Scientific workflow scheduling method and device
A scheduling processing and workflow technology, applied in the field of data processing, can solve problems such as large load imbalance, long time spent on scheduling algorithms, and poor quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
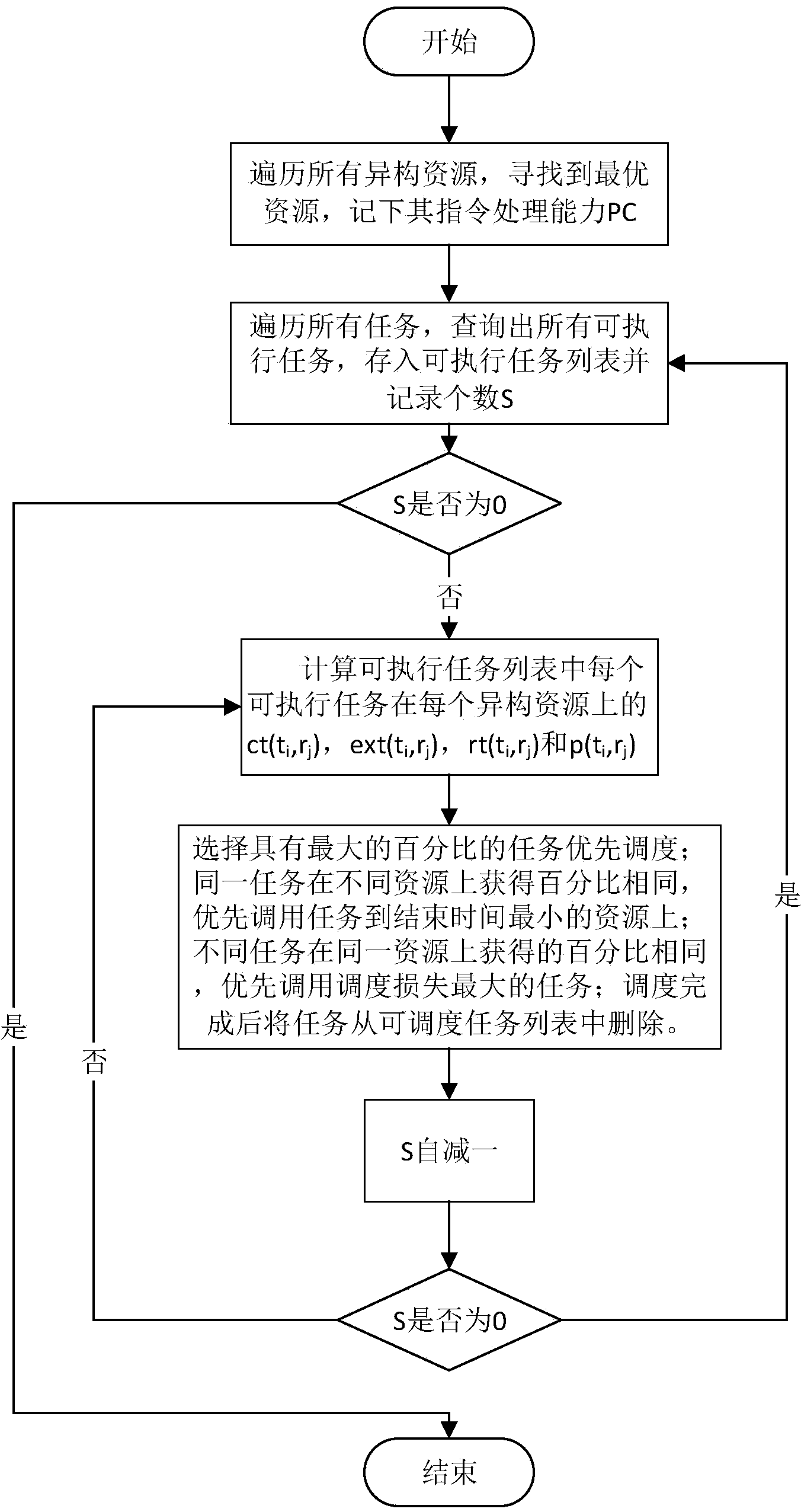
[0042] The preferred embodiments of the invention will be further described in detail below.
