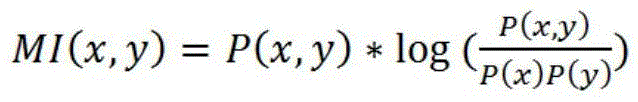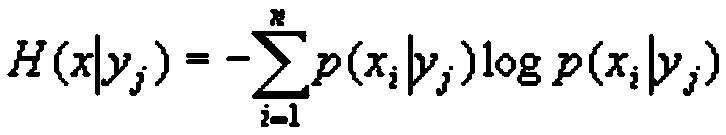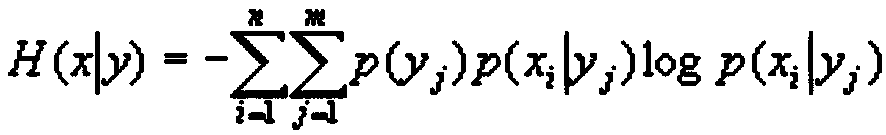Patents
Literature
55 results about "Conditional entropy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In information theory, the conditional entropy (or equivocation) quantifies the amount of information needed to describe the outcome of a random variable Y given that the value of another random variable X is known. Here, information is measured in shannons, nats, or hartleys. The entropy of Y conditioned on X is written as H(Y|X).
Network attack detection method and apparatus
ActiveCN104967629ASolve the technical problem of low attack detection accuracyImprove detection accuracyTransmissionDomain nameData set
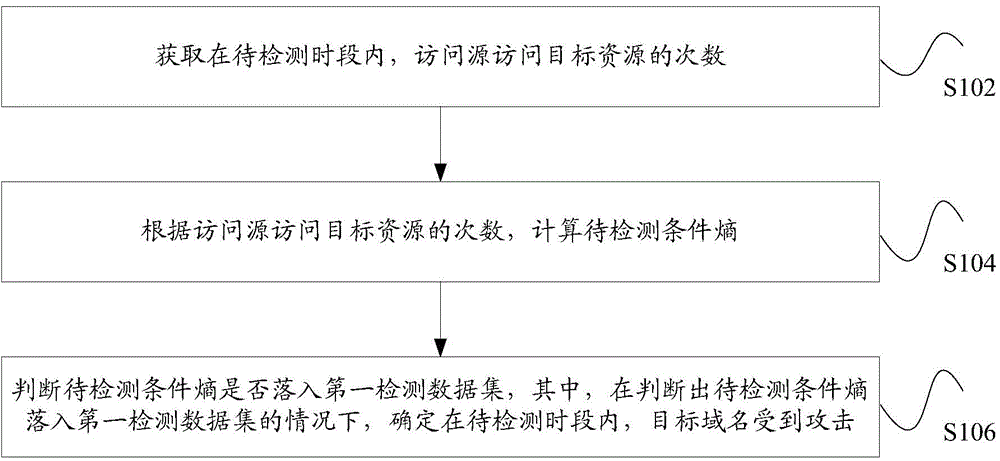
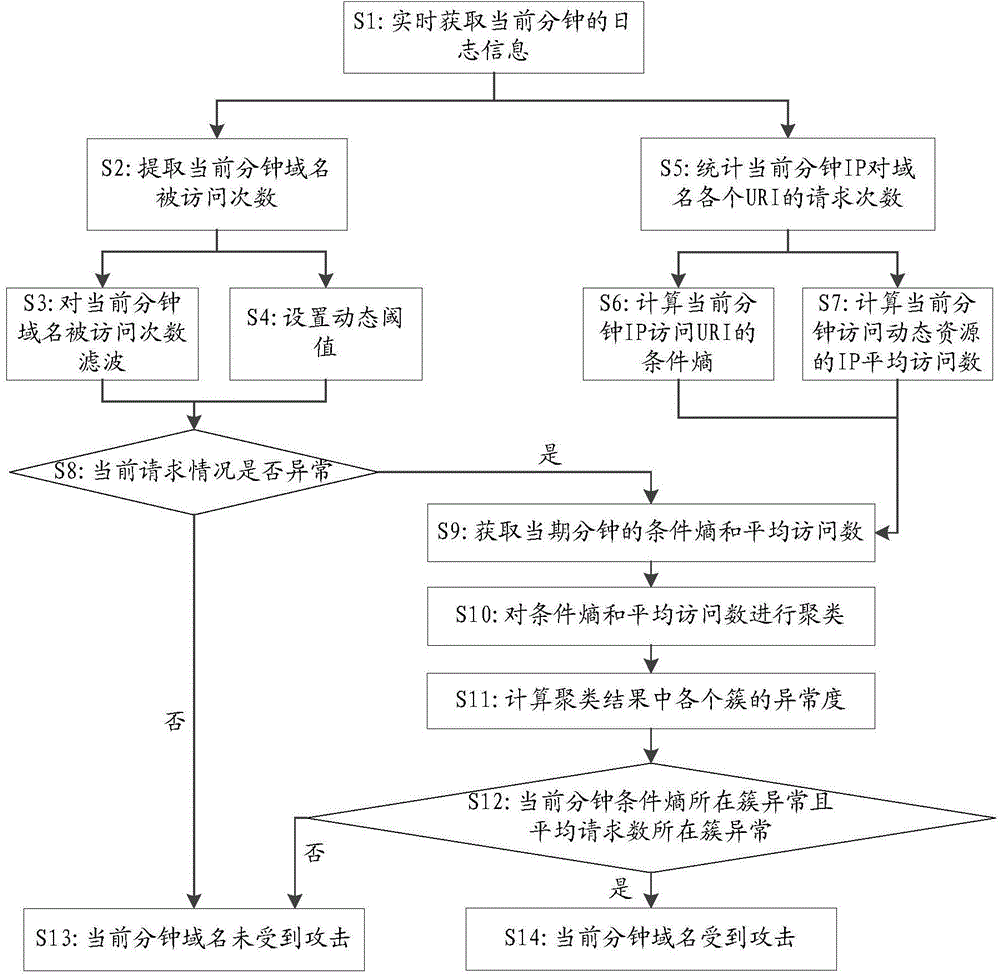
The invention discloses a network attack detection method and an apparatus. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring target resource access times of an access source in a period to be detected, wherein the target resource is at least one resource related to a target domain name; according to the target resource access times of the access source, calculating a conditional entropy to be detected, wherein the conditional entropy to be detected is a conditional entropy of the access source when the target resource is accessed in the period to be detected; determining whether the conditional entropy to be detected is in a first detection data set, wherein under the condition that the conditional entropy to be detected is in the first detection data set, a situation that the target domain name is attacked in the period to be detected is determined. In the related technology, only according to an access frequency of the access source or only according to a frequency of being accessed of the target resource, whether the target domain name is attacked is determined so that network attack detection accuracy is low. By using the method and the apparatus of the invention, the above technical problem is solved.
Owner:CHINANETCENT TECH
Automatic hot topic mining system based on internet corpora
ActiveCN105488196AReal time miningMining automaticSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationConditional entropyAlgorithm
The invention discloses an automatic hot topic mining system based on internet corpora. The system is composed of two routes: 1) crawling hot words of existing hot word statistics sites, and generating a series of hot topics through the steps of clustering, entity extraction and key word mining; and 2) extracting n-gram from massive news documents, mining high-frequency hot words from the massive news documents by calculating mutual information and conditional entropy values of the n-gram, and recognizing new topics by using an event detection method based on a time sequence. By adopting the system, not only can current hot events be mined in real time, but also can relevant keywords and named entities of a hot topic be mined when the topic is generated.
Owner:北京一览群智数据科技有限责任公司
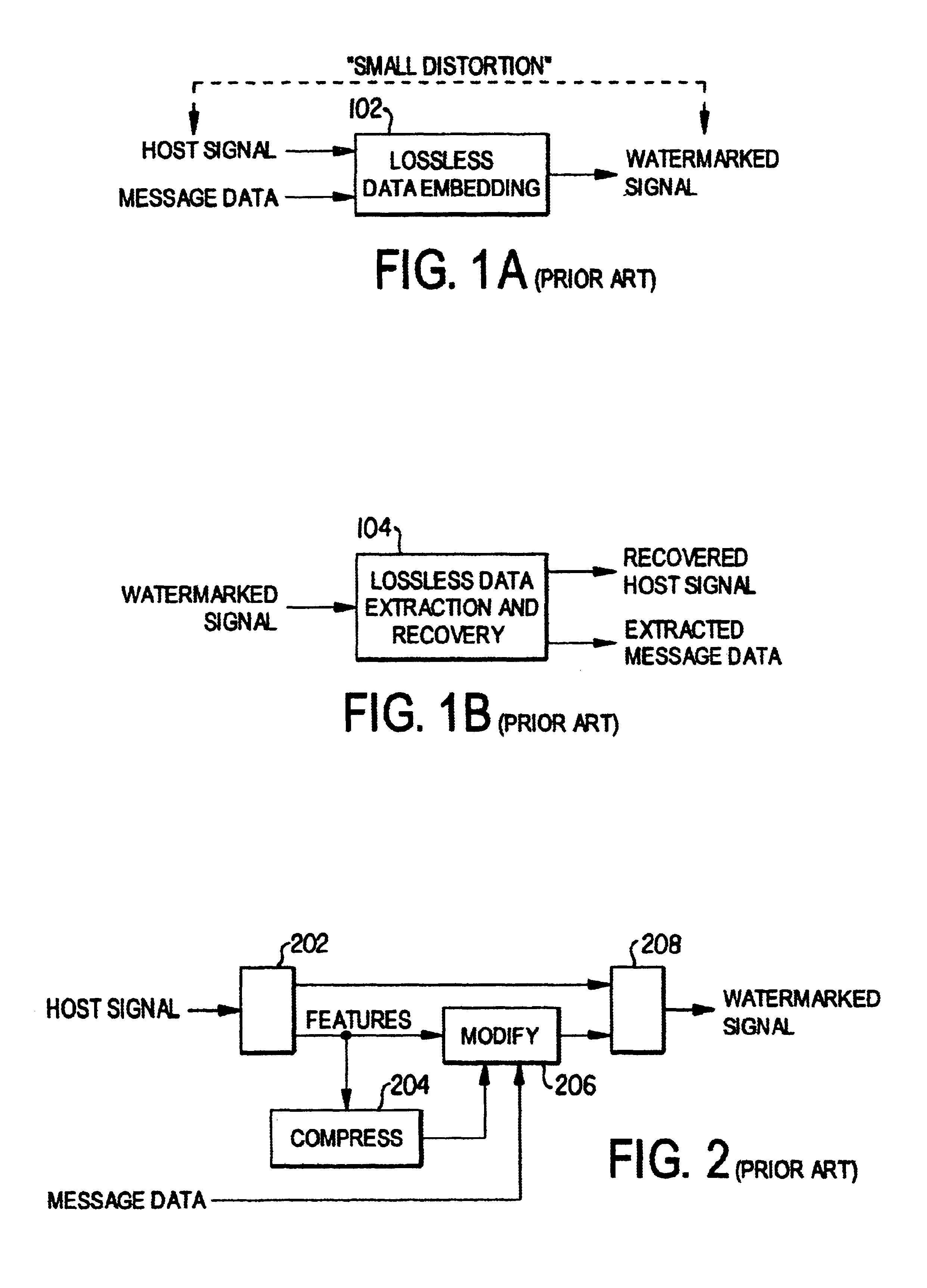
System and method for embedding information in digital signals
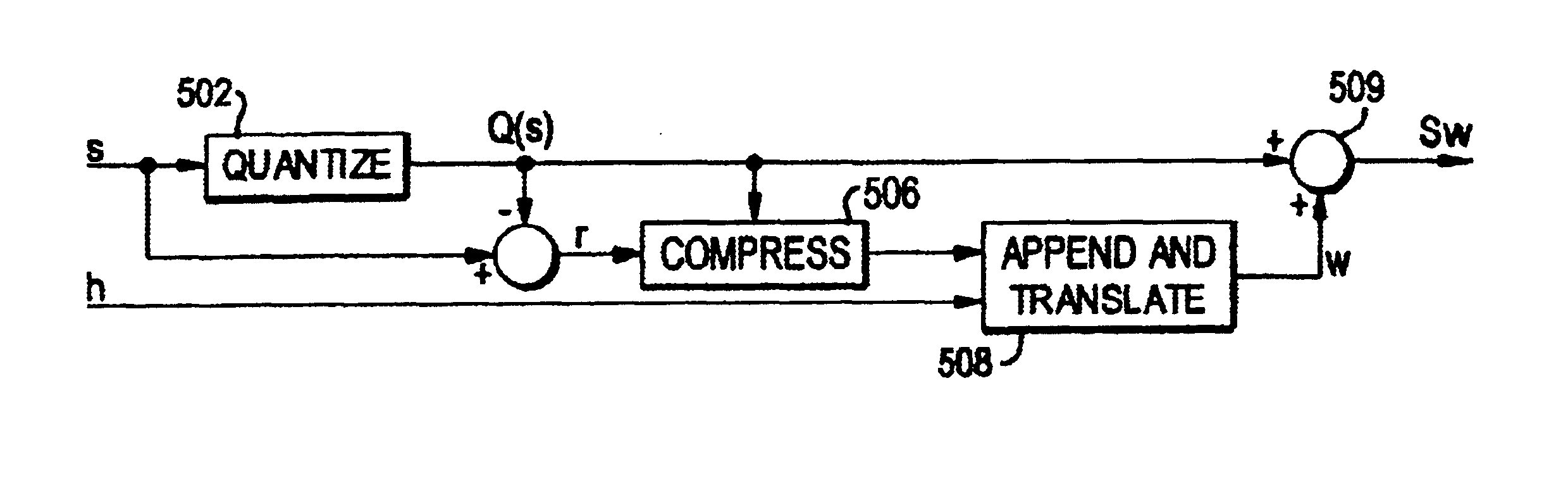
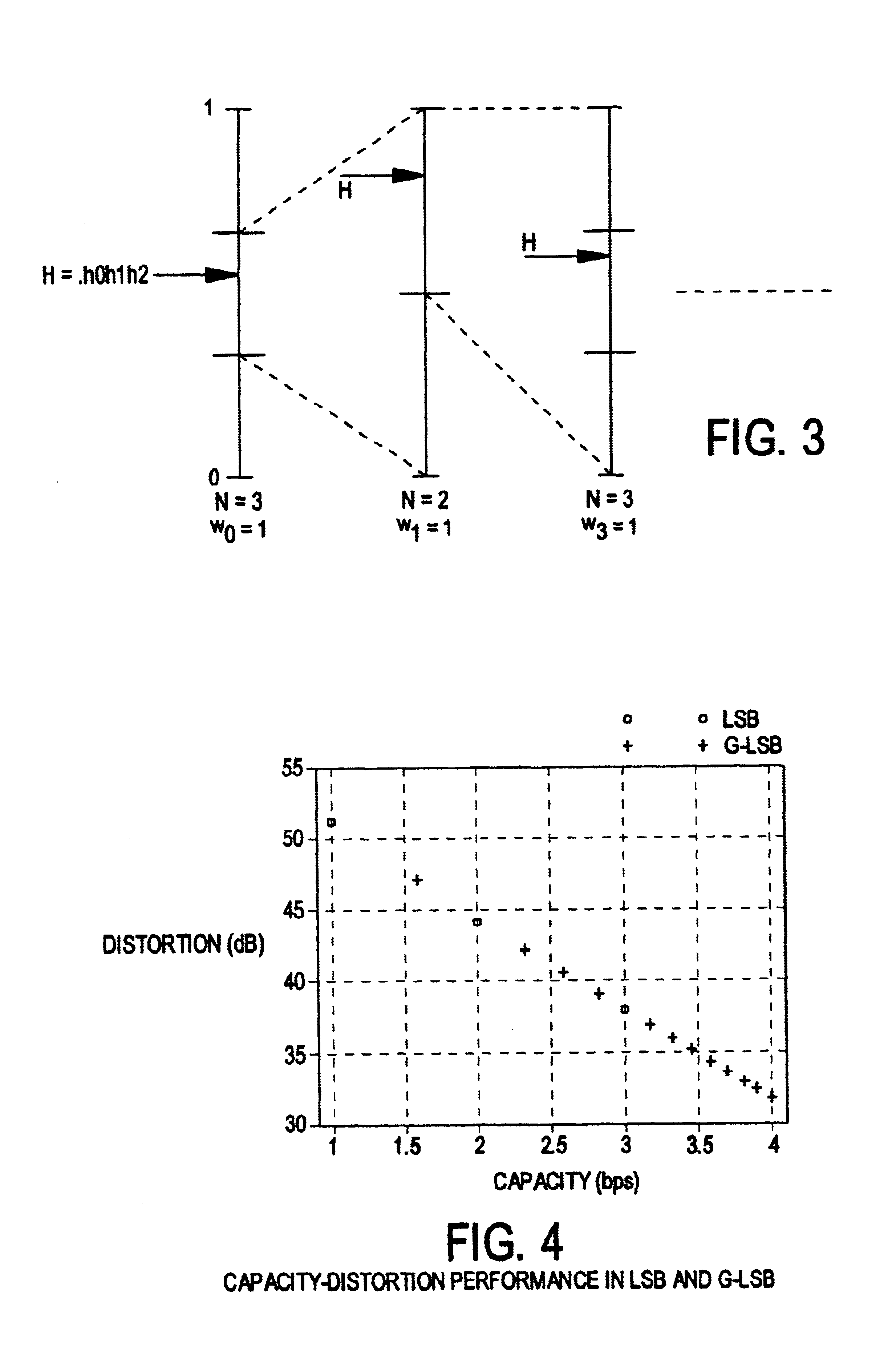
InactiveUS6895101B2Fine granularityEasy to compressCharacter and pattern recognitionImage watermarkingData capacityConditional entropy
A lossless, reversible data embedding technique uses a generalization of least-significant-bit modification. The portions of the signal that are susceptible to embedding distortion are compressed and sent as part of the embedded payload. A prediction-based conditional entropy coder uses unaltered portions of the host signal to improve lossless data capacity.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
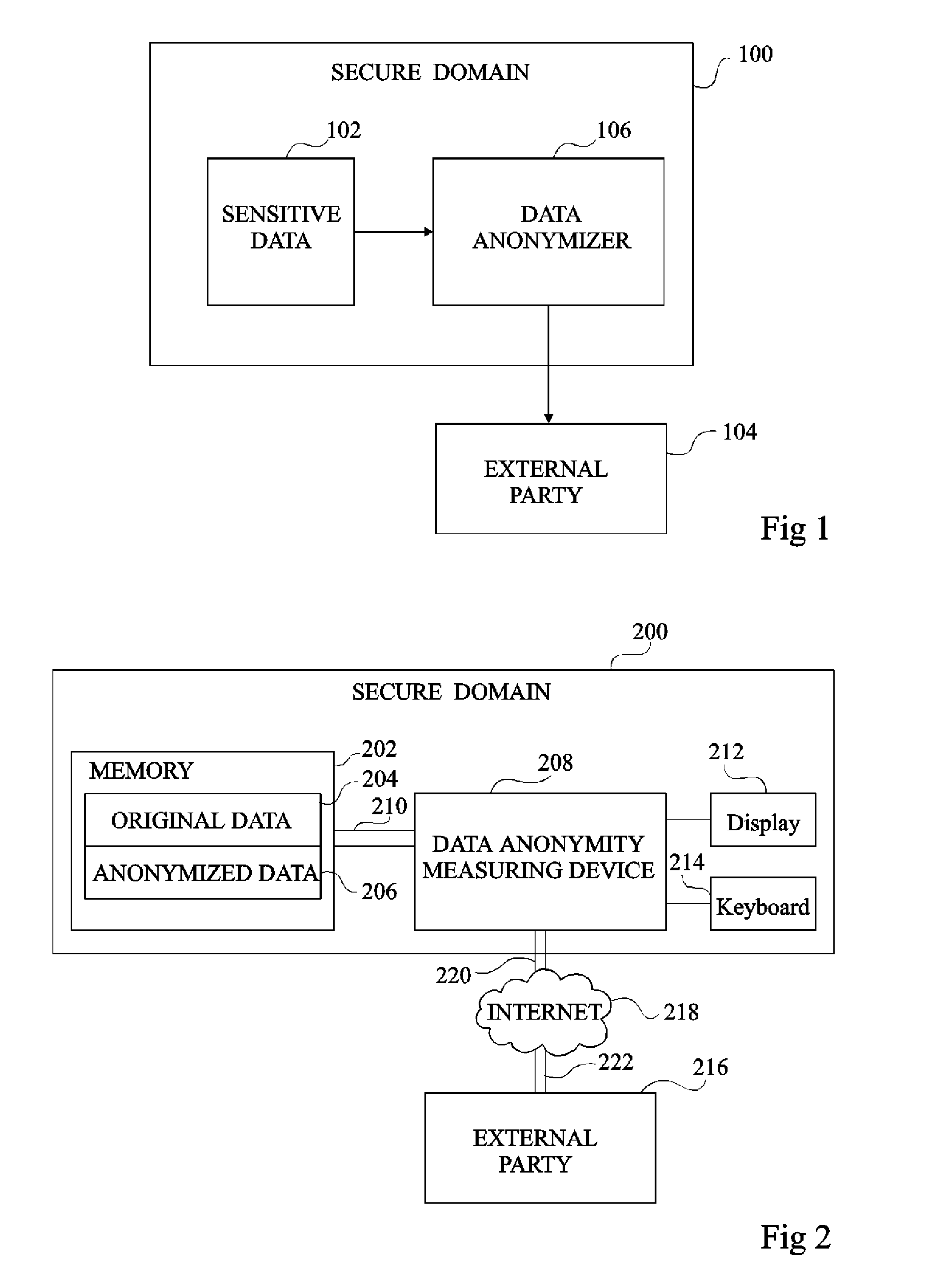
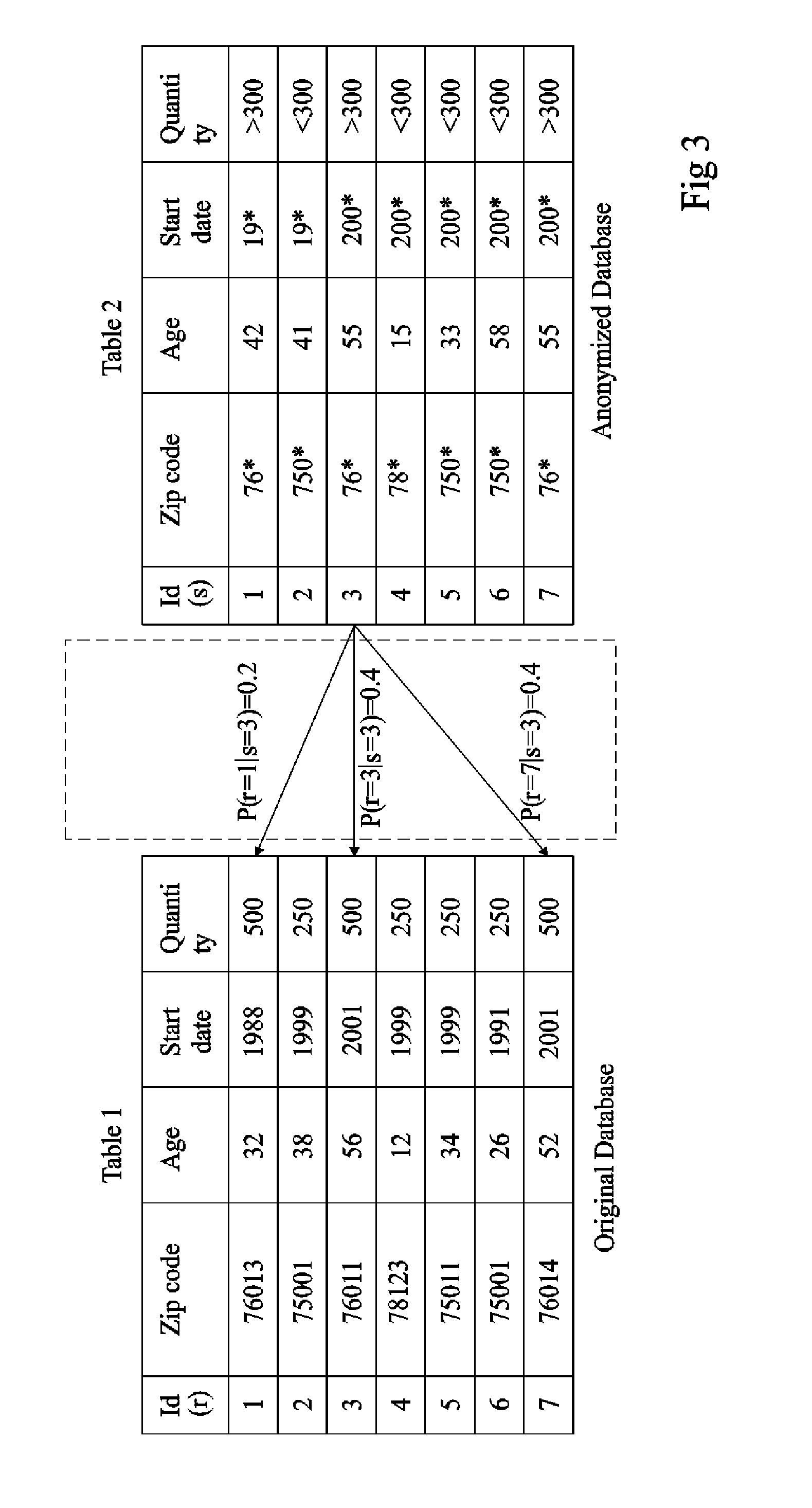
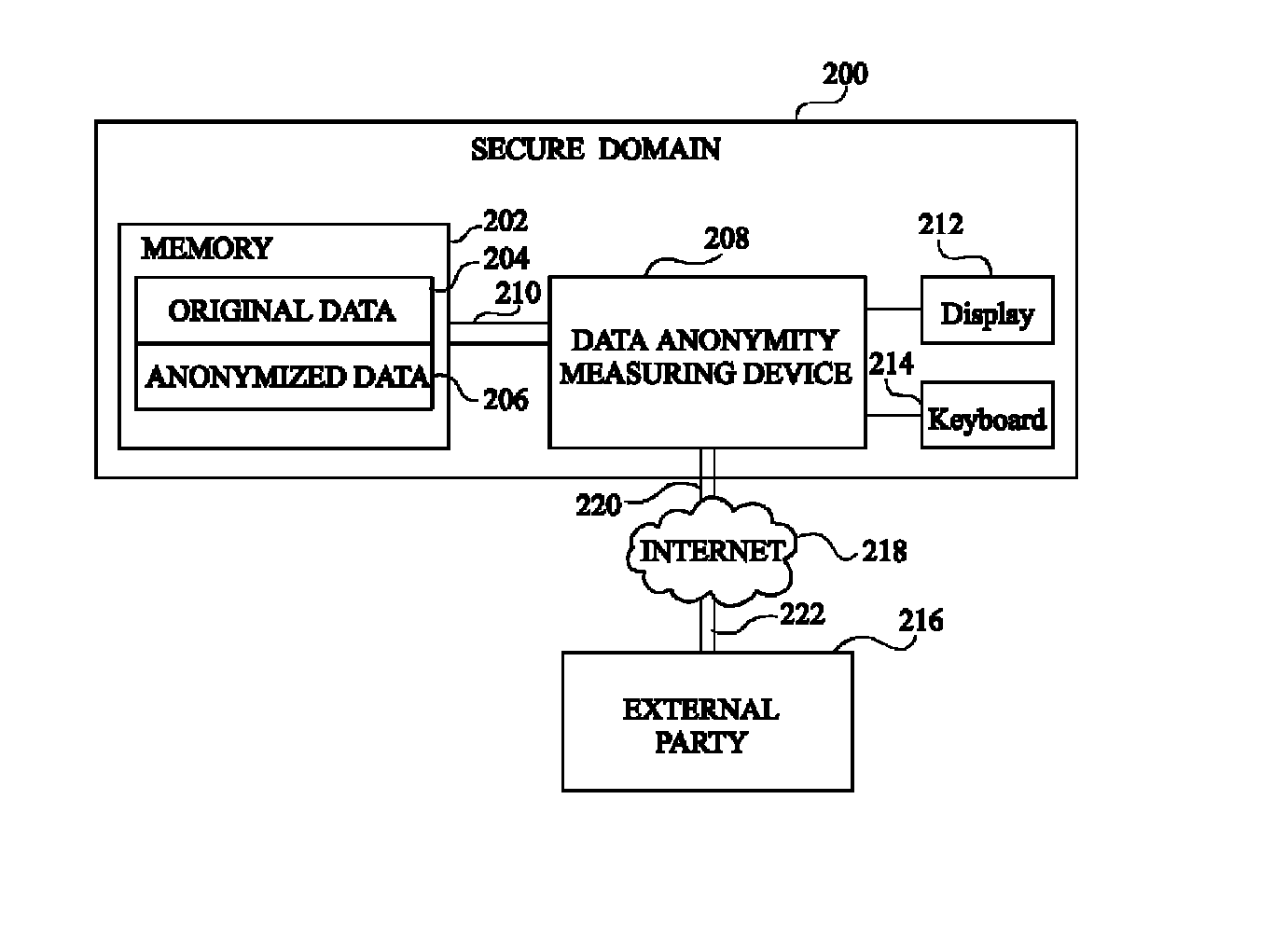
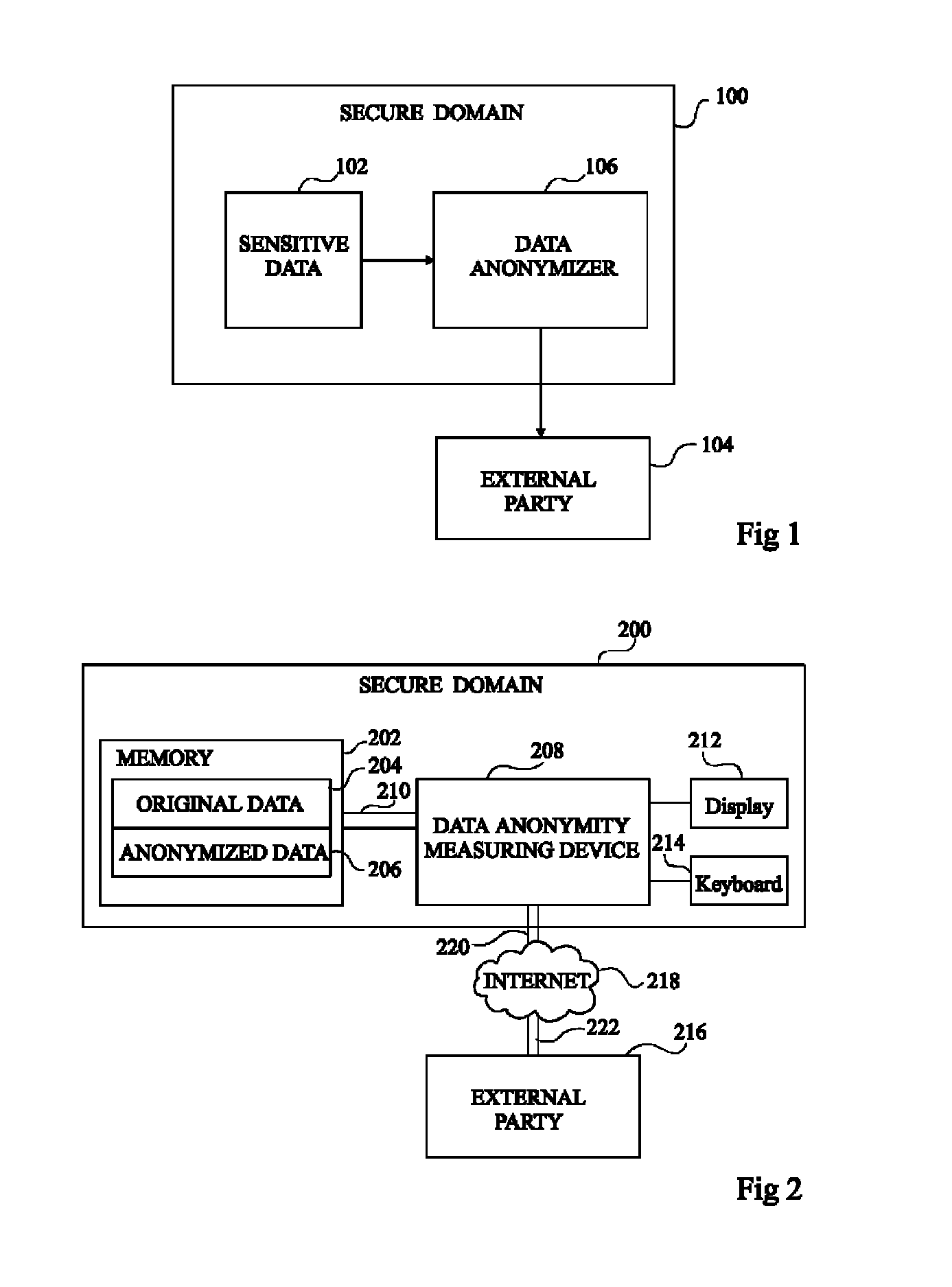
Anonymity measuring device
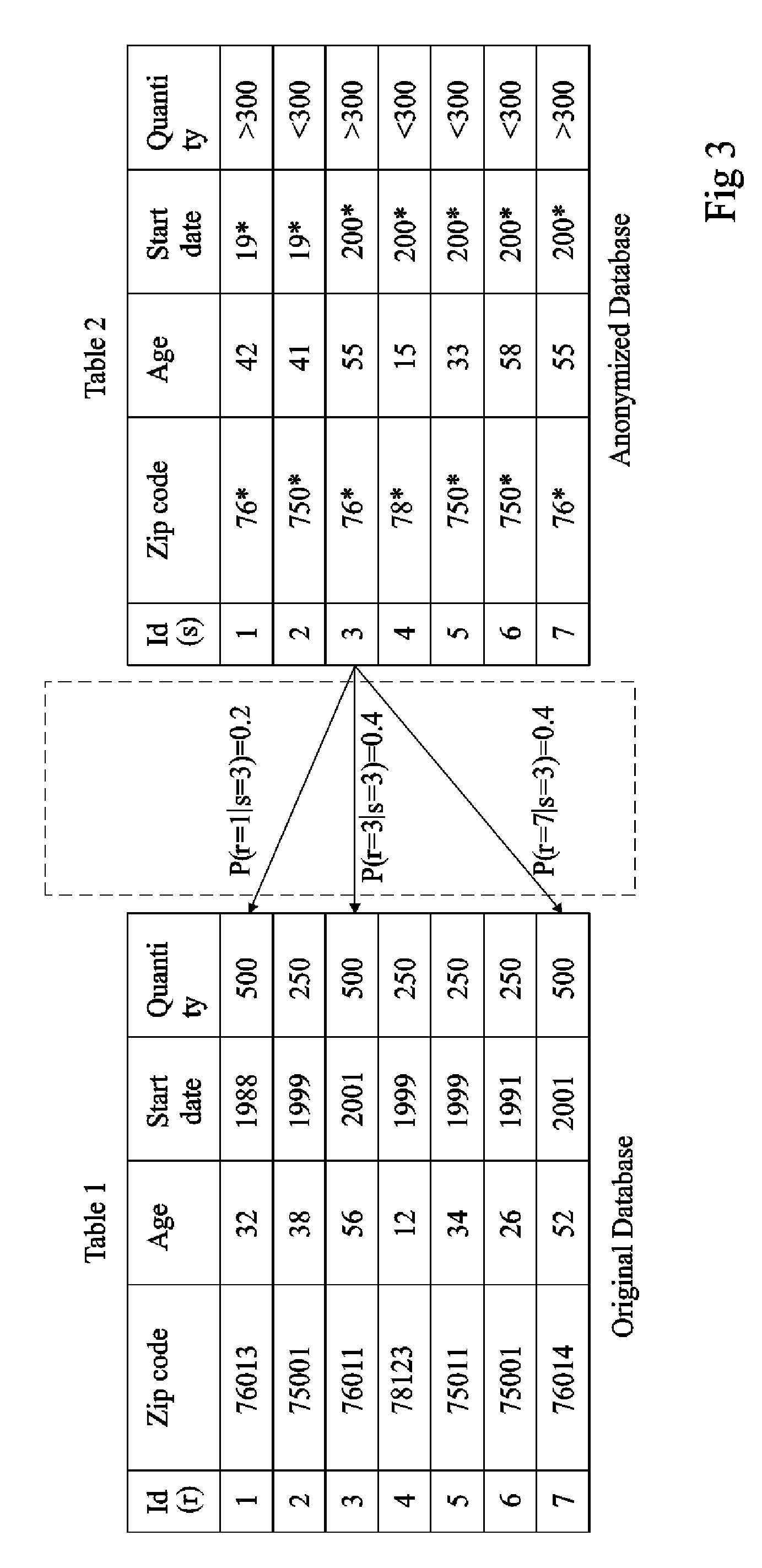
