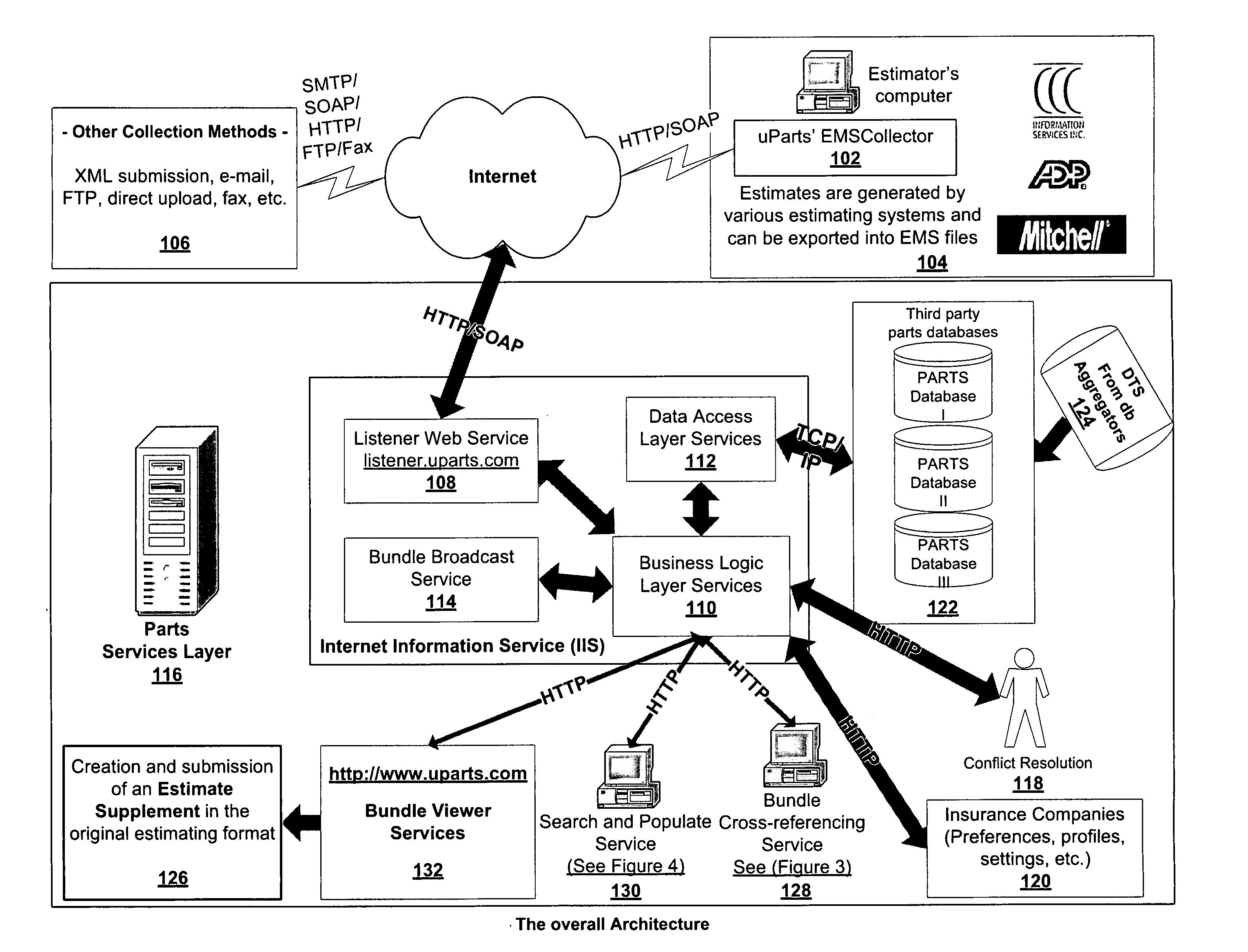
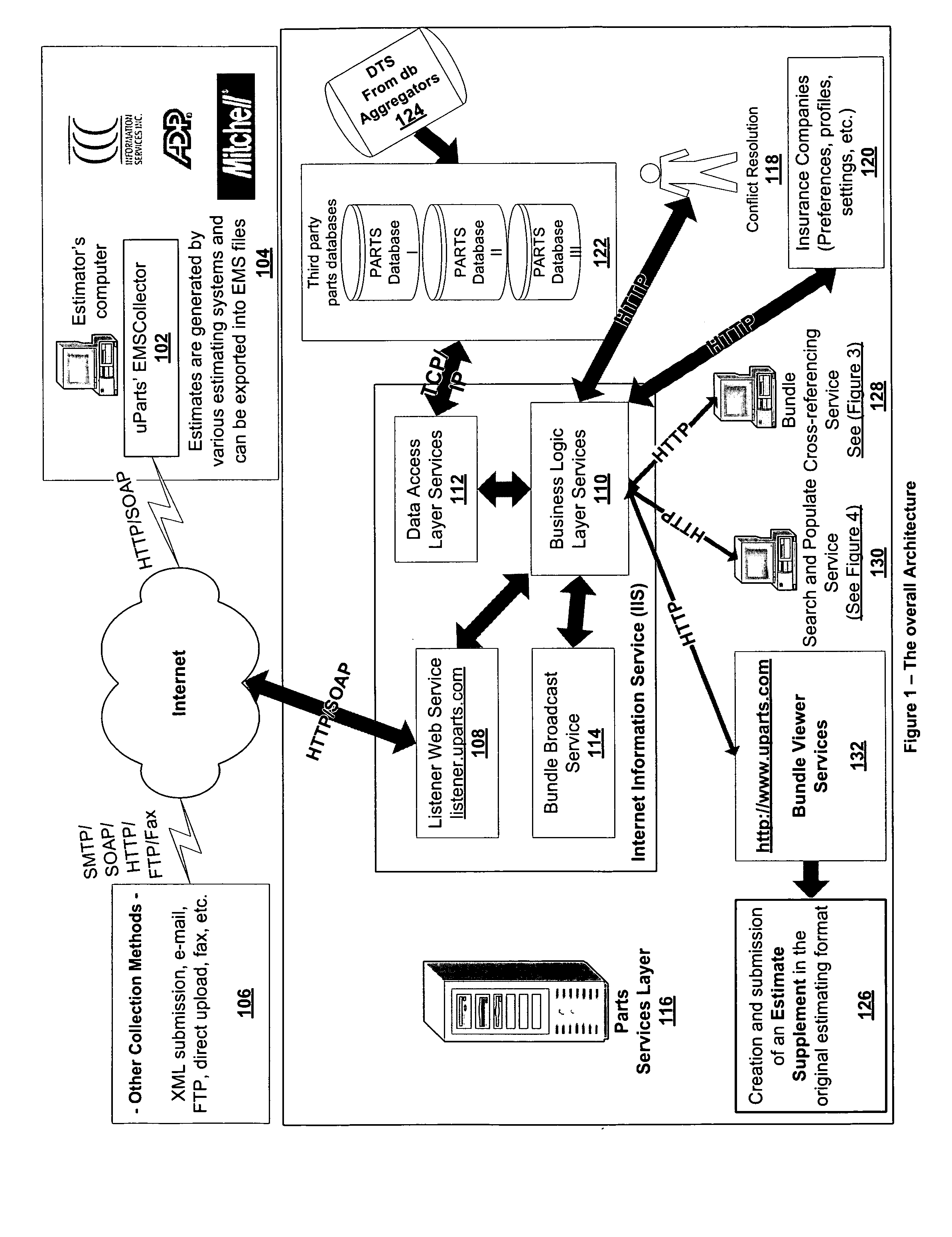
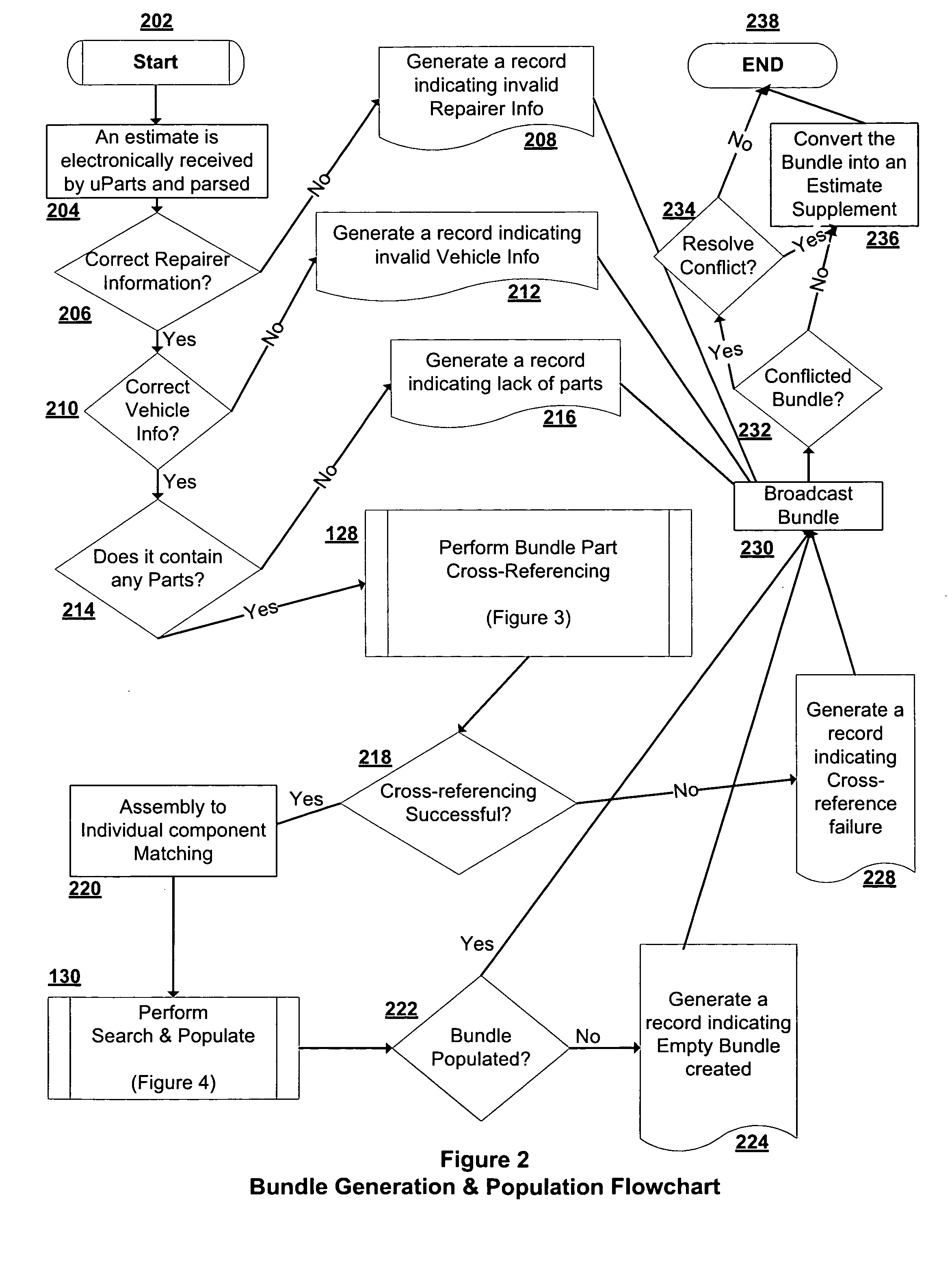
Intelligent used parts cross-referencing, search and location software application
Dynamically and intelligently identifying used parts and automatically locating actual used parts. A programmed computer system receiving an electronic vehicle repair estimate with a new part, type cross referencing a type of the new part in the estimate with a type of a used part, according to a used part type database, cross referencing the type of the used part with a used part identifier, according to a used part identifier database, identifying actual used parts corresponding to the new part by searching a used parts database based on the used parts identifier.
Owner:ALEXANDER OMEED ADEGAN
Method and system for automatic synchronous memory identification
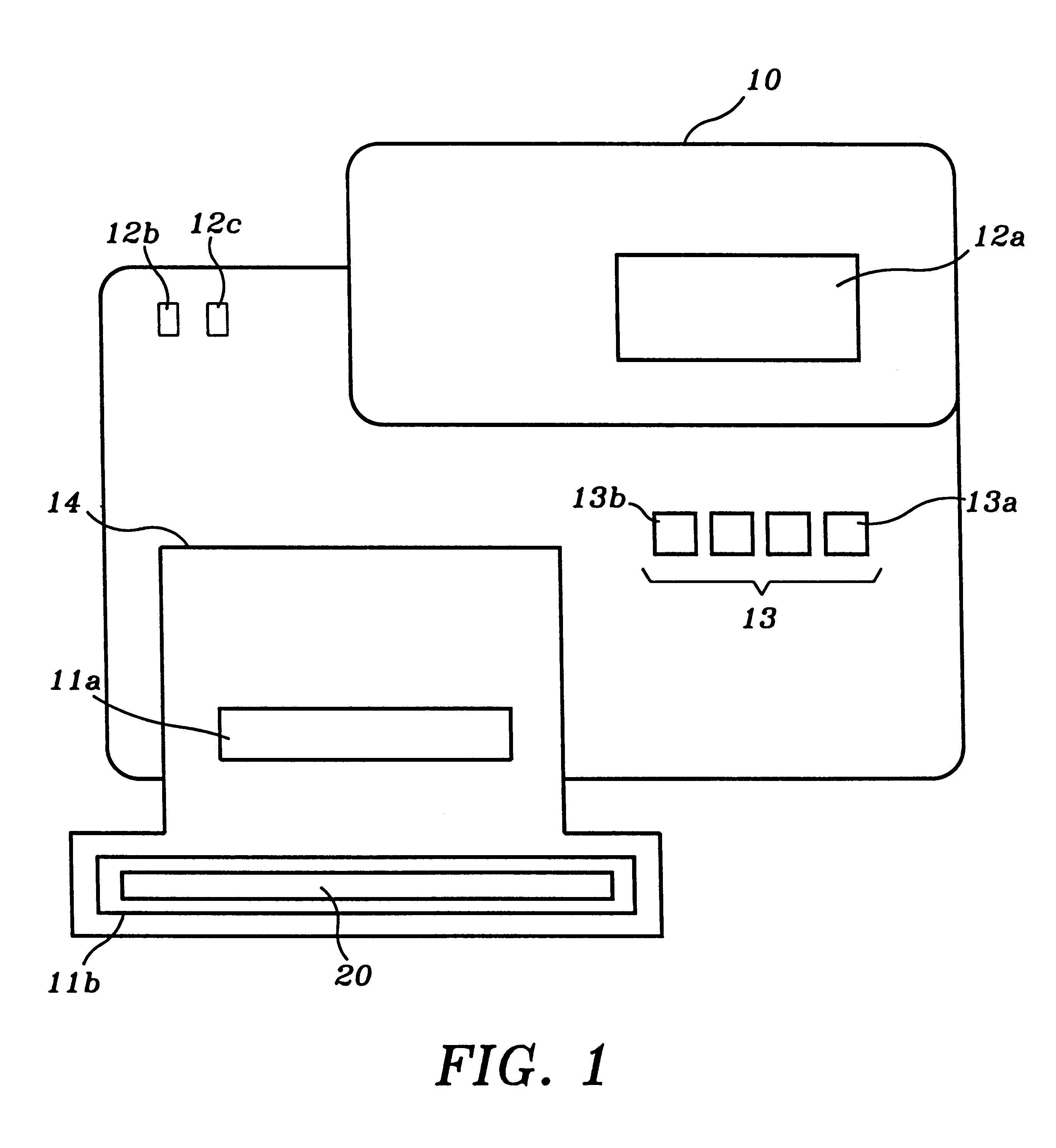
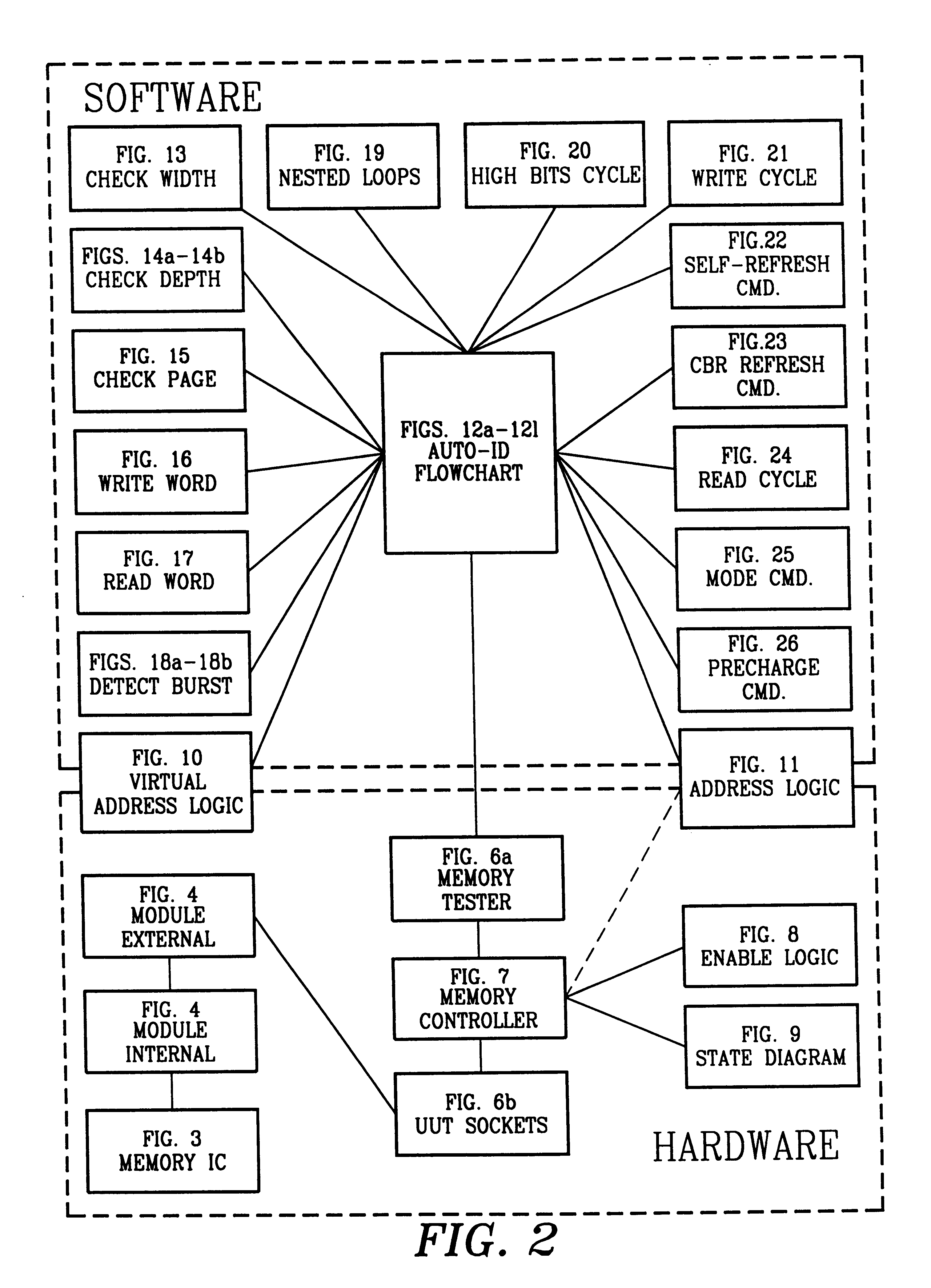
A time conserving method of identifying width, depth, access time, control line configurations, and part type of any of a plurality of different synchronous memories. A nested loop process is used to develop, and apply to a synchronous memory being identified, trial control line configurations taken from ordered entries of tables representative of the plurality of synchronous memories. The width, depth, control line configurations, and part type are determined from the responses evoked from the synchronous memory being identified. The delay between a read command issued by the test system CPU and a reading of bit patterns from the synchronous memory is incremented in finite steps in successive write / read iterations until the bit pattern read is identified to the bit pattern written into the synchronous memory, thereby identifying the access time of the synchronous memory.
Owner:TANISYS TECH +1
Curable resin composition and cold-setting adhesive
Disclosed is a moisture-curing type curable resin composition containing: a curable resin intramolecularly having a silicon-containing functional group; and a Lewis acid or a complex of the Lewis acid as a curing catalyst, the Lewis acid being selected from the group consisting of metal halides and boron halides, which is rapidly cured at room temperature. The silicon-containing functional group is represented by general formula: —SiX1X2X3 or —SiR1X1X2 (wherein, X1, X2 and X3 respectively represent a hydrolytic group and may be the same as or different from each other, and R1 represents a substituted or unsubstituted organic group having 1 to 20 carbons). If the silicon-containing functional group is —SiR1X1X2, the curable resin further contains intramolecularly a polar component that is one of urethane, thiourethane, urea, thiourea, substituted urea, substituted thiourea, amide, and sulfide bonds, and hydroxyl, secondary amino and tertiary amino groups. Two-part type adhesive is constitutible with separating the curable resin from the curing catalyst.
Owner:KONISHI CO
Data acquisition and fault diagnosis terminal for vehicle
InactiveCN102621979AReal-time monitoring of test conditionsElectric testing/monitoringGeneral Packet Radio ServiceThird generation
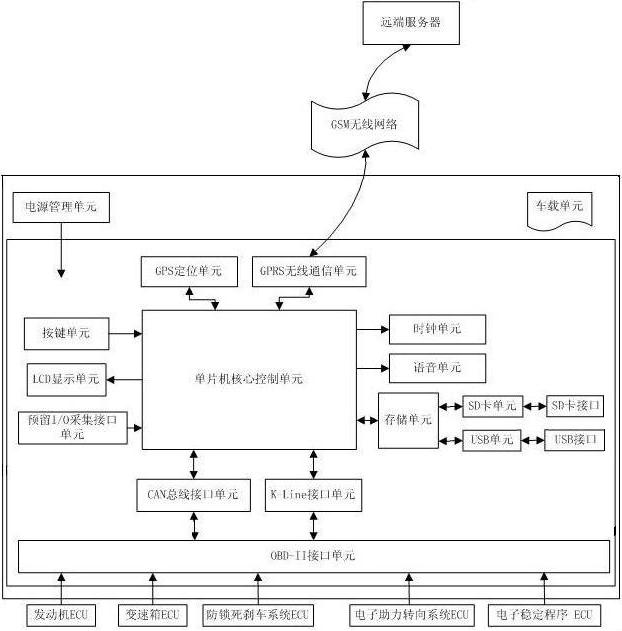
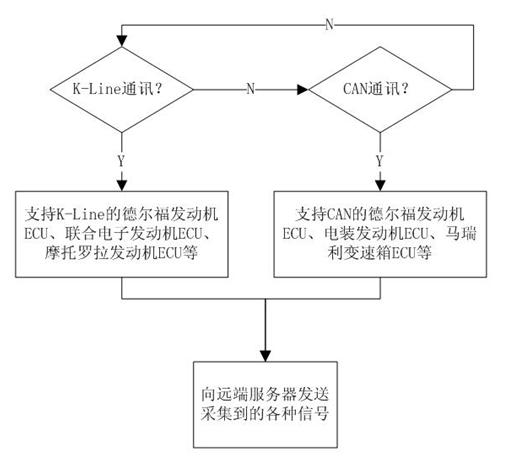
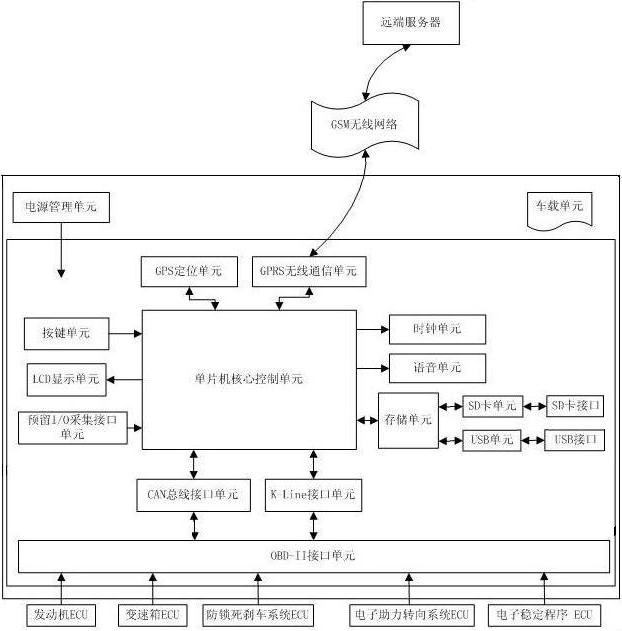
The invention discloses a data acquisition and fault diagnosis terminal for a vehicle. The terminal comprises a power management unit, an SCM (single chip machine) core control unit, a clock unit, a voice unit, a storage unit, a push-button unit, an LCD (liquid crystal display) unit and an interface unit. The terminal adopts a CAN bus and a K-line to carry out data acquisition in the vehicle, and an IO(input-output) interface is reserved to acquire the signals acquired by the CAN bus and the K line so as to enable a controller to acquire more useful signals in the vehicle. The acquired data can be stored by an SD (secure digital) card or USB (universal serial bus), and also can be transmitted to a remote server through 3G (3rd generation telecommunication) / GPRS (general packet radio service) in real time to be stored so as to realize the large capacity data storage. The terminal can automatically recognize engine types or part types of a plurality of companies. A tester can transmit GPS (global positioning system) positioning information back through a GPRS wireless communication unit arranged in the terminal so as to monitor road test conditions in real time by a far-end server.
