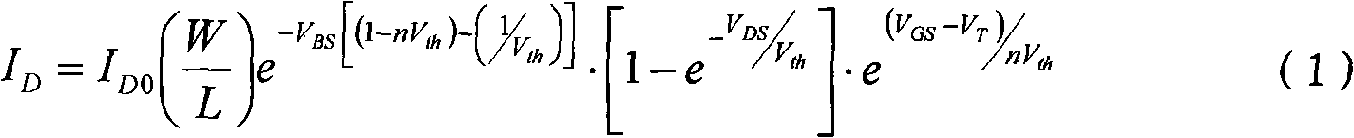Patents
Literature
75 results about "Transistor design" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
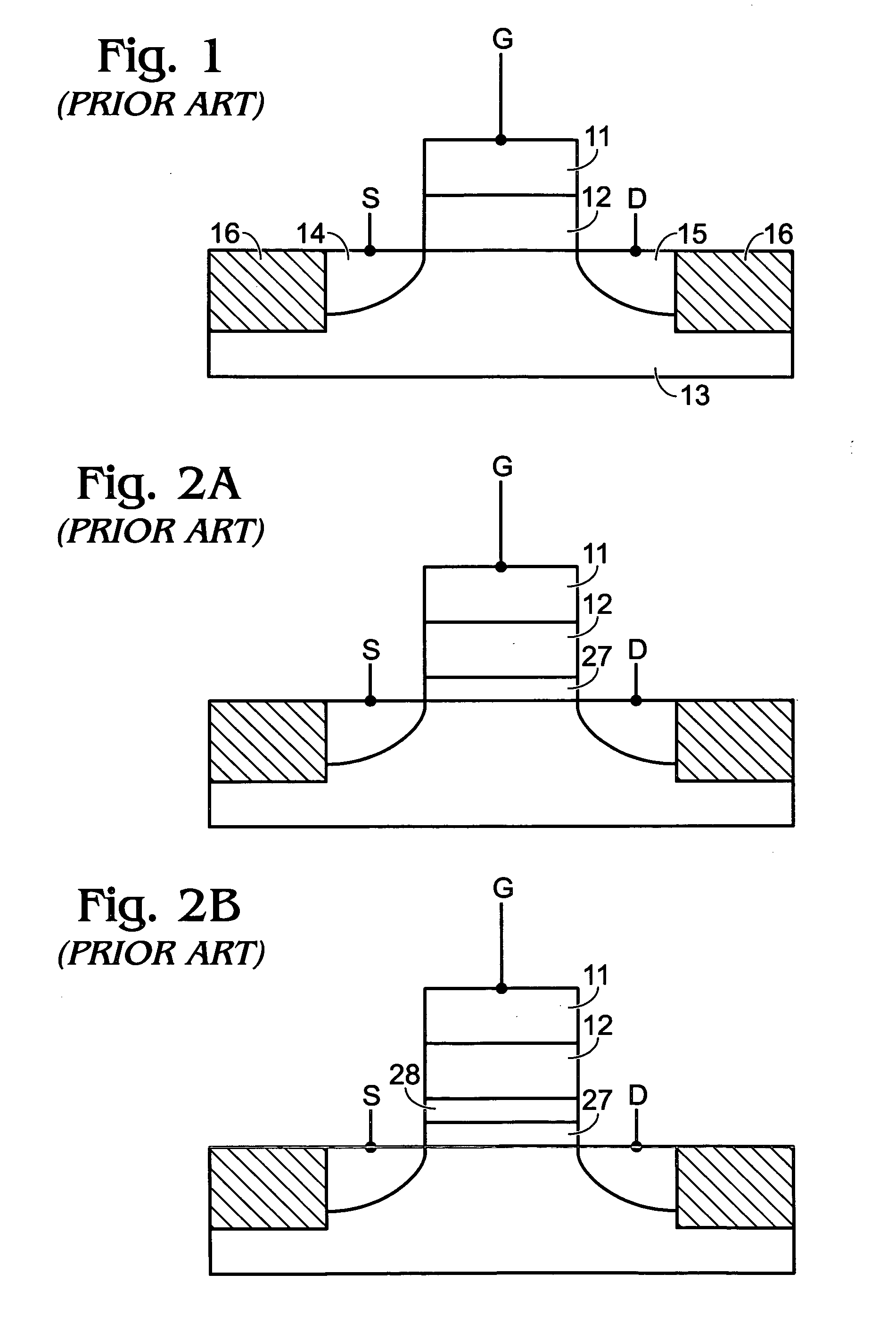
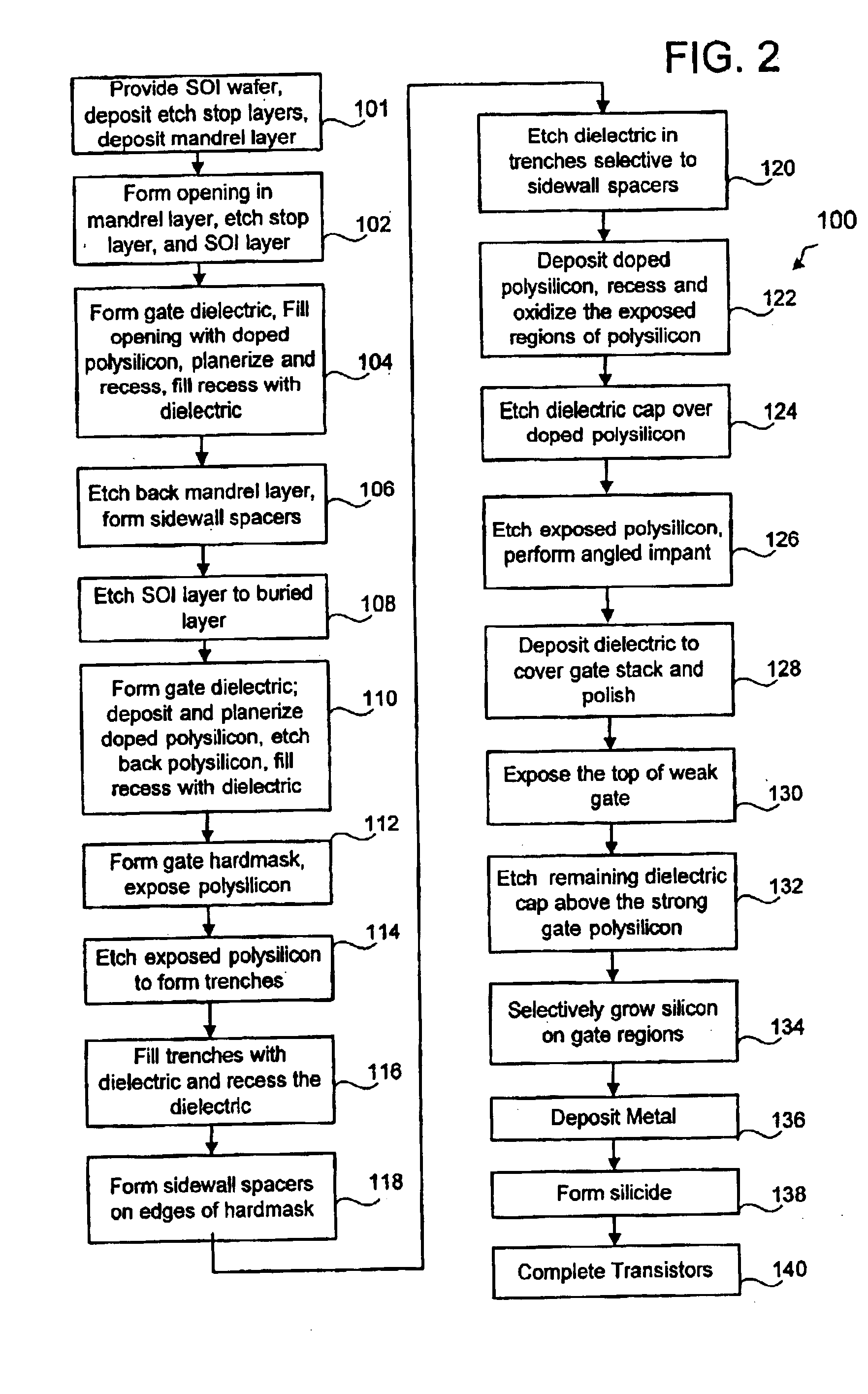
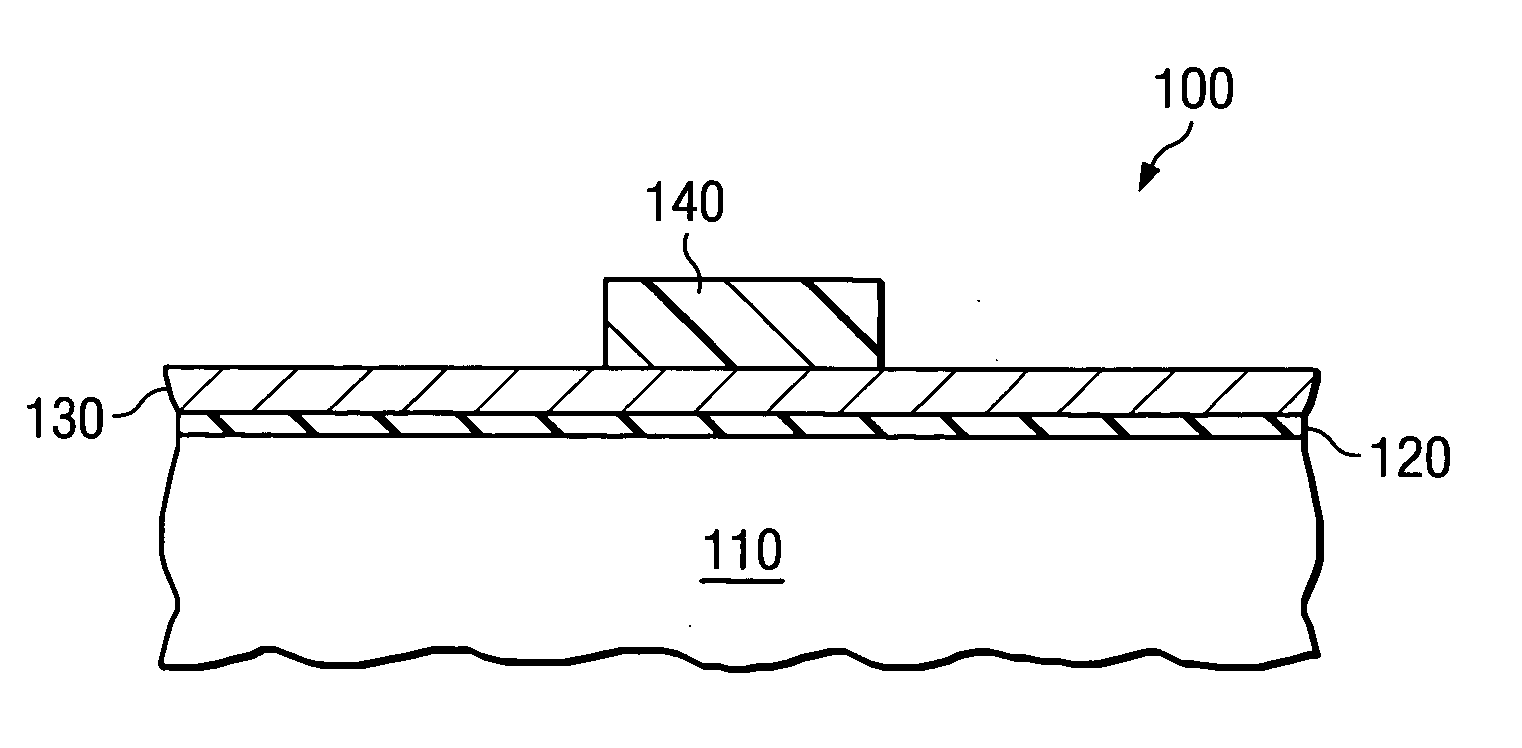
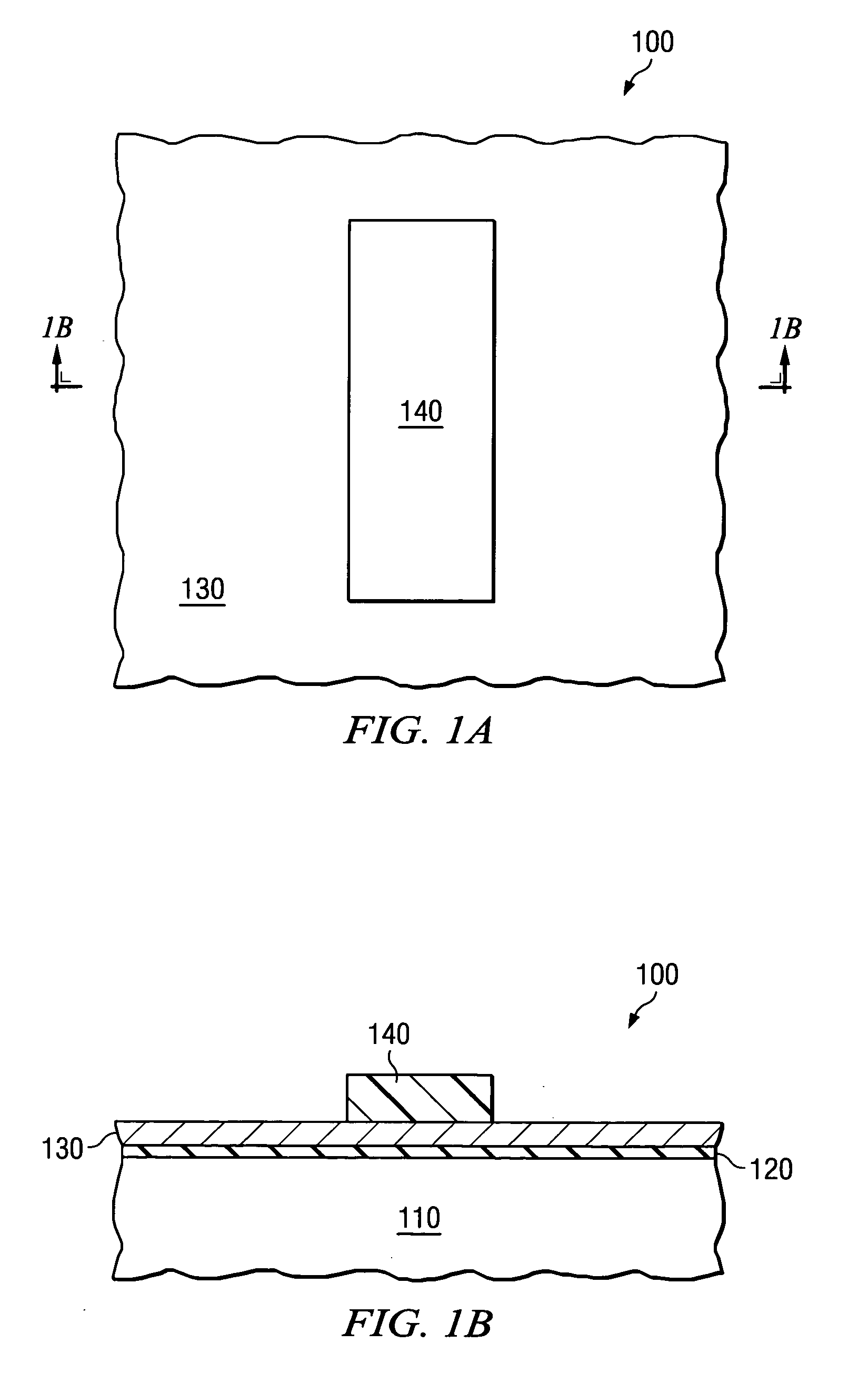
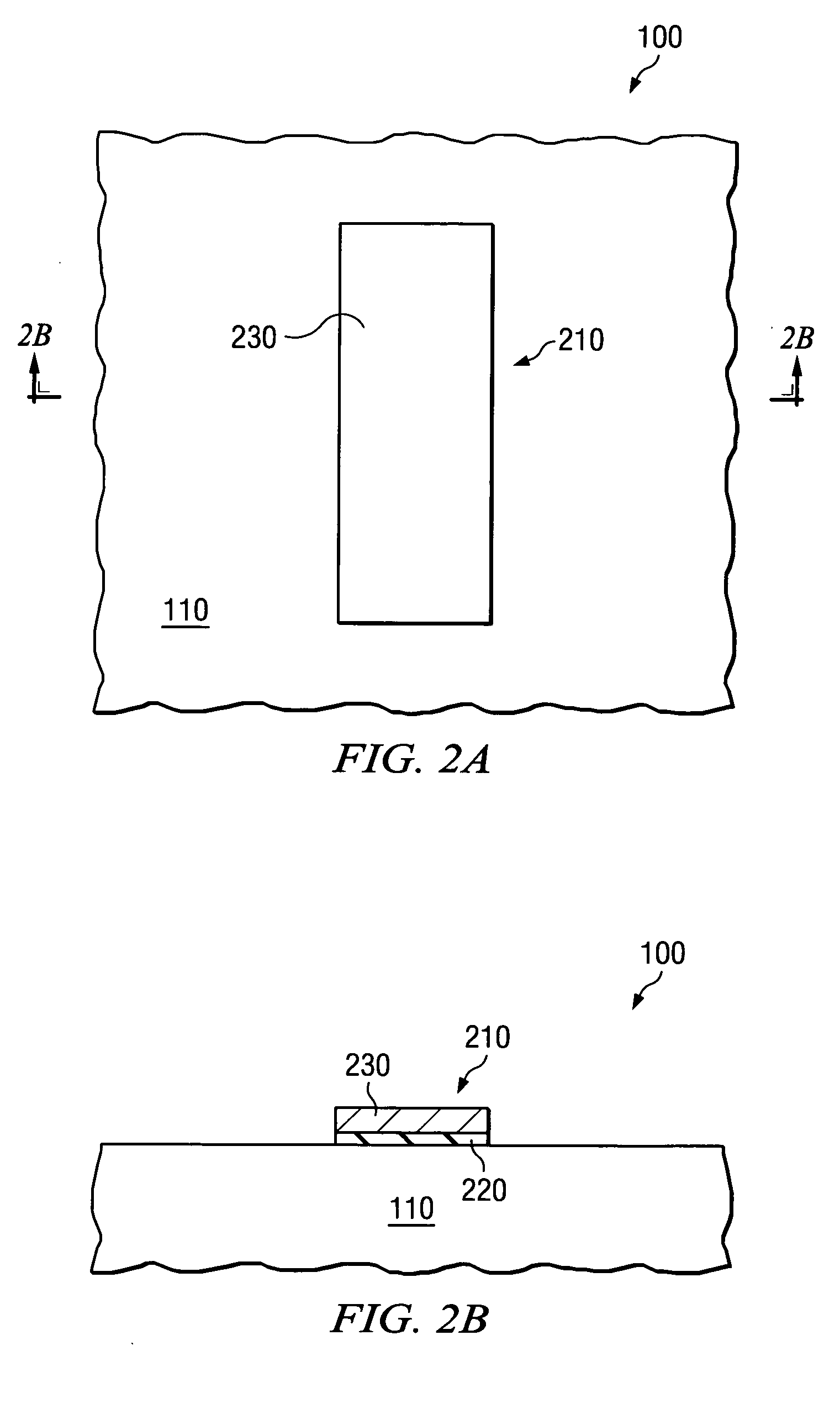
Method for converting a planar transistor design to a vertical double gate transistor design
InactiveUS7013447B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringActive layer
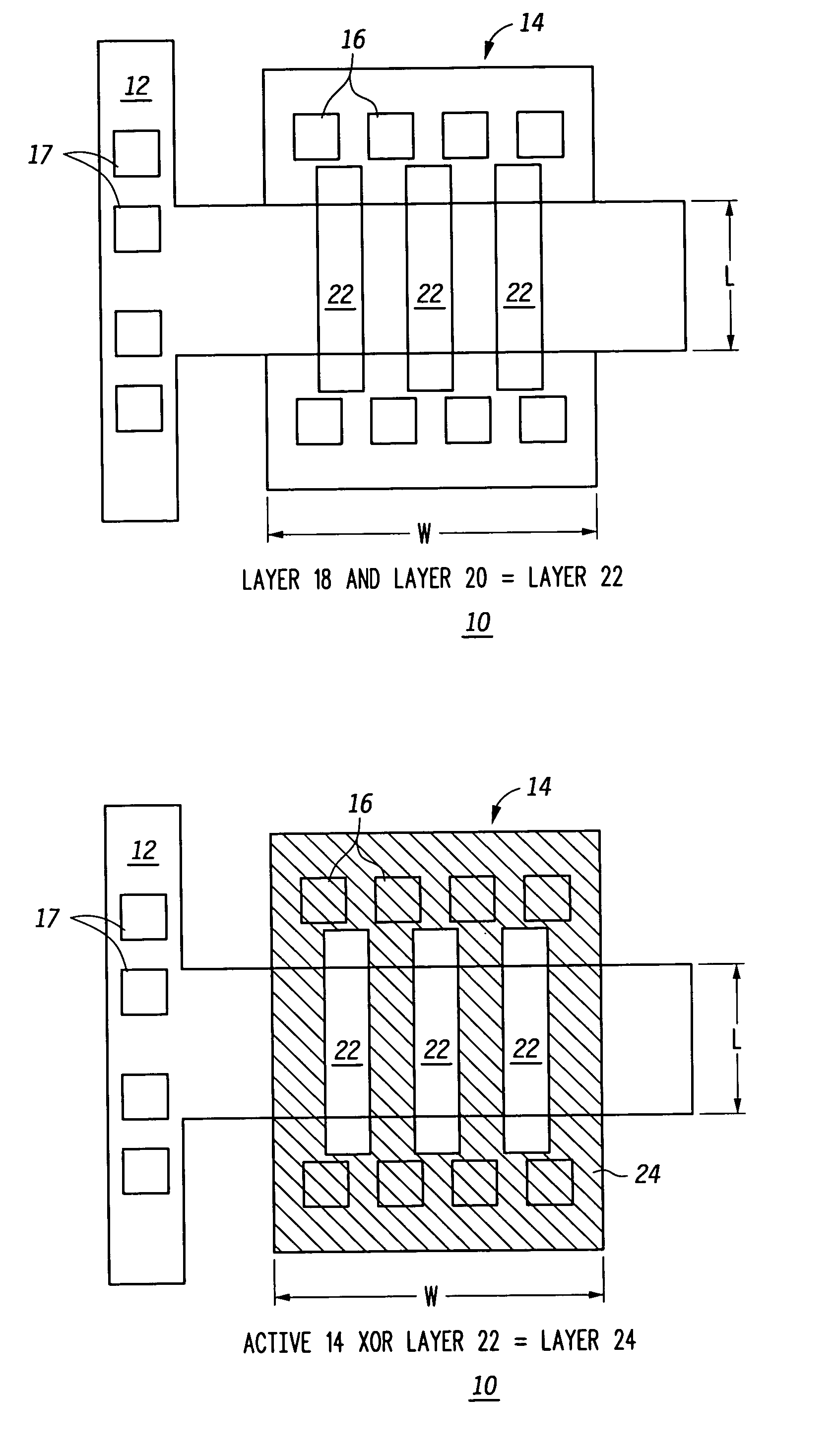
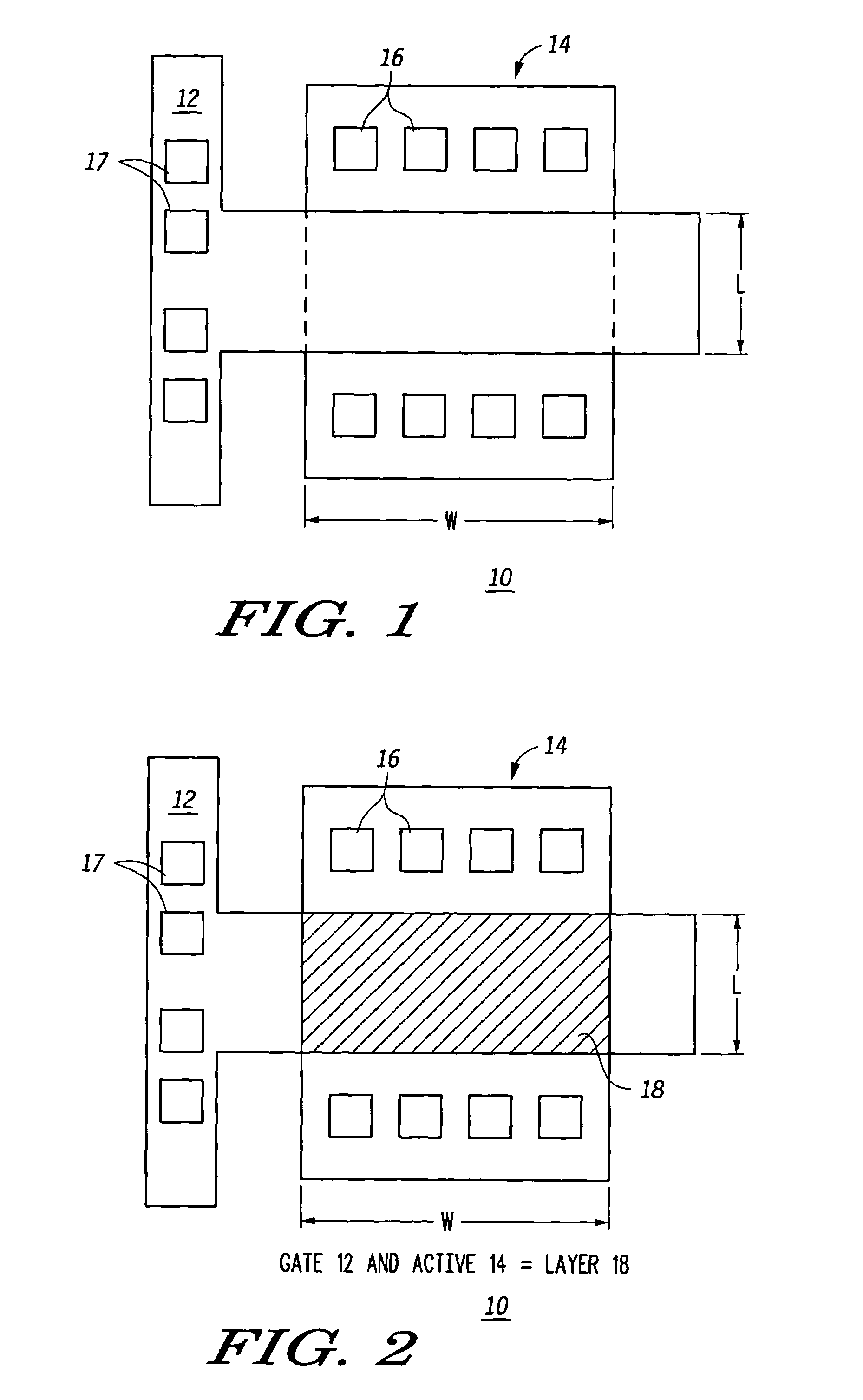
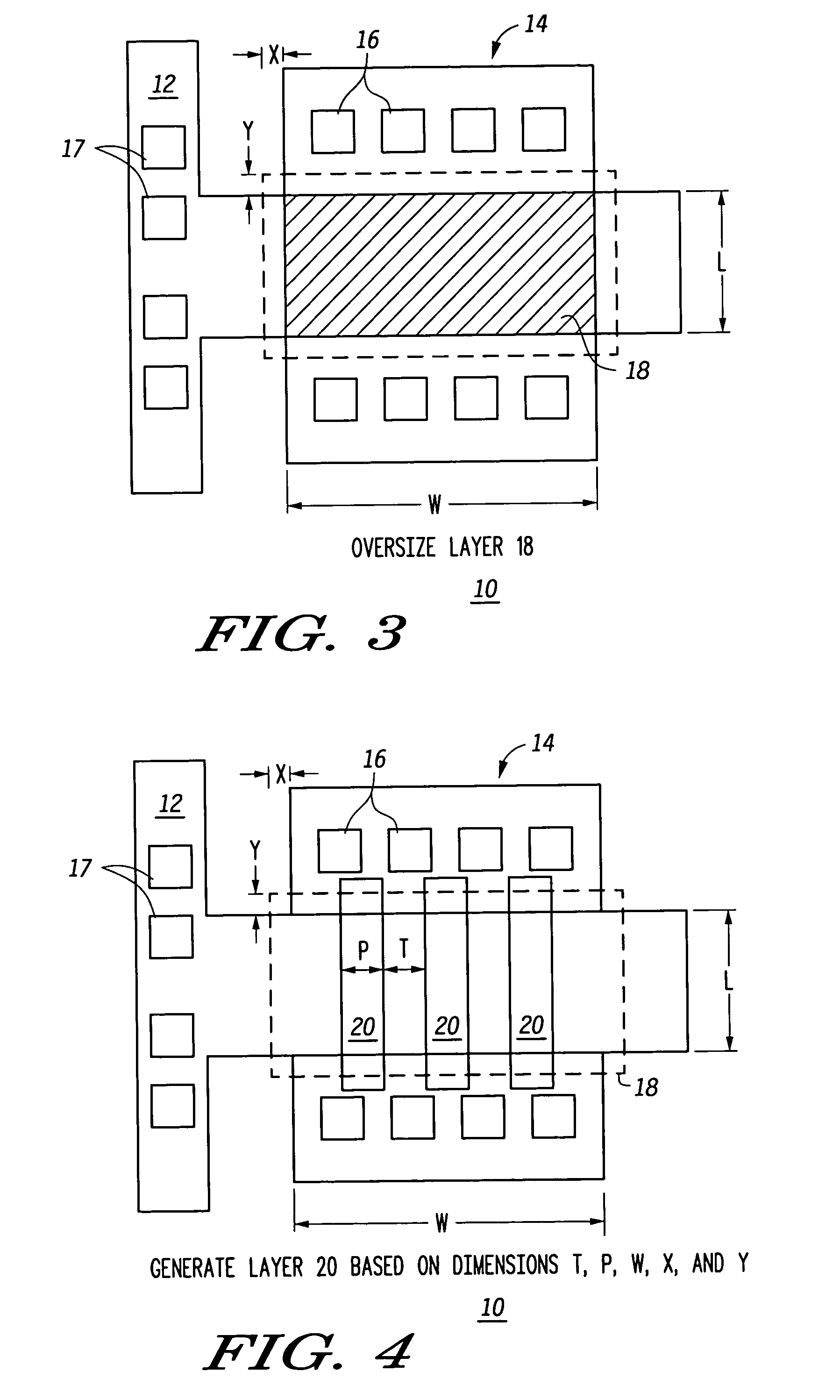
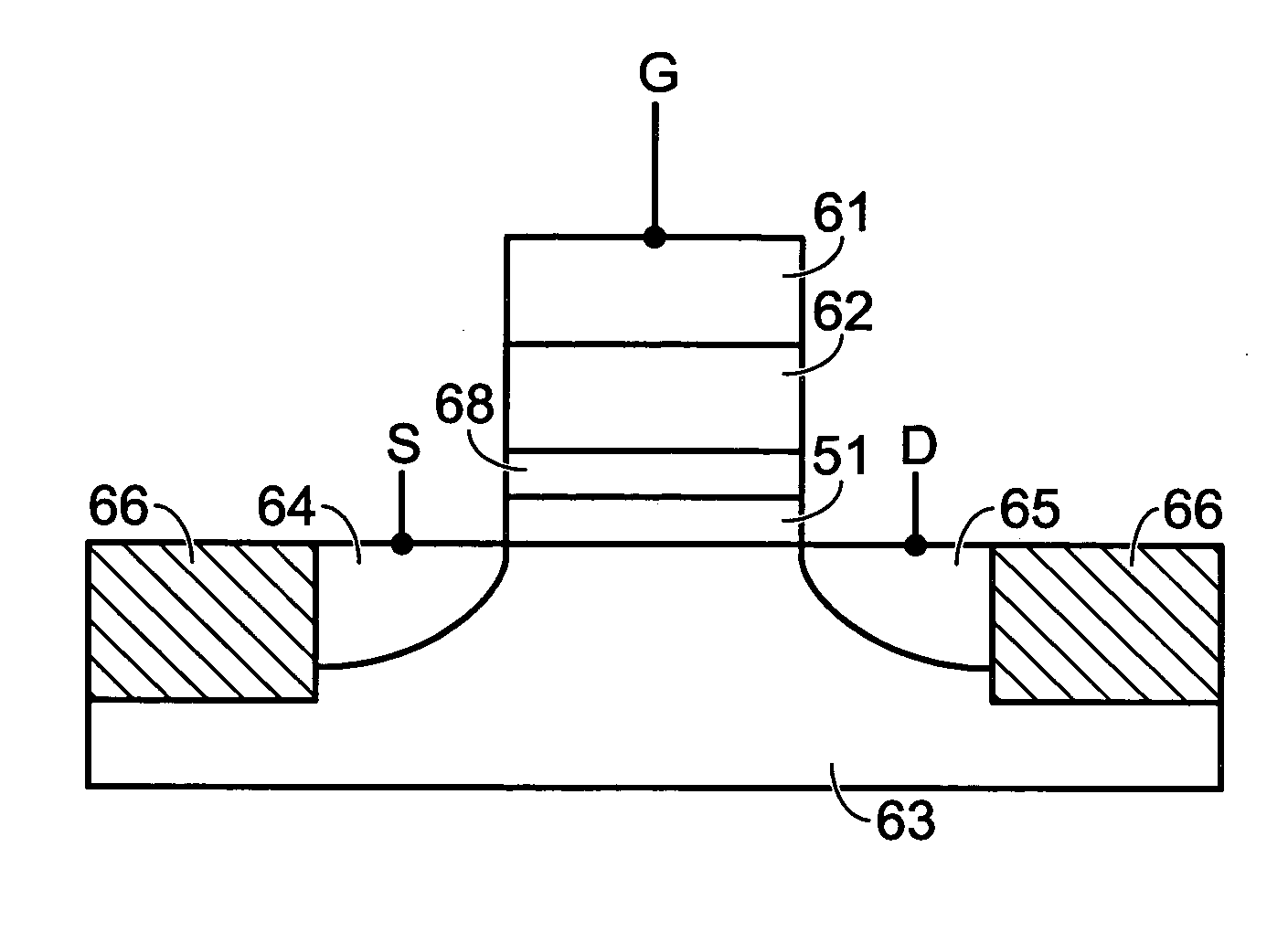
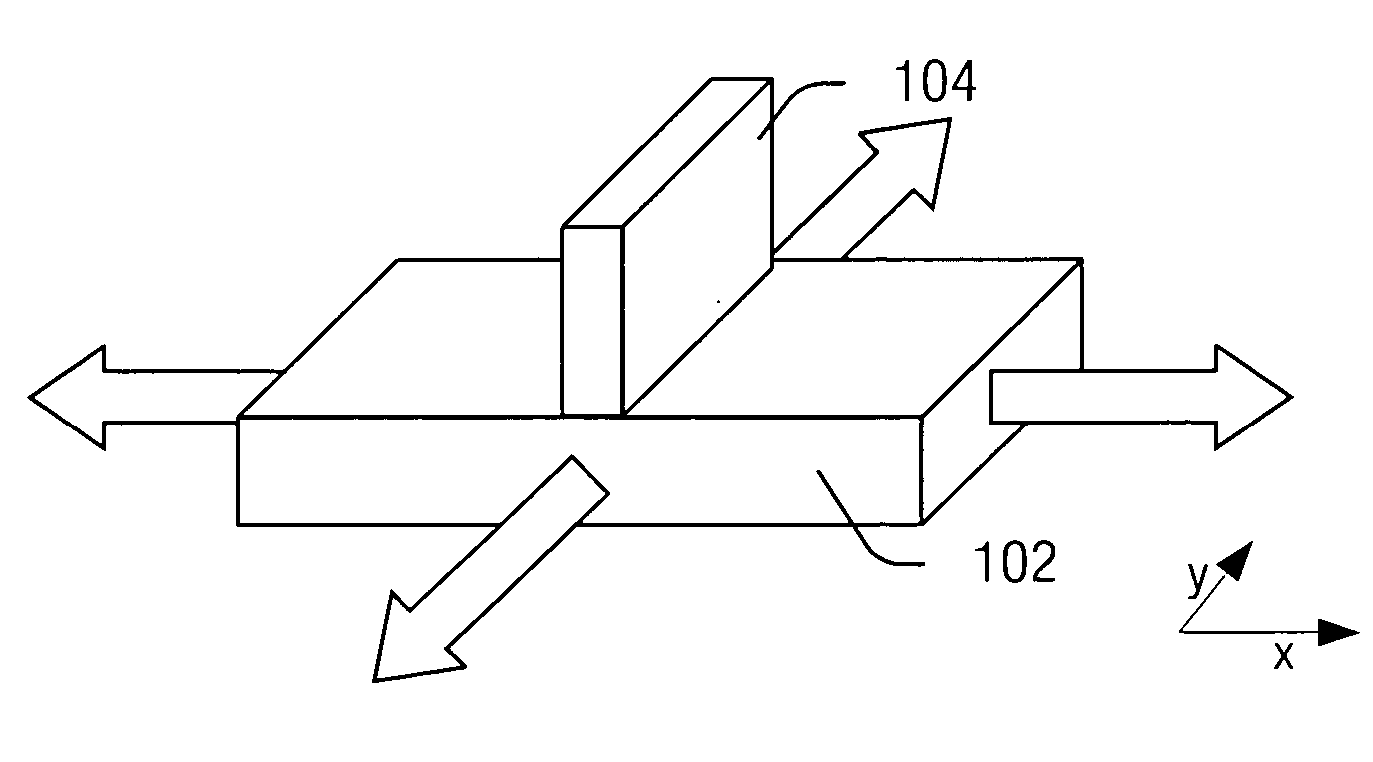
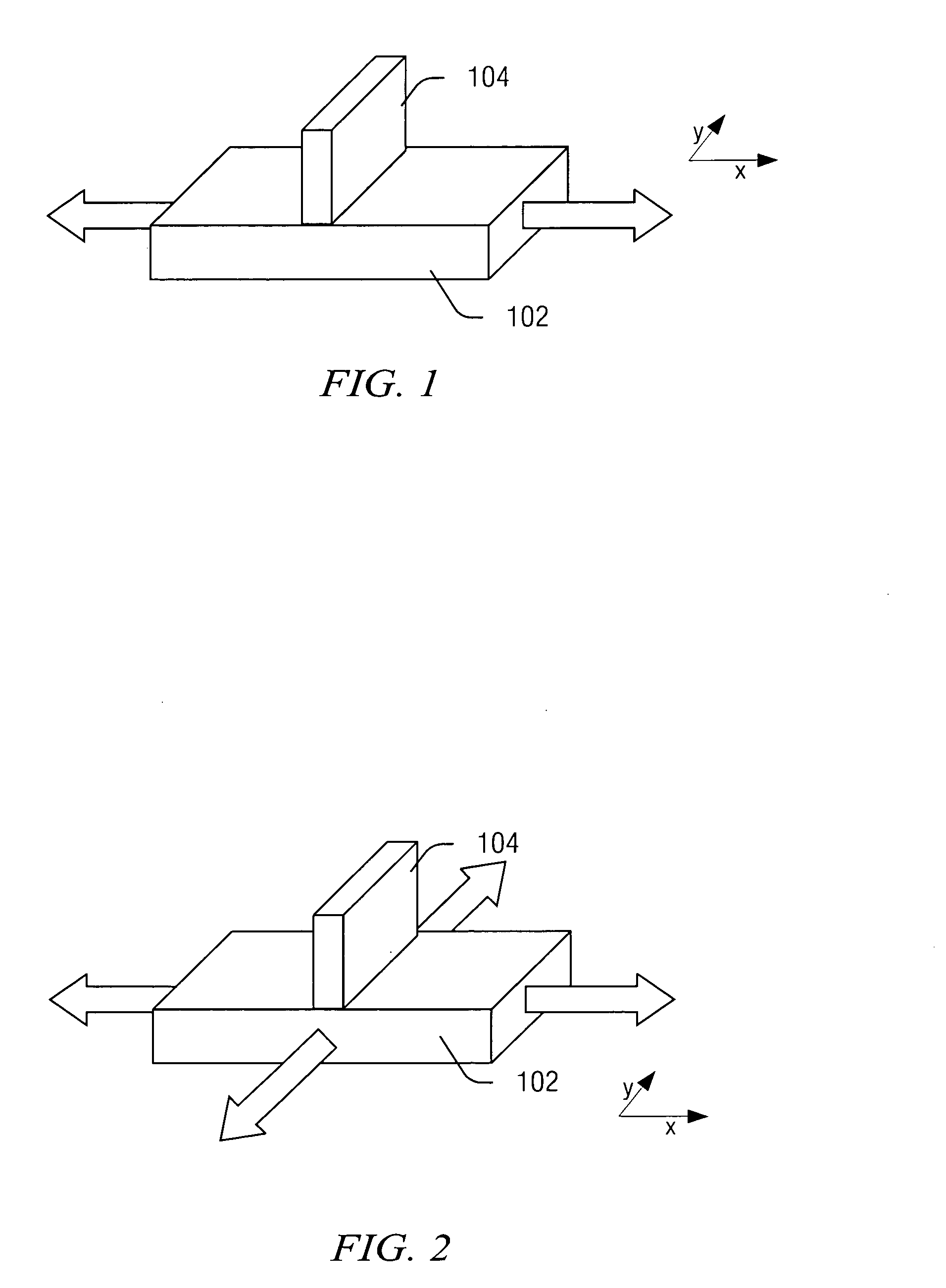
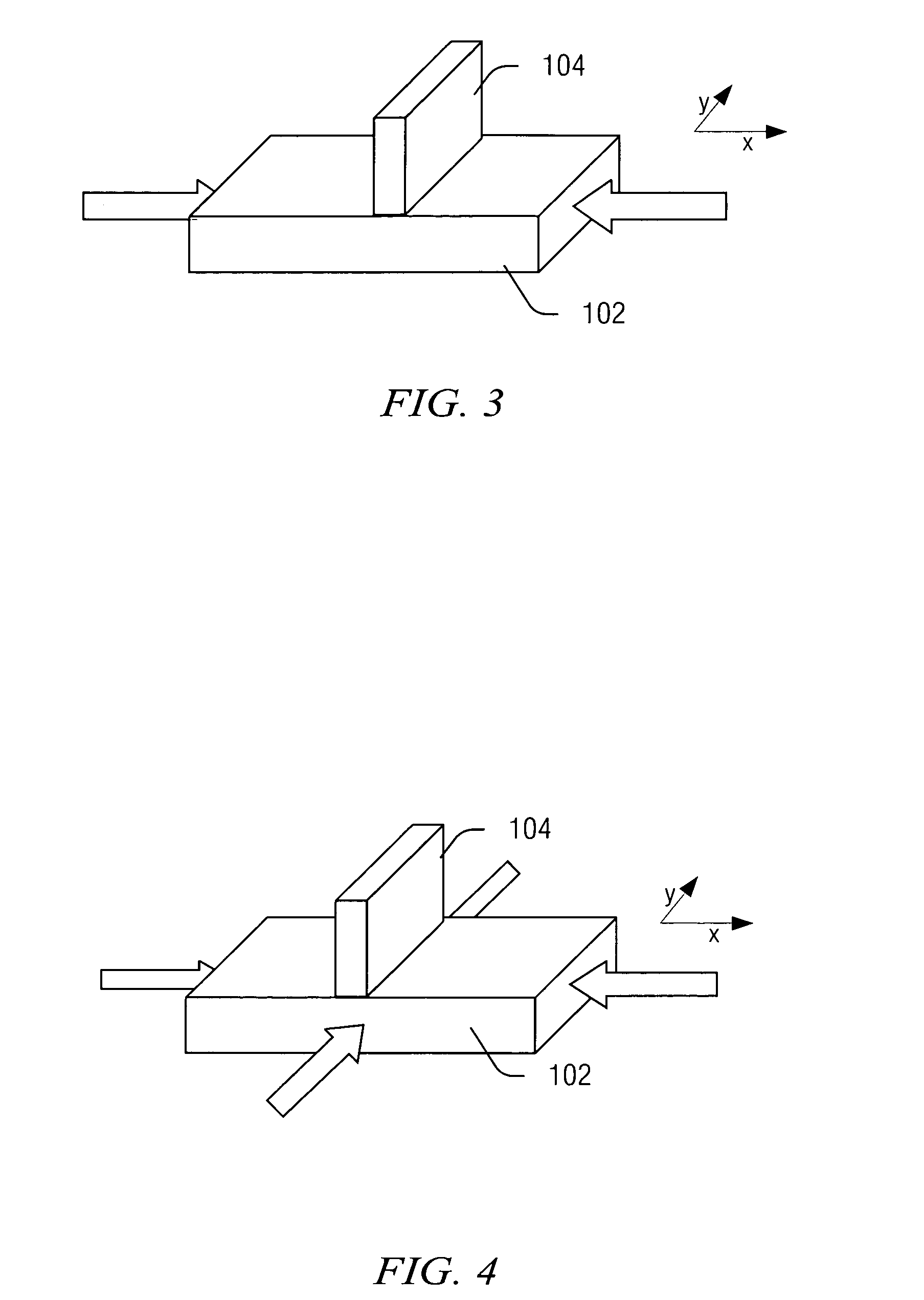
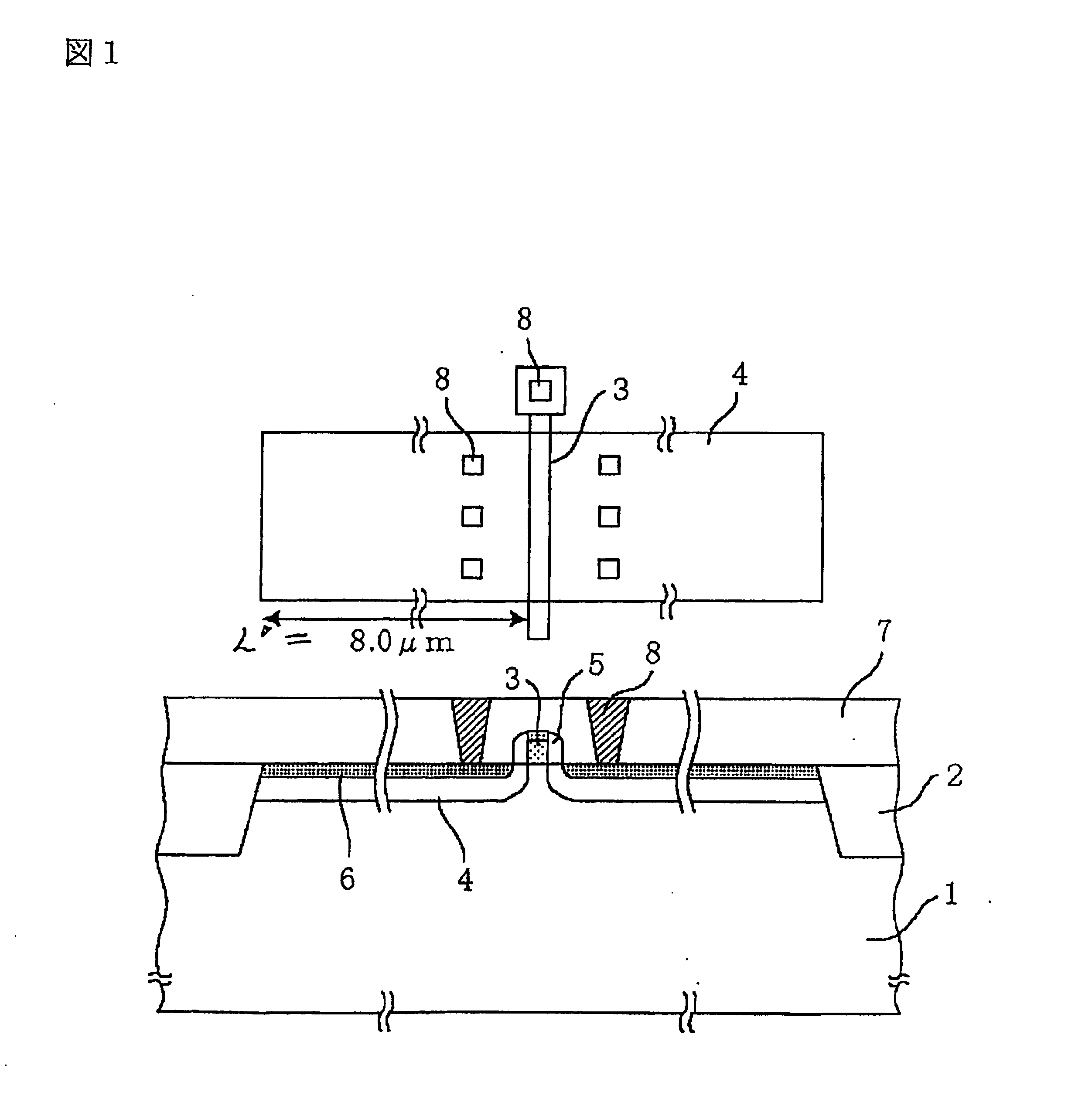
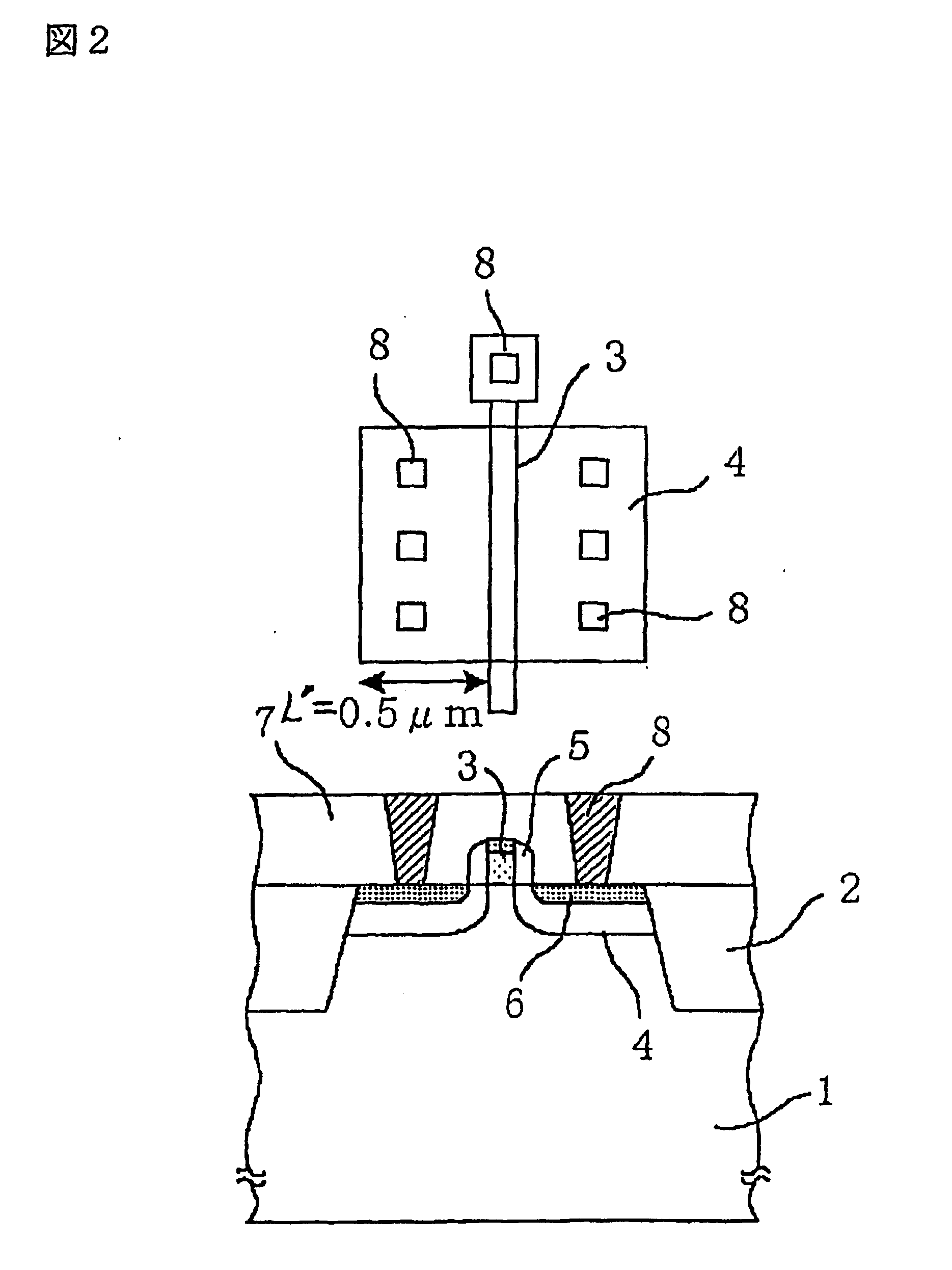
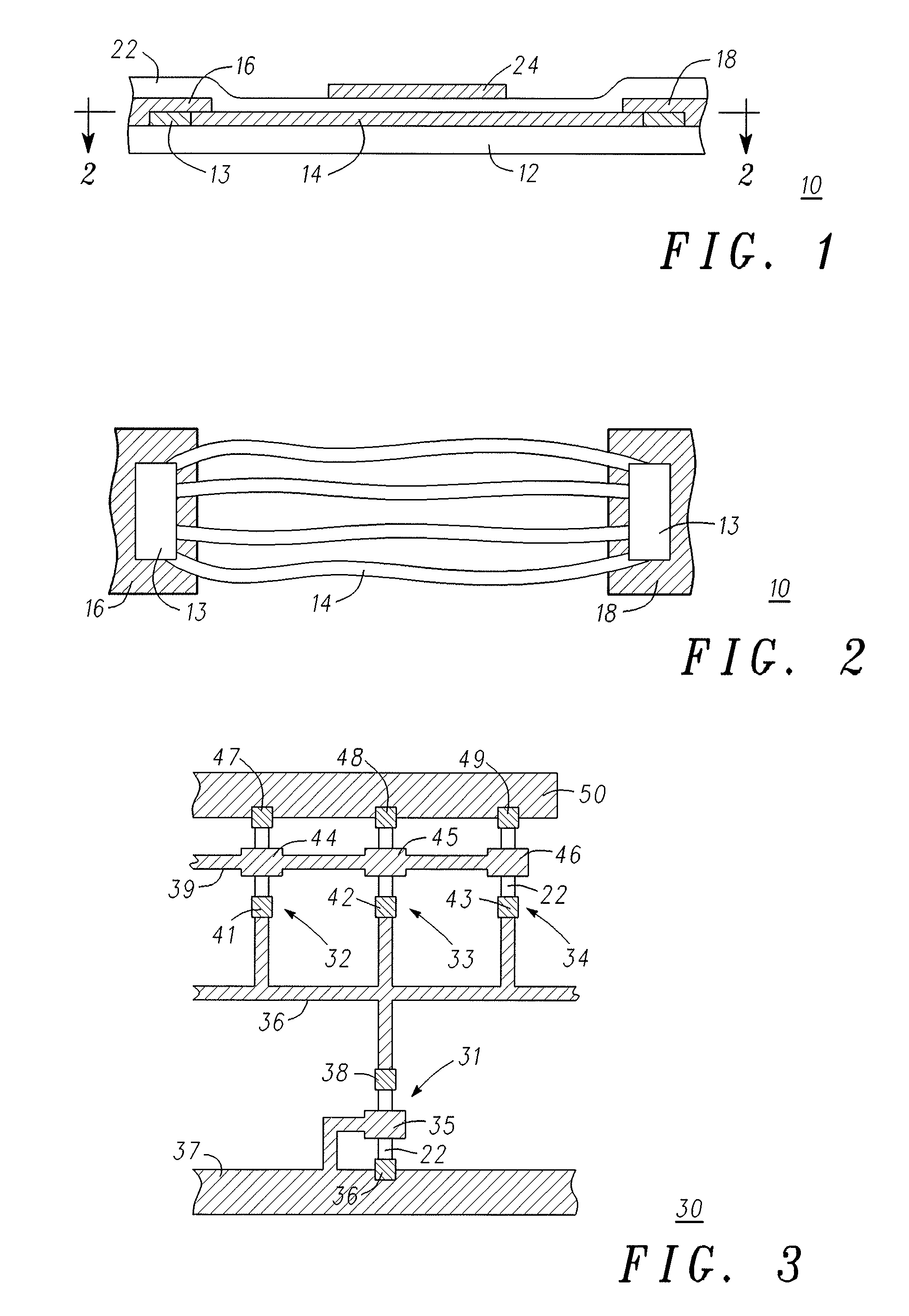
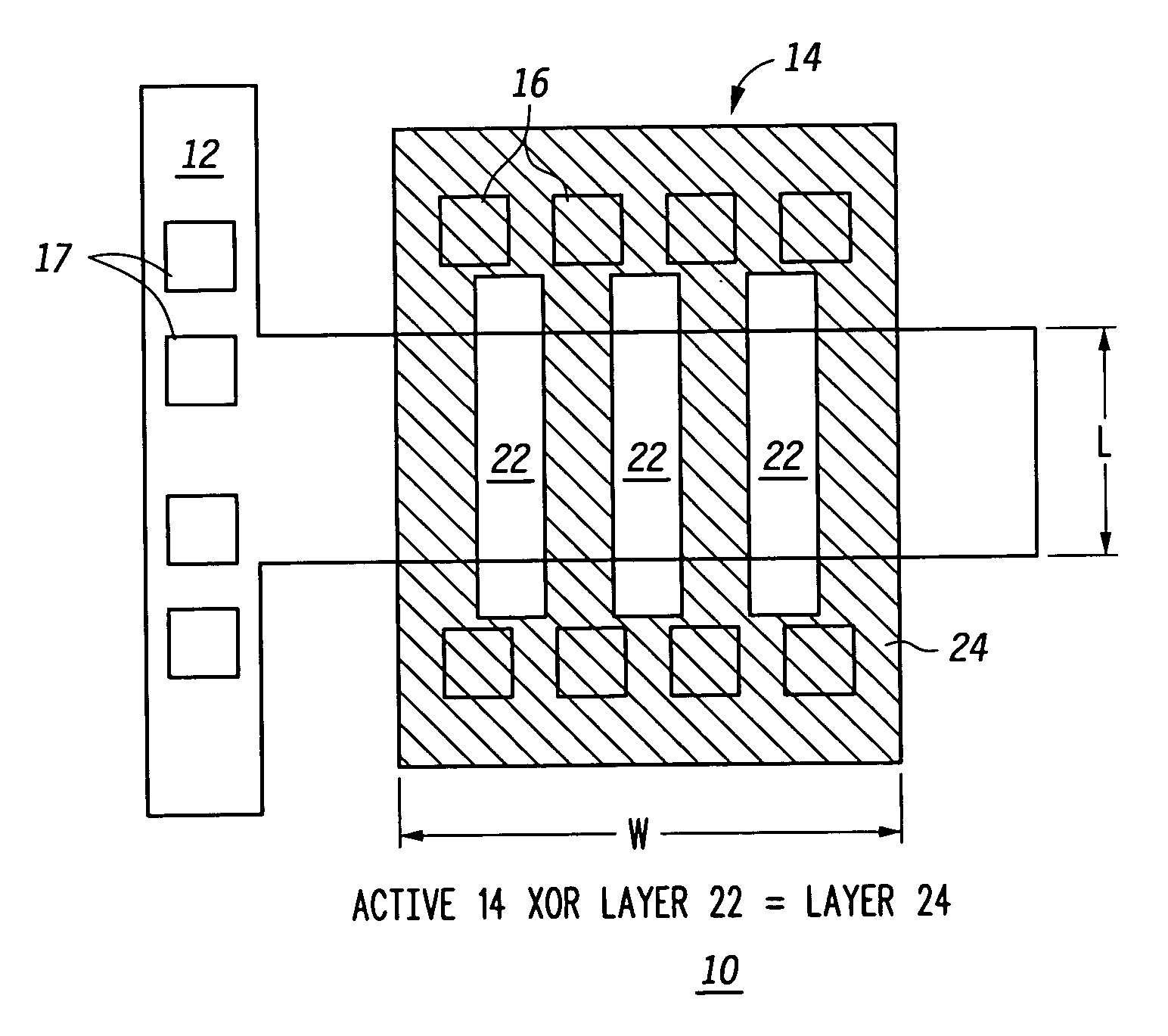
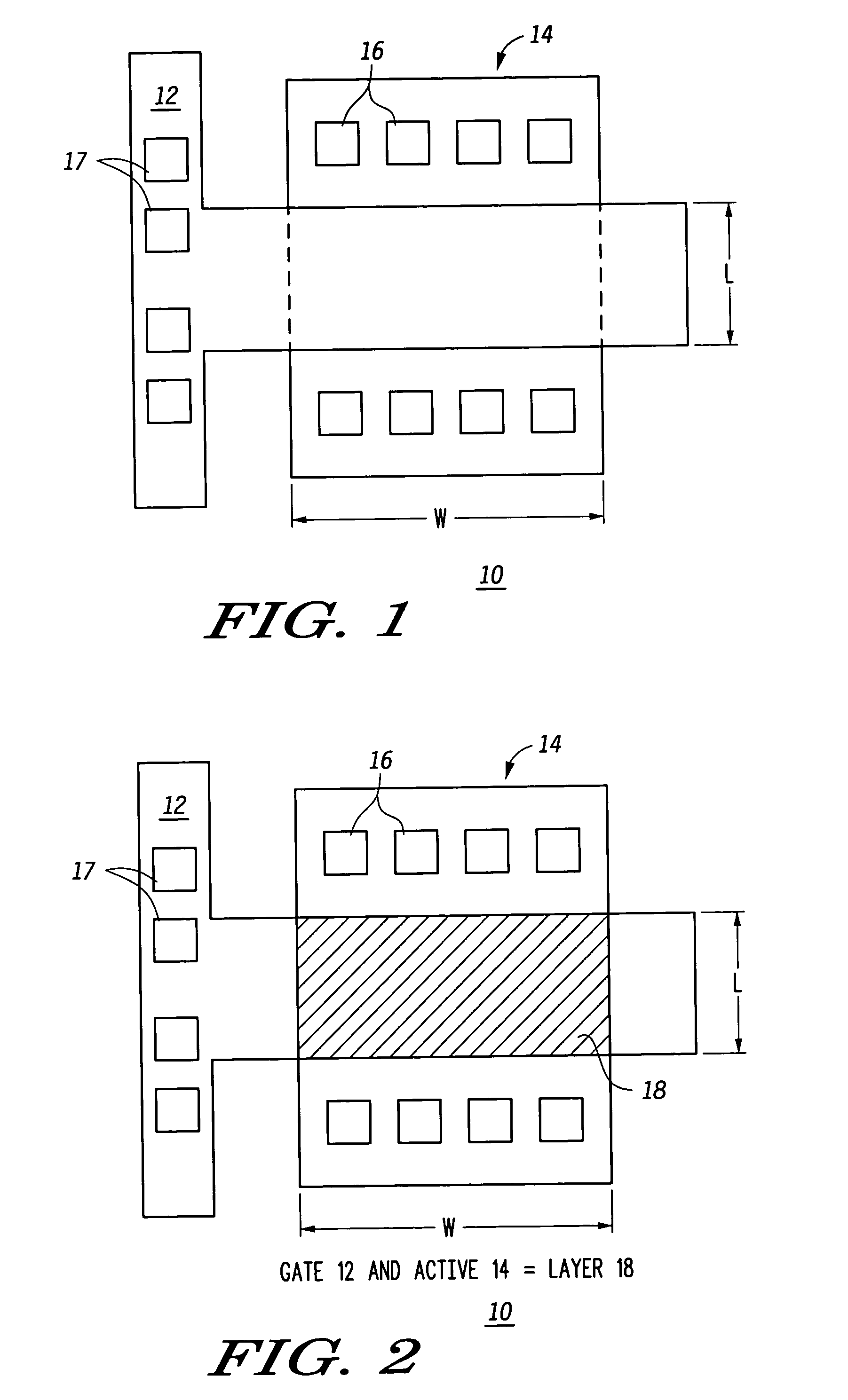
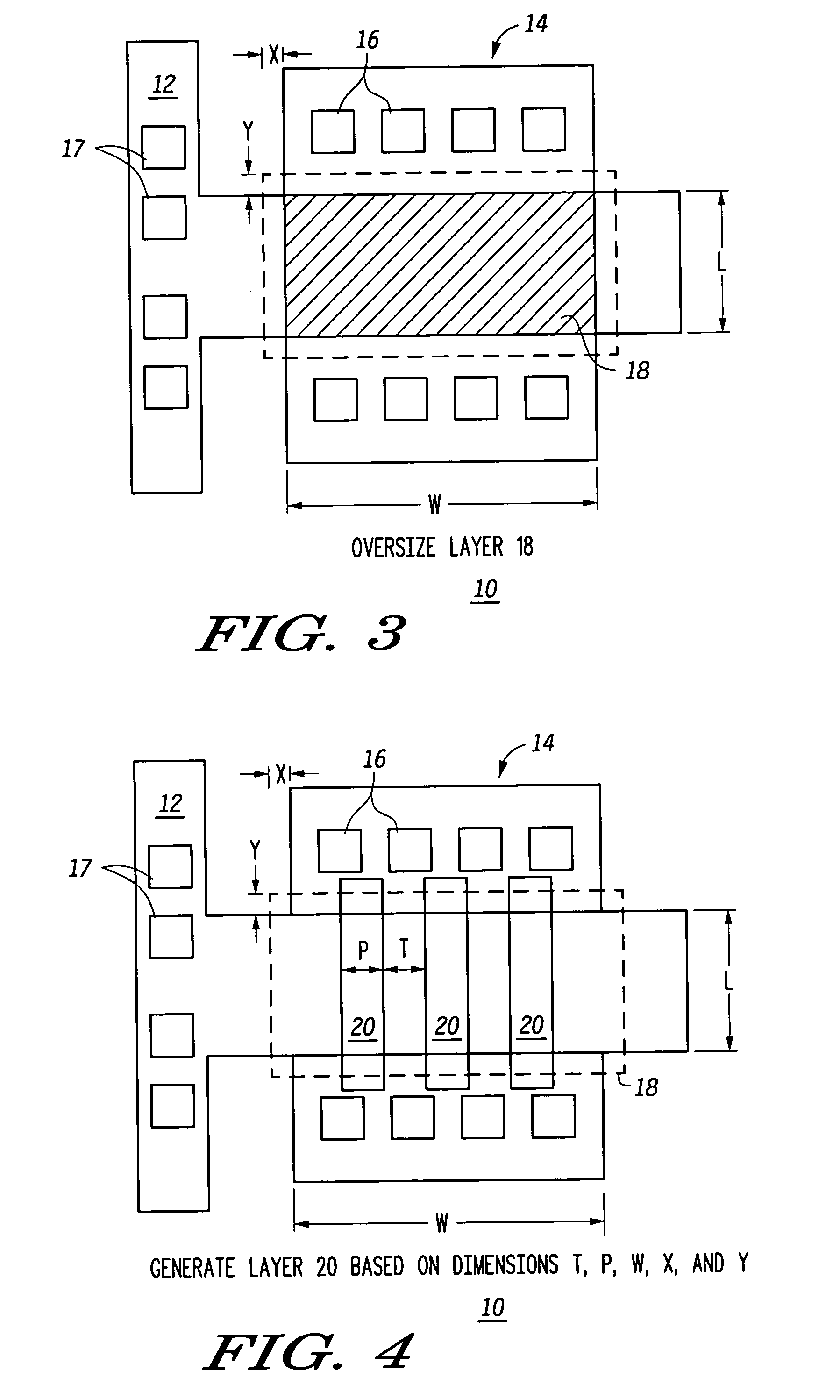
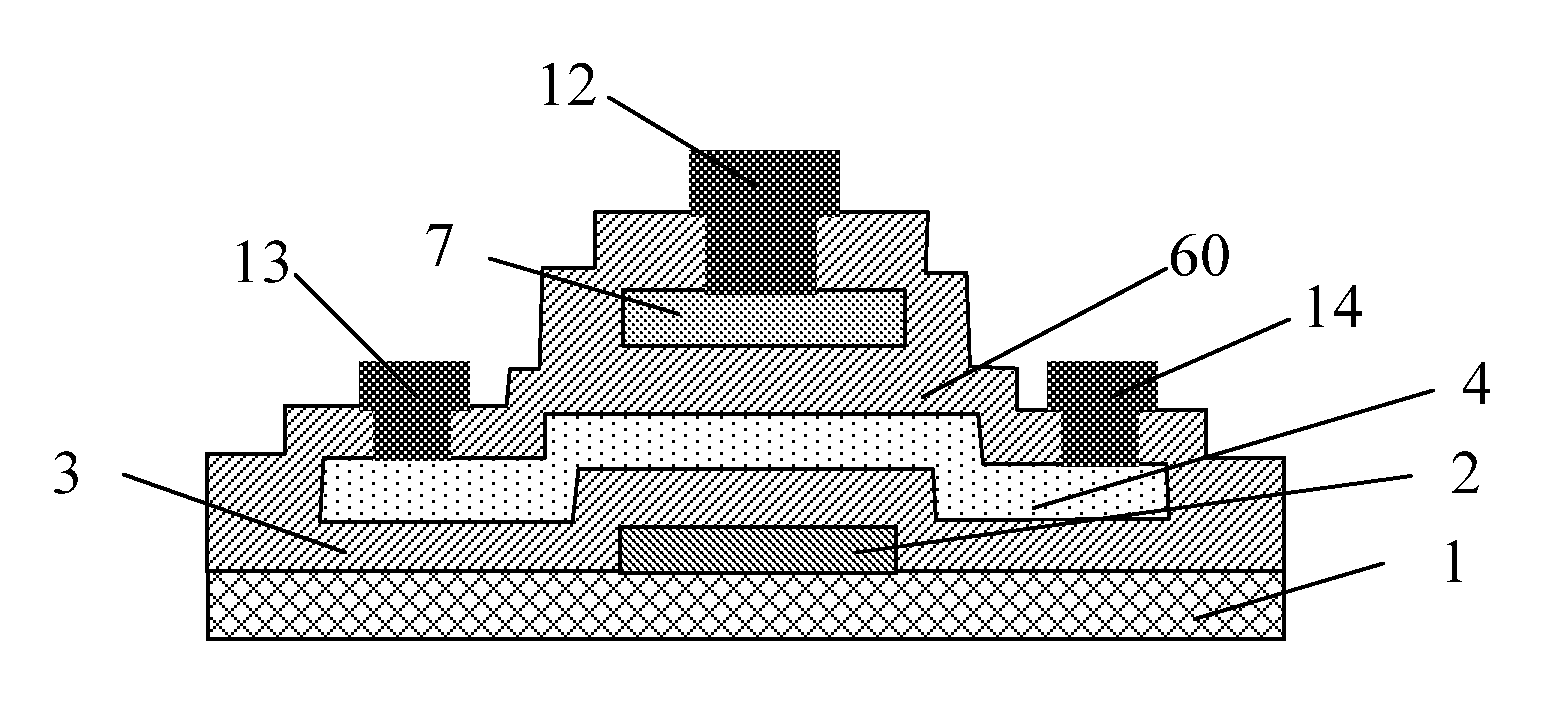
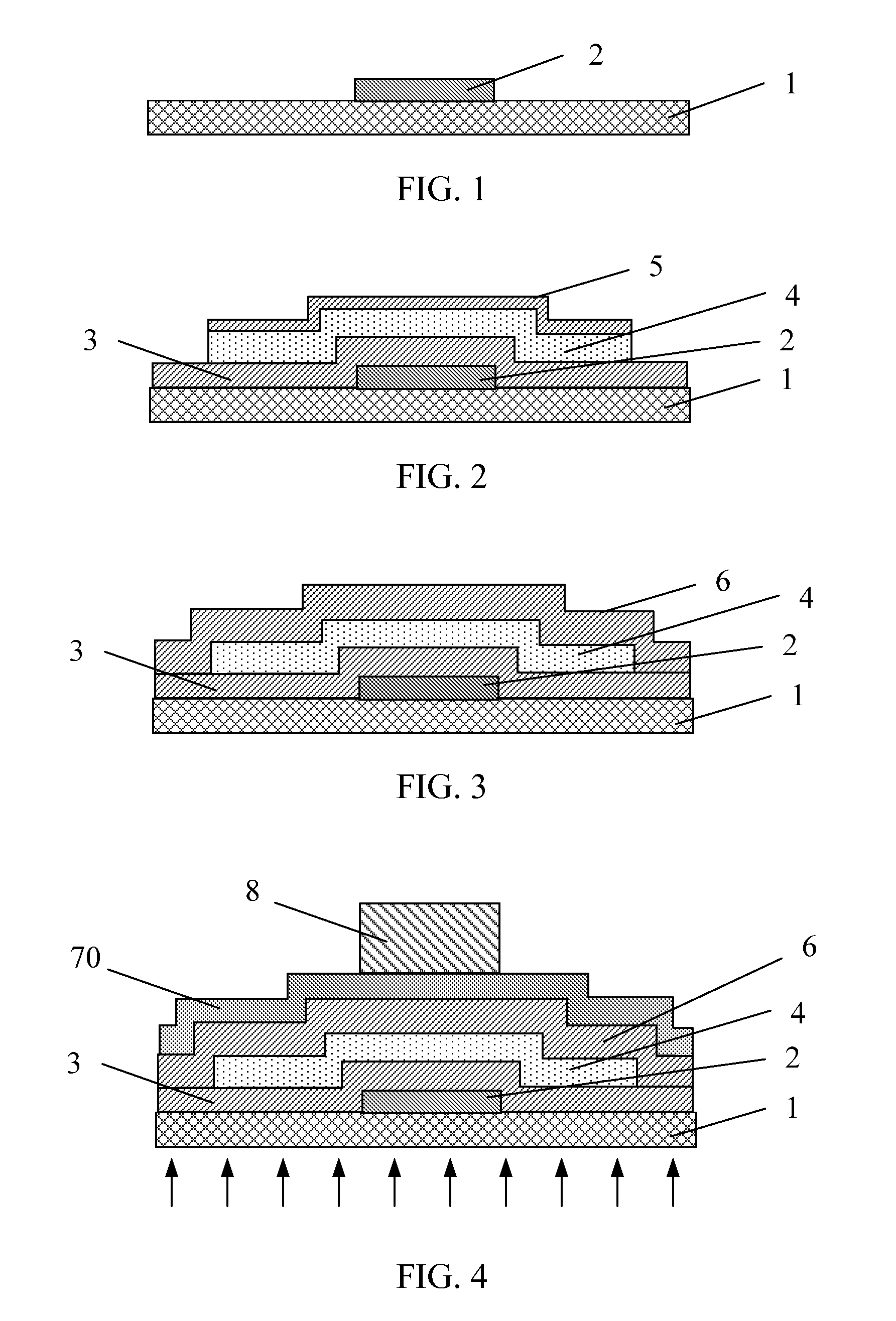
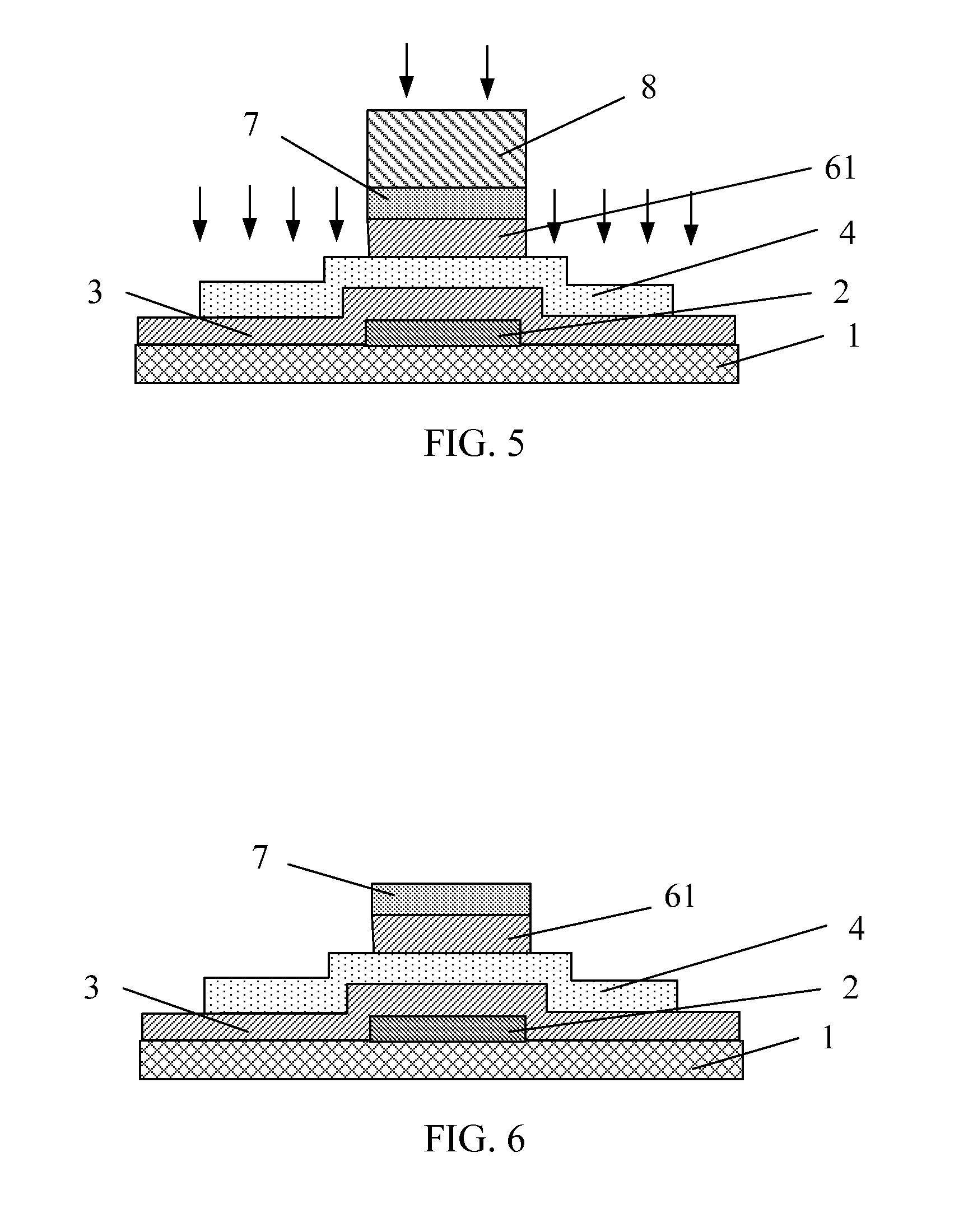
