Semiconductor device and clock data recovery system comprising semiconductor device
A semiconductor and transistor technology, applied in the fields of semiconductor devices and clock data recovery systems, can solve problems such as inability to apply a latch circuit, and achieve the effect of suppressing the decrease in gain and ensuring receiving performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
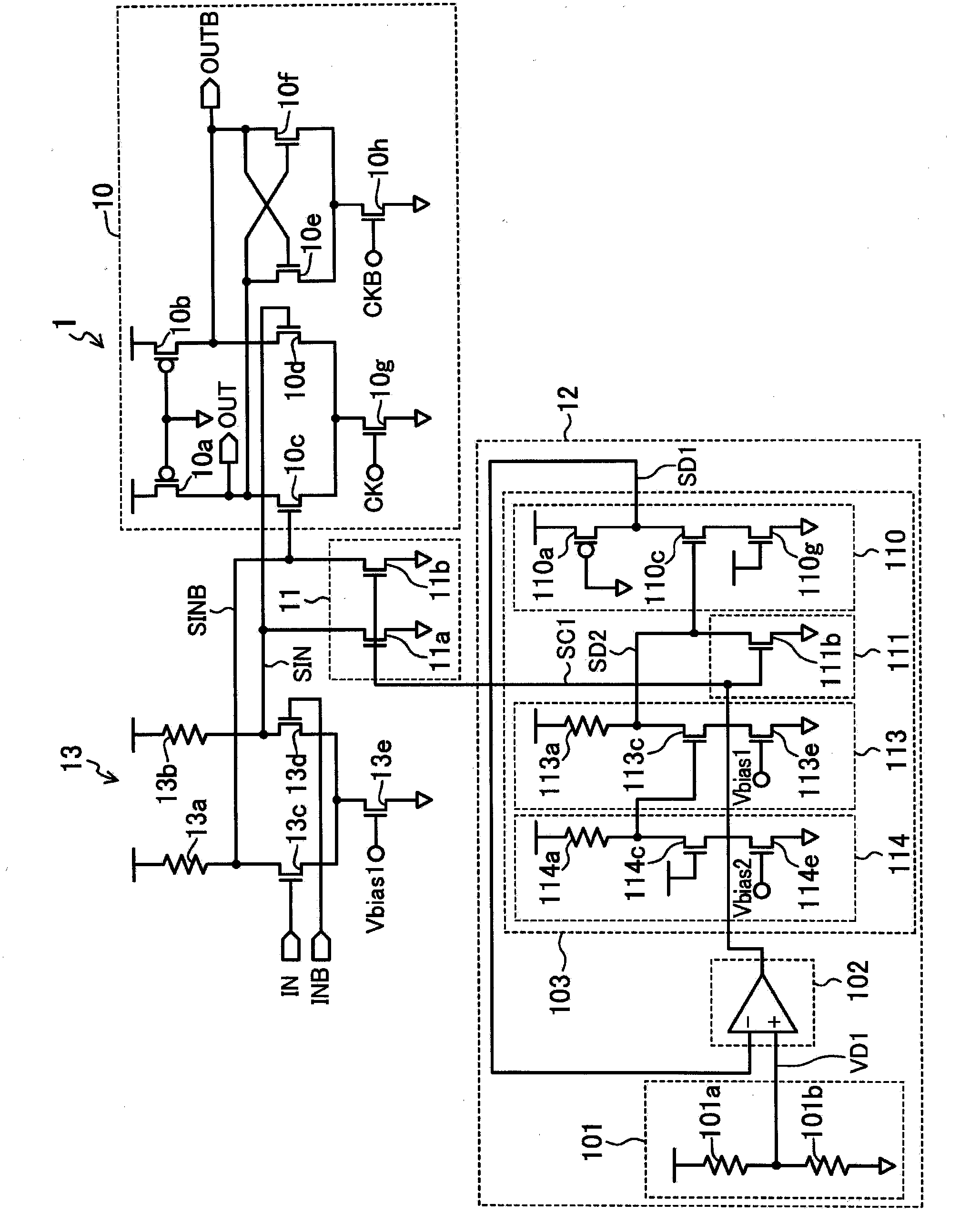
[0033] figure 1 It is a diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the semiconductor device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0034] The latch circuit 1 includes a sampling unit 10 , a common adjustment unit 11 , and a common control unit 12 .
[0035] The sampling unit 10 includes: nMOS transistors 10c and 10d as differential pair transistors whose gates are connected to the differential input nodes SINB and SIN; and a pair of transistors whose gates are connected to the drains of the nMOS transistors 10c and 10d. The nMOS transistors 10e and 10f that constitute the holding circuit; the gate receives the clock CK as the first clock signal, and the nMOS transistor 10g that performs on-off control of the actions of the nMOS transistors 10c and 10d; the gate receives the second clock signal The clock CKB is the nMOS transistor 10h that controls the on-off operation of the nMOS transistors 10e and 10f; it is connected between the powe...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0075] Figure 4 It is a diagram showing an example of the circuit configuration of the semiconductor device according to the second embodiment of the present invention. Figure 4 In the semiconductor device, with figure 1 The difference is that a plurality of sampling units 10 are provided.
