A Method for Obtaining Spatial Distribution of Parametric Array Sound Field Based on Conserved Upwind Pattern
A technology of spatial distribution and parametric array, applied in the field of parametric array sound field, can solve problems such as high requirements and coordination, achieve grid division rules and improve computing efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
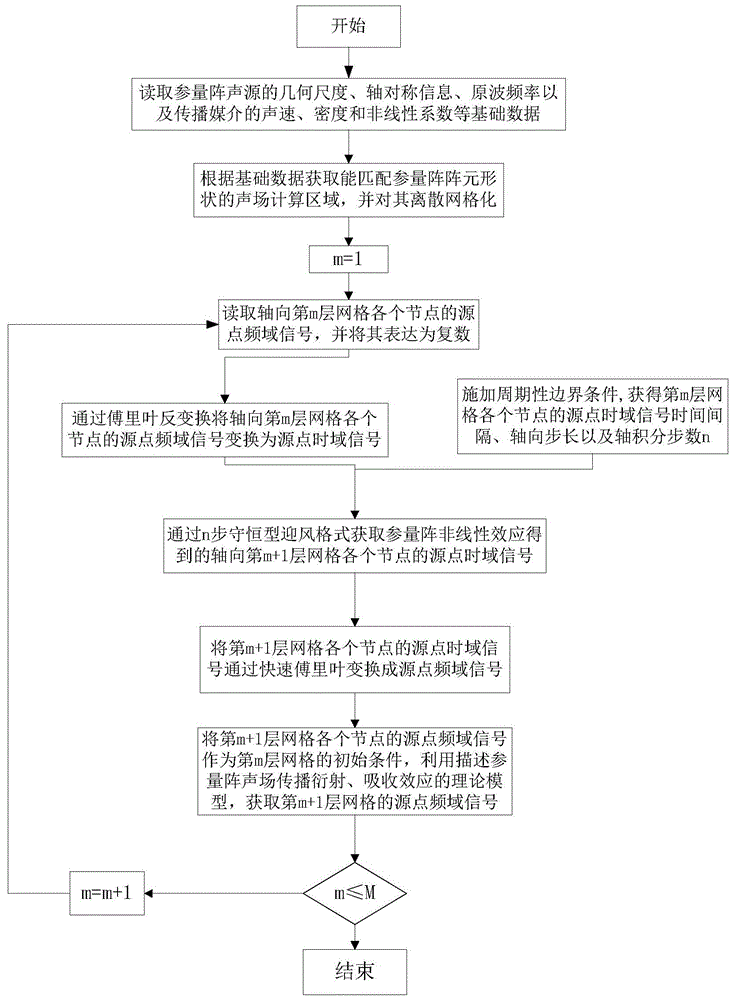
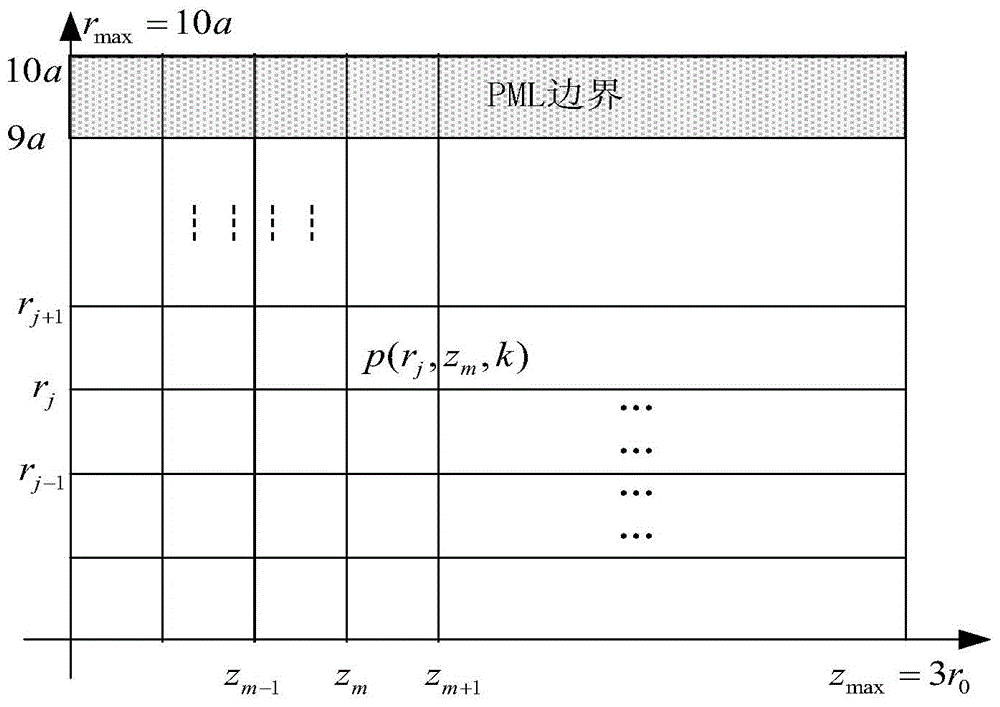
[0046] (a) Determine the limited calculation area of the parametric array sound field according to the basic data of the parametric array sound source and the propagation medium, and discretize it into a grid model; take the sound field radiated by the circular piston sound source as an example, and divide the three-dimensional calculation area into two In the dimensional roz plane, the calculation area is divided by the rectangular grid with the best fit to the boundary, and the limited calculation area model of the parametric array sound field is established. Set 0 max The interval is divided into M sections, and each layer corresponds to an axial position z m , Call m=1 as the first layer, and the radial coordinate subscript j of each layer along the radial direction, that is, in the r direction, changes from 1 to J, that is, J sound pressure values must be calculated for each layer;
[0047] (b) According to the formation conditions of the parameter array, read z 1 The k-...