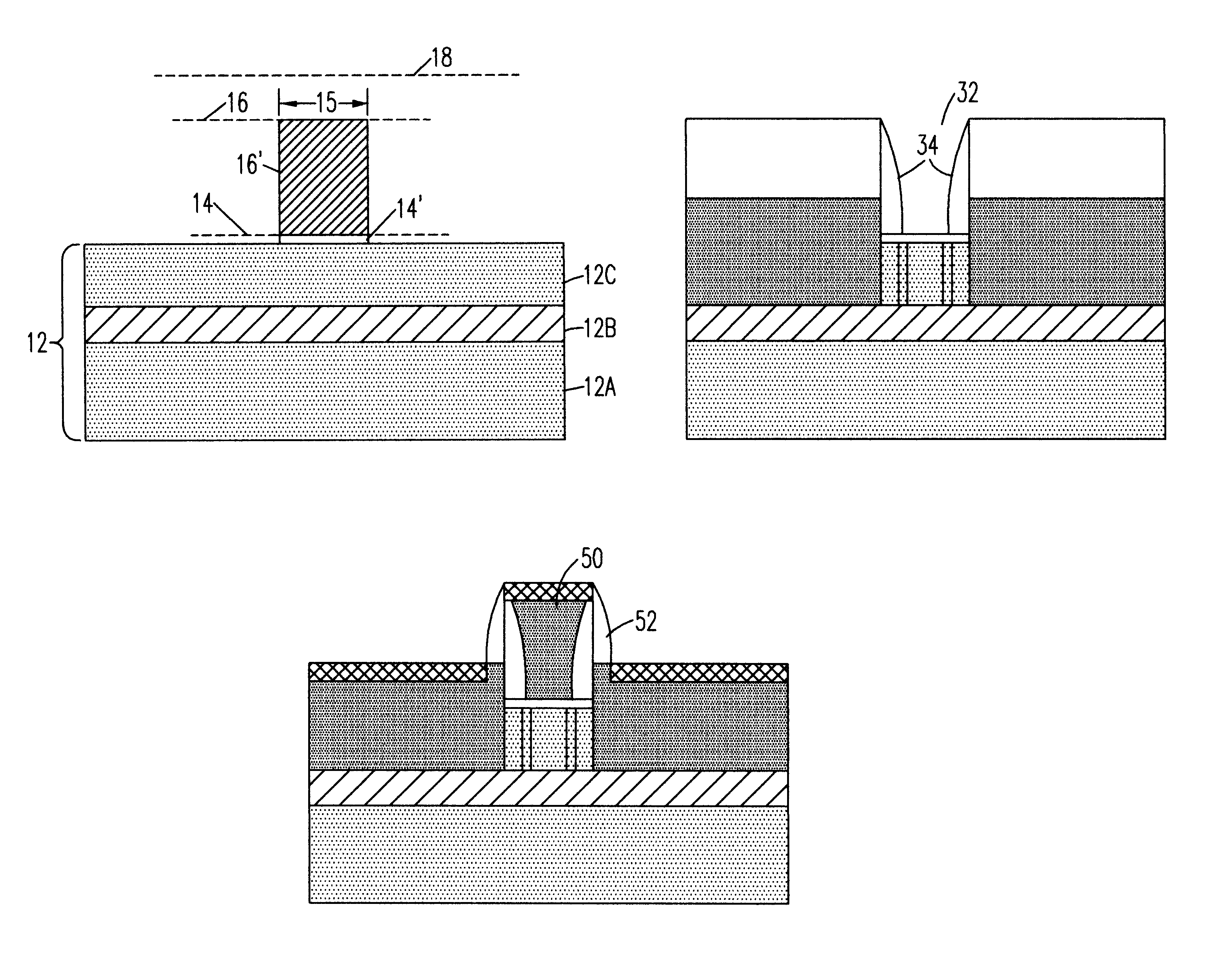
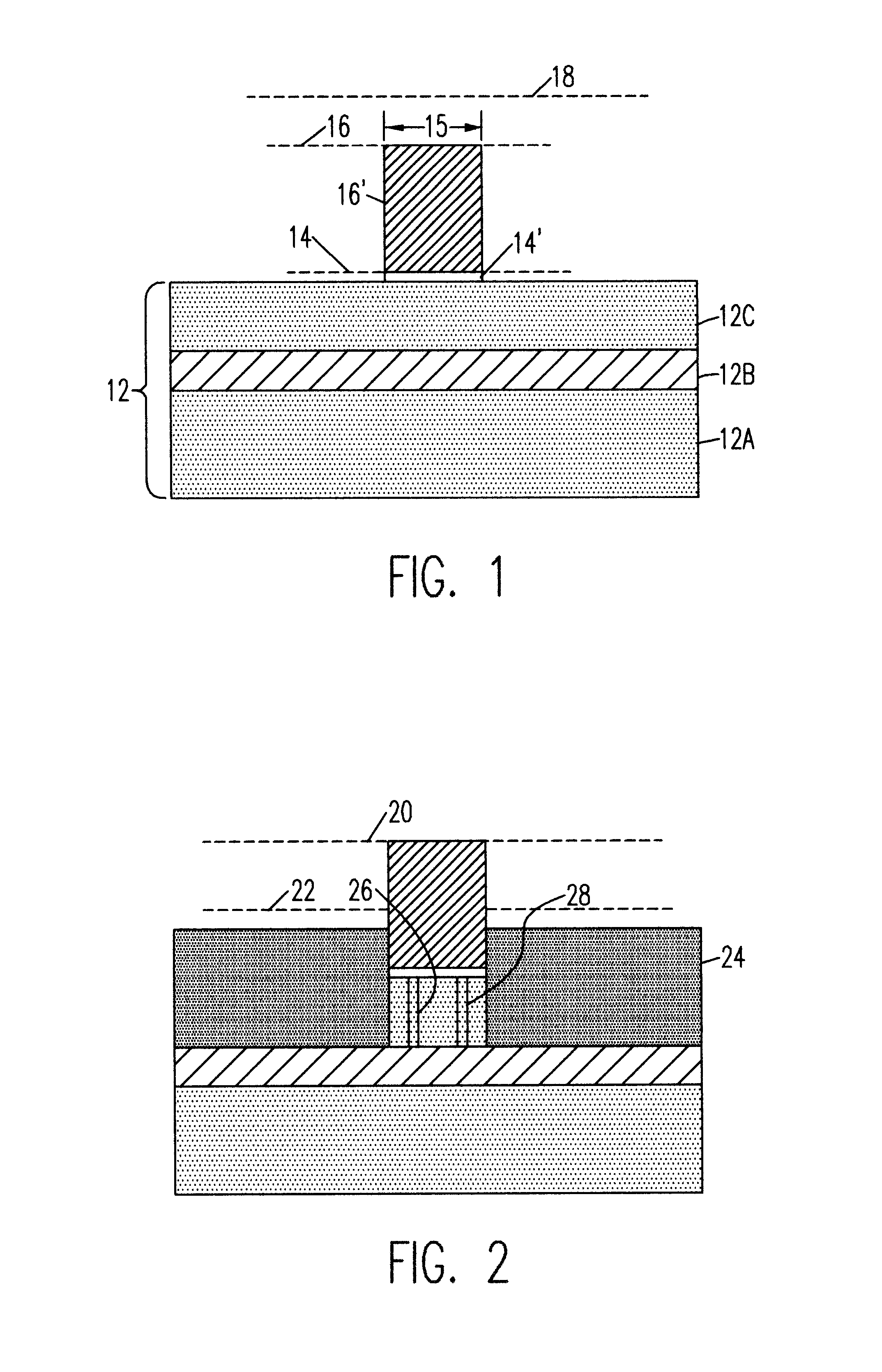
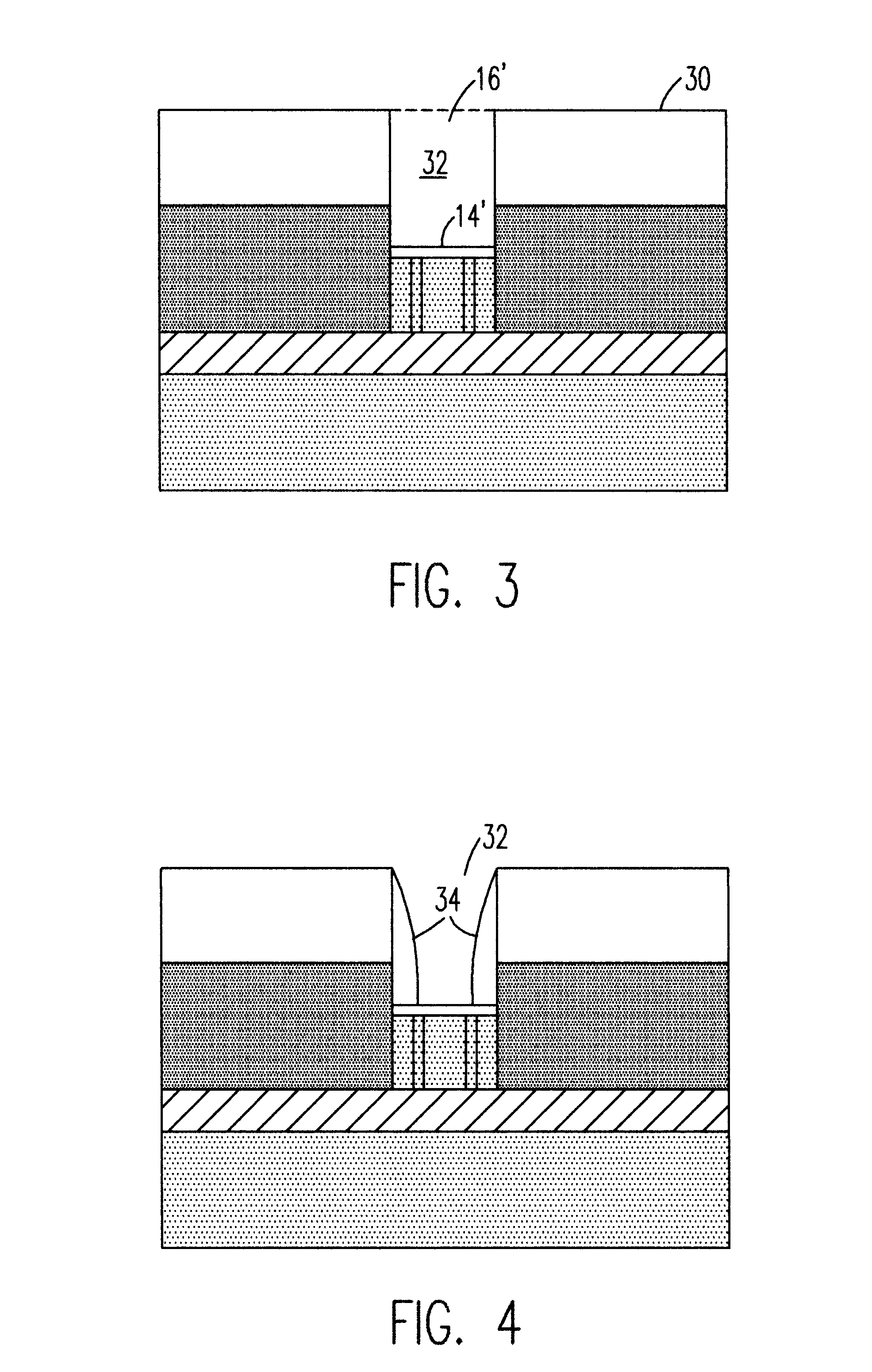
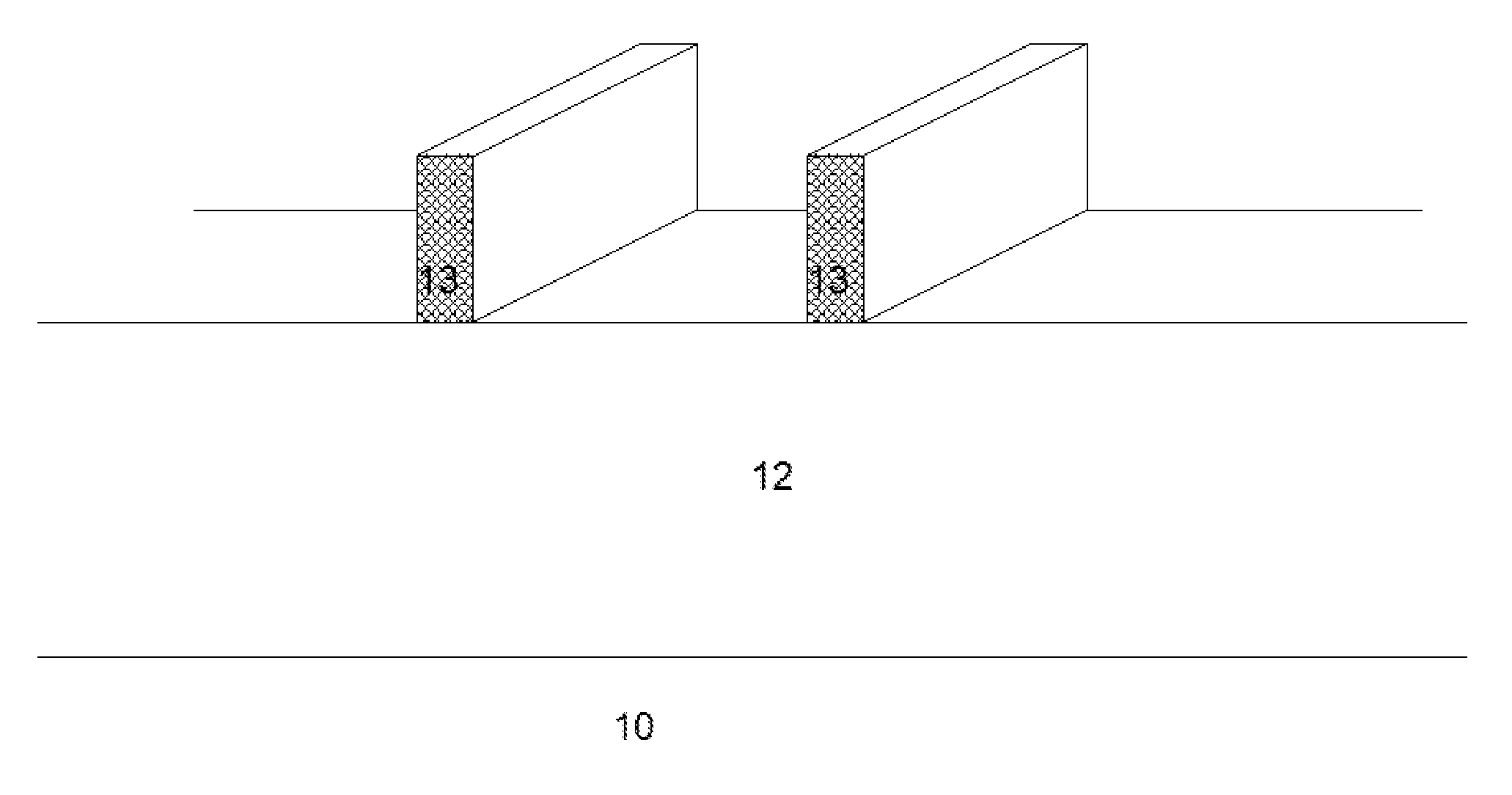
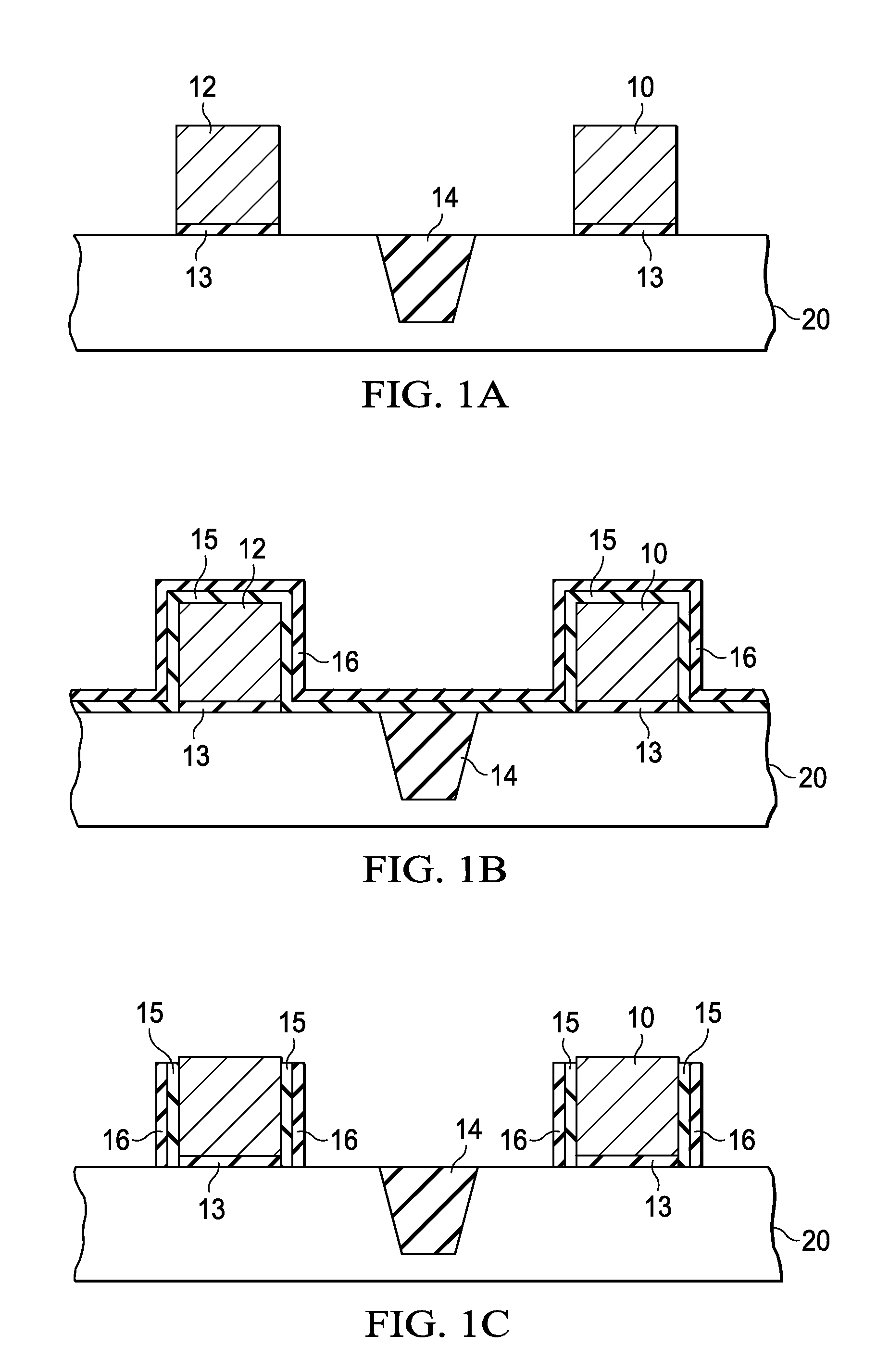
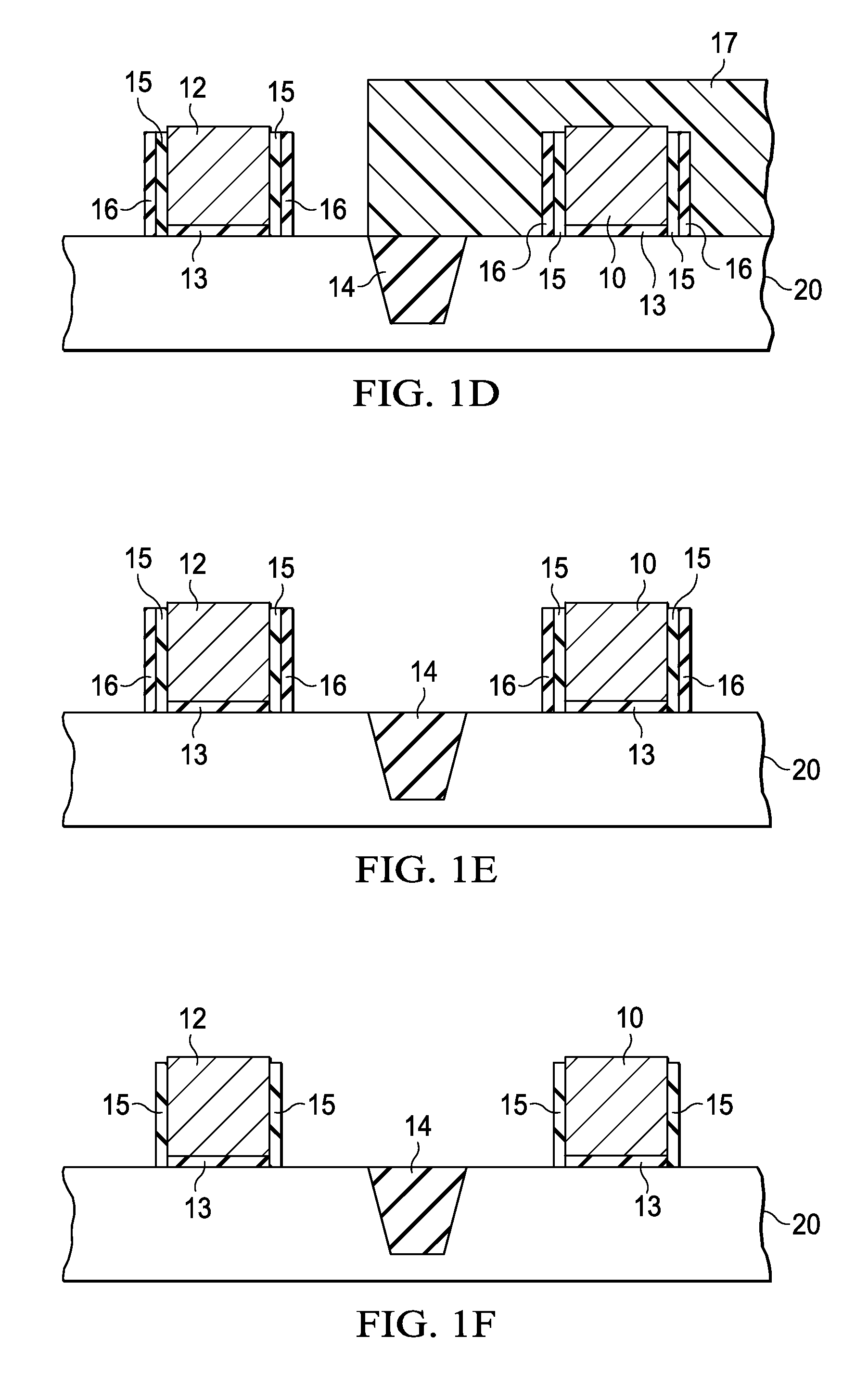
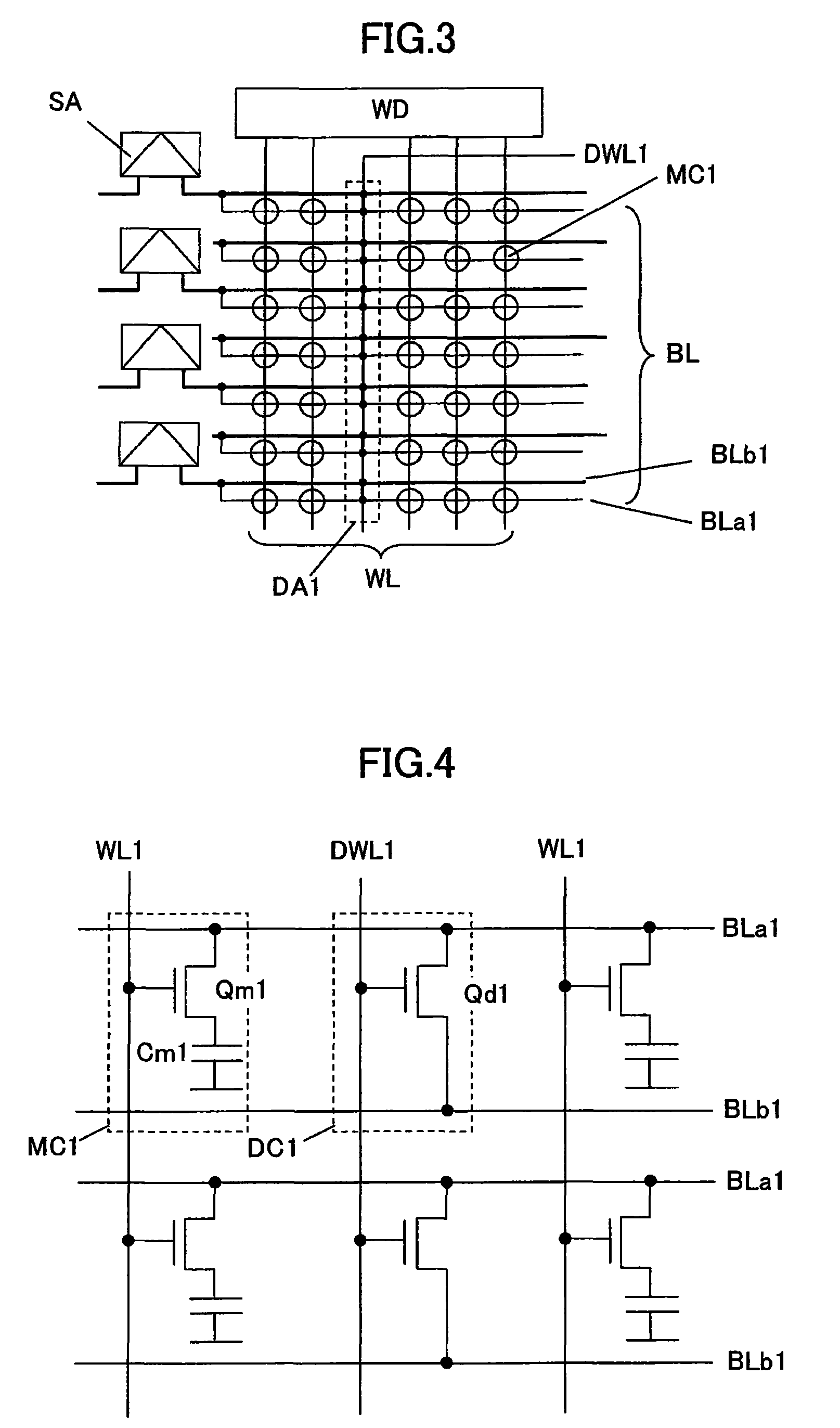
A method for creating a vertical double-gate transistor design includes providing a planar transistor layout (10) having a gate layer (12) overlying an active layer (14). In one embodiment, a first intermediate layer (18) is defined based on an overlapping region of the gate and active layers, and, using the first intermediate layer, a second intermediate layer (22) is defined which defines a spacing between at least two fins of the vertical double-gate transistor design. The second intermediate layer may also define a length and a width of the at least two fins. One embodiment modifies a dimension of the first intermediate layer prior to defining the second intermediate layer. The method further includes defining a resulting layer (24) based on a non-overlapping region of the second intermediate layer and the active layer. The resulting layer may then be used to create a mask and a semiconductor device (30) corresponding to the vertical double-gate transistor design.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