The invention concerns a data anonymity measuring device for selectively transmitting an anonymised database to a third party comprising: calculation means (402) coupled to at least one memory, the memory storing an original database (204) and said anonymized database (206), said calculation means arranged to calculate the conditional entropy for each entry in said anonymized database based on entries in said original database; comparing means (406) arranged to compare at least one of said conditional entropies with a threshold value; and output means (410) arranged to transmit said anonymized database based on the result of said comparison.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
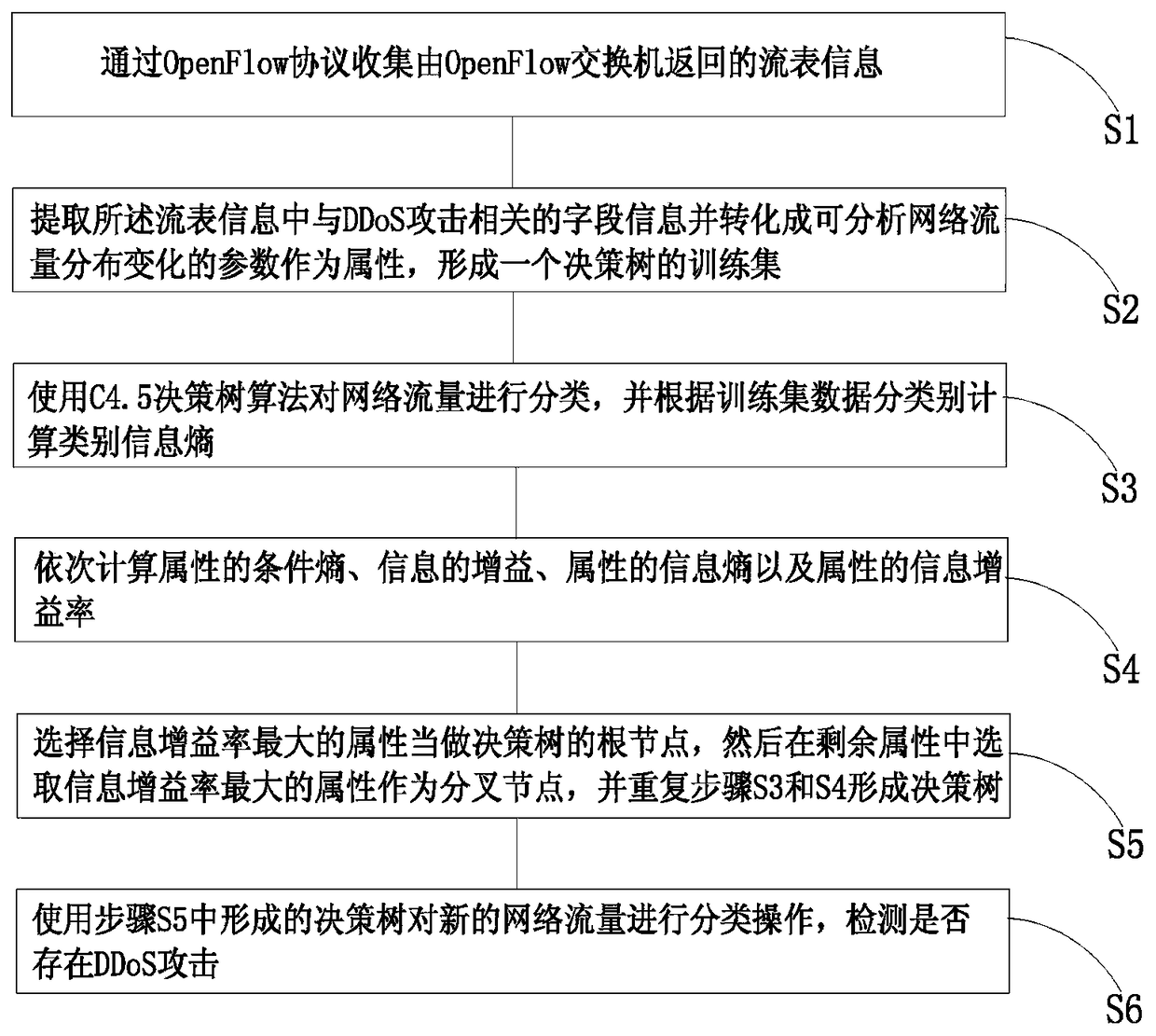
Distributed denial of service attack detection method based on C4.5 decision tree algorithm
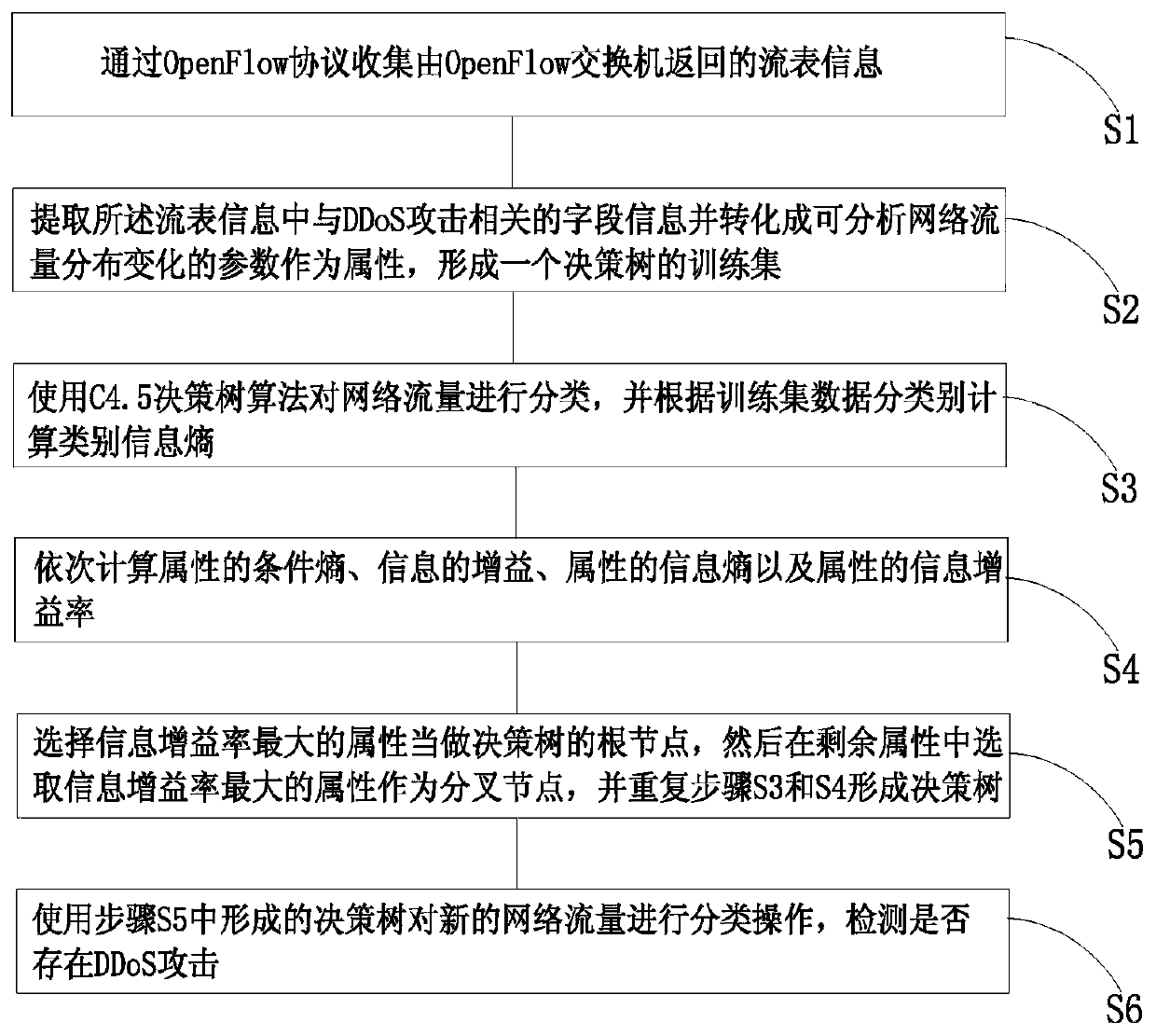
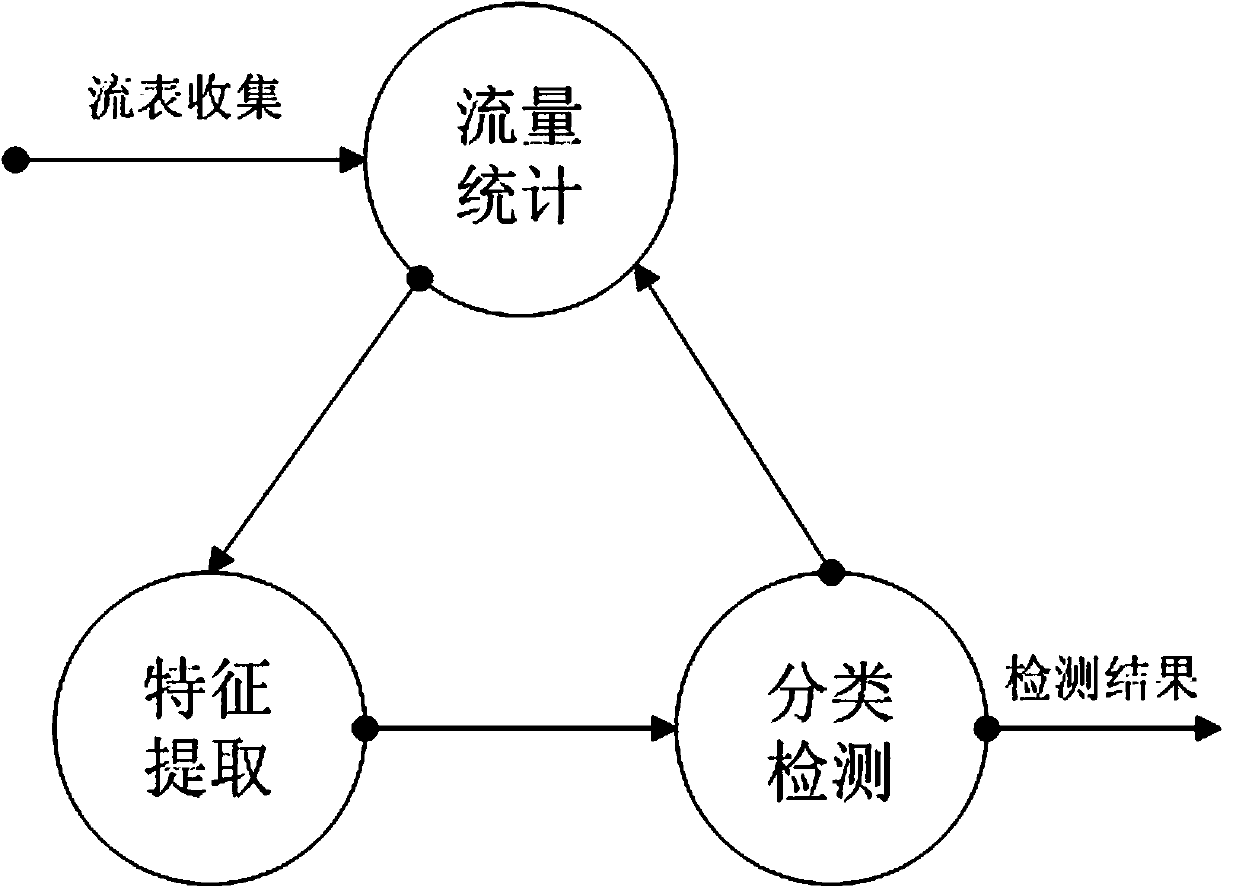
The invention discloses a distributed denial of service attack detection method based on a C4.5 decision tree algorithm in software defined network environment, and the method comprises the followingsteps: collecting flow table information returned back by an OpenFlow switch through an OpenFlow protocol; extracting field information related to a DDoS attack from the flow table information, converting the extracted information into parameters capable of analyzing network flow distribution variation and taking the parameters as attributes, and forming a training set of a decision tree; classifying flows with the C4.5 decision tree algorithm, calculating class information entropy according to training set data classes; orderly calculating conditional entropy of the attributes, gain of information, information entropy of the attributes and information gain ratio of the attributes; selecting the attribute with the highest information gain ratio as a root node of the decision tree, and selecting the attributes with highest information gain ratio from the residual attributes as a fork node, and repeating the steps above until forming the decision tree; and using the finally formed decision tree to perform classification operation for the new network flow, and detecting whether the DDoS attack exists. The method can detect the DDoS attack more accurately.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Sensor arrangement method for reducing uncertainty of structural mode recognition
ActiveCN108875178AReduce uncertaintyGuaranteed uncertaintyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsConditional entropyEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of civil engineering structure health monitoring, and provides a sensor arrangement method for reducing the uncertainty of structural mode recognition. Theinfluences of structure model errors and measurement noises on measurement data are separated; the structural rigidity changes are used as the model errors; and Gaussian noises are used as the measurement noises. By adopting a Monte Carlo method, a large number of possible situations are simulated to obtain a structural mode matrix under the condition of the model errors; a conditional entropy index is proposed for quantifying and calculating the uncertainty of a mode recognition parameter result; and the problem of an uncertain Fisher information array, which cannot be solved by a traditional information entropy method is solved by using the conditional entropy index. A position corresponding to the minimum value of the conditional entropy index is an optimal sensor arrangement position.According to the sensor arrangement method provided by the invention, the influences of the structural mode errors and the measurement noises on the structural mode recognition are fully considered;and a great help is provided for improving the precision of structural mode parameter recognition.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
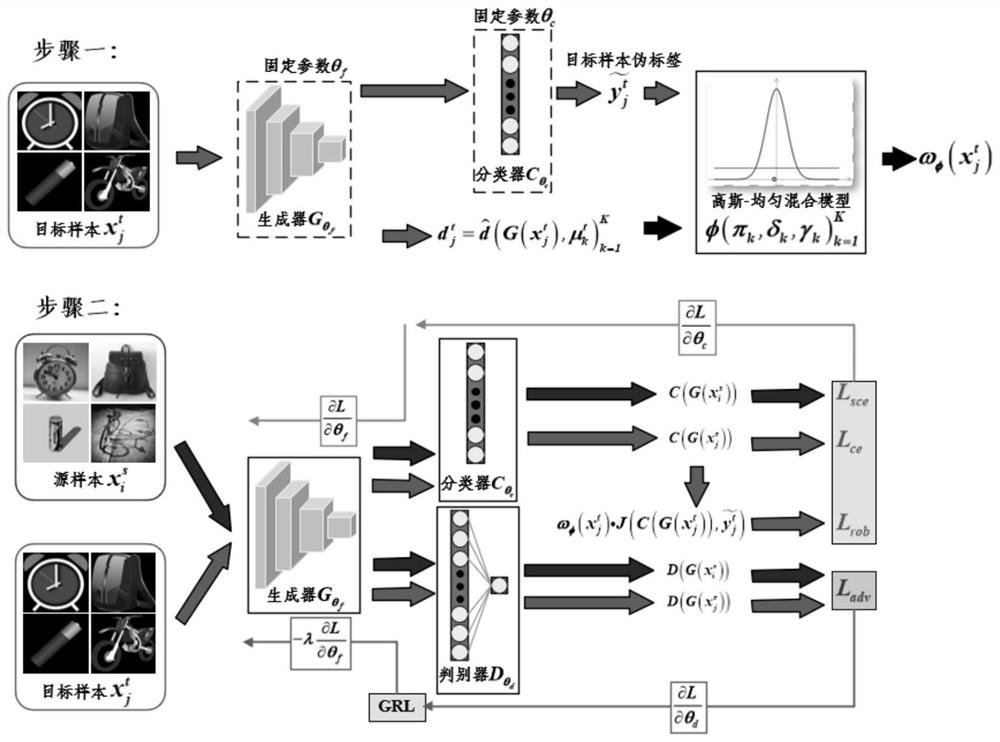
Pseudo label loss unsupervised adversarial domain adaptive picture classification method based on Gaussian uniform mixture model
PendingCN114492574ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsConditional entropyDecision boundary
