Random noise correction method and device
A random noise and correction method technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problems of large statistical errors and large system errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0145] Figure 4 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 1 of a method for correcting random noise in the present invention, and the method includes:
[0146] Step 401: collecting the scan data of the detector to obtain the instant chord diagram, delayed chord diagram and single photon count rate.
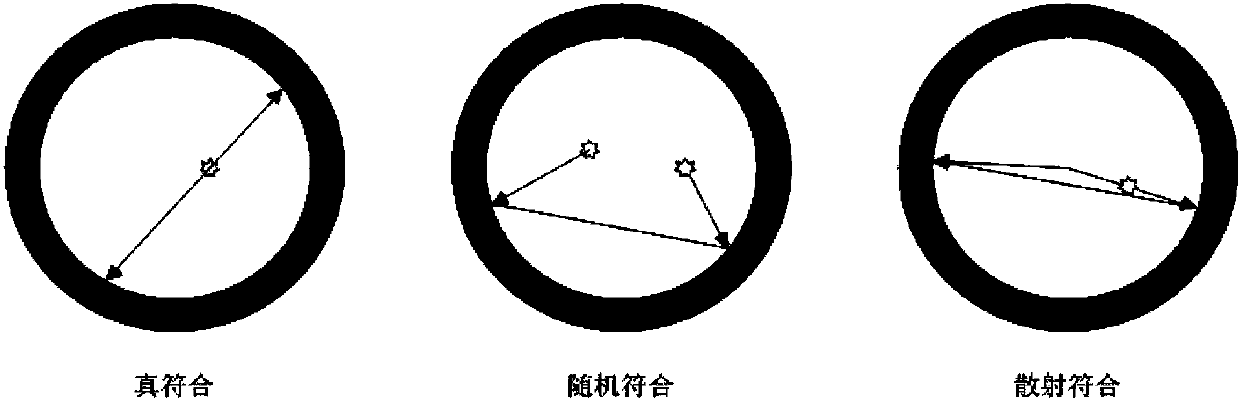
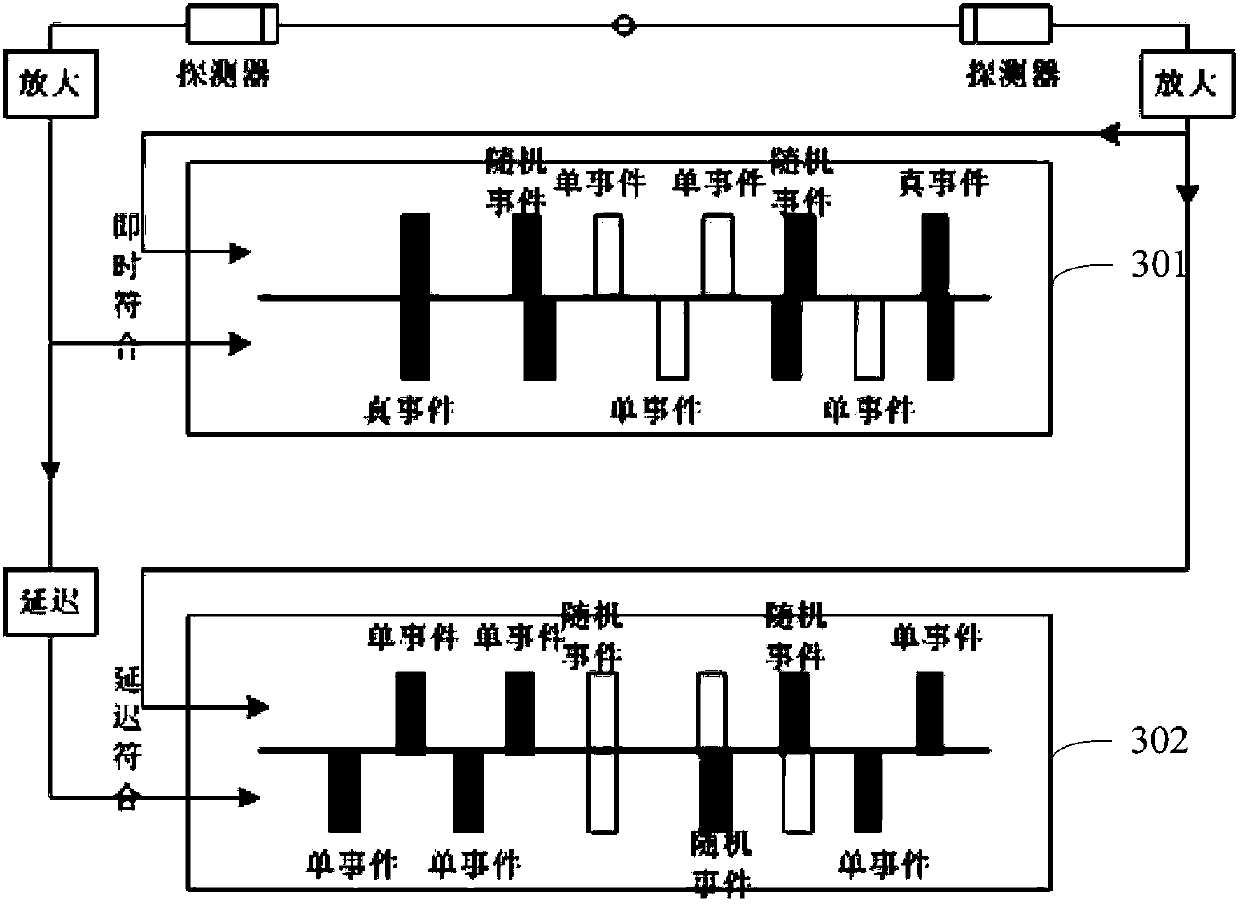
[0147] The two event sequences received by the two detectors are arranged in two columns in chronological order, as shown in Figure 301, and the two event sequences are matched to obtain an instant chord diagram. In the instant chord diagram, the event produced by two detectors receiving two photons produced by the same positron annihilation in the same time window is a real event. The event produced by two detectors receiving different photons generated by positron annihilation in the same time window is a random event, and the random event is the noise in the real-time chord diagram.
[0148] The two detectors record the two sequences of events received, and delay one of the sequence ...
Embodiment 2
[0176] Figure 5 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 2 of a random noise correction method of the present invention. Compared with Embodiment 1, Embodiment 2 obtains a compressed random chord graph according to the compressed position of the compressed real-time chord graph, and uses the compressed random chord graph to correct the compressed real-time chord graph , the method includes:
