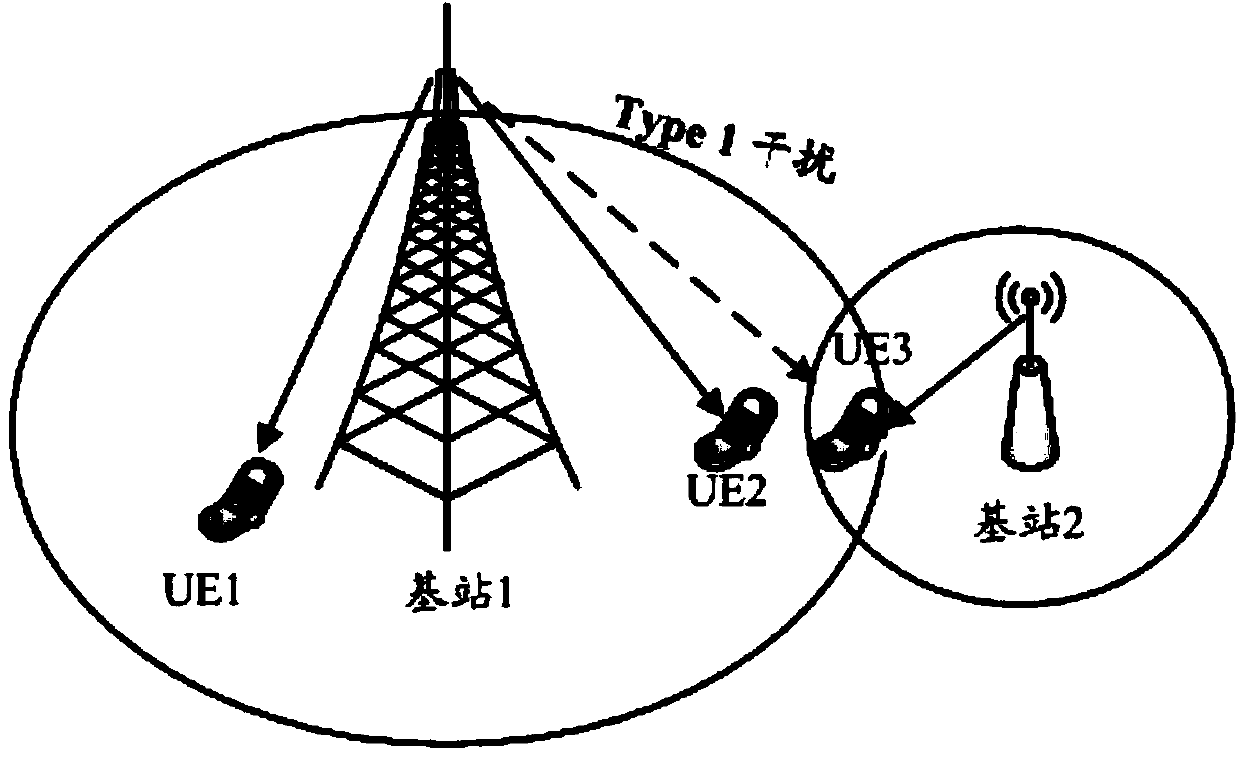
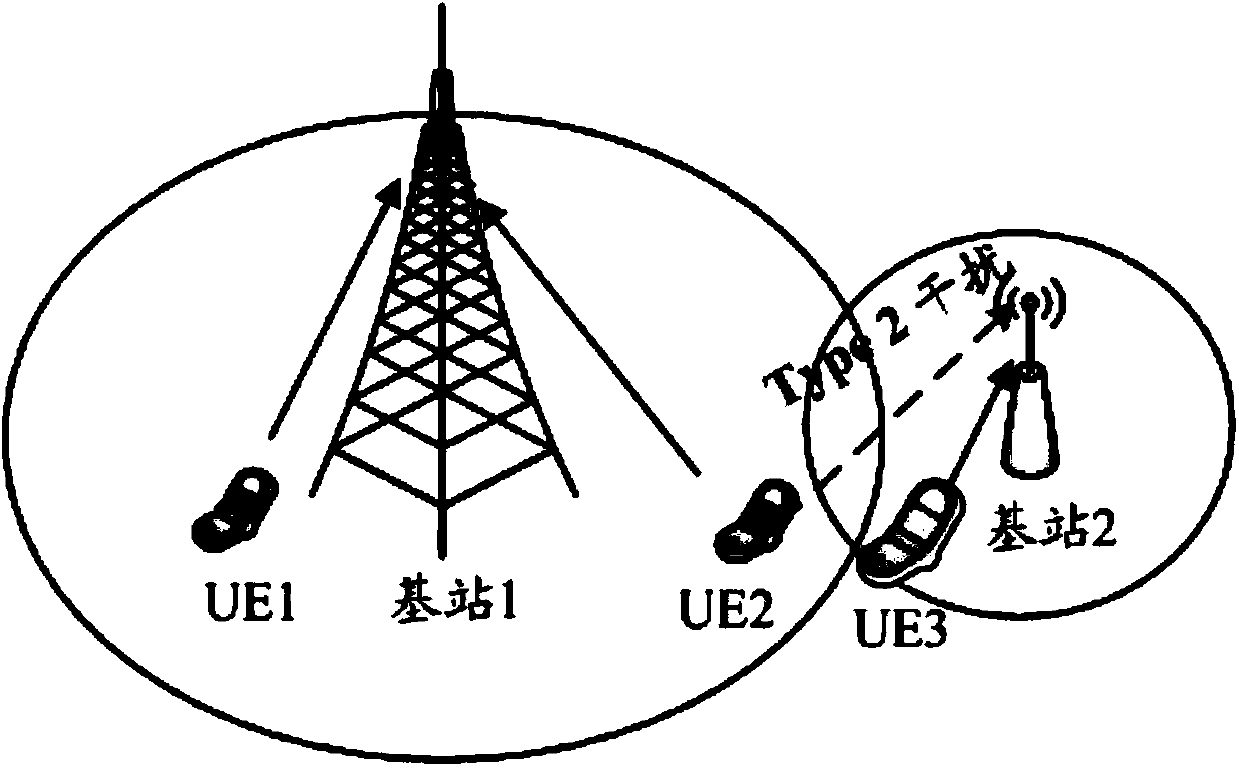
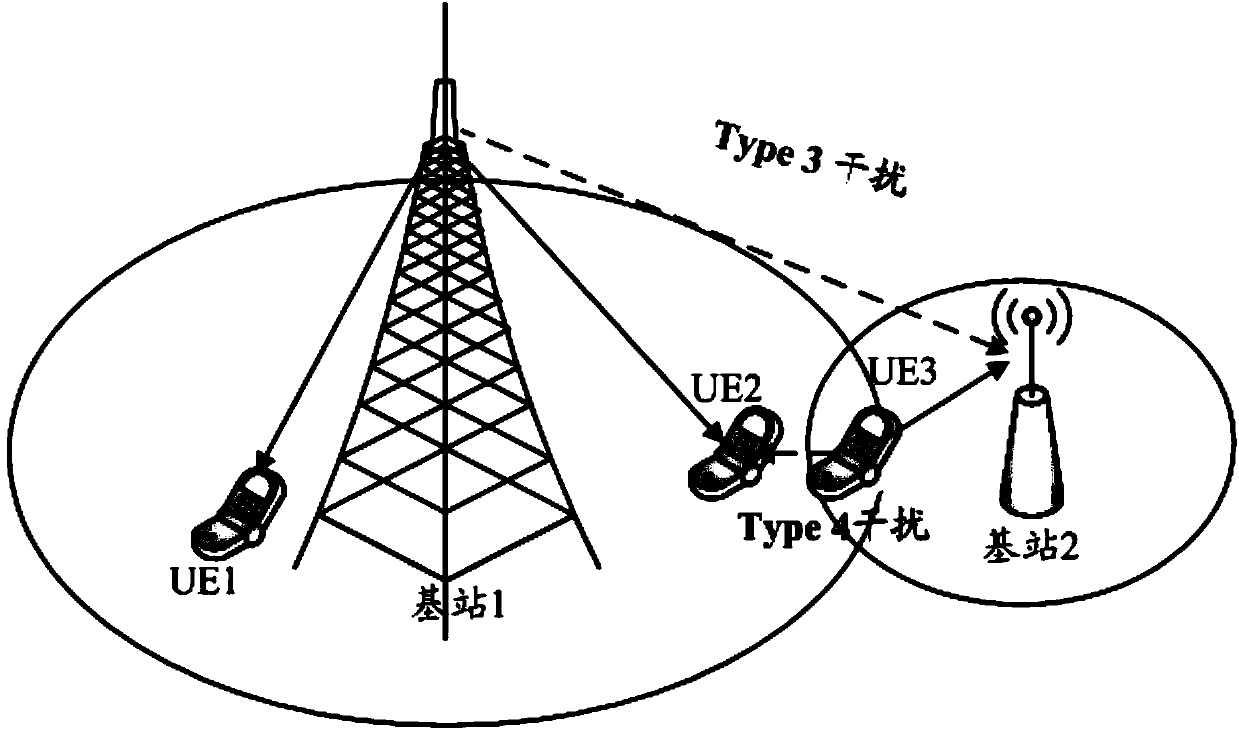
Base station frequency resource allocation method and network device
A frequency resource and configuration method technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as large signaling transmission requirements, and achieve the effect of avoiding inter-cell interference and rational configuration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0060] In the first specific embodiment, for each adjacent cell, the first weighting factor a is calculated 1 The product of the load of the adjacent cell in the basic frequency resource, and the second weighting factor a 2 and the sum of the products of the interference of the adjacent cell to the cell in the basic frequency resource to obtain the single-cell frequency priority coefficient of each adjacent cell to the cell;
[0061] Calculate the weighted sum of the single-cell frequency priority coefficients of each adjacent cell to obtain the frequency priority coefficient I of the basic frequency resource Rseg .