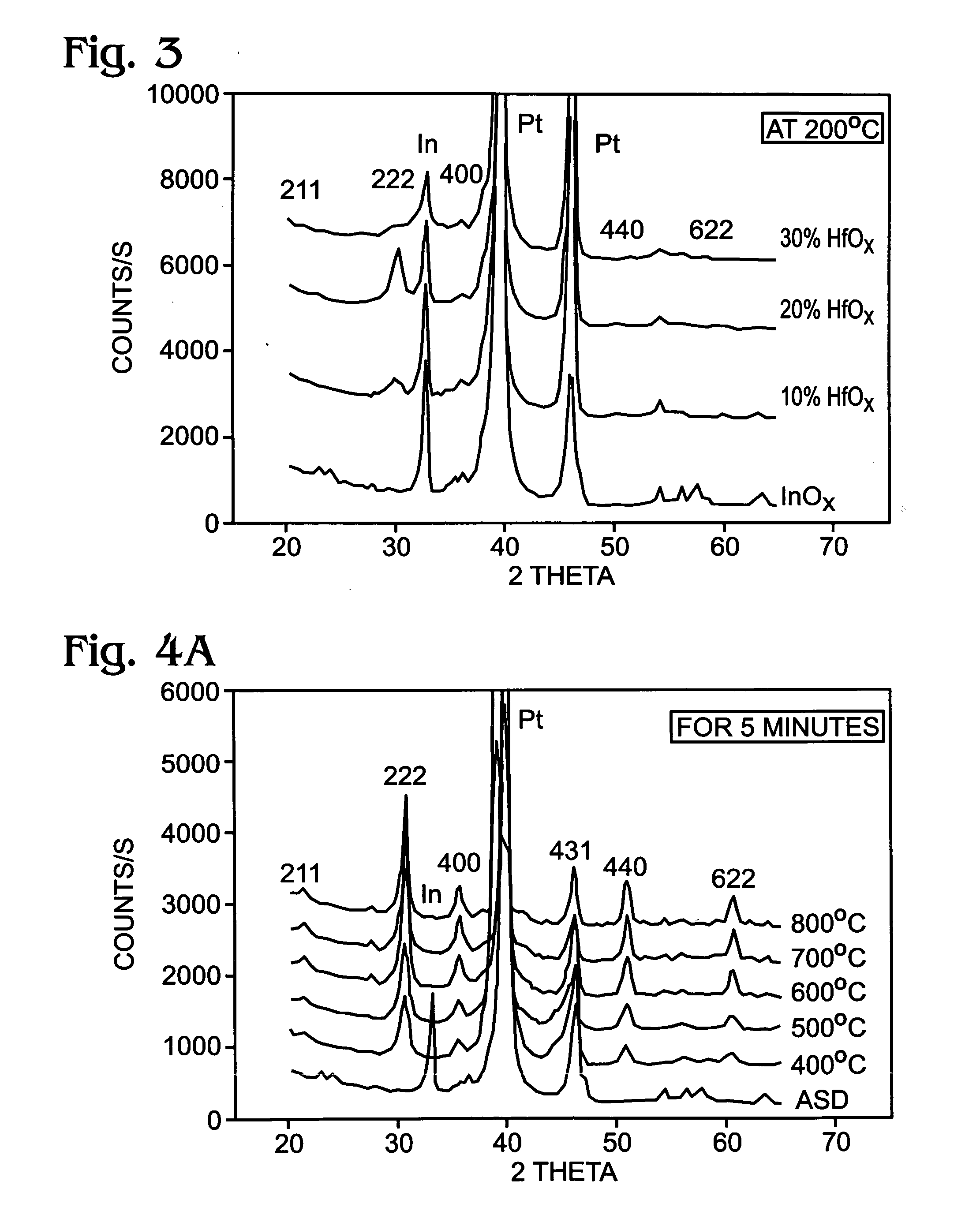
In2O3 thin film resistivity control by doping metal oxide insulator for MFMox device applications
ActiveUS20050151210A1Reduce chargeImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMemory retentionFilm resistance
The present invention discloses a novel ferroelectric transistor design using a resistive oxide film in place of the gate dielectric. By replacing the gate dielectric with a resistive oxide film, and by optimizing the value of the film resistance, the bottom gate of the ferroelectric layer is electrically connected to the silicon substrate, eliminating the trapped charge effect and resulting in the improvement of the memory retention characteristics. The resistive oxide film is preferably a doped conductive oxide in which a conductive oxide is doped with an impurity species. The doped conductive oxide is most preferred to be In2O3 with the dopant species being hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, or aluminum oxide.