Owner:TIANJIN FAW XIALI AUTOMOBILE +1
Control method of large-sized mining grinding mill end flange welding deformation
InactiveCN101412157AReduce welding distortionReduce workloadWelding/cutting auxillary devicesArc welding apparatusButt jointPart type
The invention provides a method for controlling welding deformation of an end flange of a large-sized mine mill, which comprises two contents: 1. the groove butt joint mode and welding mode before the end flange(2) and a barrel body(1) are welded are improved, the groove butt joint mode has three types which are small inner part and big outer part type, equal inner part and outer part type and big inner part and small outer part type respectively, and the welding mode correspondingly has three types; and 2. the correction is performed after welding, which has obvious effect, and the product quality is effectively ensured. By utilizing one welding stress to overcome the other welding stress, the welding stresses inside and outside the connecting part between the barrel body and the flange are balanced (i.e. the transverse shrinkages of the welding seams are the same); in the end, when the barrel body of the mill is subjected to relief annealing, the welding stresses inside and outside the barrel body of the mill are equally released, so that the method has the advantages of having little welding deformation, reducing the work load of correction after welding, improving the production efficiency, shortening the production cycle and lowering the production cost.
Owner:CITIC HEAVY INDUSTRIES CO LTD
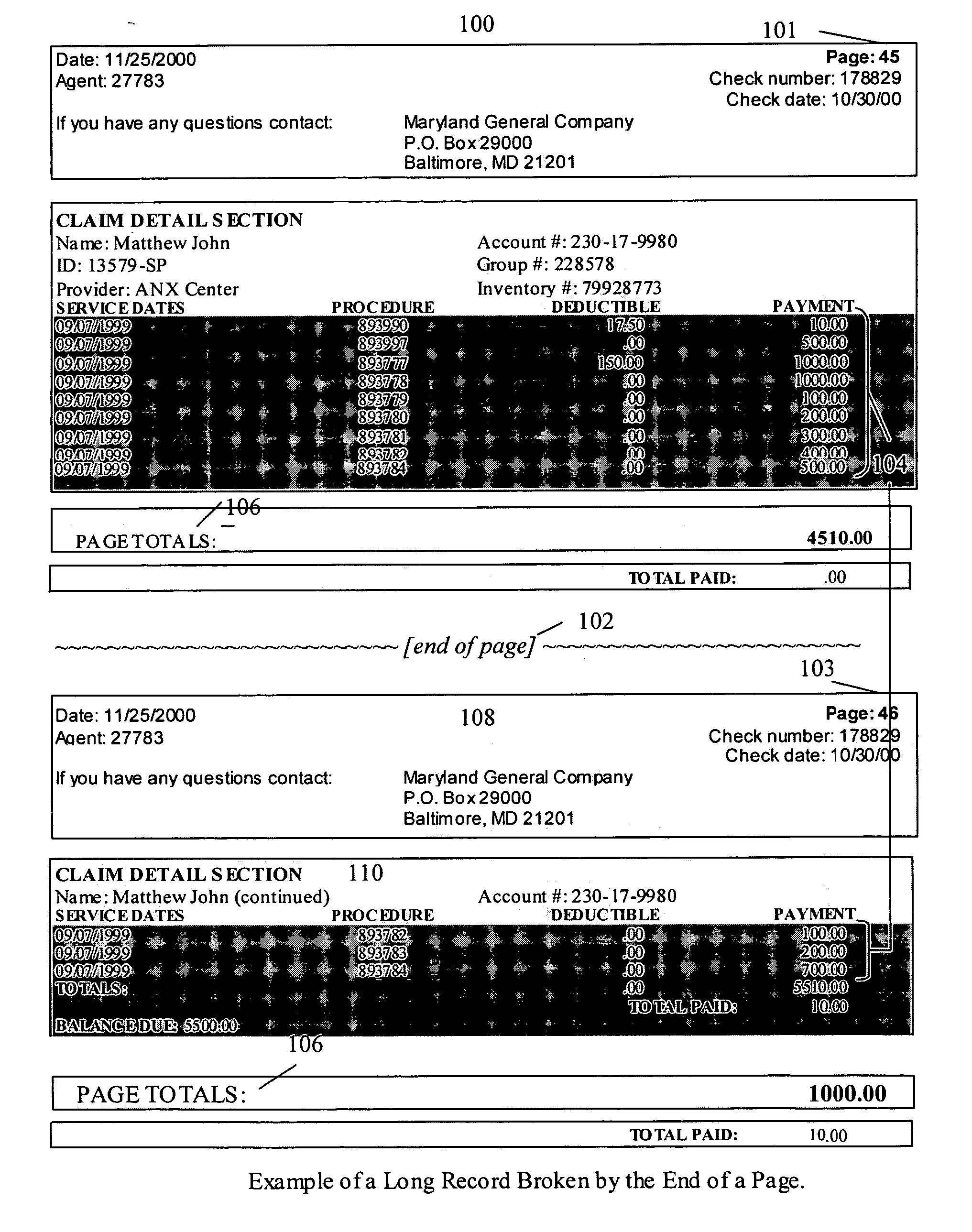
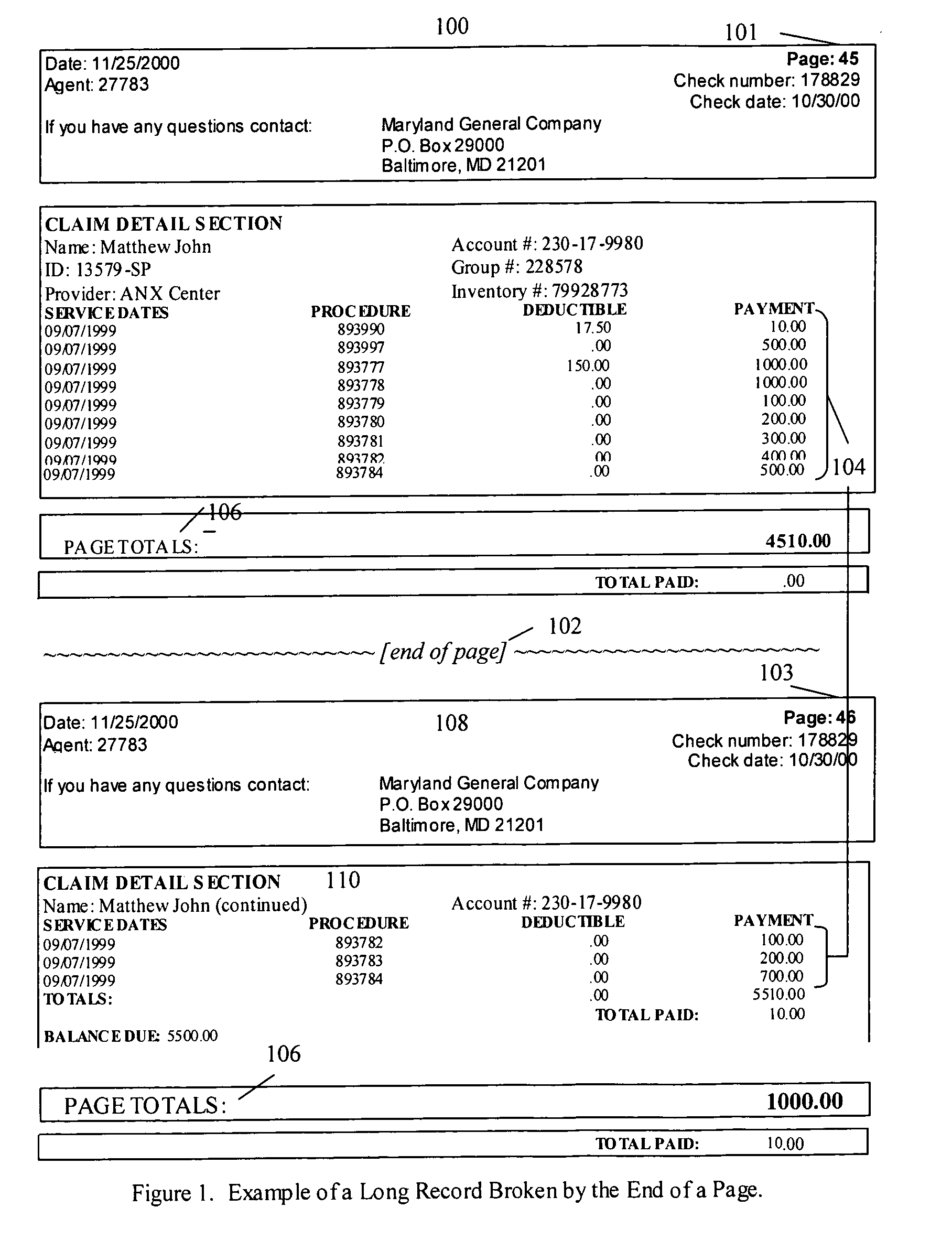
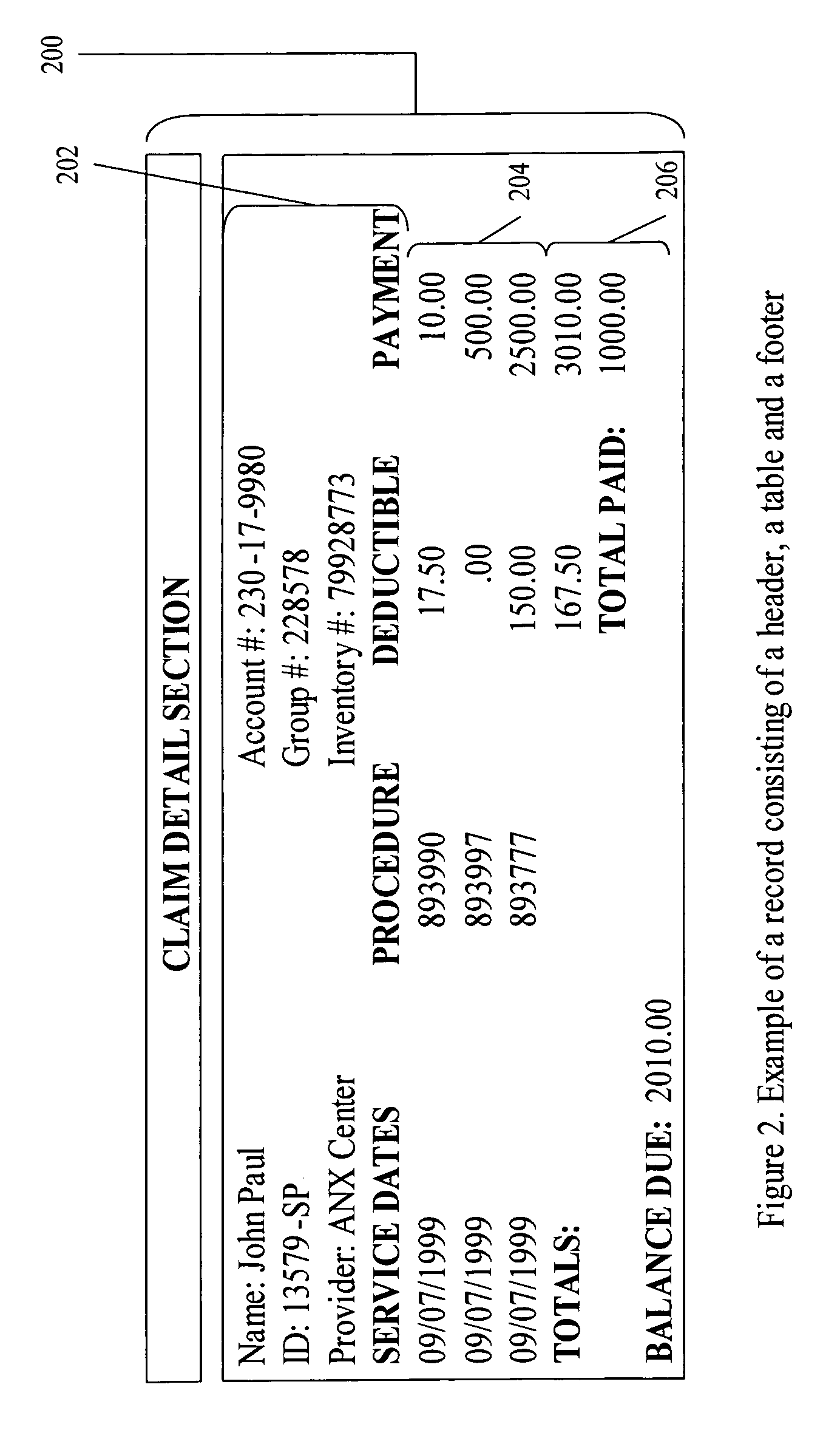
Method and system for extracting information from a document
A computer-implemented method for extracting information from a population of subject documents. The method includes modeling a document structure. The modeled document structure includes at least a document component hierarchy with at least one record type. Each record type includes at least one record part type and at least one record part type comprising at least one data element type. For a subject document exhibiting at least a portion of the modeled document structure, preferred embodiments of the invention identifying data of a type corresponding to at least one modeled data element type. Identified subject document data is then associated with the corresponding modeled data element type.
Owner:SCI APPL INT CORP
Hardware-level based test script automatic generating system and method
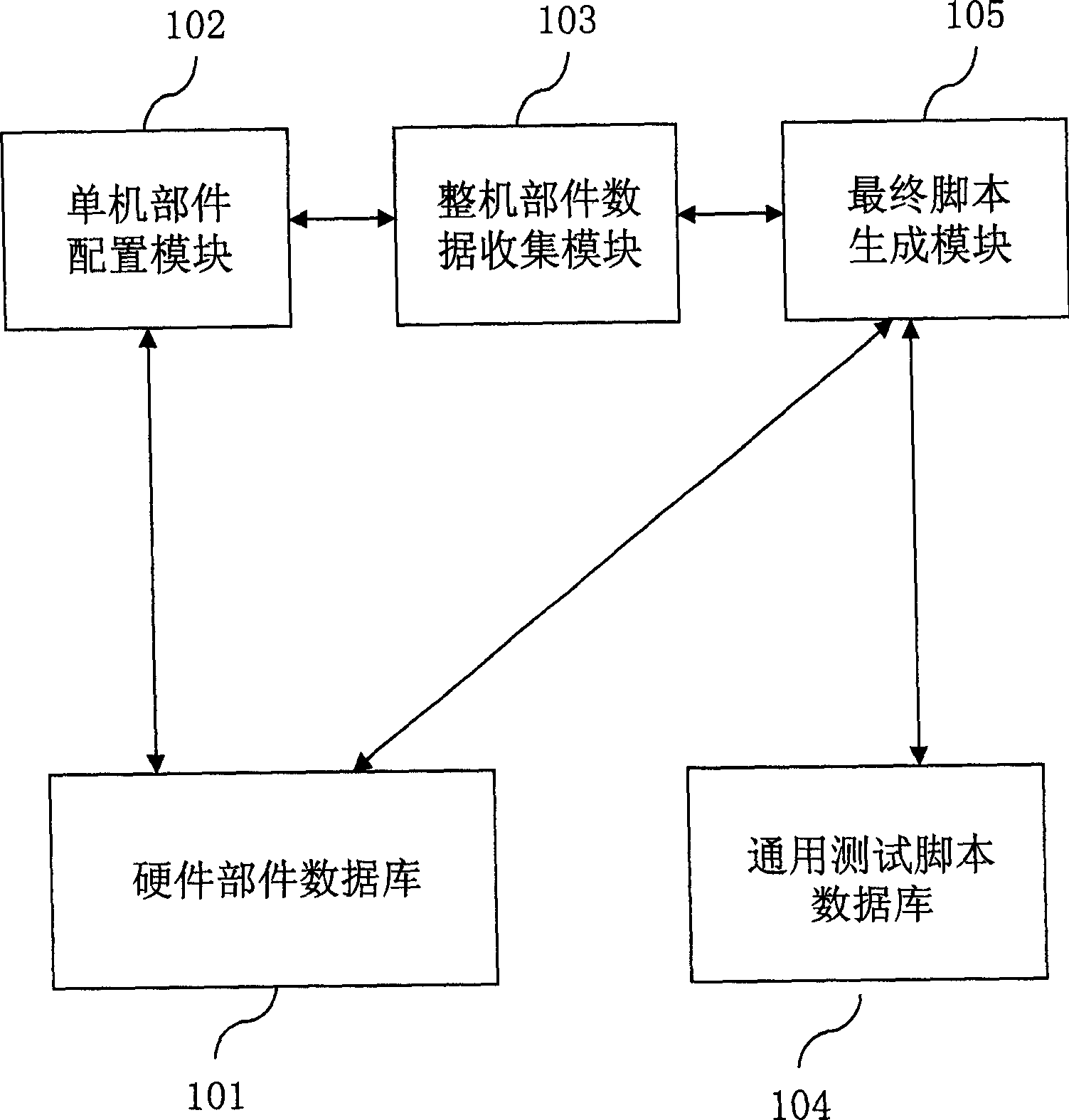
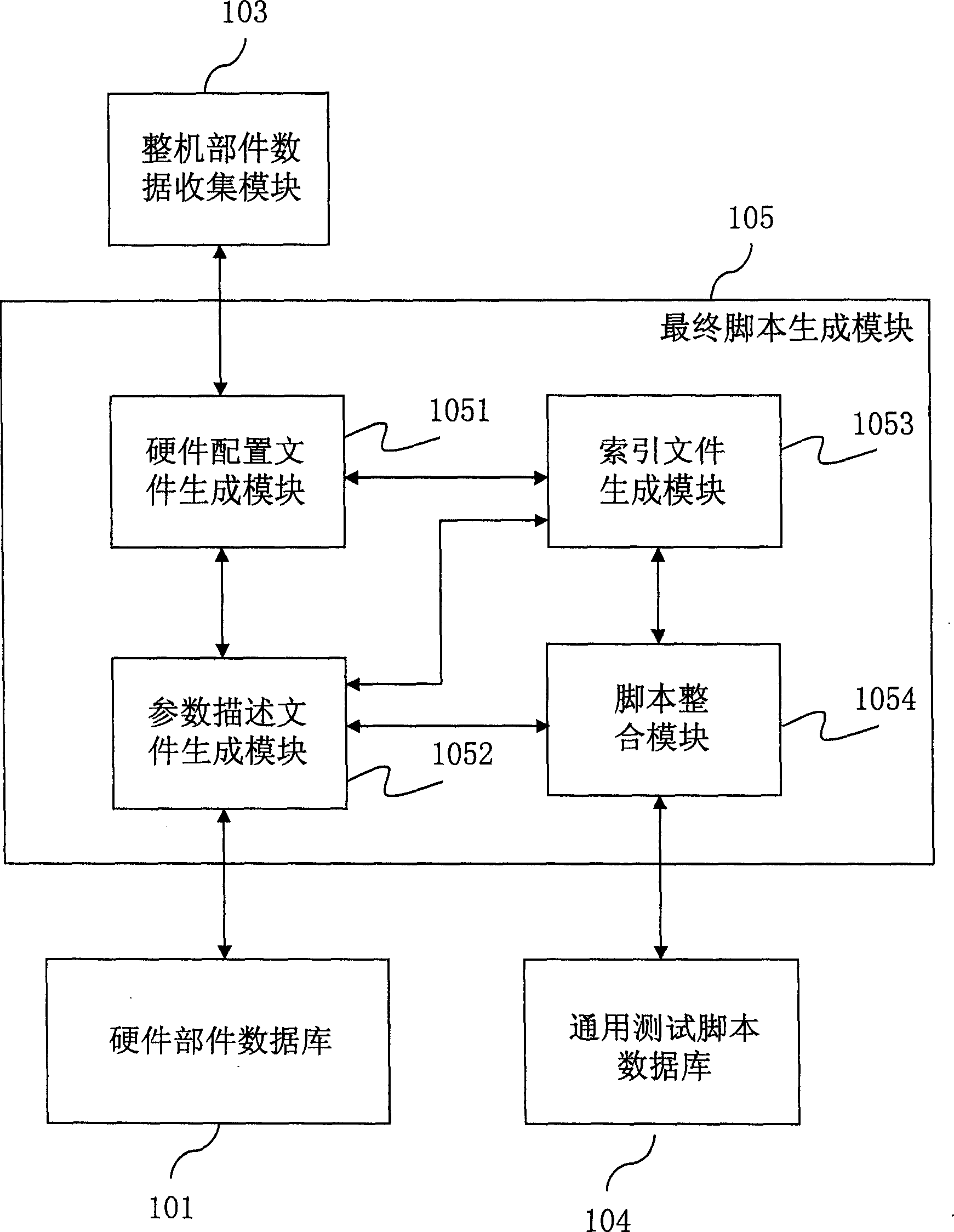
InactiveCN1635497AReduce workloadIncrease productivitySpecial data processing applicationsTest scriptMachine parts
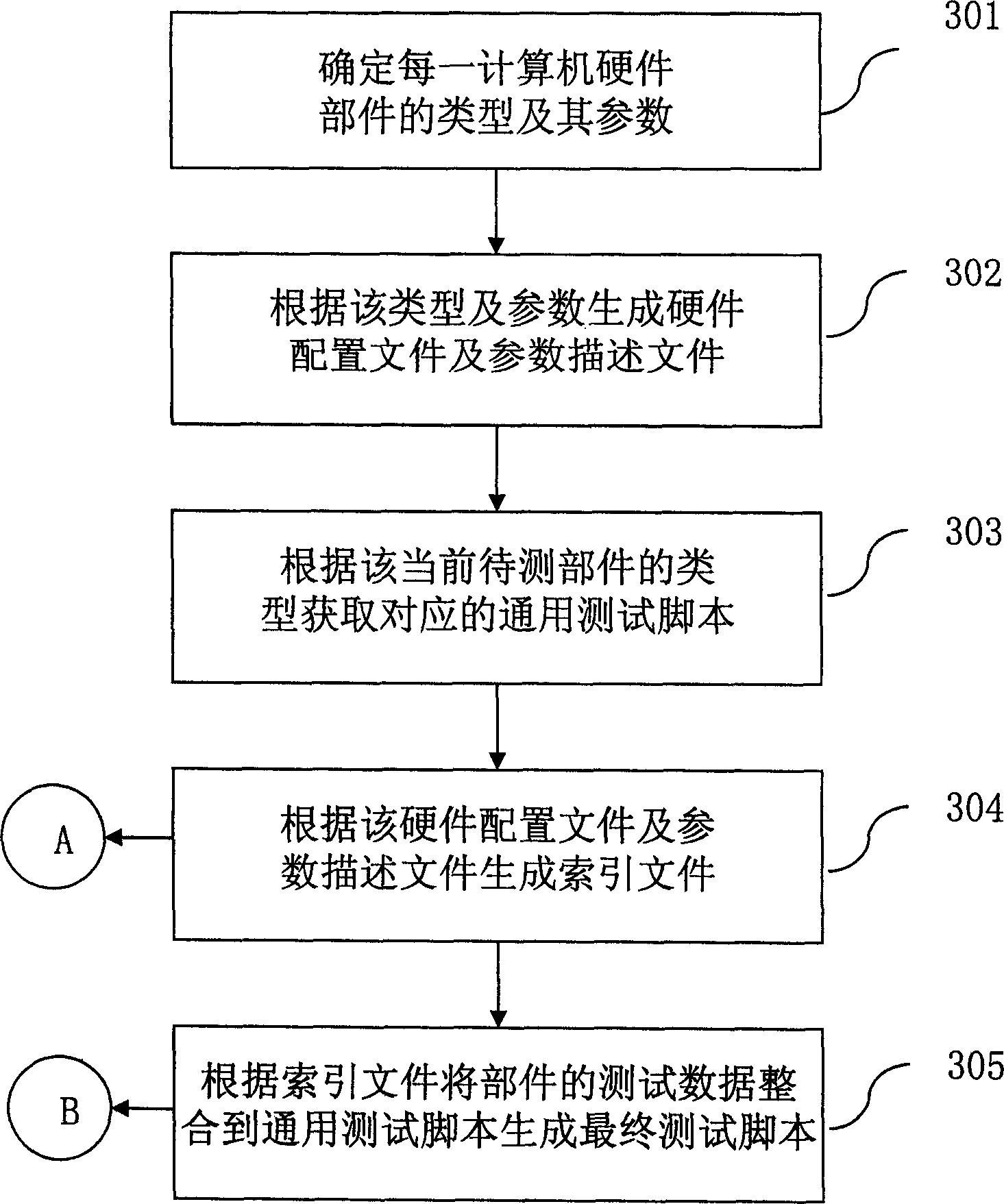