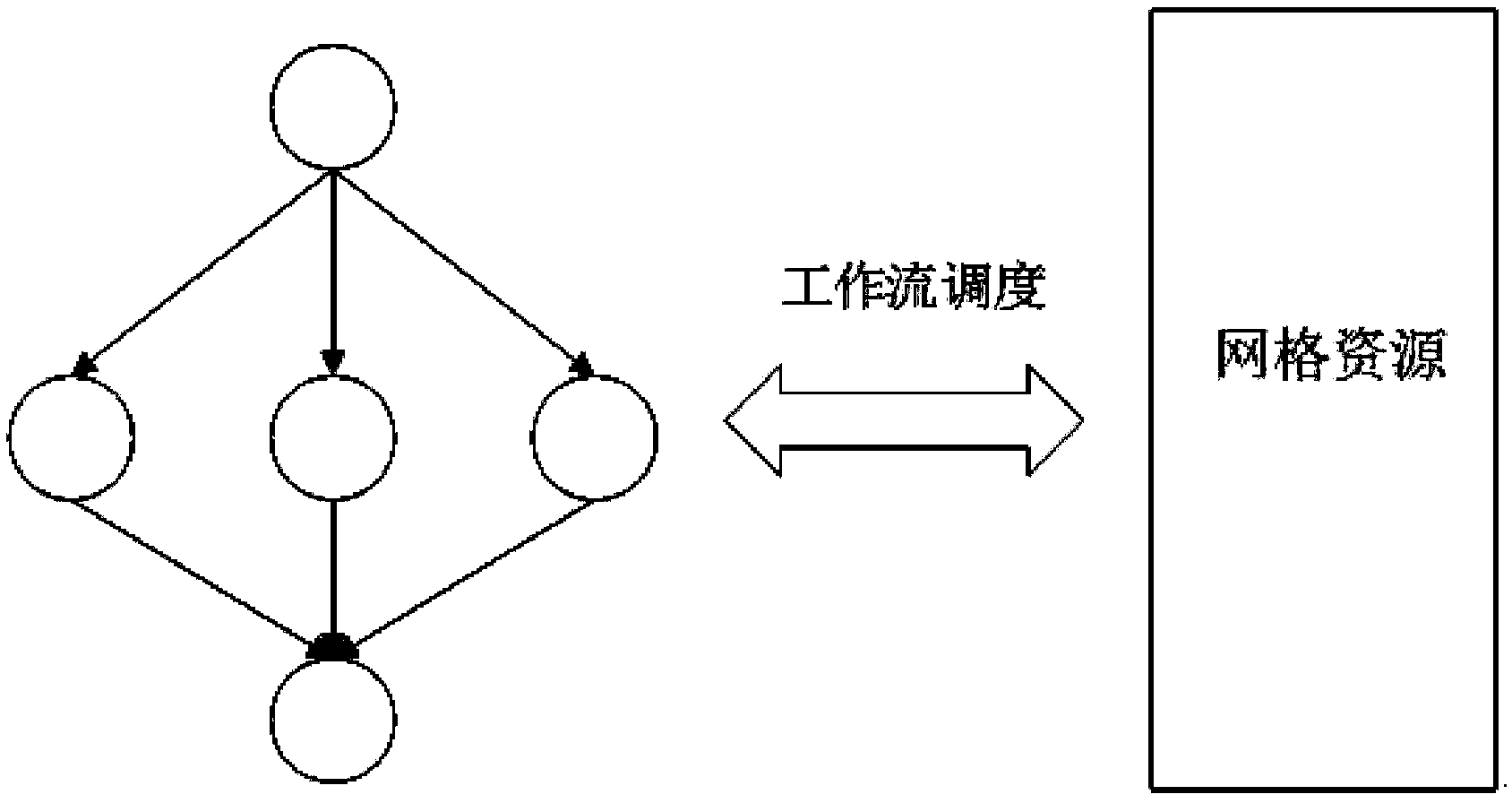
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown in , the graph shows the mapping relationship between scientific workflow and grid heterogeneous computing resources. Scheduling of scientific workflow is the process of mapping different tasks to different heterogeneous computing resources for execution.
