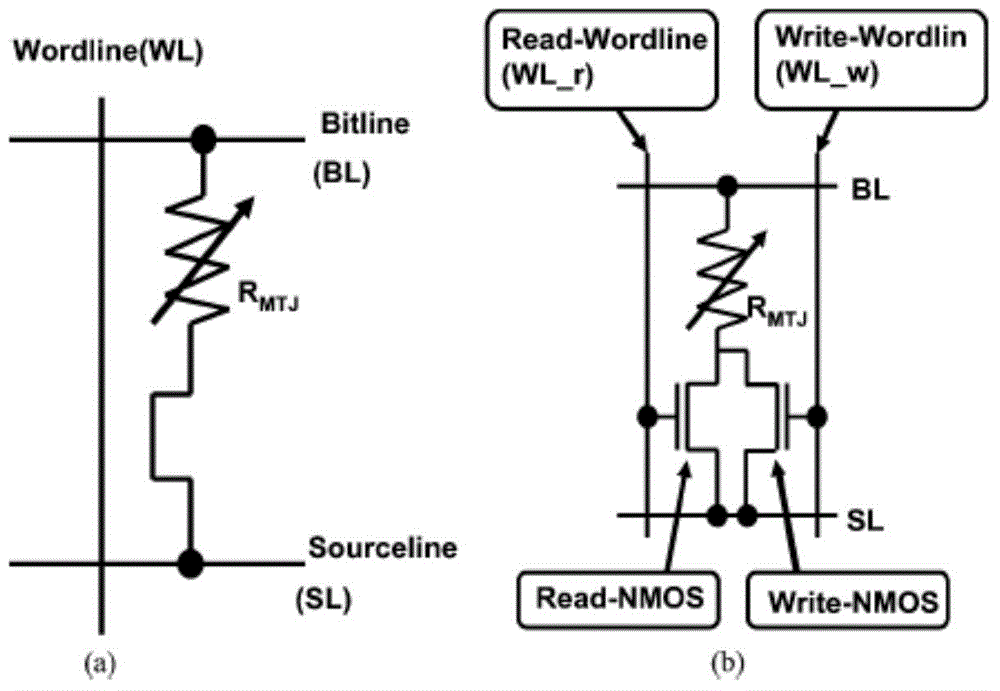
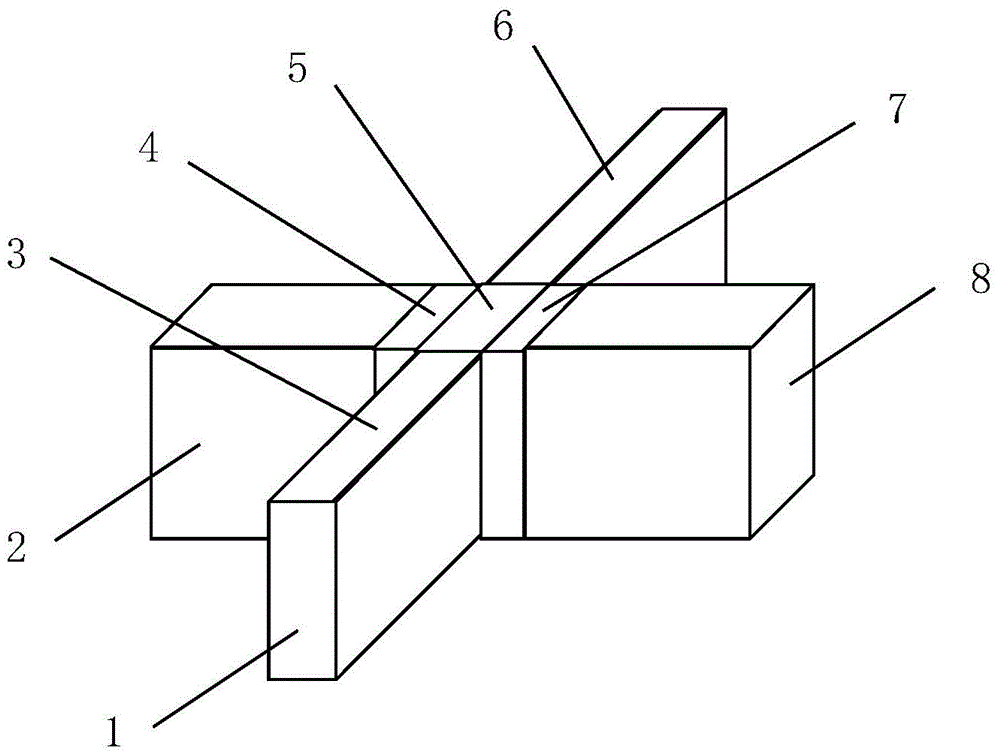
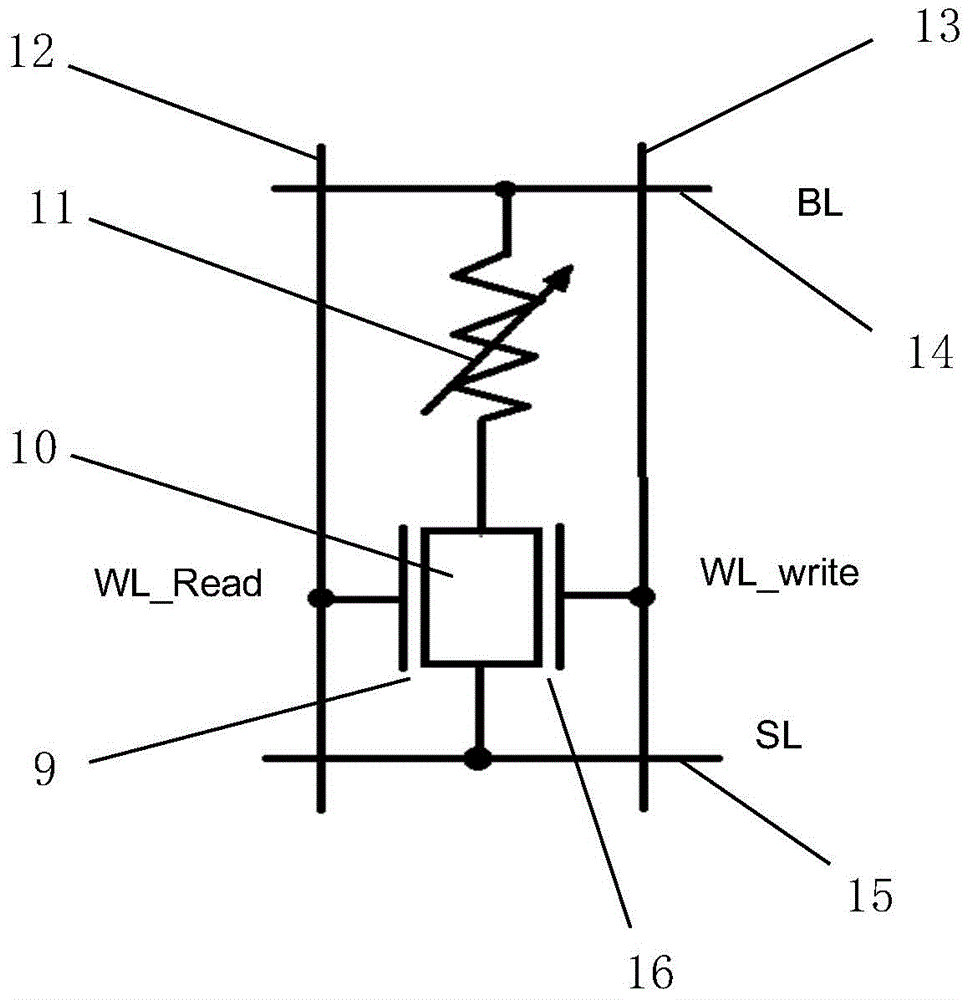
STT-MRAM (Spin-transfer torque magnetic random access memory) memory cell
A technology for memory cells and MOS devices, applied in the field of transistors, can solve problems such as wasted area, achieve large applicability, reduce device size, and improve read and write stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] In this example, see figure 2 , figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a FinFET device of an STT-MRAM storage unit in the present invention. The STT-MRAM storage unit of the present invention includes a magnetic tunnel junction and a selection transistor, and the transistor is a Fin Field Effect Transistor (FinFET). As shown in the figure, the figure is a schematic structural diagram of a FinFET device. The FinFET in the figure includes a silicon fin (Fin) 1 structure formed on a substrate and two gates 2 and 8 independent of each other. Both ends of Fin1 have a source region 3 and a drain region 6, and two gates 2 and 8 are located on both sides of Fin1, specifically on both sides of the channel region between the source region 3 and the drain region 6 of Fin1. Wherein, the gate 2 and the source region 3 and the drain region 6 of Fin1 constitute a MOS device; the gate 8 and the source region 3 and drain region 6 of Fin1 constitute another MOS device. The...
Embodiment 2
[0049] In this example, see Figure 4 , Figure 4It is another structural schematic diagram of a FinFET device of an STT-MRAM storage unit in the present invention. In Embodiment 1, the FinFET device uses one Fin as the driving device in the STT-MRAM unit. The