[0062] In a specific implementation, the product of the single-cell frequency priority coefficient of each adjacent cell and the weight coefficient corresponding to the adjacent cell is calculated and summed to obtain the frequency priority coefficient I of the basic frequency resource. Rseg .
[0063] Among them, in the basic frequency resource, the single-ce...
no. 1 Embodiment
[0140] The first specific embodiment, as attached Image 6 As shown, the specific process of requesting the allocation of frequency resources for the newly opened cell by the base station is as follows:
[0141] In this specific embodiment, when the base station is powered on or the base station wants to activate a cell under the base station, it sends a request to the centralized node, and the centralized node allocates frequency resources for the newly opened cell.
[0142] Step 601: The base station establishes a connection with the network, and reports frequency point and bandwidth capability information to the centralized node.
[0143] Step 602: Optionally, if the centralized node can determine the basic information of the adjacent cell of the newly opened cell, it notifies the base station of the basic information of the adjacent cell, and the basic information of the adjacent cell is mainly the frequency point information of the adjacent cell. .
[0144] Step 603: Th...
specific Embodiment 6
[0225] Specific embodiment 6, the centralized node allocates frequency resources with the least interference and / or the least load to different cells. In this specific embodiment, the influence of the center frequency band is not considered, and frequency resources are allocated to the newly accessed cells according to the principle of the least interference within the bandwidth. .
[0226] For example, if the width of the basic frequency resource is 2.5MHz, to allocate a 5MHz bandwidth resource for the newly accessed cell, the frequency priority coefficients of the basic frequency resources Rseg1, Rseg2, and Rseg3 are IRseg1=0.2, IRseg2=0.2, IRseg3 respectively =0.3, adjacent cells have used frequency band resources (Rseg1+Rseg2) and frequency band resources (Rseg2+Rseg3), according to the principle of minimum interference and / or minimum load, regardless of whether the center frequency band overlaps, allocate frequency band resources for newly accessed cells (Rseg1+Rseg2).
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com