City smart power grid planning method on basis of land conversion risk
A smart grid and land technology, applied in the direction of instruments, data processing applications, information technology support systems, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to popularize and apply, unreasonable planning schemes, difficult planning schemes, economic value and investment efficiency, etc., to improve accuracy , optimization evaluation model, and scientific and reasonable effect of power grid planning scheme
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0056] The preferred embodiments will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. It should be emphasized that the following description is only exemplary and not intended to limit the scope of the invention and its application.
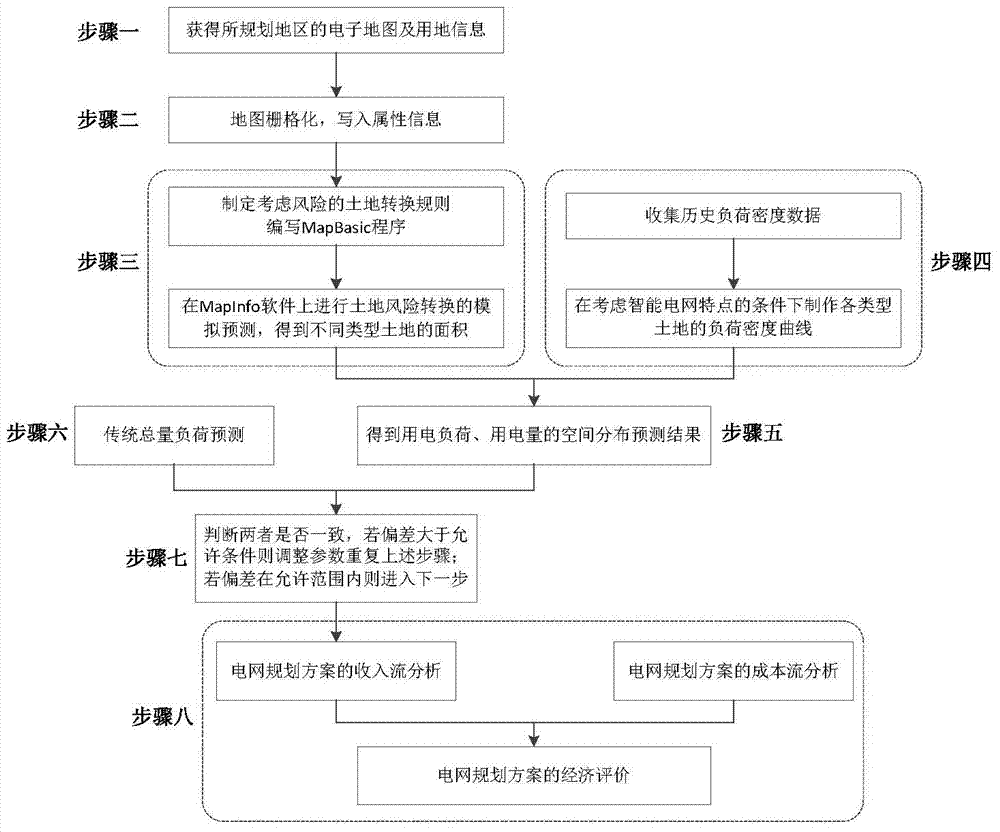
[0057] Such as figure 1 Shown, the realization of the present invention comprises:
[0058] Step 1: Obtain the electronic map of the planning area, as well as the current land use information and future urban land use planning of all areas in the map. These information include: the current use type of different blocks of land, the use period, and the land after 5 years Whether it is included in urban land planning, the type of use planned, etc.
[0059] Step 2: Perform rasterization processing on the electronic map to obtain a raster map, and assign current land use information as attribute information to each raster. Specifically divided into:
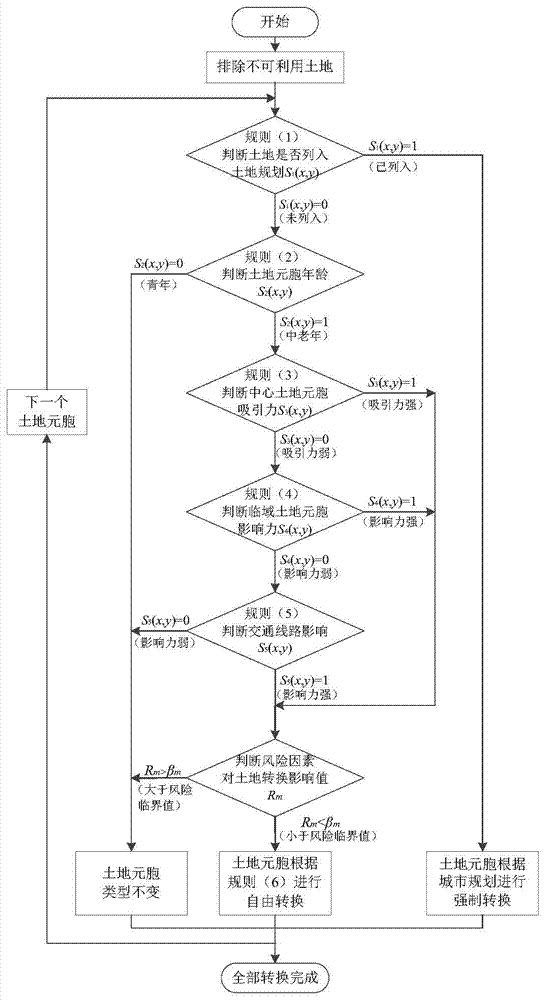
[0060] (1) Using MapInfo software to preprocess the electronic map of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com