Nucleic acid probe and preparation method and use thereof
A technology of nucleic acid probes and nucleic acid molecules, which is applied in the field of biotechnology and can solve problems that need to be improved
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0158] Example 1: Synthesis of nucleic acid probe library
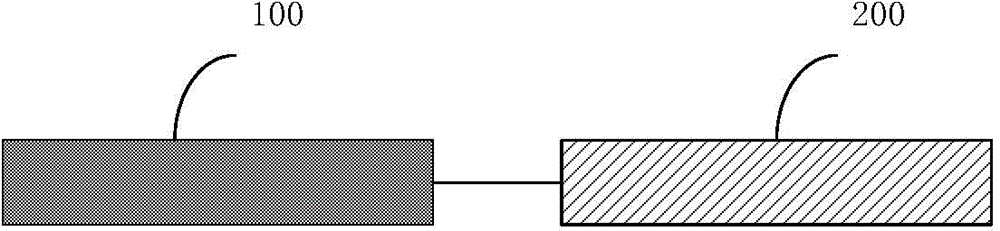
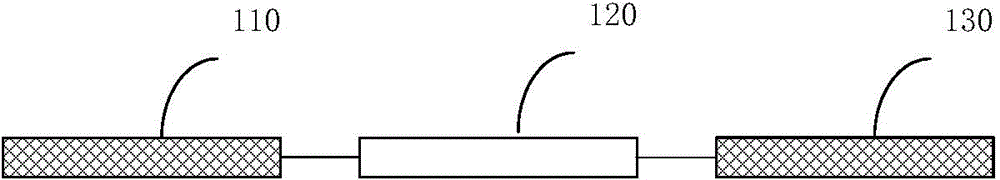
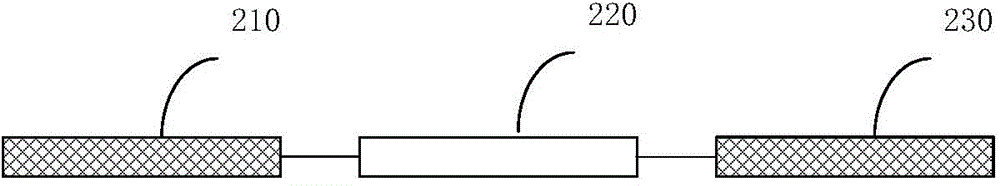
[0159] The entire molecular probe is composed of two parts: the target recognition catalytic sequence (FL) and the substrate sequence (FS). FL and FS are linked together to form a complete nucleic acid probe (MP). FL sequence is composed of primer sequence (FP1 and RP1) and core sequence (ie recognition sequence, N40). The substrate sequence (FS) and primer fragments (FP1 and RP1) are fixed sequences, which are the same in all nucleic acid probes. The core sequence (recognition sequence, N40) is composed of 40 randomly distributed A, T, C, and G base molecules and is the core sequence of nucleic acid probes.
[0160] among them,
[0161] FL: 5’-CACGGATCCTGACAAG-N40-CAGCTCCGTCCG-3’;
[0162] FS: 5'-ACTCTTCCTAGCFrAQGGTTCGATCAAGA-3', where F refers to dT labeled with fluorescein, rA refers to adenine ribonucleotides, and Q refers to dT labeled with the quencher DABCYL. All common reagents are commercially available;
[0163] ...
Embodiment 2
[0182] Example 2 Screening of nucleic acid probes that recognize breast cancer
[0183] The cell types used in this embodiment are breast cancer cells and normal breast cells, specifically breast cancer MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 cells, and normal breast cells MCF-10A.
[0184] The probe screening process is: (1) Add 50 microliters of 2* screening buffer (which contains 100mM HEPES (pH7.5), 400mM NaCl, and 10mM divalent metal ion Mg(II)) to the probe library, vortex Rotate for 5 minutes and then centrifuge briefly; (2) Add 50 microliters of extracellular fluid for negative selection (or intracellular fluid for negative selection, filtered with a 0.2 micron filter before use), and incubate at 25 degrees Celsius for 30 minutes; (3) ) Add 100 microliters of stop buffer (which contains 50mM EDTA and 4M urea); (4) ethanol precipitation, 10% dPAGE inspection; (5) cut the uncut fragments, gel recovery, ethanol precipitation; (6) repeat ( 1-5) process, in which the extracellular fluid (or intracel...
Embodiment 3
[0228] Example 3 Amplify the screened nucleic acid probe
[0229] First, the first round of PCR was performed using the nucleic acid probes screened in Example 2 above as a template, and the PCR conditions were as follows:
[0230]
[0231] The thermal cycle process is as follows: 94 degrees Celsius for 1 min (denaturation); 14 cycles of 94 degrees Celsius for 30 seconds, 56 degrees Celsius for 45 seconds, and 72 degrees Celsius for 45 seconds; the final 72 degrees Celsius is extended by 1 minute.
[0232] Then, the PCR product of the first round of PCR is used as a template for the second round of PCR, and the conditions for the second round of PCR are as follows:
[0233]
[0234] The thermal cycling process is the same as the first round of PCR, except that the number of cycles is increased to 17 cycles.
[0235] The product of the second round of PCR was recovered, and the recovered product was used as a molecular library, and molecular probes were prepared according to the method o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com