The invention discloses a pseudo label loss unsupervised adversarial domain adaptive picture classification method based on a Gaussian uniform mixture model. According to the method, knowledge is migrated to a related target domain in a cross-domain manner by using a large amount of available annotation data of a related source domain through a transfer learning or domain adaptation method to obtain target data with labels; according to the domain adaptation method, Gaussian uniform mixture model detection outliers and a deep neural network are fused for image classification, the Gaussian uniform mixture model is used for modeling a cosine distance from target sample features of each class to a class mean value, and a target sample posterior probability is obtained and serves as an importance degree for estimating a target sample pseudo label; adding auxiliary pseudo tag loss proposed based on a target sample pseudo tag generated in the training process into training of the neural network; meanwhile, conditional entropy loss is minimized, so that learned features are far away from a decision boundary; a large number of experiments prove that the method can improve the picture classification accuracy of the deep network model.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
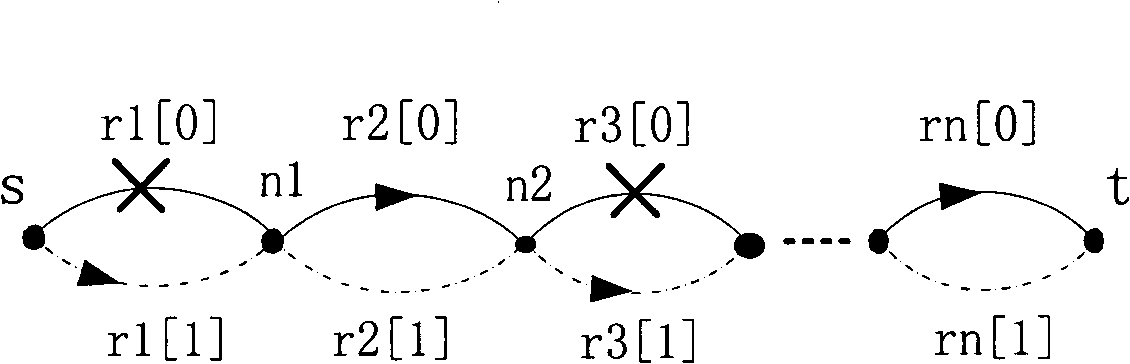
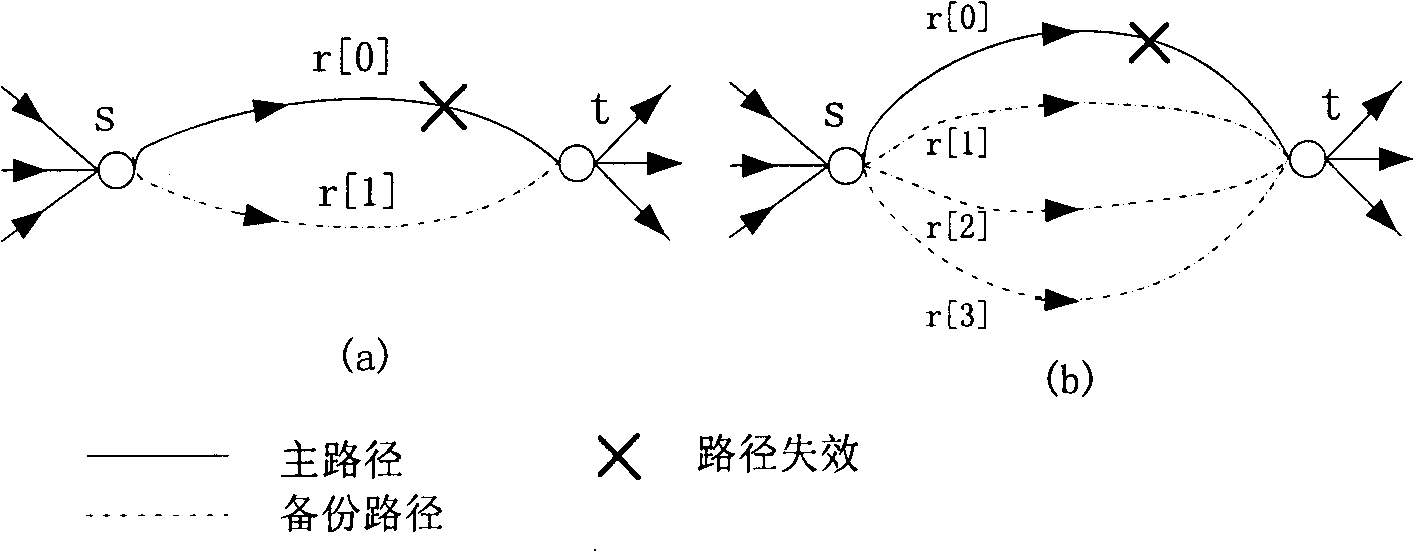
Route interference impact metering method based on information entropy
InactiveCN101360053AWide applicabilityImprove accuracyData switching networksPresent methodConditional entropy
The invention provides a method of route interfering and affecting metric based on information entropy, comprising the following steps: (1) expressing a pair of a source point and a sink communicated in the network and a plurality of paths between the source point and the sink as point to point network; (2) under the condition that any data flow is on the appointed primary path, conducting statistics on the actual path used by a transmit packet to obtain used probability distribution of a path set, and the probability distribution is used as the condition probability distribution on the condition of the appointed primary path; (3) calculating the conditional entropy according to the condition probability distribution on the condition of the appointed primary path, and the conditional entropy is used as the route interfering and affecting metric on the condition of the appointed primary path; (4) conducting statistics of all the paths to take the paths as the probability of the primary path which is used as the used probability distribution of the primary path aggregation, and conducting statistical average on the route interfering and affecting metric of the appointed primary path obtained in the step (3) aiming at the used probability distribution of the primary path aggregation to obtain the route interfering and affecting metric of the whole independent path network. The method is more applicable and accurate compared with the present method.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Anonymity measuring device
The invention concerns a data anonymity measuring device for selectively transmitting an anonymised database to a third party comprising: calculation means (402) coupled to at least one memory, the memory storing an original database (204) and said anonymized database (206), said calculation means arranged to calculate the conditional entropy for each entry in said anonymized database based on entries in said original database; comparing means (406) arranged to compare at least one of said conditional entropies with a threshold value; and output means (410) arranged to transmit said anonymized database based on the result of said comparison.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
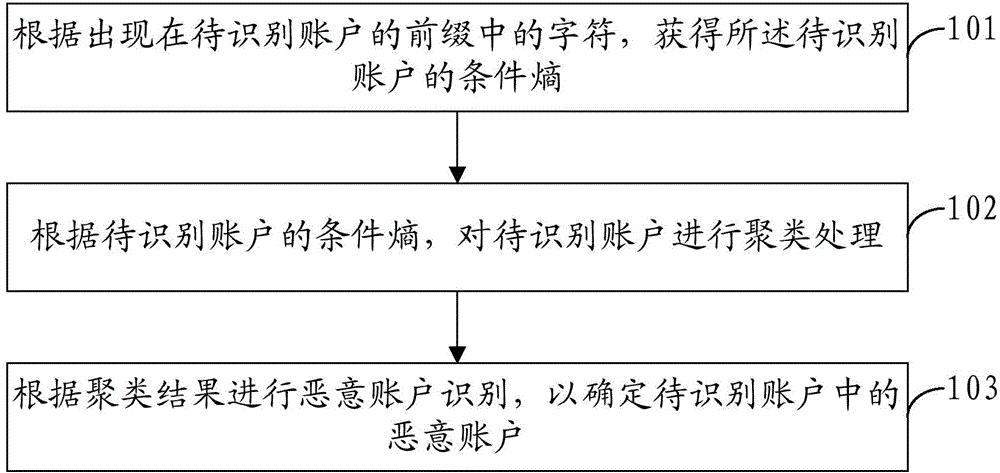
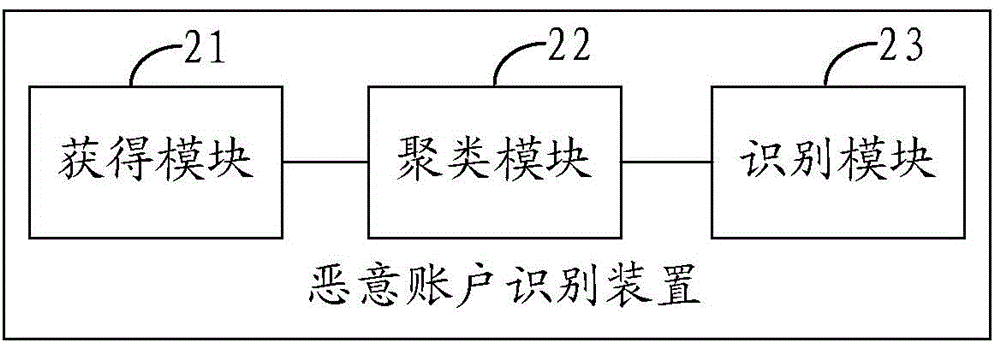
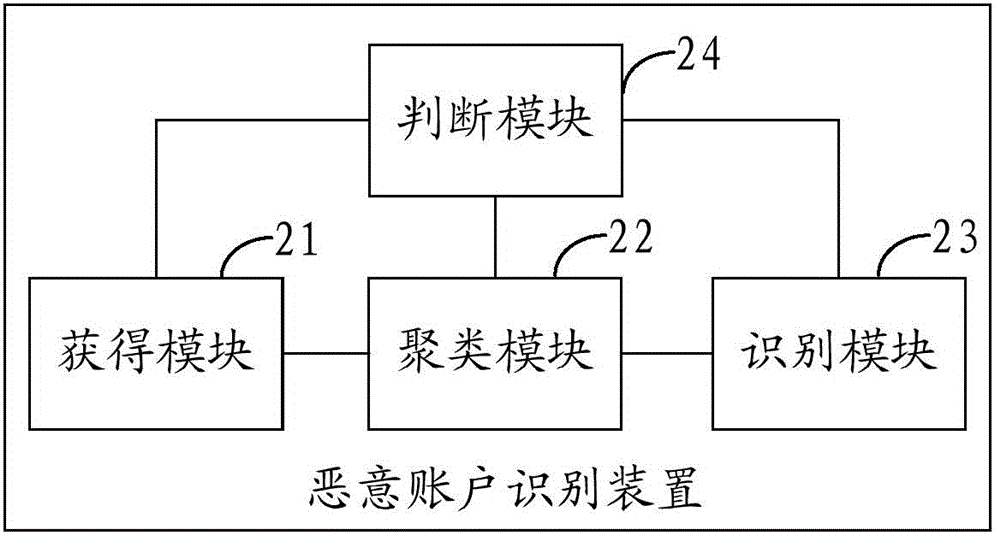
Malicious account identification method and device
ActiveCN105991620AImprove recognition efficiencyReduce the amount of identification dataTransmissionConditional entropyComputer security
The invention provides a malicious account identification method and device. The method comprises a step of obtaining the conditional entropy of an account to be identified according to the character which appears in the prefix of the account to be identified, a step of carrying out clustering processing on the account to be identified according to the conditional entropy of the account to be identified, and a step of carrying out malicious account identification according to the clustering result so as to determine the malicious account in the account to be identified. Based on the clustering result of the account to be identified, the malicious account identification is carried out rather than the individual identification of each account, and the improvement of the identification efficiency of the malicious account is facilitated.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
