Manufacturing method for PMOS transistor and manufacturing method for NMOS transistor
A manufacturing method and transistor technology, applied in the direction of transistors, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as slow carrier mobility, improve process compatibility, improve migration rate, increase compressive stress or tension The effect of stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] In this embodiment, two stacked stepped sigma-shaped grooves are taken as an example to describe the manufacturing method of the PMOS transistor in detail.
[0048] Figure 1 to Figure 8 is a cross-sectional view of a PMOS transistor at different fabrication stages in an embodiment of the present invention, which will be combined below Figure 1 to Figure 8 The production method will be described in detail.
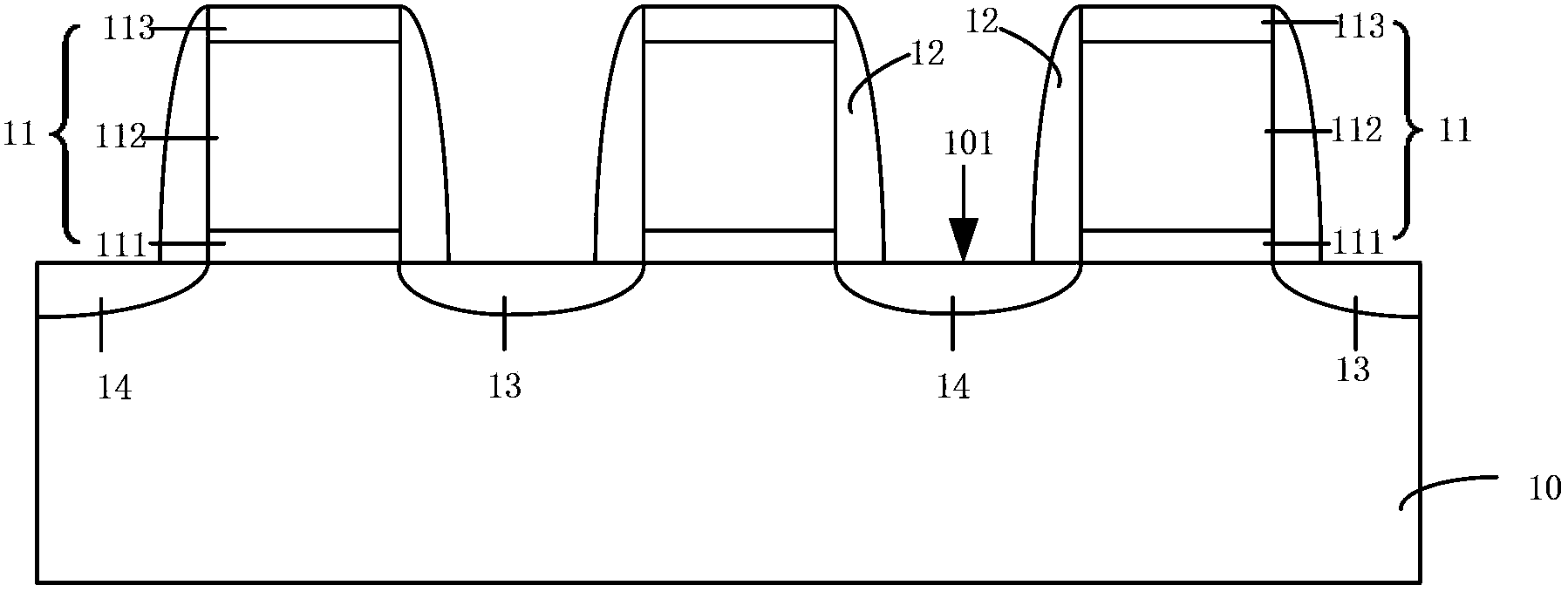
[0049] Step S1 is first performed: provide a silicon substrate, and form a gate structure on the silicon substrate. The gate structure includes a gate dielectric layer formed on the silicon substrate and a gate electrode formed on the gate dielectric layer.
[0050] Such as figure 1 As shown, the substrate 10 is a single crystal silicon substrate having a surface 101 . A shallow trench isolation structure (Shallow Trench Isolation, STI for short) (not shown) may be formed in the substrate 10 to isolate active regions in the substrate 10 .