Owner:SHARP KK
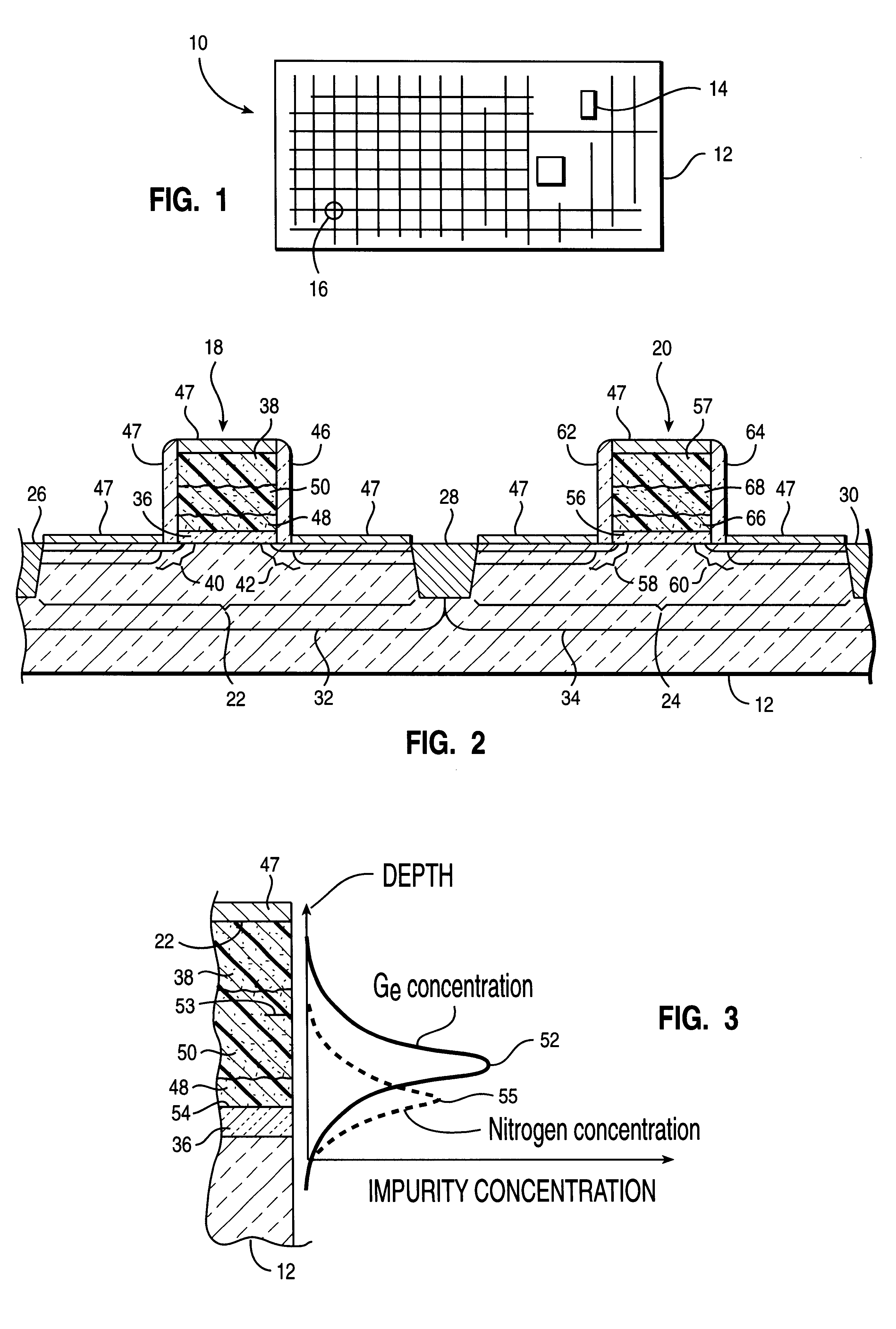
CMOS transistor design for shared N+/P+ electrode with enhanced device performance
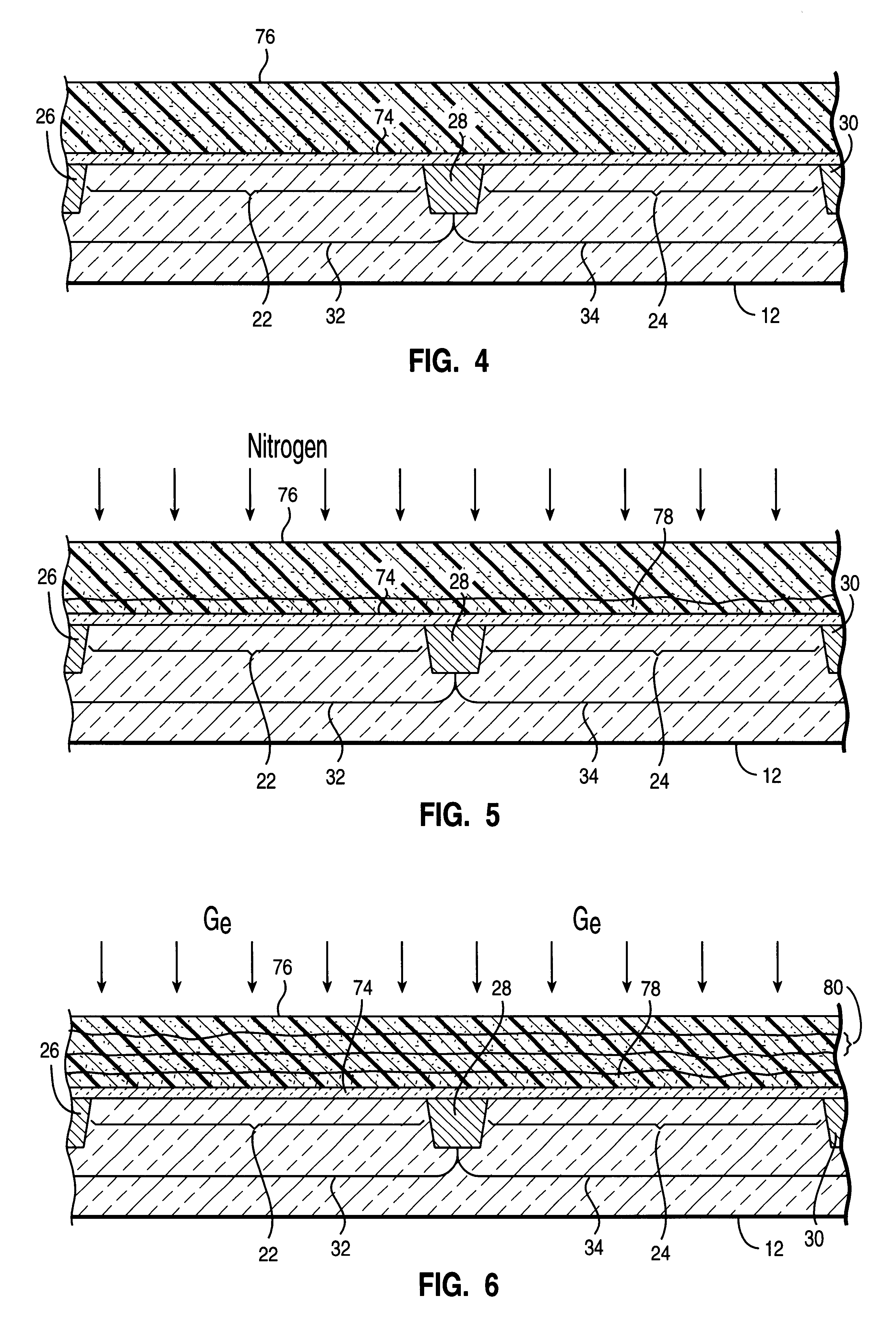
An integrated circuit and a method of making a transistor thereof are provided. In one aspect, the method includes the steps of forming a gate dielectric layer on the substrate and forming a gate electrode on the gate dielectric layer with a lower surface, a midpoint, and a quantity of p-type impurity. A quantity of nitrogen is introduced into the gate electrode whereby the quantity nitrogen has a peak concentration proximate the lower surface. A quantity of germanium is introduced into the gate electrode and first and second source / drain regions are formed in the substrate. The method enables simultaneous formation of n-channel and p-channel gate electrodes with work functions tailored for both types of devices.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
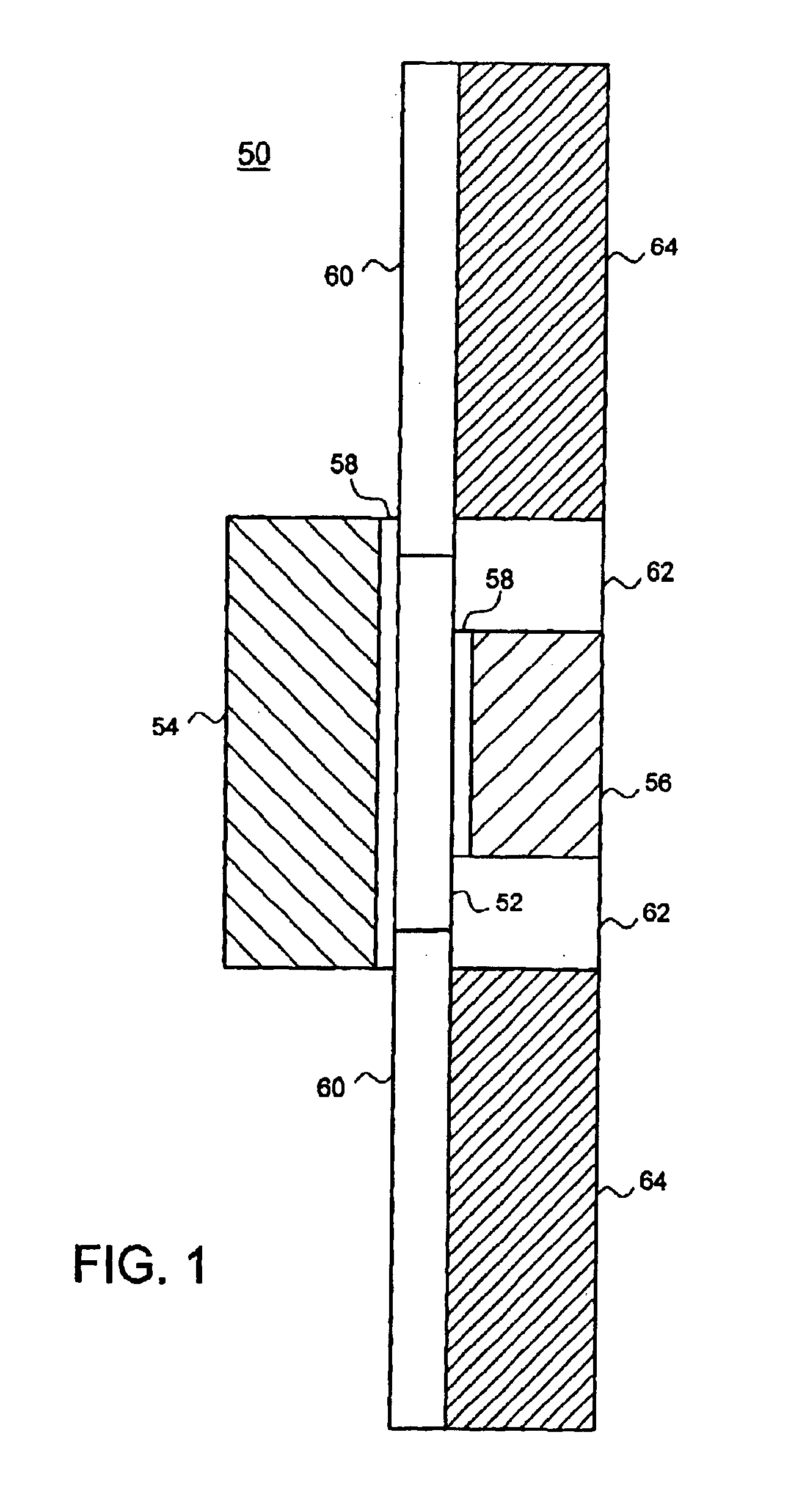
Doubly asymmetric double gate transistor structure
The present invention provides a double gated transistor and a method for forming the same that results in improved device performance and density. The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a double gated transistor with asymmetric gate doping, where one of the double gates is doped degenerately n-type and the other degenerately p-type. By doping one of the gates n-type, and the other p-type, the threshold voltage of the resulting device is improved. Additionally, the preferred transistor design uses an asymmetric structure that results in reduced gate-to-drain and gate-to-source capacitance. In particular, dimensions of the weak gate, the gate that has a workfunction less attractive to the channel carriers, are reduced such that the weak gate does not overlap the source / drain regions of the transistor. In contrast the strong gate, the gate having a workfunction that causes the inversion layer to form adjacent to it, is formed to slightly overlap the source / drain regions. This asymmetric structure allows for the performance benefits of a double gate design without the increased capacitance that would normally result.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transistor design and layout for performance improvement with strain
ActiveUS20050139929A1Improve performanceFacilitate fabricationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialEngineering
The present invention facilitates semiconductor device fabrication and performance by providing a semiconductor device that can improve channel mobility for both N type and P type transistor devices. The semiconductor device of the present invention is fabricated on a semiconductor substrate 802 that has a first and second crystallographic orientation axes (e.g., <110>, <100>) 804 and 806. Source to drain channel regions for P type devices are formed 904 and aligned along the first crystallographic orientation axis. Source to drain channel regions for N type devices are formed 906 rotated from the channel regions of the P type devices by an offset angle so that the source to drain channel regions for the N type devices are aligned with the second crystallographic orientation axis. Subsequently, a uniaxial or biaxial tensile stress 908 is applied to the source to drain channel regions of the N type devices and a uniaxial or biaxial compressive stress 910 is applied to the source to drain channel regions of the P type devices.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Mos semiconductor device
While using conventional manufacturing processes, it is intended to apply a compressive strain in the channel direction to the p-channel MOS field effect transistor and also apply a tensile strain in the channel direction to the n-channel MOS field effect transistor for increasing both MOS currents. In the MOS semiconductor device isolated by a trench device isolation region, the p-channel MOS field effect transistor is designed so that a length of a source / drain region in the channel direction is not more than 1 micrometer, and the gate length is not more than 0.2 micrometers. The n-channel MOS field effect transistor is designed so that a face of the source / drain region in parallel to the gate width direction is adjacent to the device isolation film with the inserted silicon nitride film, and a face of the source / drain region parallel to the gate length direction is adjacent to the device isolation film comprising the silicon oxide film only.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Doubly asymmetric double gate transistor structure
The present invention provides a double gated transistor and a method for forming the same that results in improved device performance and density. The preferred embodiment of the present invention provides a double gated transistor with asymmetric gate doping, where one of the double gates is doped degenerately n-type and the other degenerately p-type. By doping one of the gates n-type, and the other p-type, the threshold voltage of the resulting device is improved. Additionally, the preferred transistor design uses an asymmetric structure that results in reduced gate-to-drain and gate-to-source capacitance. In particular, dimensions of the weak gate, the gate that has a workfunction less attractive to the channel carriers, are reduced such that the weak gate does not overlap the source / drain regions of the transistor. In contrast the strong gate, the gate having a workfunction that causes the inversion layer to form adjacent to it, is formed to slightly overlap the source / drain regions. This asymmetric structure allows for the performance benefits of a double gate design without the increased capacitance that would normally result.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
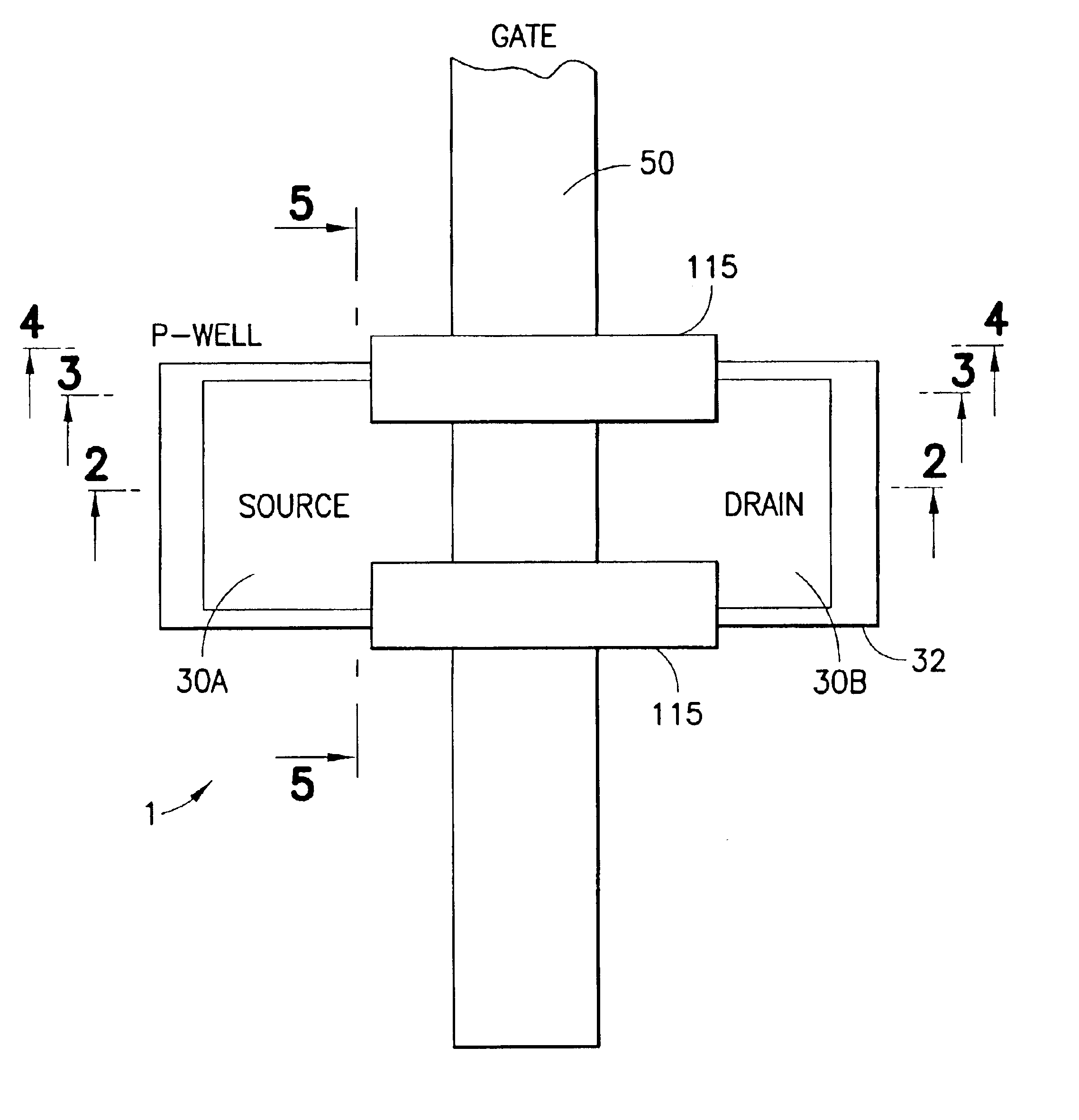
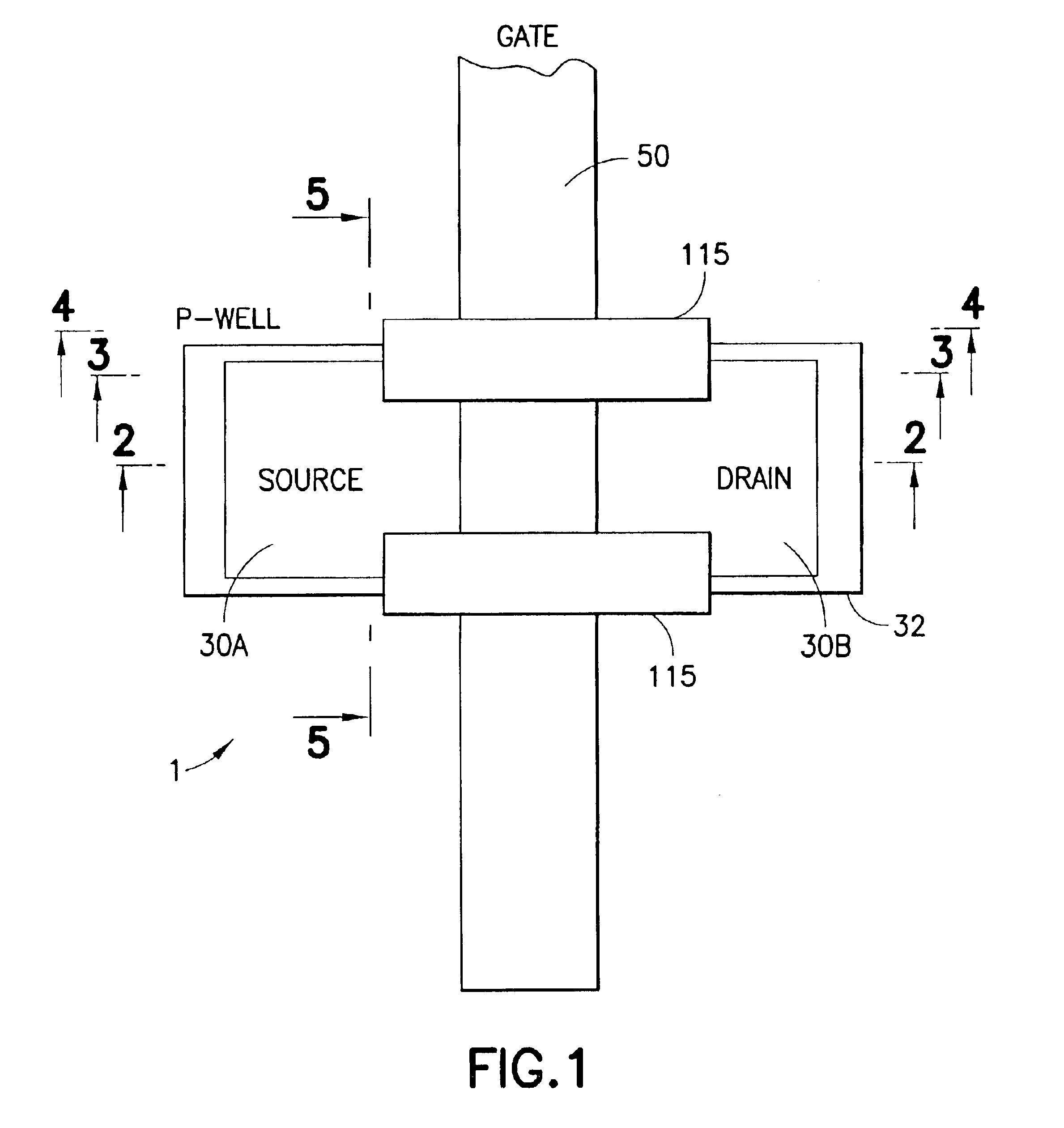
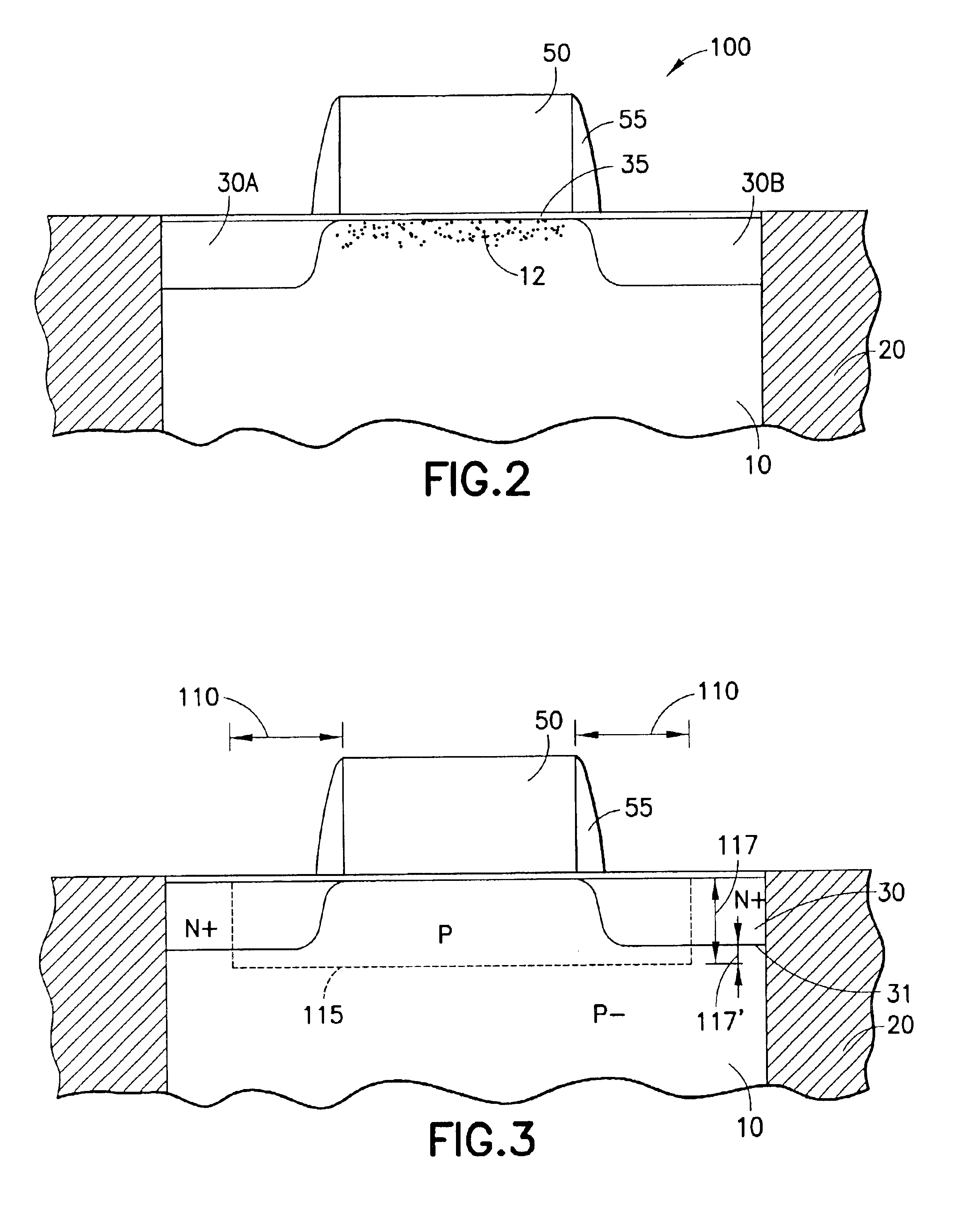
Radiation-hardened transistor fabricated by modified CMOS process
InactiveUS6847065B1Undesirable effectReduce complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsField-effect transistorThreshold voltage
An NMOS field effect transistor (1) is made radiation hard by a pair of guard band implants (115) of limited horizontal extent, extending between the source (30A) and drain (30B) along the edge of the transistor body, and extending only to a limited extent into the field insulator and into the interior of the transistor, leaving an unimplanted area in the center of the body that retains the transistor design threshold voltage.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Carbon nanotube circuits design methodology
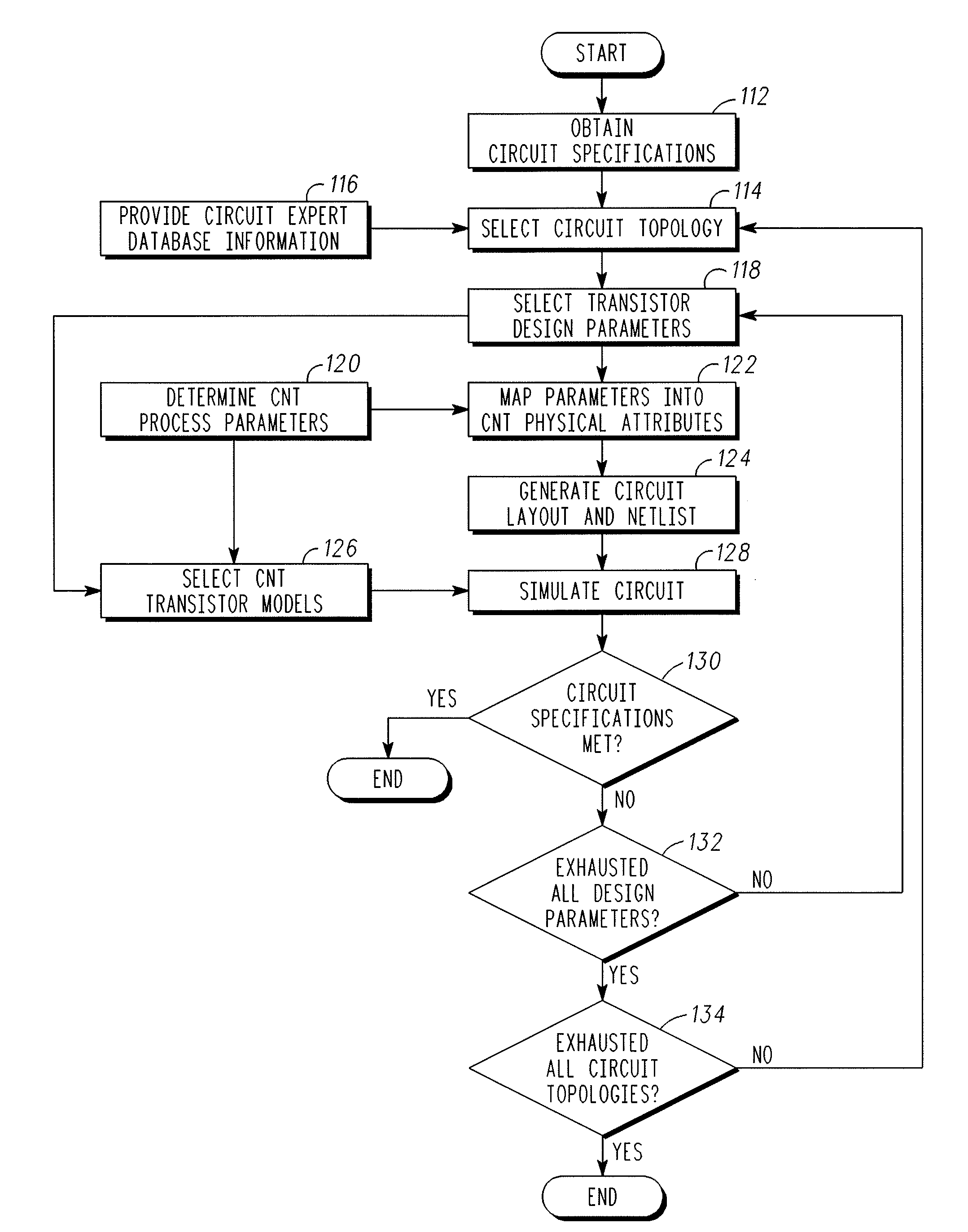
InactiveUS20090217216A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeEngineering
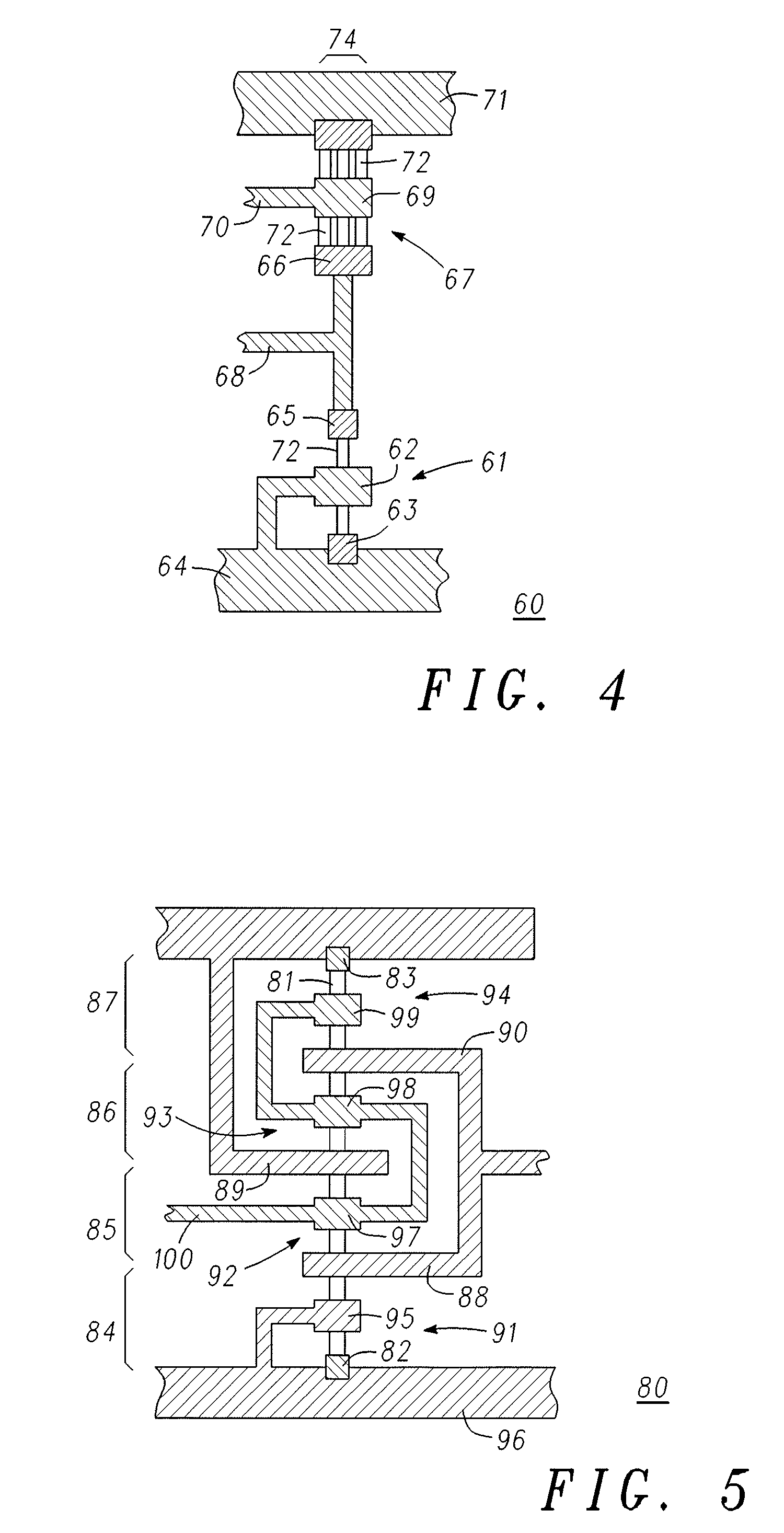
A methodology is provided for optimizing circuit parameters of circuits including carbon nanotube transistors. The method comprises mapping (122) selected transistor design parameters (118), based on carbon nanotube process parameters (120) and selected circuit topologies (114), into carbon nanotube physical attributes. A circuit layout is generated (124) from the carbon nanotube physical attributes and simulated (128). The steps are repeated until circuit specifications (130) are met. The carbon nanotube physical attributes may include, for example, the catalyst width (74) for growing a plurality of carbon nanotubes (72) or number of segments in a serpentine electrode structure (88, 89, 90) contacting a single carbon nanotube (81).