This invention relates to test script automatic generation system and method, which comprises the hardware part database, single machine part alignment module, complete part data collection module, general test script database and final script generation module. The method comprises the following steps: first determining the part type and parameters; generating hardware alignment file and parameter description file and then generating index file; then acquiring the relative general test script according to the current test part type; integrating the test data to the general test script to form final test script.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
Method and system of identifying a problem prone part
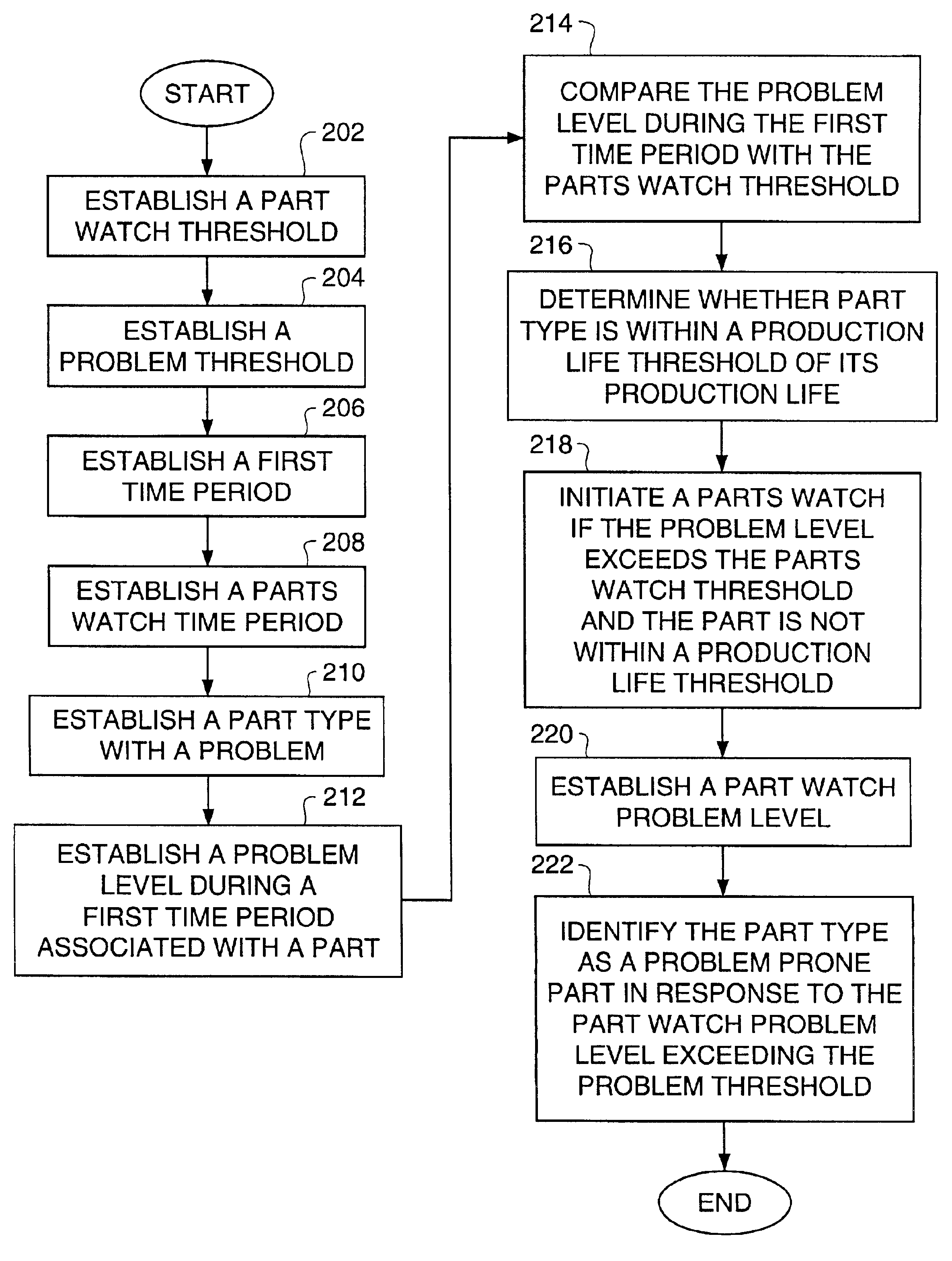
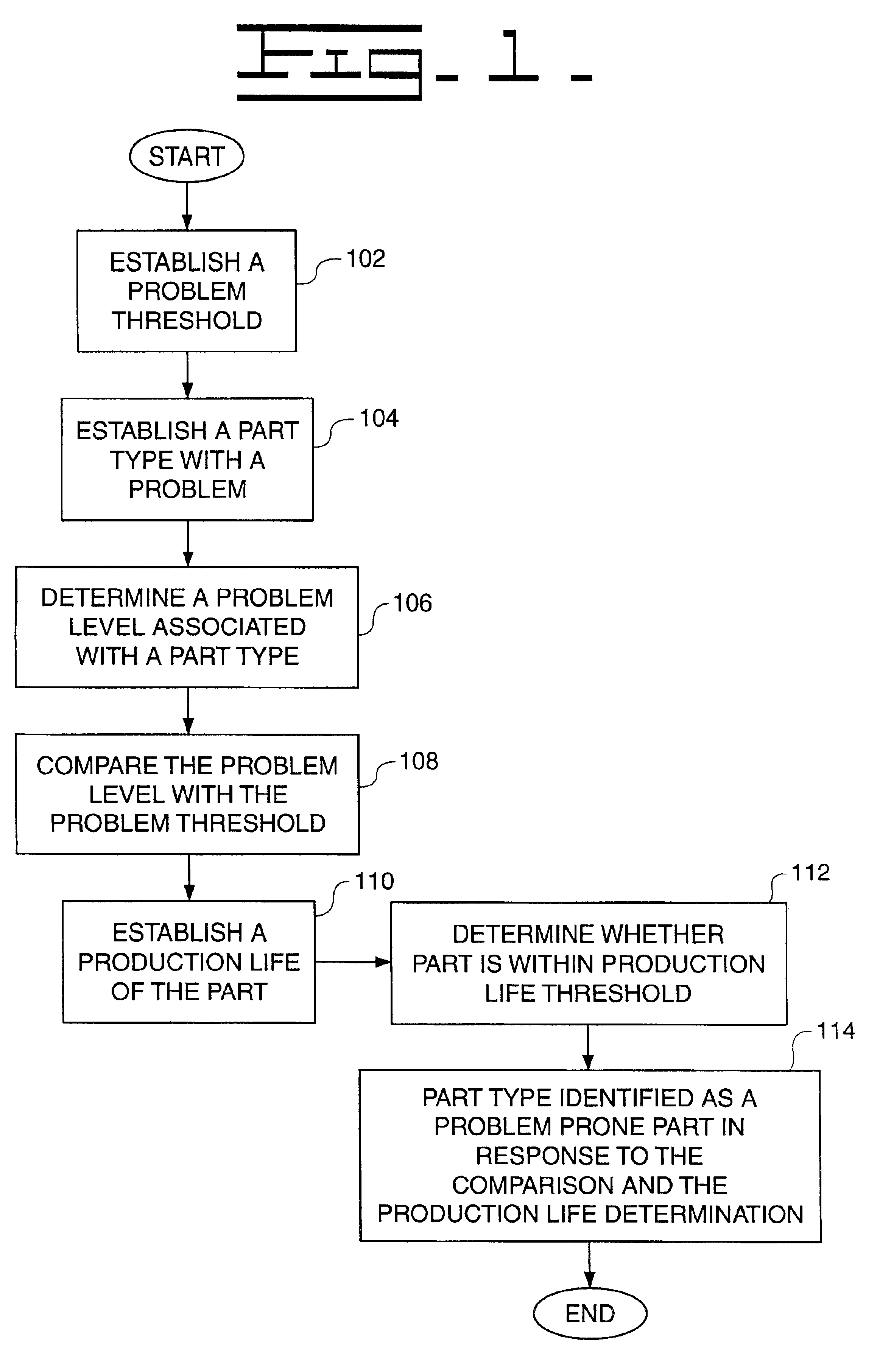
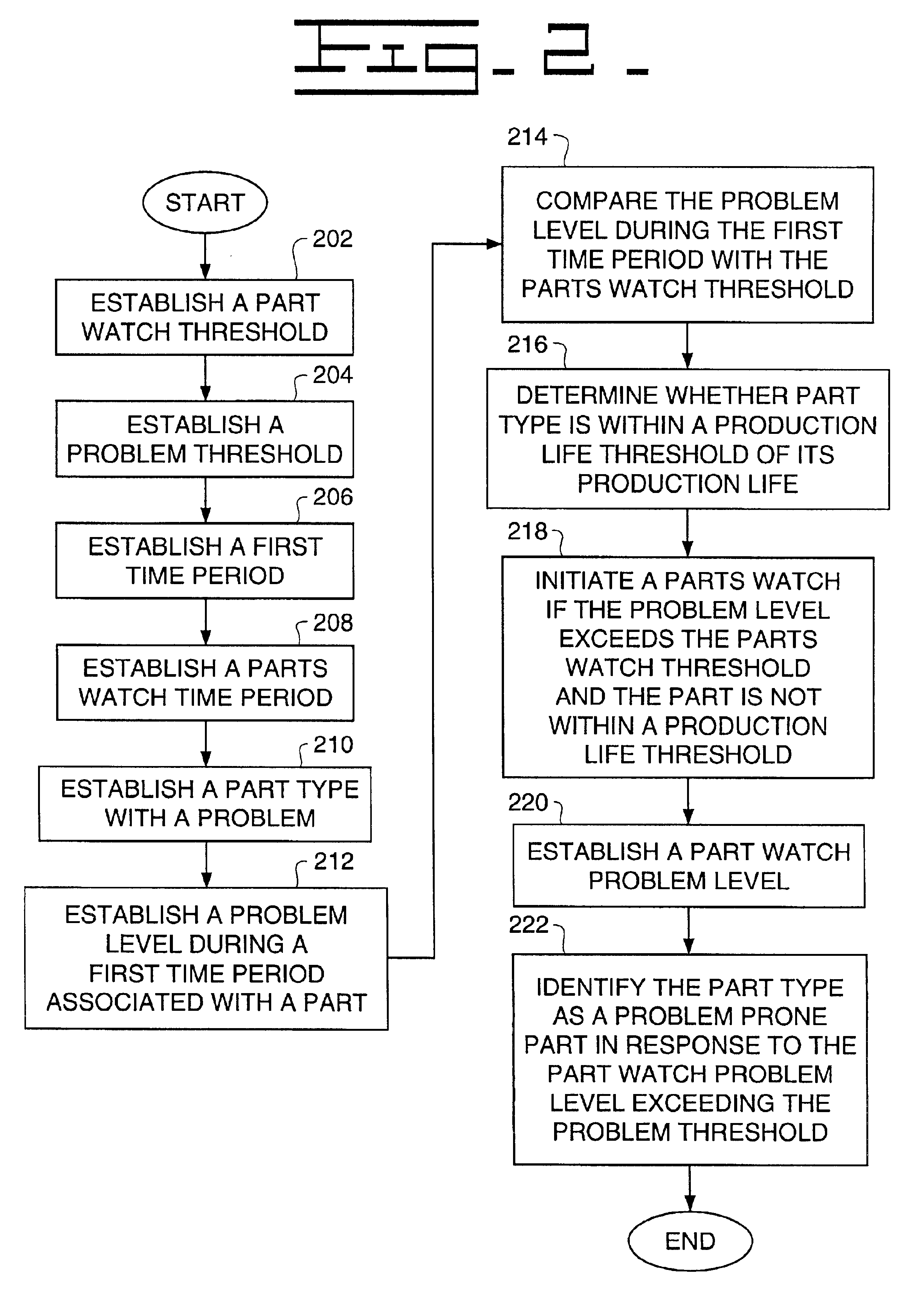
The present invention includes a method and system of identifying parts prone to problems. The method includes the steps of establishing a problem threshold, establishing a part type with a problem, determining a problem level with the part type in response to the part type problem level, comparing the problem level with said problem threshold, establishing a production life of the part type, determining if the part type is within a threshold of the production life, identifying the part type as the problem prone part in response to the comparison and the production life determination.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
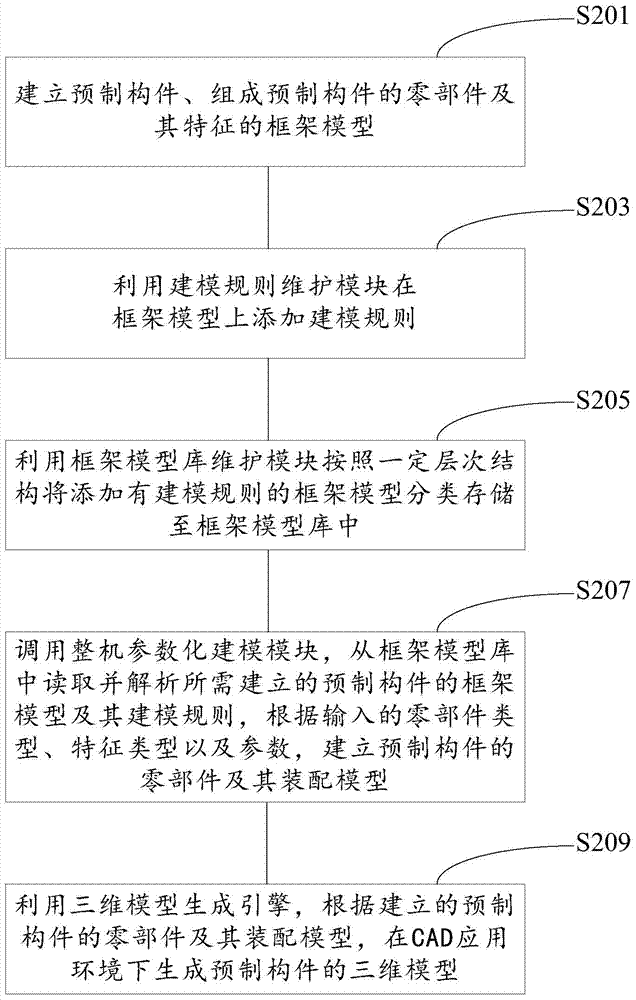
Three-dimensional modeling system and method for prefabricated parts
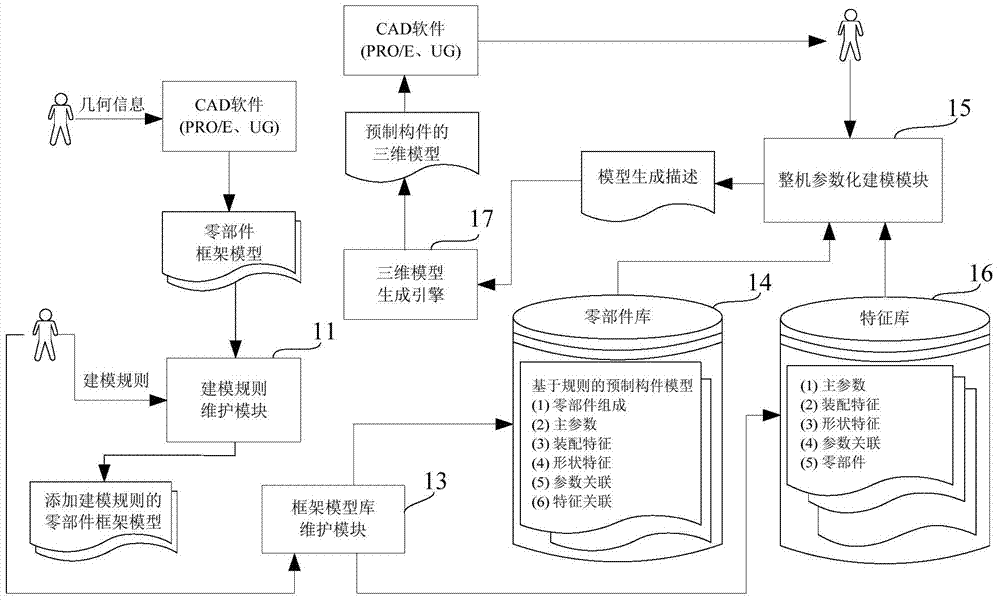
The invention provides a three-dimensional modeling system and method for prefabricated parts. The three-dimensional modeling system comprises a modeling rule maintenance module, a frame model base maintenance module, a whole machine parameterization modeling module and a three-dimensional model generation engine, wherein the whole machine parameterization modeling module is used for reading and analyzing to-be-built frame models of the prefabricated parts and modeling rules of the frame models in a frame model base, instantiating the frame models according to input part types, characteristic types and parameters, and building the parts and assembly models of the prefabricated parts; and the three-dimensional model generation engine is used for generating three-dimensional models of the prefabricated parts according to the built parts and assembly models of the prefabricated parts. According to the three-dimensional modeling system and method, the modeling rules and the frame models of the prefabricated parts are separated, the modeling rules of the prefabricated parts can be added and modified conveniently, and complete machine parameterization modeling meeting different design requirements as well as the three-dimensional models of the prefabricated parts can be generated rapidly through general and customizable part bases and the modeling rules.
