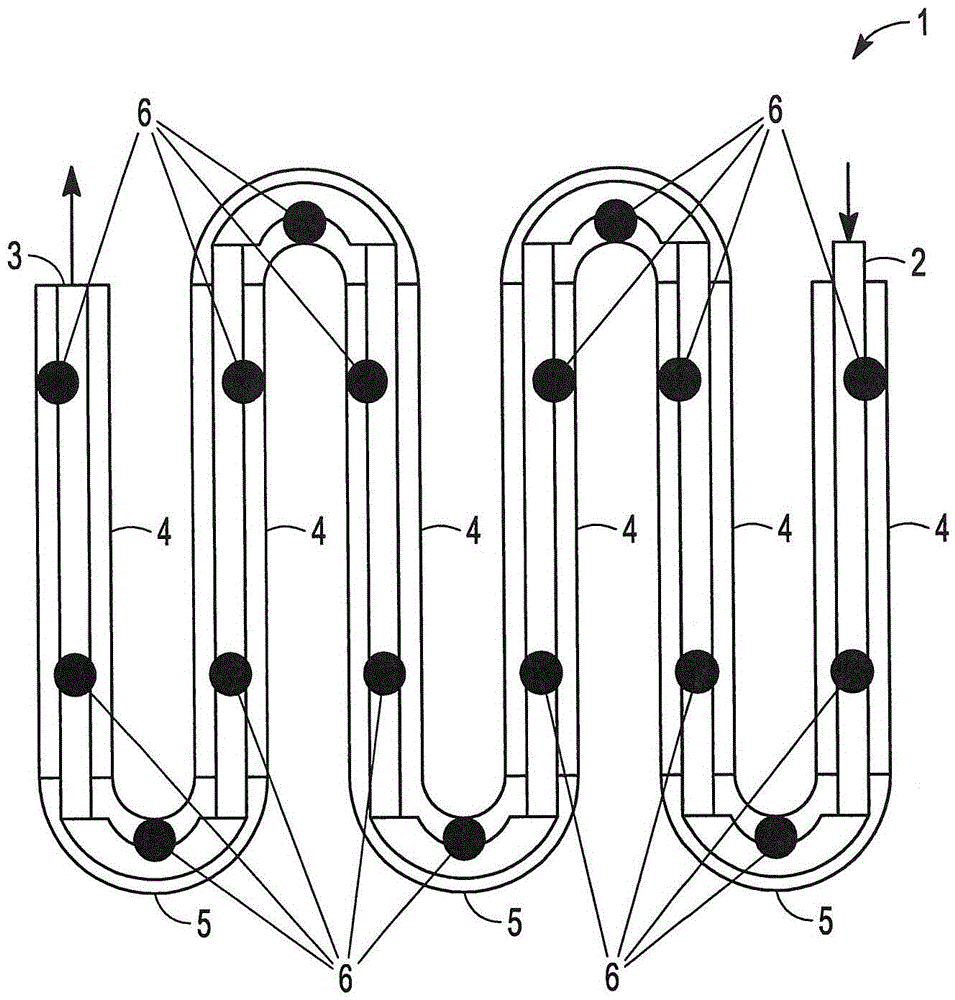
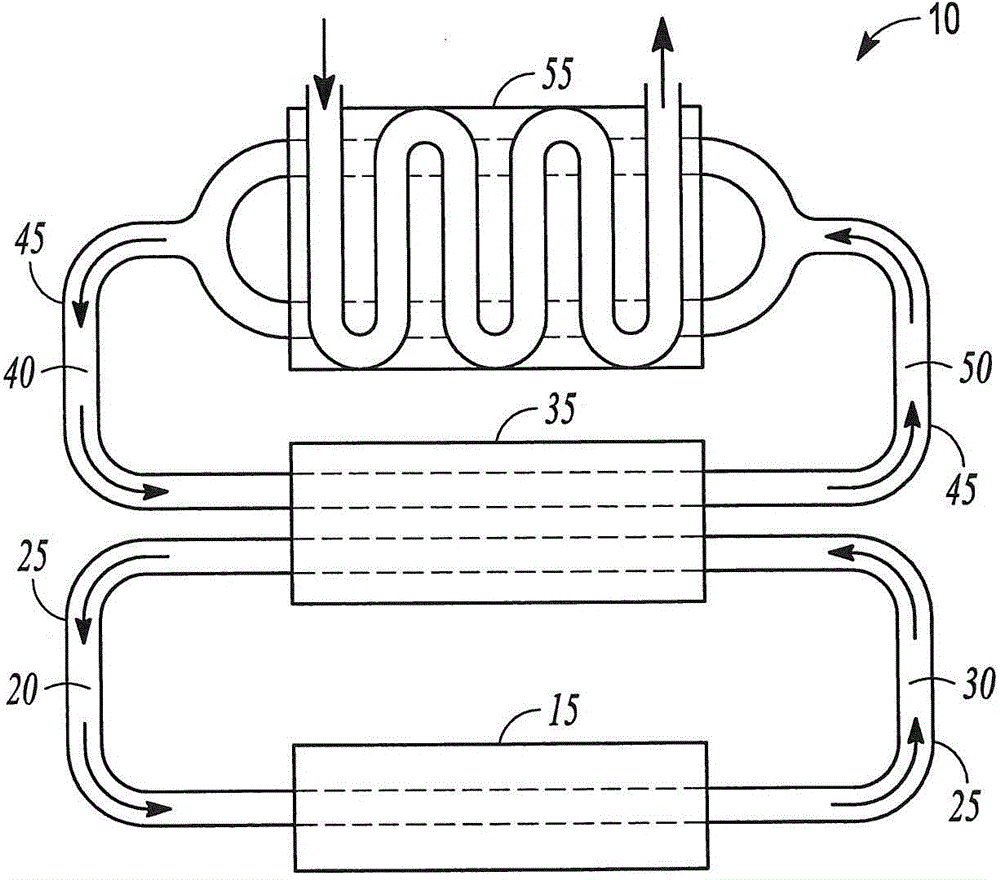
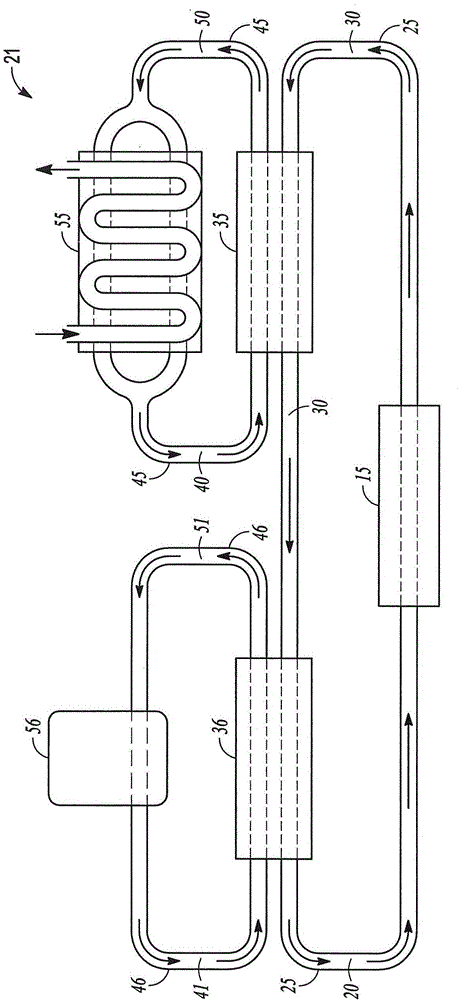
Tubular reactor with improved design and method of using the same
A tubular reactor and pipeline technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, chemical/physical/physicochemical fixed reactors, methods for chemically changing substances using atmospheric pressure, etc., can solve the problems of fire, efficiency loss, and Convenience and other issues to achieve the effect of low risk of combustion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1a
[0111] Example 1a. Comparative Example. Liquid Phase Heat Transfer Medium in Primary Heating Loop
[0112] Will 66 is heated to approximately 340°C and circulated through a primary heating loop in a nylon-6,6 manufacturing facility. The primary heating circuit will 66 at a suitable flow rate between the power chamber and the heat exchangers on the evaporator, reactor and finisher, after which the 66 is passed back to the powerhouse for reheating. Use about 10,000,000L in the primary heating circuit 66. 66 remains liquid throughout the process.
[0113] In the continuous nylon-6,6 manufacturing process, adipic acid and hexamethylenediamine are mixed in water in an approximately equimolar ratio to form an aqueous mixture containing nylon-6,6 salt, and the aqueous mixture has about 50 % by weight water. The brine solution was delivered to the evaporator at approximately 105 L / min. transfer heat from the primary heating circuit to the 66 is passed to the evaporato...
Embodiment 1b
[0116] Example 1b. Comparative Example. Vapor Phase Heat Transfer Medium in Primary Heating Loop