City CA model establishment method based on maximum entropy principle
ActiveCN108376183APreserve maximum randomnessUnbiasedCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationConditional entropyConditional probability
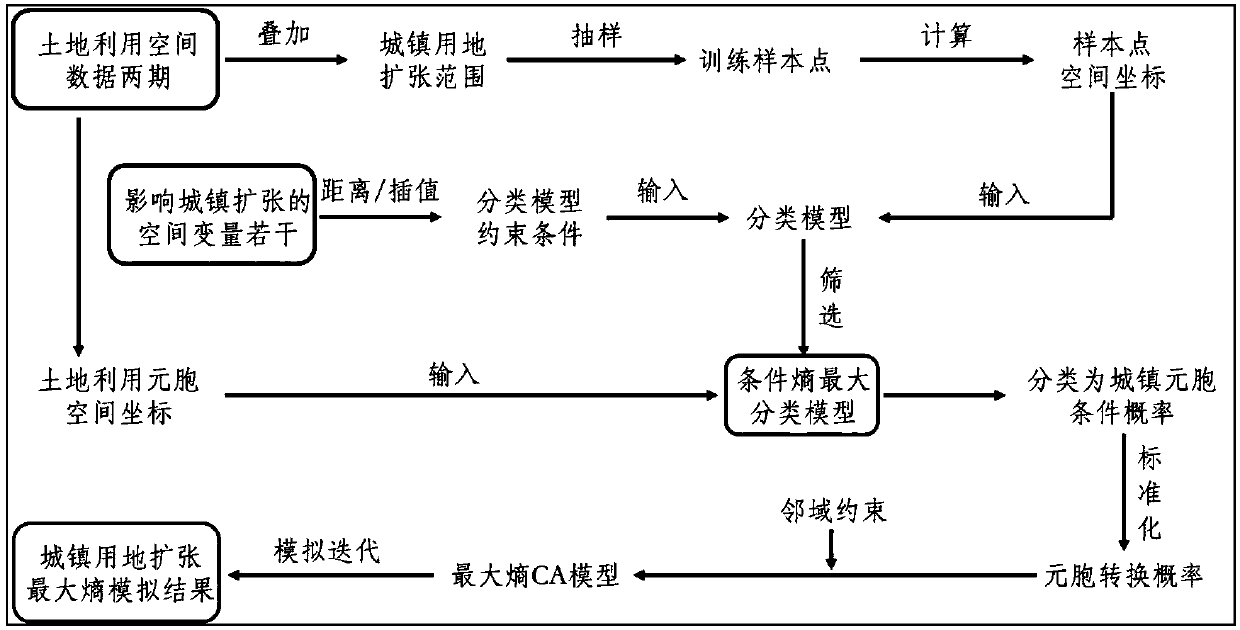
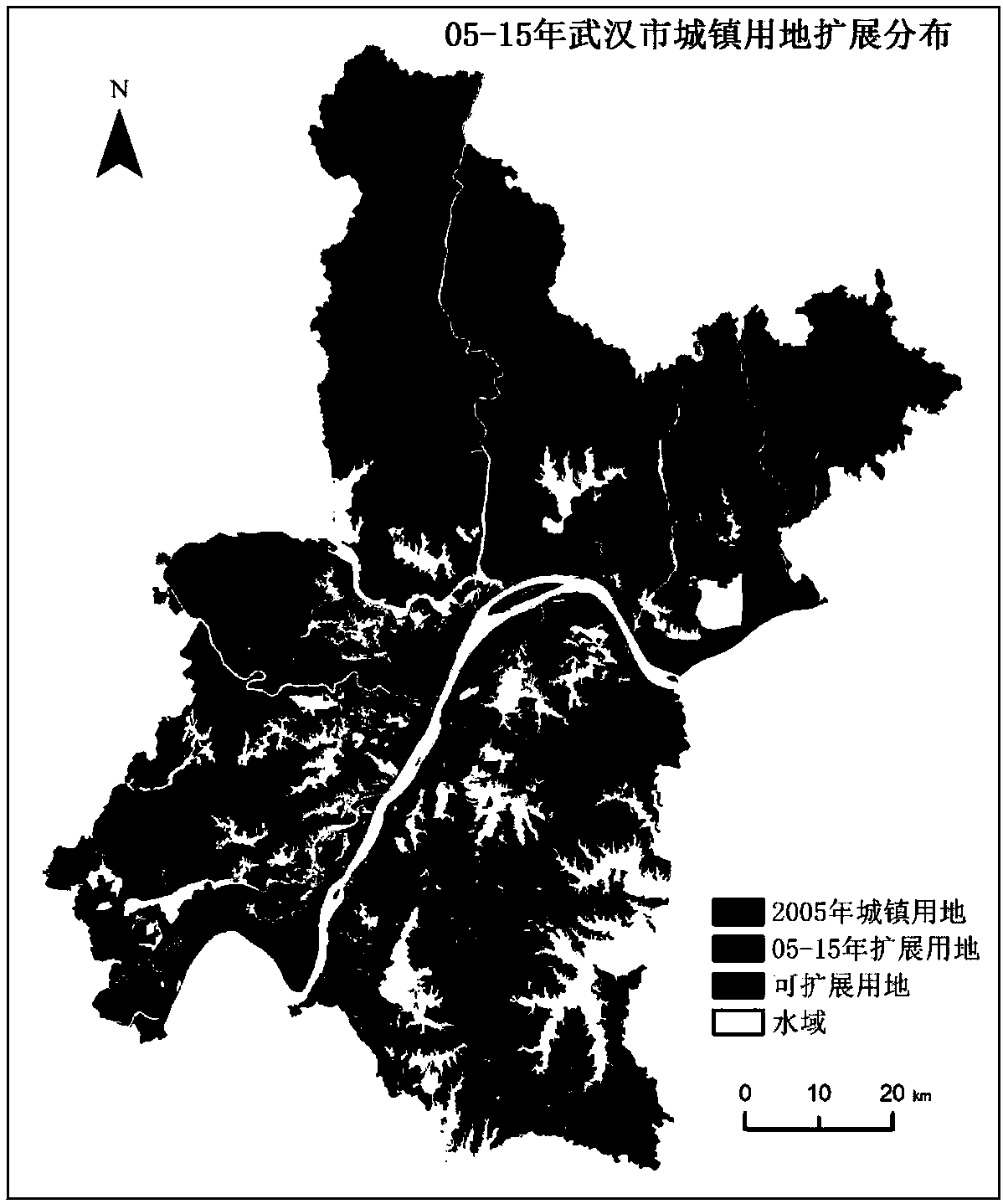
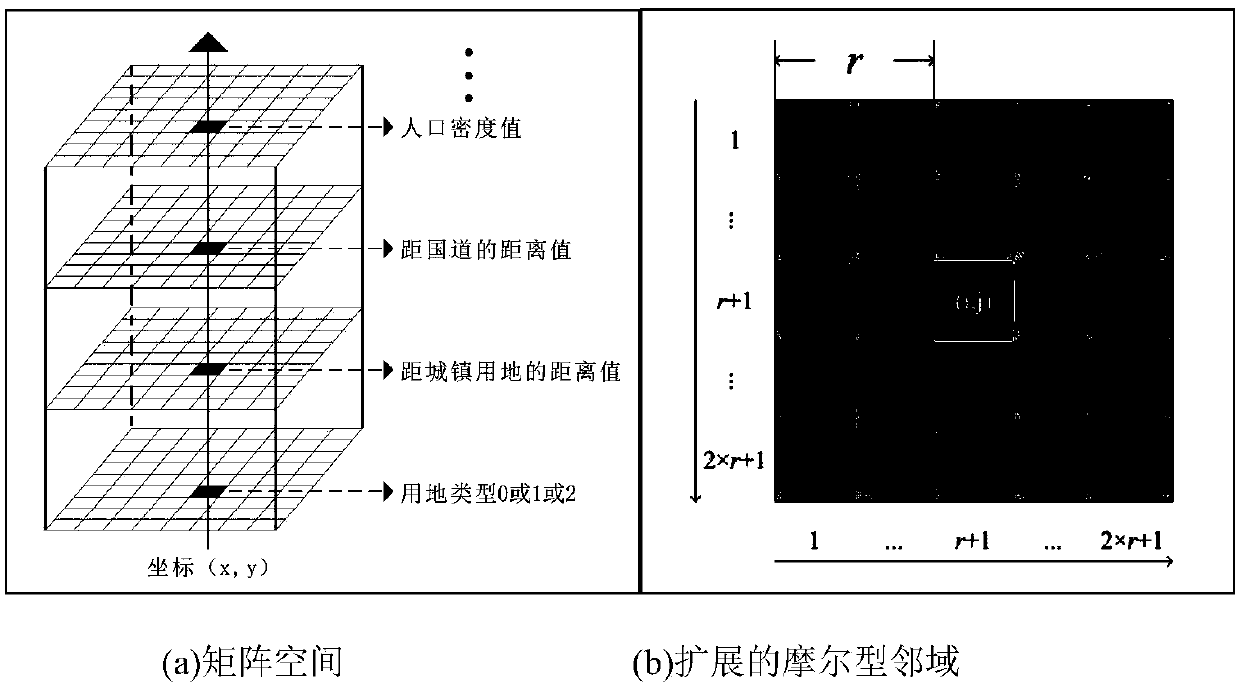
The invention discloses a city CA model establishment method based on a maximum entropy principle. The method comprises the steps that two-stage land utilization grid data is acquired and reclassified; the classified data is superimposed to obtain a city land utilization increase range, and random sampling and coordinate calculation are conducted in the range to obtain sample point data; a space variable influencing city land utilization extension is processed, and a result is used as a classification model constraint condition; a sample point and the constraint condition are used for model training to obtain a classification model with the maximum conditional entropy; a land utilization matrix and a cell corresponding to a matrix element are established, a space coordinate of the cell isinput into the model, the conditional probability of each cell classified as urban land under influence of the constraint condition is obtained and used as the CA model cell transition probability, and a city extension CA model is established on the basis of the CA model cell transition probability and in combination with neighborhood constraint. According to the method, the CA model with the maximum entropy is established and applied to urban land extension simulation, the randomness problem is considered, and the method helps to more precisely simulate city development.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
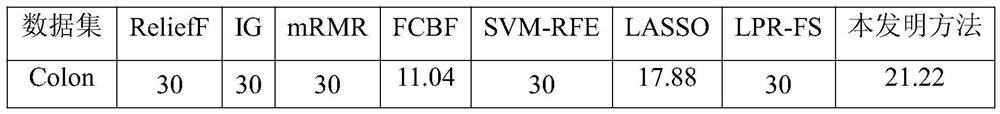
Feature selection method based on self-adaptive LASSO
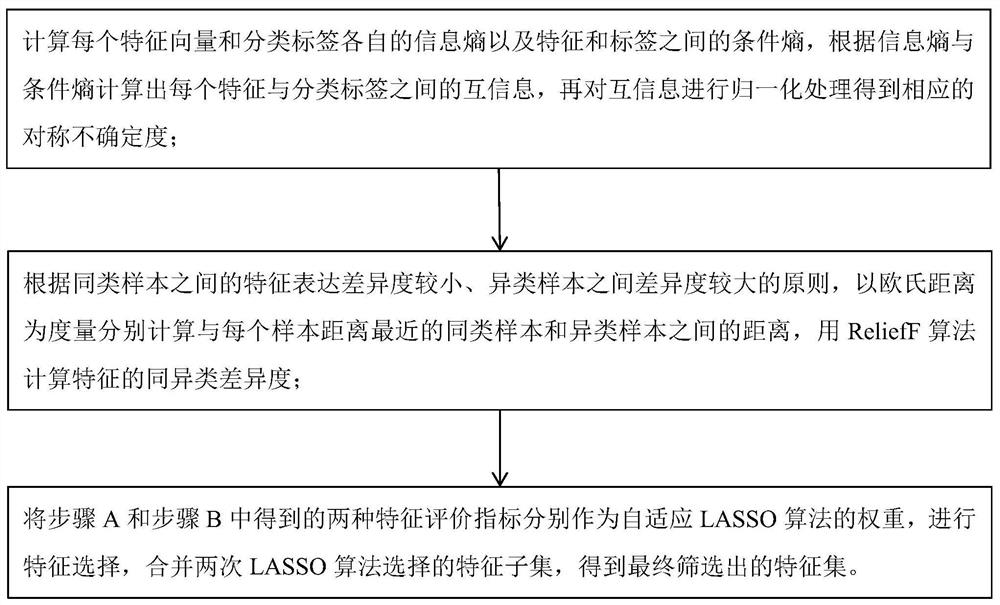
The invention provides a feature selection method based on self-adaptive LASSO. The method is suitable for feature selection of gene microarray data with the characteristics of high dimension and lowsample size. The method comprises the steps of firstly, calculating the information entropy of each feature vector and the information entropy of each classification label and the conditional entropybetween the features and the labels to obtainin the symmetry uncertainty between each feature vector and the corresponding classification label; then, according to the principle that the feature expression difference degree between similar samples is small and the difference degree between heterogeneous samples is large, using the ReliefF algorithm for calculating the isomerism difference degree of each feature; and finally, respectively taking the two evaluation indexes as feature weights of an adaptive LASSO algorithm to perform feature selection, and combining the obtained two batches of feature subsets to generate a finally screened feature set.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
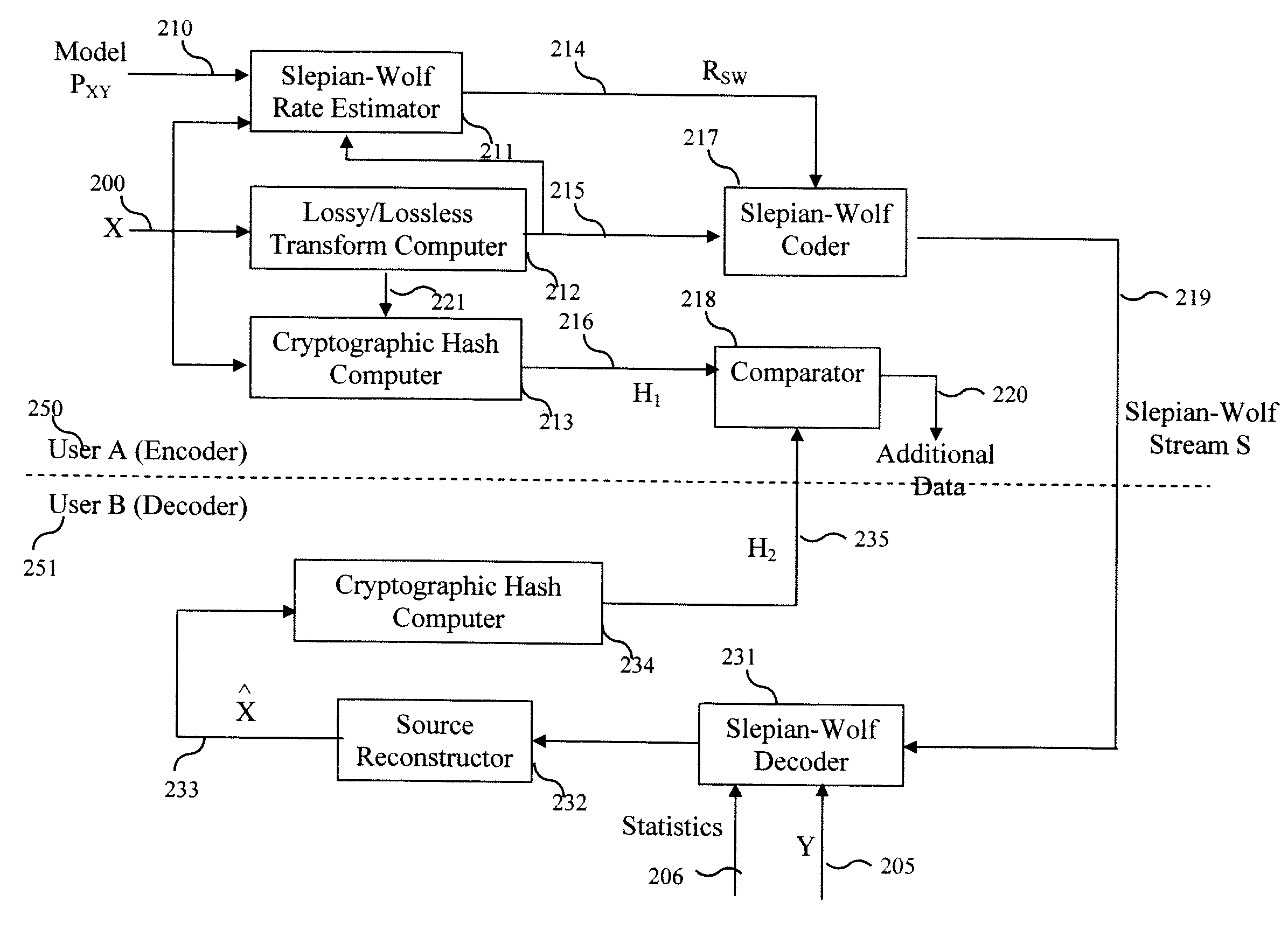
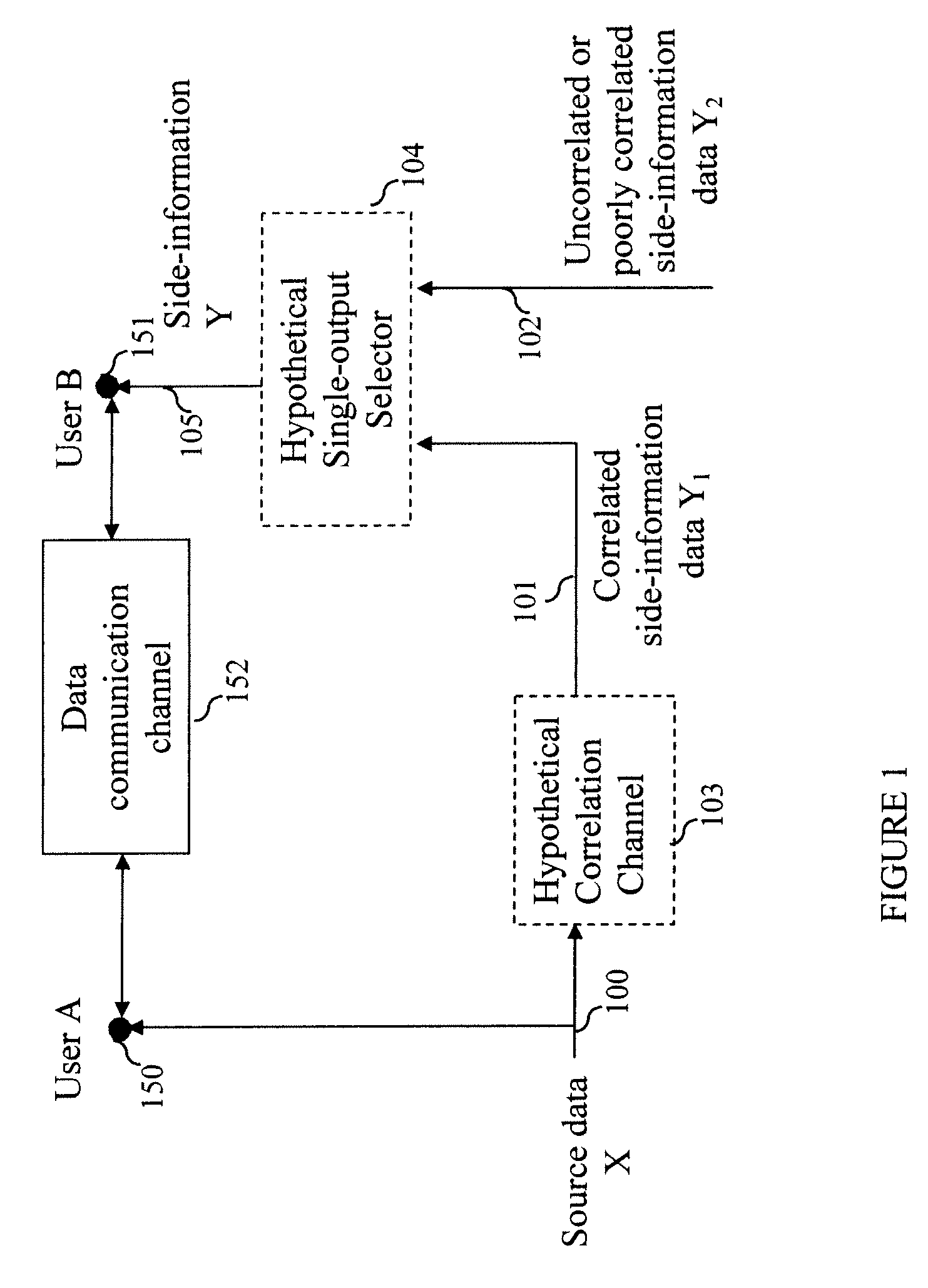
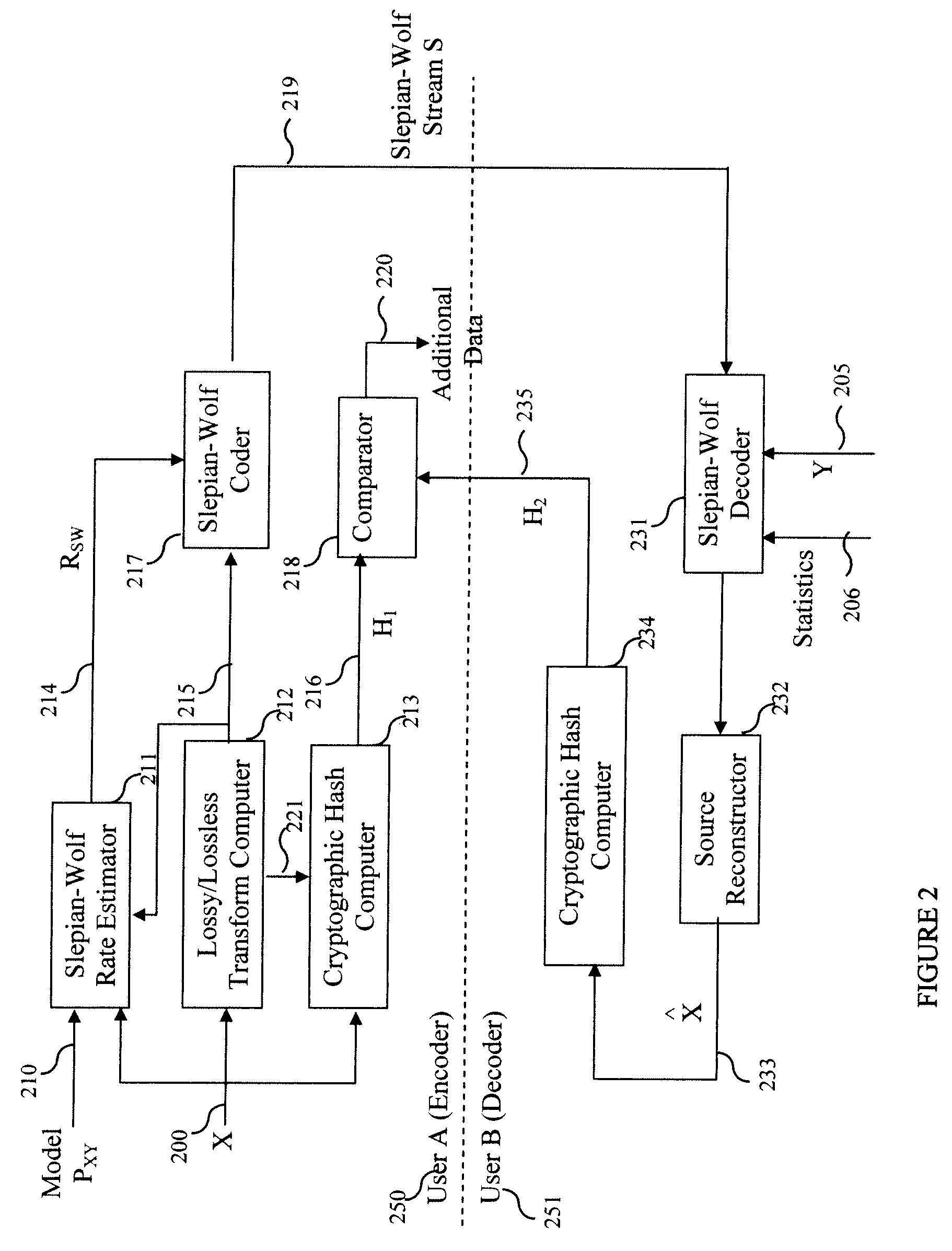
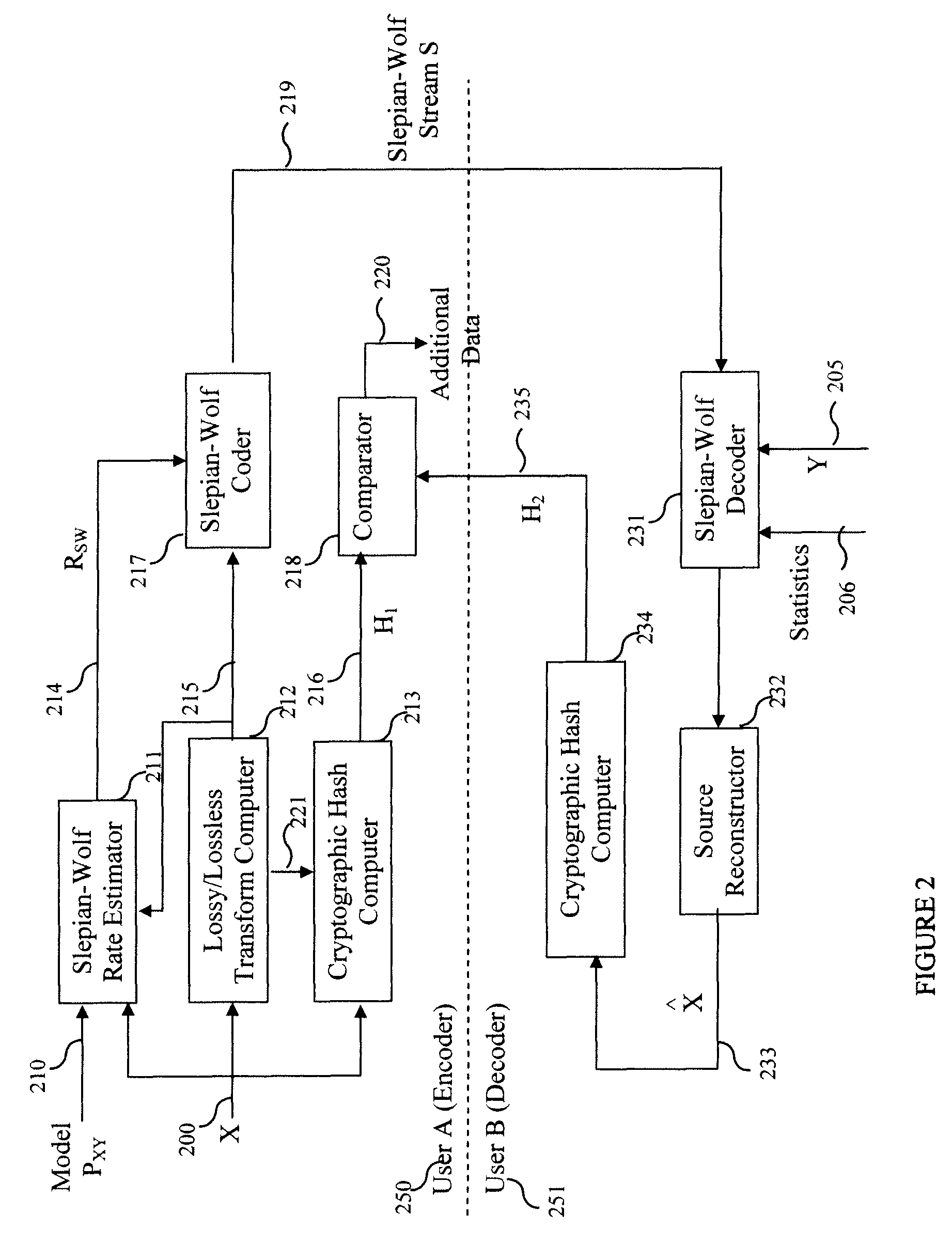
Method and System for Secure Collaboration Using Slepian-Wolf Codes
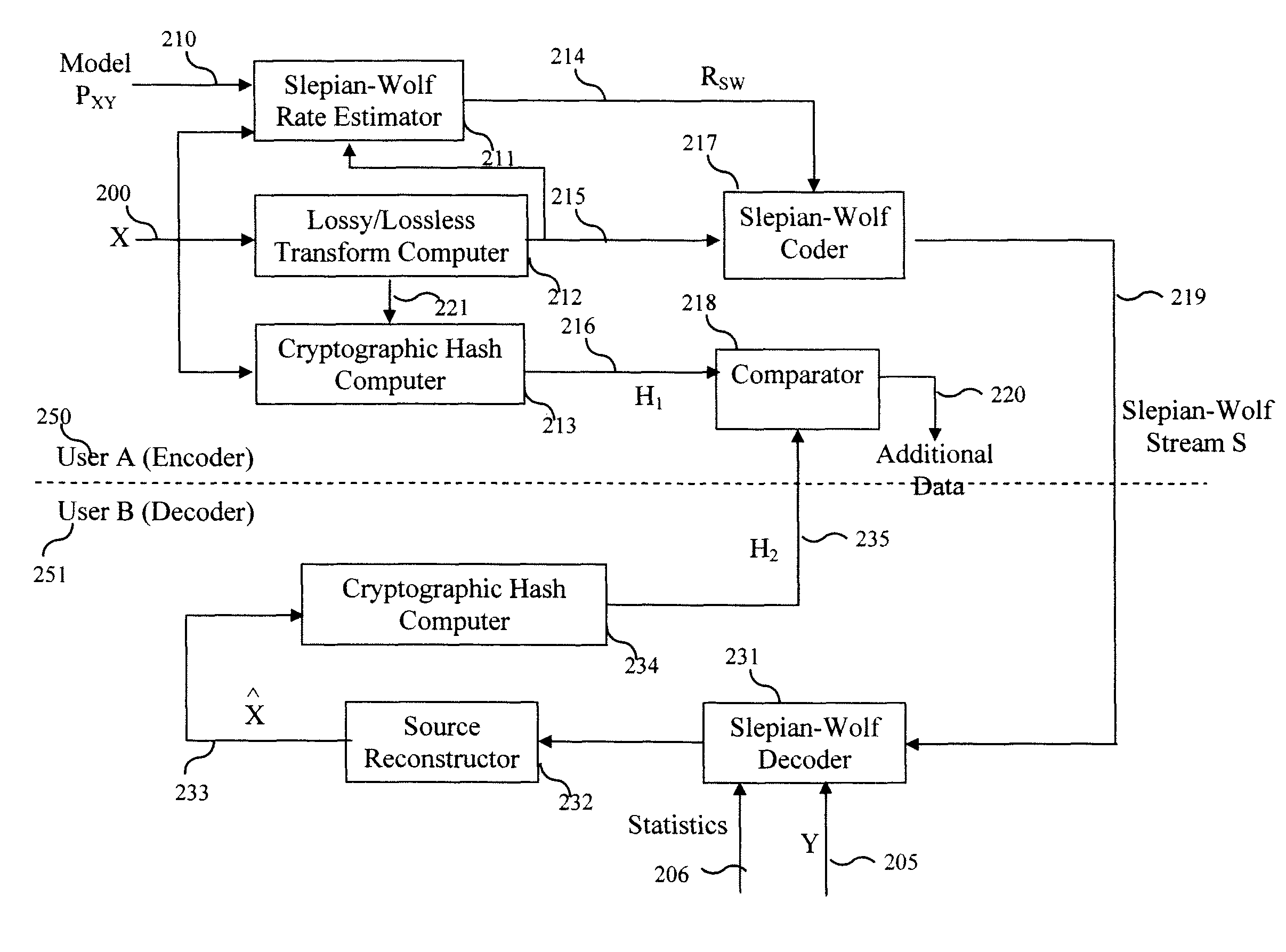
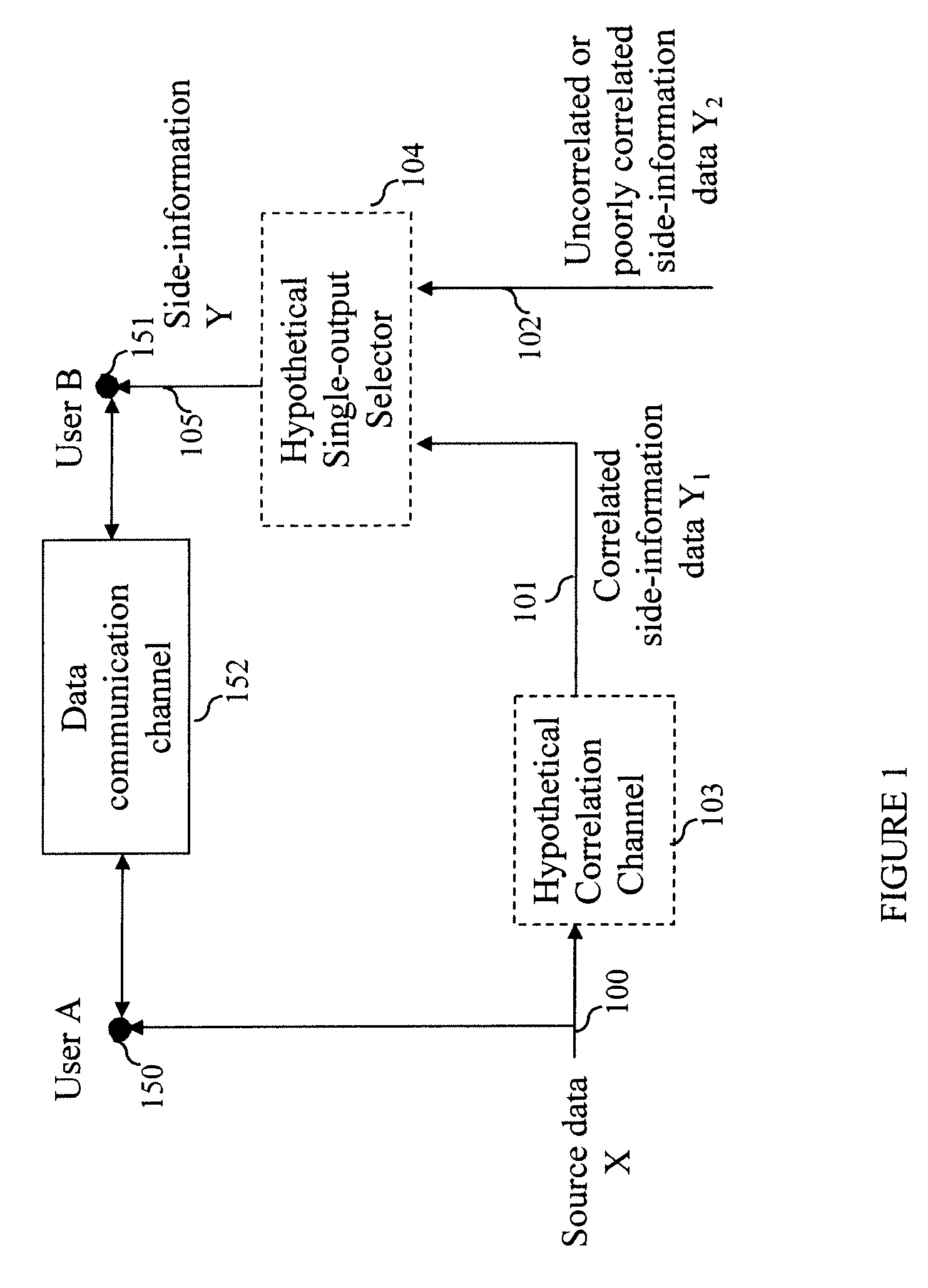
InactiveUS20100095116A1Data stream serial/continuous modificationUser identity/authority verificationConditional entropySide information
A method and system provide for secure sharing of arbitrary data between users with limited mutual trust. A user can encode its information by using a Slepian-Wolf code at a rate which enables a second user to correctly decode only if the side-information it has satisfies a conditional entropy constraint. The key advantages are as follows. Firstly, it is very flexible, in that it enables secure sharing for general data including multimedia data. Secondly, by appropriate Slepian-Wolf code selection, it enables compression in conjunction with security. Thirdly, it can be used for the case where the data model is imperfectly known and trust is to be built up incrementally.