Owner:CHINA CONSTR EIGHT ENG DIV CORP LTD
Authority management system, device and method
ActiveCN105049423AGood advertising effectMeet the needs of obtaining various network business resourcesTransmissionPart typeThe Internet
The invention discloses an authority management system, device and method, and belongs to the technical field of the computer and internet. The system comprises at least one business client terminal and a background server. The business client terminals are used for playing target contents in the process of providing network business; acquiring designated operation events completed by users in view of the target contents; and interacting with the background server to acquire target authority for logging in the user account numbers of the business client terminals with the designated operation events acting as certificates, wherein the target authority refers to authority for acquiring the target type of network business resources. A problem of sever waste of a part type of the network business resources after classification of the network business resources and corresponding setting of the acquisition authority in the prior art can be solved so that the number of receivers of the target type of the network business resources can be effectively enhanced and waste of the target type of the network business resources can be avoided.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
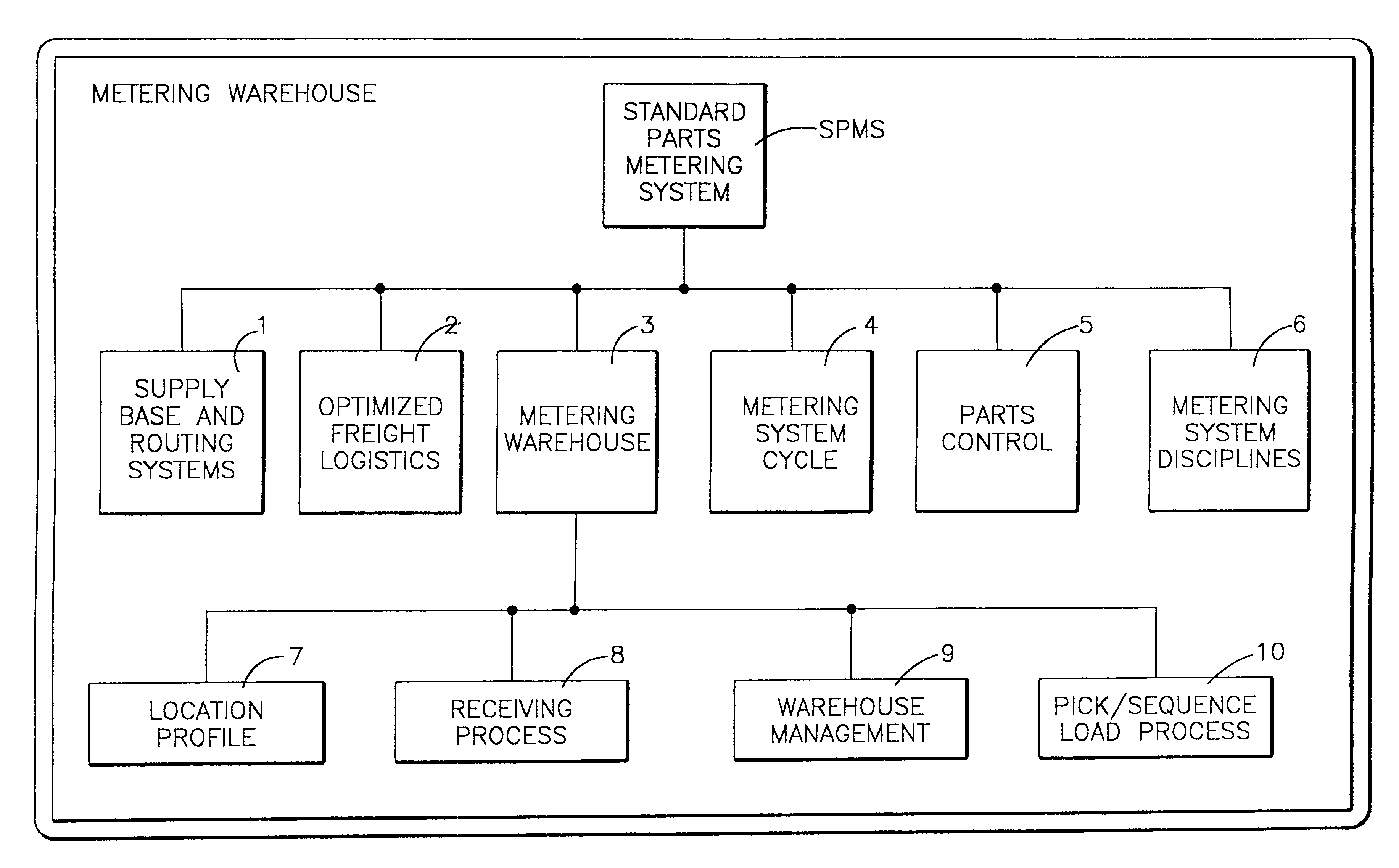
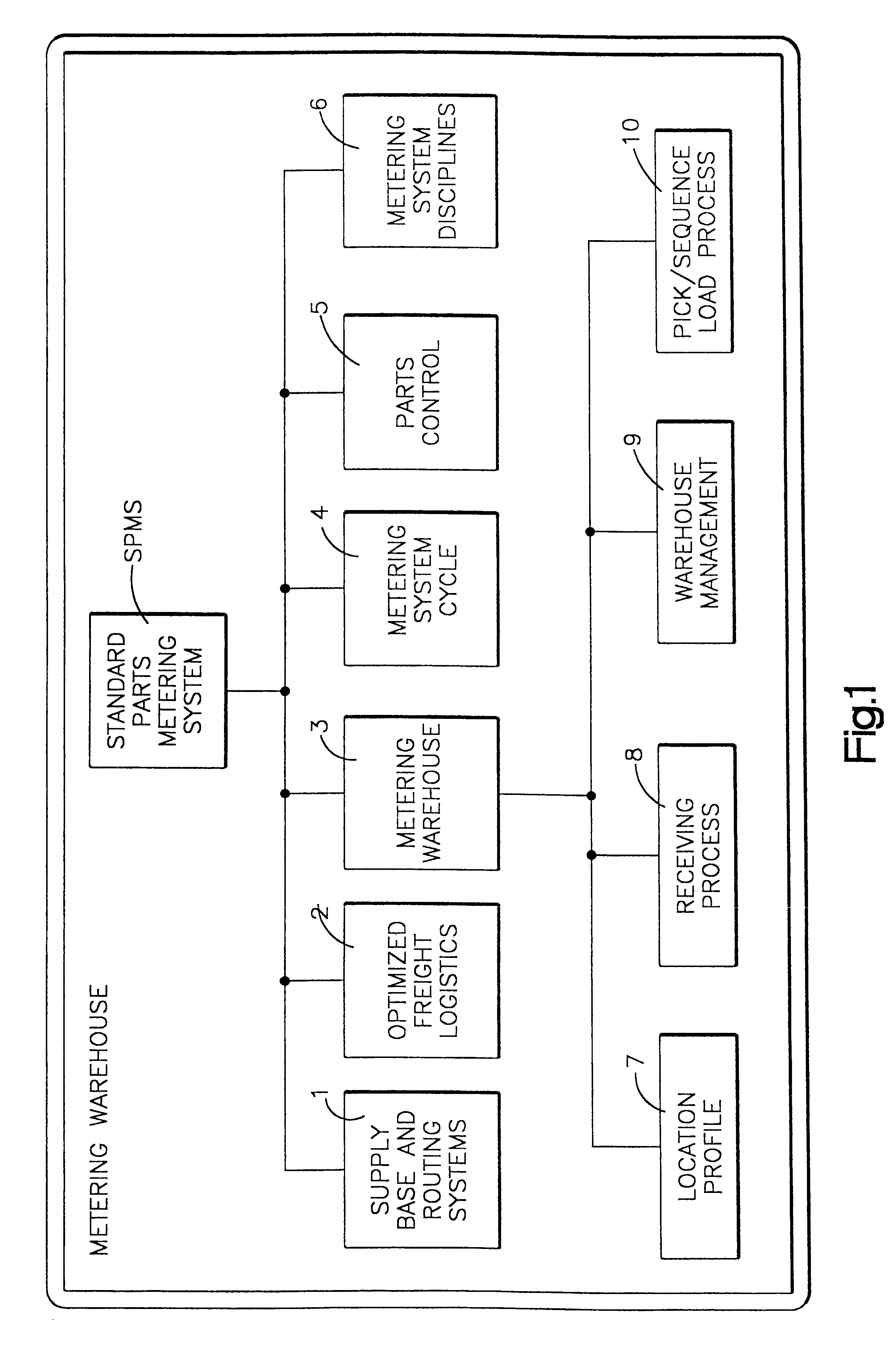
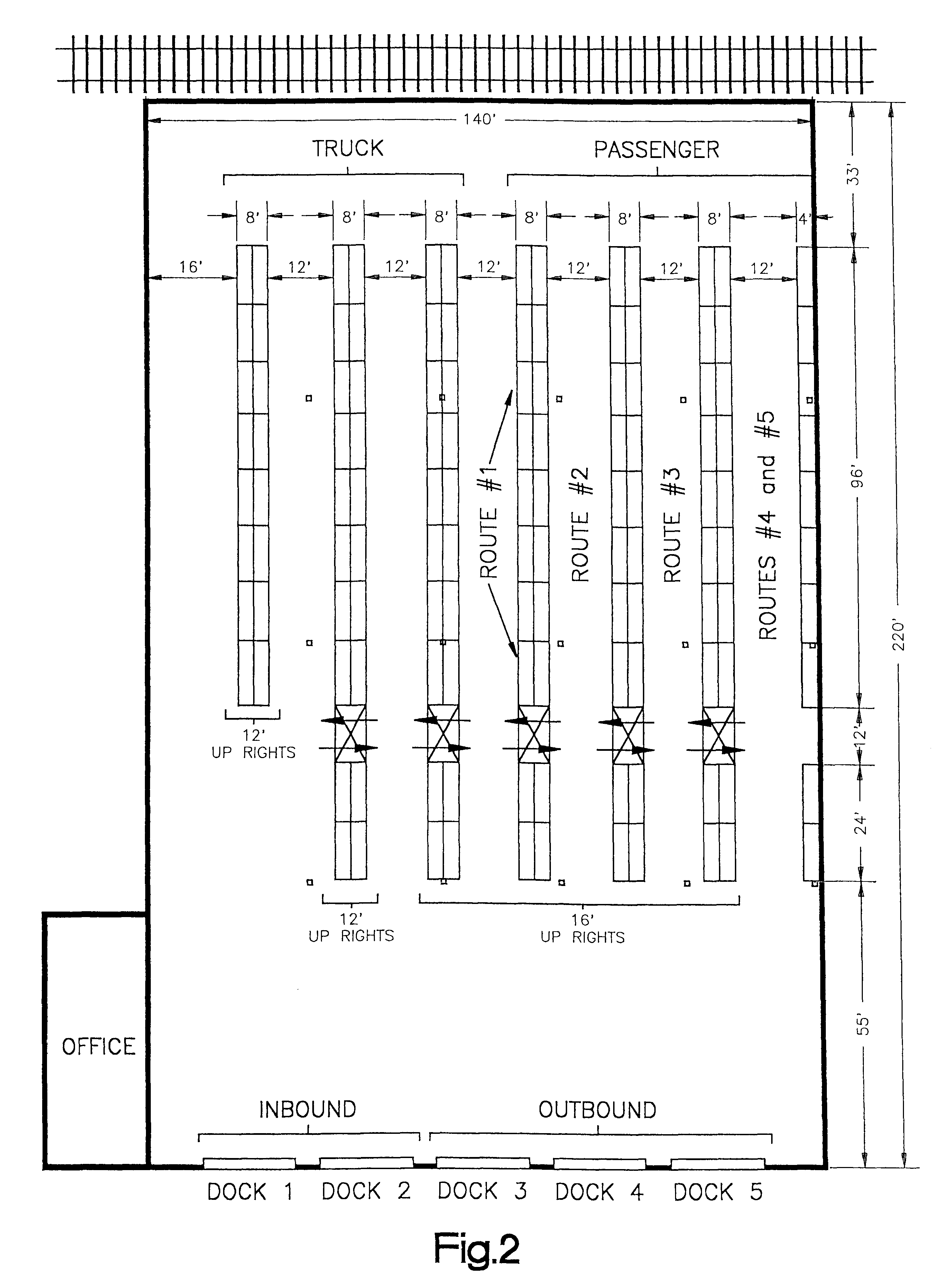
Standard parts metering system
InactiveUS6560508B1Reduced transit timeLower the volumeDigital data processing detailsLogisticsPart typeWorkstation
A system and method for collecting, inventorying, stocking and performing metered delivery of standard parts to an assembly operation. Standard parts are collected from multiple suppliers in an optimized pick-up route, and delivered to a standard parts metering warehouse. The standard parts are broken down into production shift quantities based upon production data of the assembly operation. The production shift quantities of standard parts are labeled according to part type or identity and a drop zone within the assembly operation. The standard parts are then stocked in the metering warehouse according to an optimized route which corresponds to a drop zone delivery sequence in the assembly operation. Limited production shift quantities of standard parts are then metered from the metering warehouse in accordance with a production schedule of the assembly operation, and delivered directly to pedestals at workstations at the corresponding drop zones in the assembly operation.
Owner:K&T OF LORAIN
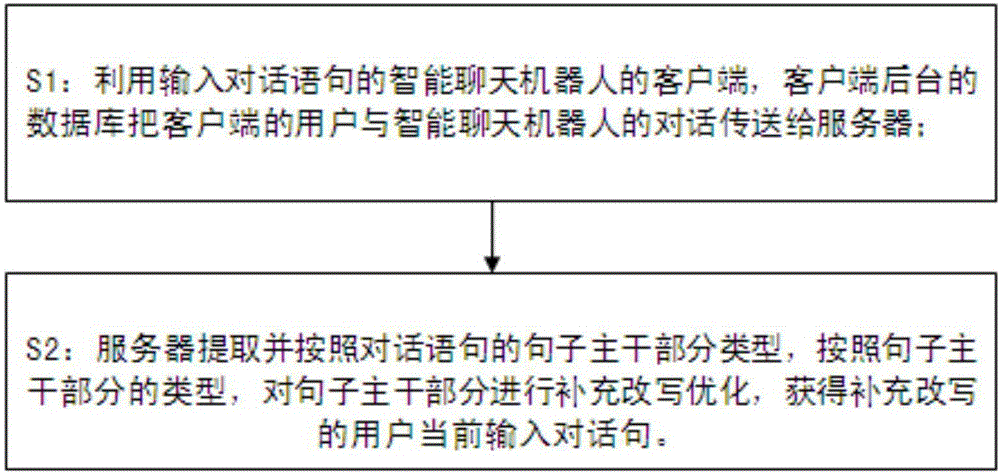
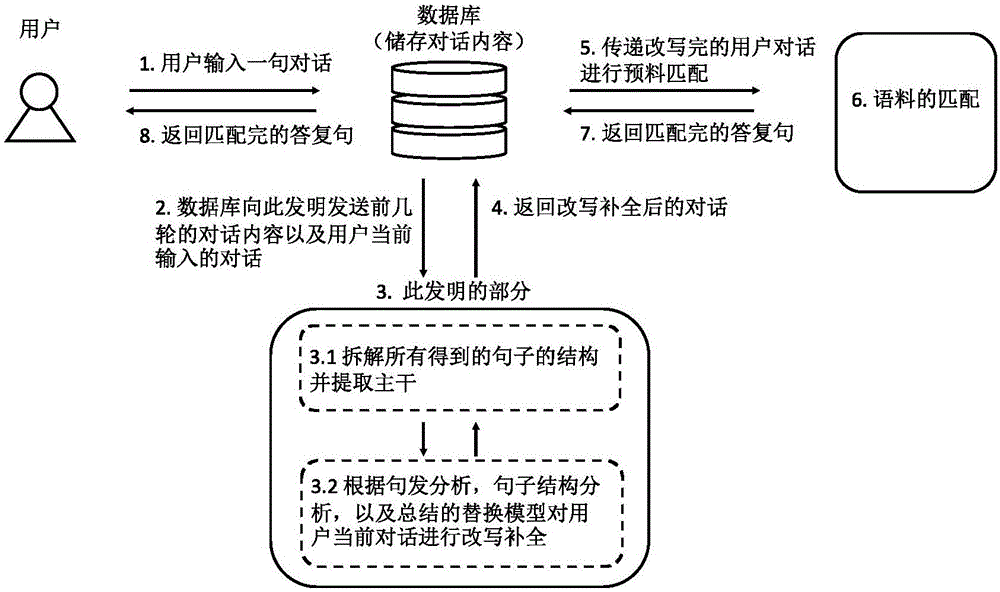
Optimization method and device of input statements in intelligent chatting robot
ActiveCN106777018AReasonable searchEasy searchSpecial data processing applicationsPart typeHuman–computer interaction
The invention provides an optimization method and device of input statements in an intelligent chatting robot. The method comprises the following steps: transmitting dialogues of a user of a client and the intelligent chatting robot to a server by utilizing a database of a client background of the intelligent chatting robot with input conversation statements; and extracting and carrying out supplementing, rewriting and optimization on a sentence trunk part according to sentence trunk part types of the conversation statements by the server, so as to obtain user current input conversation statements which are supplemented and rewritten. The device comprises the client of the intelligent chatting robot with the input conversation statements, and the server connected to the client; the database of the client background is used for transmitting the current statements and other turns of dialogues between the user and the intelligent chatting robot within reference time to the server; the server is provided with a first module, a second module and a processing module; and replying sentences which accord with willingness of the user and a current dialogue context are matched from a language database of the intelligent chatting robot, and the user current input conversation statements which are rewritten are output.
Owner:EMOTIBOT TECH LTD
One-Part Type Moisture Curable Composition
InactiveUS20090299017A1Excellent Adhesive PropertiesGood weather resistancePolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesWeather resistanceSilylene
To provide a one-part type moisture curable composition exhibiting superior adhesion properties, weather resistance, coating tolerance, and the like, and providing good operationability, which is cured by moisture in the atmosphere to form an elastic material in the form of a rubber A one-part type moisture curable composition comprising: (A) a prepolymer having a urea bond(s), a urethane bond(s), and a hydrolysable silyl group(s) at a chain end(s) or pendent position(s) thereof; and (B) a polymer comprising a polyether structure(s) and / or a polyacryl structure(s) in the main chain, and having a hydrolysable silyl group(s) at a chain end(s) or pendent position(s) thereof.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
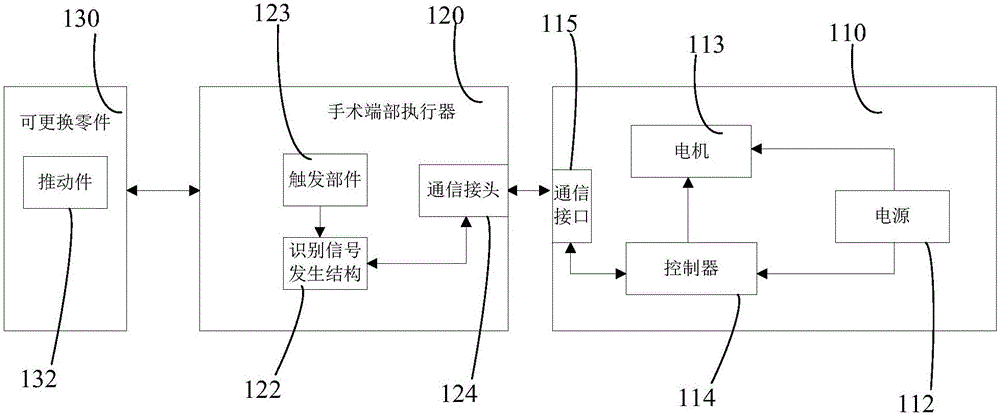
Intelligent abdomen microscope anastomat
The invention relates to an intelligent abdomen microscope anastomat. The intelligent abdomen microscope anastomat comprises a surgery end part actuator, a part type identification module, a driving shaft, a closing limiting switch and a handle; the handle is provided with a motor and a controller, a closing and triggering common switch and a closing and triggering change-over switch, wherein when the closing and triggering common switch is at a forward gear and the closing and triggering change-over switch is at a closed position, the motor is controlled by the controller to drive the driving shaft to move forward; when the driving shaft moves forward until a closing and limiting switch is triggered, the motor is controlled by the controller to stop running; after the closing and triggering common switch is at the forward gear and the closing and triggering change-over switch is at a triggered position, the motor is controlled by the controller to drive the driving shaft to continually move along a straight line; when the closing and triggering common switch is at a backward gear, the motor is controlled by the controller to drive the driving shaft to move backward along the straight line. The controller can be used for controlling the driving shaft to move forward according to gear information of the closing and triggering change-over switch and the closing and triggering common switch, so that closing and triggering actions are finished respectively, and the closing intensity does not need to be manually controlled.
Owner:SUZHOU YINGTUKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
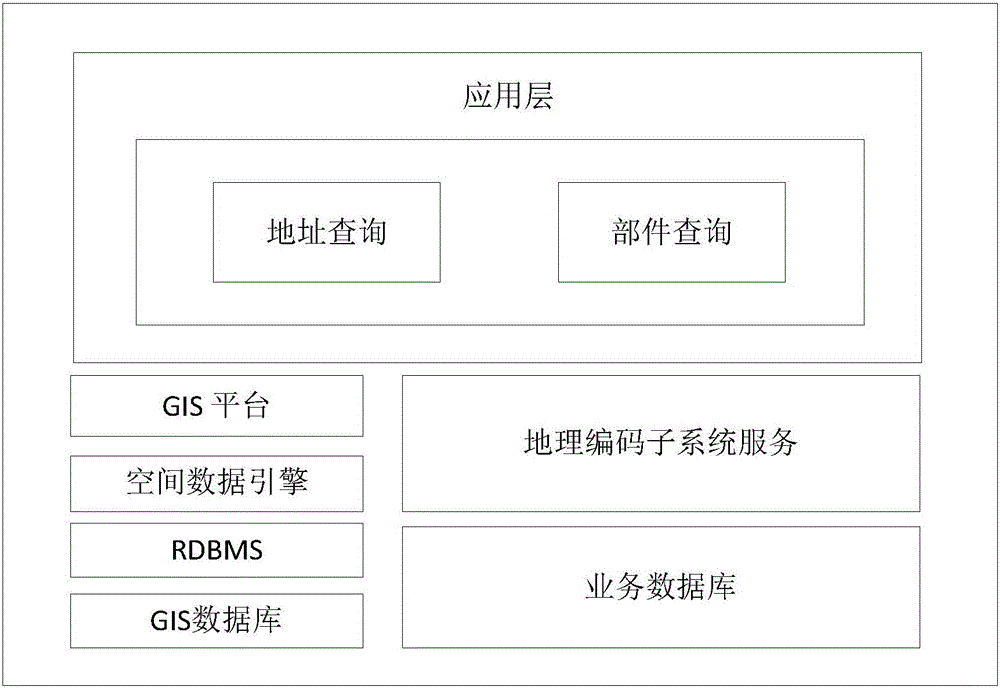
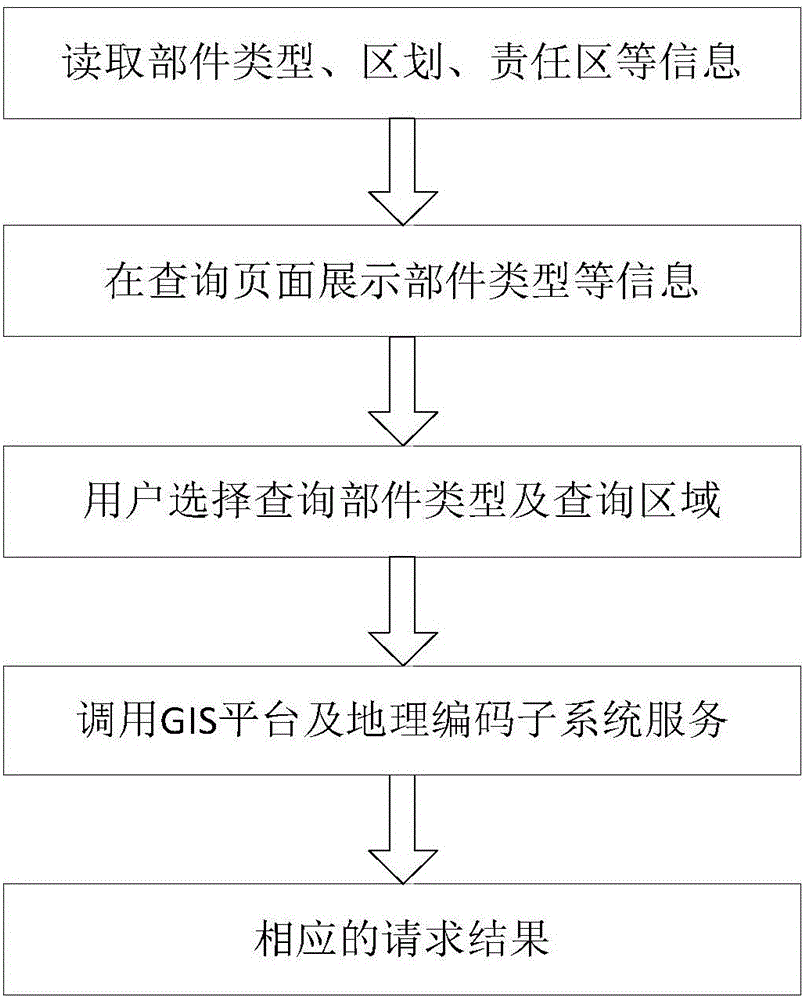
Geocoding method and geocoding system based on smart city
ActiveCN105022770AAdvanced technologyFunctionalSpecial data processing applicationsData informationPart type
The invention discloses a geocoding method and a geocoding system based on smart city. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring geographic data information, area of responsibility information, area division information and part type information, and storing the acquired information in corresponding databases; reading the area of responsibility information, the area division information and the part type information by a relational database management system and a spatial data engine, and showing the information on a GIS (Geographical Information System) platform; selecting a query part type and a query area or an address query, and calling a GIS service platform and a geocoding subsystem service to complete corresponding request results. According to the invention, the geocoding adopts a mature ArcGIS platform, which has advanced, safe and steady technology, powerful functions and high scalability.