[0076] Figure 4 In the latch circuit 1B, the gates of the differential pair transistors 10c and 10d contained in each of the plurality of sampling units 10 are respectively connected to the differential input nodes SINB and SIN, and the differential input nodes SINB and SIN are respectively connected to the common regulator The drains of the nMOS transistors 11b and 11a of the part 11. In addition, different clocks CK0 and CK1 are supplied to the nMOS transistors 10g included in the plurality of sampling units 10, respectively. Similarly, different clocks CK0B and CK1B are supplied to the nMOS transistors 10h respectively included in the plurality of sampling units 10 . other part...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
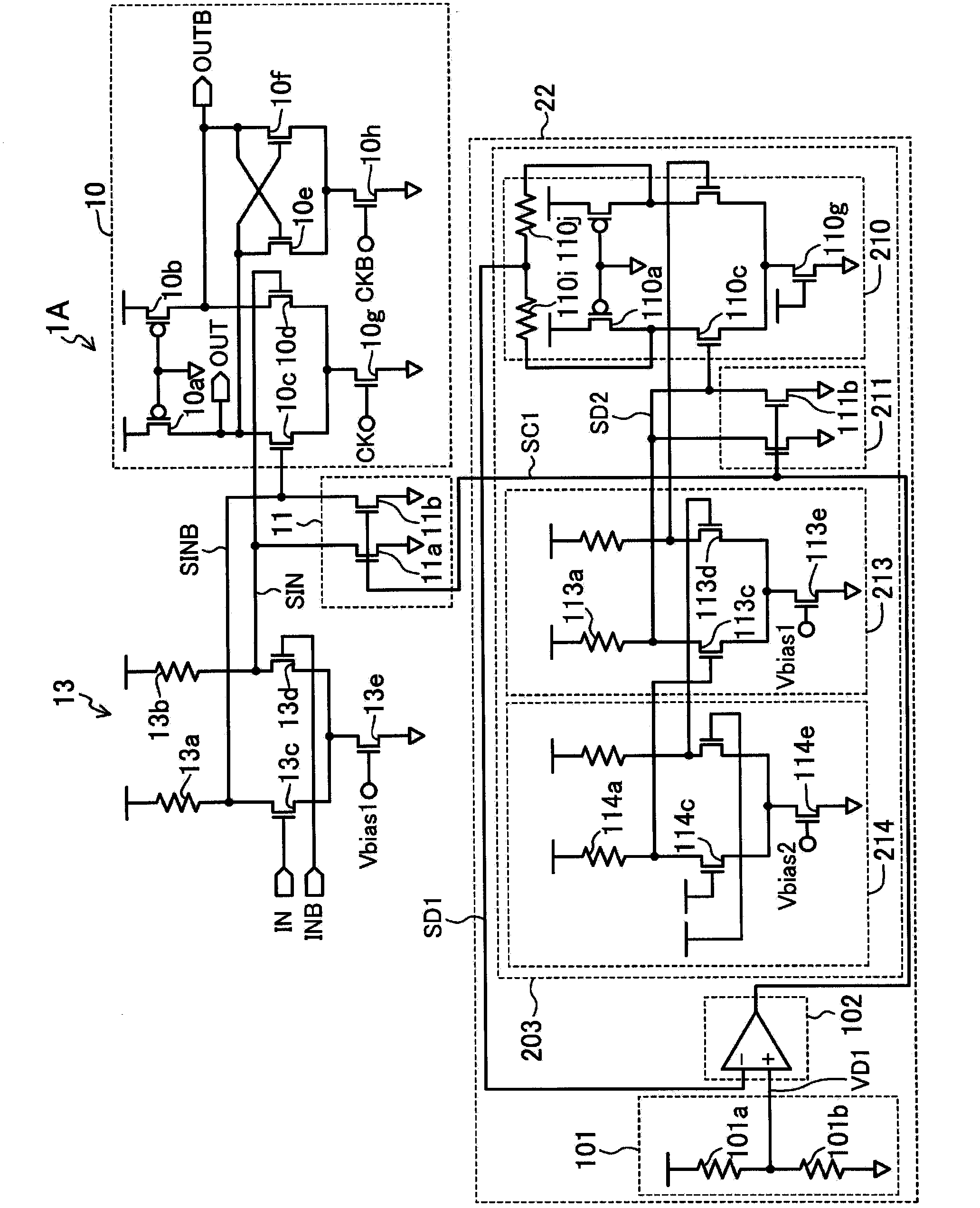
[0086] Image 6 It is a diagram showing an example of a circuit configuration of a semiconductor device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. Image 6 In the semiconductor device, with figure 1 The difference is that it has multiple output amplifiers 13 , multiple common regulators 11 and multiple sampling units 10 .
[0087] exist Image 6 In the semiconductor device of , differential input nodes SINB, SIN and differential input nodes SINB1, SIN1 to which the output signals of the plurality of output amplifiers 13 are respectively connected are connected to gates of nMOS transistors 10c, 10d of different sampling units 10, respectively. The drains of the nMOS transistors 11b and 11a of the different common regulators 11 are connected to the differential input nodes SINB and SIN and the differential input nodes SINB1 and SIN1 respectively. In addition, different clocks CK0 and CK1 are supplied to the nMOS transistors 10 g included in the plurality of sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com