A preparation method and application of boron ester-rich core-shell magnetic composite microspheres
A magnetic composite microsphere, core-shell technology, applied in the magnetic direction of organic materials/organic magnetic materials, can solve the problems of inability to enrich glycoprotein markers, adsorption, etc., and achieve excellent results, uniform particle size distribution, and hydrophilic good sex effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: shell layer thickness is about 10nm, and crosslinking degree is the core-shell type Fe of 20% 3 o 4 The preparation of / PAA-AOPB microspheres, concrete steps are as follows:
[0035] (1), preparation of magnetic clusters stabilized by sodium citrate
[0036] 1.3g ferric chloride hexahydrate (FeCl 3 •6H 2 O), 3.8g ammonium acetate (NH 4 Ac), after dissolving 0.4g sodium citrate in 70mL ethylene glycol, put it into a 150mL three-neck flask, then raise the temperature to 170°C, stir and react for 1 hour, then transfer the liquid in the flask into a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene-containing Lined autoclave, then put the autoclave into an oven at 200°C for 16 hours, take it out, and cool it to room temperature with tap water. The product is separated by magnetic separation, washed with absolute ethanol to remove unreacted reactants, and finally the product is dispersed in absolute ethanol for later use.
[0037] (2) Active vinyl modification on the surface...
Embodiment 2
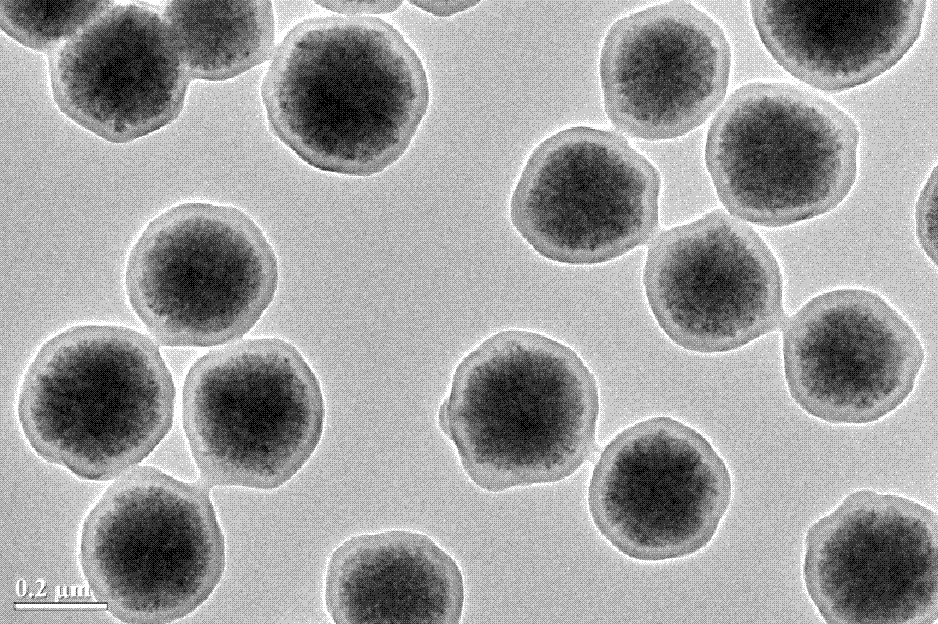
[0043] Example 2: Core-shell Fe with a shell thickness of about 30 nm and a crosslinking degree of 20% 3 o 4 Preparation of / PAA-AOPB microspheres (transmission electron microscope photos see figure 1 )
[0044] 1. The preparation of sodium citrate-stabilized magnetic clusters is the same as that described in step (1) of Example 1.
[0045] 2. Carrying out active vinyl modification on the surface of the magnetic cluster is the same as described in the step (20) of Example 1.
[0046] 3. Core-shell Fe 3 o 4 The preparation of / PAA is the same as described in Example 1 step (3). The difference is that acrylic, N, N' The dosages of -methylenebisacrylamide and 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile are 400 μL, 100 mg, and 10 mg, respectively.
[0047] 4. The reaction of modifying aminophenyl borate is the same as that described in step (4) of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3: The shell thickness is about 50nm, and the cross-linking degree is 20% core-shell Fe 3 o 4 / Preparation of PAA-AOPB Microspheres
[0049] 1. The preparation of sodium citrate-stabilized magnetic clusters is the same as that described in step (1) of Example 1.
[0050] 2. Carrying out active vinyl modification on the surface of magnetic clusters is the same as that described in step (2) of Example 1.
[0051] 3. Core-shell Fe 3 o 4 / PAA is prepared as described in Example 1 step (3). The difference is that acrylic, N, N' The dosages of -methylenebisacrylamide and 2,2-azobisisobutyronitrile are 600 μL, 150 mg, and 15 mg, respectively.
[0052] 4. The reaction of modifying aminophenyl borate is the same as described in the embodiment step (4).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com