Control method of topology variable grid-connected inverter
A control method and inverter technology, which are applied in the same direction of converting irreversible DC power input into AC power output, can solve the problems of low working efficiency of grid-connected inverters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
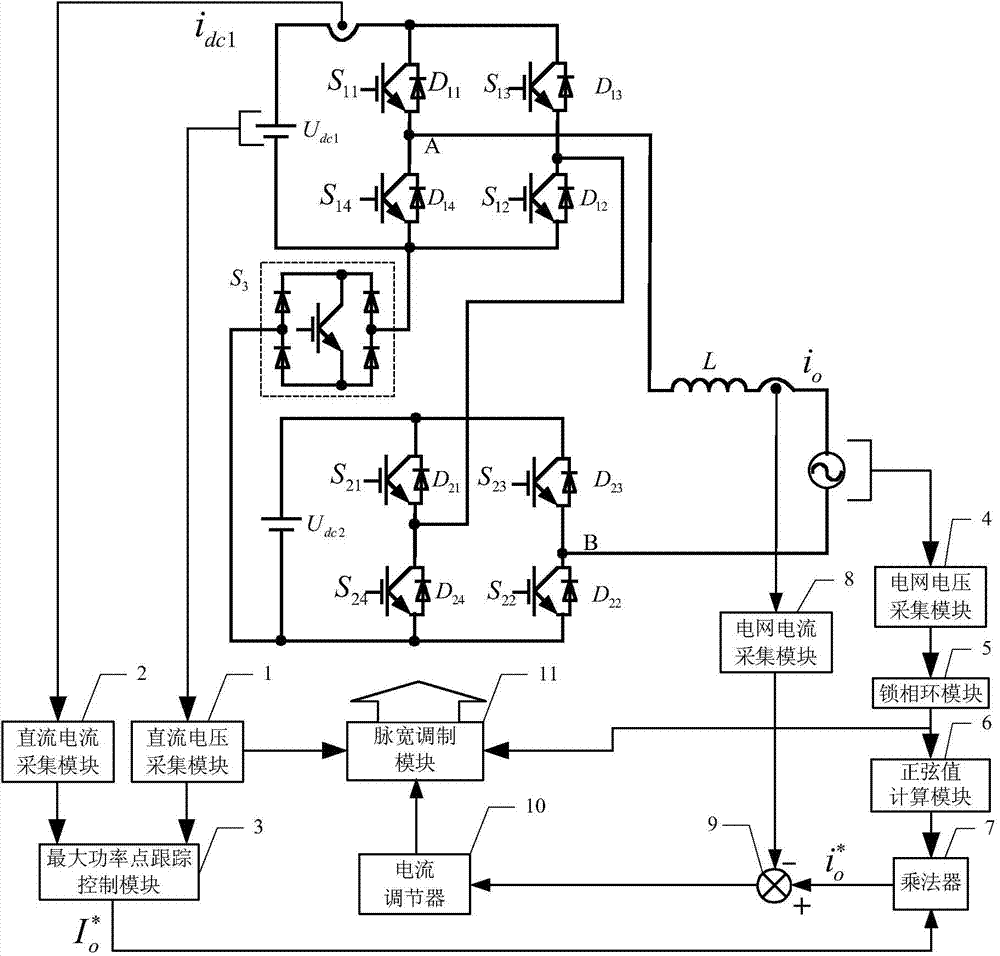
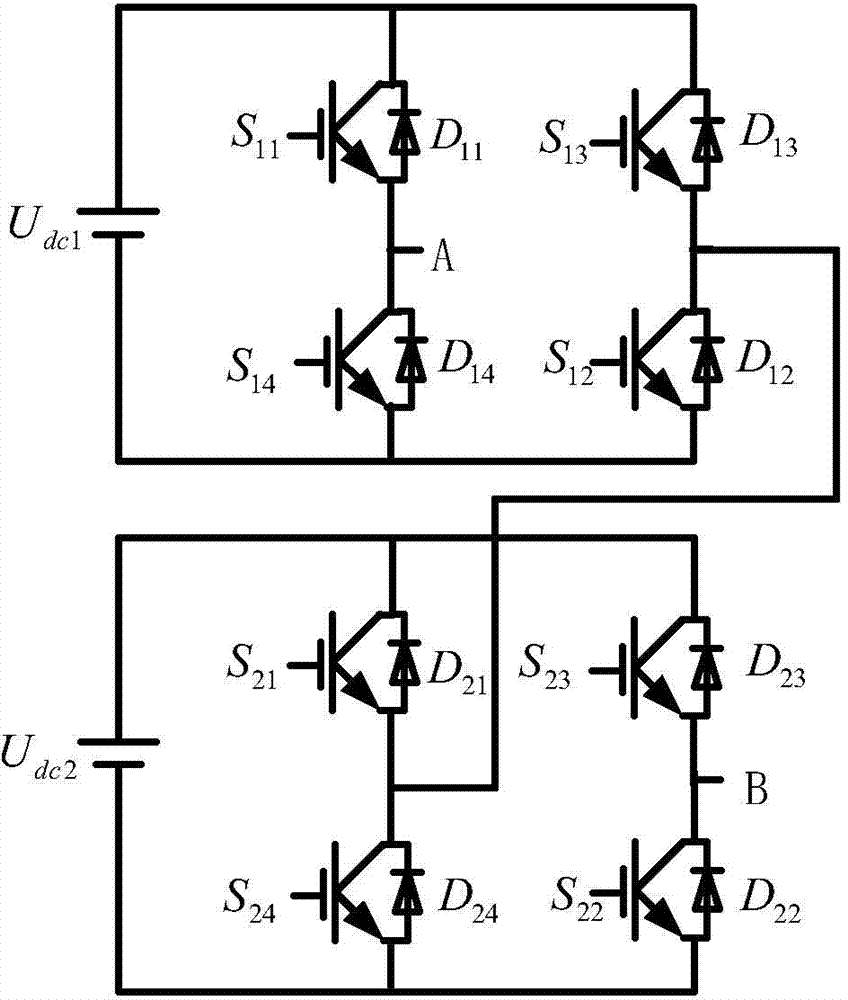
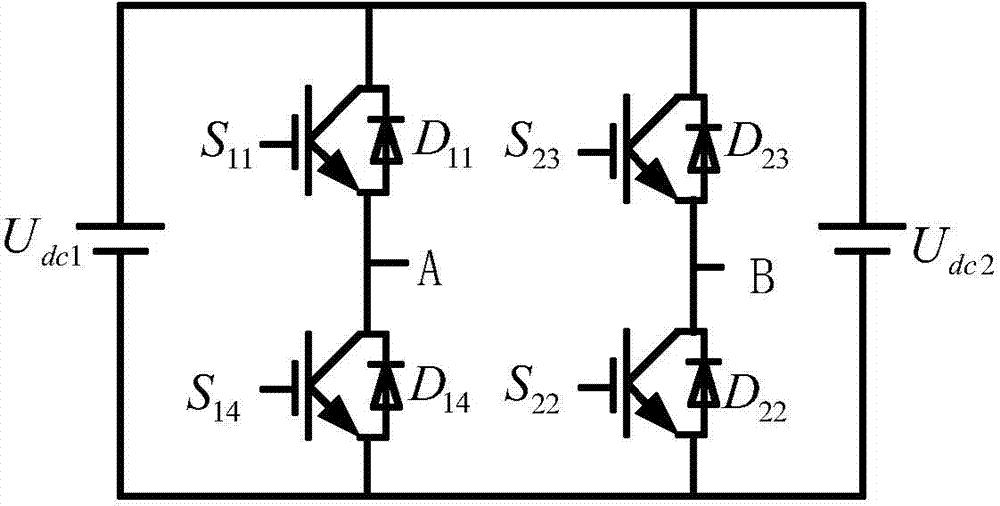
[0042] Specific embodiment one: see figure 1 , 2 And 3 illustrate this embodiment, the control method of a topology variable grid-connected inverter described in this embodiment is based on a topology variable grid-connected inverter, and the topology variable parallel The grid inverter includes a first DC power supply U dc1 , The second DC power supply U dc2 , The first power switch S 11 , The first diode D 11 , The second power switch S 12 , The second diode D 12 , The third power switch S 13 , The third diode D 13 , The fourth power switch S 14 , The fourth diode D 14 , The fifth power switch S 21 , The fifth diode D 21 , The sixth power switch S 22 , The sixth diode D 22 , The seventh power switch S 23 , The seventh diode D 23 , The eighth power switch S 24 , The eighth diode D 24 , Two-way switch S 3 And filter inductor L;
[0043] The first DC power supply U dc1 The positive pole of the first power switch S 11 The power input terminal, the first diode D 11 The cathode, t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0058] Specific implementation manner 2: see figure 1 , 2 This embodiment is described with 3. The difference between this embodiment and the control method of a topology variable grid-connected inverter described in the first embodiment is that the current regulator 10 in step 4 is proportional-integral. Regulator.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0059] Specific implementation manner three: see figure 1 , 2 And 3 illustrate this embodiment. The difference between this embodiment and the control method of a topology variable grid-connected inverter described in specific embodiments 1 or 2 is that the topology variable grid-connected inverter in step 6 The inverter works in the cascaded inverter mode, and the rest of the power switches adopt the carrier phase-shifted multi-level sine wave pulse width modulation strategy for control. The specific process is based on the instantaneous value of the inverter voltage obtained in step 4. It is compared with four triangular carriers with a certain phase difference, and the comparison result obtained is used as the control signal of the remaining power switches. The four triangular carriers with a certain phase difference are four triangular carriers with a mutual difference of 90 degrees in electrical angle. Tri1, Tri2, Tri3 and Tri4. Among them, the comparison result of the in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com