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method for converting a planar transistor design to a vertical double gate transistor design
InactiveUS20050020015A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringActive layer
A method for creating a vertical double-gate transistor design includes providing a planar transistor layout (10) having a gate layer (12) overlying an active layer (14). In one embodiment, a first intermediate layer (18) is defined based on an overlapping region of the gate and active layers, and, using the first intermediate layer, a second intermediate layer (22) is defined which defines a spacing between at least two fins of the vertical double-gate transistor design. The second intermediate layer may also define a length and a width of the at least two fins. One embodiment modifies a dimension of the first intermediate layer prior to defining the second intermediate layer. The method further includes defining a resulting layer (24) based on a non-overlapping region of the second intermediate layer and the active layer. The resulting layer may then be used to create a mask and a semiconductor device (30) corresponding to the vertical double-gate transistor design.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
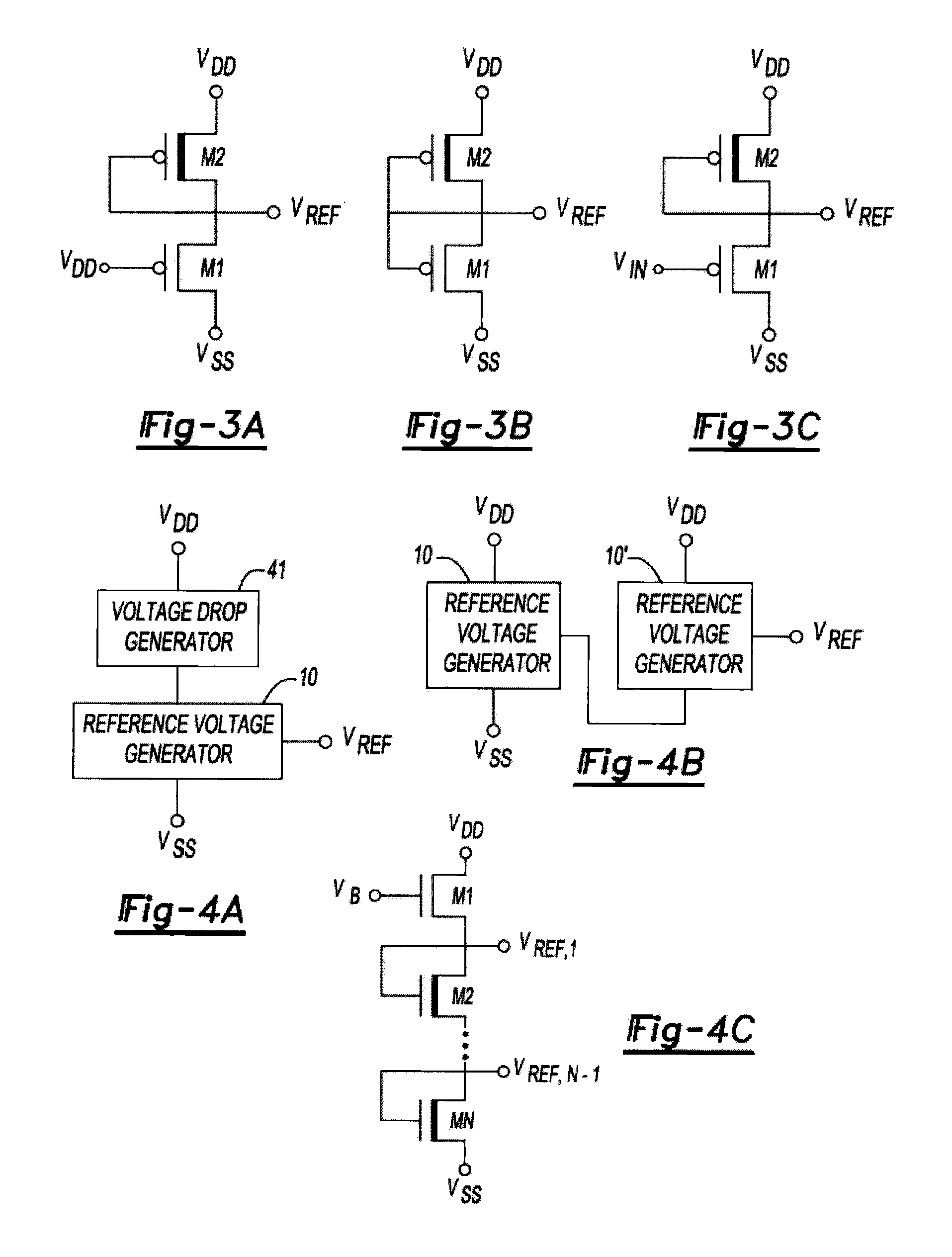
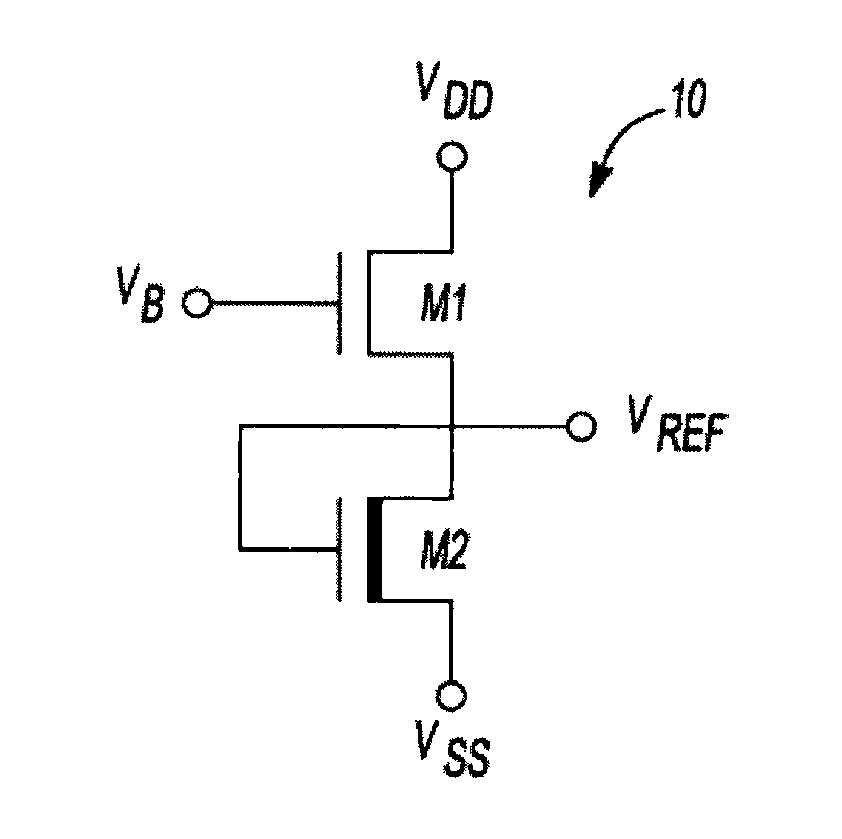
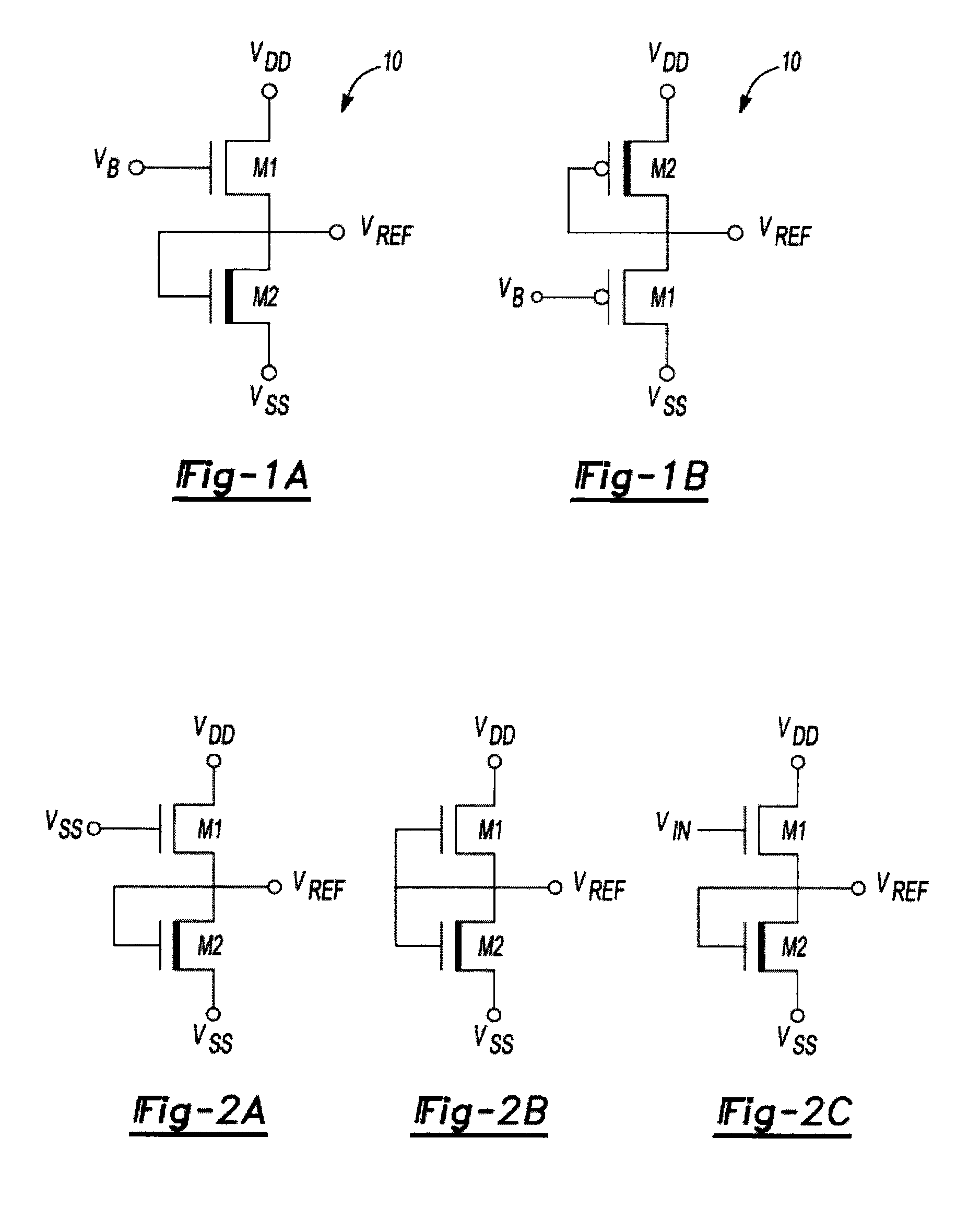
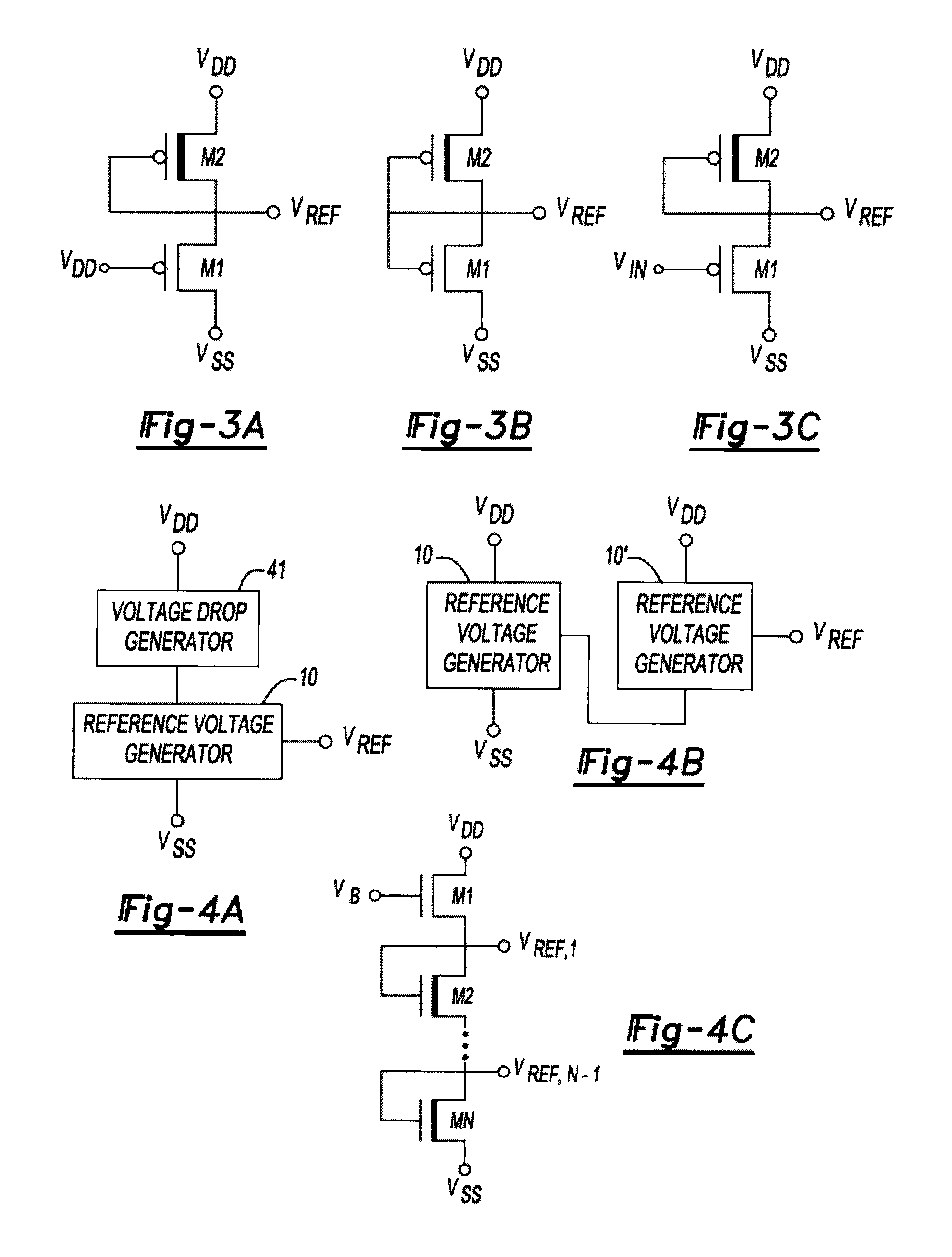
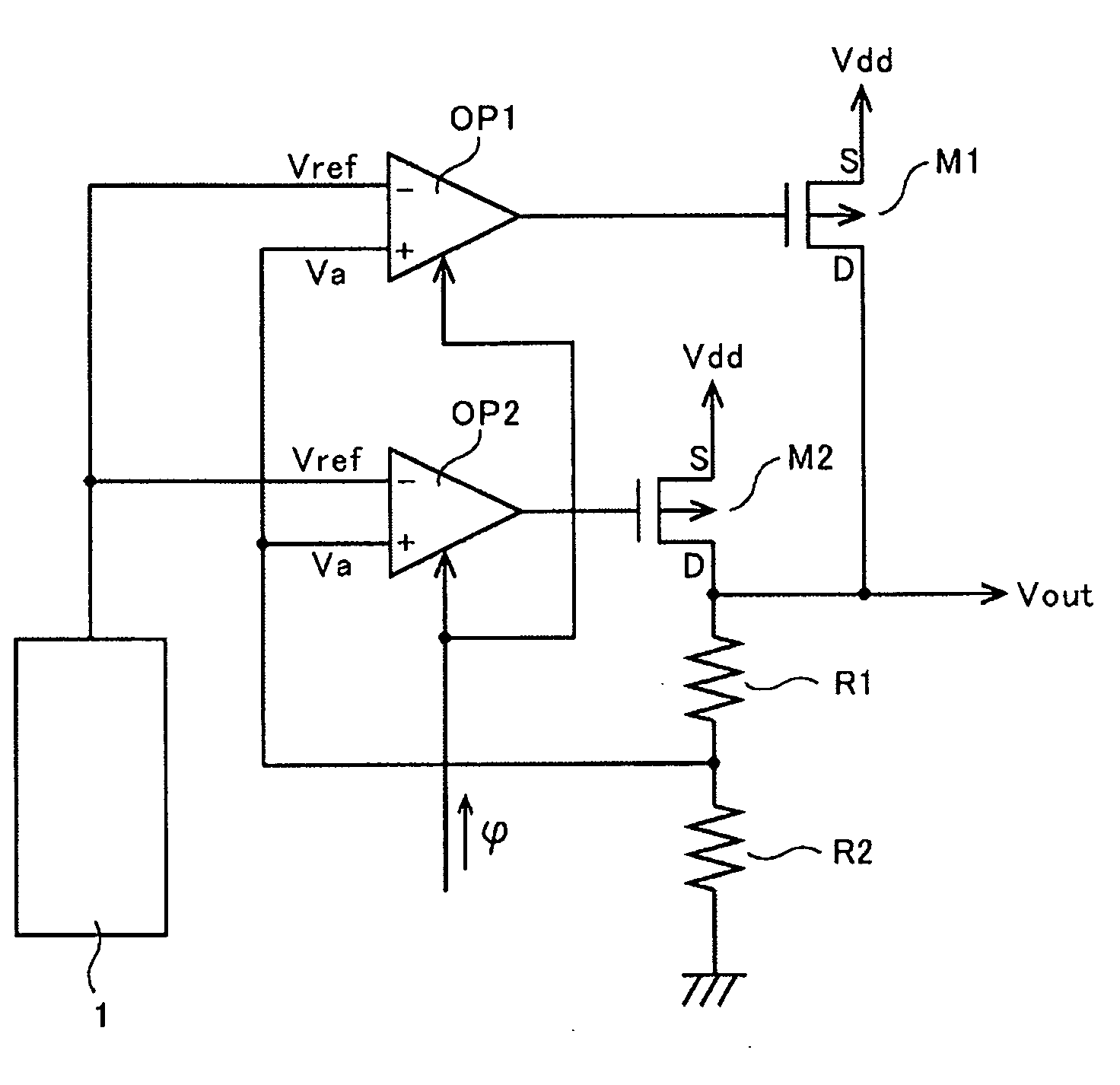
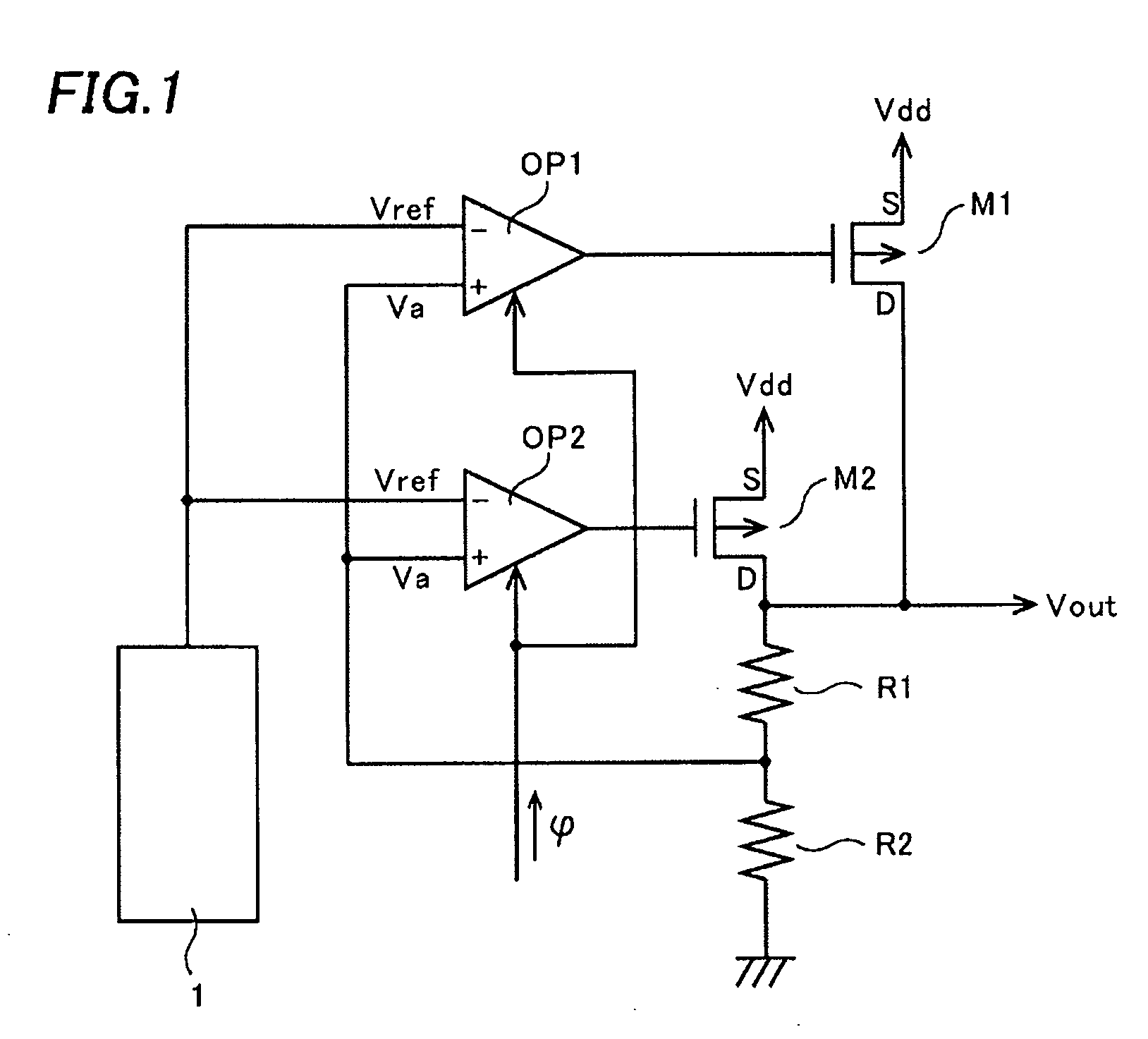
Reference voltage generator having a two transistor design
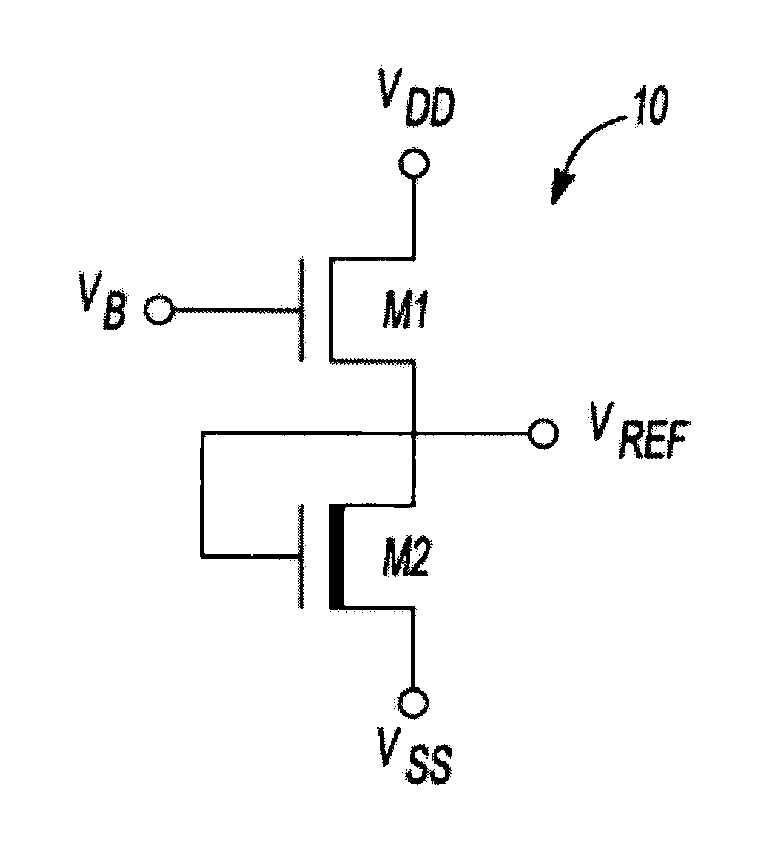
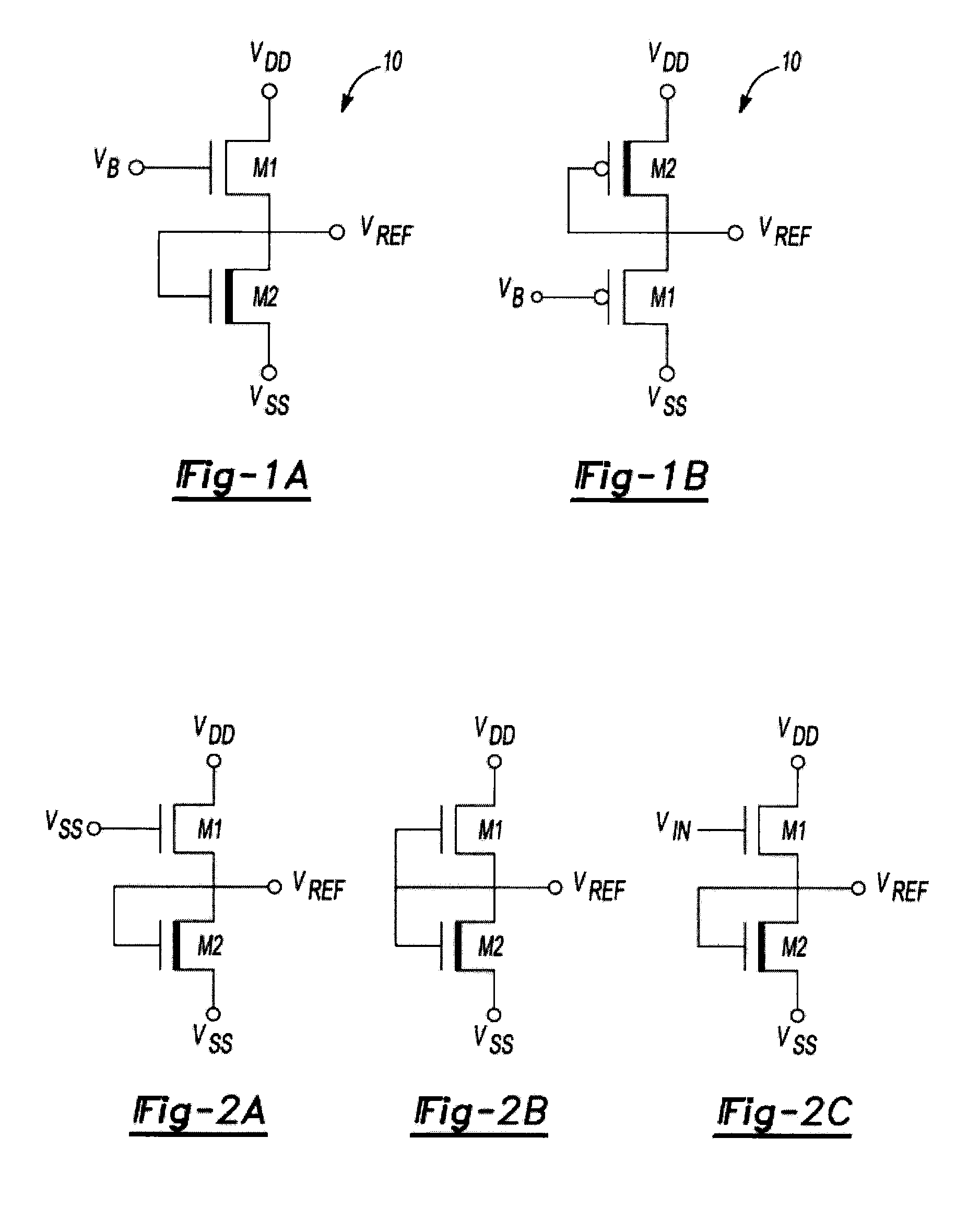
ActiveUS20100327842A1Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceElectric variable regulationVoltage generatorVoltage reference
An improved voltage reference generator is provided. The voltage reference generator comprises: a first transistor having a gate electrode biased to place the first transistor in a weak inversion mode; and a second transistor connected in series with said first transistor and having a gate electrode biased to place the second transistor in a weak inversion mode, where the threshold voltage of the first transistor is smaller than the threshold voltage of the second transistor and the gate electrode of the second transistor is electrically coupled to a drain electrode of the second transistor and the source electrode of the first transistor to form an output for a reference voltage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Ferroelectric transistor gate stack with resistance-modified conductive oxide
InactiveUS20050269613A1Reduce chargeImprove performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMemory retentionFilm resistance
The present invention discloses a novel ferroelectric transistor design using a resistive oxide film in place of the gate dielectric. By replacing the gate dielectric with a resistive oxide film, and by optimizing the value of the film resistance, the bottom gate of the ferroelectric layer is electrically connected to the silicon substrate, eliminating the trapped charge effect and resulting in the improvement of the memory retention characteristics. The resistive oxide film is preferably a doped conductive oxide in which a conductive oxide is doped with an impurity species. The doped conductive oxide is most preferred to be In2O3 with the dopant species being hafnium oxide, zirconium oxide, lanthanum oxide, or aluminum oxide.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for manufacturing transistor
