Visual-content-based method for establishing multi-level semantic map
A semantic map and content technology, applied in the field of robot navigation, can solve the problems of expensive laser sensors, no division and construction, and limit the scope of robot activities, achieve fast insertion and query speed, reduce retrieval space and path search space, and solve self-limiting problems. Effect of Position Estimation Error Accumulation Problem
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0049] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings.
[0050] The flow chart of the method for creating a multi-layer semantic map of the present invention is as follows Figure 7 As shown, including the following steps:
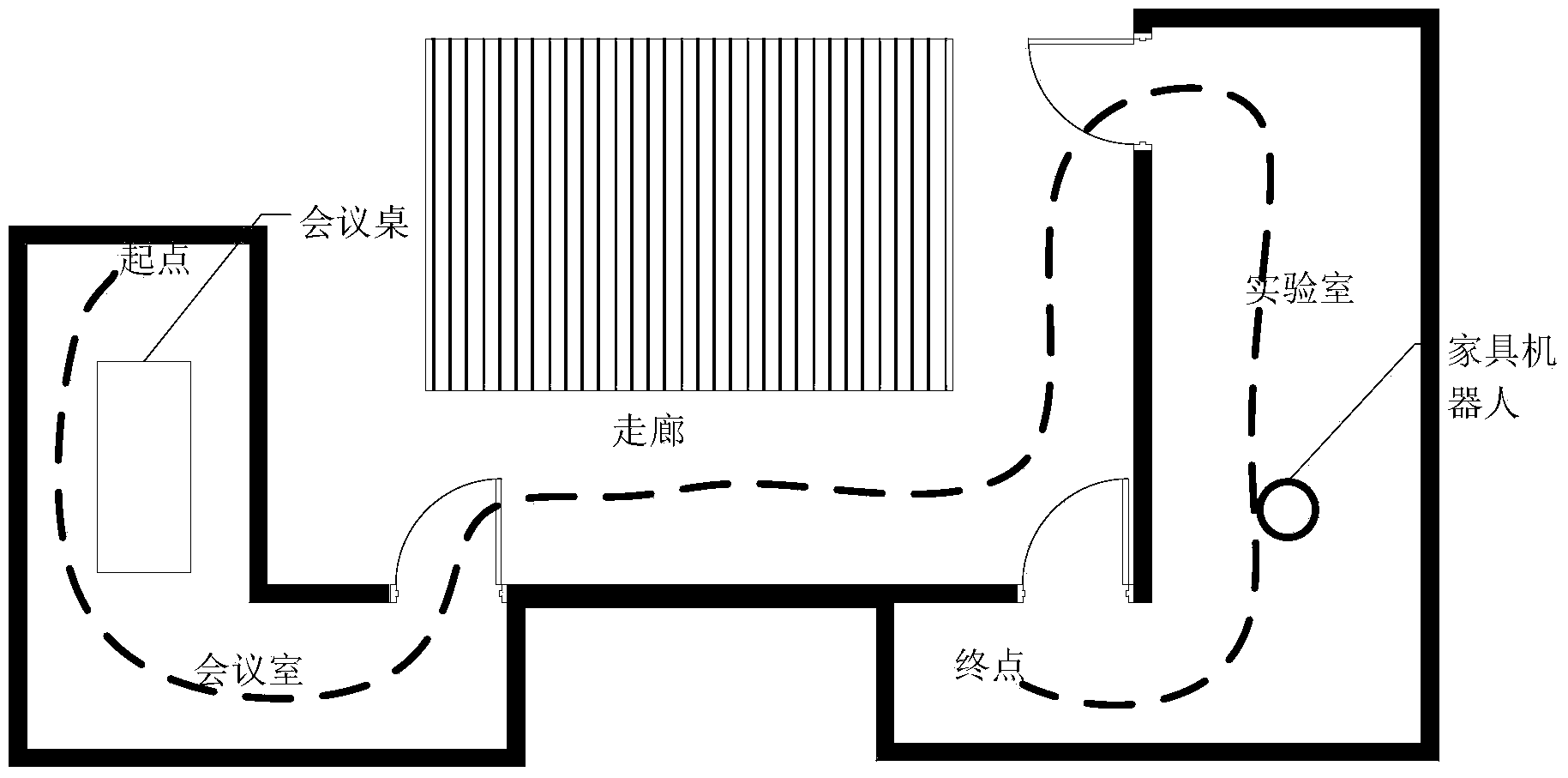
[0051] Step 1. Calibrate the camera and use an obstacle avoidance system to ensure that the robot will not collide. The robot roams in the indoor environment, saves the images taken during the roaming process, and annotates the images according to the scene and image content to which they belong to form an annotation file.