Owner:IBM CORP
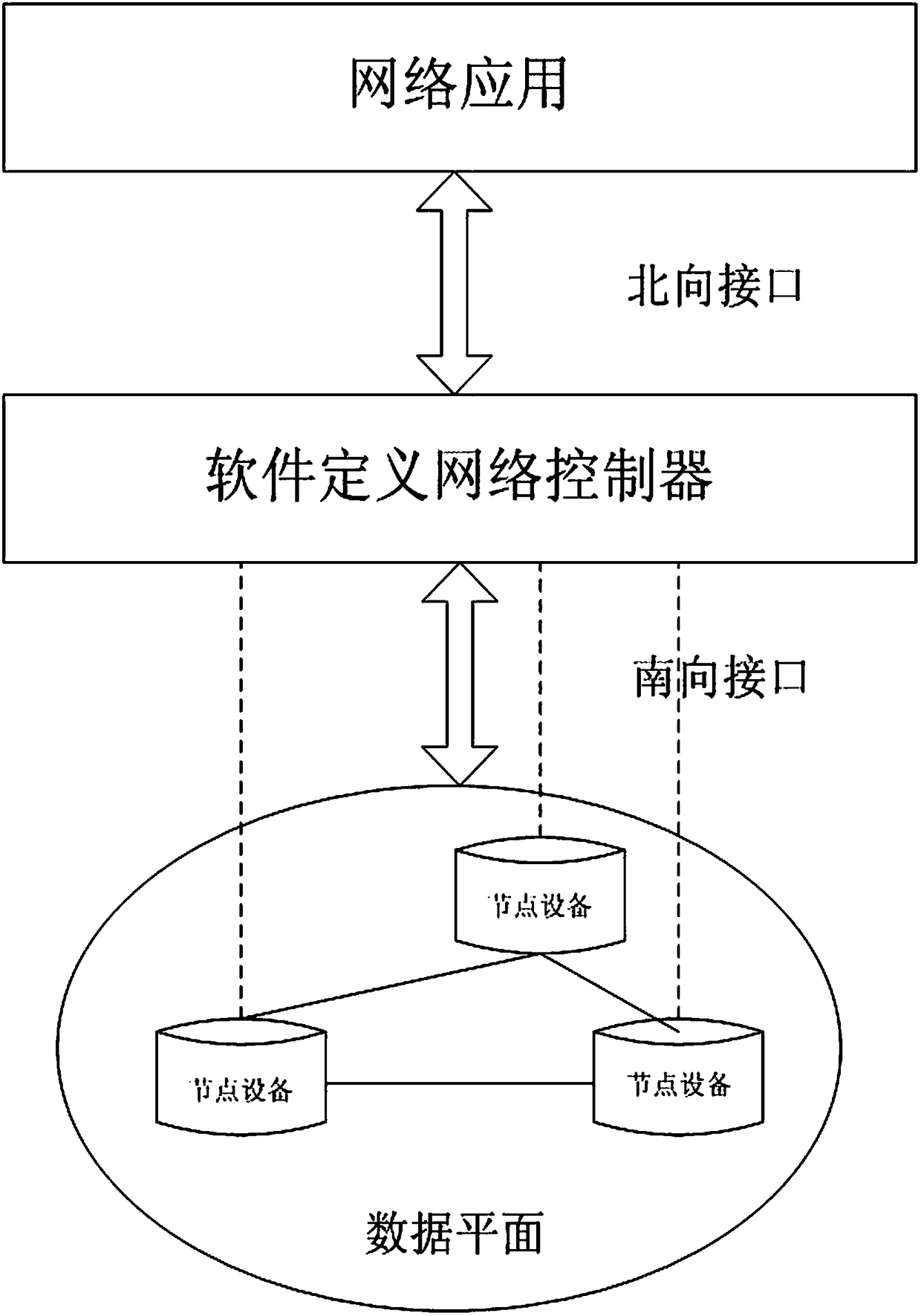
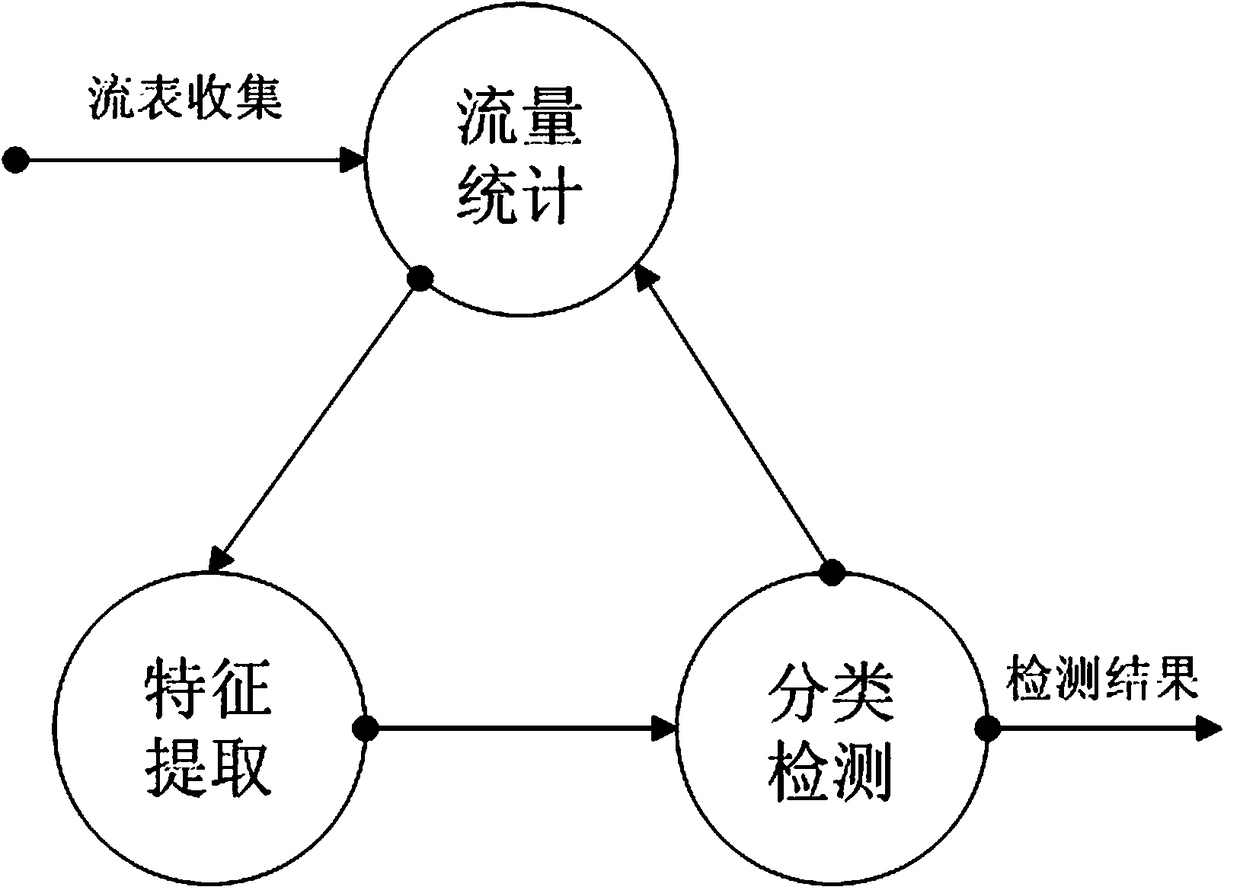
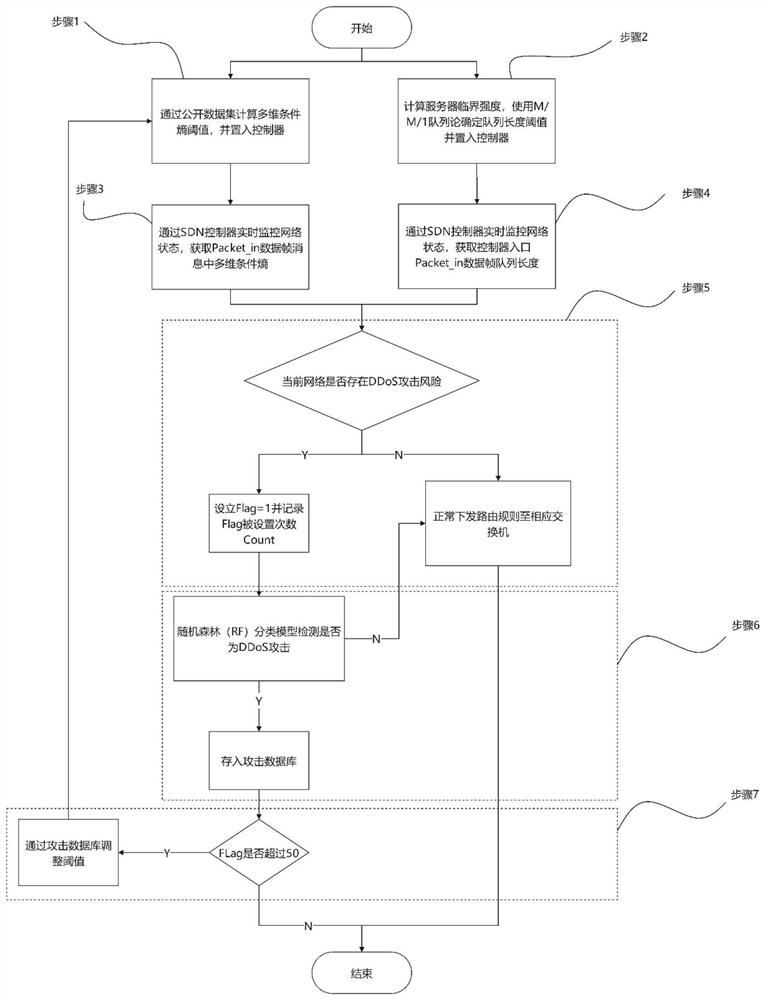
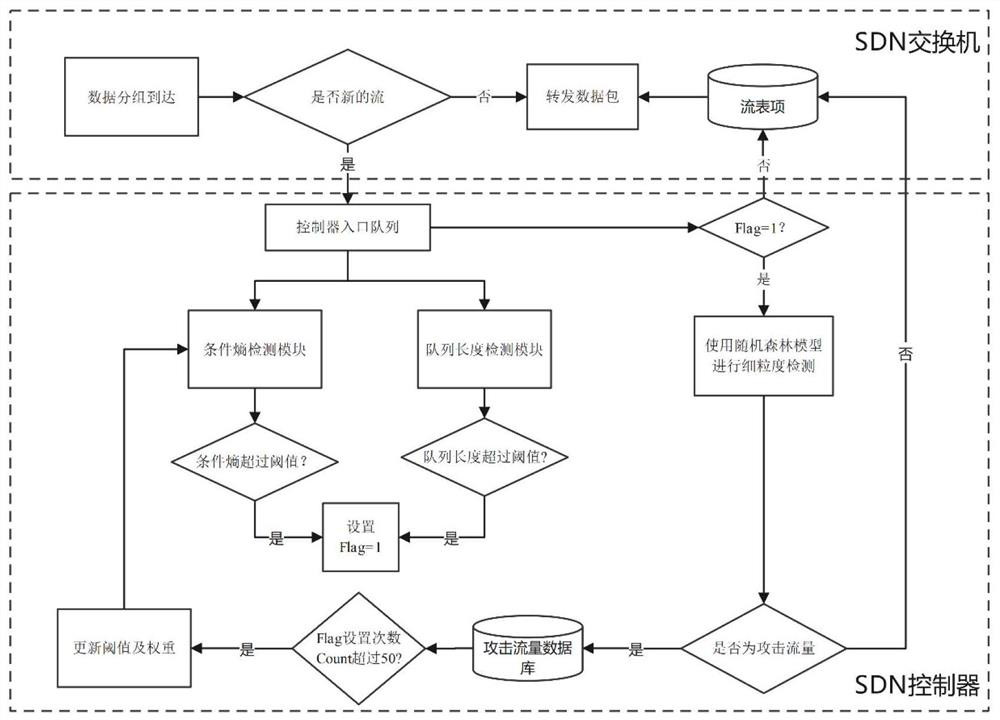
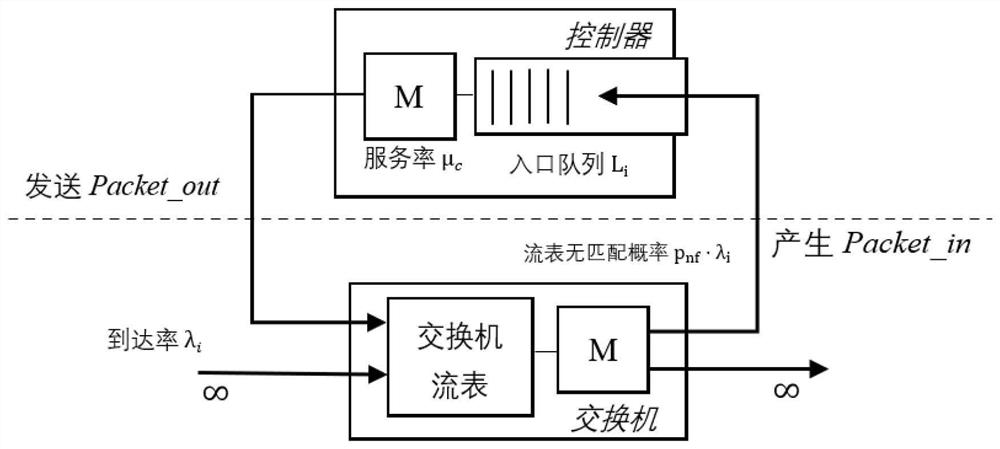
DDoS attack detection method based on SDN
InactiveCN113630420ADDoS attack warningNot attackedCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionConditional entropyAttack
The invention relates to a DDoS attack detection method based on an SDN, and belongs to the field of software defined networks. According to the method, the queue theory and the conditional entropy are used as a coarse-grained detection module of the arrival flow in the SDN environment, and machine learning is used as a fine-grained detection module, so malicious flow is accurately detected from legal packets, and the possibility that a server in a network is attacked is reduced while a controller is protected from being attacked. Coarse granularity detection is composed of two parallel detection modules, namely a multi-dimensional conditional entropy detection module and a controller entry queue length detection module, fine granularity detection is triggered when a detection result of any one module exceeds a threshold value, the fine granularity detection module collects flow table items and counter information from a switch based on an OpenFlow protocol for statistical processing, and the traffic is finally judged by using a random forest (RF) classification model which is trained and is placed in the controller, so as to effectively detect the attack traffic and prevent the controller from being damaged.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
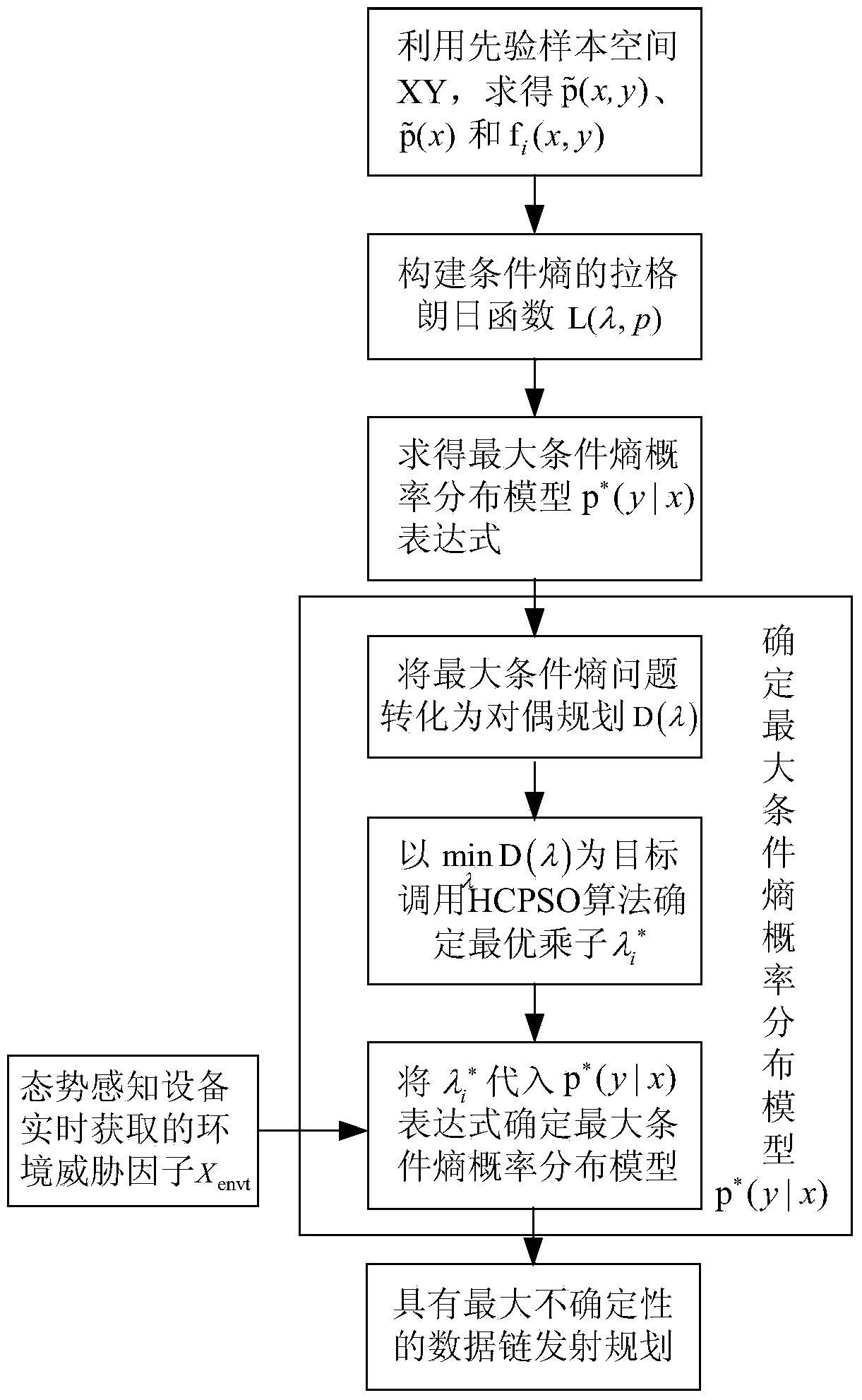
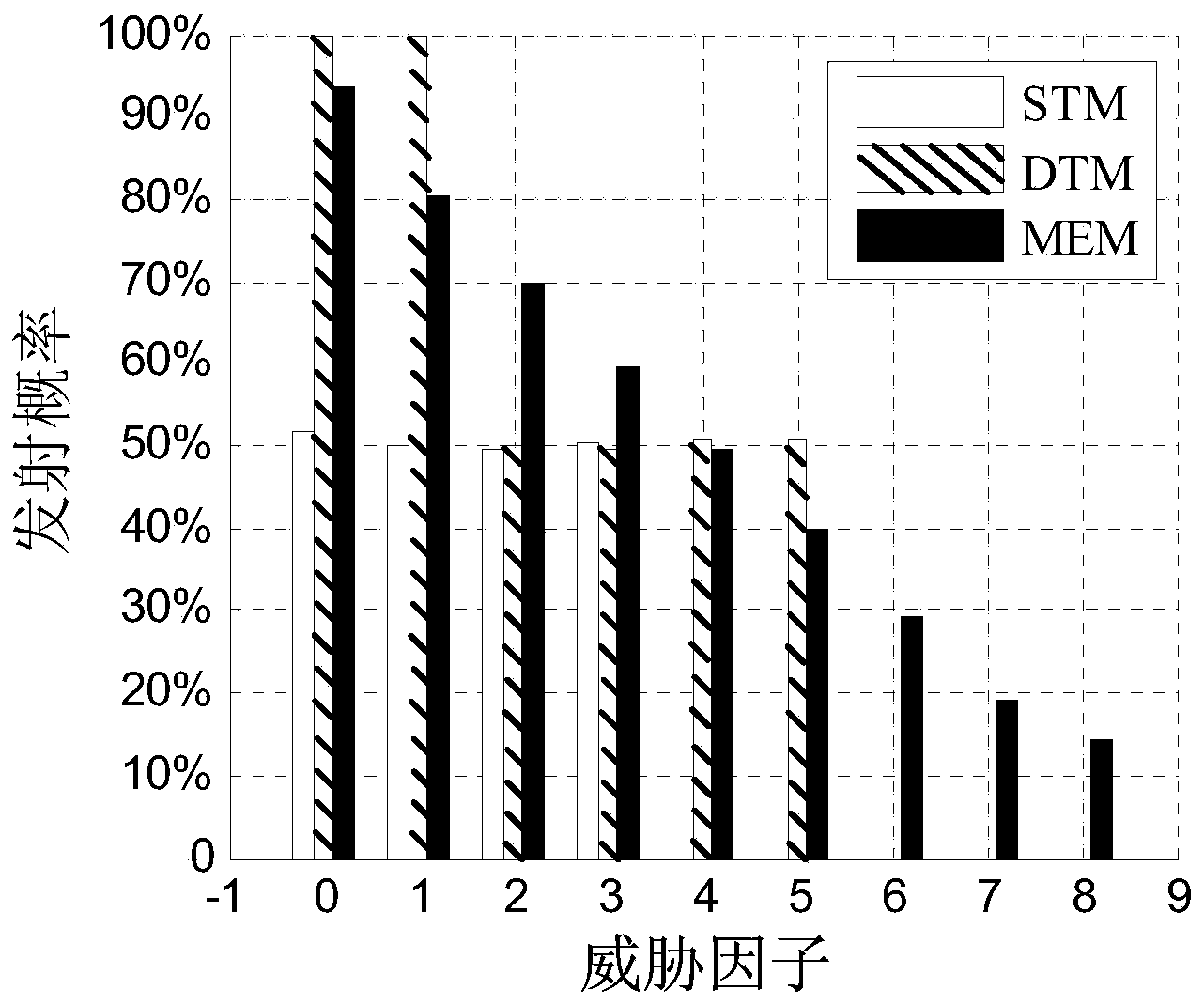
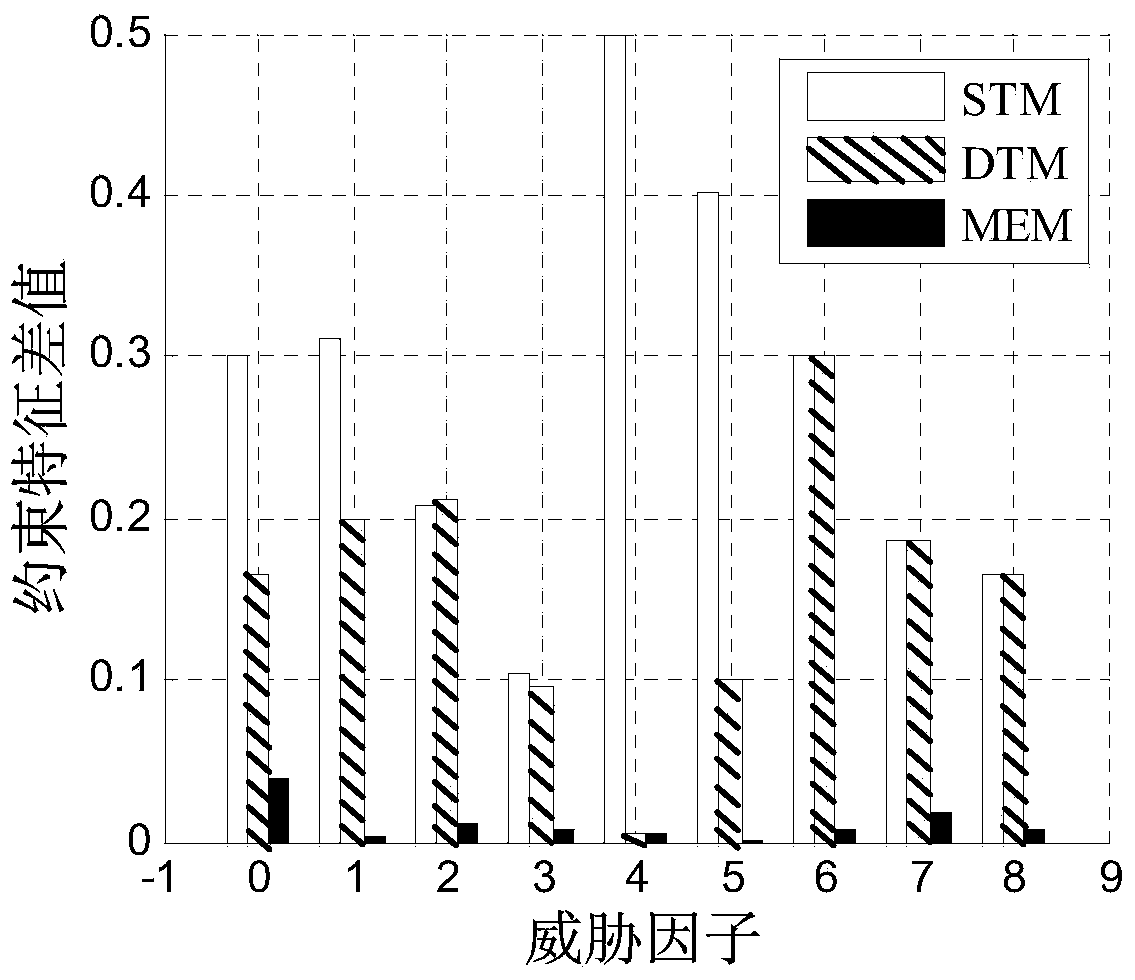
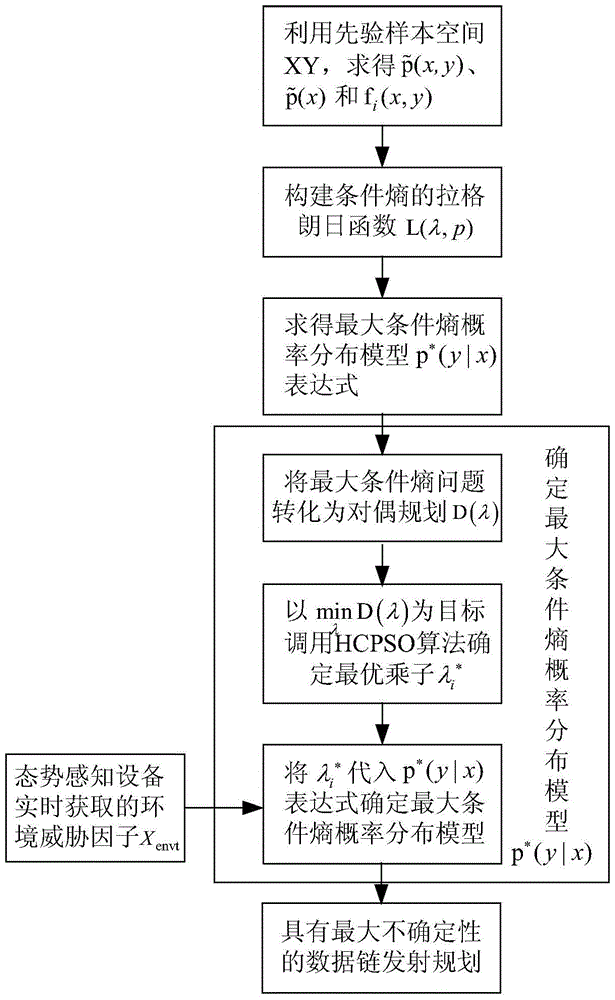
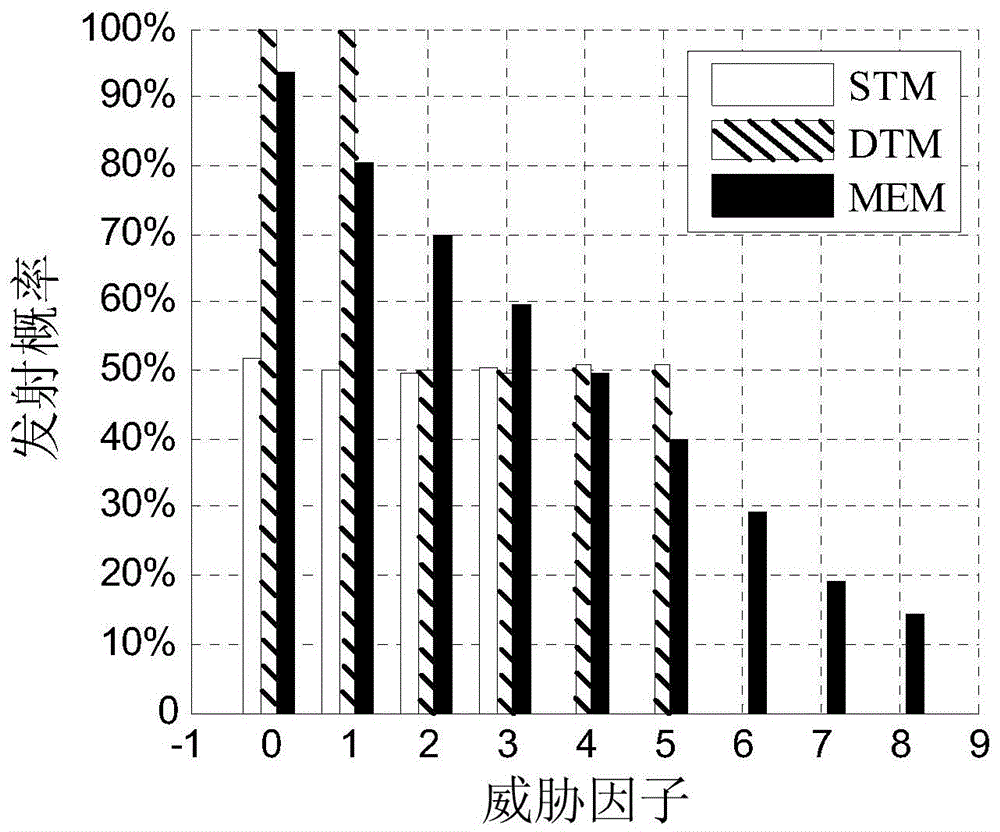
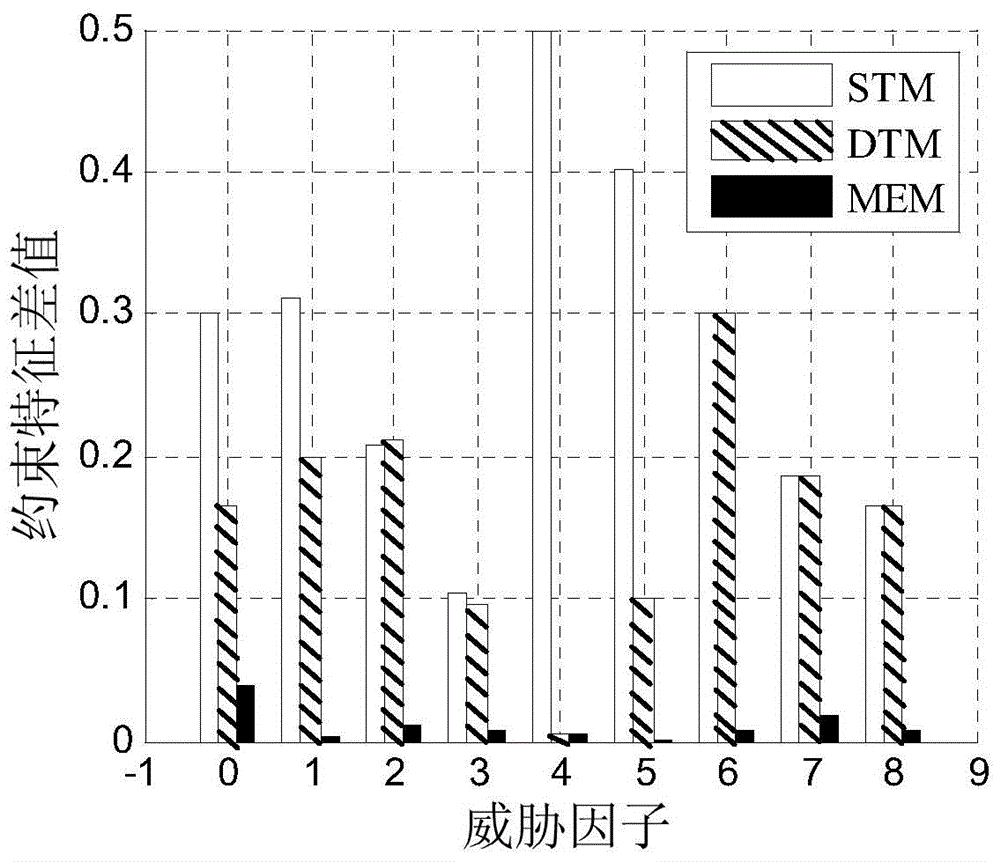
Radio frequency stealth datalink emitting state acquiring method based on maximum conditional entropy
InactiveCN103678906AImprove RF Stealth PerformanceIncrease uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsNormal densityConditional entropy
The invention discloses a radio frequency stealth datalink emitting state acquiring method based on maximum conditional entropy. A prior environmental threat factor x and a prior datalink emitting state y in historic radio frequency stealth data serve as sample spaces. Firstly, the probability density function of the sample space x, the joint probability density function of the sample space x and the sample space y and the characteristic functions of the sample space x and the sample space y are respectively worked out; secondly, a maximum conditional entropy distribution function expression is worked out by building a Lagrange function; thirdly, unknown coefficients in the maximum conditional entropy distribution function expression are worked out, and a maximum conditional entropy distribution function is acquired; fourthly, environment thread factors acquired by situation awareness equipment are input into the maximum conditional entropy distribution function, and a datalink emitting state with the largest uncertainty is acquired.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A novel false position generation method for use in nearby human applications
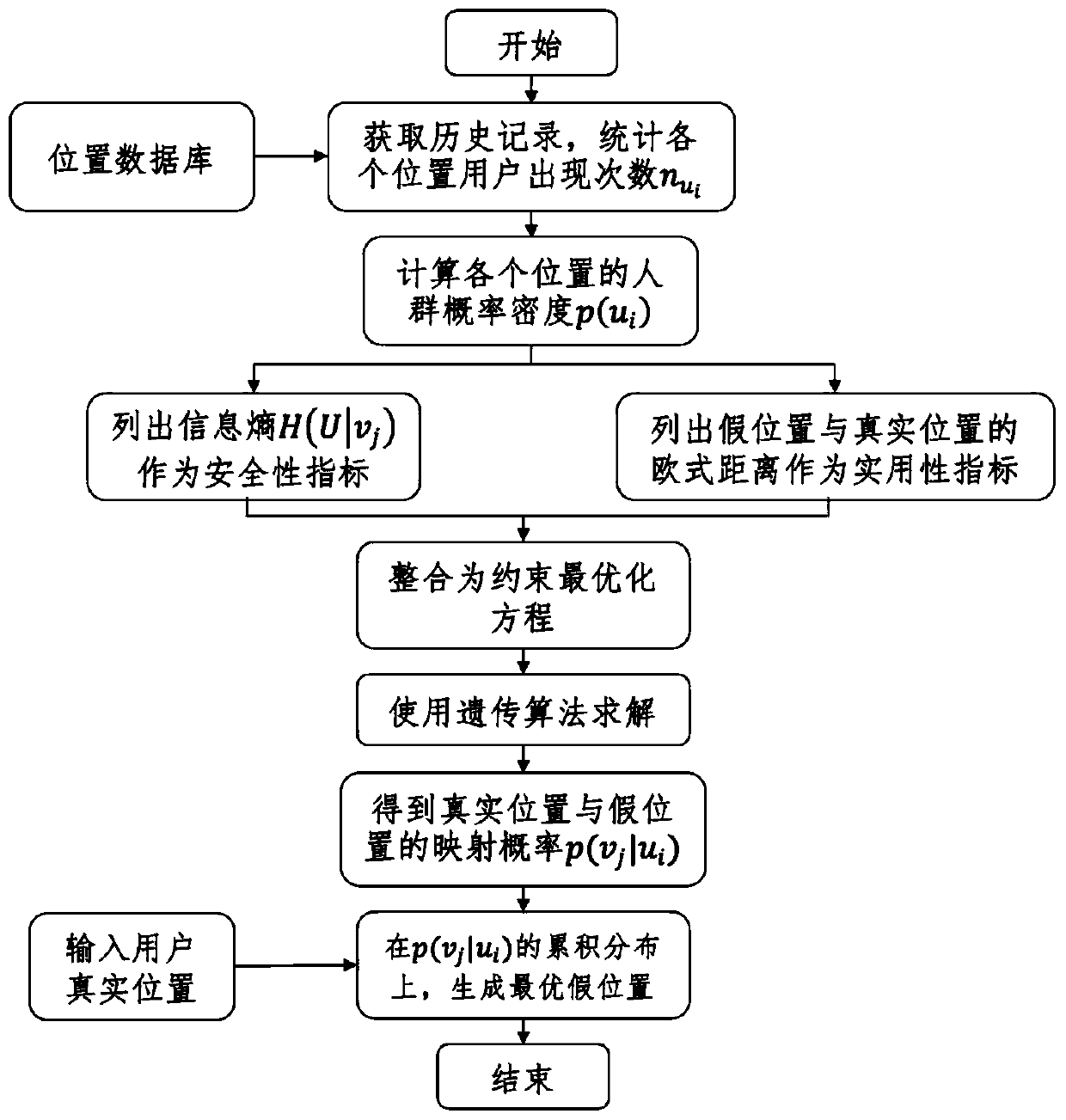
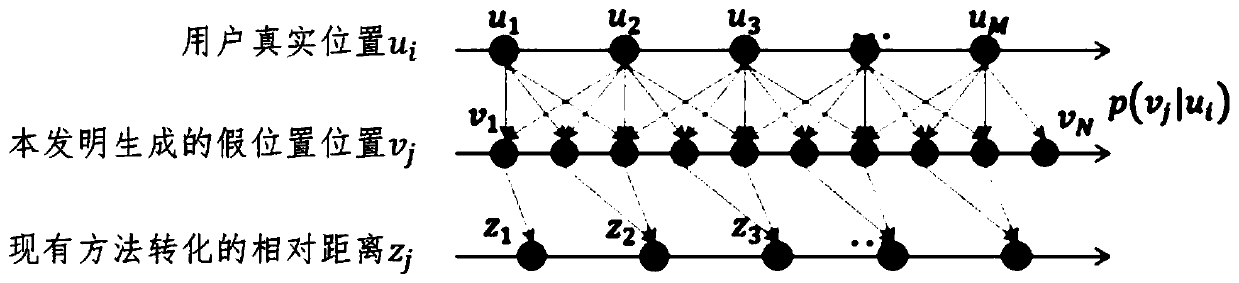
ActiveCN111464943AHighlight substantiveHighlight technological progressData processing applicationsLocation information based serviceQuality of serviceConditional entropy
A novel false position generation method for use in nearby human applications is presented. According to the method, a false position generation problem is equivalently converted into a constraint optimization problem. An optimization target is to maximize a conditional entropy of mapping a false position to a real position, that is to say, the attacker obtains the minimum information amount of the real position from the generated false position. The constraint condition is that the average error distance between the generated false position and the real position cannot be greater than a threshold value, so that the service quality of nearby human applications is prevented from being reduced. The method can be applied to a nearby human server, and the conditional probability of a group offalse position points can be generated for each user by solving the constraint optimization equation. According to the probability, each user can randomly generate an optimal false position meeting safety and practicability, so that an attacker cannot obtain the real position of the user through multi-point positioning attack.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method and system for secure collaboration using slepian-wolf codes
InactiveUS8230217B2Data stream serial/continuous modificationUser identity/authority verificationConditional entropySide information
A method and system provide for secure sharing of arbitrary data between users with limited mutual trust. A user can encode its information by using a Slepian-Wolf code at a rate which enables a second user to correctly decode only if the side-information it has satisfies a conditional entropy constraint. The key advantages are as follows. Firstly, it is very flexible, in that it enables secure sharing for general data including multimedia data. Secondly, by appropriate Slepian-Wolf code selection, it enables compression in conjunction with security. Thirdly, it can be used for the case where the data model is imperfectly known and trust is to be built up incrementally.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Non-reference quality evaluation algorithm combining multiple edge detection operators
ActiveCN108830829AImprove consistencyImprove performanceImage enhancementImage analysisMultiple edgesConditional entropy
The invention relates to a non-reference quality evaluation algorithm combining multiple edge detection operators. A combination entropy and a chain-type rule are used to define a conditional entropy.The algorithm comprises the following steps of selecting an image used for training and testing; calculating the gradient of the image, a relative gradient, and a Gaussian Laplace operator (LoG), wherein extracted image characteristics include five-dimensional characteristics of the standard deviation of a relative gradient direction RO, the conditional entropies H(GM|L) and H(L|GM) between the gradient and LoG, and the conditional entropies H (GM|L)-H (RM|L) and H(L|GM)-H(L|RM)) between the relative gradient and the LoG; according to multi-scale performance in a human eye visual system characteristic, using a downsampling method, extracting the above five-dimensional characteristics of the reduced image, and finally acquiring a ten-dimensional characteristic vector; and using AdaBoost neural network to carry out regression so as to predict an image quality score.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Simulated circuit fault testing method based on sequential testing
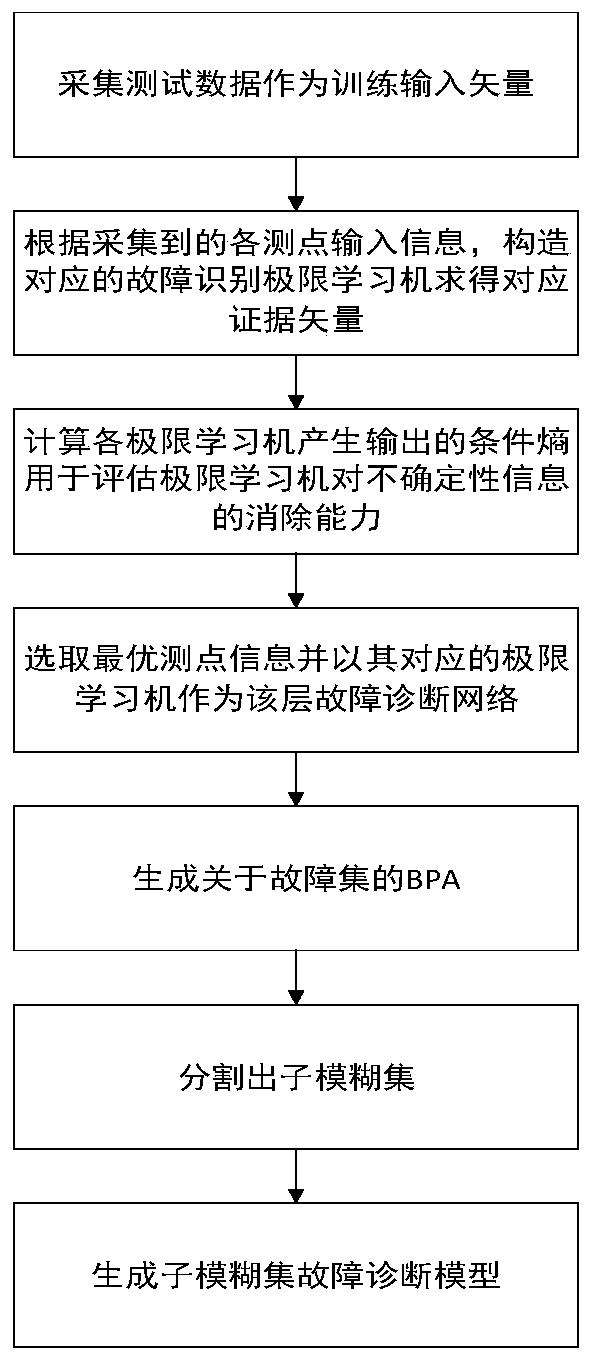