example 1
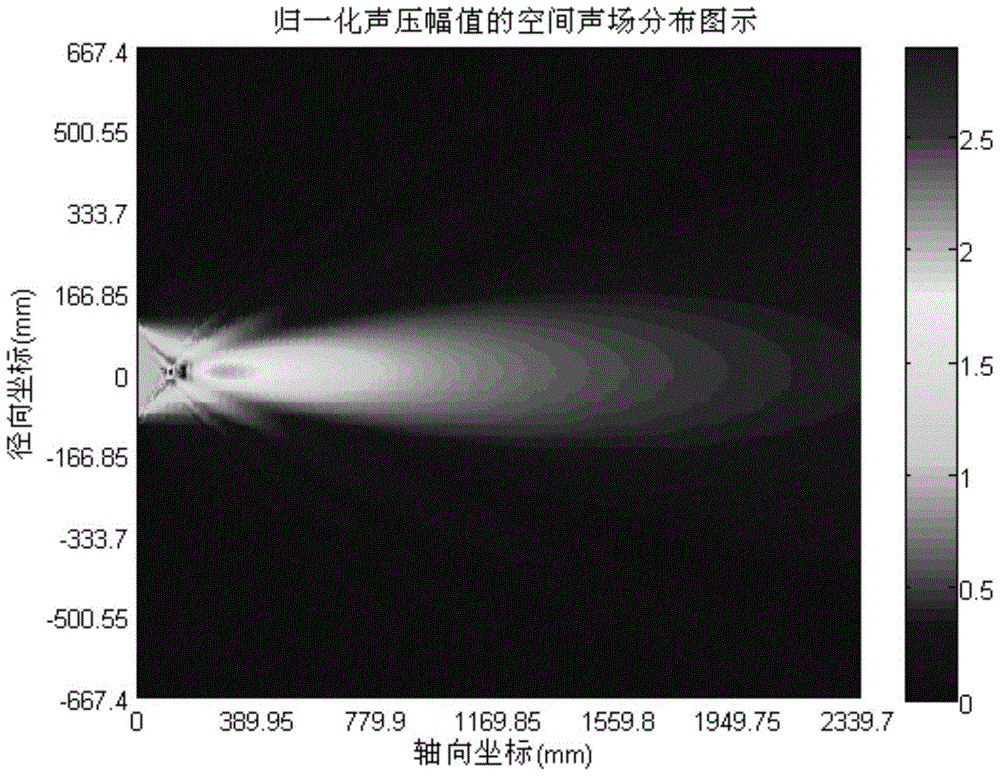
[0072] Example 1: Analysis of sound field characteristics of parametric array
[0073] The example parameter settings are as follows: Take the parametric array radiation system formed by a circular piston sound source as an example, based on the axisymmetric characteristics of the piston sound source, calculate the spatial distribution of the parametric array sound field in a limited area (such as figure 2 Shown). Suppose the radius of the transducer is a, and the radial calculation area is (0,r max ), where r max =31a, the axial calculation area of the transducer is (0,z max ), where z max =2.5d, d=πf 0 a 2 / c is the Rayleigh distance corresponding to the center frequency of the original wave radiated by the transducer. The position of the piston sound source [1,a], the radial calculation range is [1,31a], in order to reduce the interference of the boundary reflection on the calculation of the sound field, set the area [30a,31a] as the PML area, assuming that each axis...
example 2
[0081] Example 2: Analysis of the time spent in calculation
[0082] The parameters are the same as in Example 1. Set the extension length of the axial sound field to 2.5 times the Rayleigh distance, divided into 10 equal parts, and each equal part is about 0.25 times the Rayleigh distance. We set the unit Rayleigh distance to 60 , 120 equal divisions, draw a table according to the time it takes for the sound field axial deduction process to reach each axial position node, and compare the time consumption of different sound field acquisition methods.
[0083] The distributions in Table 1 and Table 2 indicate that the axial unit Rayleigh distance is divided into 60 and 120 equal divisions, and it takes time for two different methods to obtain the spatial distribution of the parametric array sound field at each axial position.
[0084] Table 1 Comparison of the time taken by the two methods to obtain the sound field process
[0085]
[0086]
[0087] Table 2 Comparison of the time consu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com