Substrate integrated waveguide ferrite switch
A substrate-integrated waveguide and ferrite technology, applied in waveguide-type devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of complex processing, narrow switching bandwidth, large switching volume, etc., and achieve low width requirements and strong heat dissipation capability. , the effect of high isolation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
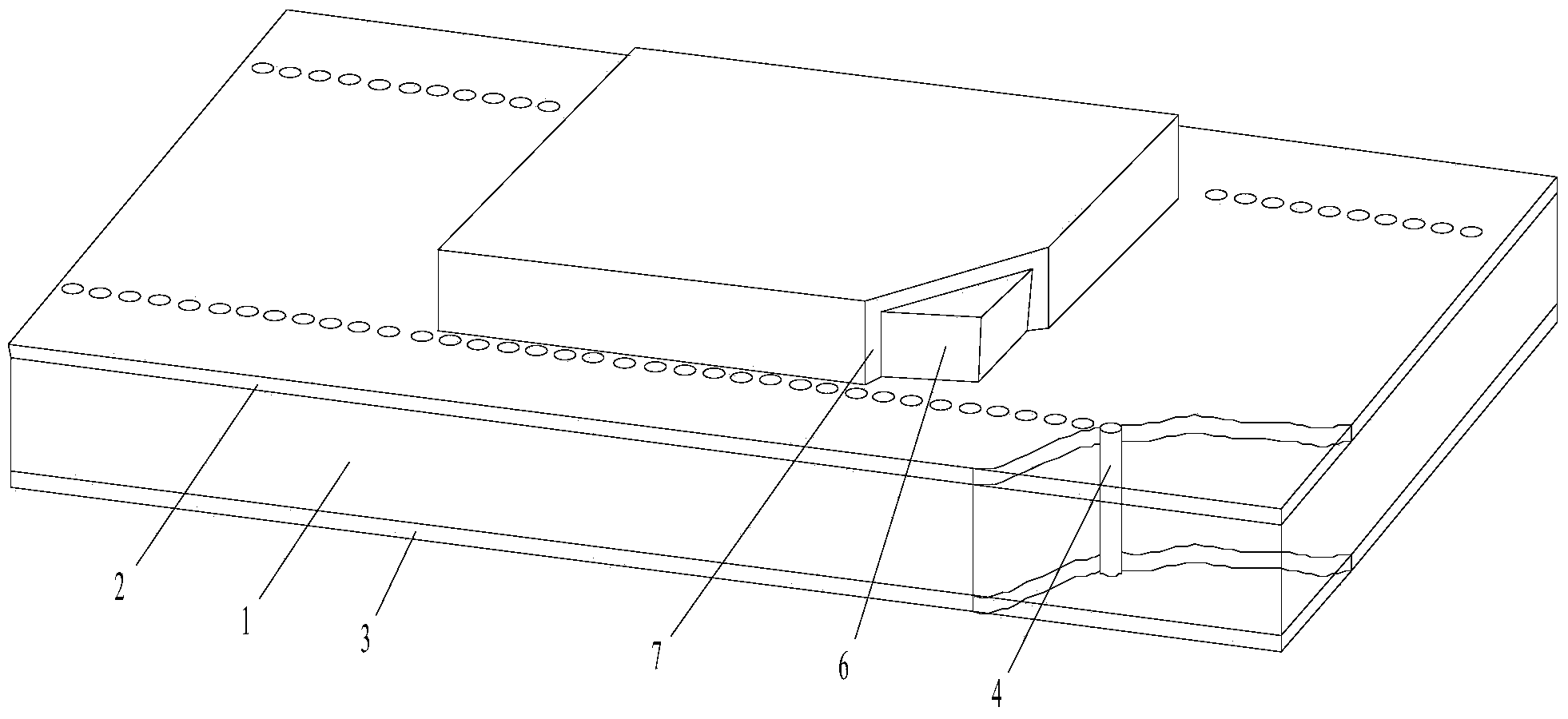
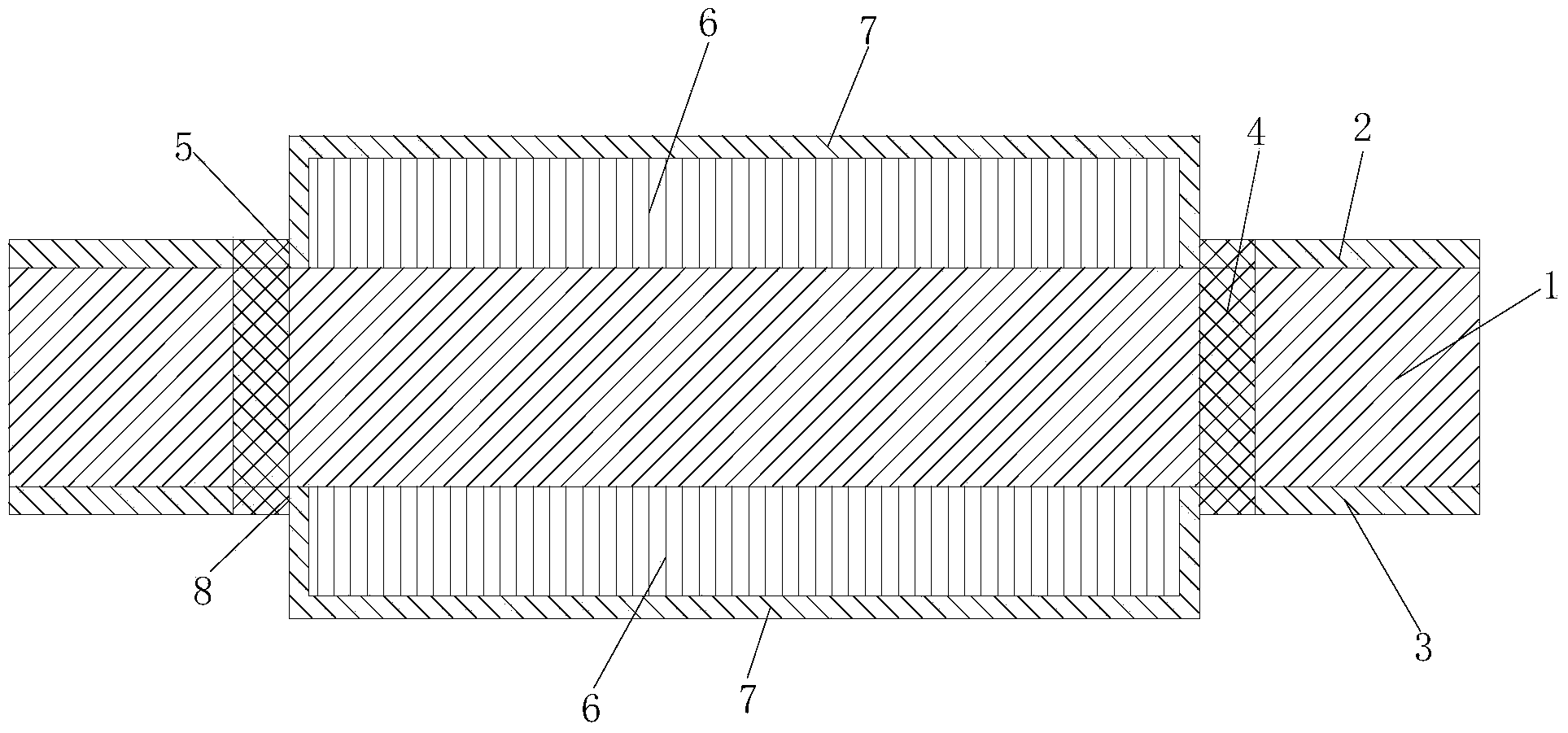
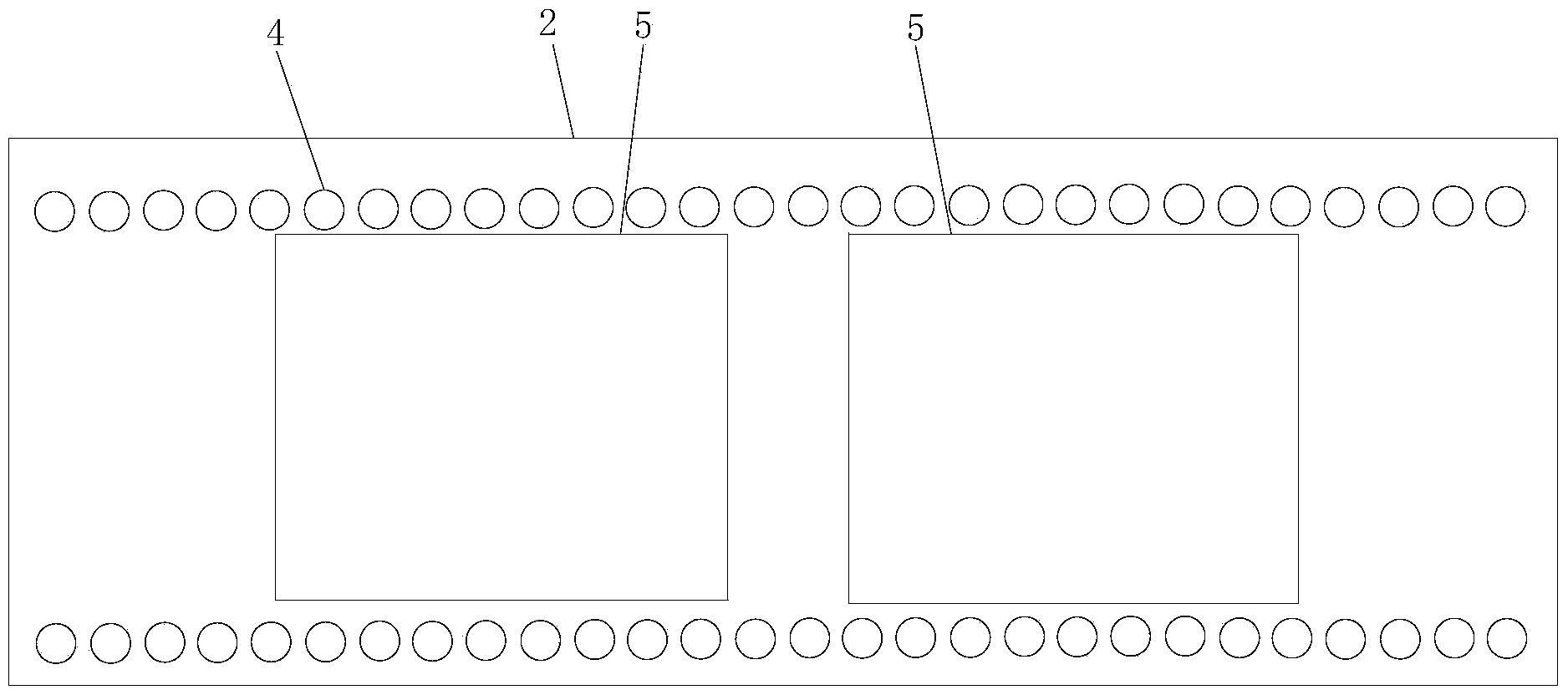
[0022] In this embodiment, the number of ferrite blocks 6 of the substrate-integrated waveguide ferrite switch is two, all of which are installed on the first metal copper clad layer 2, and the structure of the first metal copper clad layer 2 is as follows image 3 As shown, the dielectric constant of the first selected dielectric substrate 1 is 10.2, the thickness is 0.635mm, and the loss tangent is 0.0024; the ferrite block 6 is YIG-1850, the relative dielectric constant is 14.5, and the 3dB line width is 20Oe. Loss tangent 0.0002, saturation magnetization 1850Gs. The width of the substrate integrated waveguide is 8mm, the diameter of the metal through hole is 0.6mm, the distance between the through holes is 1.2mm, the thickness of the ferrite block 6 is 0.8mm, the length is 6mm, and the width is 7.4mm. The distance between the two ferrite blocks 6 is 1mm. 3010Oe. The performance comparison is shown in the table below:
[0023]
[0024] It can be seen from the above tab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com