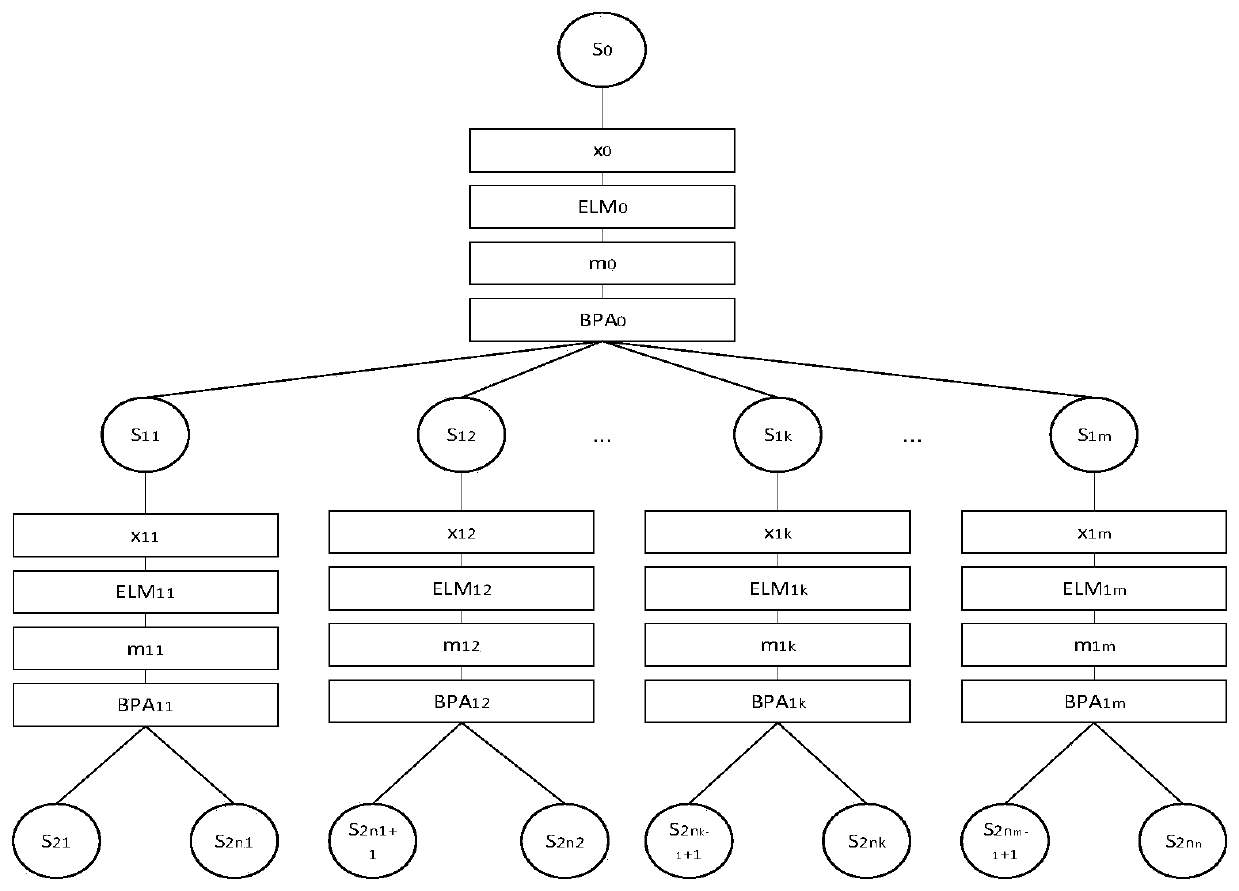
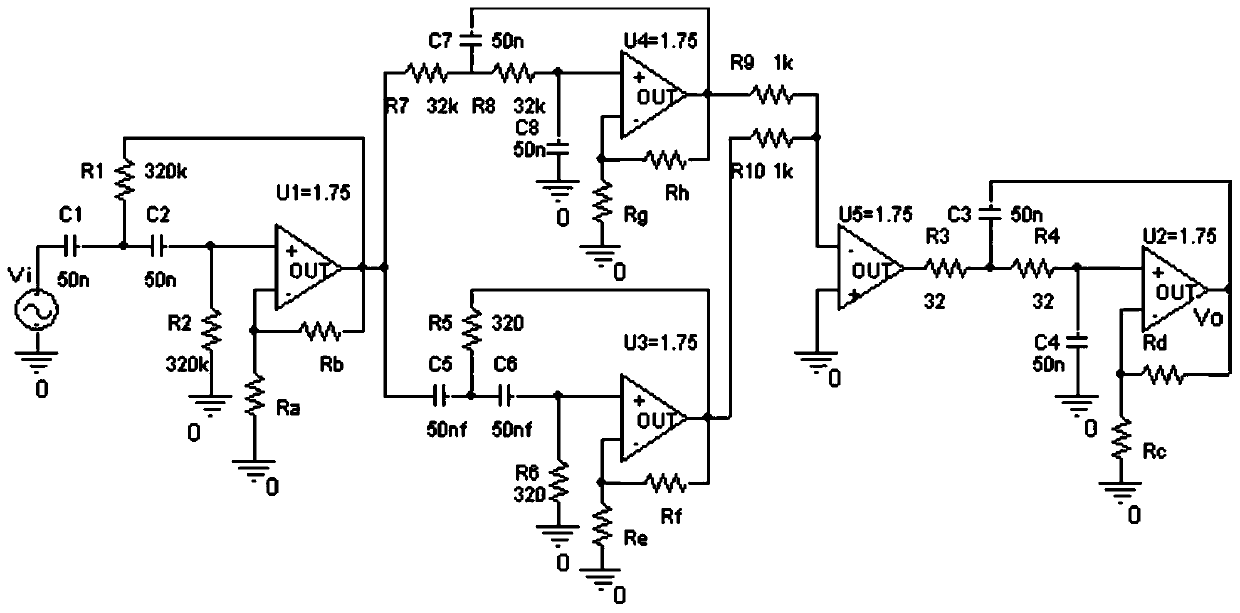
The invention discloses a simulated circuit fault testing method based on sequential testing. Effectiveness of measuring points is estimated through a conditional entropy, the characteristic value ofthe measuring points with high fault identifying ability is selected to serve as information of an input layer of an extreme learning machine, and the evidence vector for expressing the fault state identifying result is generated; and then a belief function is generated based on a D-S theory, according to affinity propagation, a fault state set is separated into a plurality of fault subsets, and diagnostic models of the fault subsets are further generated until the fault state is completely separated or separated to be in the optimal state. The simulated circuit fault testing method has the characteristics of high fault identification precision, high fault identification efficiency and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multi-modal emotion recognition method and system
ActiveCN113076847AEmotional distinguishability is goodFeature learning worksKernel methodsSpeech recognitionConditional entropyFeature learning
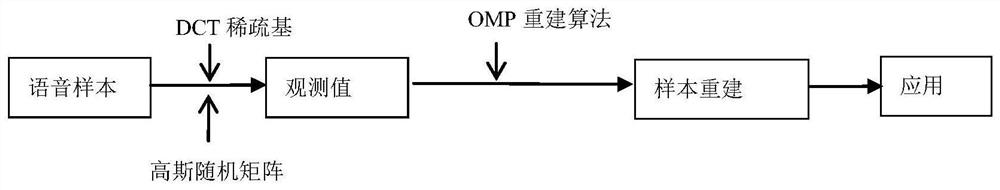
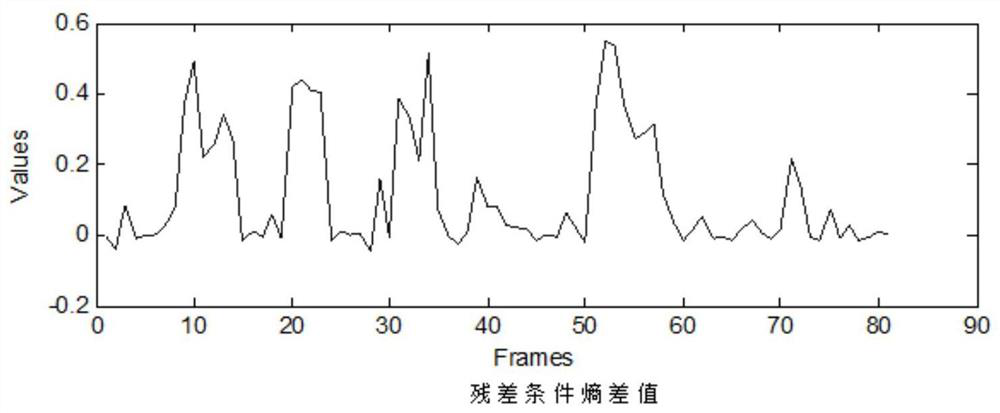
The invention provides a multi-modal emotion recognition method and system, and the method comprises the steps: employing a novel and robust endpoint detection algorithm for voice components in an emotion video sample, and employing a prediction residual conditional entropy parameter generated in a sample reconstruction process under a compressed sensing theory, calculating a residual conditional entropy difference value in the algorithm iteration process of an orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP) algorithm, completing endpoint detection according to an empirical threshold value, and completing feature learning of emotional speech of a voiced segment based on a reconstructed sample; and screening the facial expression images according to the endpoint detection result of the emotional voice, and only reserving the facial expression images with the active emotional voice in the same time period, so that the purposes of enhancing the emotional separability of the facial expression data set and reducing the redundancy are achieved; the emotion speech features and the facial expression features are fused, an effective multi-modal emotion recognition model is trained, and the purpose of effective multi-modal emotion recognition is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN +1
Short text classification method based on conditional entropy and convolution neural network
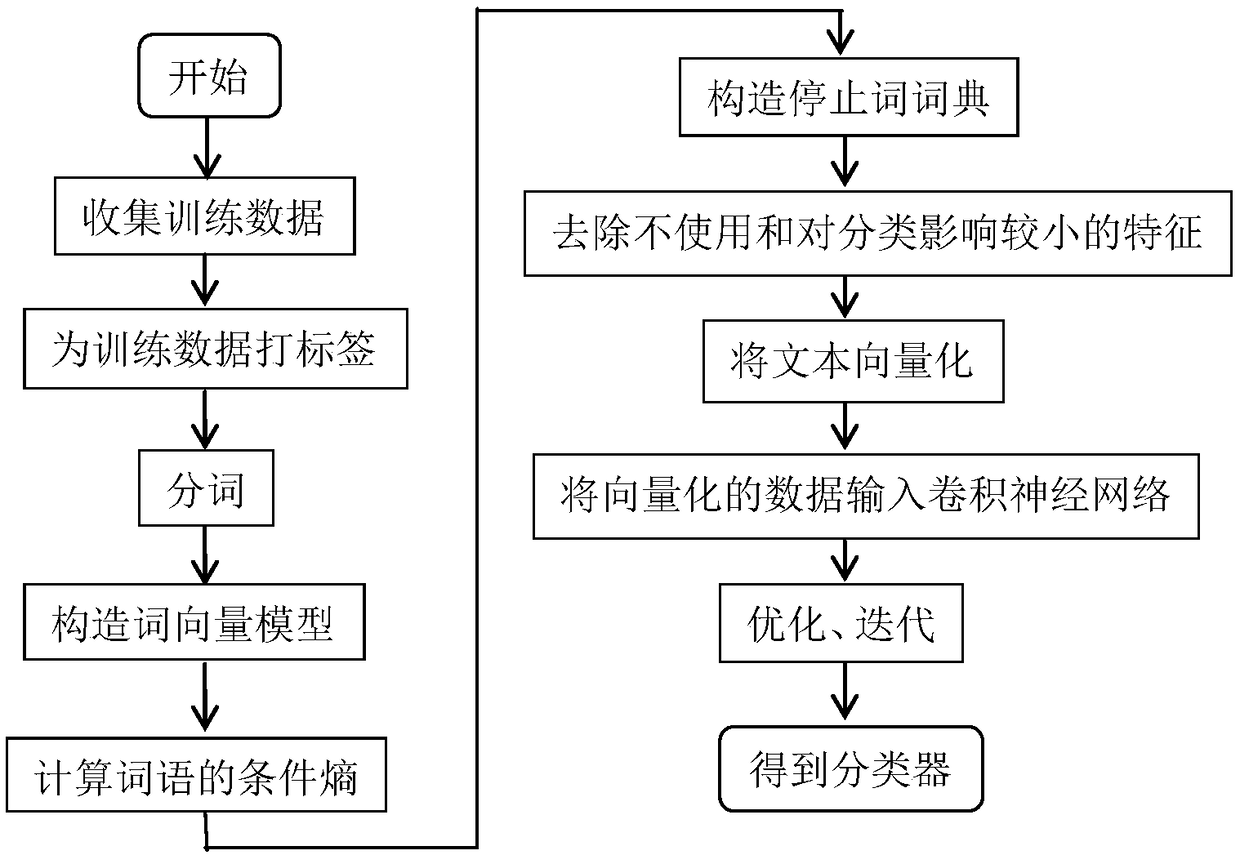
InactiveCN109299468AGood effectNatural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsData setConditional entropy
The invention discloses a short text classification method based on a conditional entropy and a convolution neural network, which relates to the natural language processing field. Comprises the following steps: S1, collecting short text according to requirements to form a training data set; 2, label that training data set accord to categories; 3, perform word segmentation processing on that traindata set; S4, constructing a word vector model; S5, calculating the conditional entropy of all words; 6, construct a stop word dictionary; S7, removing words that do not conform to the conditions andhave less influence on classification; S8, vectorizing all short texts; S9, establishing a convolution neural network model; S10, inputting the vectorized training data set into the convolution neuralnetwork model; S11, continuous iteration, optimization, and finally get the best effect of short text classifier. The invention realizes the filtering of noise words and the accuracy of filtering.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Data publishing method and system
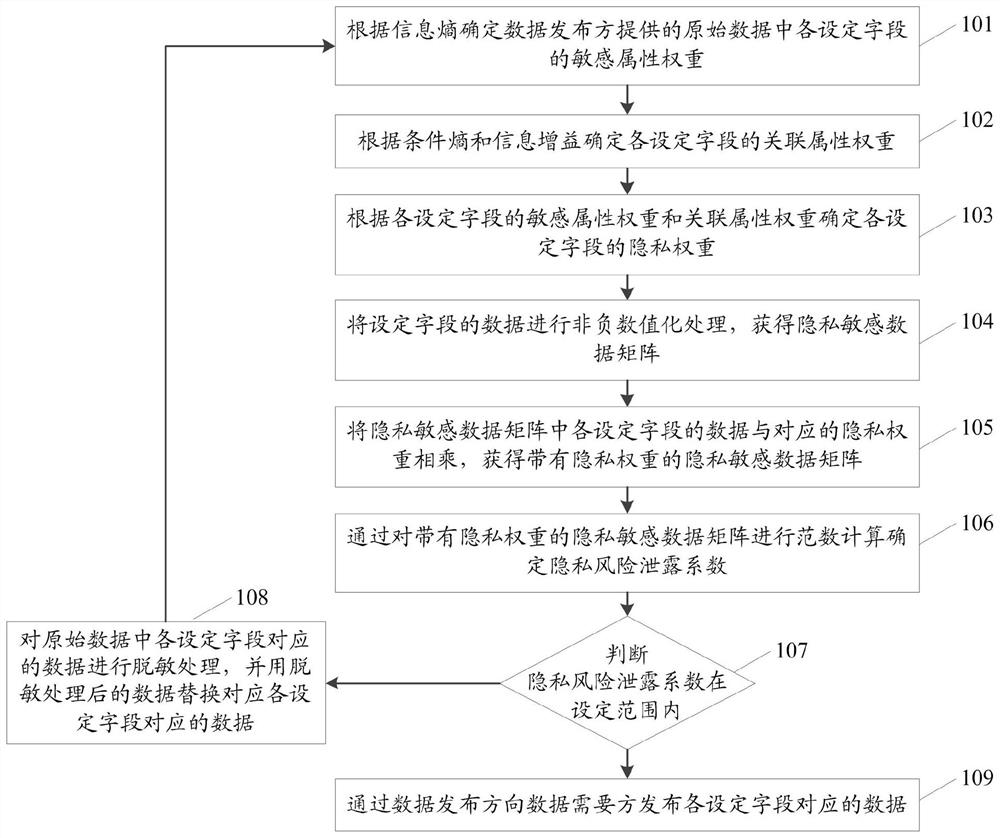
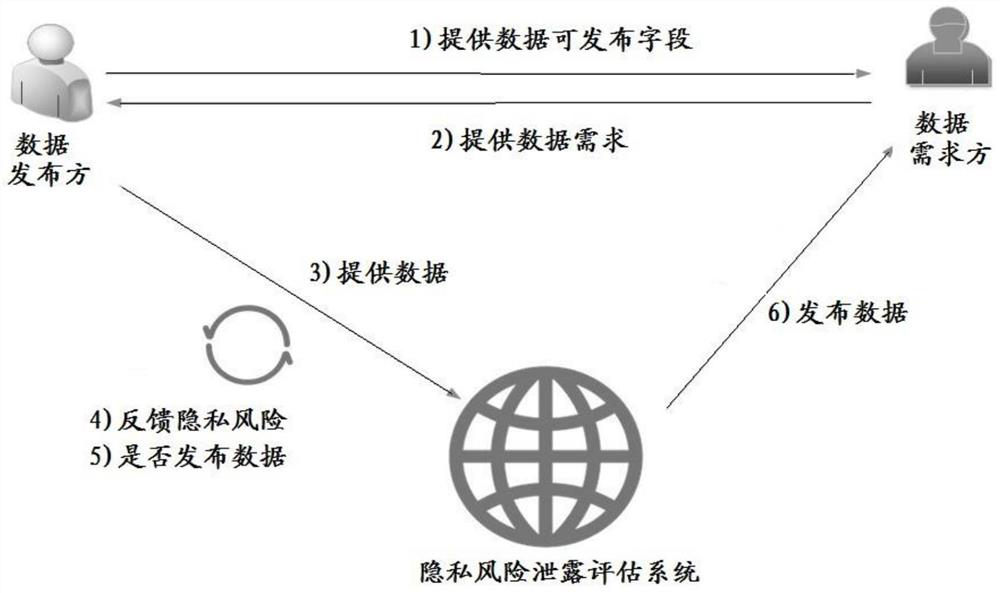
PendingCN114117525AReduce risk of leakageDigital data protectionComplex mathematical operationsConditional entropyOriginal data
The invention relates to a data publishing method and system. The method comprises the steps that sensitive attribute weights of all set fields in original data provided by a data publisher are determined according to information entropy; determining an association attribute weight of each set field according to the conditional entropy and the information gain; determining a privacy weight of each set field according to the sensitive attribute weight and the associated attribute weight; performing non-negative numeralization processing on the data of the set field to obtain a privacy sensitive data matrix; obtaining a privacy sensitive data matrix with a privacy weight; performing norm calculation on the privacy sensitive data matrix with the privacy weight to determine a privacy risk leakage coefficient; judging whether the privacy risk leakage coefficient is within a set range or not; and if the privacy risk leakage coefficient is not within the set range, desensitizing the data corresponding to each set field in the original data, replacing the data corresponding to the set fields with the desensitized data, and recalculating the privacy risk leakage coefficient until the privacy risk leakage coefficient conforms to the set range. According to the invention, the risk of data privacy leakage is reduced.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
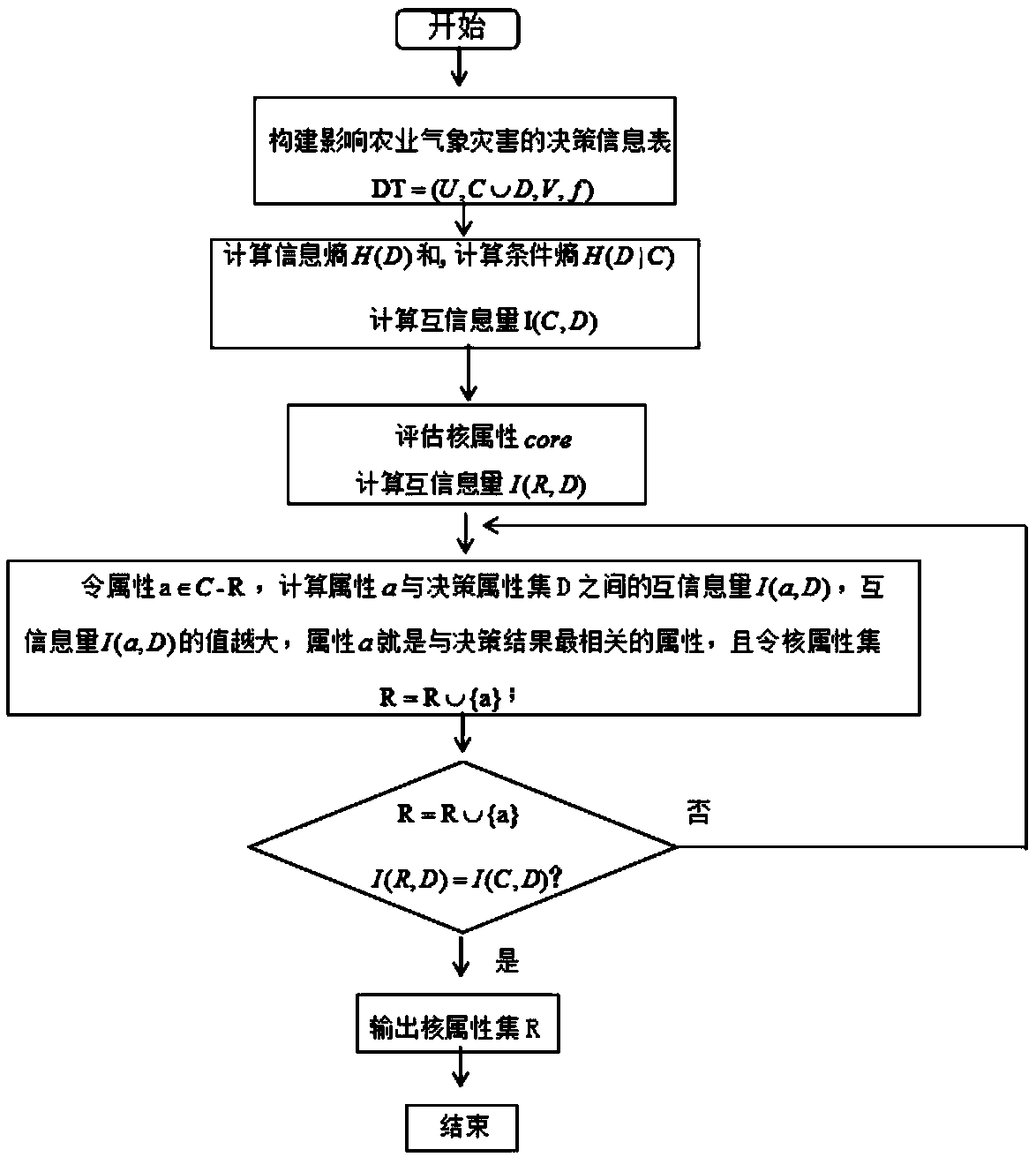
A method and system for eliminating redundancy of agrometeorological data based on information entropy
InactiveCN109636660AAvoid missingAchieve compressionData processing applicationsData dredgingValue set
The invention relates to the field of agricultural data processing, in particular to a method for eliminating redundancy of agrometeorological data based on information entropy, comprising the steps of constructing a decision information table, collecting all object sets, a condition attribute set, a decision attribute set, an attribute value set and a system function, and constructing a decisioninformation table. Calculating the mutual information amount, and obtaining the mutual information amount according to the information entropy and the conditional entropy; Determining a related attribute, if the attribute a is a related attribute, making the kernel attribute data set R = R U {a}; Determining a kernel attribute data set step of determining a value of the kernel attribute data set Rand outputting the kernel attribute data set R if the mutual information amount between the kernel attribute data set R and the decision attribute set is equal to the mutual information amount between the conditional attribute set and the decision attribute set; Disaster assessment step, performing data mining and analyzing the core attribute data set R, according to the results, assessing agro-meteorological disaster. The invention can improve the processing speed of agrometeorological data and improve the accuracy of agrometeorological disaster assessment.
