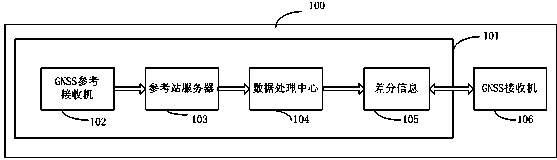
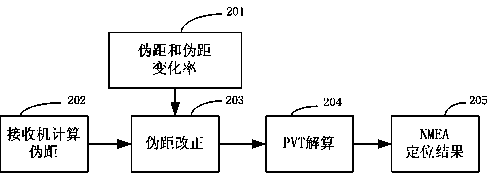
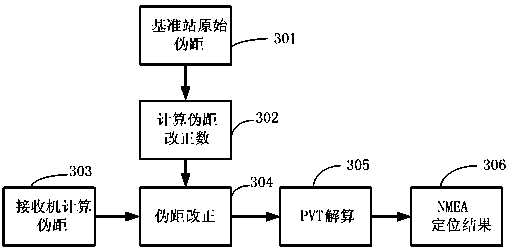
Differential information transmitting method of satellite navigation satellite navigation receiver and corresponding receiver
A technology of differential information and satellite navigation, applied in satellite radio beacon positioning systems, measuring devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as increased power consumption, increased user costs, and increased costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The receiver fixedly receives the differential information of the differential station every N (1~600) seconds, corrects the pseudo-range, and no longer receives the differential information within this time period. Usually, the value of N can be dynamically configured.
Embodiment 2
[0050] The receiver calculates its own movement speed, or obtains the speed information of the receiver from the sensor, and then determines the frequency at which the receiver receives differential information through the speed of the speed. If the receiver moves faster, the frequency of receiving differential information will be accelerated. If the receiver Slower motion reduces the frequency at which the receiver receives differential information. Table 1 illustrates the relationship between the speed of the receiver and the frequency of differential information received by the receiver. It can be seen that the faster the speed, the higher the frequency received.
[0051]
[0052] Table 1 The relationship between the speed of the receiver and the frequency of the differential information received by the receiver
Embodiment 3
[0054] The receiver calculates its own position information, and then calculates the distance between the receiver and the precise coordinates of the reference station, and then determines the frequency at which the receiver receives differential information based on the distance between the receiver and the reference station. If the receiver is far away from the reference station, it will speed up The frequency at which the receiver receives differential information. If the receiver is closer to the reference station, reduce the frequency at which the receiver receives differential information. Table 2 illustrates the relationship between the distance between the receiver and the reference station. It can be seen that the farther the distance between the receiver and the reference station, the higher the frequency received.
[0055]
[0056] Table 2 The relationship between the distance between the receiver and the reference station and the frequency of differential informa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com