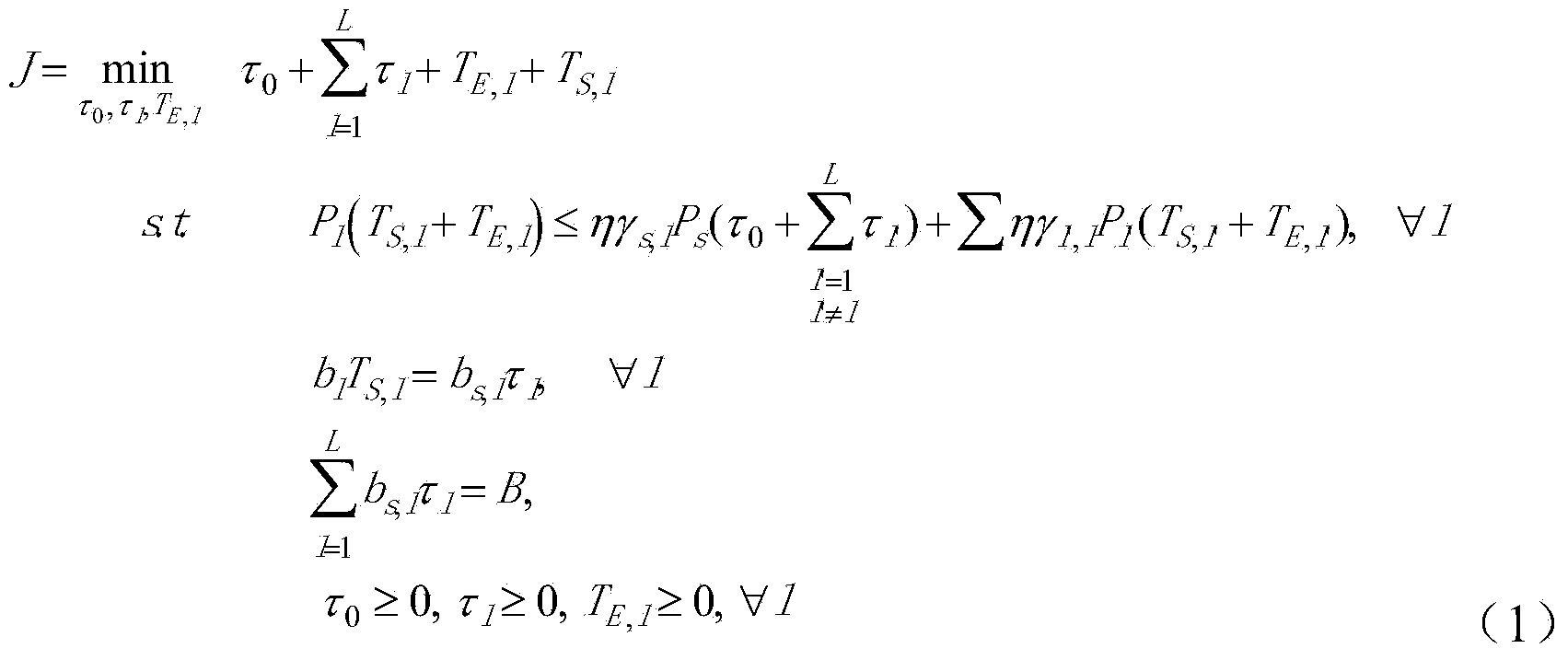Wireless energy and data combined transmission method
A technology of joint transmission and wireless energy, applied in the field of wireless communication, can solve the problems of large transmission rate, short transmission time, unconsidered, etc., and achieve the effect of large transmission rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
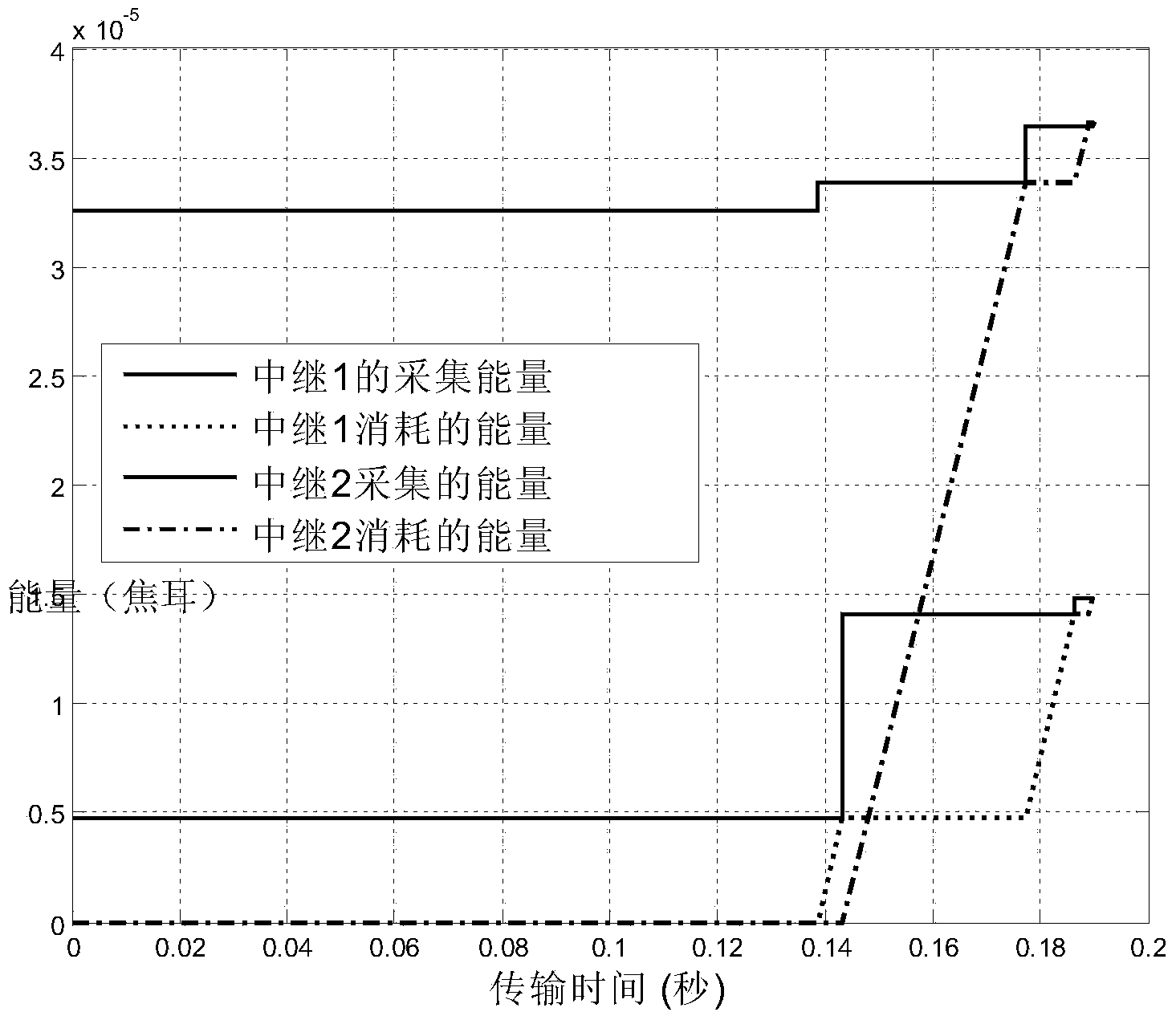
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, consider a two-hop network composed of 1 source node, 2 relay nodes and 1 destination node (the relay node is equipped with a radio frequency signal energy acquisition circuit and a signal decoding circuit). For a given set of channel gains, we can calculate the optimal time allocation τ 0 =0.09s,τ 1 =0.02s,τ 2 =0.03s. In the entire sending process, the source node first broadcasts energy to relay 1 and relay 2 in 0.09s; in the time period of 0.09-0.11, the source node sends data to relay node 1, and relay node 2 opportunistically Energy is collected from the signal; within the time period of 0.11-0.14, the source node sends data to the relay node 2, and the relay node 1 opportunistically collects energy from the radio frequency signal. In the relay transmission stage, the transmission sequence is (relay 1, relay 2). It can be seen from the figure that the relays 1 and 2 each go through two transmissions before forwarding all the data to the d...
