Distributed harmonic source identification method based on single-frequency current transmission characteristics
A technology of current harmonics and transmission characteristics, applied in the field of distributed harmonic source identification based on single-frequency AC current transmission characteristics, can solve the problem of affecting the accuracy of harmonic source identification, increasing the complexity of algorithms, and lacking the magnitude and order of admittance matrix Effective supervision and other issues to achieve reliable parameter basis and improve accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
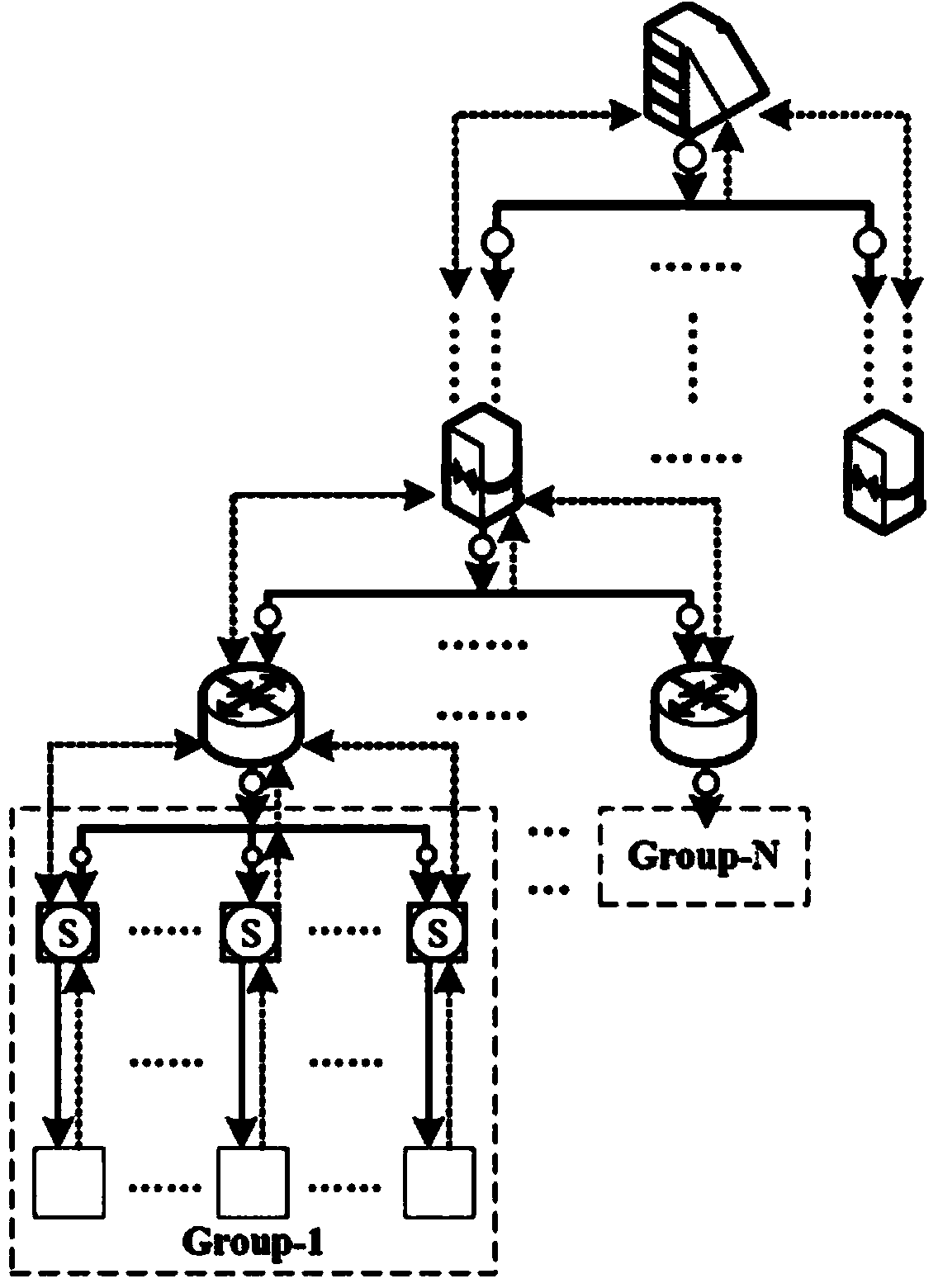
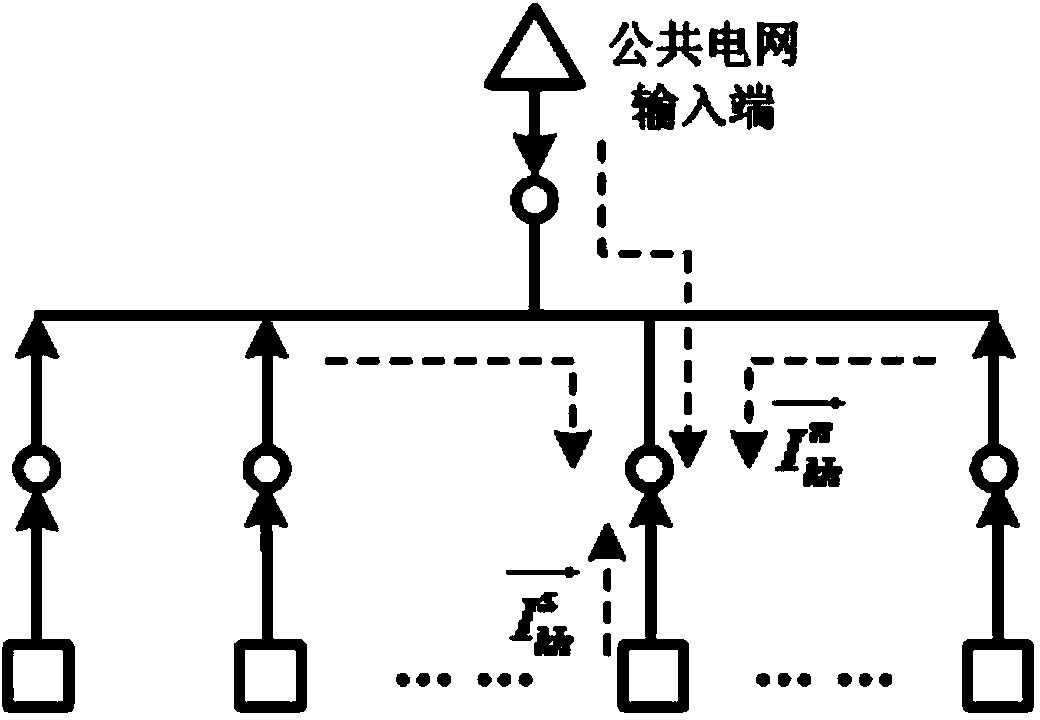
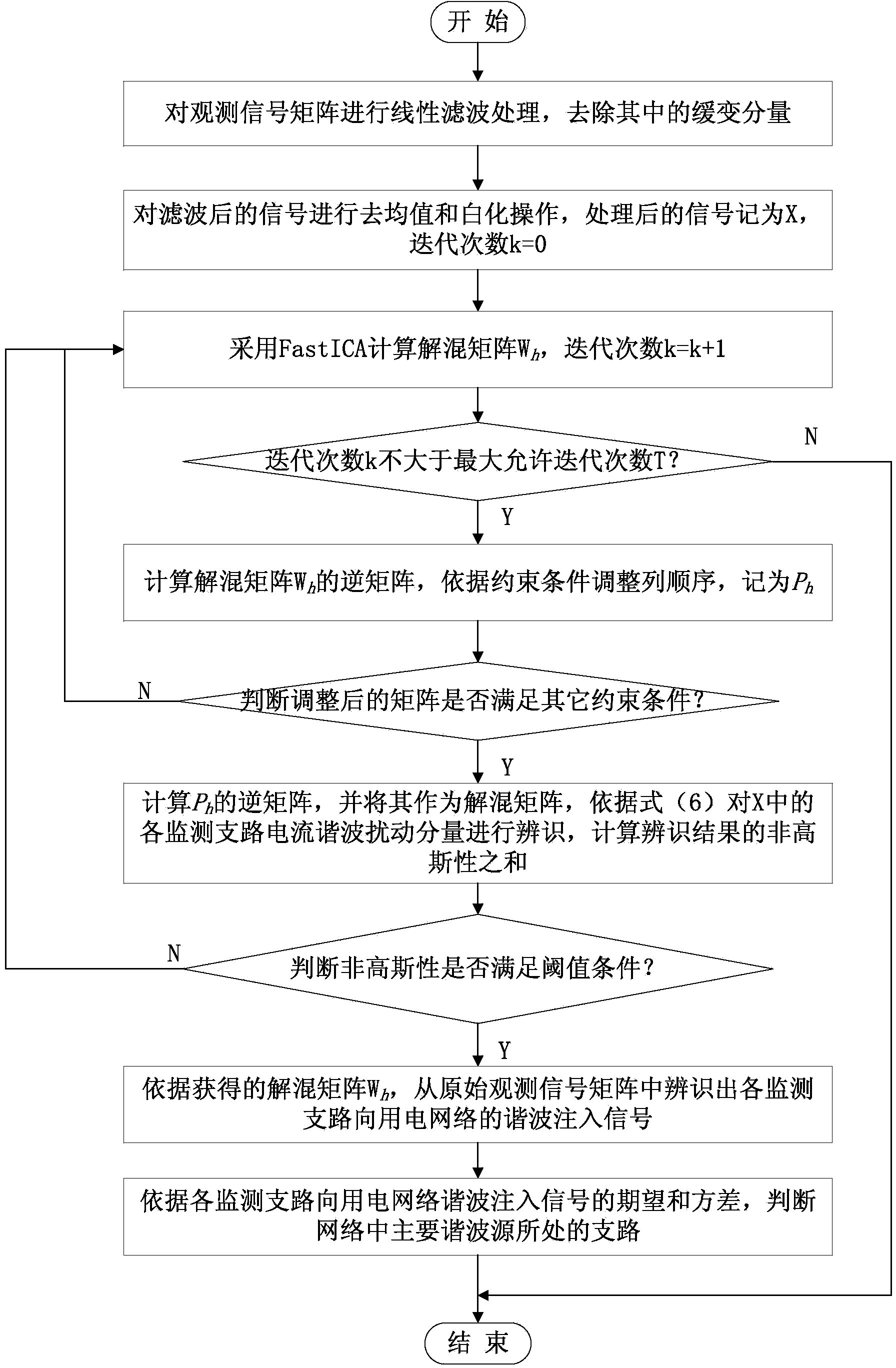
[0025] Harmonic source identification in the power consumption network refers to the analysis of the voltage harmonics and current harmonics collected by the power information sensing nodes in the network to obtain the actual harmonic injection amount of each branch monitoring object to the power consumption network, and then Realize the identification and analysis of harmonic sources in the power network and the division of disturbance responsibilities. In the actual measurement, the harmonic disturbance measured by the sensing node on the branch mainly includes two parts. One is the harmonic generated by the nonlinear equipment on the monitoring branch, which is called the internal harmonic, which reflects the impact of the branch on the entire user. The impact of the power network is also the target signal for harmonic source identification and analys...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com