present invention can also cover the situation when there are multiple Fins, that is, the FinFET device can be controlled according to the driving needs of the MTJ. Configure multiple Fins. For example, if the MTJ needs to be driven at about 150 μA, the above-mentioned single Fin device is not applicable, and a double Fin structure is required to provide a driving current of 150 μA. The read current can be adjusted as needed. Generally, a small read current will improve stability, but too small will also affect the read speed. This patent provides a more flexible option, for example, for double Fin situations, such as Figure 4 As shown, the FinFET device has a double Fin1-1 and 1-2 structure, the source and drain re...
Embodiment 3
[0051] In this example, Figure 4 The FinFET device in the device can also be used in the following circuit connection mode (the schematic diagram of the circuit structure is omitted): the gate 8-1 and 2-2 connected together are connected to the read word line end of the STT-MRAM memory cell; The poles 2-1 and 8-2 are interconnected through metal, and are connected to the writing word line terminal of the STT-MRAM storage unit. The drain ends of the two Fin1-1 and 1-2 are connected in parallel to one end of the magnetic tunnel junction, and the source end is connected in parallel to the ground wire of the STT-MRAM memory cell; the other end of the magnetic tunnel junction is connected to the bit line of the STT-MRAM memory cell . In this case, the reading speed of the cell will be faster. In actual design, it can be configured in the manner of Embodiment 2 or Embodiment 3 according to application requirements.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com