Rainfall foundation monitoring method based on GNSS signal depolarization effect
A rainfall intensity and depolarization technology, applied in rainfall/precipitation meters, measurement devices, ICT adaptation, etc., can solve problems such as unseen theoretical research and experimental results, and achieve rich signal resources, self-protection, and strong continuity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
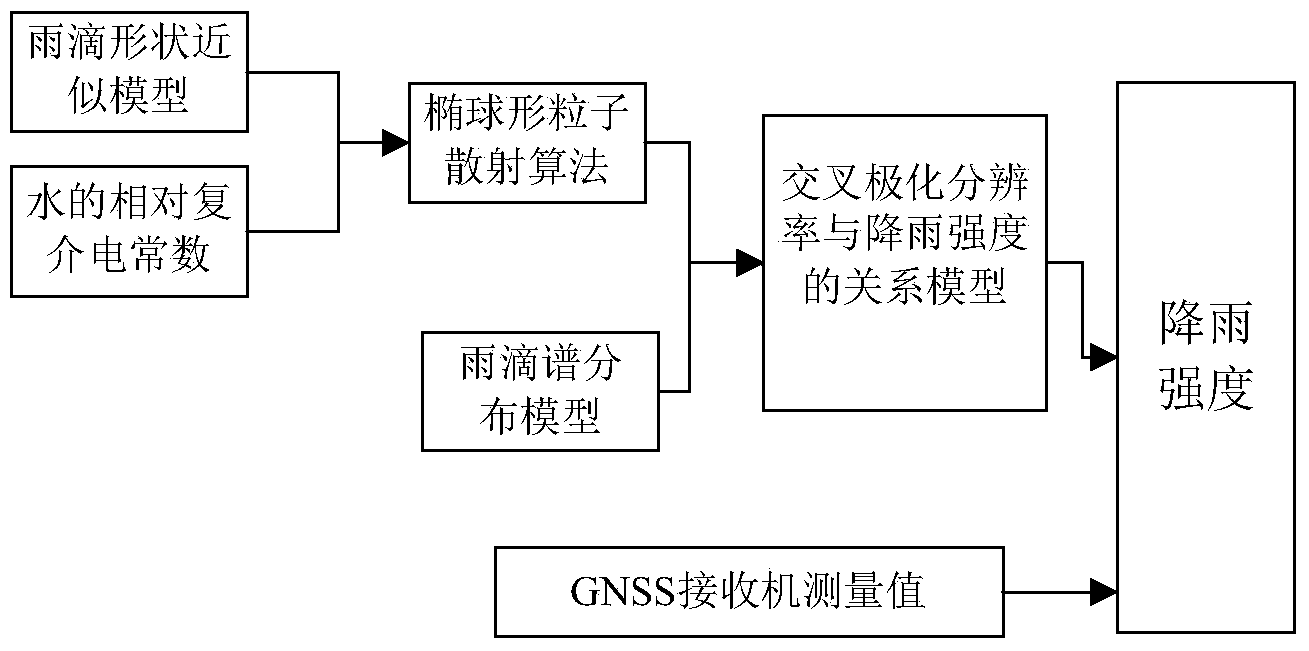
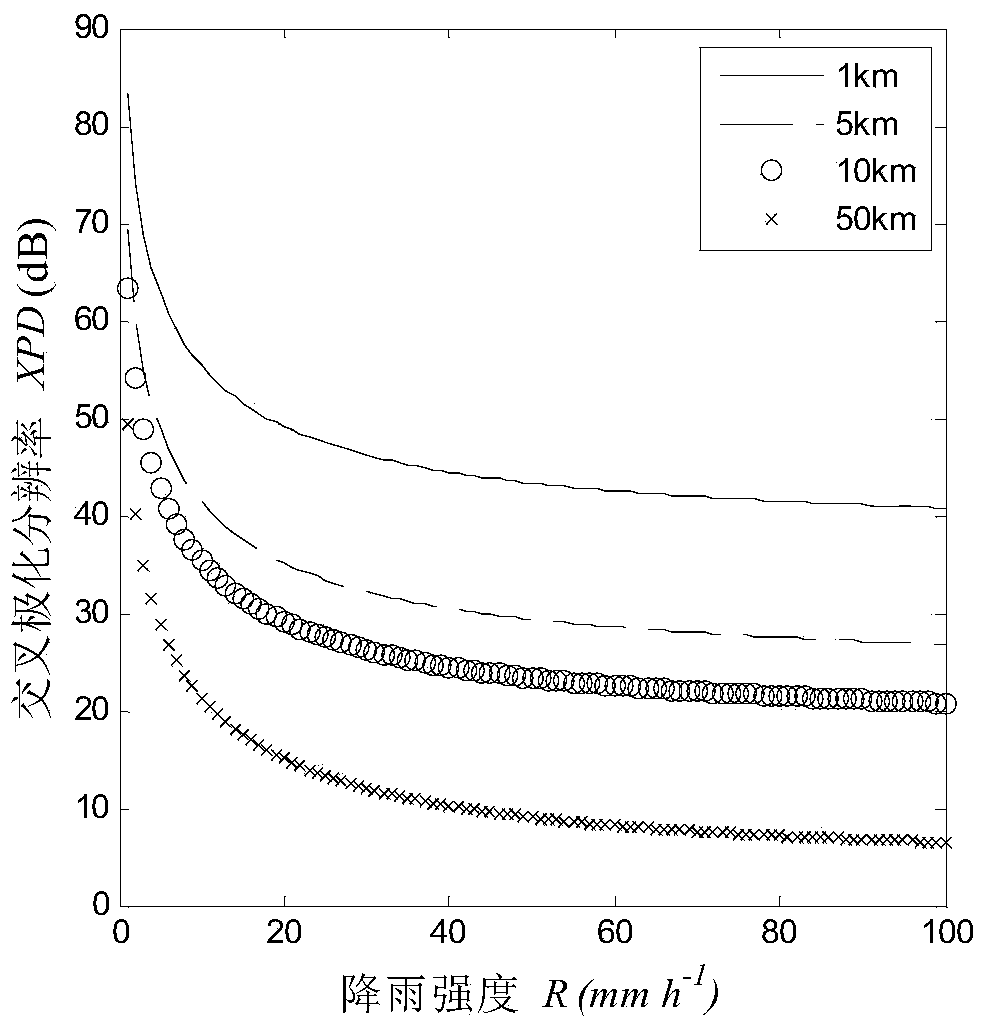
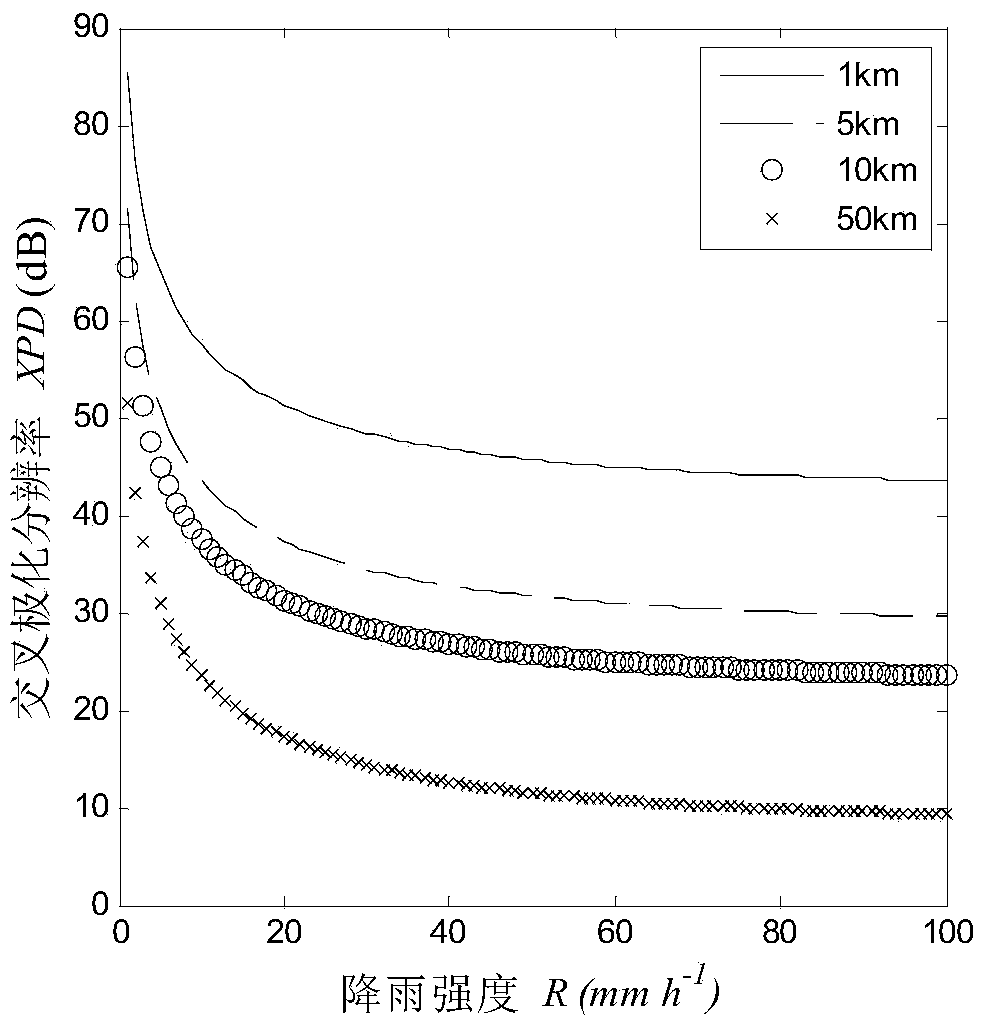
[0071] The GPS L1 frequency band signal (frequency 1575.42MHz) with right-hand circular polarization is taken as an example for analysis.
[0072] 1. Calculate the forward scattering amplitude
[0073] The GPS L1 frequency band signal that can be collected by the GNSS receiver after passing through the rain area is selected for calculation; assuming that when it rains, the temperature of the raindrop is 20°C, and the relative complex permittivity of the raindrop at this time is calculated using the Ray formula. According to the actual raindrop shape approximation model, the Rayleigh approximate ellipsoidal particle scattering algorithm is used to calculate the forward scattering amplitude f in the horizontal direction after the GPS signal of this frequency is incident on a single raindrop with different particle radii h and the forward scatter amplitude f in the vertical direction v .
[0074] 2. Calculate the propagation constant
[0075] According to the forward scatterin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com