[0052] Step 2. Build a hierarchical vocabulary tree.
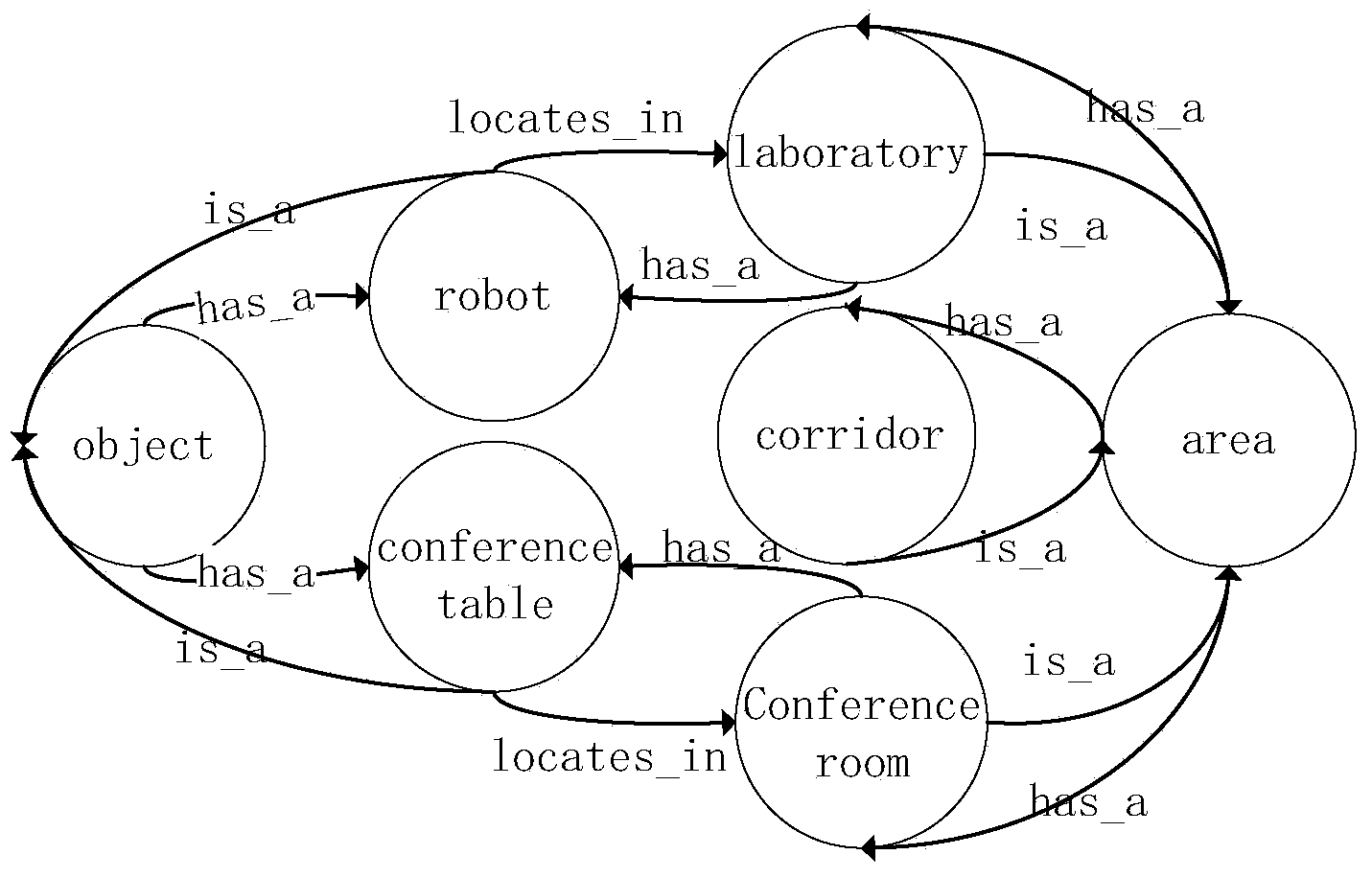
[0053] Extract all image feature vector sets, use the K-means algorithm to cluster the feature vector sets (root nodes) to form sub-feature vector sets (child nodes), iteratively perform K-means clustering on each sub-feature vector set until Satisfy the depth limit, save the cluster center of the child nodes stored in each node, and complete the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com