ActiveUS9129992B2Precise alignmentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistBottom gate
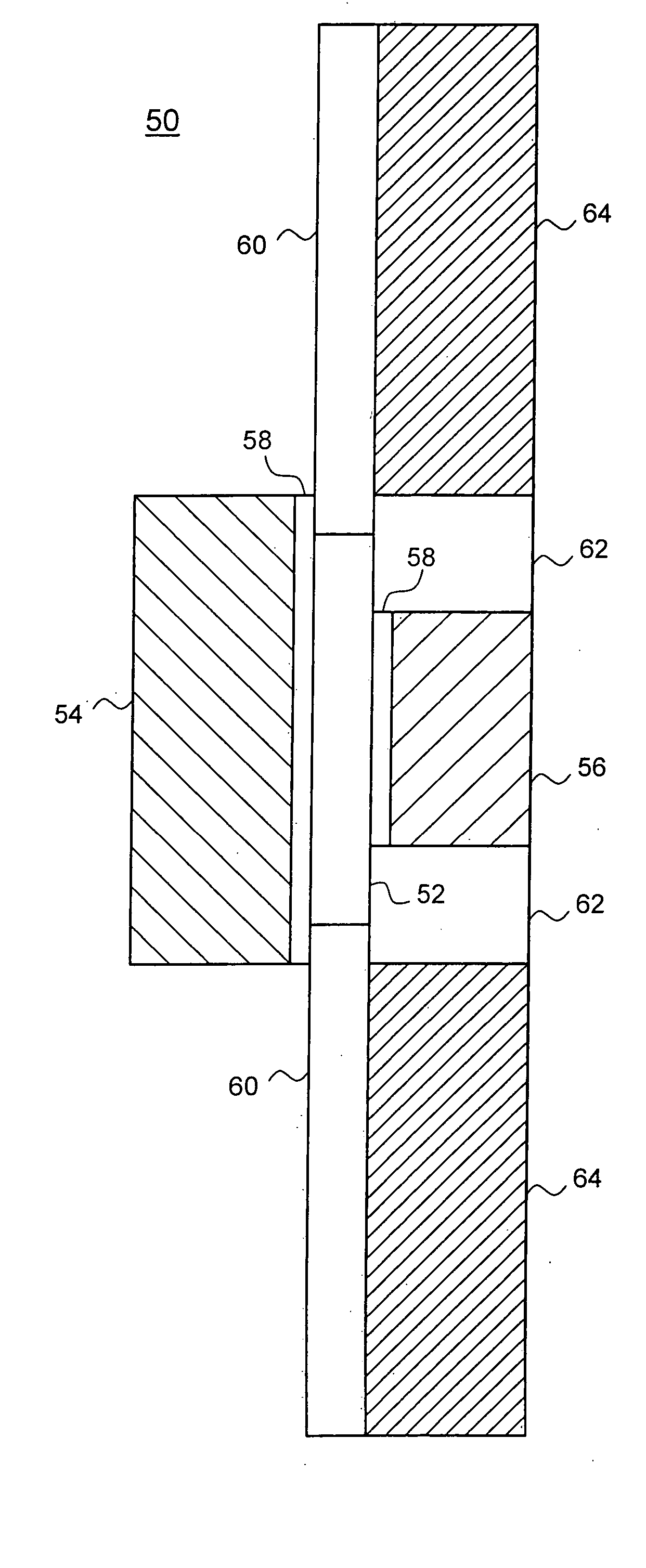
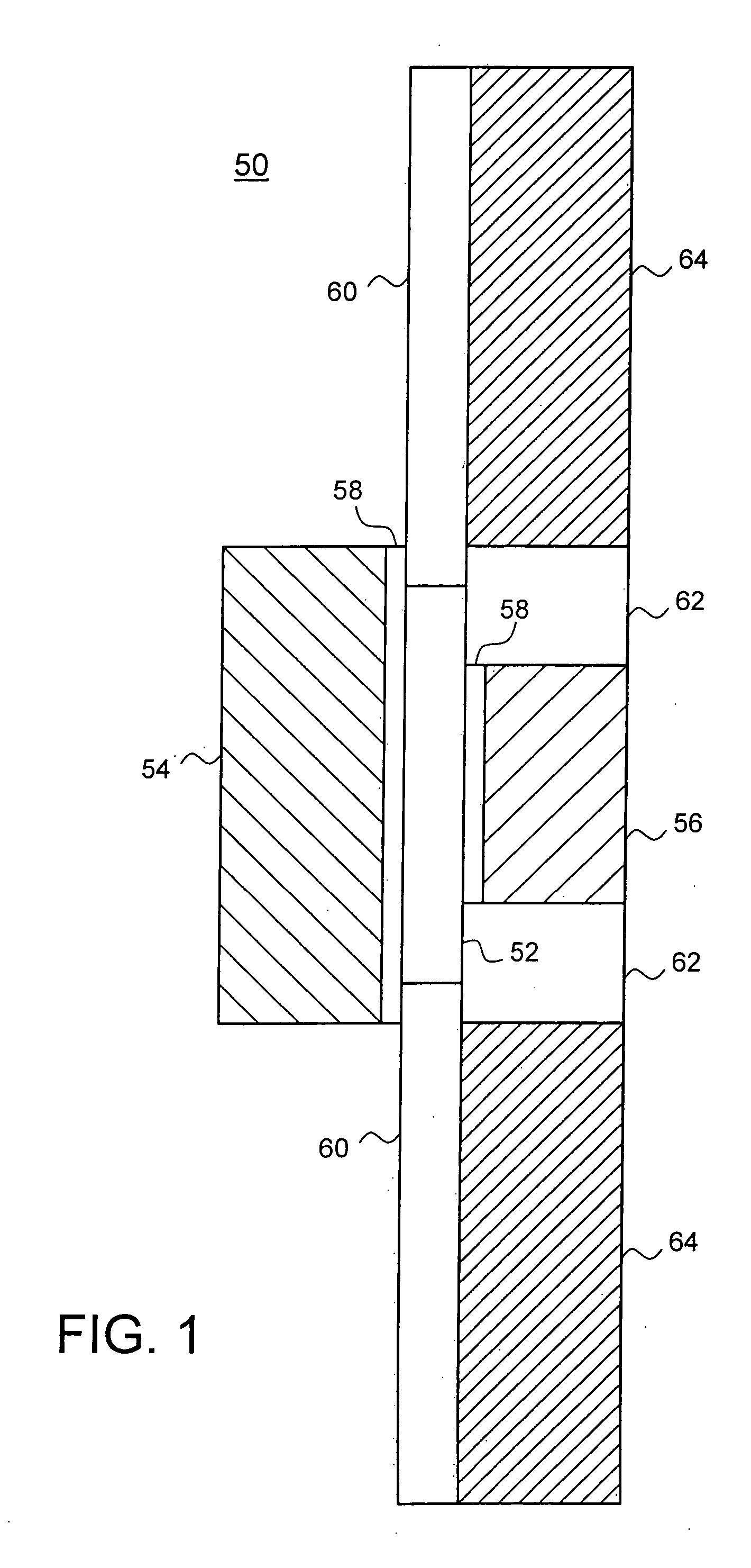
Designs and fabrication of dual-gate thin film transistors are provided. An active region and a top gate electrode of the transistor can be made of a transparent thin film material. A photoresist can be coated onto a surface of the transparent conductive thin film for forming the top gate electrode. Light is from the bottom of the substrate during exposure. After the development, a photoresist pattern aligned with the bottom gate electrode is formed on the surface of the conductive thin film. The top gate electrode aligned with the bottom gate electrode is formed by etching the conductive thin film. The bottom gate electrode can be used as a mask, which may save the cost for manufacturing the transistor and improve the accuracy of alignment between the top gate electrode and the bottom gate electrode and the performance of the dual-gate thin film transistor.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Polysilicon doped transistor using silicon-on-insulator and double silicon-on-insulator
InactiveUS6645795B2High and improved performanceExcellent characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsConcentration gradient
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Semiconductor storage device
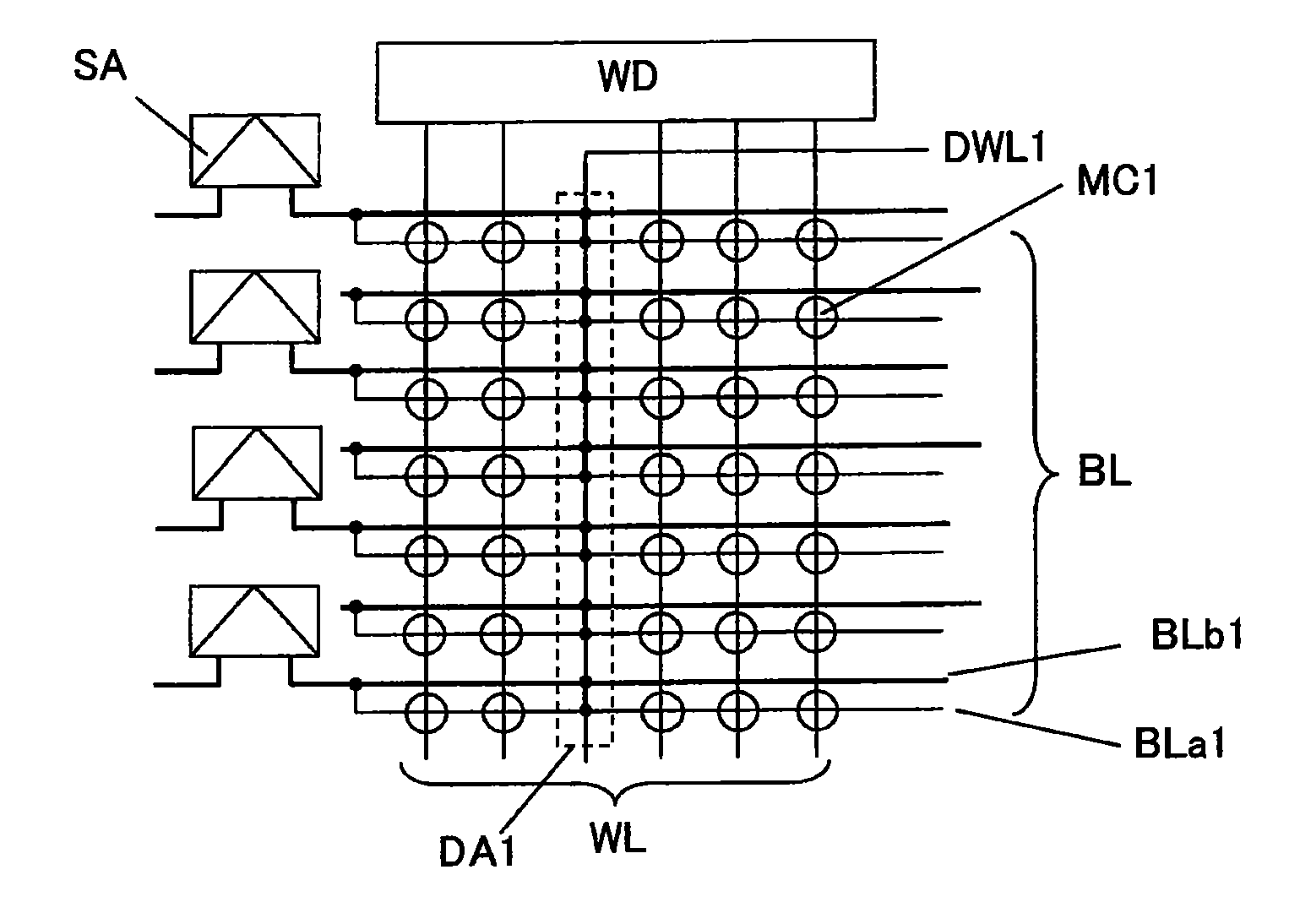
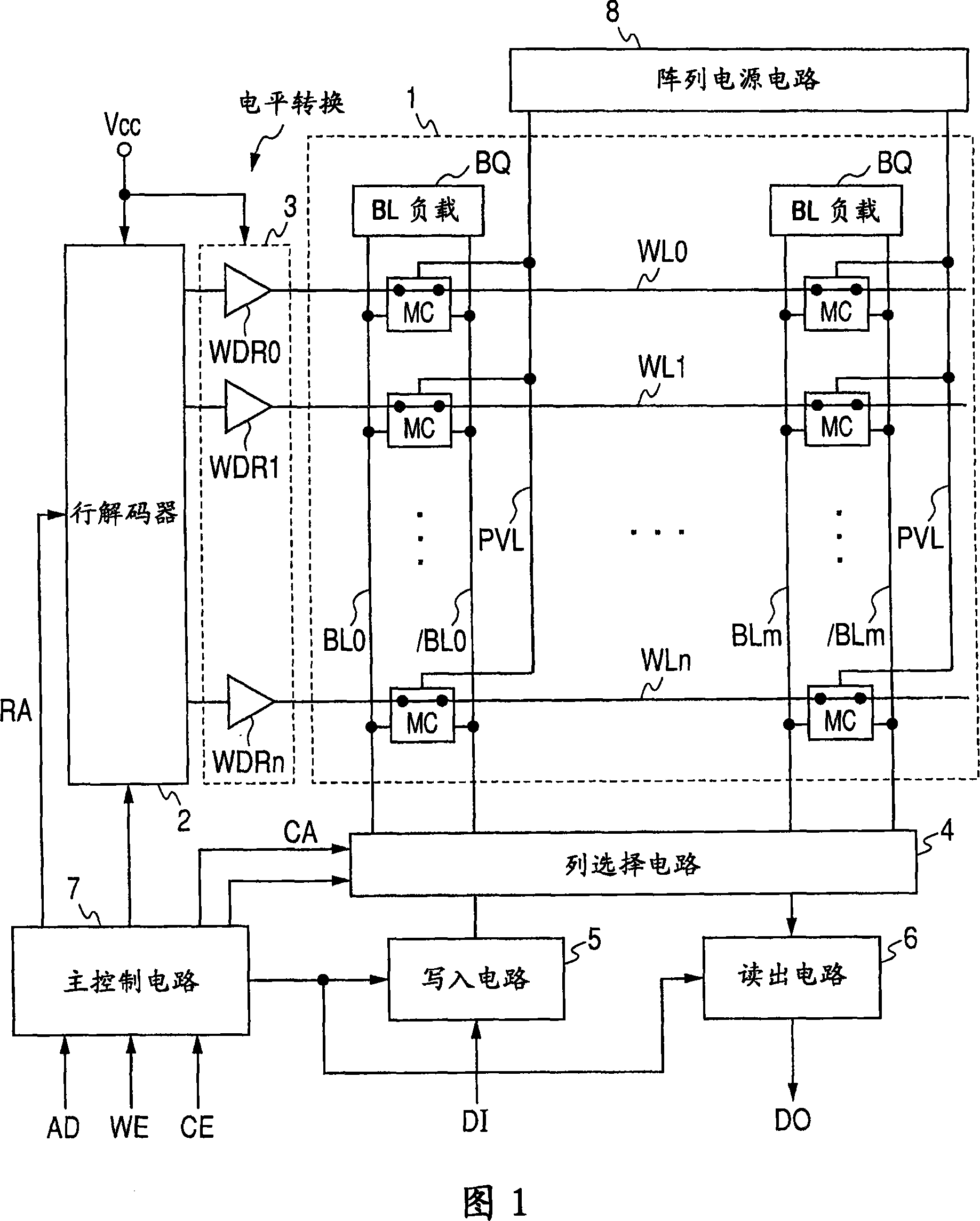
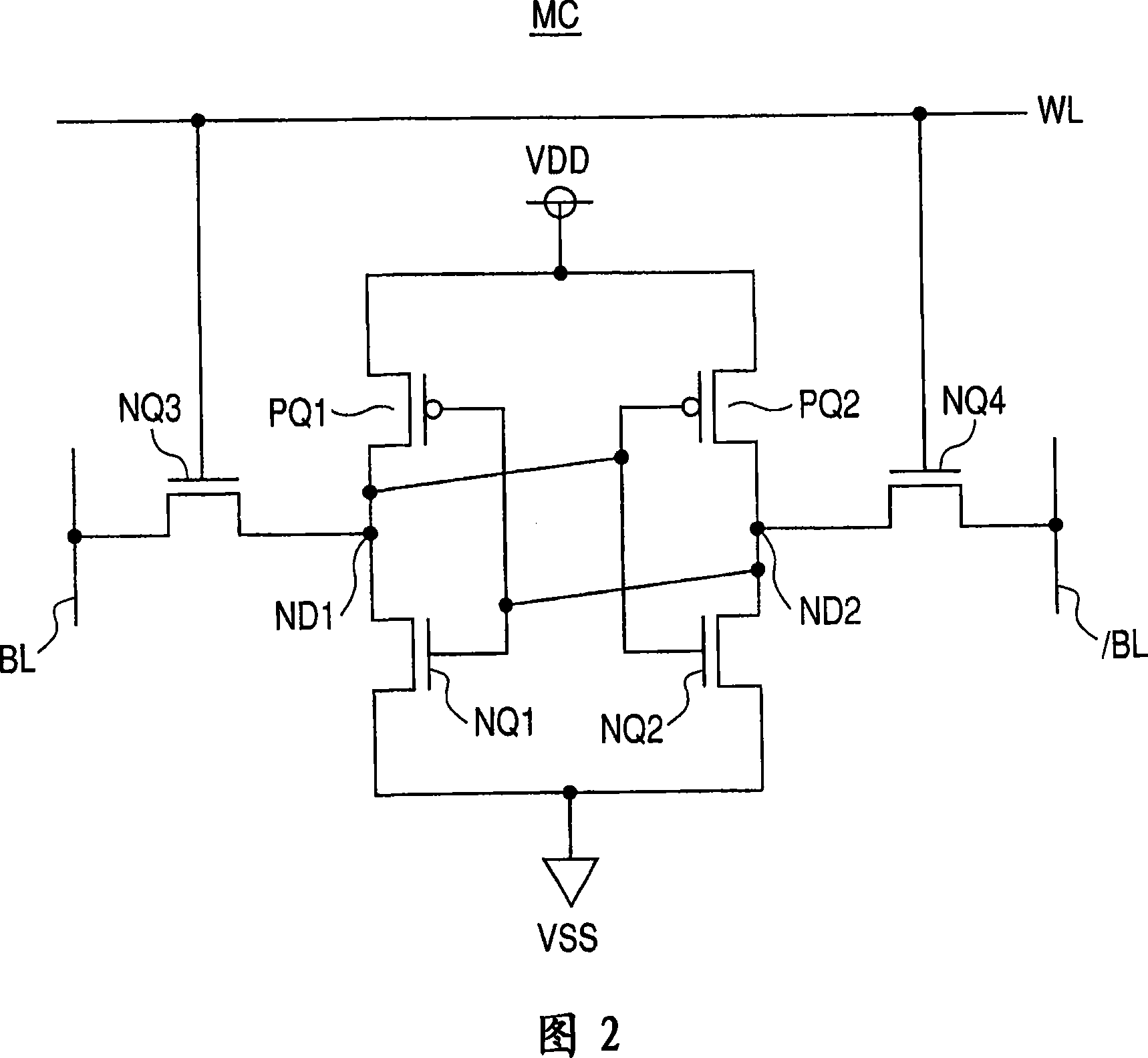
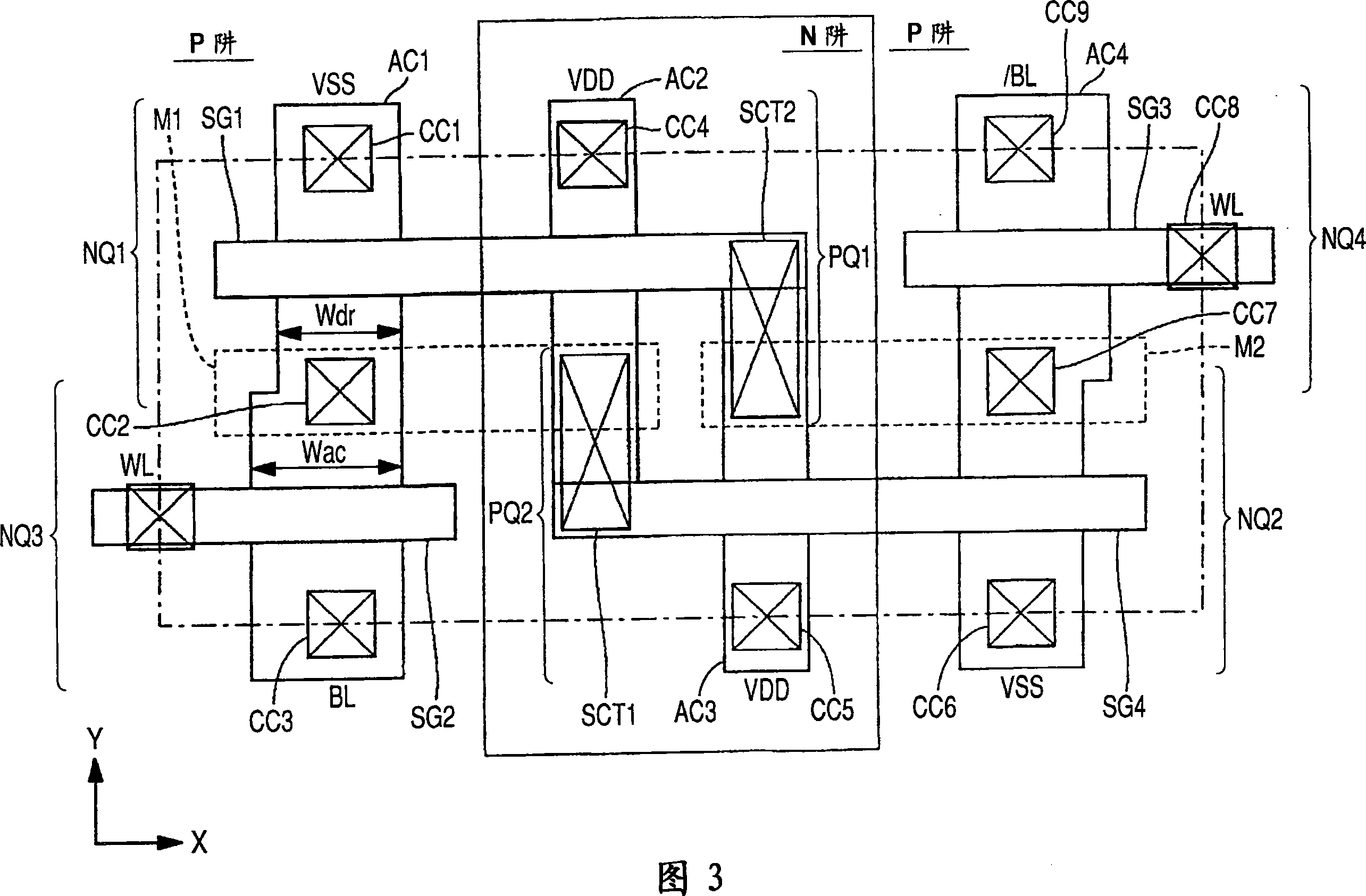
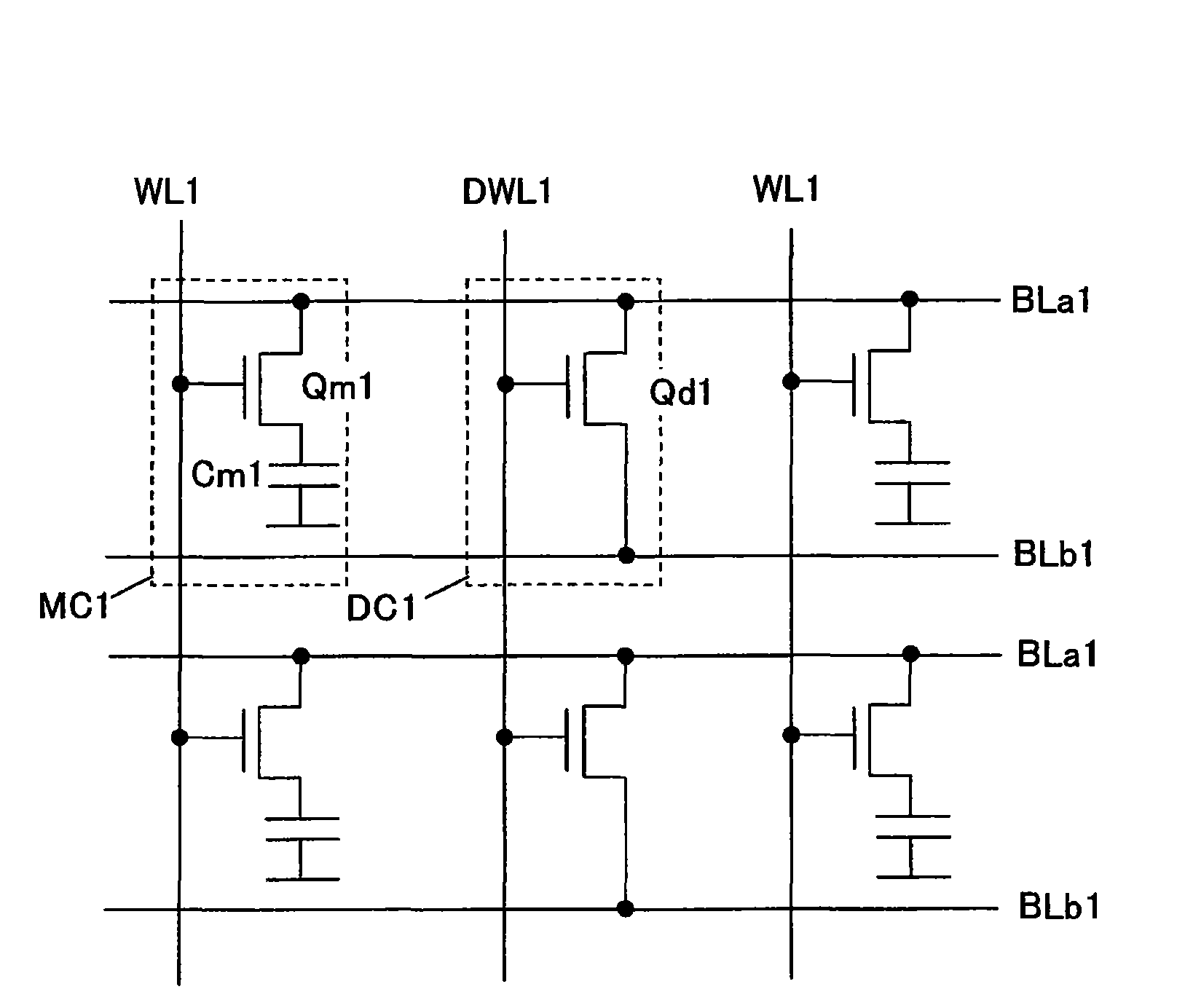
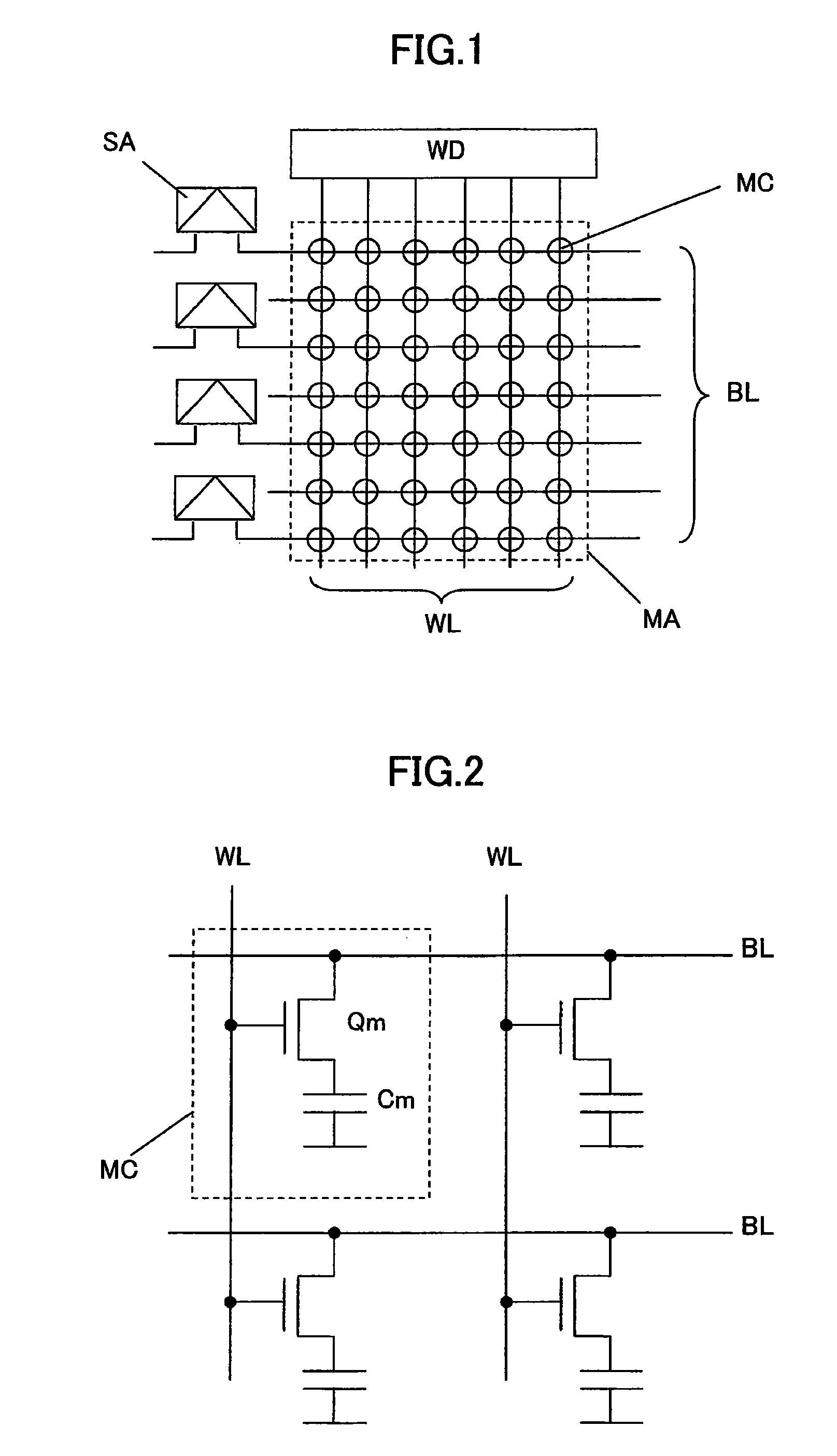
In a 4F2 memory cell designed using an SGT as a vertical transistor, a bit line has a high resistance because it is comprised of a diffusion layer underneath a pillar-shaped silicon layer, which causes a problem of slowdown in memory operation speed. The present invention provides a semiconductor storage device comprising an SGT-based 4F2 memory cell, wherein a bit line-backing cell having the same structure as that of a memory cell is inserted into a memory cell array to allow a first bit line composed of a diffusion layer to be backed with a low-resistance second bit line through the bit line backing cell, so as to provide a substantially low-resistance bit line, while suppressing an increase in area of the memory cell array.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Random Doping Fluctuation Resistant FinFET
InactiveUS20140103437A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
An improved fin field-effect transistor (FinFET) is built on a compound fin, which has a doped core and lightly doped epitaxial channel region between that core and the gate dielectric. The improved structure reduces FinFET random doping fluctuations when doping is used to control threshold voltage. Further, the transistor design affords better source and drain conductance when compared to prior art FinFETs. Three representative embodiments of the key structure are described in detail.