example 2
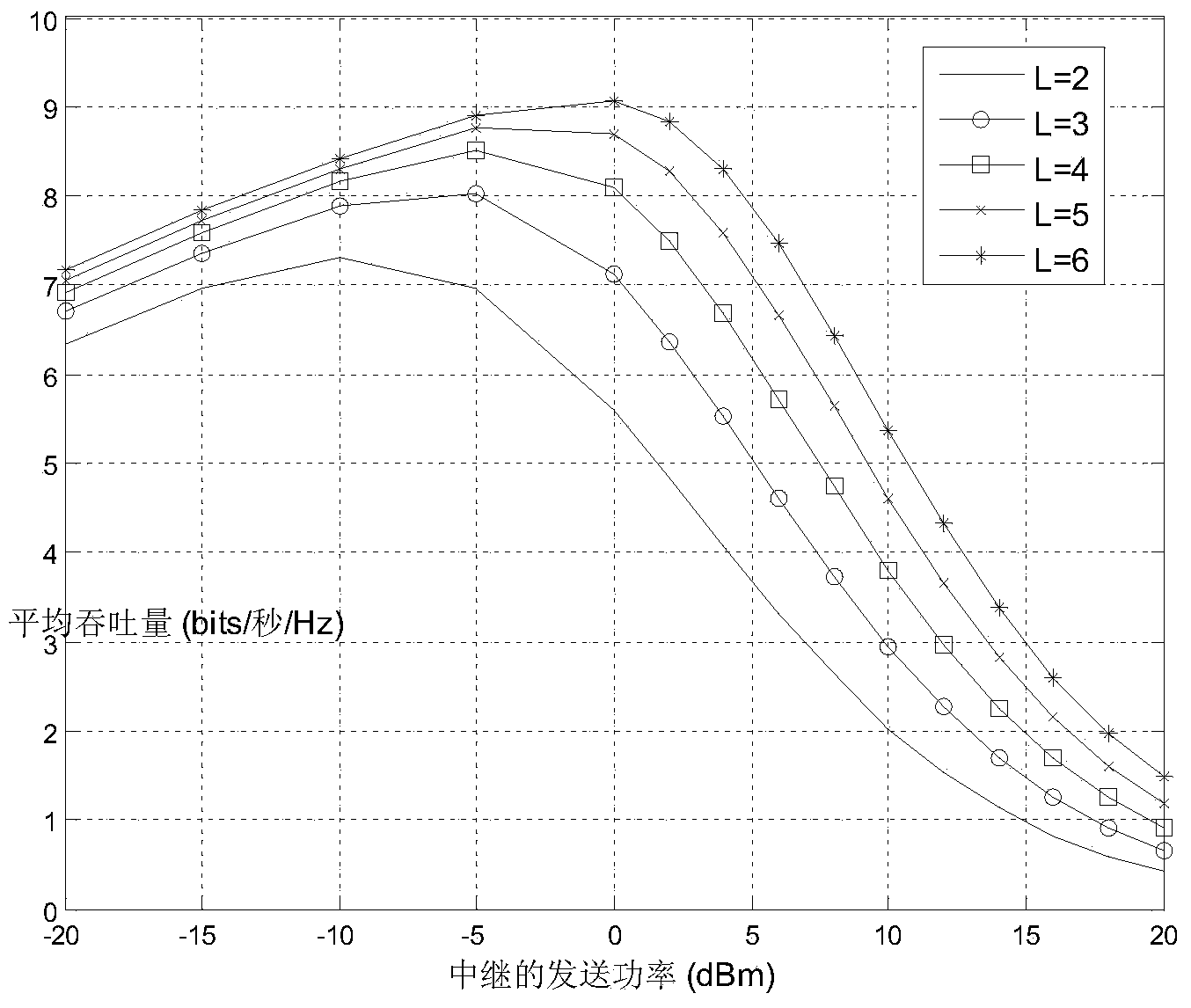
[0035] In this experiment, the signal bandwidth is 10MHz, the power spectral density of the receiver noise is -170dBm / Hz, and the conversion efficiency of the energy harvesting circuit is 0.7. The distance between the source node and the destination node is 6m. Source node transmit power P s = 100mW.
[0036] Such as figure 2 Shown: the relationship between the transmission power of the relay node and the average throughput. In the proposed transmission scheme, the total transmission time includes the energy receiving time of the relay node, the data receiving data of the relay node, and the data sending time of the relay node. The greater the transmitting power of the relay node, the shorter the data transmission time of the node, but the correspondingly longer energy collection time is required. From the figure, we can find the transmission power of the relay node that minimizes the total transmission time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com