Owner:GUANGDONG KINGPOINT DATA SCI & TECH CO LTD
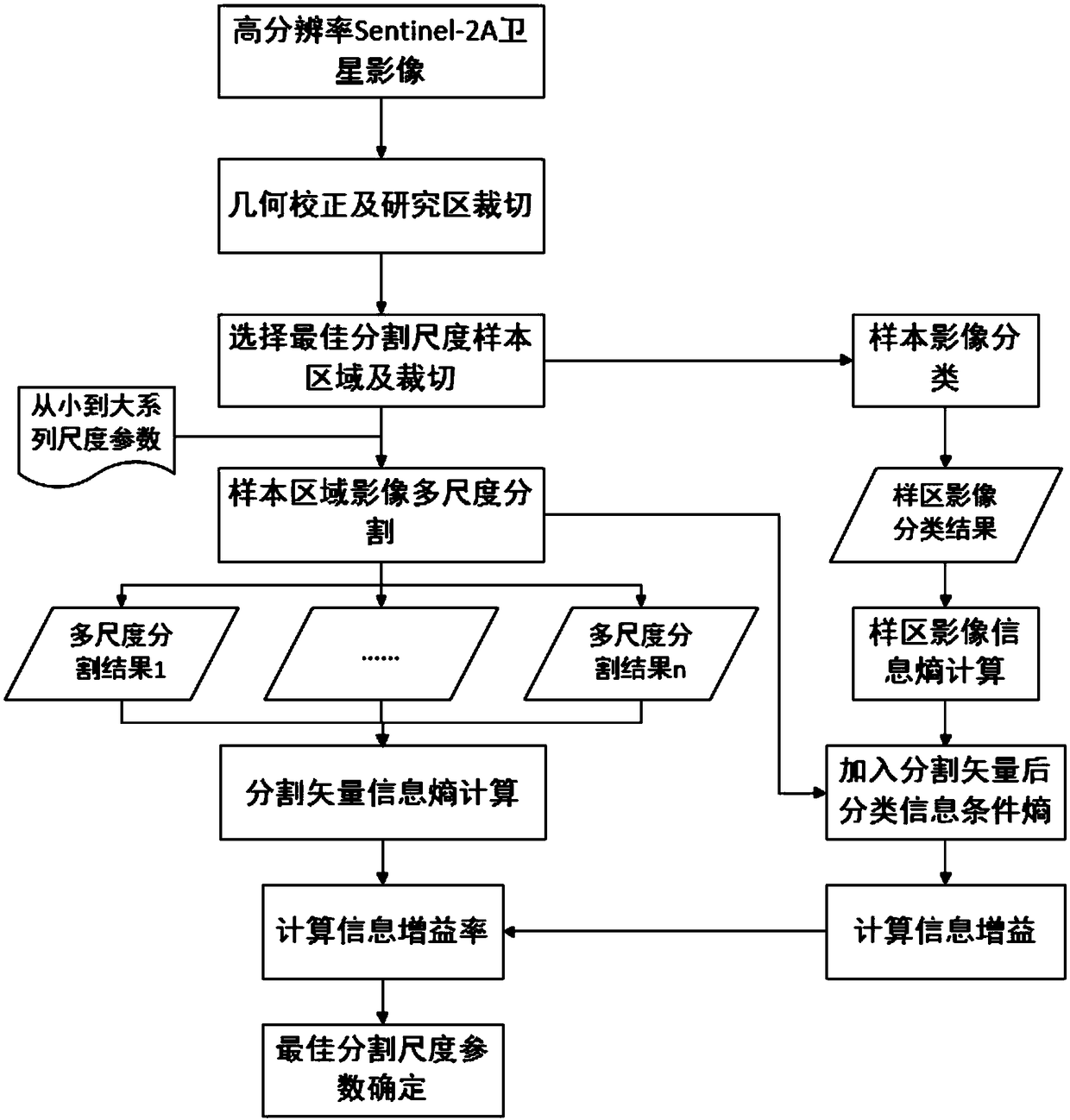
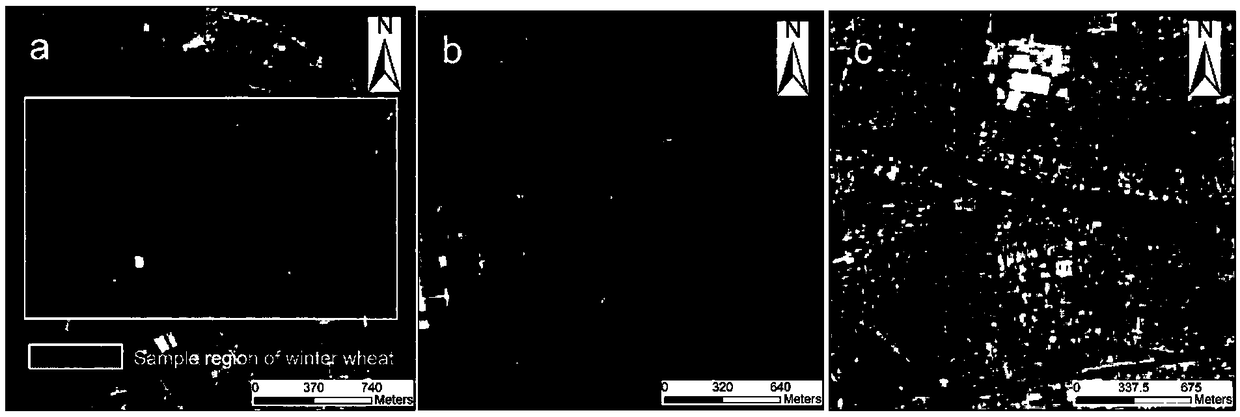
Method for determining the optimal segmentation scale of satellite image segmentation based on information gain ratio
ActiveCN109063577AImprove classification accuracyImprove the effect of multi-scale segmentationCharacter and pattern recognitionConditional entropyInformation gain ratio
The invention discloses a method for determining the optimal segmentation scale of satellite image segmentation based on information gain rate, includes obtaining high-resolution satellite remote sensing image, preprocessing, selecting representative region as sample region determined by optimal segmentation scale, classifying surface features of sample region, obtaining image classification result of sample region as reference image determined by optimal segmentation scale, and obtaining image classification result of sample region as reference image determined by optimal segmentation scale;setting a series of segmentation scale parameters from small to large, using multi-scale segmentation technology, the sample image is segmented in multi-scale to obtain a series of segmented object vectors; Based on Shannon information entropy formula, the information entropy of reference image and segmentation vector is calculated, and the conditional entropy of reference image with segmentationvector is calculated, then the information gain and information gain ratio of segmentation vector are calculated. The optimal segmentation scale is selected according to the principle of maximum information gain rate. Finally, based on the optimal segmentation scale, the original image is segmented at multiple scales.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
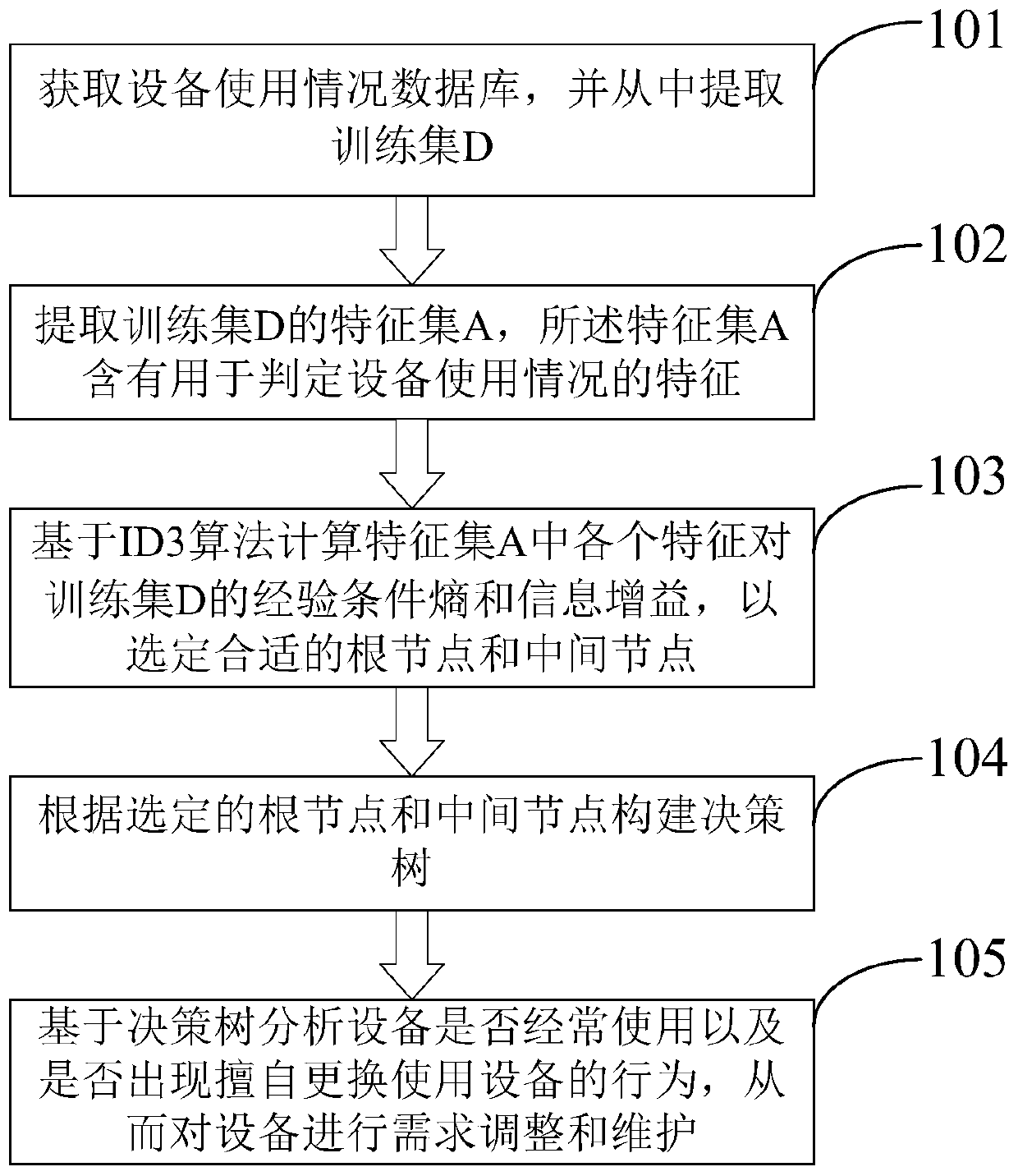
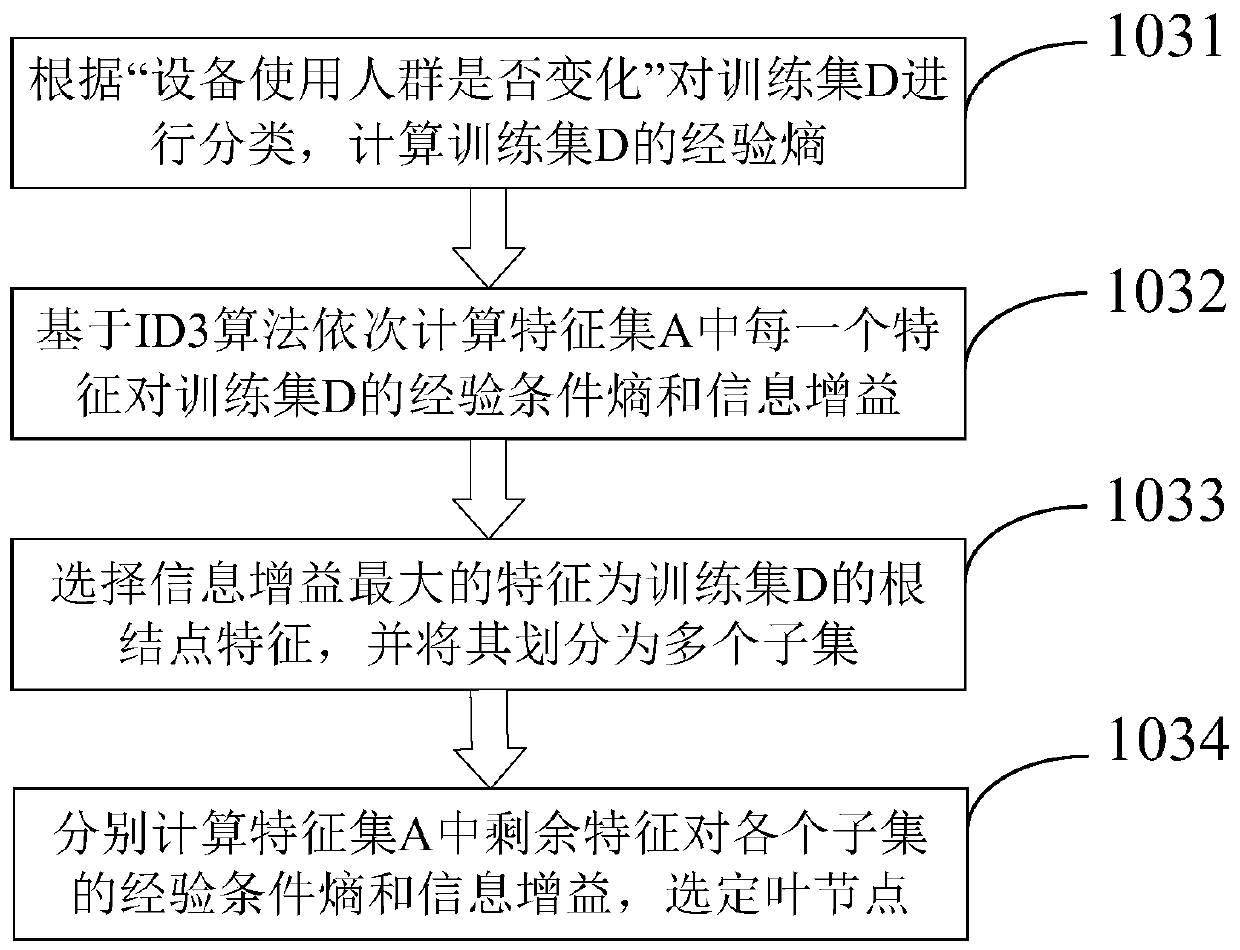
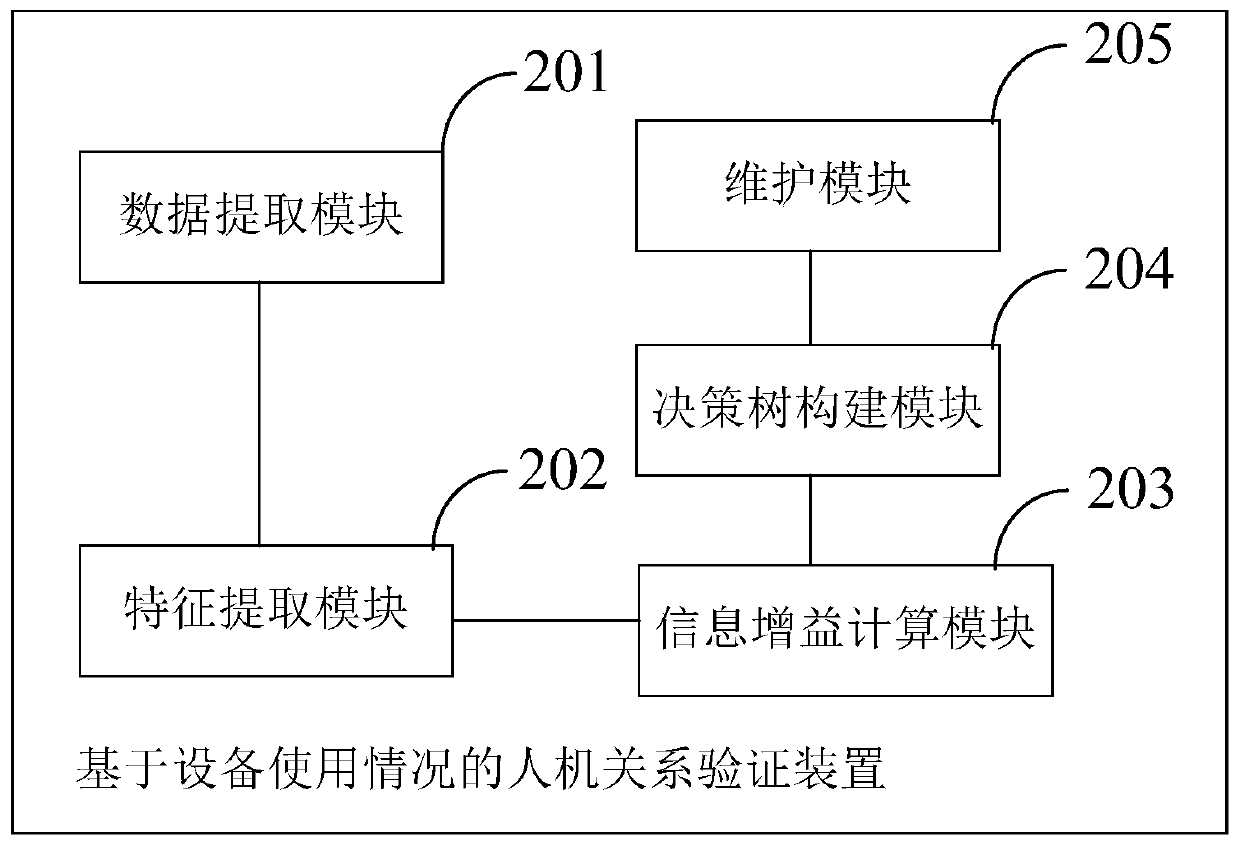
Man-machine relationship verification method and device based on equipment use conditions
PendingCN111008646AImprove securityImprove accuracyData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature setConditional entropy
The invention discloses a man-machine relationship verification method and device based on equipment use conditions. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an equipment use condition database, and extracting a training set D from the equipment use condition database; extracting a feature set A of the training set D, wherein the feature set A contains features for judging the use condition of the equipment; calculating the empirical conditional entropy and the information gain of each feature in the feature set A to the training set D based on an ID3 algorithm so as to select a proper root node and a proper intermediate node; constructing a decision tree according to the selected root node and the intermediate node; and analyzing whether the equipment is frequently used or notand whether the equipment is replaced and used arbitrarily or not based on the decision tree so as to adjust and maintain the requirements of the equipment. The invention further discloses a corresponding device. Whether the equipment is frequently used or not and whether the behavior of replacing the equipment without permission occurs or not can be discovered in time through equipment feature identification calculation so that the information security and accuracy are improved, and the problems that the equipment is idle and the user of the equipment can be replaced without permission are solved.