Owner:TAIHUA WISDOM IND GRP CO LTD
One-pack type adhesive composition for dental use
ActiveUS20070100020A1High bonding strengthGood storage stabilityCosmetic preparationsImpression capsAdditive ingredientPart type
A hydrophobic acidic group-containing polymeric monomer (a); a water-soluble polymeric monomer (b); water (c); a photopolymerization initiator (d); an aromatic tertiary amine (e) having an electron-withdrawing group; a cross-linkable polymeric monomer (f); and a basic compound (g) for producing a water-soluble salt through a reaction with a part of the hydrophobic acidic group-containing polymeric monomer (a) are included as essential compounding ingredients. A one-part dental adhesive composition that exhibits high adhesive strength and high storage stability in adhesion between a teeth, and more particularly enamel or dentine, and a dental repairing material, and more particularly a resin material, is provided. Since the adhesive composition is one-part type, there is no need to mix in an adhering operation, and in addition, it exhibits high adhesive strength without performing preprocessing (etching processing and priming processing), it is suitably used as a one-step type dental adhesive composition for performing an adhering operation in a teeth repairing treatment in one processing.
Owner:KURARAY NORITAKE DENTAL
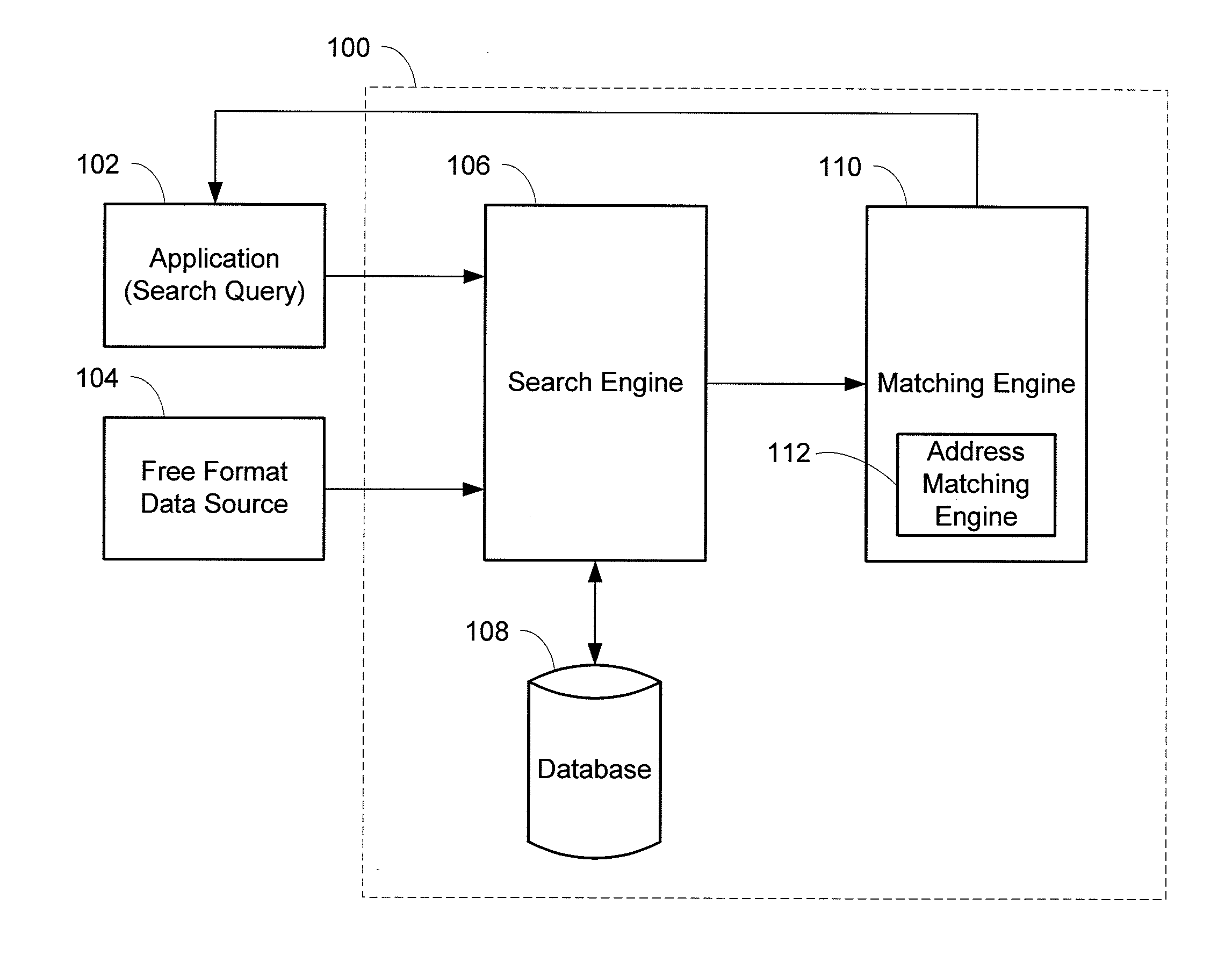
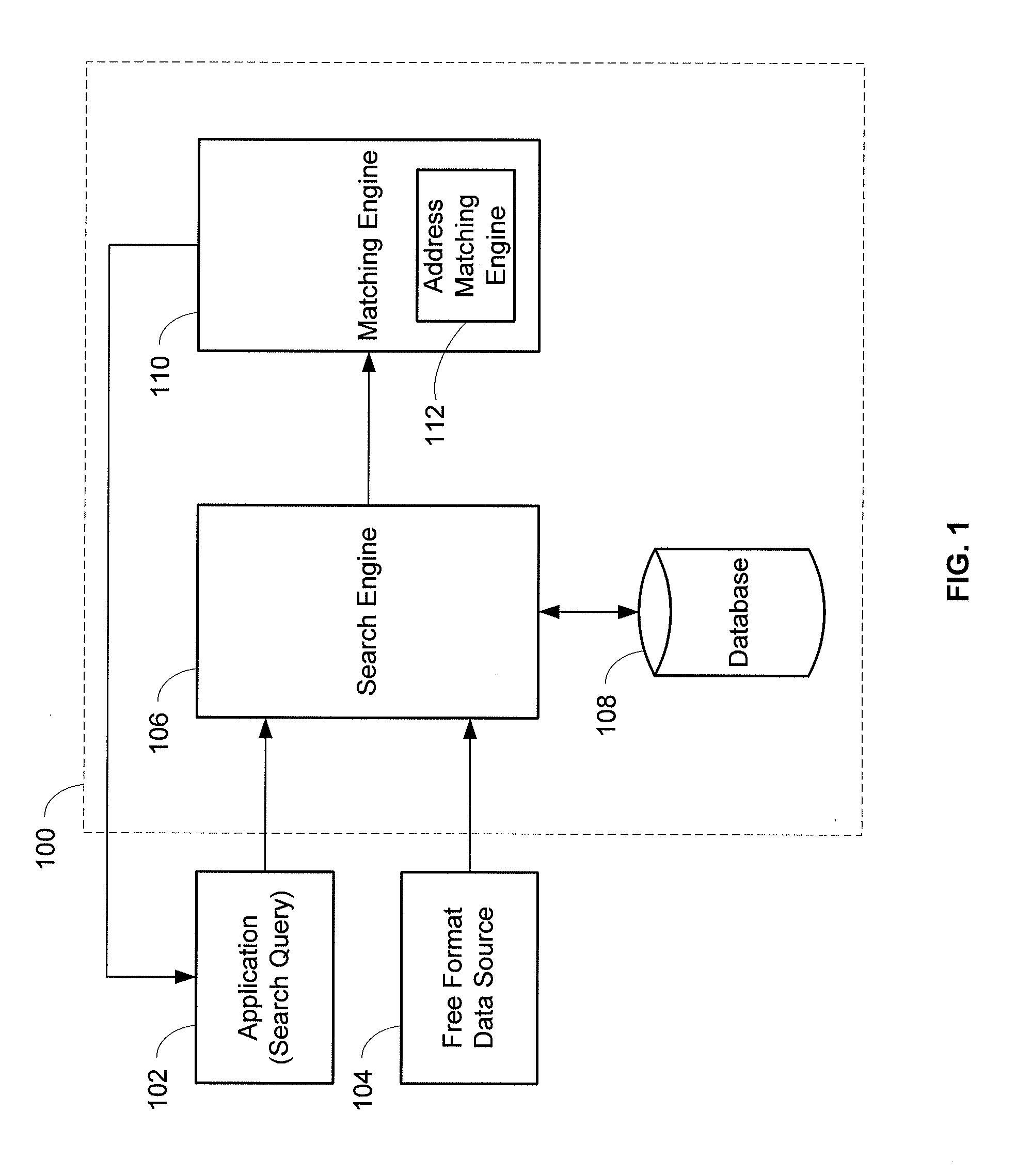
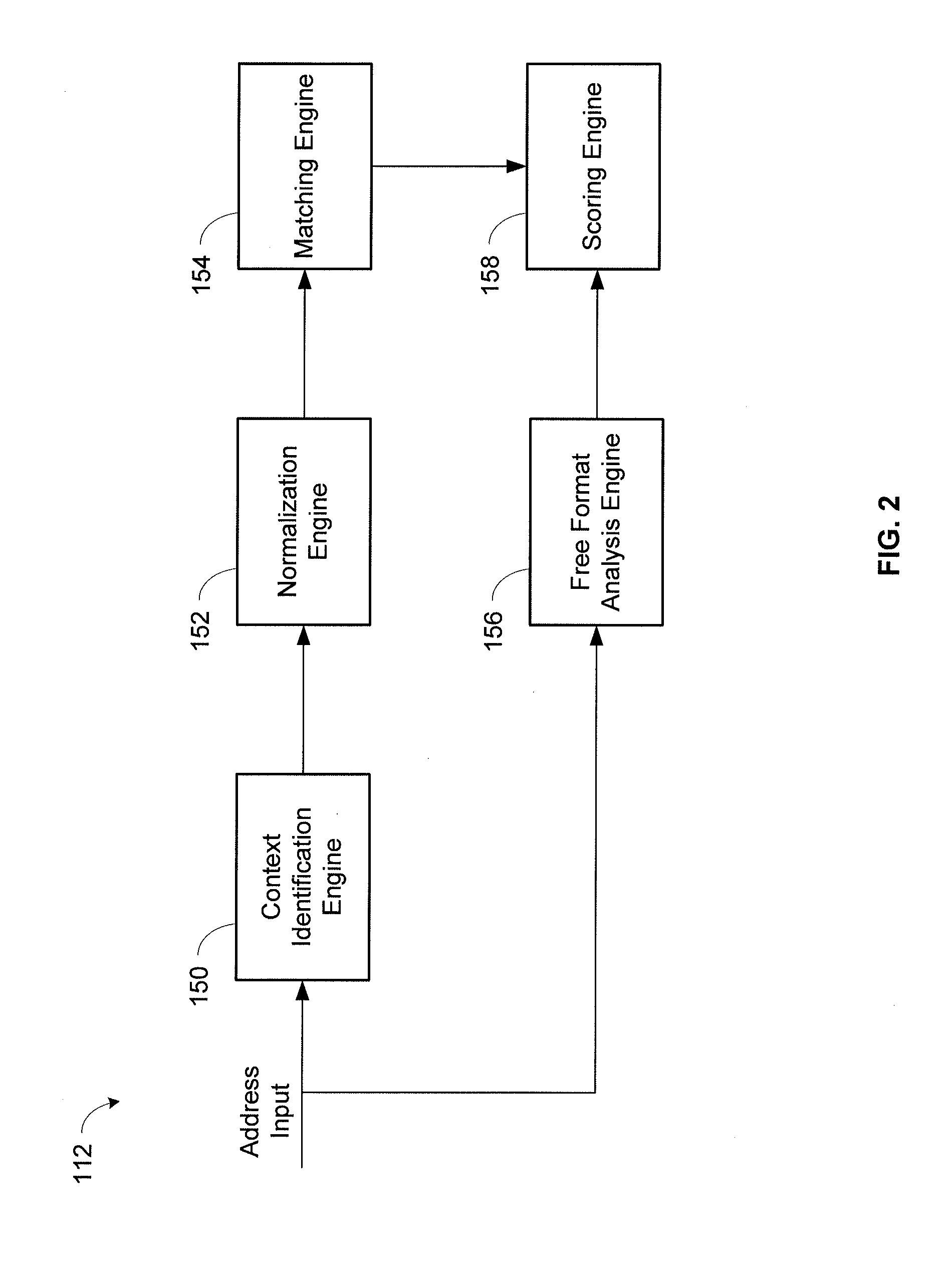
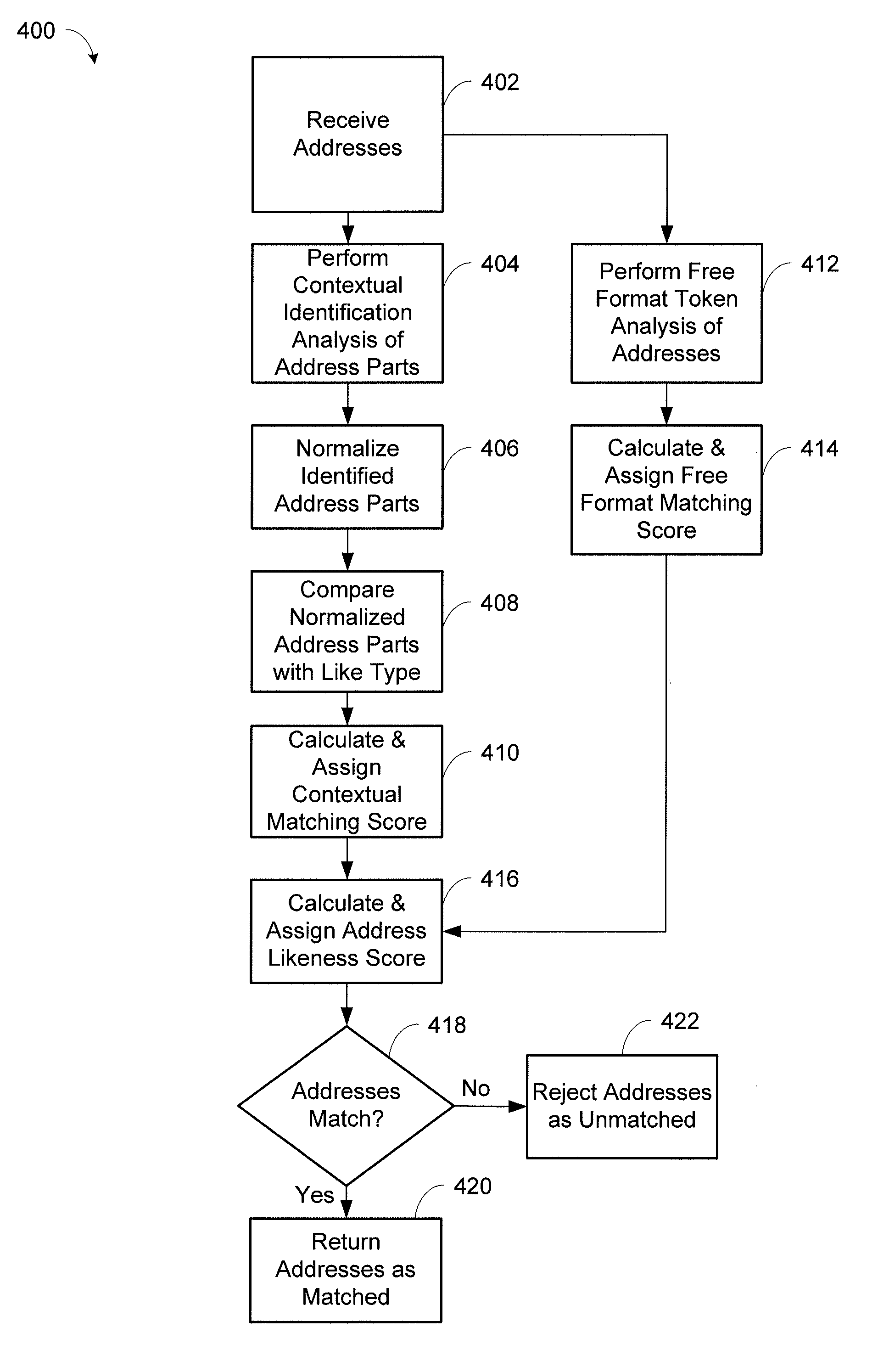
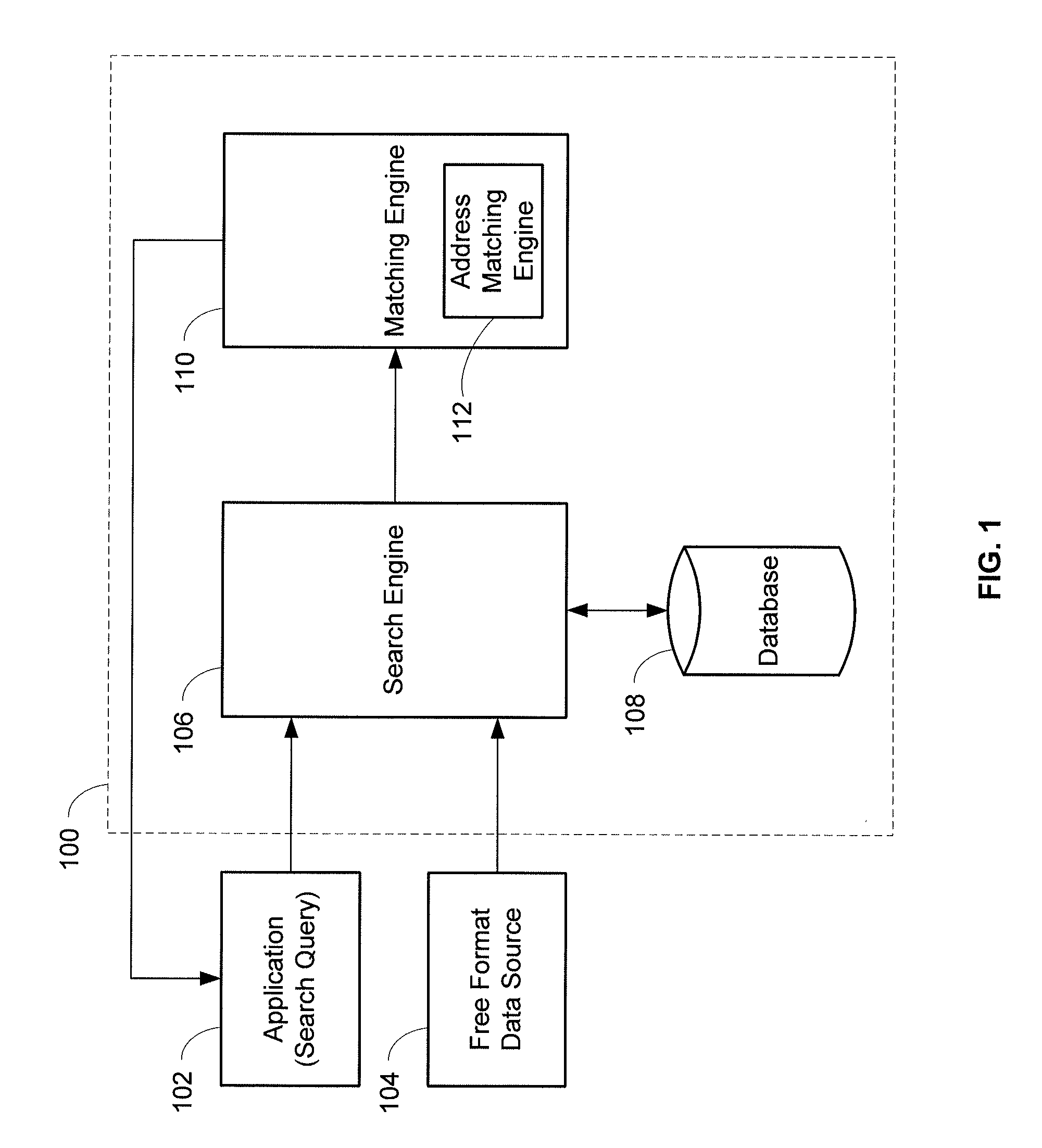
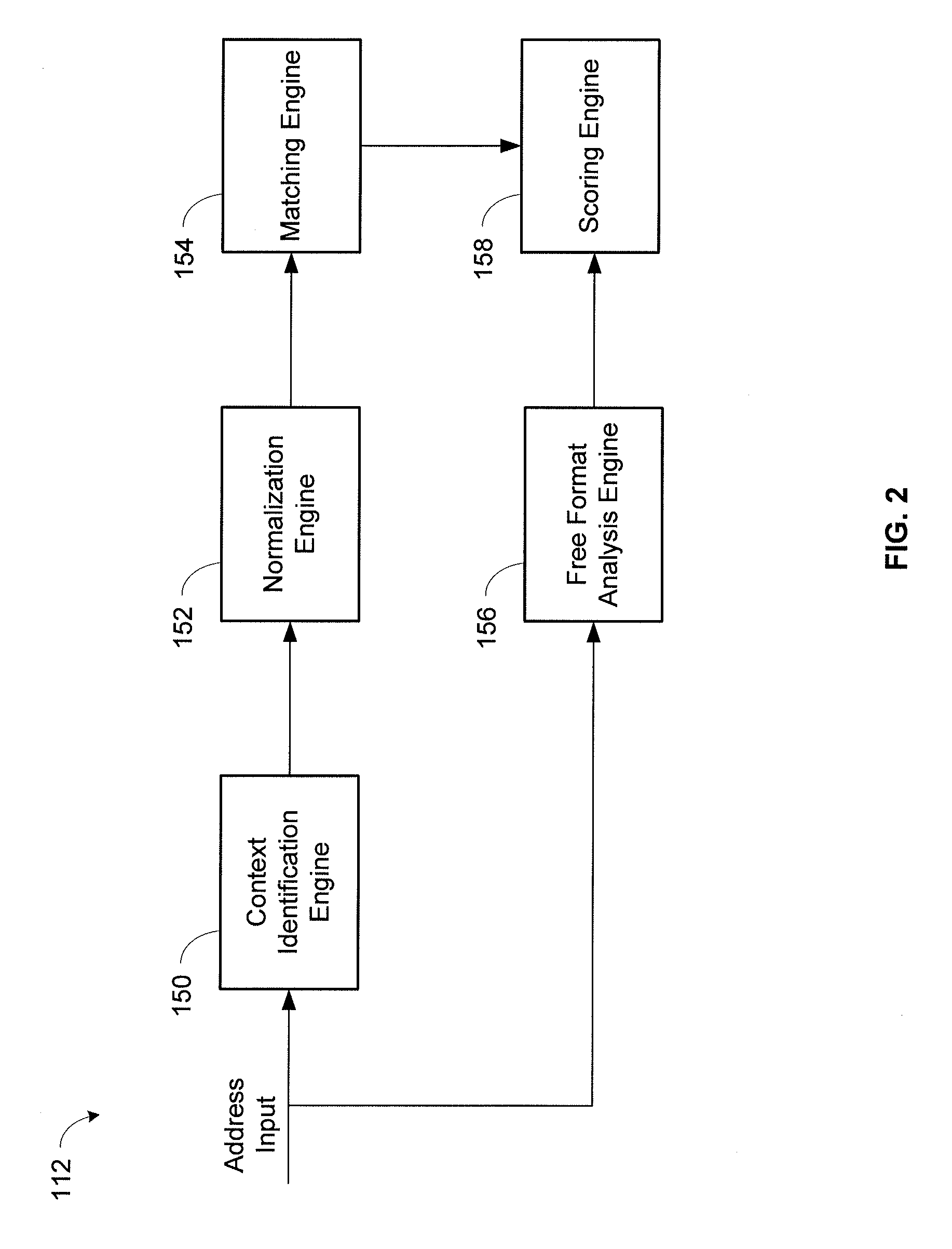
System and method for contextual and free format matching of addresses
A system and method for the matching addresses is provided. Addresses may be received from a search engine or other source for purposes of matching. Address parts in the addresses may be contextually identified. Identified address parts, including their associated data, that have address part types that are alike may be compared to one another and a contextual matching score may be calculated and assigned. A free format token analysis of the addresses may also be performed in parallel with, before, or after, the contextual identification, and a free format matching score may be calculated. An address likeness score may be calculated and assigned based on the contextual matching score and the free format matching score.