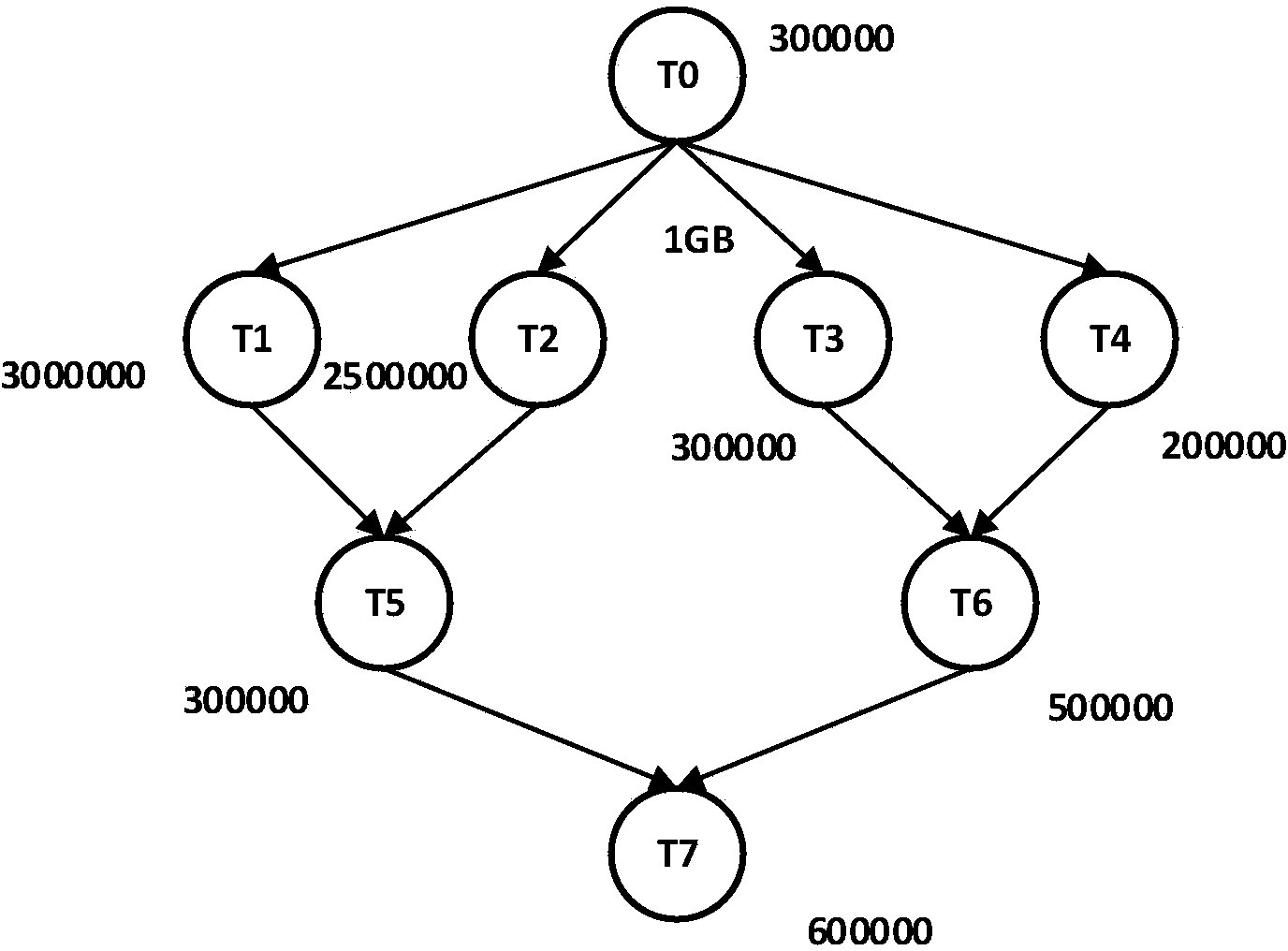
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a directed acyclic graph of a scientific workflow, each circle represents a node, each node represents a task in the scientific workflow, and these nodes form a task set T={T0,T 1 ,T 2 ,T 3 ,...T i ...}, the number next to each node indicates the size of the corresponding task, and the size of the task can be represented by MI (million instructions). For example, the sizes of tasks T0 and T1 are 300,000 and 2,500,000, respectively. Assume that the output file size of each task is 1GB (GigaByte, one billion bytes). The arrow relationship in the figure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com