Magnetic field sensor sensitivity tuning method based on fiber bragg grating laser
A magnetic field sensor, fiber grating technology, applied in the size/direction of the magnetic field, magnetic field measurement using magneto-optical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult to apply point measurement occasions, the sensor is not flexible enough, etc., to improve sensitivity and wide adaptability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
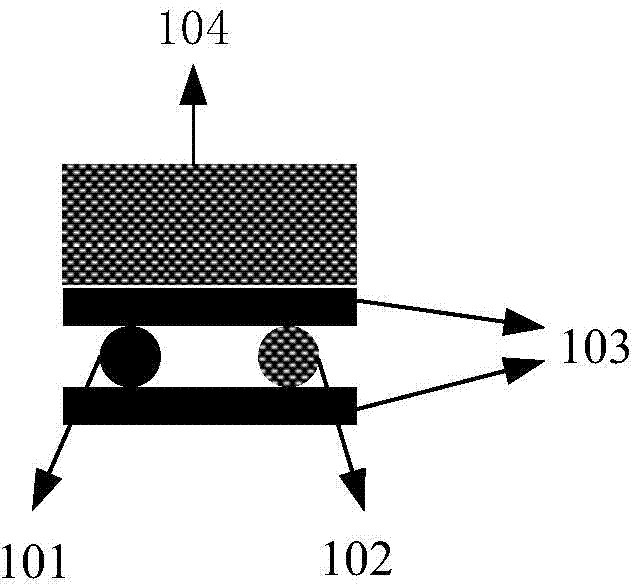
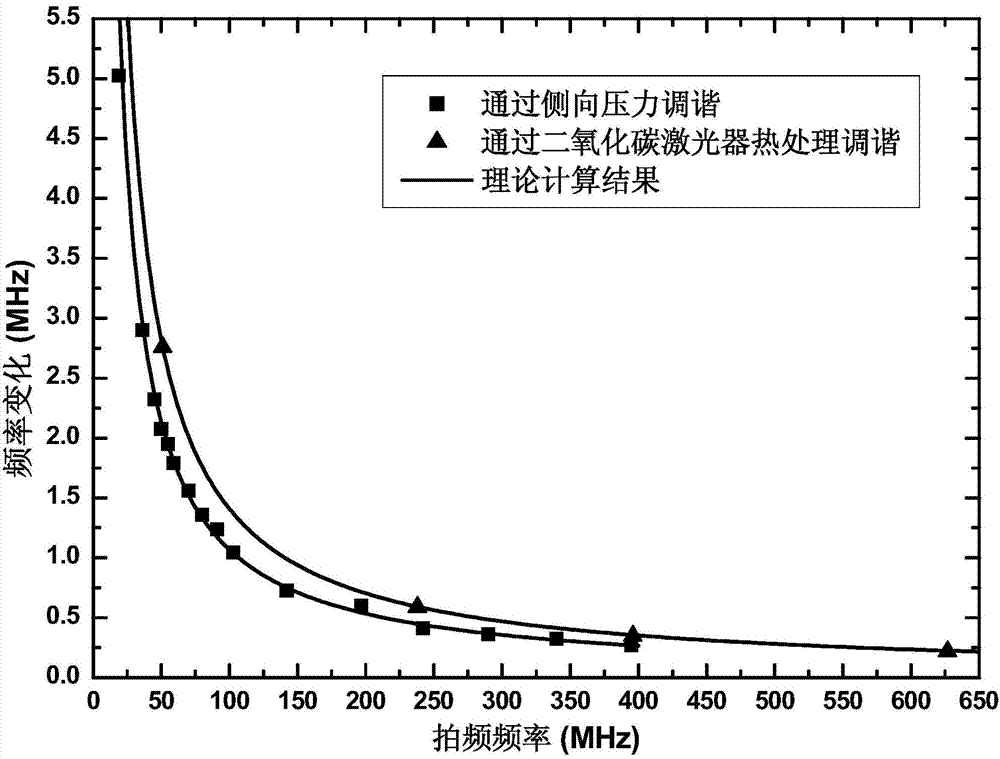
[0023] This example figure 1 As shown, the sensitivity can be tuned by temporarily changing the magnitude of the linear birefringence. In this solution, a fiber Bragg grating laser 101 and an idle fiber 102 (idle fiber 102 has the same outer diameter as the fiber Bragg grating laser) are placed in parallel and are clamped between two glass plates 103 together. The idle optical fiber 102 placed in parallel plays a supporting role and ensures that the force applied by the glass plate 103 to the fiber grating laser is perpendicular to the fiber grating laser. A weight 104 of a certain weight is placed on the glass plate above the fiber grating laser, and lateral pressure is applied to the fiber grating laser through gravity to change the shape of the fiber grating laser, thereby changing the linear birefringence in the laser cavity. By changing the weight of the weight, the linear birefringence in the laser cavity can be adjusted. In this embodiment, the linear birefringence tu...
Embodiment 2
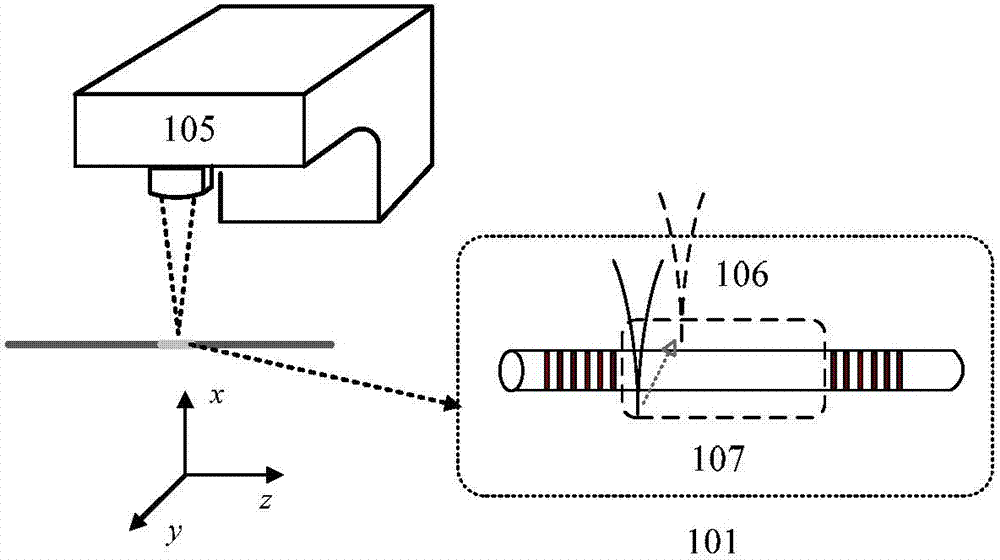
[0045] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1 in terms of realization principle; figure 2 As shown, the magnitude of the linear birefringence in the laser cavity of a fiber grating laser can be permanently changed. In this scheme, a fiber grating laser 101 is placed at the focal plane of a scanning laser beam 106 of a carbon dioxide laser 105 . The carbon dioxide laser emits a laser pulse with a repetition rate of 3 kHz, which is focused on a spot with a diameter of about 100 μm at the irradiation area 107 of the fiber grating laser through a ZnSe lens.
[0046] The beam of the CO2 laser is swept across the fiber in steps of 40 μm along the z-axis shown in the figure. Simultaneously, at each point scanned on the z-axis, the CO2 laser beam is swept across the fiber along the y-axis shown in the figure. In the process of carbon dioxide laser irradiation and scanning, the optical fiber absorbs the light with a wavelength of 10.6 μm emitted by the carbon dioxide ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com