Owner:TRANSUNION
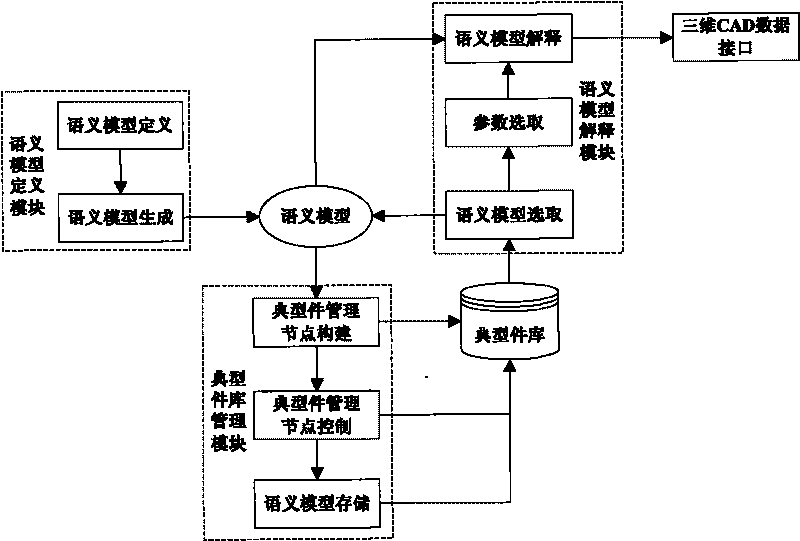
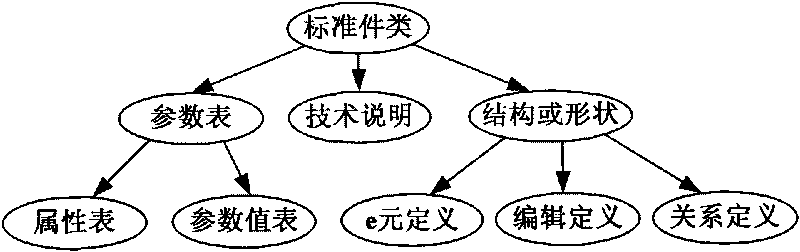
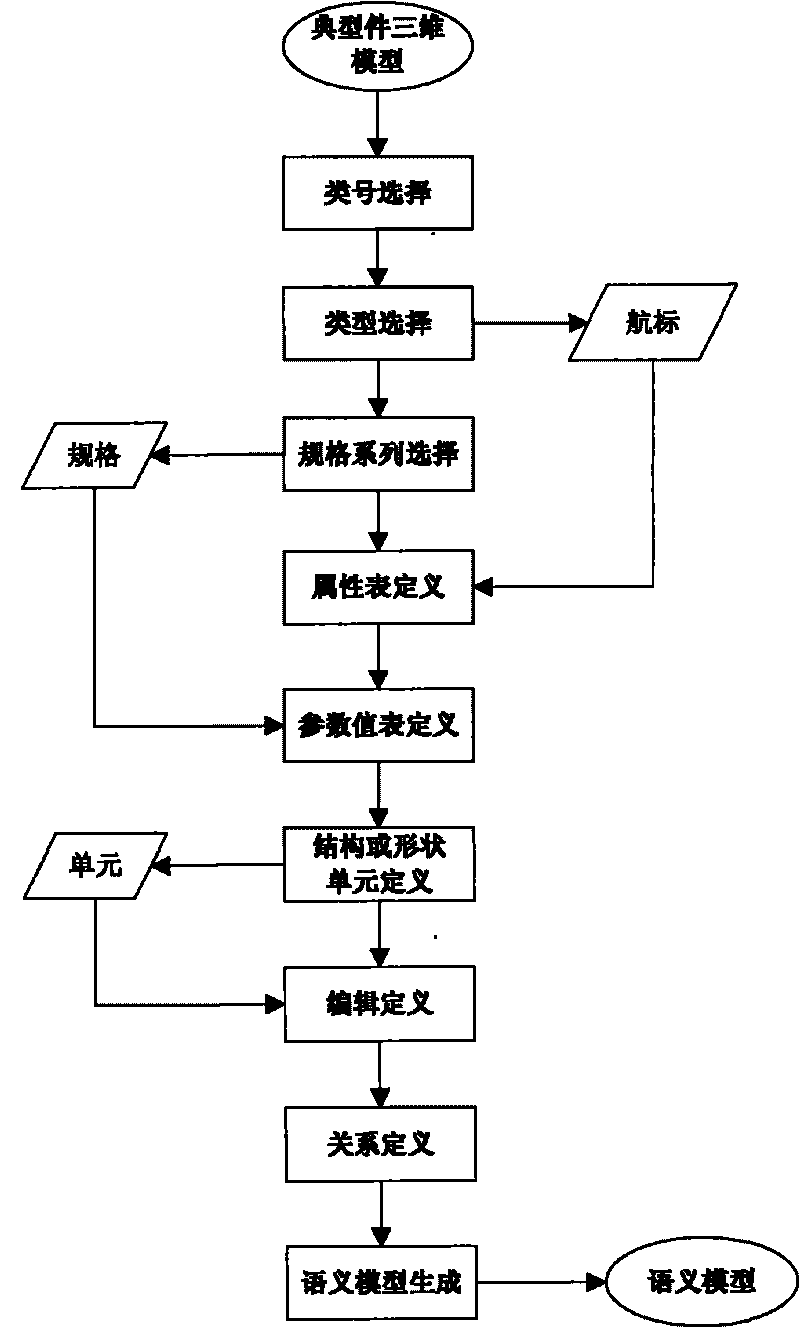
Management system of numerical control machining tool typical parts of complex parts of airplane and method
InactiveCN101763066AImprove design efficiencyImprove design qualityProgramme controlComputer controlNumerical controlPart type
The invention provides a management system of numerical control machining tool typical parts of complex parts of an airplane and a method. The system comprises a semantics model defining module facing to the three-dimensional parameterization of the typical parts, a typical parts storeroom management module and a semantics model explaining module. The method comprises the processes of defining, memorizing and explaining the semantics model. The invention can effectively manage the parts type and the assembled parts type typical parts of the numerical control machining tool of the complex parts of the airplane, provides support to quickly design the numerical control machining tool, and can be popularized and applied to the design field of the other mechanical products.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT CORP +1
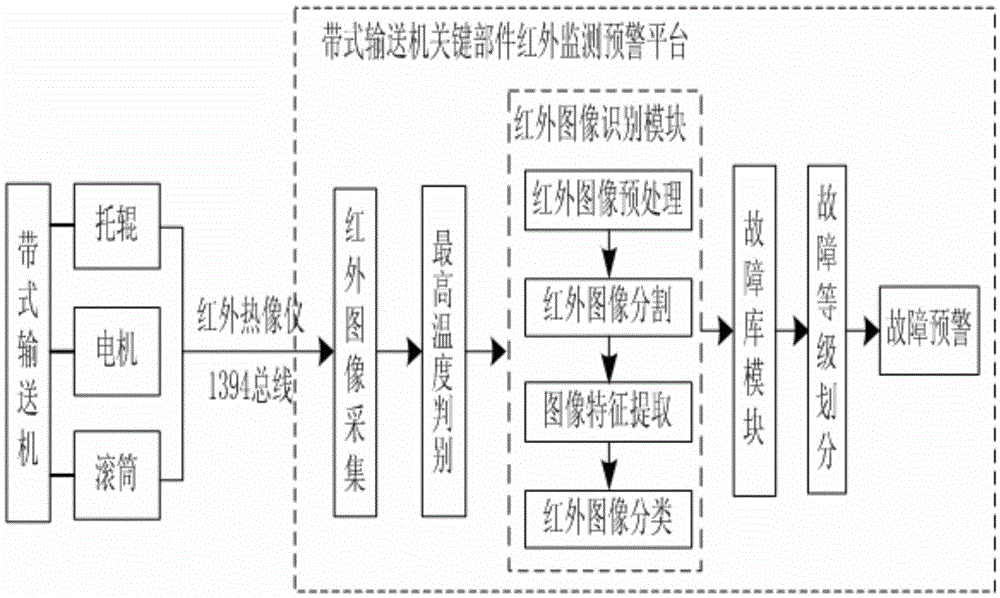
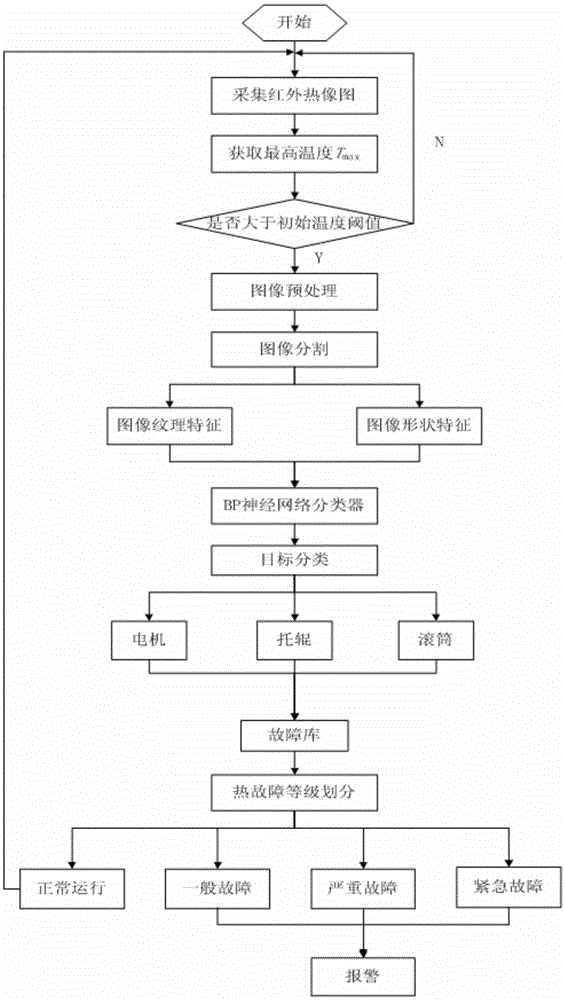
Infrared monitoring early warning system for belt conveyer key part
InactiveCN105608475AImprove efficiencyRealize the needs of monitoring and early warningCharacter and pattern recognitionImage segmentationOperability
The invention discloses an infrared monitoring early warning system for a belt conveyer key part. According to the system, an infrared thermal imaging instrument is utilized to acquire infrared images of a motor, a carrying roller and a roller of a belt conveyer, through pretreatment, image segmentation, characteristic extraction and classification of the infrared images, automatic identification of the motor, the carrying roller and the roller is realized, according to the identified part types, a temperature rising fault grade is determined, and fault early warning is carried out. The system integrates the infrared thermal imaging technology and the computer image identification technology, monitoring and early warning of the key part of the belt conveyer based on infrared thermal imaging are realized, and great importance on safe operation of the belt conveyer is realized. The system has advantages of excellent interactivity and operability, strong practicality and high popularization and application values.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
System and method for contextual and free format matching of addresses
A system and method for the matching addresses is provided. Addresses may be received from a search engine or other source for purposes of matching. Address parts in the addresses may be contextually identified. Identified address parts, including their associated data, that have address part types that are alike may be compared to one another and a contextual matching score may be calculated and assigned. A free format token analysis of the addresses may also be performed in parallel with, before, or after, the contextual identification, and a free format matching score may be calculated. An address likeness score may be calculated and assigned based on the contextual matching score and the free format matching score.
Owner:TRANSUNION
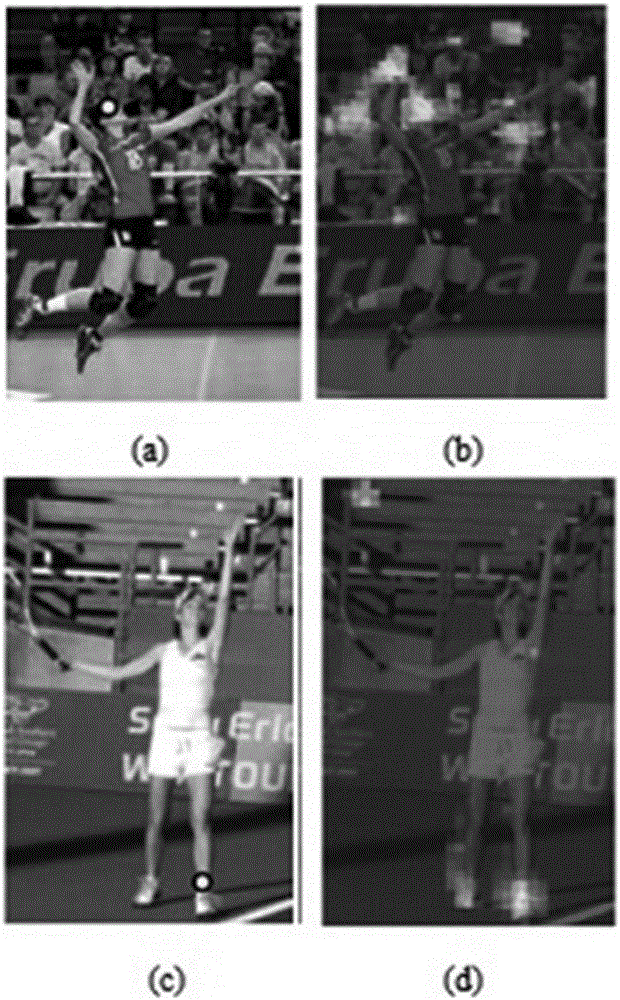
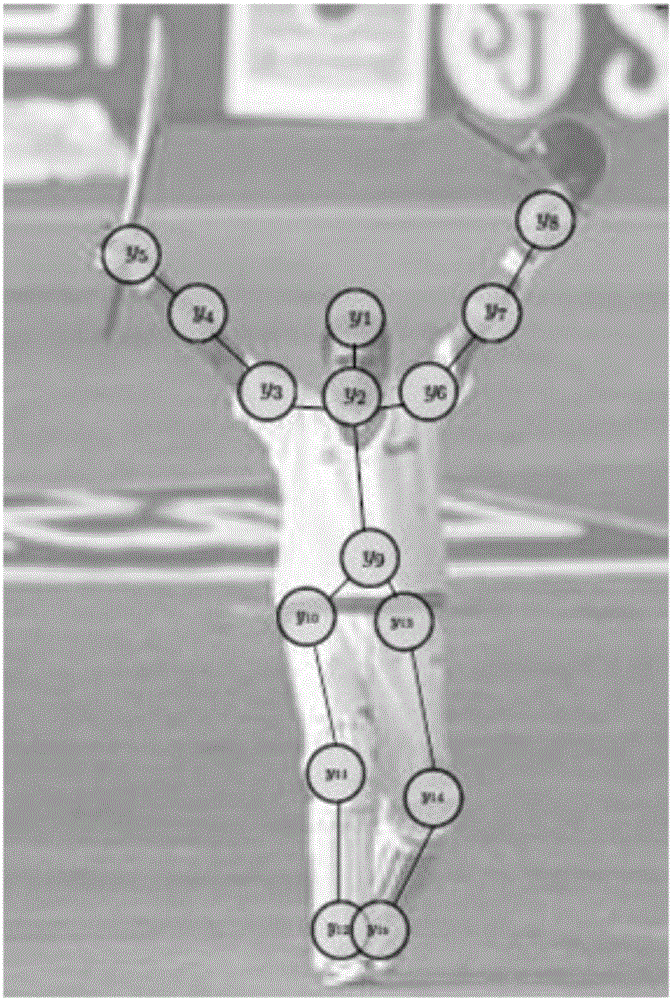
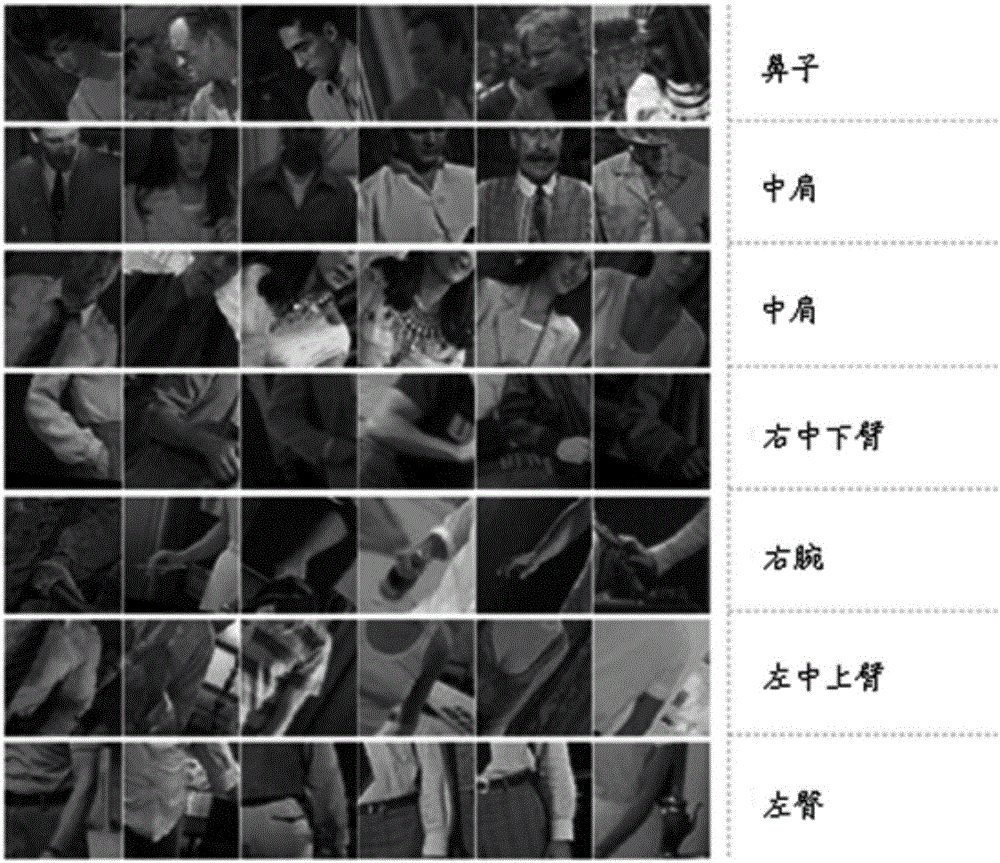
Pose estimation method and device as well as computer system
The invention relates to a pose estimation method and device as well as a computer system. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting features corresponding to each body part in a plurality of body parts of an object in an image so as to generate a plurality of feature charts, wherein each body part corresponds to at least one part type; predicting a part type score for each feature in each feature chart, and establishing a plurality of part type score charts according to the predicted part type scores; for at least one point in each part type score chart, optimizing the established part type score charts according to messages related to adjacent body parts of the body part corresponding to the point; and determining an estimated position and an estimated part type of each body part according to the optimized part type score charts, so as to obtain an estimated pose of the object.
Owner:BEIJING SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
Industrialized polyimide fiber drafting method
ActiveCN102943331ASmall impact heat loadImproved physical-mechanical propertiesTextiles and paperYarnPart type
Disclosed is an industrialized polyimide fiber drafting method. The method includes that a certain deniers of polyimide yarn sheets with uniform tension are placed in a four-part type hotbox environment and clamped by a rubber roller, under a certain feeding speed, the yarn sheets achieve a certain multiple drafting through a speed difference between a front drafting machine and a rear drafting machine, and the four-part type hotbox is a combination of a prehearing section hotbox, a superheated steam humidifying section hotbox, a high temperature drafting hotbox and a setting hotbox. During the process of the fiber treatment, the temperature changing gradient is reasonable, the impact thermal load which is stressed on the fibers is small, and the probability that the yarn sheets generate broken filaments is remarkably reduced. The fibers are subjected to superheated steam humidifying treatment before the high temperature drafting, the static electricity in the yarn sheets is eliminated, the drafting force of the same number of fibers is reduced by 25%, the draft multiple is increased by 30%, and the strength of the fibers is increased 40%. After the polyimide fibers are subjected to the drafting and high temperature setting, the internal stress of the polyimide fibers is eliminated, the stability of the fiber structure is improved, and the shrinking rate of the polyimide fibers is maintained about 2%.
