Feeder interconnection converter
A technology of converters and feeders, which is applied in power transmission AC networks, AC network load balancing, and AC networks to reduce harmonics/ripples, etc., and can solve problems such as low voltage, volatility, and voltage fluctuations at the end of radial feeder lines , to achieve the effect of improving power quality, balancing power distribution, and reducing burden
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
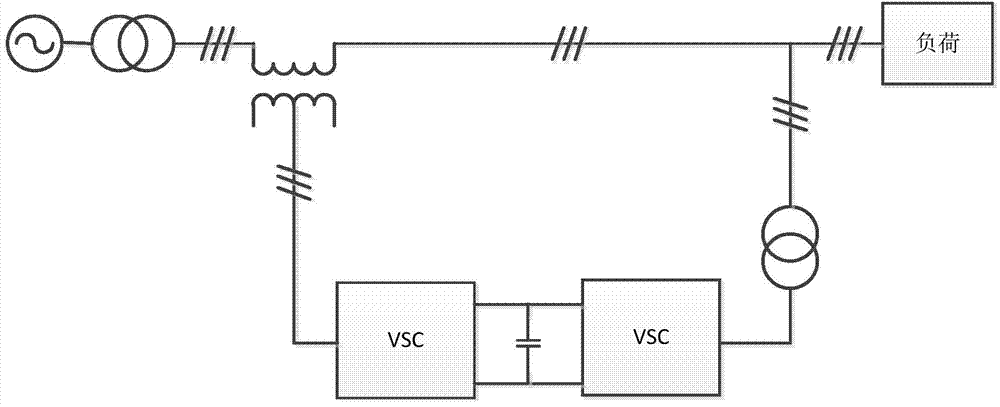
[0042] Embodiment 1 of the present invention such as figure 2As shown, the present invention includes a distributed power generation unit 33 , a first controlled power source 30 , a second controlled power source 32 , a first feeder unit 10 and a second feeder unit 20 . The distributed power generation unit 33 may be various energy power generation systems such as photovoltaic power generation, wind power generation or fuel cell power generation. The first feeder unit 10 includes a power supply and a load, and the load may be a common load or a sensitive load. The second feeder unit 20 includes a power supply and a load, and the load may be a common load or a sensitive load. The power supply of the first feeder unit 10, the load of the first feeder unit 10 and the isolation transformer 14 output by the first controlled power supply 30 are connected; the power supply of the second feeder unit 20, the load of the second feeder unit 20 and the second received The isolation tra...
Embodiment 2
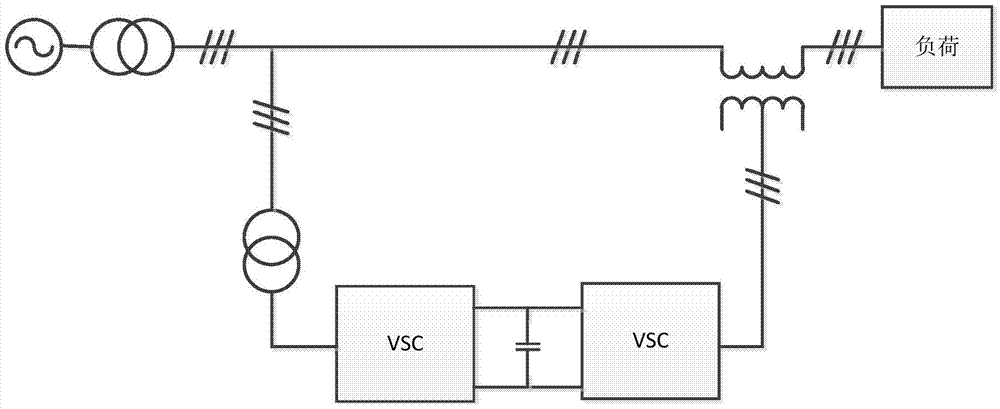
[0050] Figure 7 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of the main circuit of Embodiment 2 of the feeder interconnection converter. Contains an energy storage unit 33, a first controlled power supply 30, a second controlled power supply 32, a first feeder unit 10 and a second feeder unit 20; the first feeder unit 10 includes a power supply and a load, and the load can be an ordinary load or Can be sensitive load. The second feeder unit 20 includes a power supply and a load, and the load may be a common load or a sensitive load. The power supply of the first feeder unit 10, the load of the first feeder unit 10 and the isolation transformer 14 output by the first controlled power supply 30 are connected; the power supply of the second feeder unit 20, the load of the second feeder unit 20 and the second received The isolation transformer 17 output by the control power supply 32 is connected. The energy storage unit 33 is respectively connected to the DC bus bars of the first...
Embodiment 3
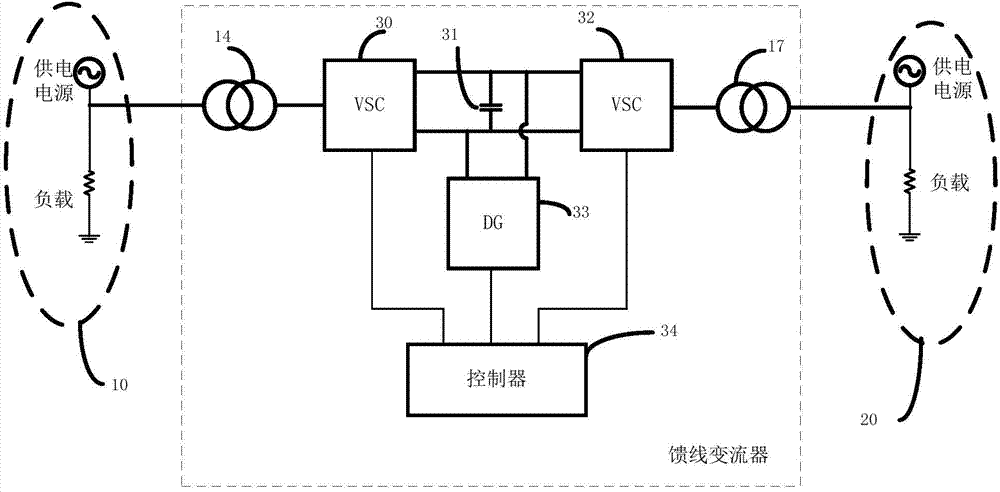
[0053] Figure 8 The main circuit of the feeder-interconnected converter shown does not contain distributed generation units. The feeder interconnection converter includes a first controlled power supply 30, a second controlled power supply 32, a first feeder unit 10 and a second feeder unit 20; the first controlled power supply 30 passes through the isolation transformer 14 and the first feeder unit 10 connection, the first controlled power supply 30, the capacitor 31 and the second controlled power supply 32 are connected in series through the DC bus, and the second controlled power supply 32 is connected to the second feeder unit 20 through the isolation transformer 15; the two controlled power supplies 30, 32 connects the first feeder unit 10 and the second feeder unit 20 to realize the flow of active power and reactive power between the two feeder units.
[0054] In the method of transferring active power between multiple feeder units, the sampling detection unit in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com