Owner:SEMI SOLUTIONS +1
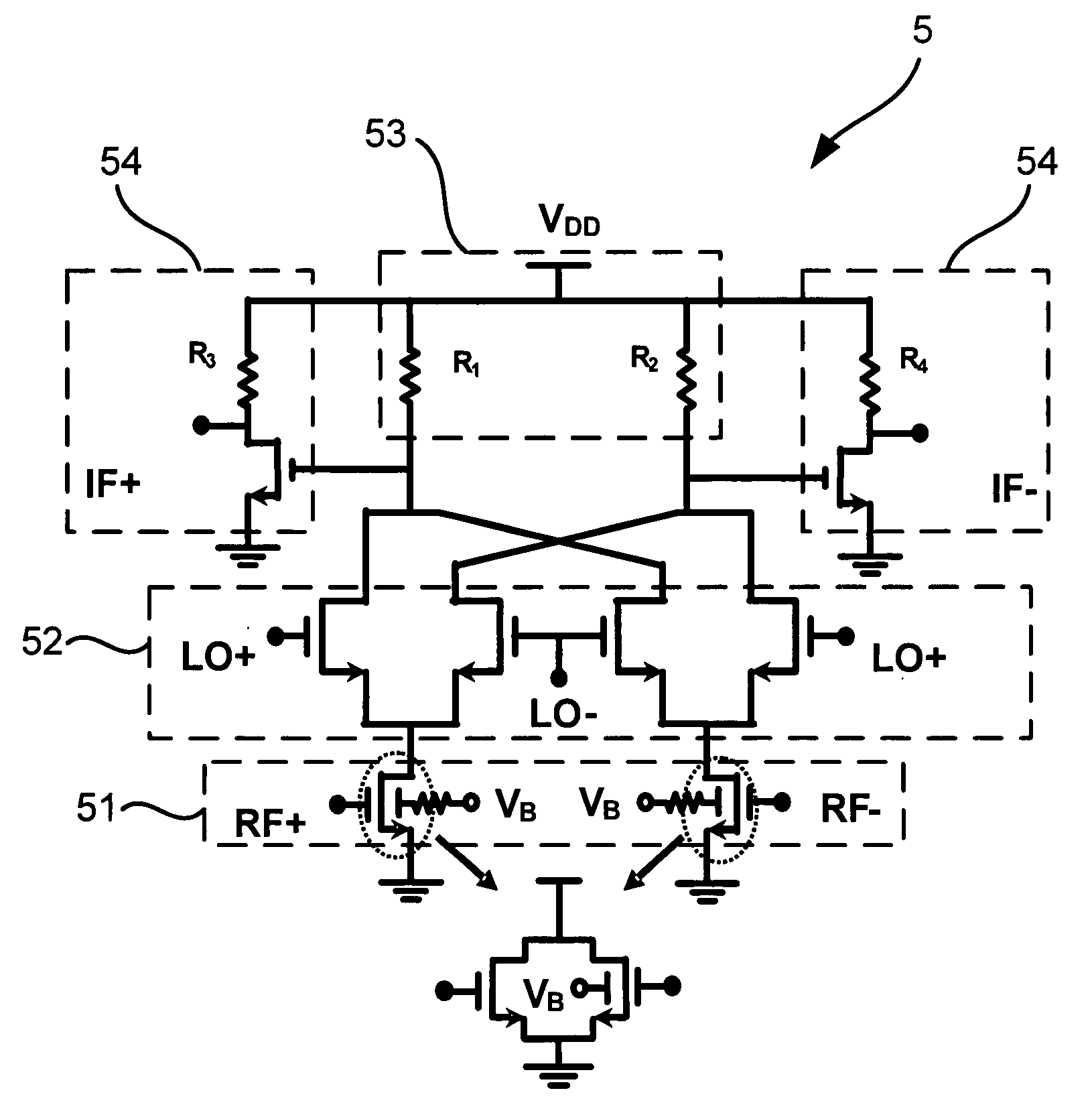
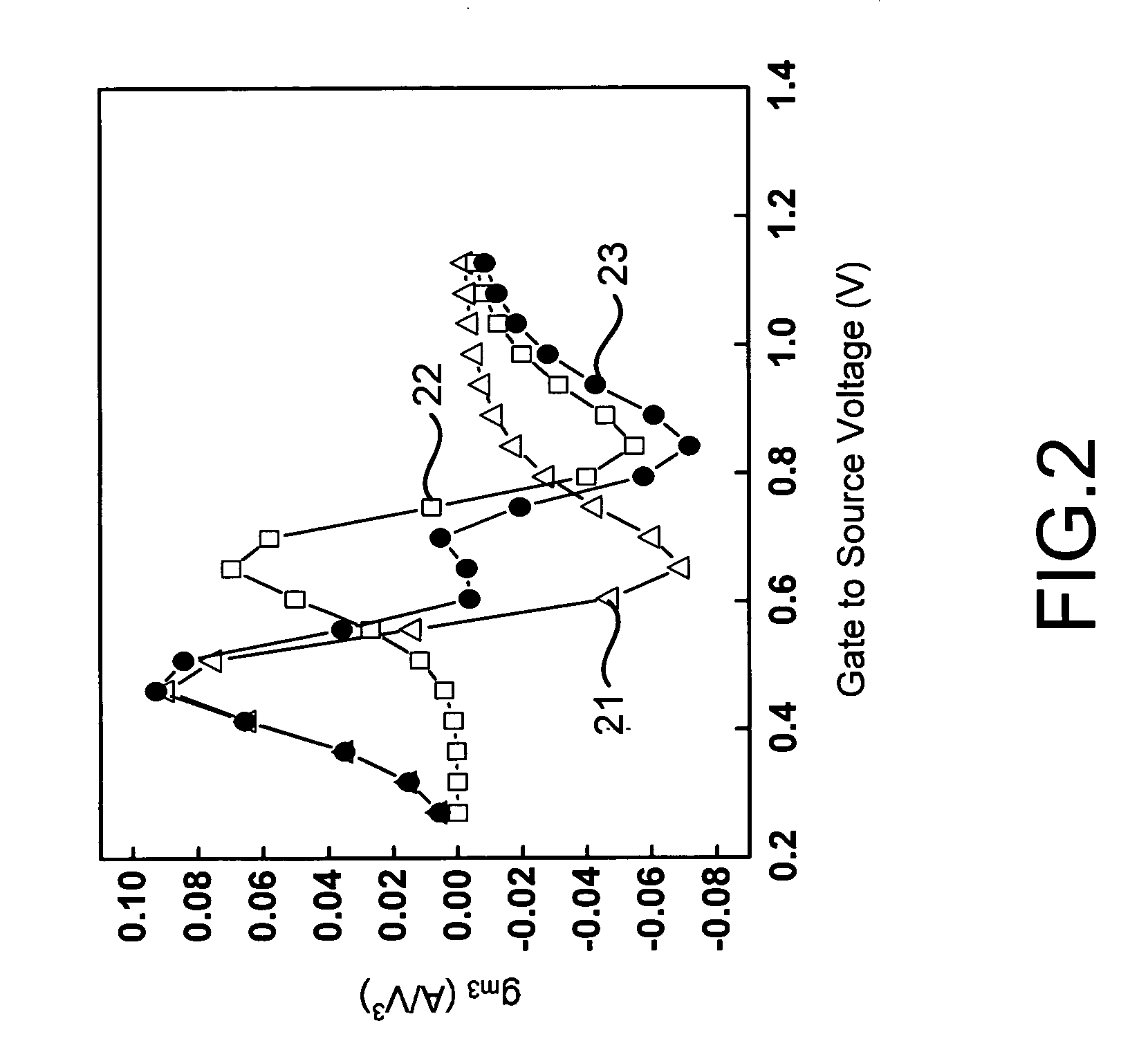
Method of third-order transconductance cancellation and linear mixer thereof
InactiveUS20090174460A1Low costImprove linearityModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesCMOSFrequency mixer
A third-order transconductance (gm3) cancellation is utilized to obtain a highly linear mixer. Transistors obtain good linearity with complementary gm3 values. The transistor thus obtained can be operated in a wide bandwidth and is applicable to various frequency specifications of systems, like Bluetooth, wireless LAN, Ultra-Wide Band (UWB), etc. Then the transistors are applied to design a transconductance-stage input of the mixer. Hence, the present invention can be widely applied to receiver modules and be realized with a low-cost CMOS transistor.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Reference voltage generator having a two transistor design
An improved voltage reference generator is provided. The voltage reference generator comprises: a first transistor having a gate electrode biased to place the first transistor in a weak inversion mode; and a second transistor connected in series with said first transistor and having a gate electrode biased to place the second transistor in a weak inversion mode, where the threshold voltage of the first transistor is smaller than the threshold voltage of the second transistor and the gate electrode of the second transistor is electrically coupled to a drain electrode of the second transistor and the source electrode of the first transistor to form an output for a reference voltage.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
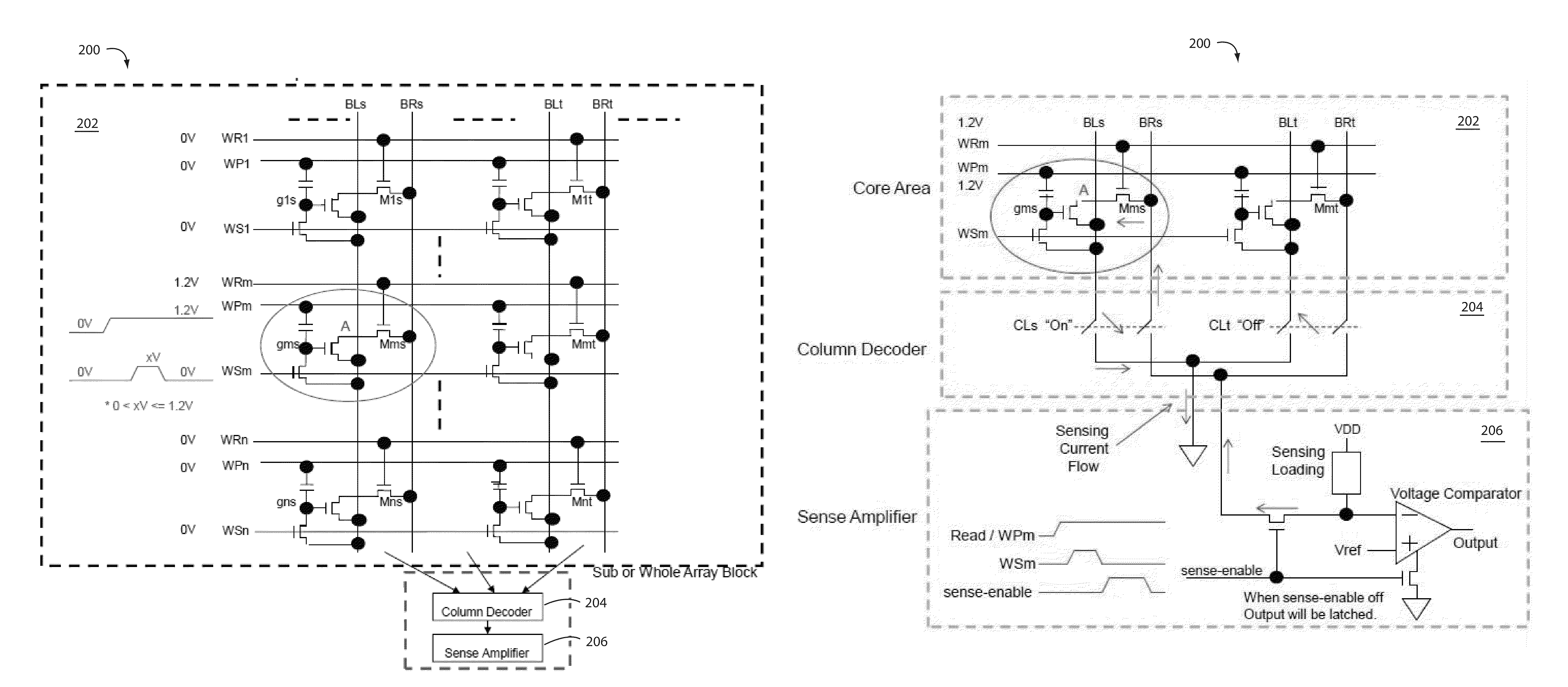
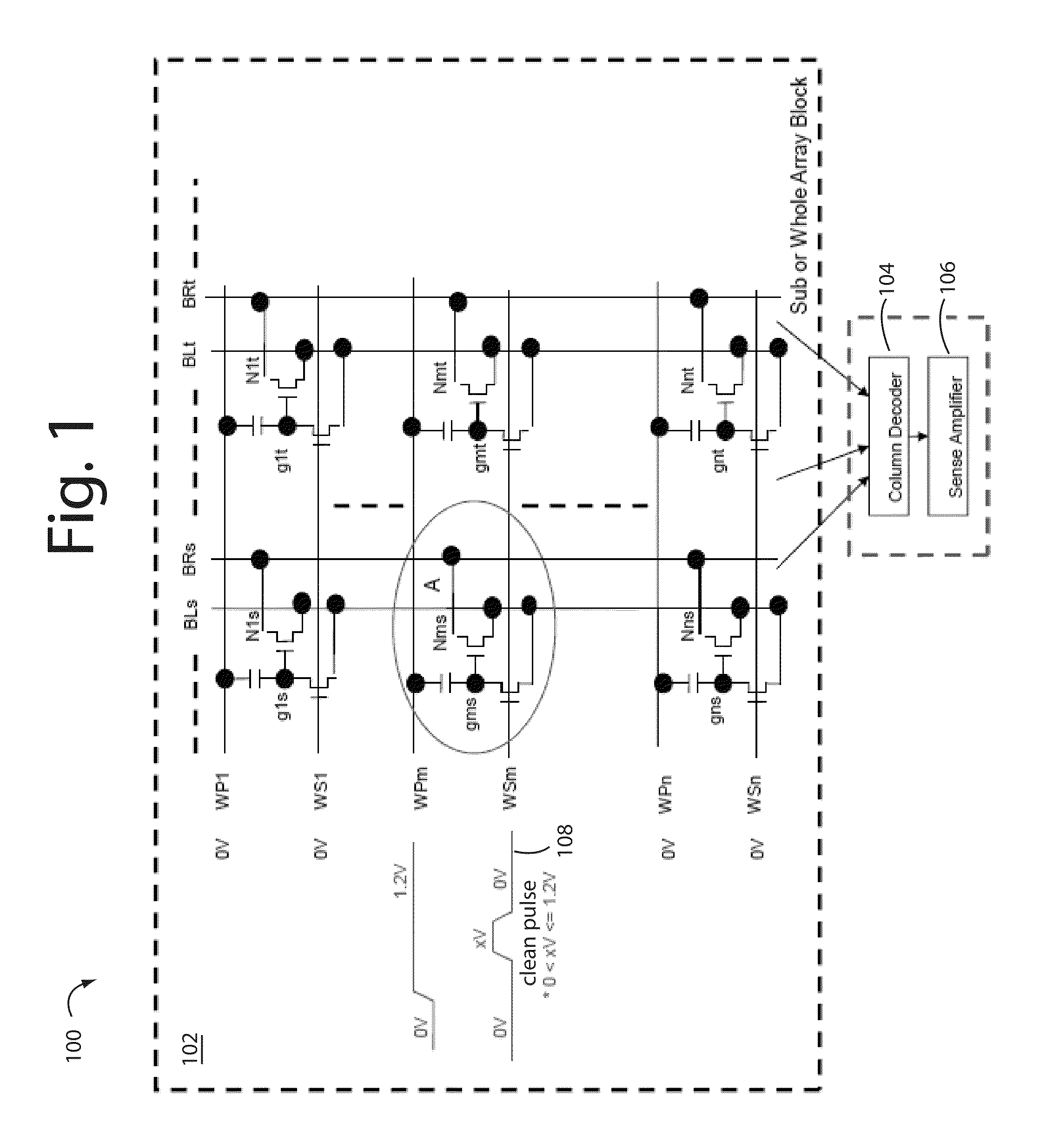
Spurious induced charge cleanup for one time programmable (OTP) memory
ActiveUS8780660B2Reduce layout sizeReduced Power RequirementsRead-only memoriesDigital storageShunt DeviceBit line
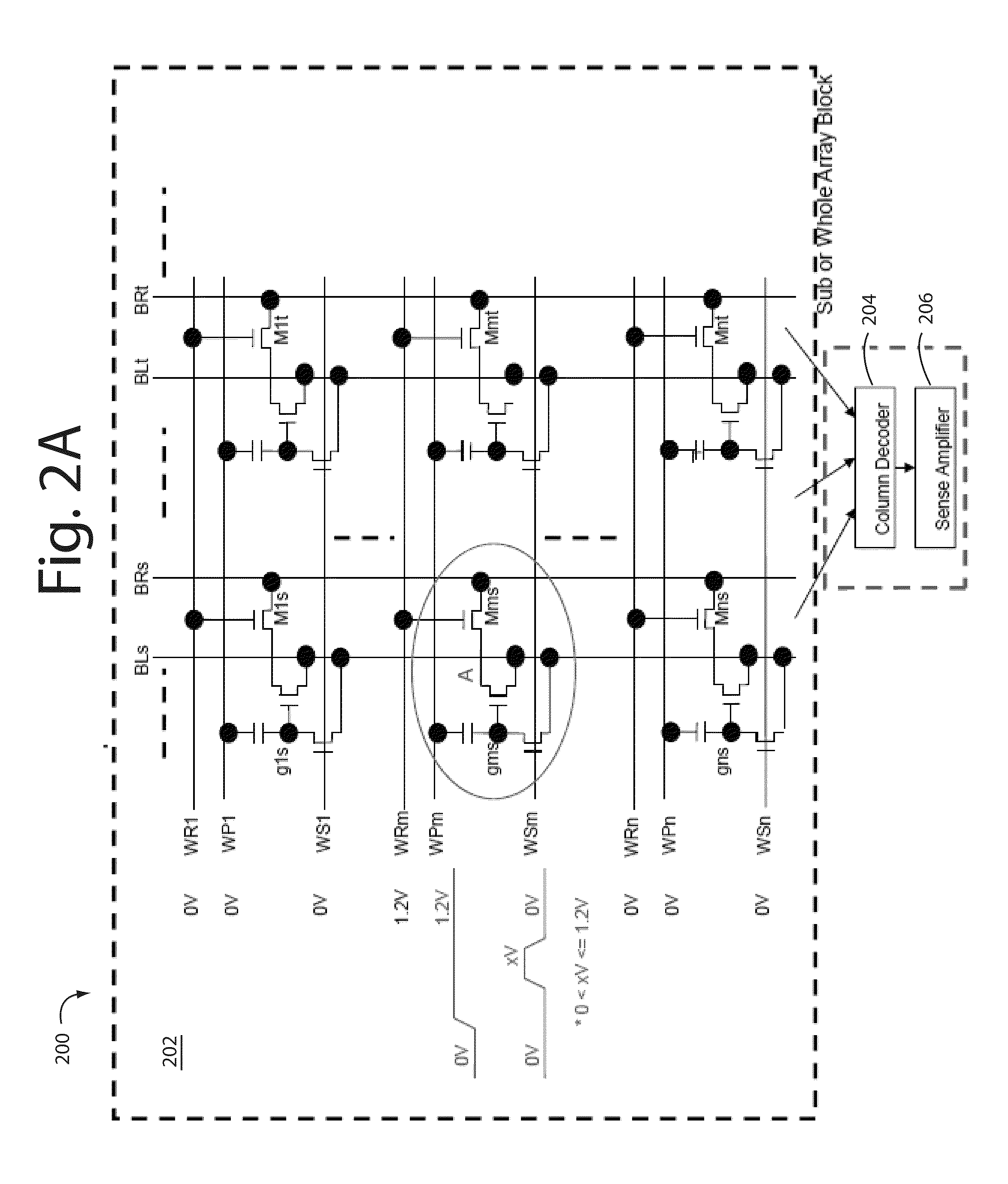
A high density, low voltage, and low-power one time programmable (OTP) memory is based on core cells with a one transistor design. A CLEAN pulse is directed to a single shunt device at the output of the column decoder so spurious charges that may have been stored in the floating nodes can be cleaned up. Such arrangement also allows for the simultaneous initialization of bit lines, data lines, and sensing lines to zero. Core area layout size is substantially reduced, and operational power requirements are exceeding low making these particularly suitable in HF and UHF RFID applications.
Owner:CHENGDU KILOWAY ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveCN101127356AIncreased characteristic varianceReduce the amount of impuritiesTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringChannel width
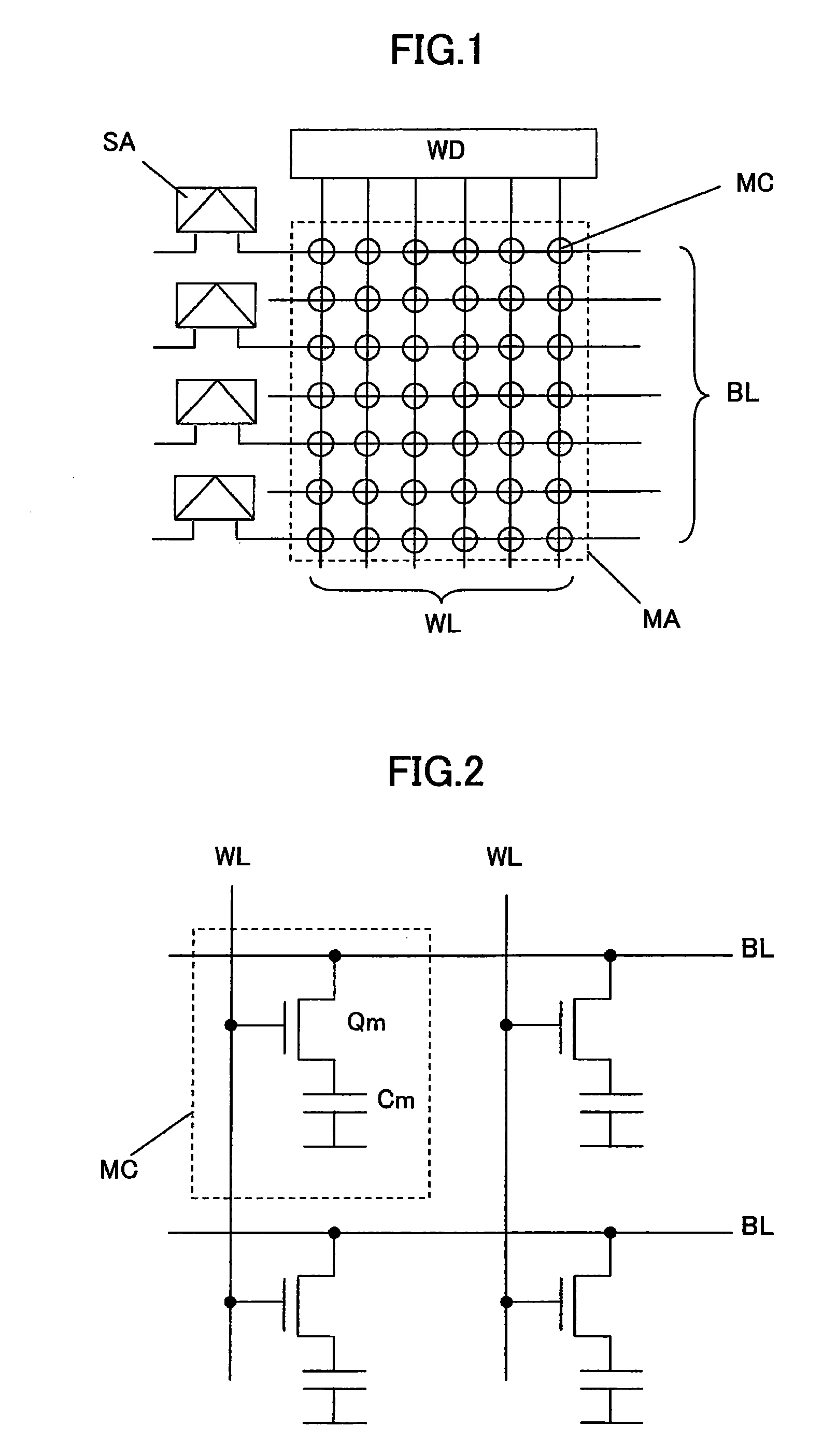
The semiconductor memory device which can suppress that the characteristics variation of a transistor increases in connection with microfabrication is offered. In the memory cell of the present invention, channel width of an access transistor is made larger than the channel width of a driver transistor about the relation of the channel width of an access transistor and a driver transistor. That is, since the access transistor can make channel area increase from the driver transistor designed with the minimum designed size, it becomes possible to suppress the increase in the characteristics variation of an access transistor.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
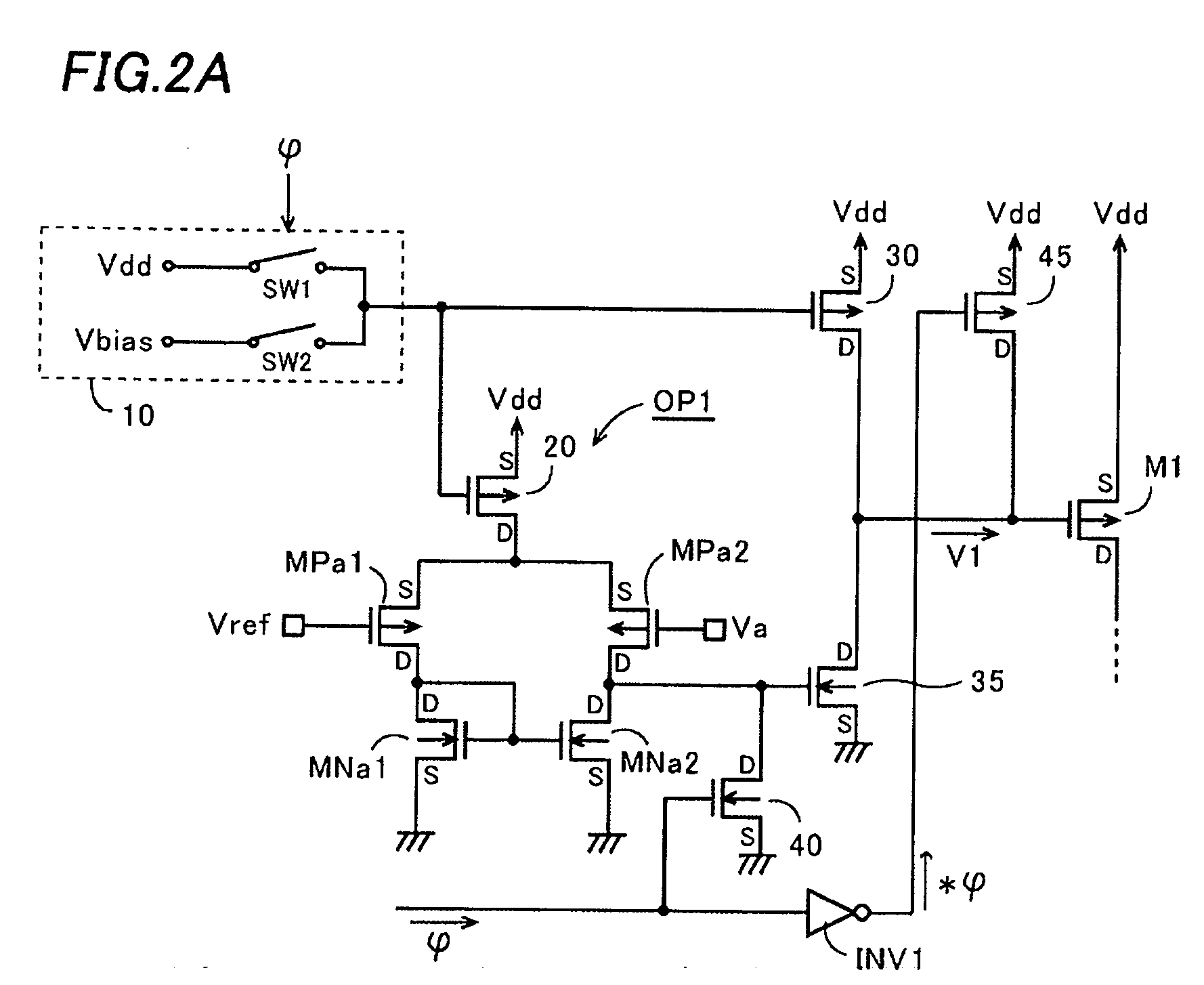
Regulator circuit
A regulator circuit is offered to resolve a problem that an unnecessary operating current flows in a semiconductor integrated circuit in a low power consumption state. Channel width to channel length ratios of an output transistor in a first operational amplifier and a first control MOS transistor are designed large in order to obtain an operating current in a normal operation state, while channel width to channel length ratios of an output transistor in a second operational amplifier and a second control MOS transistor are designed small to obtain an operating current in the low power consumption state. There is provided a switching circuit that selectively put in operation one of the operational amplifiers according to the state of the integrated circuit. The first operational amplifier and the first control MOS transistor having higher current driving capabilities operate in the normal operation state. The second operational amplifier and the second control MOS transistor having lower current driving capabilities operate in the low power consumption state.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
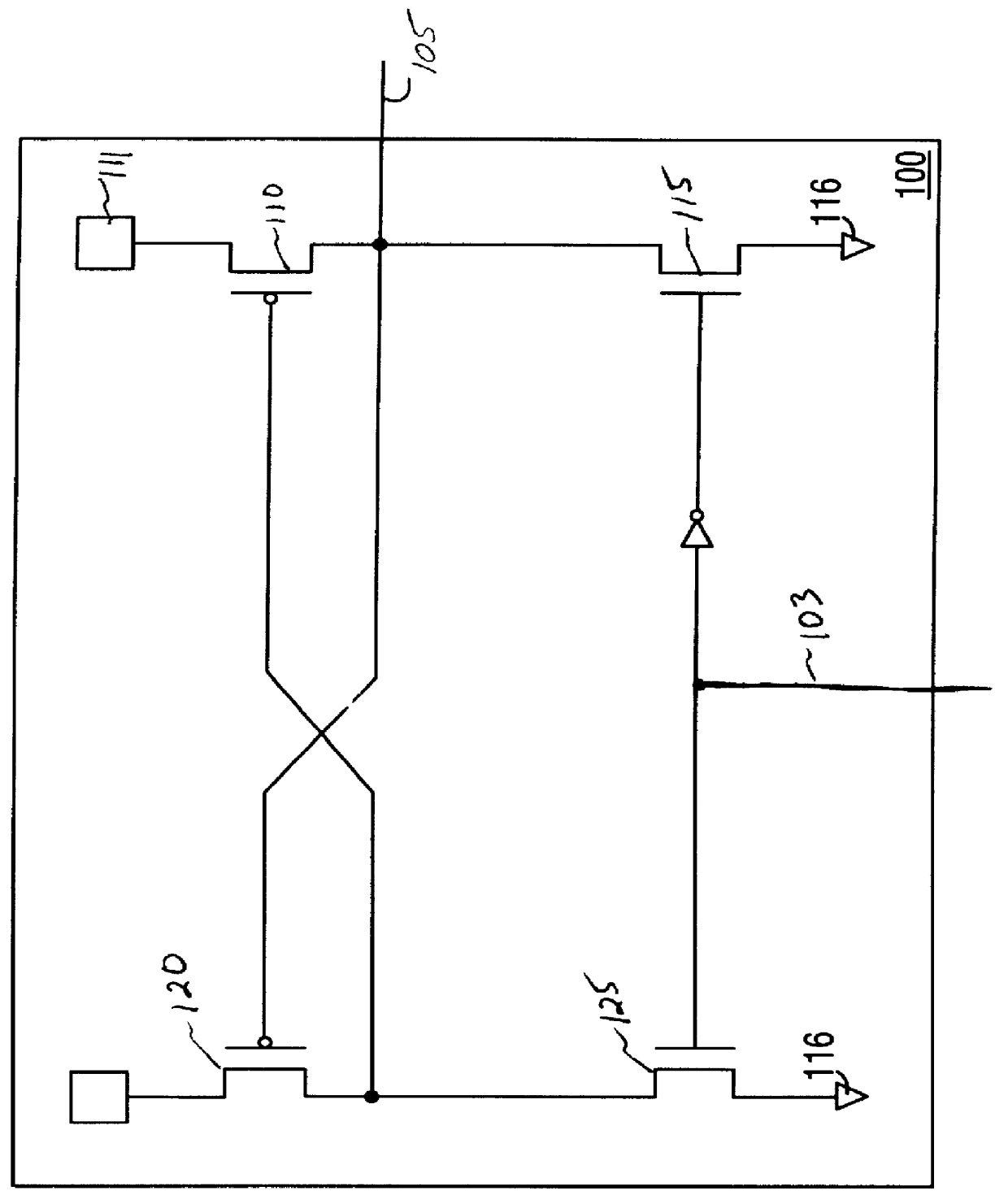
Output buffer for a mixed voltage environment
InactiveUS6054875ALogic circuits characterised by logic functionElectronic switchingVoltage sourceData buffer
An output buffer to serve as an interface between a main logic circuit and a peripheral device is described. The output buffer includes a first transistor adapted to be coupled to a first voltage supply and an output terminal. The first transistor is designed to charge the output terminal to a first state. A pull-down network to charge the output terminal to a second state is also included. The pull-down network is adapted to be coupled between the output terminal and a second voltage supply and is designed for alternate operation with the first transistor. The output buffer also includes a logic circuit to enable the first transistor and the pull-down network. The logic circuit is coupled to an enable terminal of the first transistor, the pull-down network, the first voltage supply, and the second voltage supply.