[0051] The gate struc...
Embodiment 2
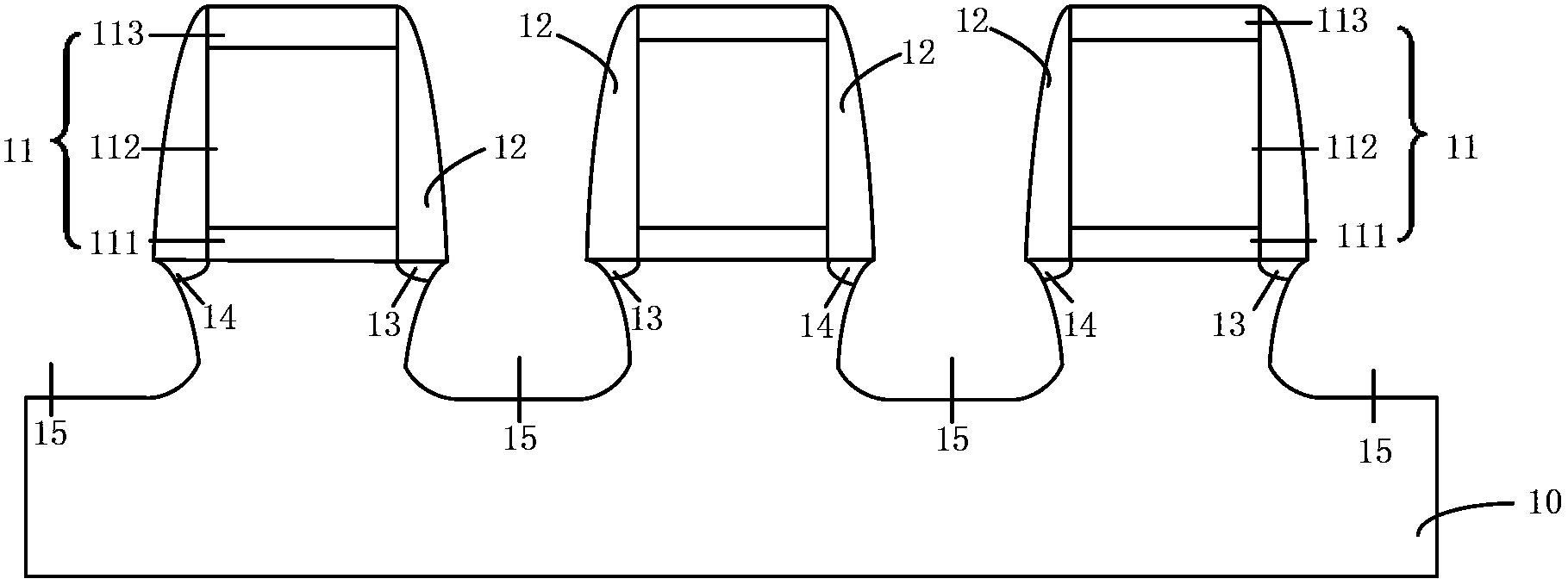
[0080] As described in Embodiment 1, a plurality of stacked sigma-shaped grooves deep into the silicon substrate are formed in the source and drain regions, and in the direction from the surface of the silicon substrate to the inside of the silicon substrate, each sigma-shaped groove The tip of the groove that goes deep into the channel tends to gradually move away from the channel. Filling such a plurality of stacked sigma-shaped grooves with silicon germanium material can increase the hole carrier mobility rate of the channel of the PMOS transistor.