[0117] will DOWTHERM TM A is heated to a vapor at about 340°C and a pressure of about 400KPa and circulated through a primary heating loop between the powerhouse and the multiple unit operations in a nylon-6,6 manufacturing facility, where it transfers heat to the multiple unit operations, after which Transfer back to the powerhouse for reheating. Use approximately 10,000,000L of DOWTHERM in the primary heating circuit TM a. DOWTHERM TM A is maintained as a vapor throughout the process and is circulated at a rate sufficient so that the material does not drop below the saturation temperature in circulation.
[0118] The continuous nylon-6,6 manufacturing process was carried out as described in Example 1a, but using vapor DOWTHERM throughout the process TM a. DOWTHERM per Kg compared to other methods using heat transfer materials that undergo a phase change during heat t...
Embodiment 1c
[0119] Example 1c. Comparative Example. Volatile Heat Transfer Medium in Primary Heating Loop with Condensation
[0120] As in Example 1b, but using DOWTHERM with a certain cycle rate TM A so that during heat transfer to multiple unit operations from DOWTHERM TM A absorbs enough heat to cause DOWTHERM in the primary heating loop TM Part of A condenses. To recycle the liquid produced to the rest of the unit operations and back to the powerhouse, additional equipment is required, including a liquid knock out tank, additional piping and pumps to return the condensate to the powerhouse for reheating and regasification. Maintaining precise temperature for each unit operation such as a tubular reactor is difficult because the temperature of the heat transfer medium can only be adjusted as a whole and not for individual units.
[0121] Example 1d. Comparative Example. Volatile Heat Transfer Medium in Leaky Primary Heating Loop
[0122] As in Example 1b. There is a leak in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com