Owner:INTEL CORP
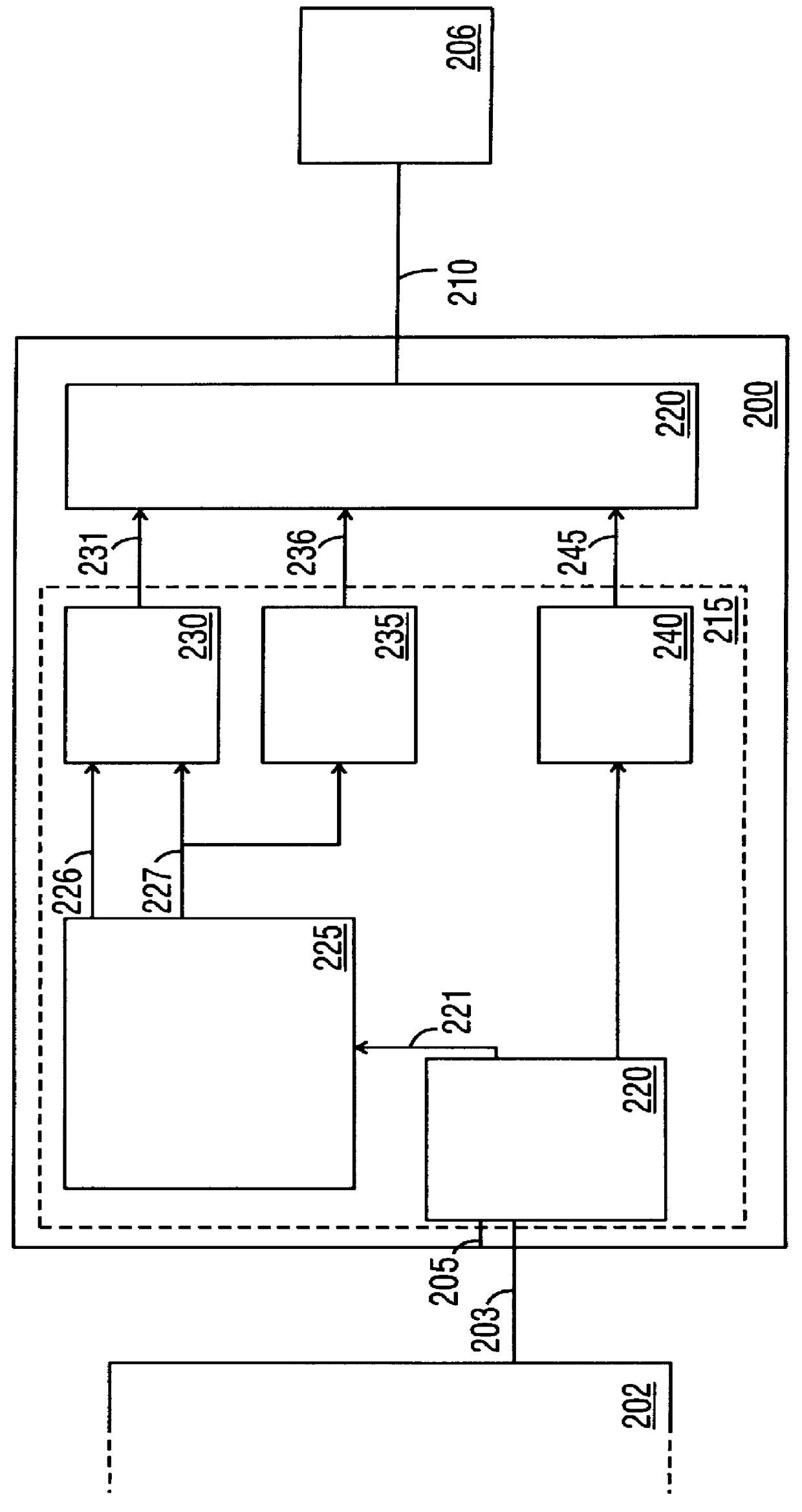
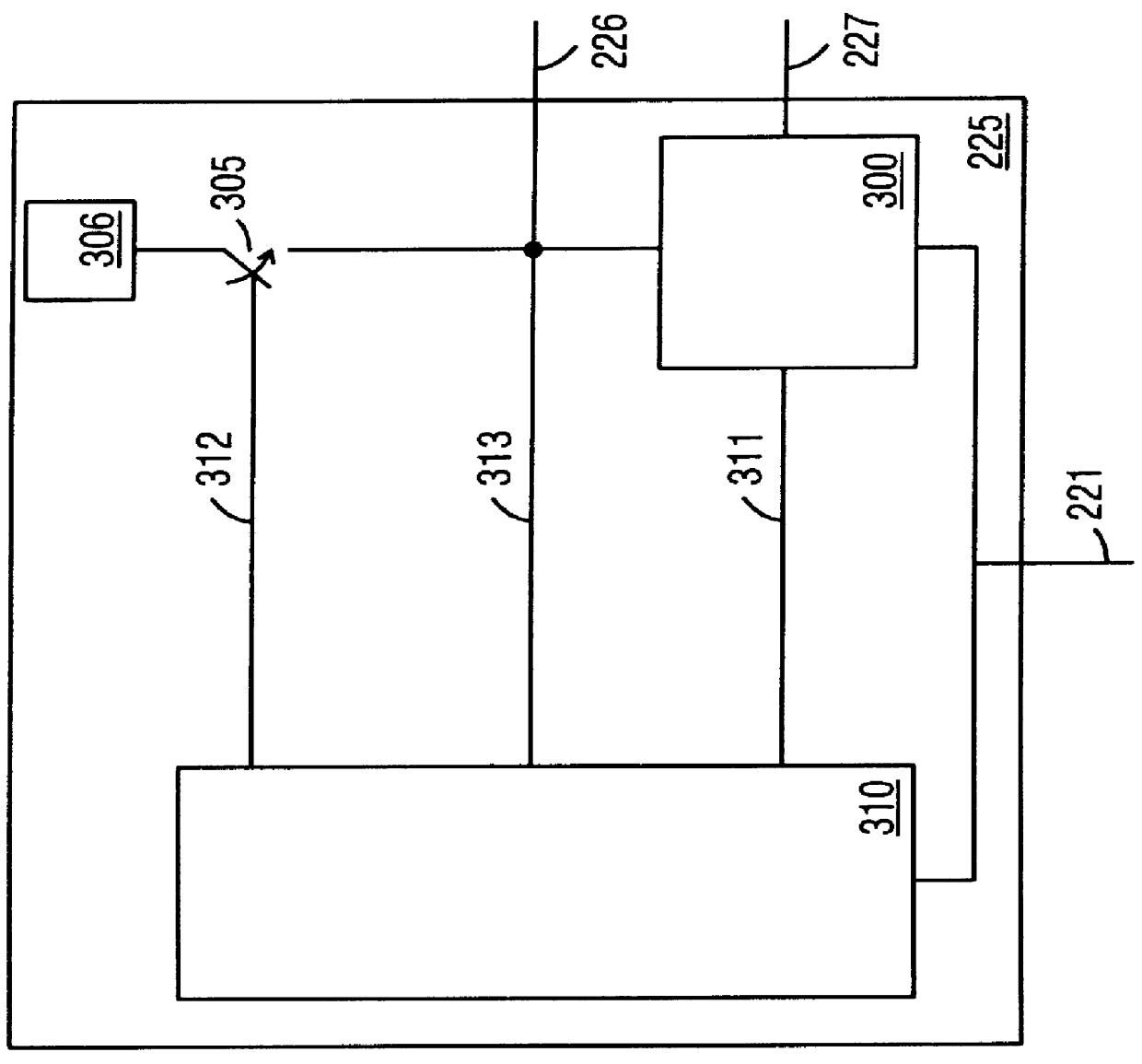
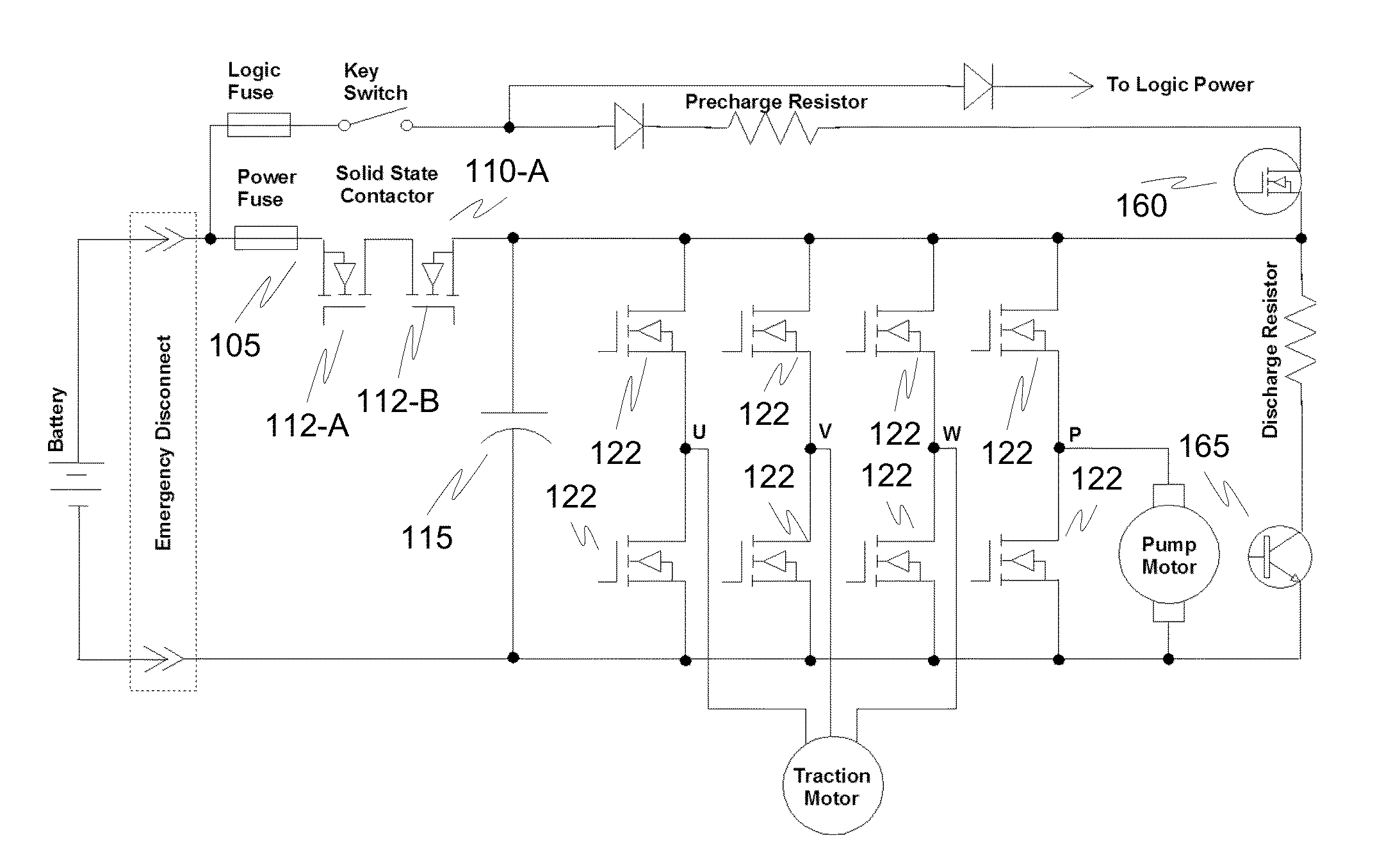
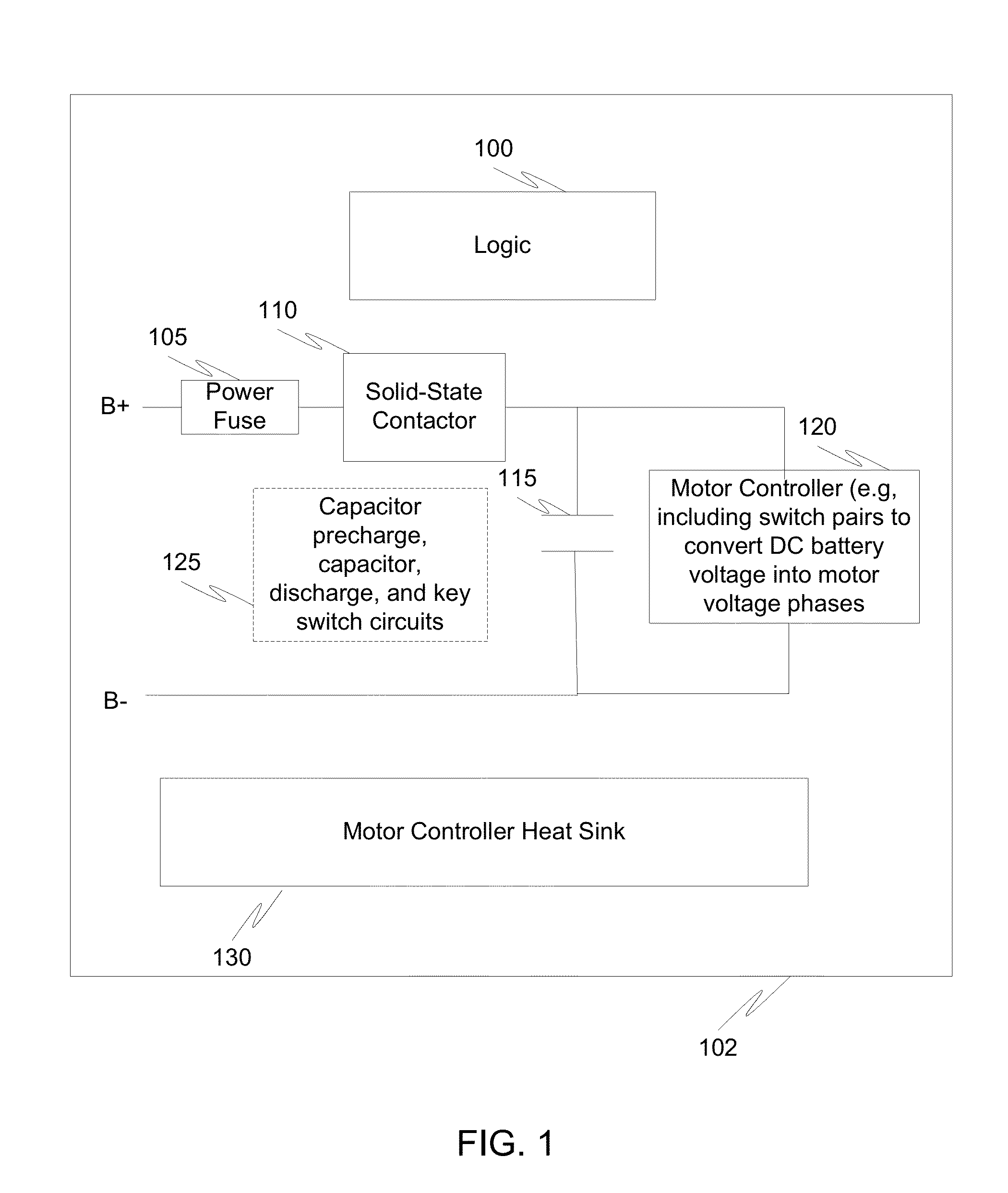
Motor controller with integrated safety function to eliminate requirement for external contactor
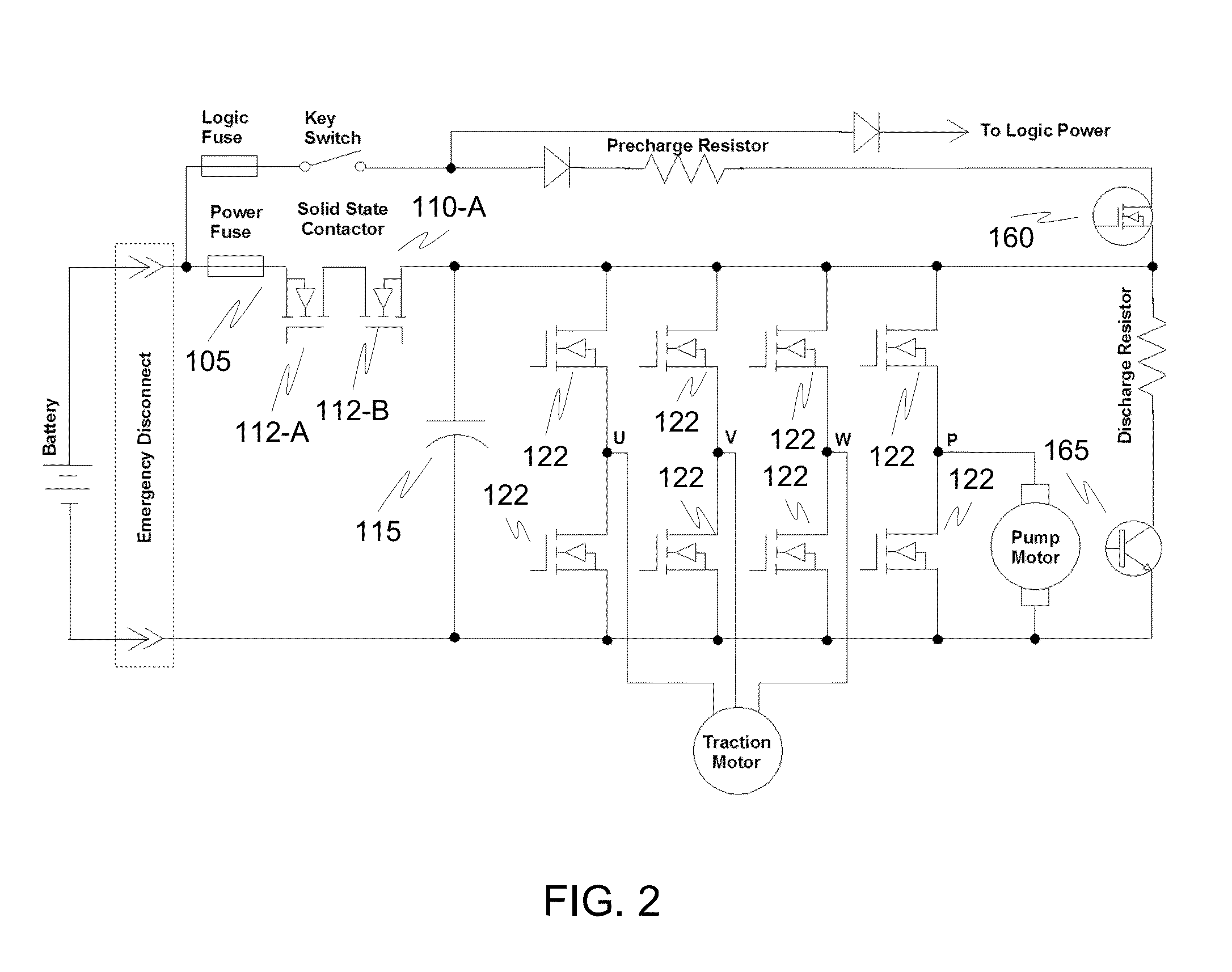
ActiveUS20130257149A1Reduce the number of partsImprove heat sinkHybrid vehiclesDC motor speed/torque controlElectricityElectrical Failure
Circuits, systems, and methods are disclosed to eliminate the requirement for an external electromechanical contactor. Integrating contactor circuits with a motor controller reduces cost. Additionally, the cost of the contactor circuit may be reduced by providing transistors designed to block current in only one direction in the event of an electrical fault corresponding to an electrical drive direction.
Owner:CURTIS INSTRUMENTS INC
Diode and transistor design for high speed I/O
InactiveUS7012304B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit including a performance circuit occupying a first area of an integrated circuit substrate and a protection circuit coupled to the performance circuit and occupying a second area of an integrated circuit substrate separate from the first area. Also, a method of forming an integrated circuit including the steps of: Forming a performance circuit occupying a first area of an integrated circuit substrate, forming a protection circuit occupying a second area of an integrated circuit separate from the first area, and coupling the protection circuit to the performance circuit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Fully Depleted Silicon On Insulator Flash Memory Design
The present invention relates to a flash memory system wherein one or more circuit blocks utilize fully depleted silicon-on-insulator transistor design to minimize leakage
Owner:SILICON STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
Differential offset spacer
A method of fabricating a CMOS integrated circuit includes the steps of providing a substrate having a semiconductor surface, forming a gate dielectric and a plurality of gate electrodes thereon in both NMOS and PMOS regions using the surface. A multi-layer offset spacer stack including a top layer and a compositionally different bottom layer is formed and the multi-layer spacer stack is etched to form offset spacers on sidewalls of the gate electrodes. The transistors designed to utilize a thinner offset spacer are covered with a first masking material, and transistors designed to utilize a thicker offset spacer are patterned and first implanted. At least a portion of the top layer is removed to leave the thinner offset spacers on sidewalls of the gate electrodes. The transistors designed to utilize the thicker offset spacer are covered with a second masking material, and the transistors designed to utilize the thinner offset spacer are patterned and second implanted. The fabrication of the integrated circuit is then completed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor storage device
In a 4F2 memory cell designed using an SGT as a vertical transistor, a bit line has a high resistance because it is comprised of a diffusion layer underneath a pillar-shaped silicon layer, which causes a problem of slowdown in memory operation speed. The present invention provides a semiconductor storage device comprising an SGT-based 4F2 memory cell, wherein a bit line-backing cell having the same structure as that of a memory cell is inserted into a memory cell array to allow a first bit line composed of a diffusion layer to be backed with a low-resistance second bit line through the bit line backing cell, so as to provide a substantially low-resistance bit line, while suppressing an increase in area of the memory cell array.
Owner:UNISANTIS ELECTRONICS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
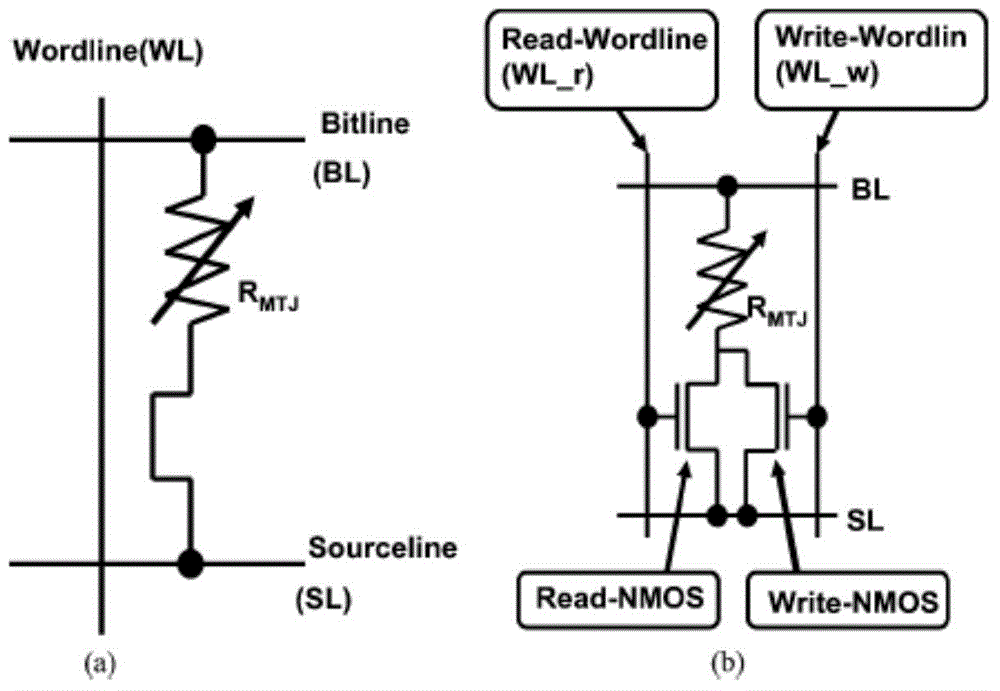
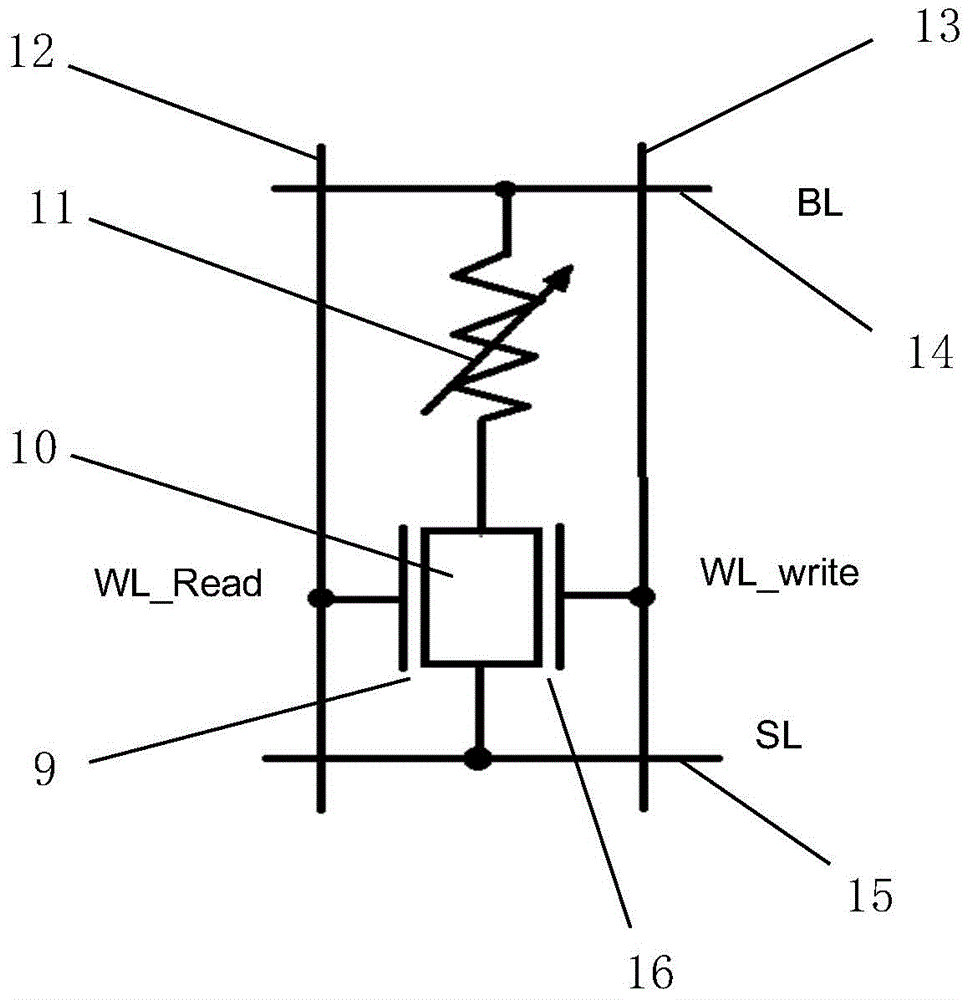
STT-MRAM (Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory) memory cell
InactiveCN104134456AImprove read stabilityWrite current enhancementGalvano-magnetic devicesSolid-state devicesSpin-transfer torqueEngineering
The invention discloses a STT-MRAM (spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory) storage cell; a transistor of the STT-MRAM storage unit is designed into a FinFET (Fin Field-Effect Transistor) form with independent double gates, two MOS (metal oxide semiconductor) devices are formed respectively by two gate electrodes on both sides of the Fin and a Fin source, and a drain region, the two MOS devices share the source and the drain region, and the two gate electrodes are mutually back gates, and can respectively control Fin to open or close a conductive channel; by use of the gate-controlled features of a FinFET device with the independent double gates, the two MOS devices are formed in one FinFET device to achieve a small read current and a larger write current required by the STT-MRAM storage cell, the STTMRAM read-write stability can be effectively improved, and the size of the device can be further reduced under the same drive current conditions.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
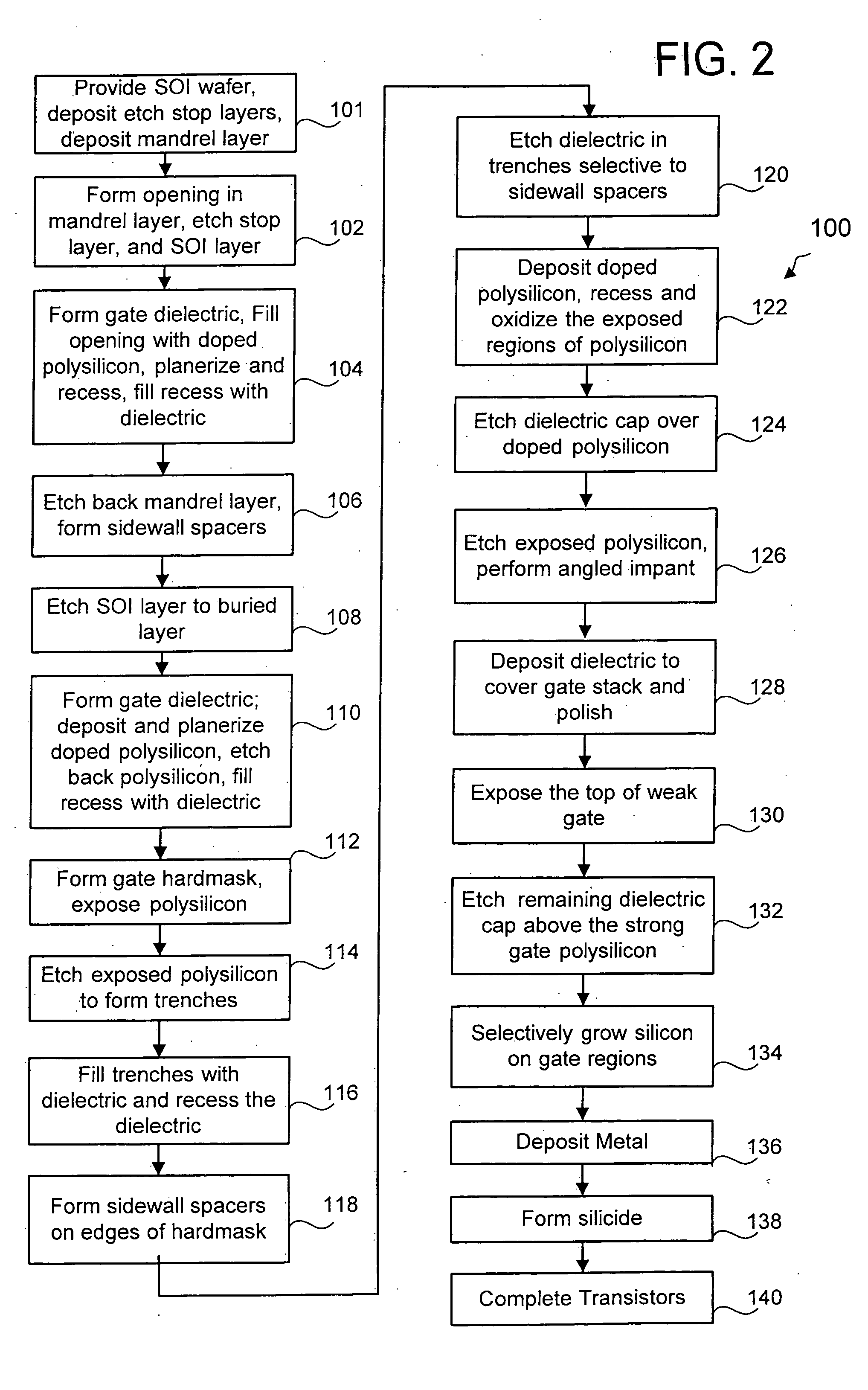
Transistor design self-aligned to contact
ActiveUS20070059908A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
The present invention provides a method of manufacturing a transistor device, a transistor device, and a method for manufacturing an integrated circuit. In one aspect, the method of manufacturing a transistor device includes providing a gate structure (140) over a substrate (110). An insulating layer (310) is formed over the gate structure (140), and openings (710) to the substrate (110) are formed therein, thereby removing a portion of the gate structure (140). The openings (710) are filled with a conductor (1410), thereby forming an interconnect (1510).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
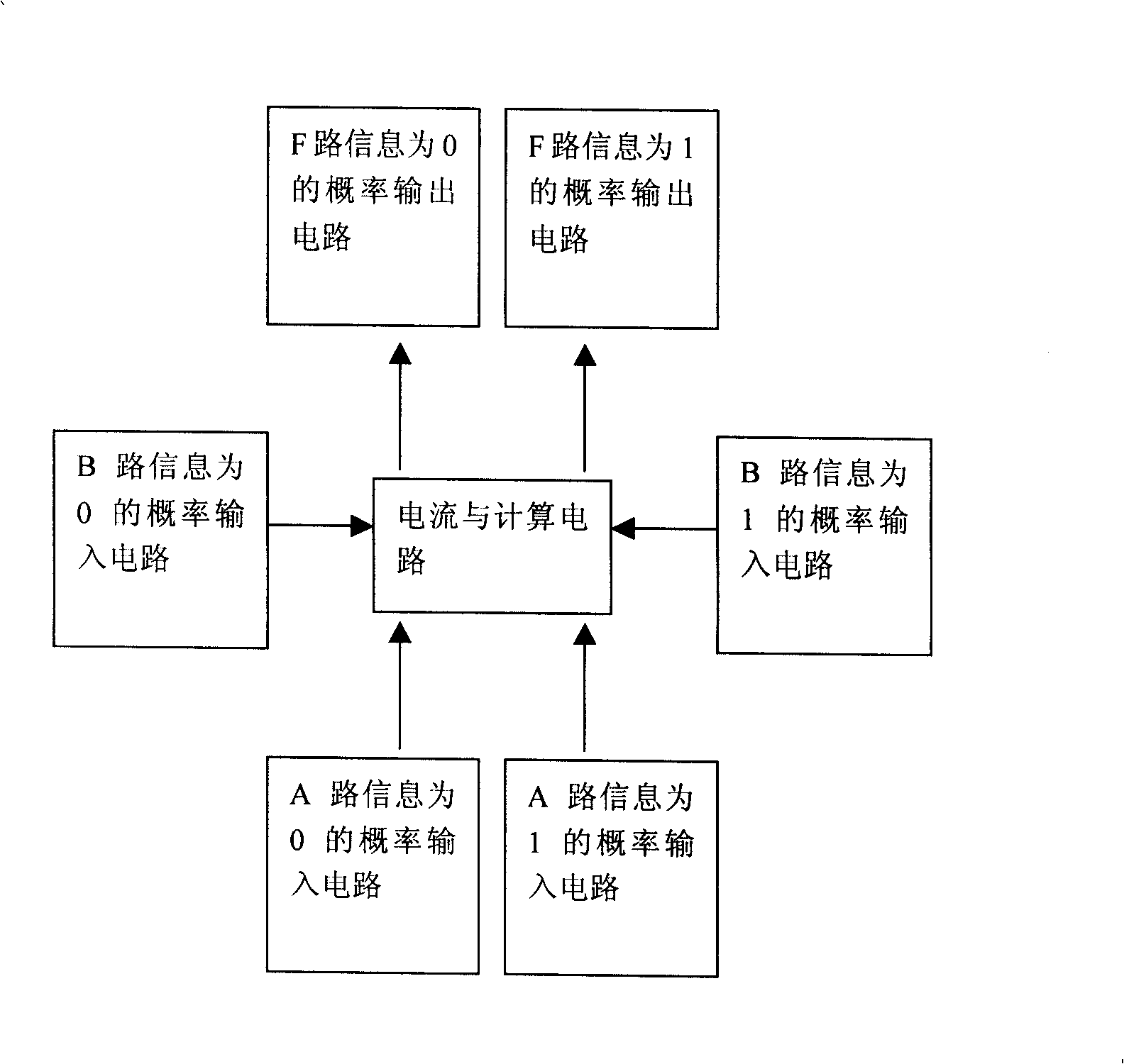
Analog probability AND gate circuit designed by CMOS transistor
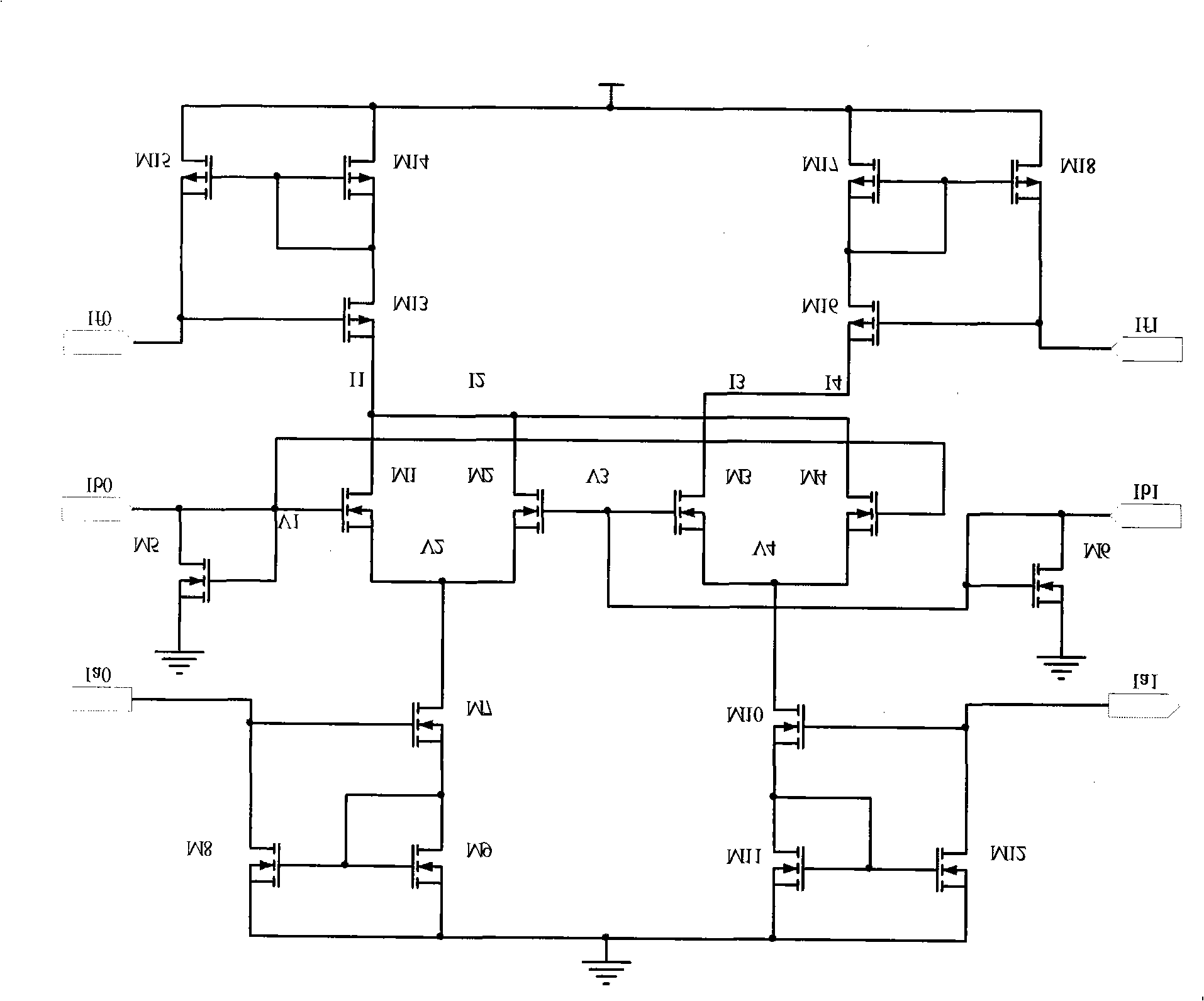
InactiveCN101404493ASimple structureRealize the multiplication relationshipLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCode conversionModularityCMOS
The invention discloses a probability simulation AND gate circuit which is designed by utilizing a CMOS transistor and mainly consists of a current mirror circuit and an analog multiplier circuit. The AND calculation on the probability is realized by different structure modes of the circuit and by using the input and output current values to represent the input and output probability values; the probability simulation AND gate circuit can be applied to the calculation on an electronic NN and the channel decoding calculation in the digital communication field, thus leading the calculation to be improved by two orders of magnitude than the traditional digital logic gate circuit on the aspects of speed and power consumption. The circuit is a modular circuit and can be broadly applied to biology, digital communication and other chip designs which need probability simulation.
Owner:杨曙辉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com