Owner:国网浙江武义县供电有限公司 +1
A Method for Acquiring Transmission State of Radio Frequency Stealth Data Link Based on Maximum Conditional Entropy
InactiveCN103678906BImprove RF Stealth PerformanceIncrease uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsNormal densityConditional entropy
The invention discloses a radio frequency stealth datalink emitting state acquiring method based on maximum conditional entropy. A prior environmental threat factor x and a prior datalink emitting state y in historic radio frequency stealth data serve as sample spaces. Firstly, the probability density function of the sample space x, the joint probability density function of the sample space x and the sample space y and the characteristic functions of the sample space x and the sample space y are respectively worked out; secondly, a maximum conditional entropy distribution function expression is worked out by building a Lagrange function; thirdly, unknown coefficients in the maximum conditional entropy distribution function expression are worked out, and a maximum conditional entropy distribution function is acquired; fourthly, environment thread factors acquired by situation awareness equipment are input into the maximum conditional entropy distribution function, and a datalink emitting state with the largest uncertainty is acquired.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Distributed Denial of Service Attack Detection Method Based on C4.5 Decision Tree Algorithm
The invention discloses a distributed denial of service attack detection method based on a C4.5 decision tree algorithm in software defined network environment, and the method comprises the followingsteps: collecting flow table information returned back by an OpenFlow switch through an OpenFlow protocol; extracting field information related to a DDoS attack from the flow table information, converting the extracted information into parameters capable of analyzing network flow distribution variation and taking the parameters as attributes, and forming a training set of a decision tree; classifying flows with the C4.5 decision tree algorithm, calculating class information entropy according to training set data classes; orderly calculating conditional entropy of the attributes, gain of information, information entropy of the attributes and information gain ratio of the attributes; selecting the attribute with the highest information gain ratio as a root node of the decision tree, and selecting the attributes with highest information gain ratio from the residual attributes as a fork node, and repeating the steps above until forming the decision tree; and using the finally formed decision tree to perform classification operation for the new network flow, and detecting whether the DDoS attack exists. The method can detect the DDoS attack more accurately.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
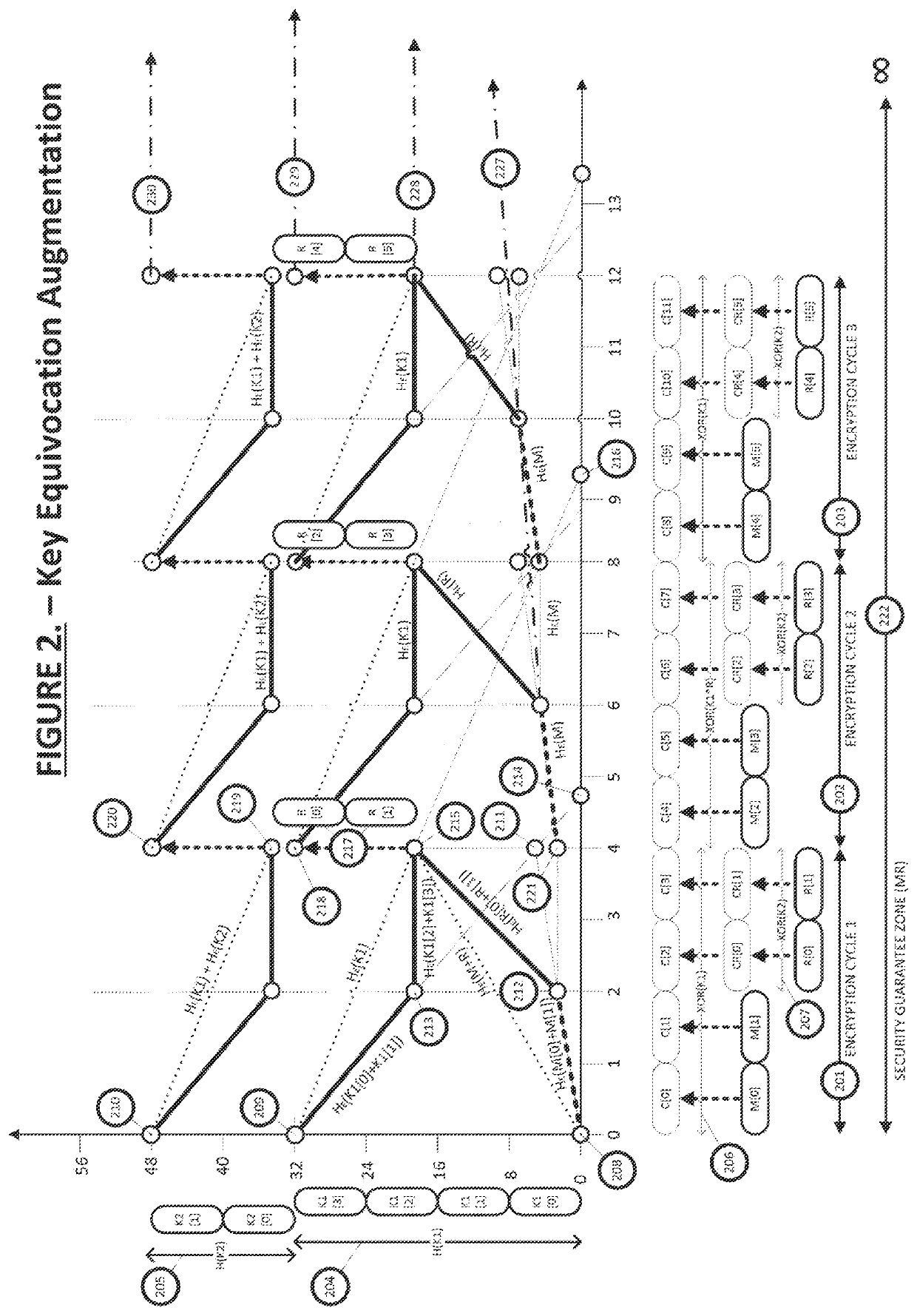
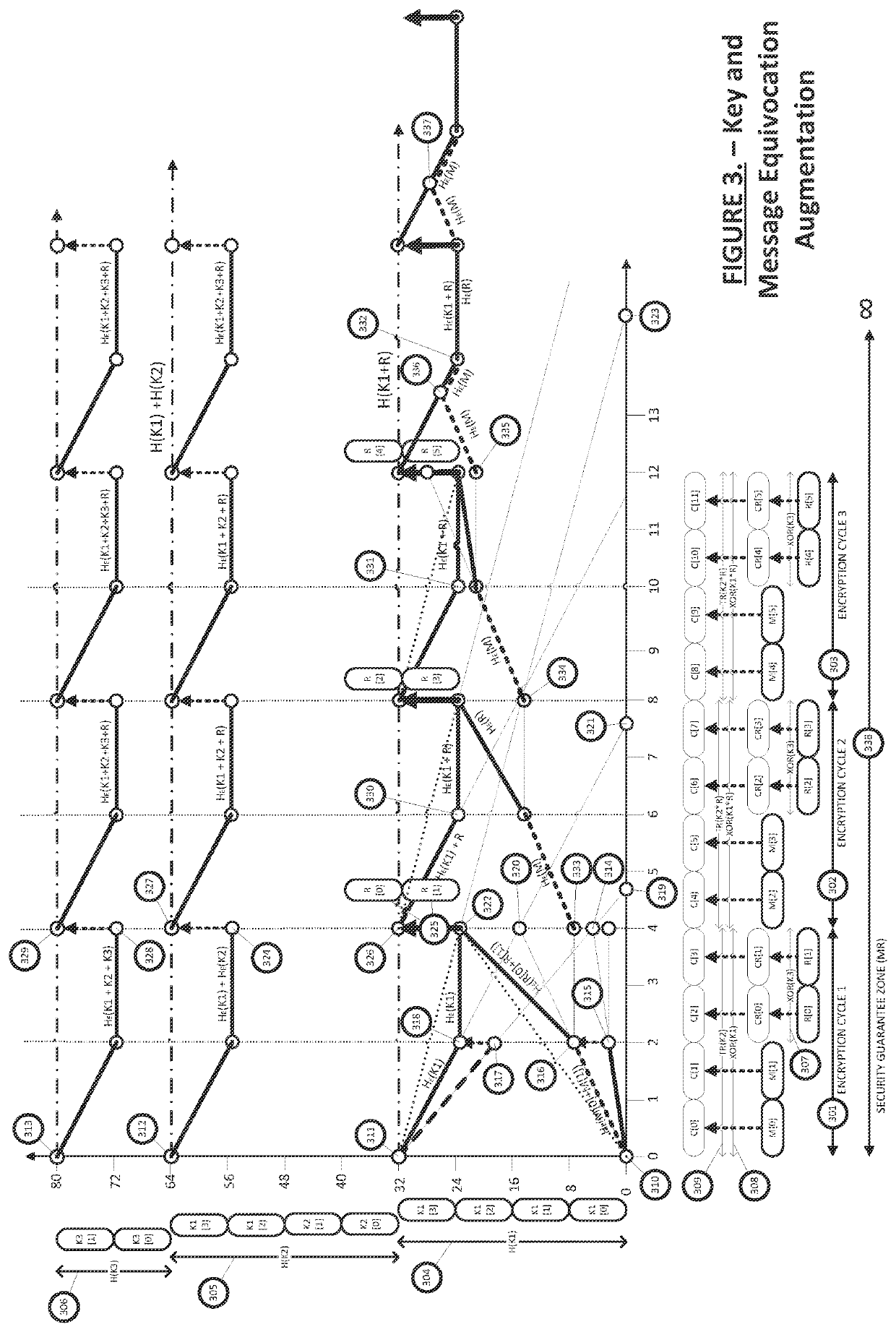
Equivocation augmentation dynamic secrecy system
ActiveUS11233628B2Eliminate requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageSecurity solutionBrute force
Owner:FIGUEIRA HELDER SILVESTRE PAIVA
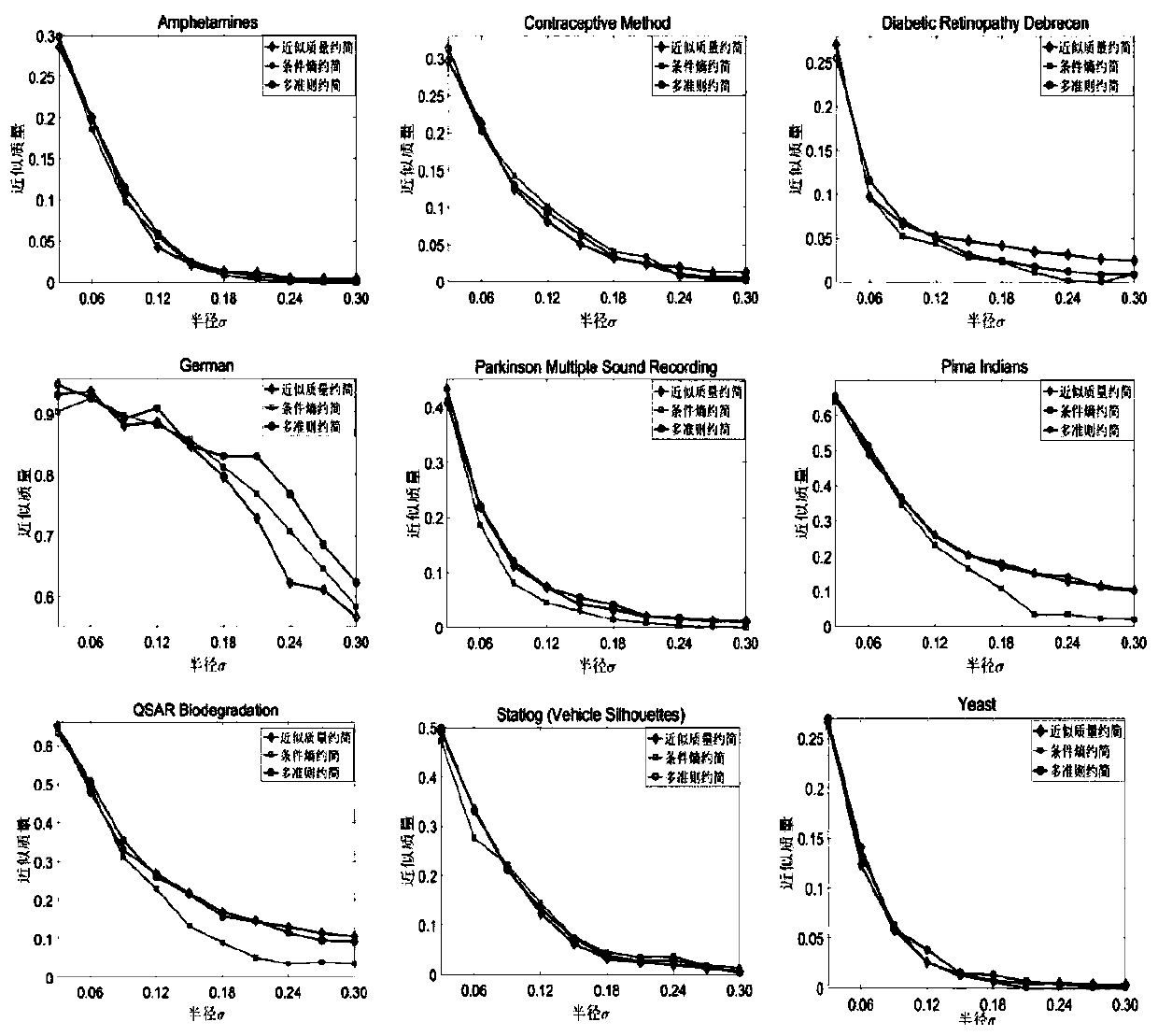
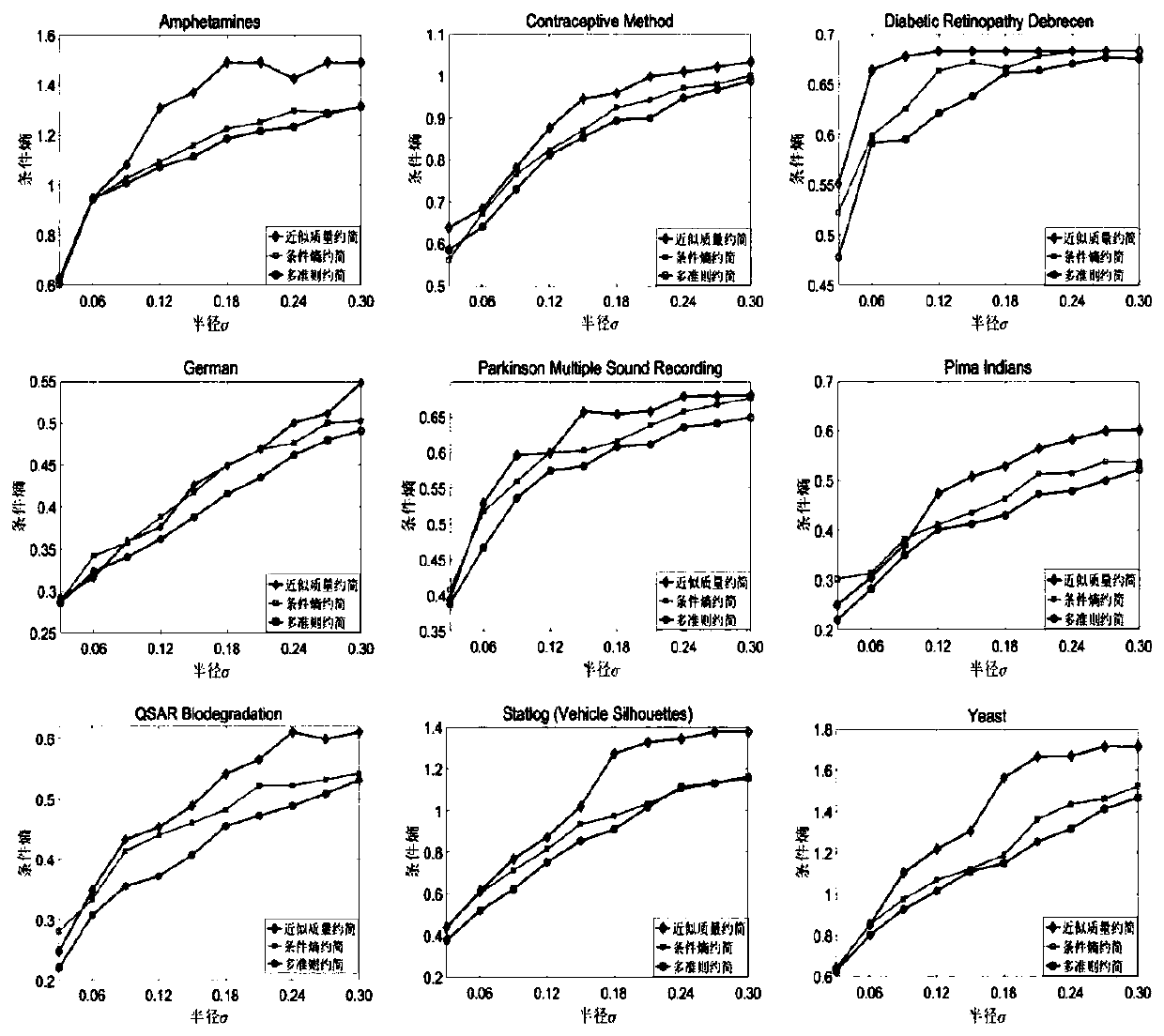
Attribute reduction method based on approximate quality and conditional entropy
InactiveCN110674870AConditional Entropy DecreaseImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionDecision systemConditional entropy
The invention discloses an attribute reduction method based on approximate quality and conditional entropy. The method comprises: using a heuristic algorithm for solving approximate quality reduction;wherein the input is a neighborhood decision system DS = (U, ATU {d}), constraint conditions, metrology criterion gamma, the output is an approximate mass reduction red. Although an attribute reduction result based on a single criterion on a neighborhood rough set can meet constraint conditions of corresponding measurement indexes, the attribute reduction result can meet the constraint conditions. However, other measurement criteria cannot be still met. Therefore, the algorithm provided by the invention fuses multiple criteria of approximate quality and conditional entropy to serve as a new reduction method of measurement indexes, and experimental results show that the new reduction not only can reduce the conditional entropy on the basis of keeping the approximate quality unchanged obviously, but also can effectively improve the classification precision.
Owner:文辉祥
Multi-target feature selection method and device for image classification and storage medium
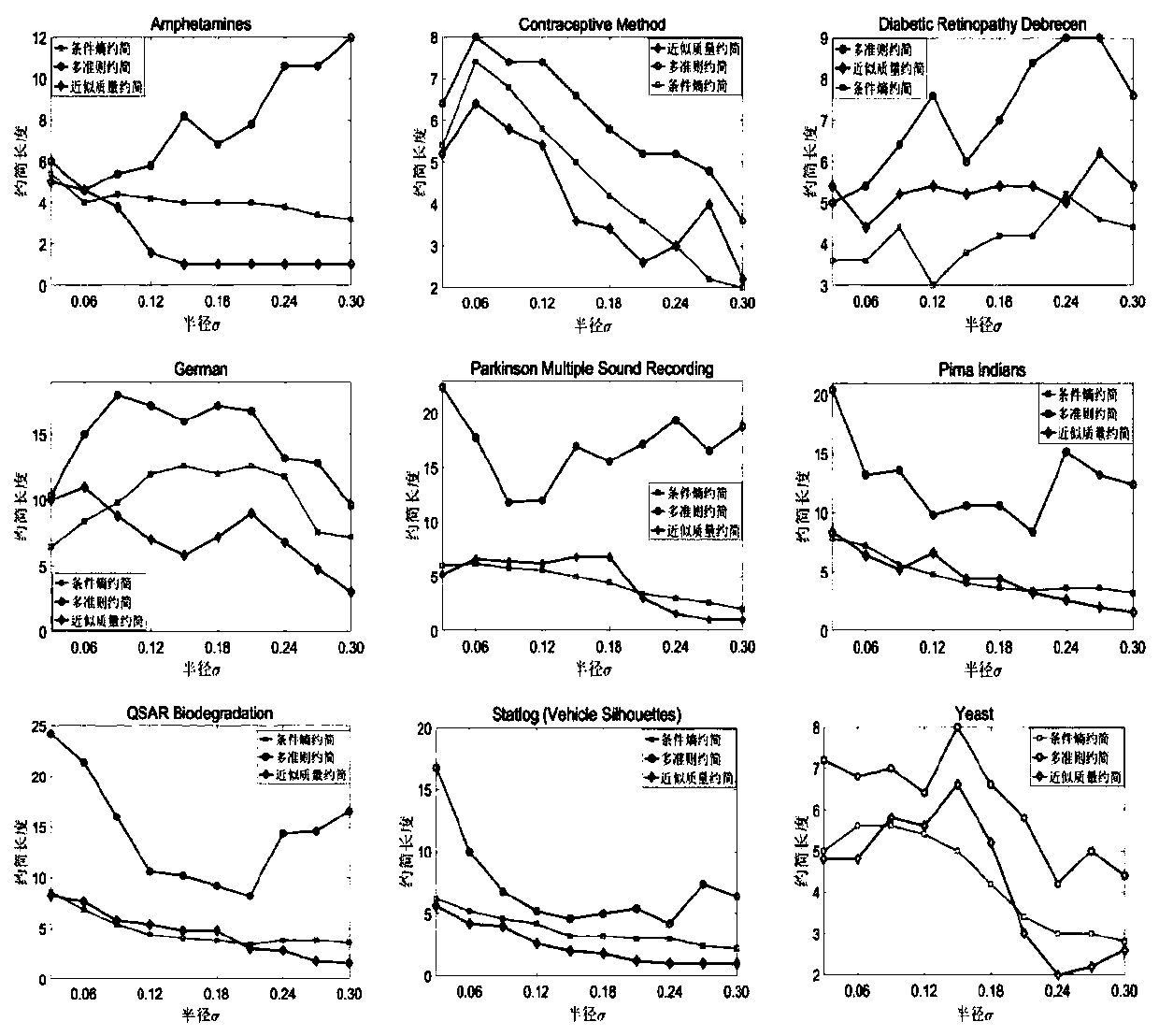
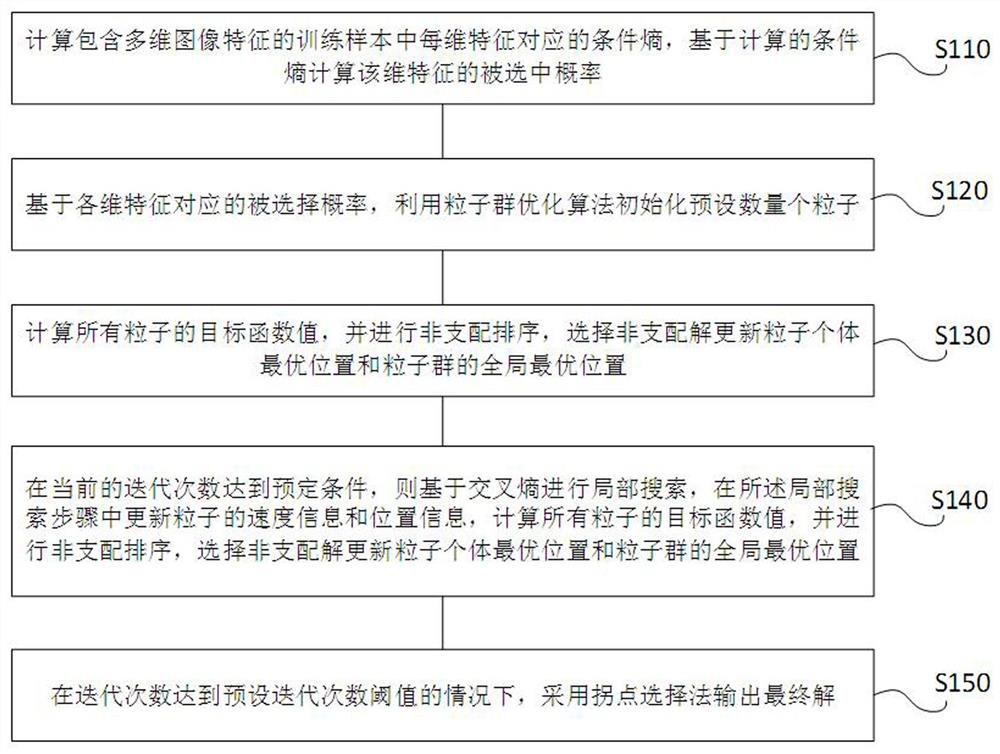
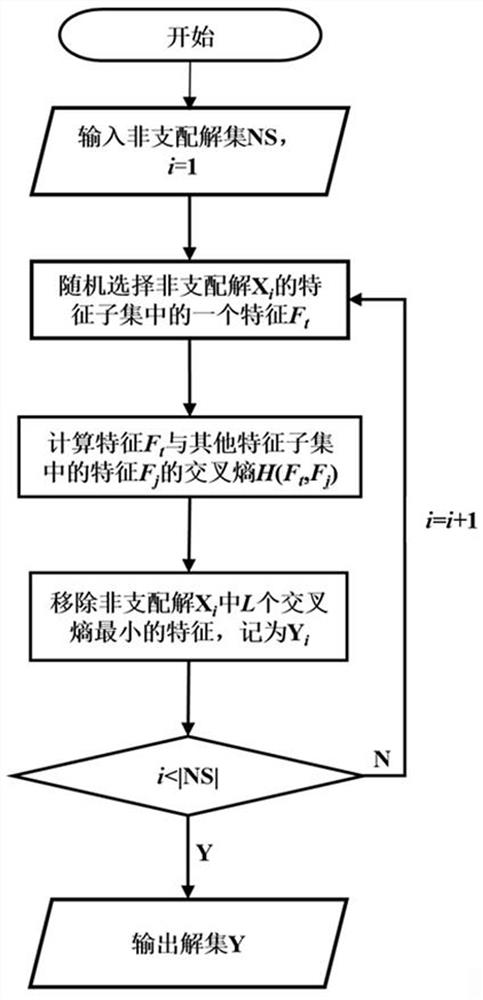
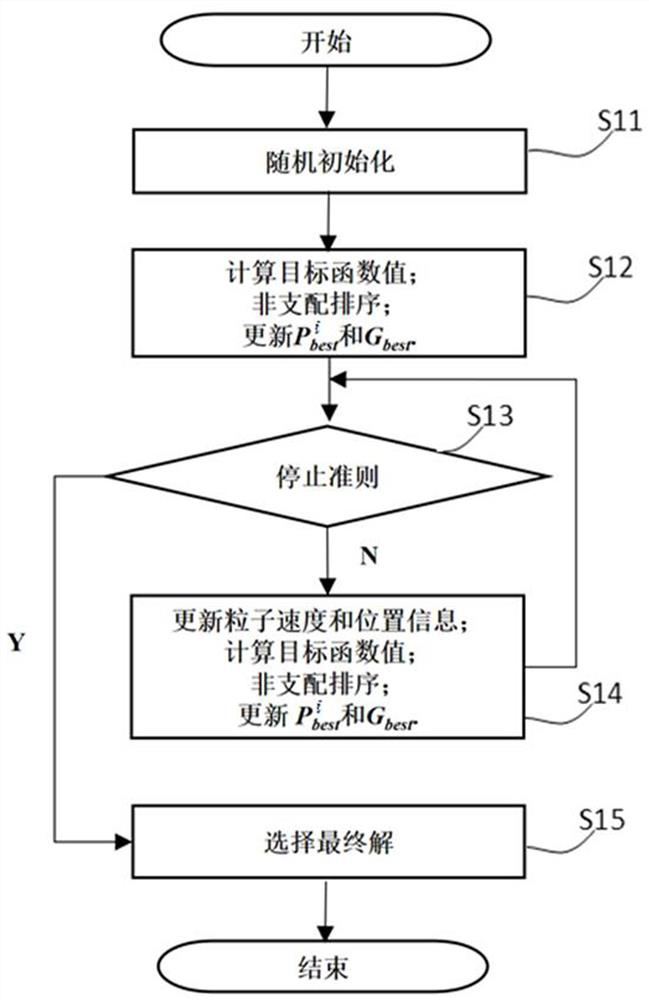
ActiveCN113688950ASmall scaleQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionArtificial lifeLocal search (optimization)Conditional entropy
The invention provides a multi-target feature selection method and device for image classification and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: calculating the conditional entropy corresponding to each dimension of feature in a training sample containing multi-dimensional image features, and calculating the selected probability of the dimension of feature; initializing a preset number of particles by using a particle swarm optimization algorithm; calculating target function values of all particles, performing non-dominated sorting, and selecting a non-dominated solution to update the optimal position of a particle individual and the global optimal position of a particle swarm; when the current number of iterations reaches a preset condition, carrying out local search based on cross entropy, updating speed information and position information of particles in the local search step, calculating target function values of all particles, carrying out non-dominated sorting, and selecting a non-dominated solution to update the optimal position of a particle individual and the global optimal position of a particle swarm; and outputting a final solution by adopting an inflection point selection method under the condition that the number of iterations reaches a preset number of iterations threshold.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com