Owner:JIANGSU AOSHEN HI TECH MATERIALS CO LTD
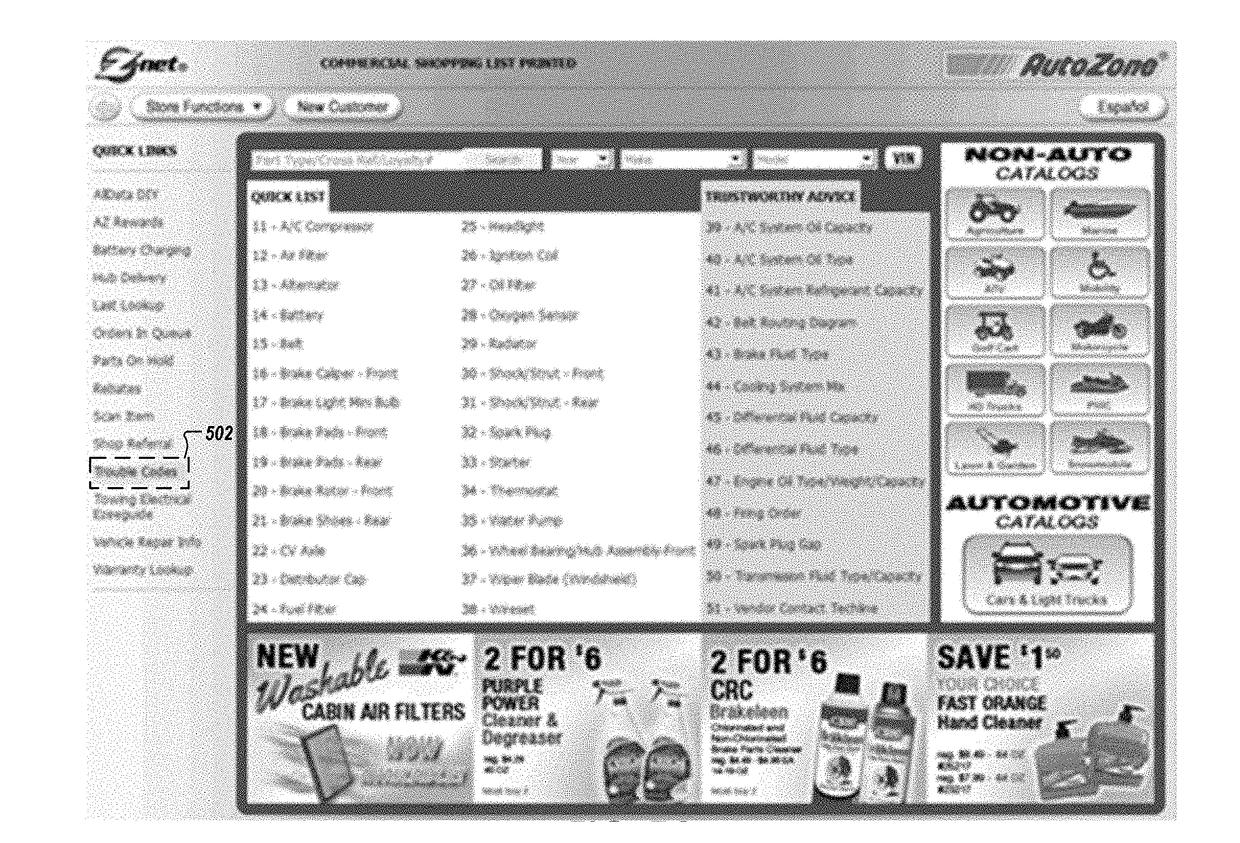
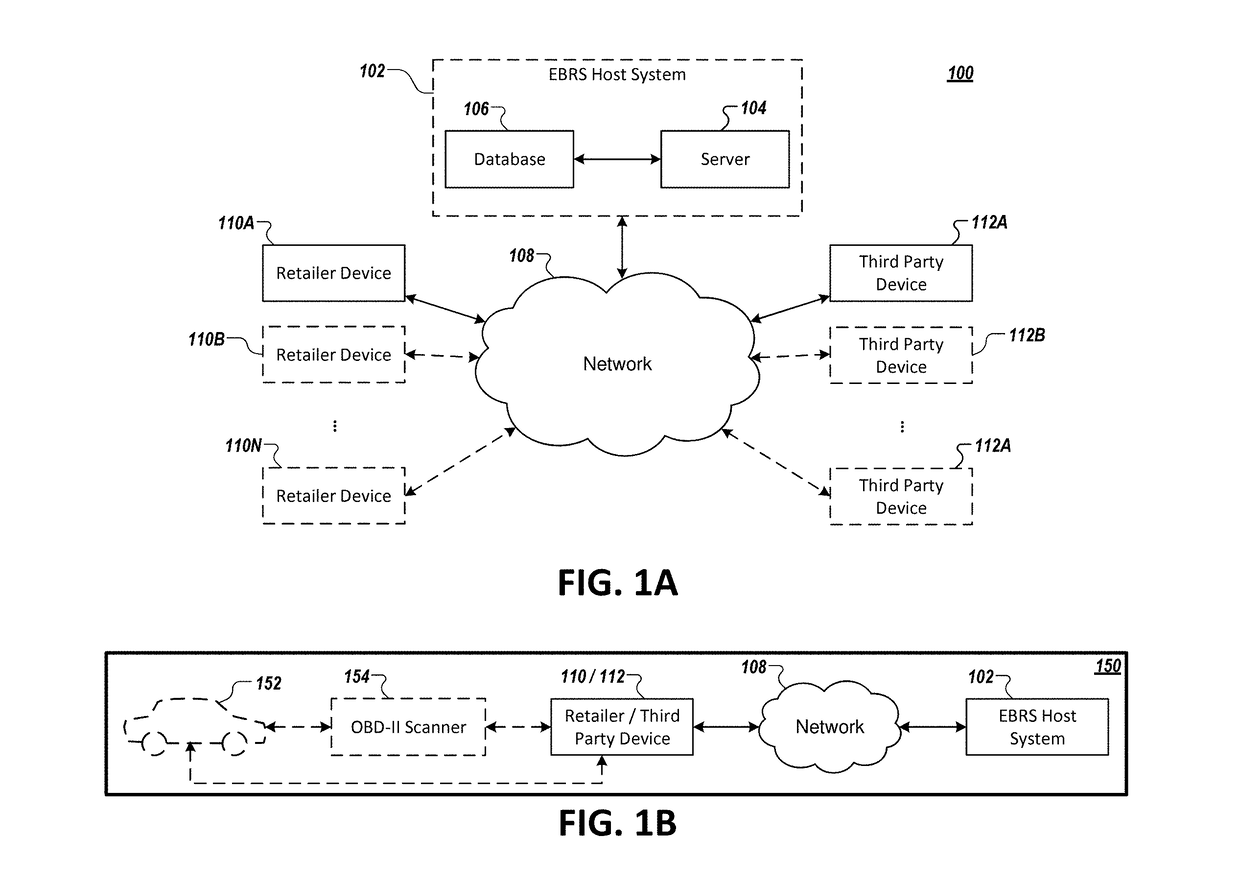
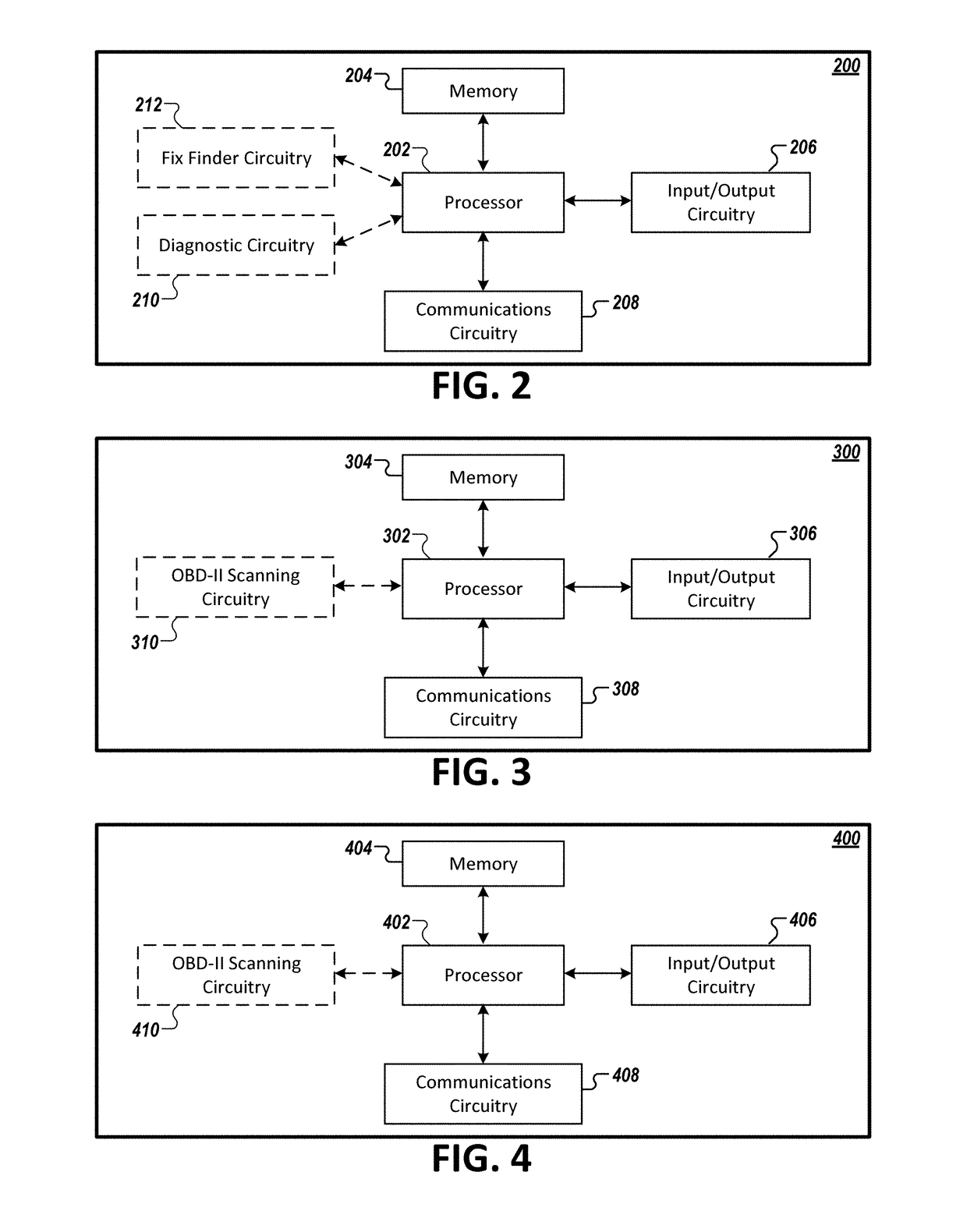
Systems and apparatuses facilitating a do-it-yourself experience-based repair solution
ActiveUS20170262815A1Easy to collectEasy to buyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsLogisticsPart typeDiagnostic information
Embodiments are disclosed for facilitating Do-It-Yourself (DIY) repairs. In the context of a method, an example embodiment includes receiving, by an experience-based repair service (EBRS) host system, vehicle diagnostic information identifying one or more vehicle problems. This example embodiment of the method further includes evaluating the vehicle diagnostic information, generating, based on the evaluation of the vehicle diagnostic information, required part types and required tools for addressing the one or more vehicle problems, and generating, based on the evaluation of the vehicle diagnostic information, recommended part types for addressing the one or more vehicle problems. Finally, this example embodiment of the method further includes causing presentation of an interface facilitating purchase of required parts from each of the generated required part types, the required tools, and recommended parts from each of the generated recommended part types. Corresponding apparatuses and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:AUTOZONE PARTS INC
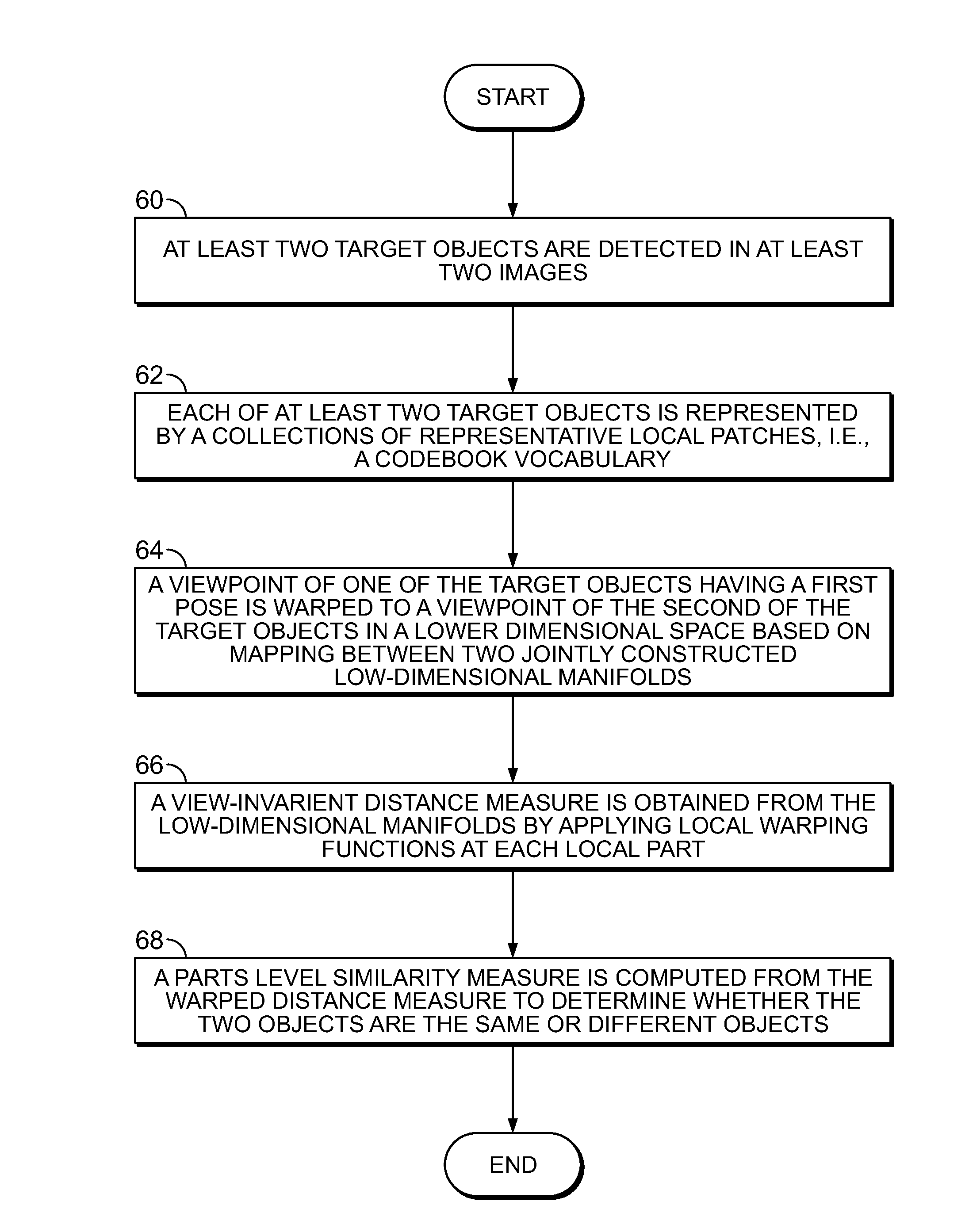
Method for pose invariant vessel fingerprinting
ActiveUS20100328452A1Character and pattern recognitionColor television detailsPart typeComputer science
A computer-implemented method for matching objects is disclosed. At least two images where one of the at least two images has a first target object and a second of the at least two images has a second target object are received. At least one first patch from the first target object and at least one second patch from the second target object are extracted. A distance-based part encoding between each of the at least one first patch and the at least one second patch based upon a corresponding codebook of image parts including at least one of part type and pose is constructed. A viewpoint of one of the at least one first patch is warped to a viewpoint of the at least one second patch. A parts level similarity measure based on the view-invariant distance measure for each of the at least one first patch and the at least one second patch is applied to determine whether the first target object and the second target object are the same or different objects.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Dual-purpose part identification method and device, and production line using the same
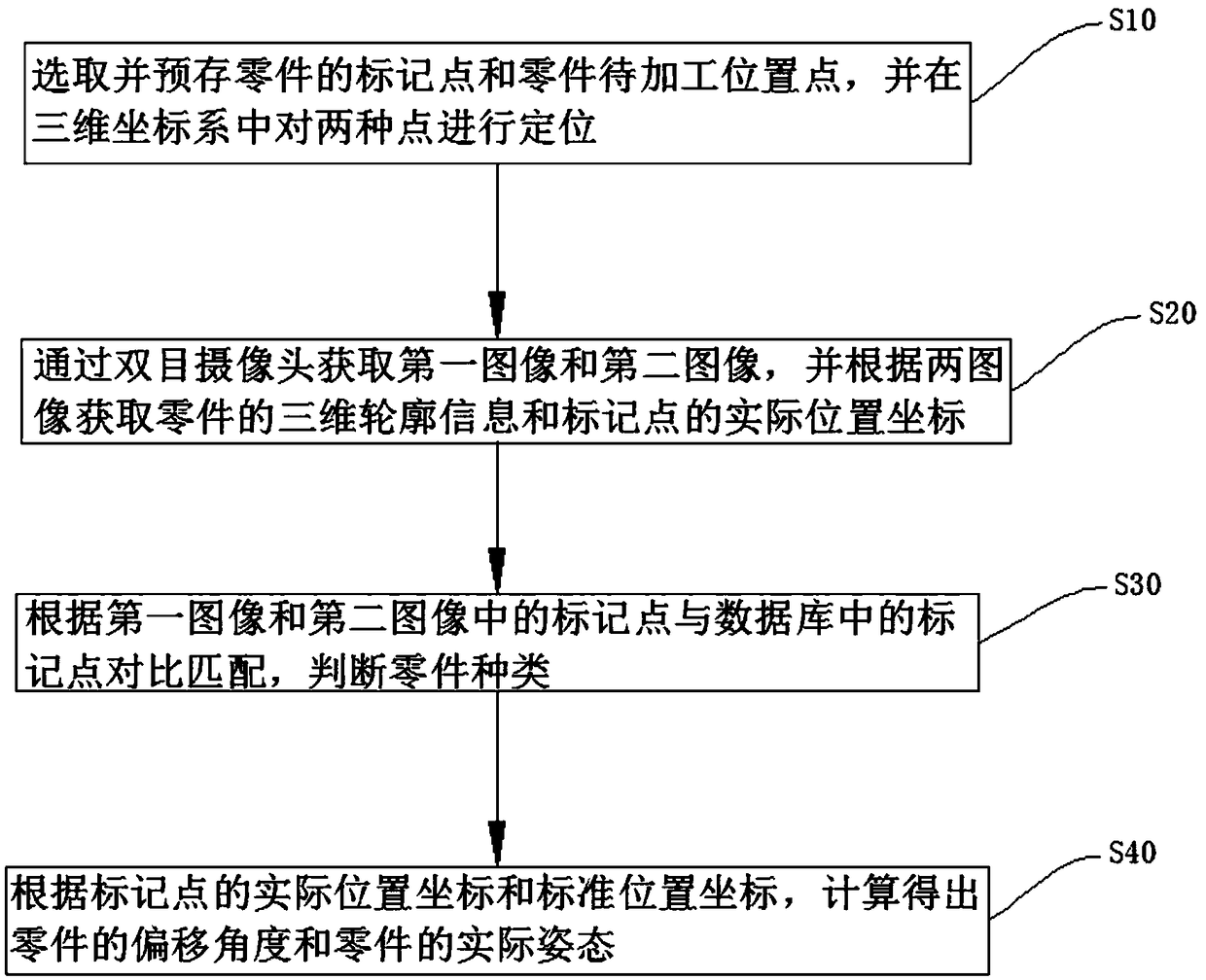
The invention provides a dual-purpose part identification method and device and a production line using the same. Part information is pre-stored; two images of the part at the same position are captured through a binocular camera; the part type and the posture of the part actually in a production line are identified according to identification points on the image; calculation is carried out according to the obtained part posture to obtain an actual position and posture of a to-be-processed position of the part so as to bring convenience for a control unit to adjust the angle of a manipulator picking the part; under the premise of ensuring the production quality, the labor capacity of workers is reduced, and the investment in the production line is reduced.
