Method for WLAN indoor positioning Radio Map updating based on information entropy
An indoor positioning and update method technology, applied in the field of information theory, can solve problems such as poor positioning accuracy, heavy update workload, and complex positioning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: WLAN indoor positioning Radio Map update and positioning method based on information entropy. It includes the following steps:
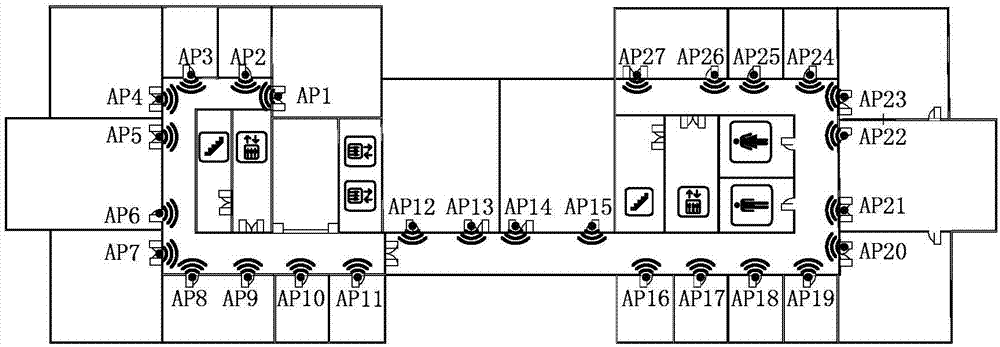
[0021] Step 1: According to the relevant characteristics of radio propagation indoors and the frequency bands that APs can use, reasonably deploy APs to ensure that the signal strengths from at least two APs can be collected anywhere in the environment, and the signal power is greater than or equal to -95dBm;
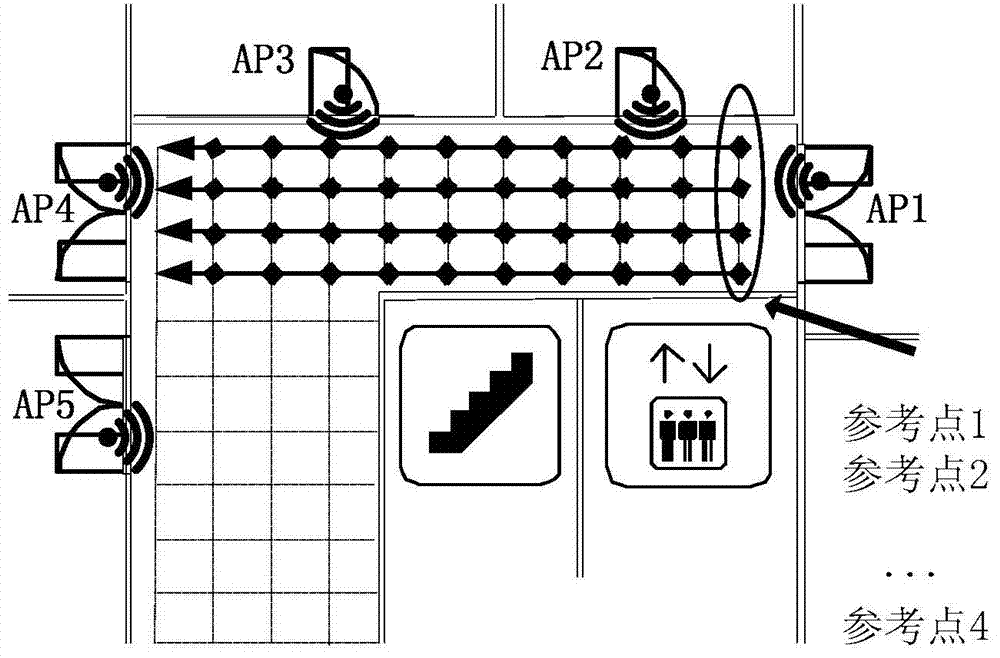
[0022] Step 2: According to the indoor environment that needs to be positioned, select the appropriate coordinate origin to establish a two-dimensional rectangular coordinate system, set the reference points evenly and calibrate the coordinates of each reference point according to the rectangular coordinate system, and measure the distance from each AP at each reference point Radiation signal strength and save the two-dimensional coordinates of the reference point and the measured AP signal strength in the Radio Map;
[0...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Specific embodiment two: In step 2 of this embodiment, "measure the radiation signal strength from each AP at each reference point and save the two-dimensional coordinates of the reference point and the measured AP signal strength in the Radio Map" The specific operation steps are:
[0028] At each reference point in the area to be updated, use the signal receiver to collect and record the received signal strength RSS value from each AP n times and record the two-dimensional coordinates of the reference point, forming N×n×(M+2) Matrix, where N is the number of reference points in the area to be updated, n is the number of signal acquisitions at each reference point, M in M+2 represents the number of APs in the environment, 2 represents two-dimensional coordinates, and is saved in Radio Map middle.
