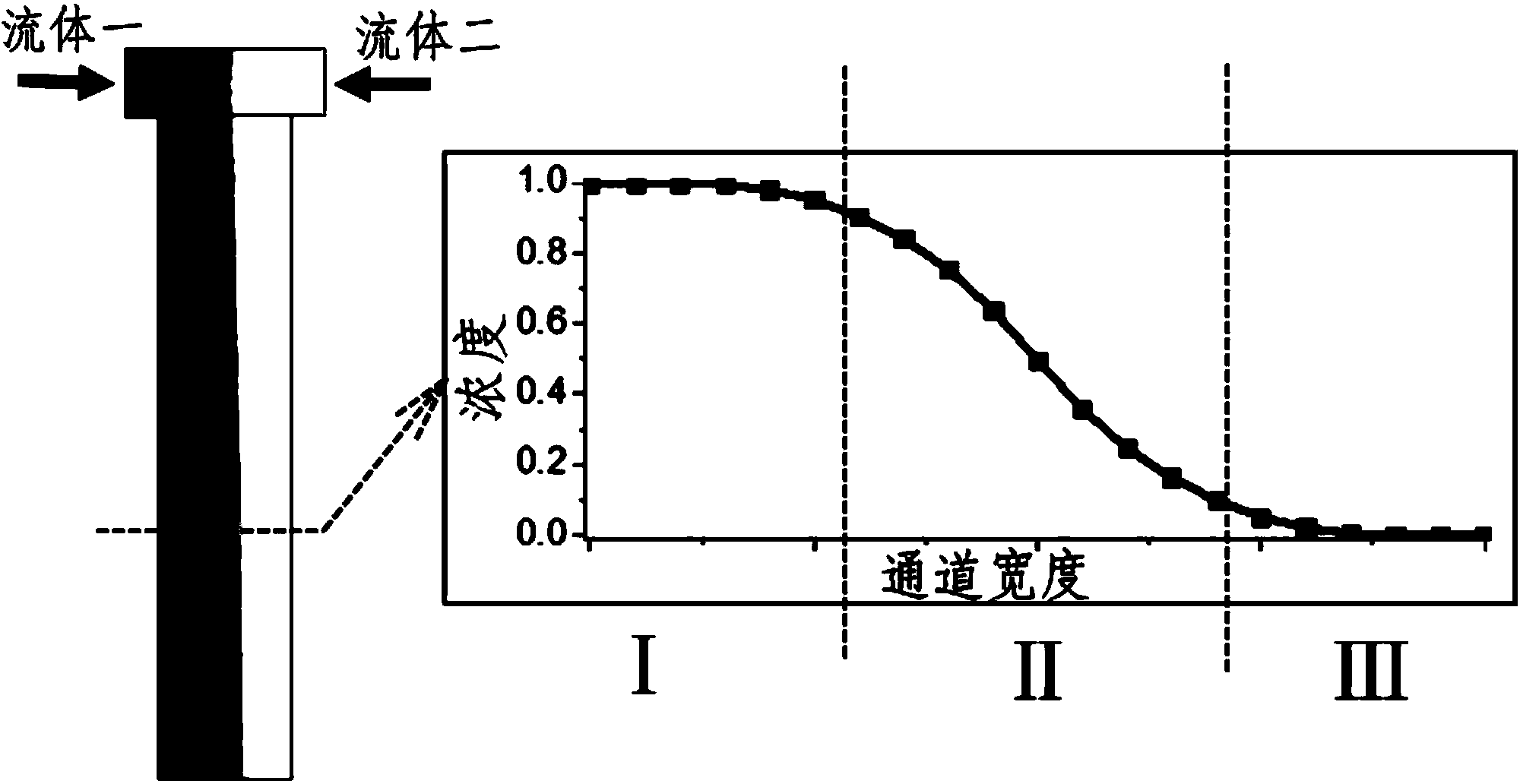
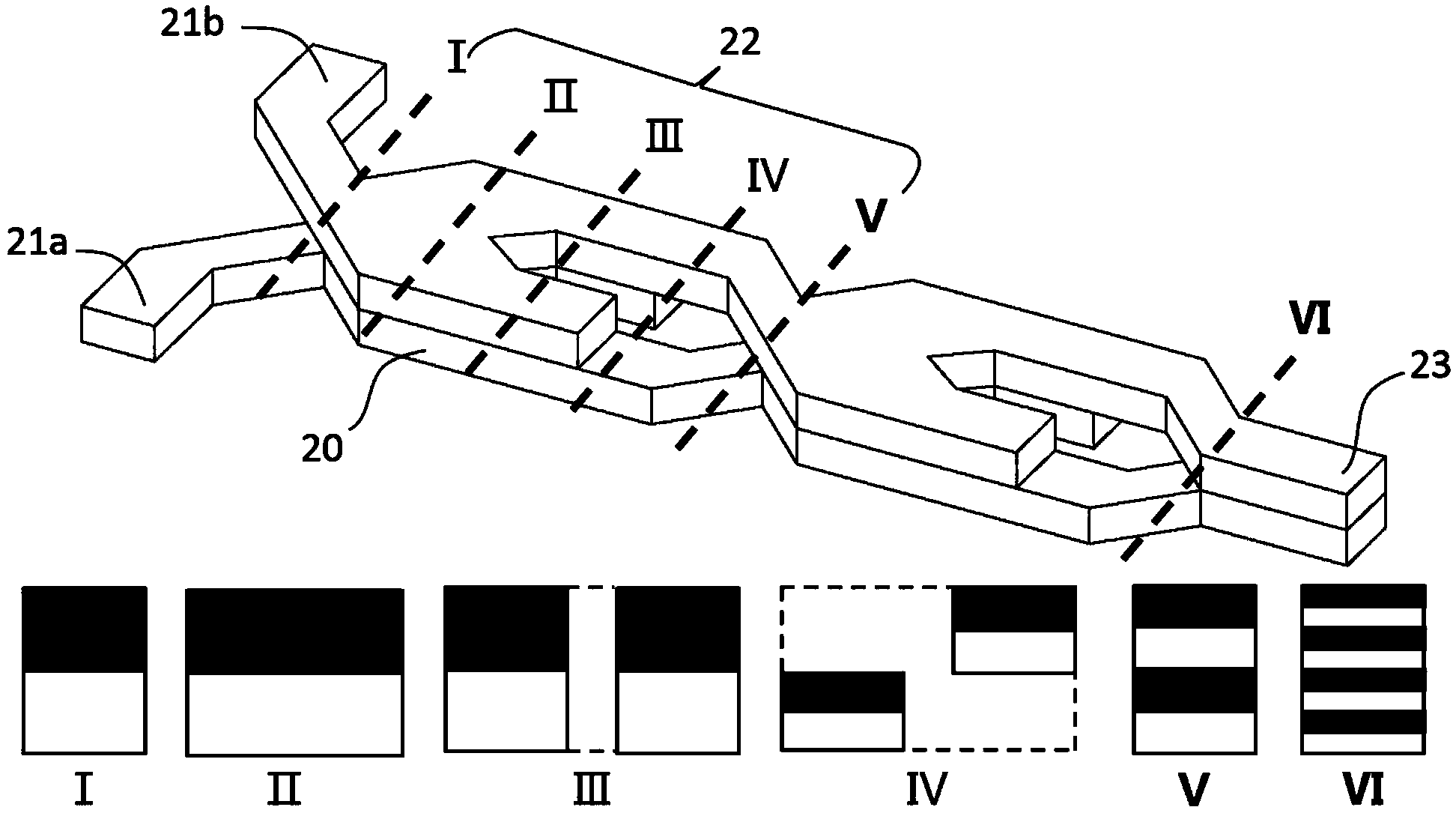
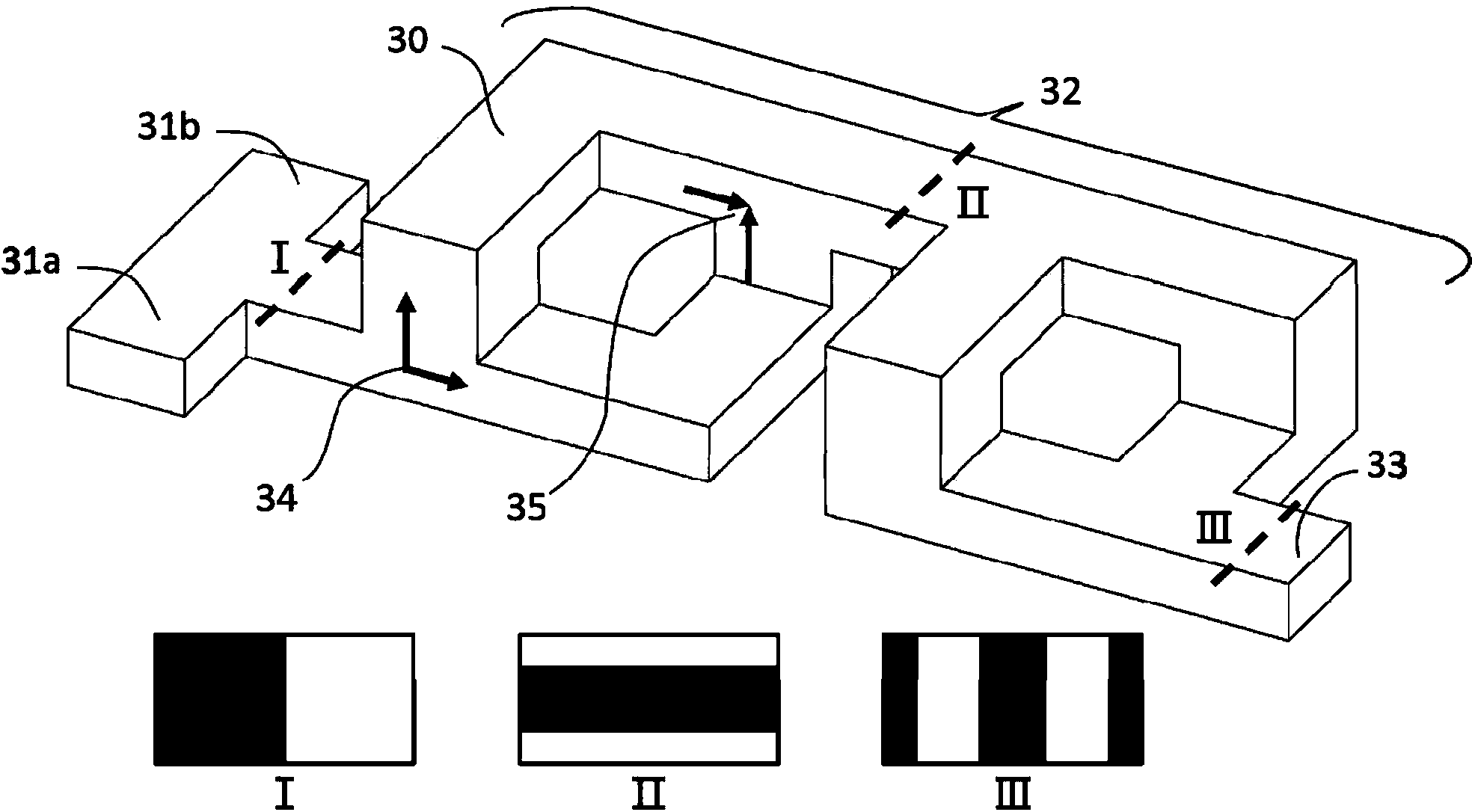
Split and recombined passive micromixer with bridge-type structure
A bridge structure and mixer technology, applied in mixers, laboratory containers, laboratory utensils, etc., can solve the problems of limited effective working Reynolds number range, inability to effectively mix fluids, etc., to increase the contact area. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0052] It is characterized in that: the number of mixing units is selected to be 3; the thickness of the lower layer structure (51) is about 3 mm, and the square-wave channel (44) on it is 50 μm deep, L 1 ==W 1 = 100 μm; the middle layer structure (52) is 50 μm thick, and the size of the 8 through holes (45a) on it is L2=80 μm, W2=40 μm; the upper layer structure (53) is about 3 mm thick, and The 4 inclined channels (45b) are 50 μm deep.
Embodiment 3
[0054] It is characterized in that: the number of mixing units is selected to be 6; the thickness of the lower structure (51) is about 3 mm, and the square-wave channel (44) on it is 50 μm deep, L 1 ==200μm, W 1 = 100 μm; the middle layer structure (52) is 20 μm thick, and the size of the 8 through holes (45a) on it is L2=200 μm, W2=60 μm; the upper layer structure (53) is about 3 mm thick, and The 4 inclined channels (45b) are 30 μm deep.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com