Semiconductor structure with improved channel stack and method for fabrication thereof
A semiconductor, stacking technology used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electro-solid devices, etc., to solve problems such as diffusion of dopant materials, degradation of performance, and interference with reliable transistor operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
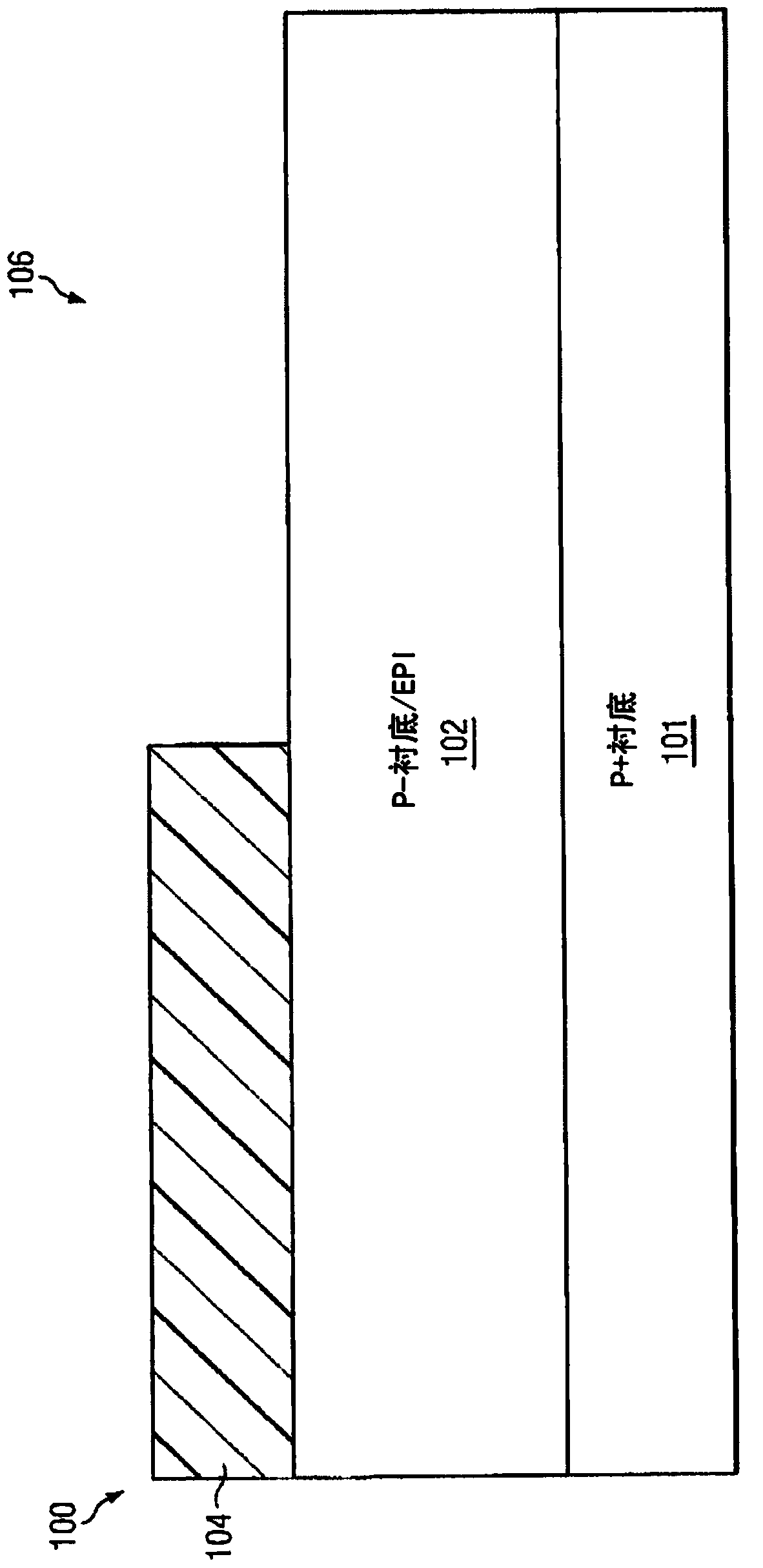
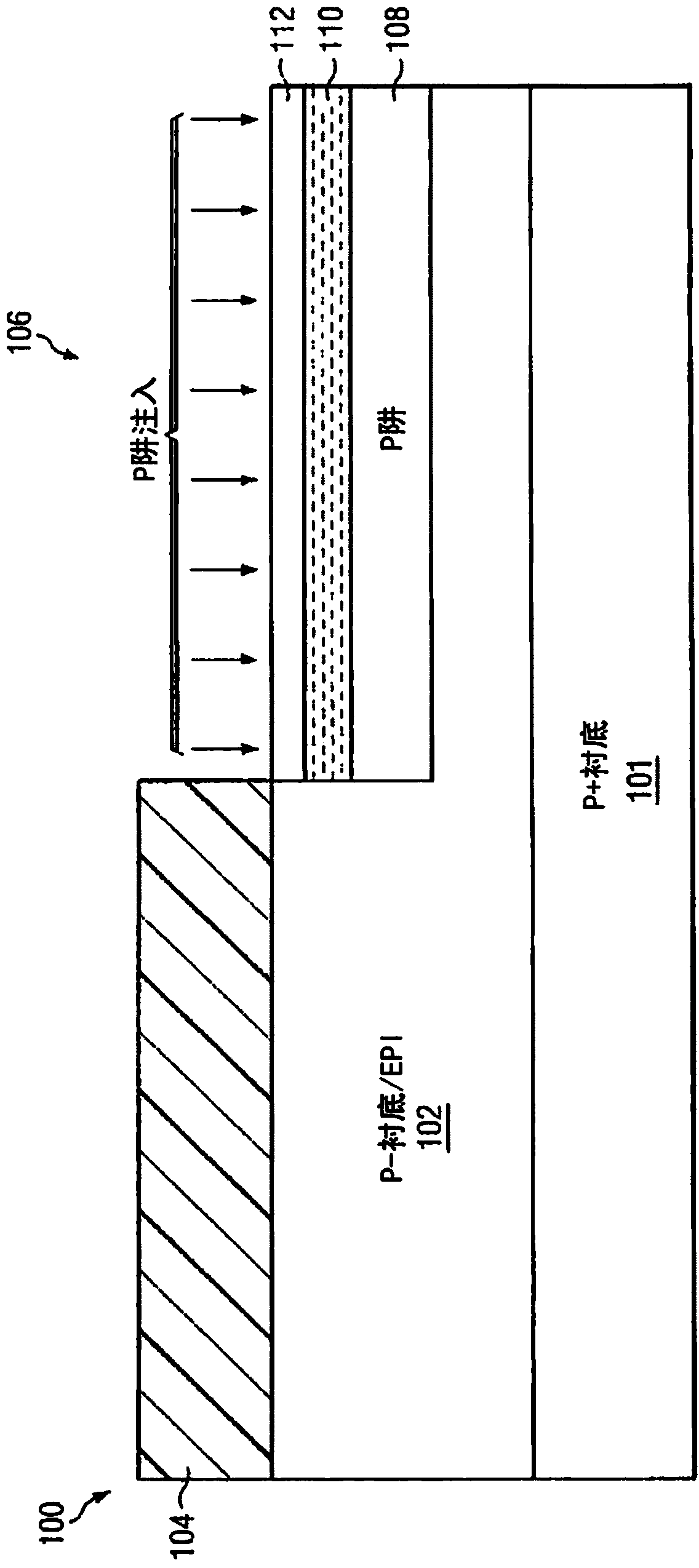
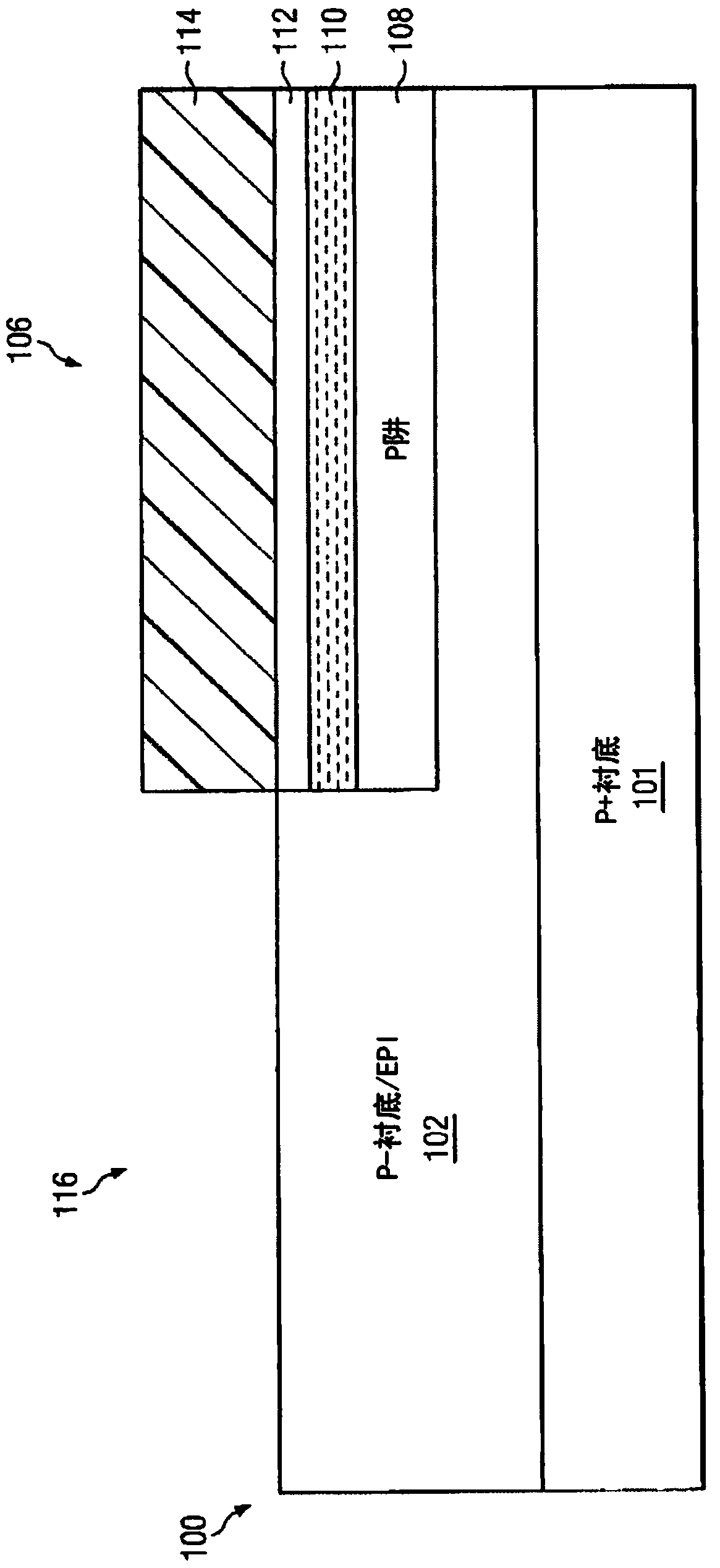
[0023] Various methods can be used to build a transistor element with a channel stack having a shielding layer for shielding the charge on the gate, a threshold voltage control layer for adjusting the threshold voltage of the transistor element, and a layer for high Mobility and reduced random doping fluctuation properties of an intrinsic channel. Each method has different advantages and disadvantages. Typically, two trade-offs are considered when building transistor elements on a semiconductor die, namely the number of steps in the process (related to manufacturing cost) and channel formation (related to transistor performance). Fewer mask steps and total steps needed to build a design translate to lower build costs. Forming the channel late in the thermal cycle of the fabrication process facilitates control of the channel doping profile and avoids the diffusion of undesired contaminants into the channel from other parts of the transistor design.
[0024] Figures 1A to 1K...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com