[0029] Other implementation manners are the same as the specific implementation manner 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
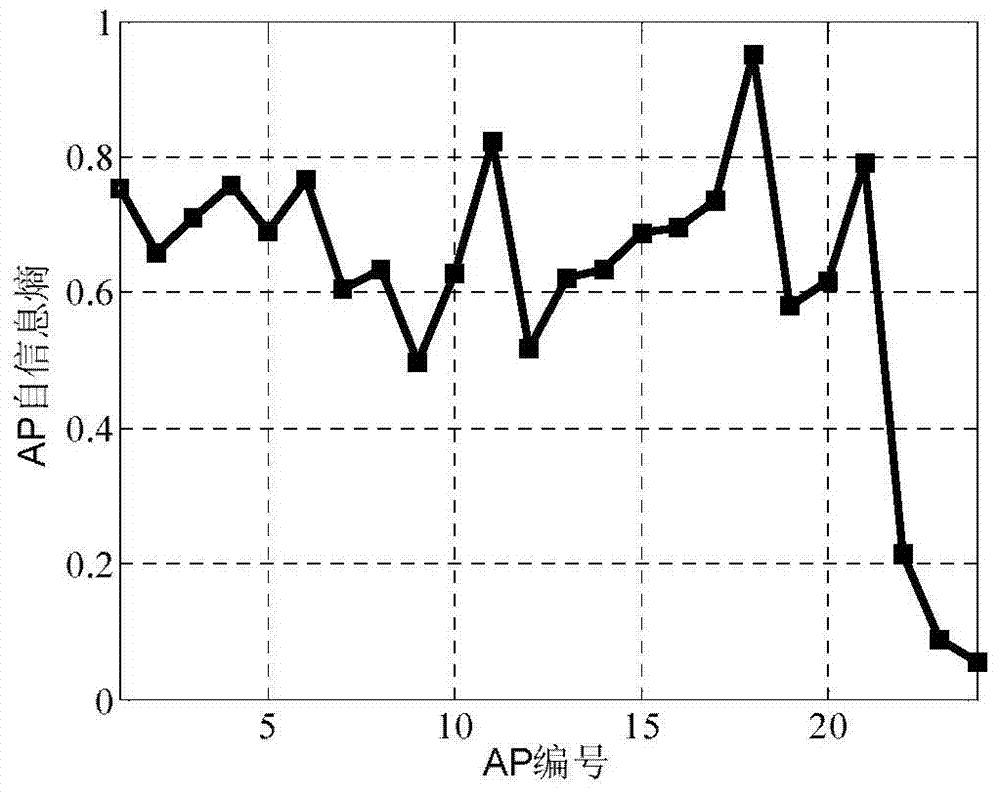
[0030] Specific implementation mode three: the specific operation steps of "selecting r APs with larger information entropy gains" in step 3 of this implementation mode are as follows:
[0031] Step 3.1: Calculate the information entropy gain (Information Gain, IG) of each AP in the area to be updated, according to the formula (1), where H(l) represents the information entropy of the user location, as shown in the formula (2), where p(l g ) means that when the user is at position l g , the probability at g={1,2,…N}, for the convenience of use, it is considered that the probability of the user at each reference point is equal to Thus formula (2) is shown in formula (4), when the test point is obtained from the ith AP (AP i When the signal strength RSS value of ) is known, the uncertainty of the actual position of the test point, that is, the conditional entropy value H(l|AP i ) is calculated as formula (4), where p(l g |AP i =v e ) stands for AP i =v e Under the condit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com