Method for measuring axial heat conductivity of one-dimensional material
A measurement method and thermal conductivity technology, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of expensive equipment and complex optical signal process, and achieve the effect of reversible effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
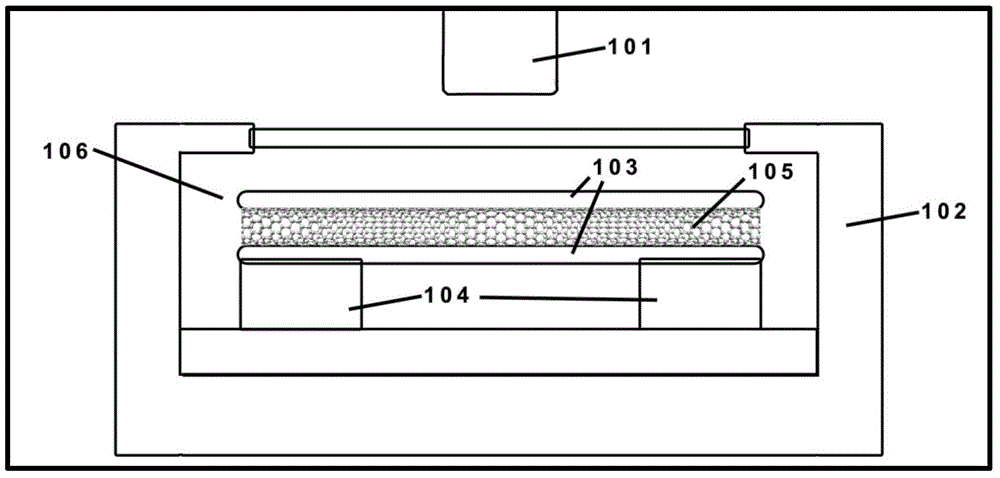
[0039] The "one-dimensional material" referred to in the present invention is a nano-scale one-dimensional material or a micron-scale one-dimensional material, wherein the nano-scale one-dimensional material includes nanowires, nanotubes, nanobelts, nanofibers or nanorods.
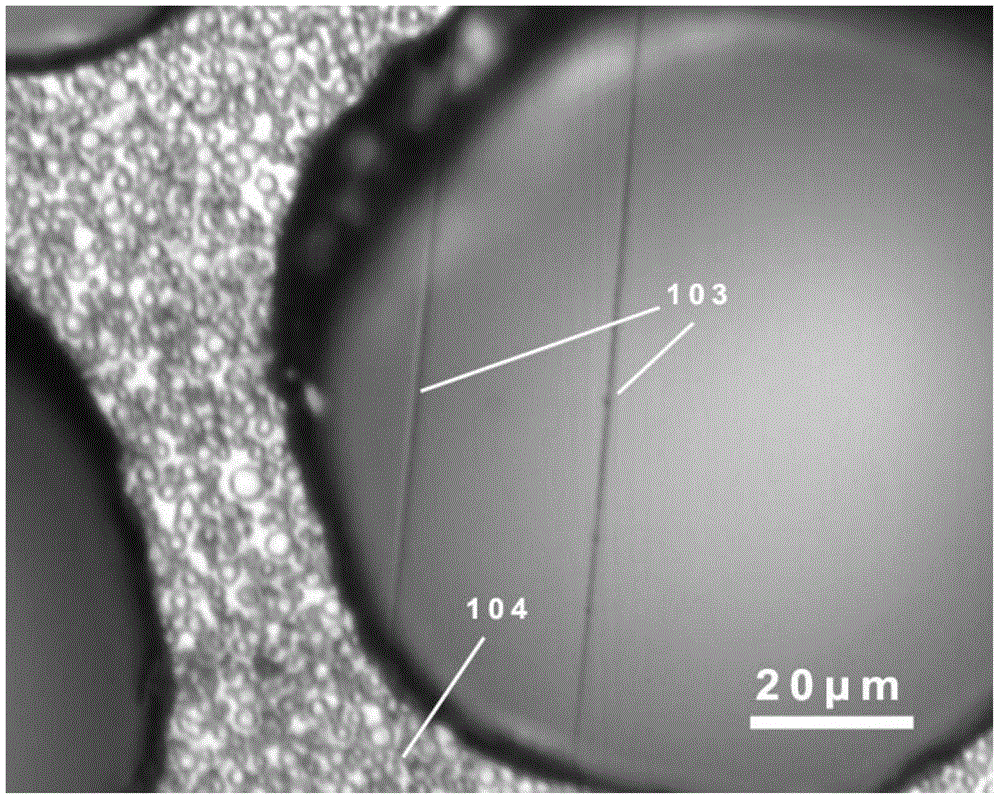
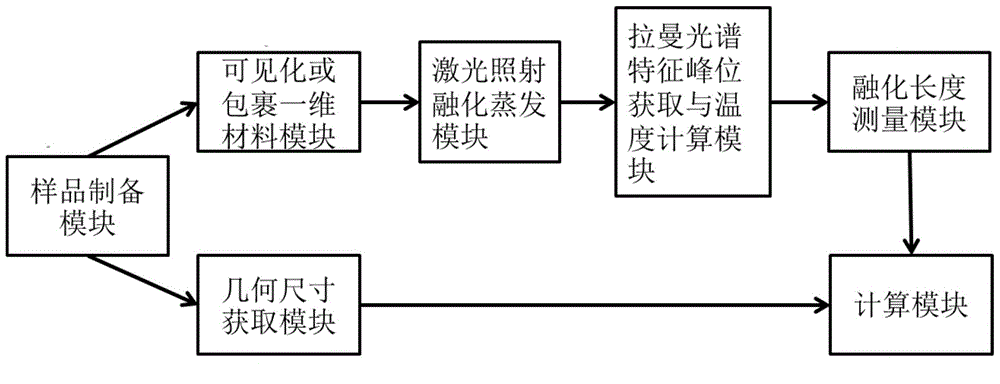
[0040] In order to solve the need for precise positioning accuracy when measuring the thermal conductivity of extremely small-sized one-dimensional materials, it is difficult to achieve small-sized detection accuracy and spatial accuracy with traditional infrared thermometers, and the macroscopic scale The contact of a temperature probe with a one-dimensional material is likely to cause a huge change in the temperature of the material itself. The invention provides a method for measuring the thermal conductivity of a one-dimensional material. The measuring method includes: forming a wrapped section and a bare section adjacent to the wrapped section on the one-dimensional material. Wherein, at the wrapping ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com