Delay action catalyst for improving the stability of polyurethane systems having halogen containing blowing agent
A foaming agent, reactive technology, applied in the field of catalyst composition, can solve problems such as accelerating epoxy resin curing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
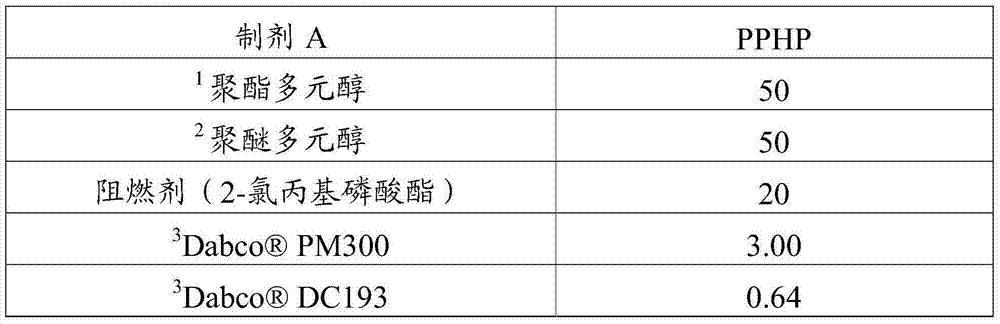
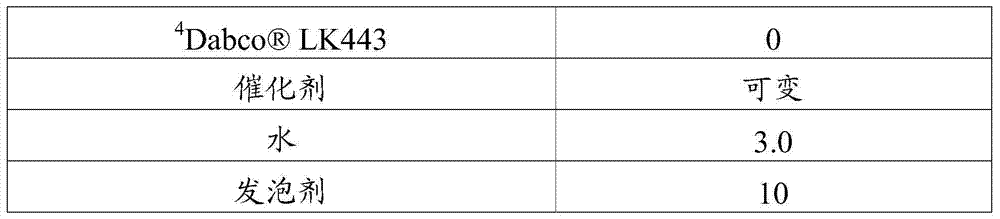
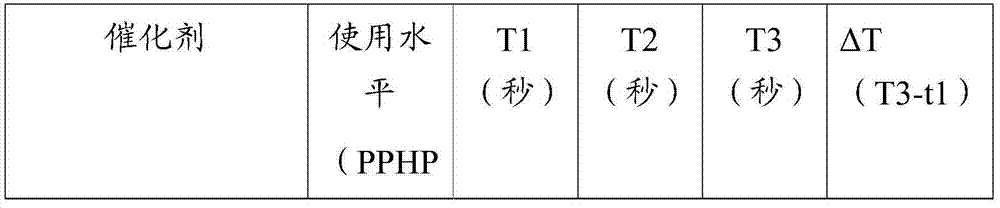
[0085] Example 1: Evaluation of formulations containing conventional amine catalysts in the presence of trans-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene HFO as a blowing agent
[0086] A conventional polyurethane formulation can be used to prepare foams according to methods known in the art, and the polyurethane formulation has been added with a urethane catalyst containing one or more alkyl tertiary amines. The amount of polyisocyanate used in the polyurethane formulation according to the present invention is not limited, but will generally be within those ranges known to those skilled in the art. Exemplary ranges are given in the table, expressed by reference to "NCO Index" (Isocyanate Index). As known in the art, the NCO index is defined as the number of isocyanate equivalents divided by the total number of active hydrogen equivalents, multiplied by 100. The NCO index is expressed by the following formula.
[0087] NCO index=[NCO / (OH+NH)]×100.
[0088] In some embodiments of the present i...
Embodiment 2
[0097] Example 2: Evaluation of formulations containing sterically hindered amine catalysts and functionalized tertiary amine catalysts with NCO reactive groups in the presence of HFO blowing agent trans-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene
[0098] In this example, for Polycat The evaluation of -12 (typically hindered tertiary amine) is used to illustrate the benefits and shortcomings of this type of compound using spray rigid foam formulation B. In addition, in this example, DABCO The performance of -T is shown as an example of typical tertiary amines with OH groups (NCO reactive groups) commonly used in spray foam applications.
[0099] Table 2-Spray rigid foam formulation B
[0100] Component
Parts by weight (pphp)
70
2 Mannich Polyol
30
3 Surfactant (LK443)
2.0
20
Water
1.5
Amine catalyst
Variable
5 Metal catalyst
1.0
[0101] 6 Trimerization catalyst (TMR7)
0.1-10
Flame retardant (2-chloropropyl phosphate)
30.0
Polyme...
Embodiment 3
[0110] Example 3: Using HFO as the blowing agent trans-1-chloro-3,3,3-trifluoropropene, in the presence of standard organic monocarboxylic acids, evaluation of sterically hindered amine catalysts and NCO reactive groups Formulation of functionalized tertiary amine catalyst
[0111] In this example, in the presence of organic monocarboxylic acids, the sterically hindered tertiary amine catalyst Polycat -12 and OH-containing tertiary amine catalyst DABCO -T.
[0112]
[0113]
[0114]
[0115] Will have Polycat -12 and DABCO The premix mixture of -T and acid was stored at 50°C and samples were taken every seven days to determine the ability and kinetics of the aged premix B to produce polyurethane foam. The kinetics and polymerization parameters of the aged premix were measured and compared with the data from the unaged premix. The data shows that DABCO -T combined with monocarboxylic acid relative to free DABCO -T helps to improve stability. However, the stability of the sys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com