[0177] Step 501: collecting the scan data of the detector to obtain the delay chord diagram and the single photon count rate, and compressing the scan data to obtain the compressed instant chord diagram.
[0178] Here, it is similar to Embodiment 1, and reference is made to the description of Embodiment 1, and details are not repeated here.
[0179] Step 502: Obtain a distribution chord diagram according to the single photon count rate.
[0180] The obtaining the distribution chord diagram according to the single photon count rate comprises:
[0181] Obtaining a count rate chord diagram accor...
Embodiment 3
[0192] Figure 6 It is a flow chart of Embodiment 3 of a random noise correction method of the present invention. Compared with Embodiment 1, Embodiment 3 compresses the delayed chord diagram and the single photon counting rate according to the compressed position of the collected compressed instant chord diagram to obtain the compression Delaying the chord diagram and compressing the single photon count rate, using the compressed chord diagram to correct the compressed instant chord diagram, the method includes:
[0193] Step 601: collecting the scan data of the detector to obtain the delayed chord diagram and the single photon count rate, and compressing the scanned chord diagram to obtain the compressed instant chord diagram.
[0194] Here, it is similar to Embodiment 1, and reference is made to the description of Embodiment 1, and details are not repeated here.
[0195] Step 602: Obtain the compressed position of the compressed instant chord diagram.
[0196] Step 603: C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com