Owner:天津玛特智能科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for extensible utility network part types and part properties in 3D computer models
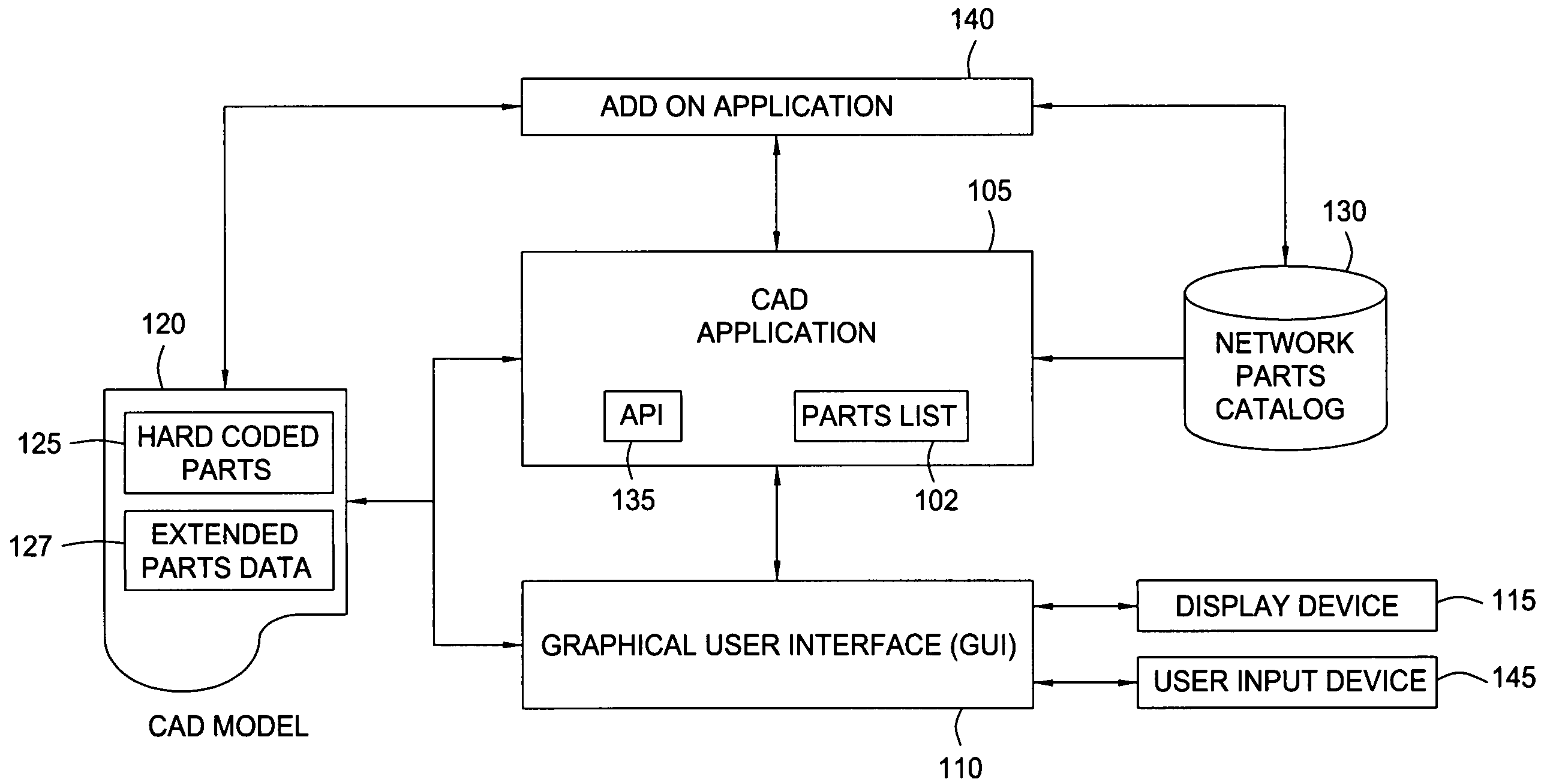
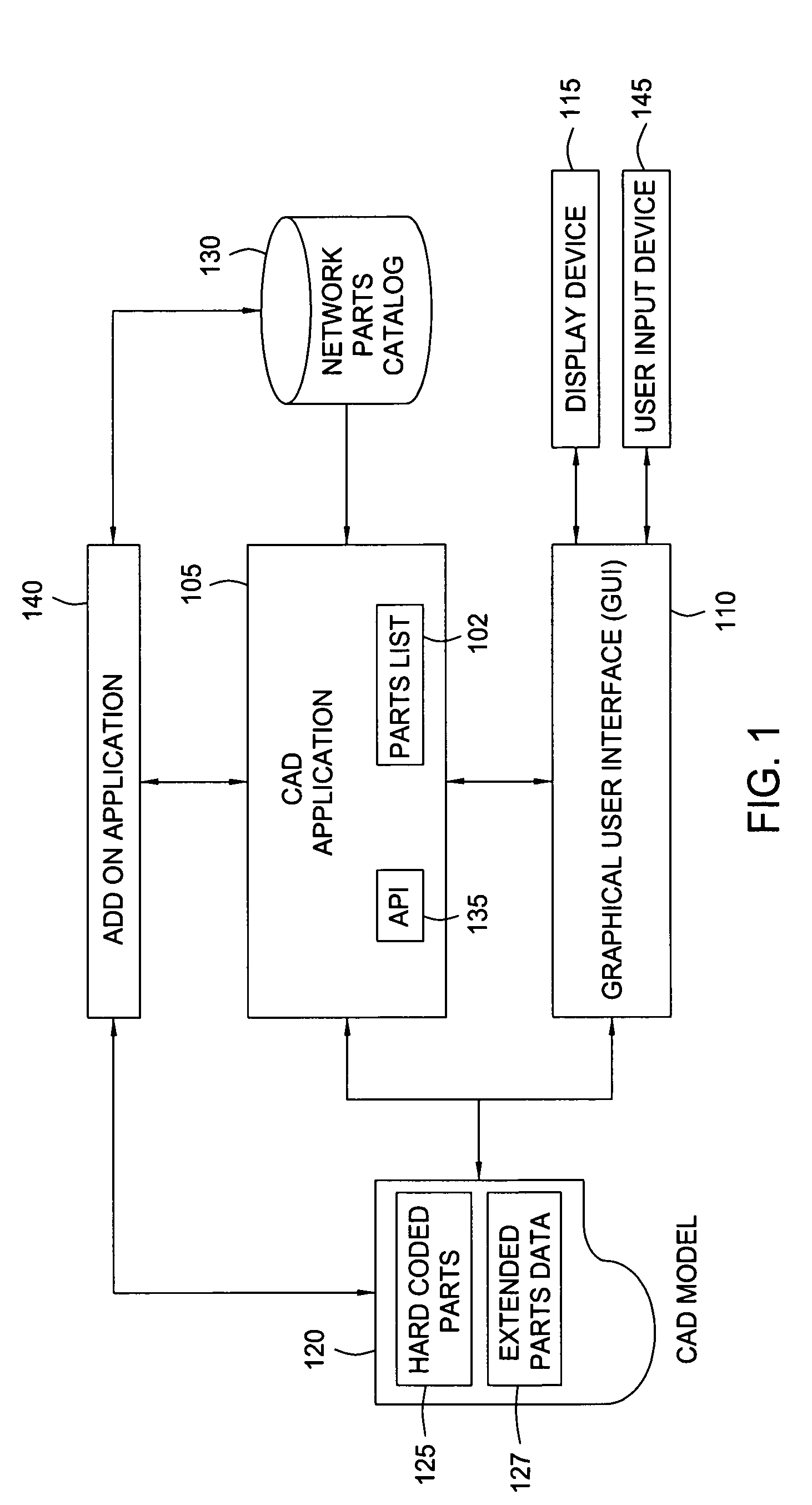
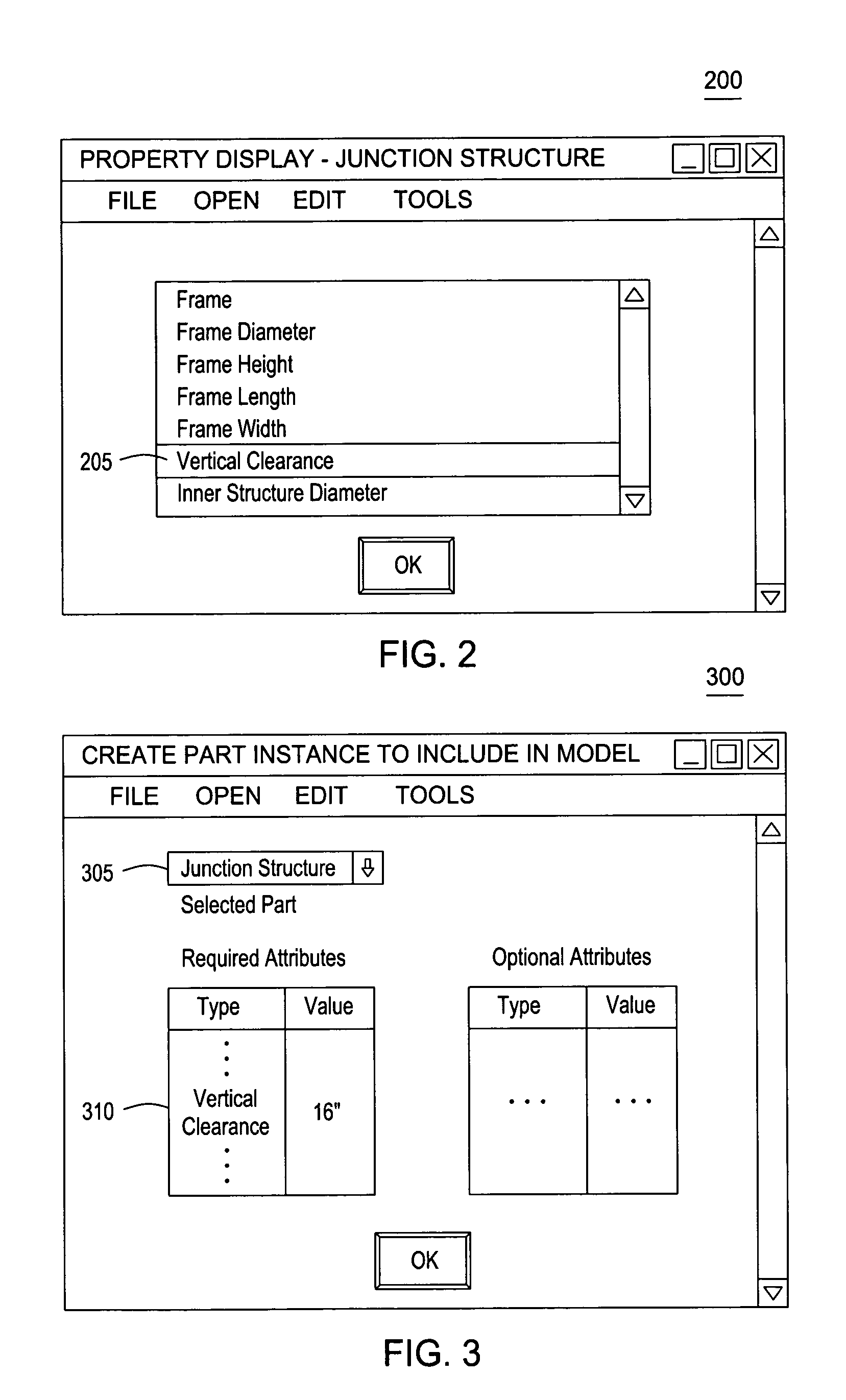
One embodiment of the invention provides a method for extending a schema of network parts types and part type attributes hard-coded by a CAD application. The network parts may be used to compose a CAD model. Users may extend the network part schema by adding an attribute or property for an existing network part, or define an entirely new part by associating the new network part with a set of part type attributes. At the same time, the CAD application may use either a hard-coded or dynamically assigned enumeration value to perform a variety of functions using both the hard-coded and user declared network part types and part properties. For example, functions such as searching a network part list or traversing the elements included in a CAD model may operate using the enumeration values, allowing the CAD application to perform these operations efficiently.
Owner:AUTODESK INC
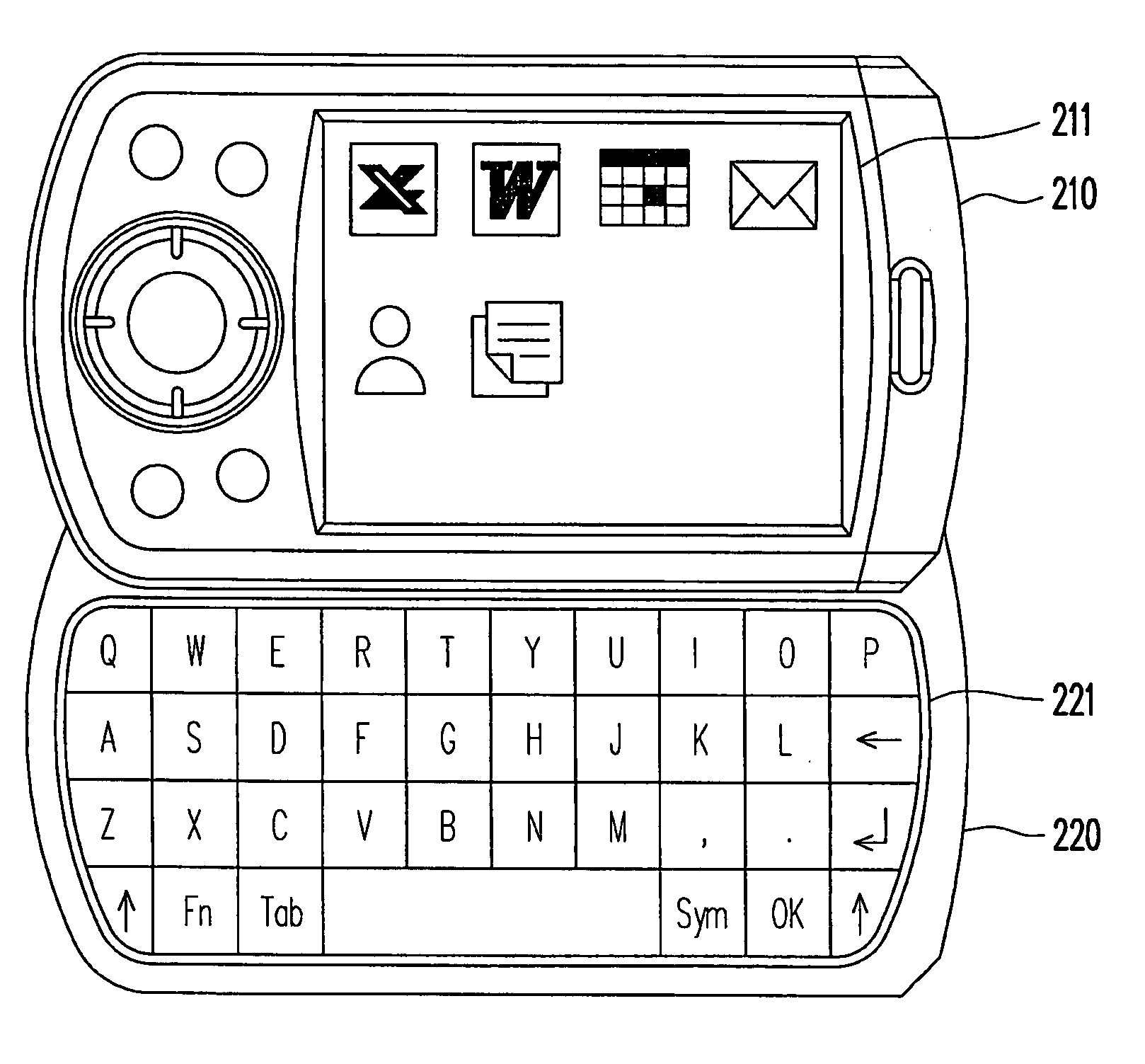
Handheld electronic device and method for switching user interface thereof
ActiveUS20090172530A1Improve operational convenienceShorten the timeDigital data processing detailsSubstation equipmentPresent methodPart type
A handheld electronic device and a method for switching a user interface thereof are provided. The present method is suitable for a handheld electronic device having a first part and a second part. The first part comprises a screen, and the second part is slidingly disposed below the first part along a specific path. A part type of the second part is detected when the second part is slid out along the specific path relative to the first part. Then, the user interface is switched and displayed on the screen according to the part type, wherein the displayed user interface is corresponding to application programs relative to the part type. As a result, convenience of executing application programs on the handheld electronic device can be improved.
Owner:HTC CORP
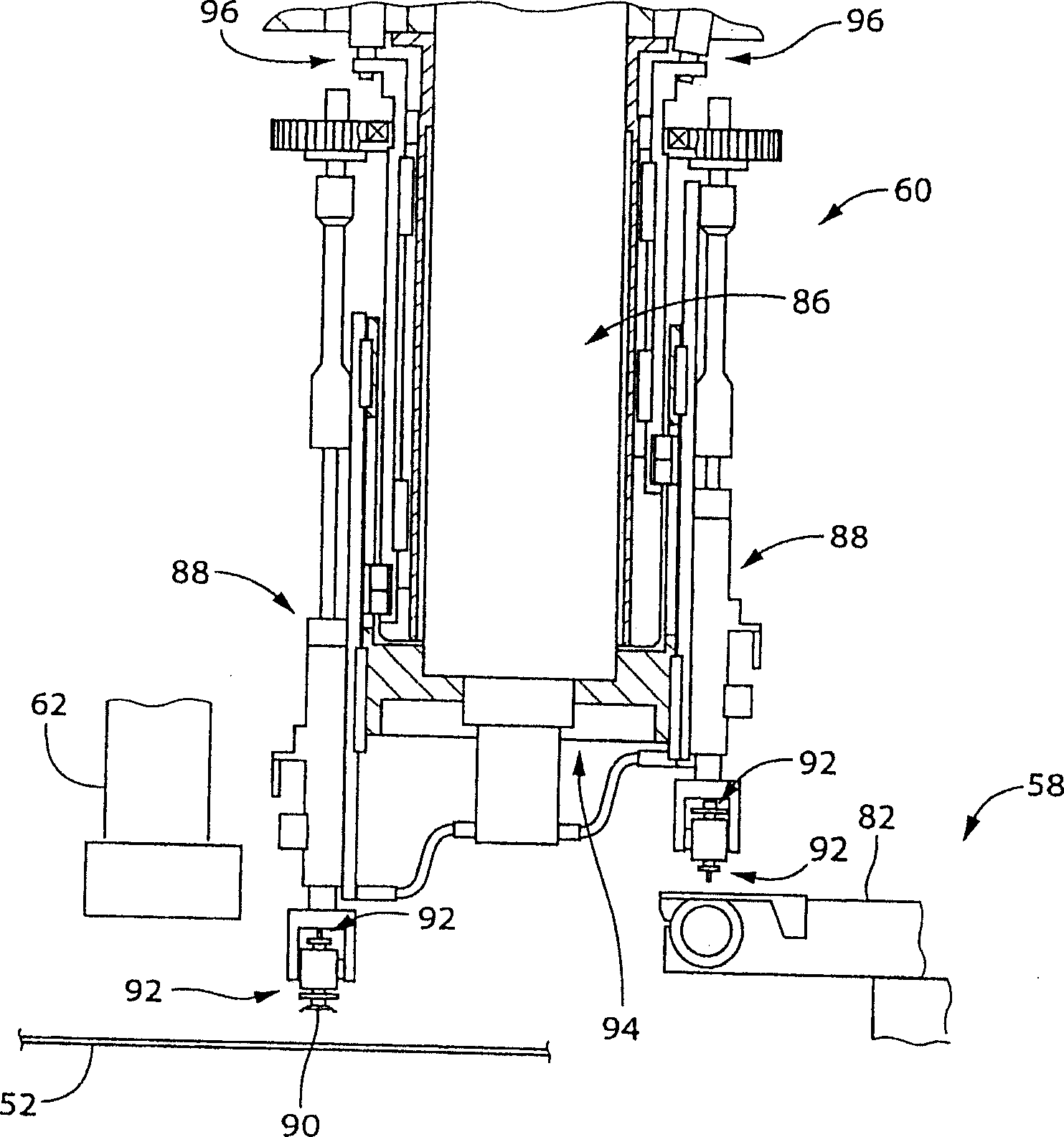
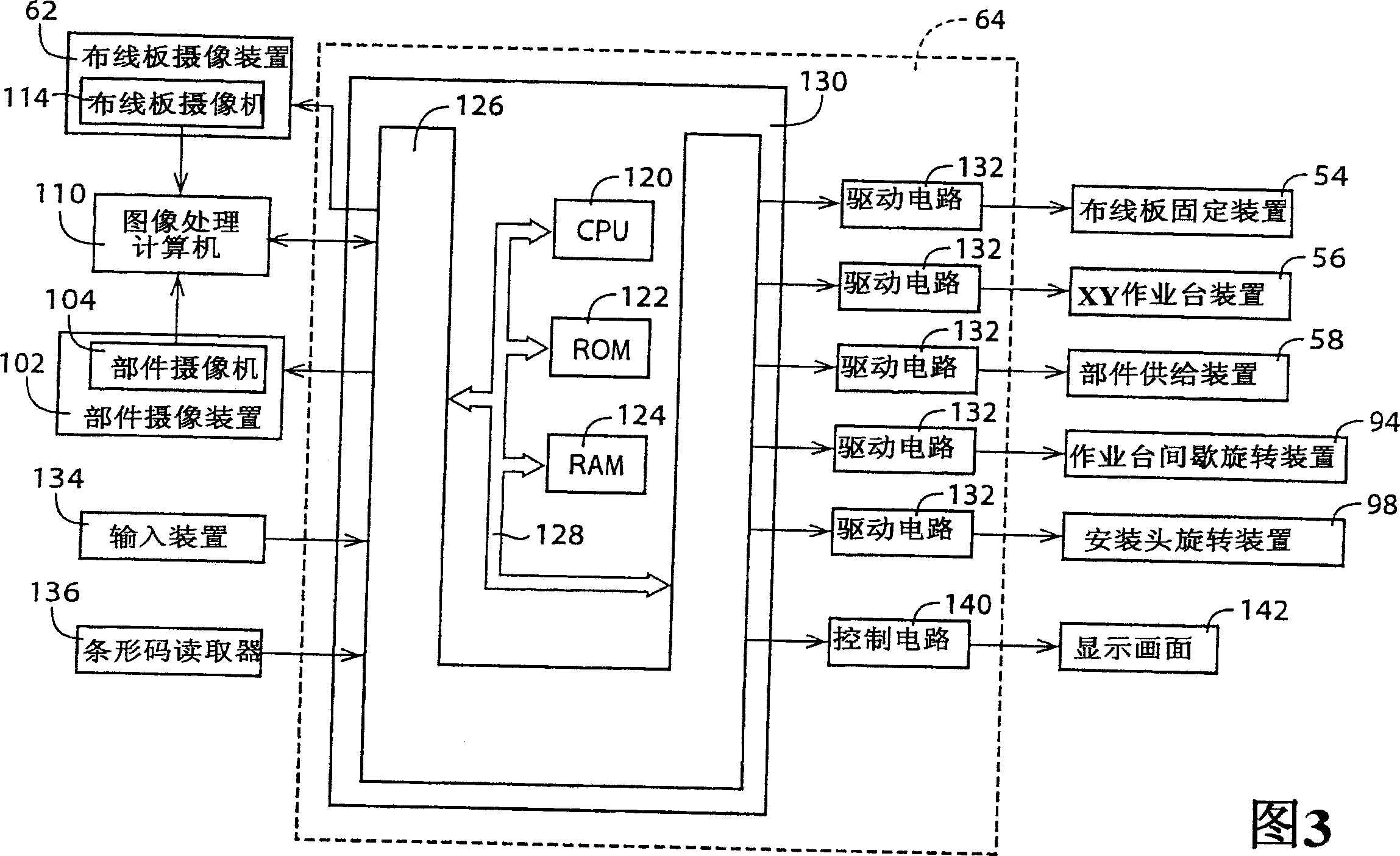
Pair circuit substrate operating machine
In a pair circuit substrate operating machine, a part of an image picked up by an image pickup device is selected and displayed without requiring operation by an operator. An adsorption nozzle receives an electronic circuit part from a feeder at the part reception position. After this a part camera performs imaging to acquire a holding position error. The error is corrected, and the image is mounted on a printed circuit board. If an image processing results in an error and the error occurrence ratio exceeds a set ratio, a display condition is set (S7 to S13 and the like). The display condition is set manually by the operator or automatically by a computer. At least one of the part type, the adsorption nozzle, and the feeder should be identical to the part type which has caused the error, the adsorption nozzle holding the part, and the feeder which has supplied the part. After the condition is set, image data of the image matched with the condition is stored in a memory regardless of the presence / absence of an error and displayed on the display screen, so that the operator analyzes the error cause (S32 to S38).
Owner:FUJI KK
Method for realizing bridged collection of IP multimedia subsystem
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for optimizing arrangement of part types, and device for optimizing arrangement of part types
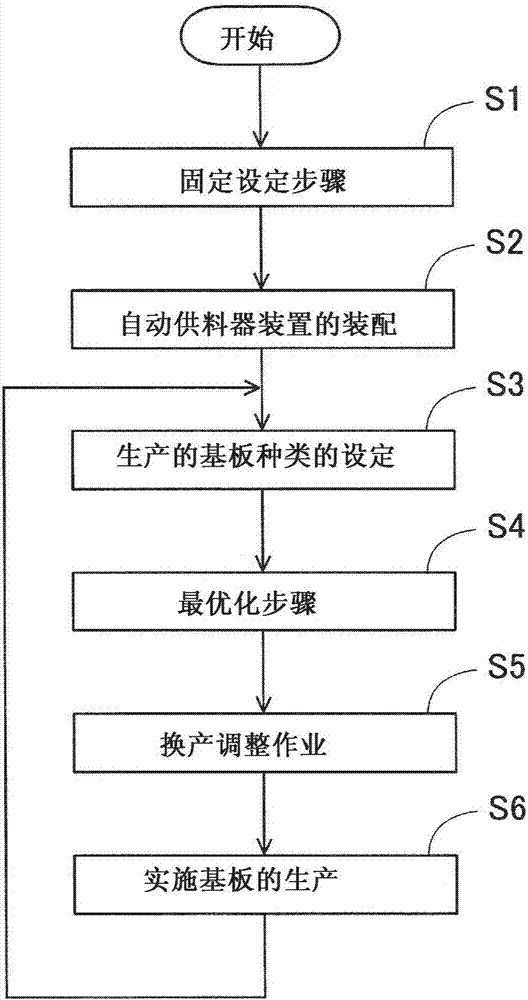
ActiveCN107409486AShorten the work time for production changeover and adjustmentIncrease productivityGeometric CADConfiguration CADPart typeCycle time
Provided is a method for optimizing the arrangement of part types, with which a plurality of part types (P1-P9) are optimally arranged in a plurality of disposal positions when disposing an automatic feeder device (9), which automatically loads part storage tapes (85, 86), a manual feeder device (7), which does not load automatically, and a reel holding device (6) in disposal positions (first through ninth slots SL1-SL9) on a shared pallet (5). The method has: a step (S1) for setting a portion (SL3-SL7) of the disposal positions as fixed positions, and fixing the automatic feeder device at a fixed position; and an optimization step (S4) for carrying out a simulation in which the part types are optimally arranged in the disposal positions under the condition that the manual feeder device can be moved to any of the disposal positions other than the fixed positions, and that the automatic feeder device does not move from the fixed position. As a result, the automatic feeder device can be utilized effectively, and production efficiency can be improved in comprehensive consideration of set-up change operation time and mounting cycle time.
Owner:FUJI KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com