Self-setting epoxy resin containing acid anhydride radicals and preparation method thereof
An epoxy resin, self-curing technology, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, can solve the problem of inability to form thermosetting cross-linked polymers, achieve high modulus and strength, and easy to use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
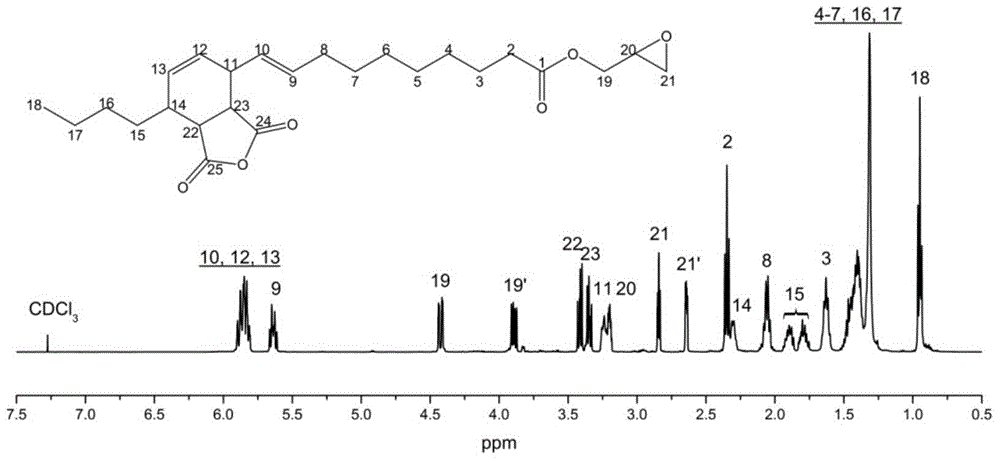
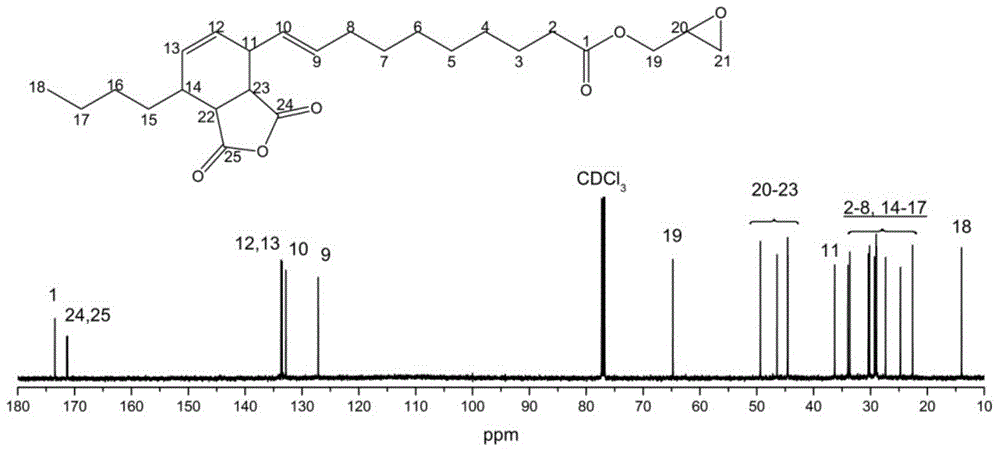
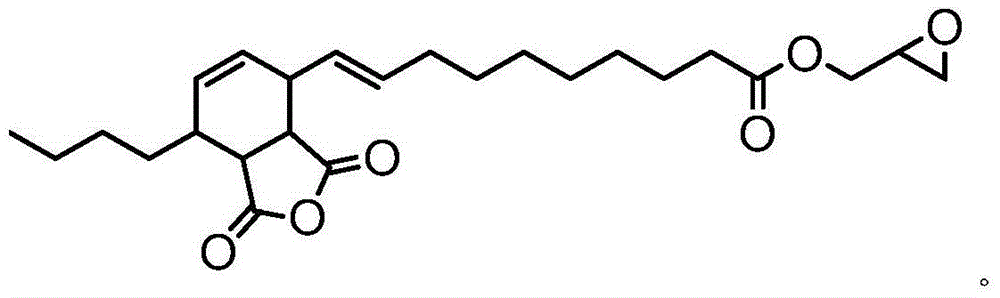
[0021] Add 1 mole of α-caryoic acid and 6 moles of epichlorohydrin into a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer and a reflux condenser, and raise the temperature to 117° C. for 2 hours. Cool to 20°C, add 1 mole of solid sodium hydroxide and 0.001 mole of benzyltriethylammonium chloride, and stir for 12 hours. Filtrate and recover excess epichlorohydrin to obtain α-glycidyl chertate. 1 mole of α-glycidyl cartonate was reacted with 1 mole of maleic anhydride at 90°C for 2 hours to obtain a self-curing epoxy resin containing anhydride groups.
[0022] 100 grams of self-curing epoxy resin containing anhydride groups obtained in Example 1 and 0.1 grams of 2-ethyl-4-methylimidazole catalyst are mixed, injected into the V type mold designed according to ASTM D638, at 120 ° C Curing was performed for 2 hours, followed by post-curing at 160° C. for 4 hours. After demoulding, 5 parallel specimens were obtained, and tensile tests were performed on the specimens according to AS...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add 1 mole of α-carnitic acid and 6 moles of epichlorohydrin into a three-neck flask equipped with a thermometer and a reflux condenser, and raise the temperature to 100° C. for 6 hours. Cool to 60°C, add 1 mole of solid sodium hydroxide and 0.001 mole of benzyltriethylammonium chloride, and stir for 6 hours. Filtrate and recover excess epichlorohydrin to obtain α-glycidyl chertate. 1 mole of α-glycidyl chertate was reacted with 1 mole of maleic anhydride at 110° C. for 0.5 hour to obtain a self-curing epoxy resin containing anhydride groups.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Add 1 mole of dehydrated ricinoleic acid and 6 moles of epichlorohydrin into a three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer and a reflux condenser, and raise the temperature to 117° C. for 2 hours. Cool to 20°C, add 1 mole of solid sodium hydroxide and 0.001 mole of benzyltriethylammonium chloride, and stir for 12 hours. Filtrate, recover excess epichlorohydrin to obtain dehydrated castor oil glycidyl ester. 1 mole of dehydrated castor oil glycidyl ester was reacted with 1 mole of maleic anhydride at 90°C for 2 hours to obtain a self-curing epoxy resin containing acid anhydride groups.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com