A method for detecting whether a protein disulfide bond is broken
A protein and disulfide bond technology, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
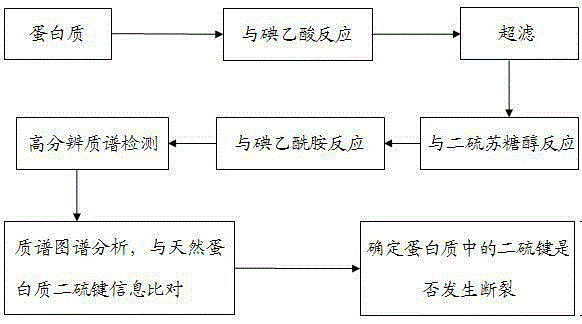
[0033] 1. Reaction of protein free sulfhydryl groups with iodoacetic acid
[0034] (1) Preparation of protein solution: dissolve with 50mM ammonium bicarbonate solution to obtain 1.0mg / ml protein solution;
[0035] (2) Preparation of iodoacetic acid solution: prepare 100mM iodoacetic acid solution with ultrapure water;
[0036] (3) Reaction of protein free sulfhydryl groups with iodoacetic acid: mix 10 μl protein solution with 3 μl iodoacetic acid solution, mix well, and place in the dark for 30 minutes;
[0037] (4) Remove iodoacetic acid that did not participate in the reaction: Use a 3000Da ultrafiltration centrifuge tube to remove excess iodoacetic acid that did not participate in the reaction.
[0038] 2. Dithiothreitol breaks protein disulfide bonds
[0039] (1) Dithiothreitol solution preparation: prepare 100mM dithiothreitol solution with ultrapure water;
[0040] (2) Dithiothreitol breaks protein disulfide bonds: add 2 μl of dithiothreitol solution to the protein s...
Embodiment 2
[0056] 1. Reaction of protein free sulfhydryl groups with iodoacetic acid
[0057] (1) Preparation of protein solution: dissolve with 100mM ammonium bicarbonate solution to obtain 1.0mg / ml protein solution;
[0058] (2) Preparation of iodoacetic acid solution: prepare 100mM iodoacetic acid solution with ultrapure water;
[0059] (3) Reaction of protein free sulfhydryl groups with iodoacetic acid: mix 20 μl protein solution with 3 μl iodoacetic acid solution, mix well, and place in the dark for 30 minutes;
[0060] (4) Remove iodoacetic acid that did not participate in the reaction: Use a 2000Da ultrafiltration centrifuge tube to remove excess iodoacetic acid that did not participate in the reaction.
[0061] 2. Dithiothreitol breaks protein disulfide bonds
[0062] (1) Dithiothreitol solution preparation: prepare 100mM dithiothreitol solution with ultrapure water;
[0063] (2) Dithiothreitol breaks protein disulfide bonds: add 2 μl of dithiothreitol solution to the protein ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com