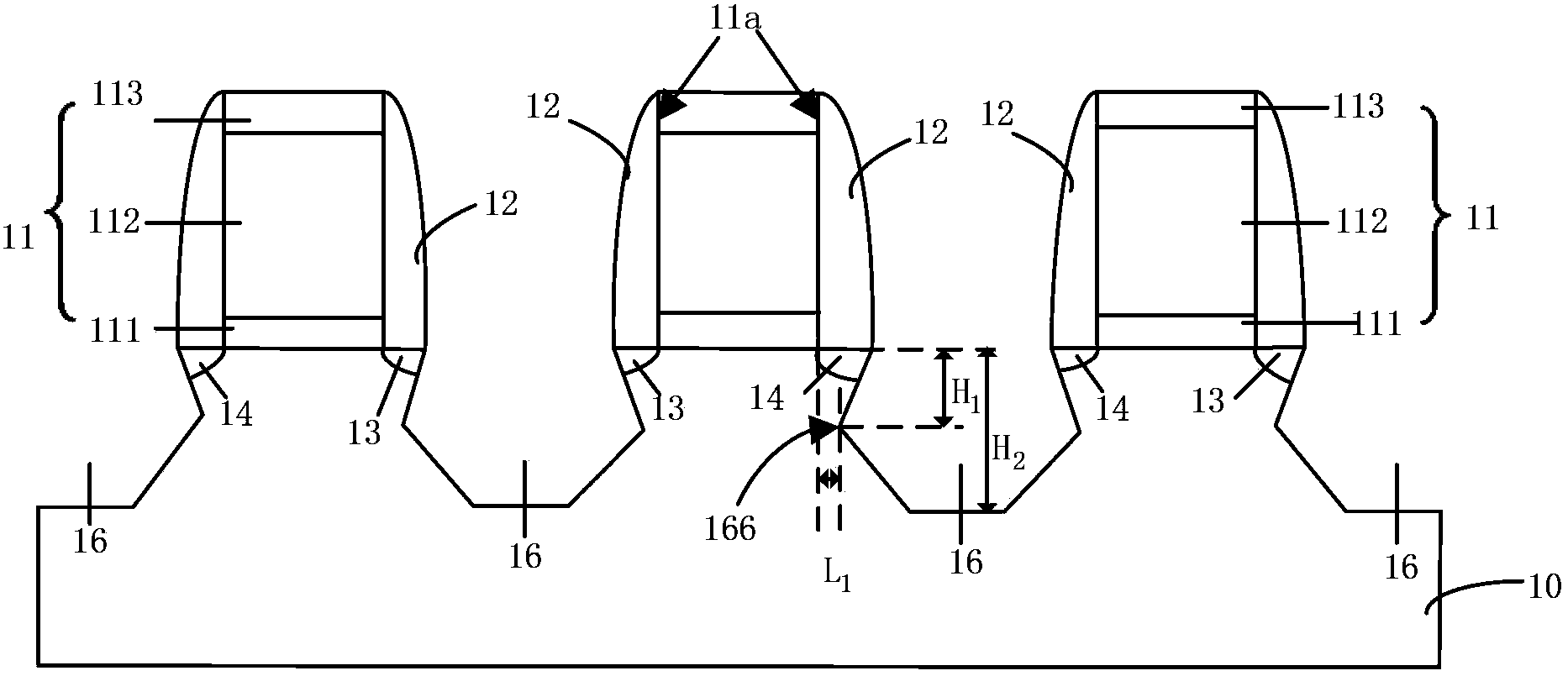
[0081] Based on the above inventive concept, the second embodiment proposes to form a third sigma-shaped groove in the silicon substrate at the bottom of the second sigma-shaped groove, and form a fourth sigma-shaped groove in the silicon substrate at the bottom of the third sigma-shaped groove. Groove, ... and so on, forming a stepped sigma-shaped groove in which a plurality of sigma-shaped grooves are stacked, and the distance...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The third embodiment provides an NMOS transistor and its formation method, except that silicon carbide is filled in multiple stacked stepped sigma-shaped grooves to apply tensile stress to the channel, and the rest of the method and structure are the same as those of the first to first embodiments above. The two are the same, by making the direction from the surface of the silicon substrate to the inside of the silicon substrate, the groove tip of each sigma-shaped groove deep into the channel is a stepped sigma-shaped groove that gradually moves away from the channel to improve the silicon carbide The filling amount of material to increase the mobility of electron carriers in the channel.
[0085] The process of filling silicon carbide into multiple stacked stepped sigma-shaped grooves refers to the existing process.
[0086] In the present invention, each embodiment adopts a progressive writing method, focusing on the differences from the foregoing embodiments. For th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com