A large-scale quantitative inoculation identification method for wheat bushy dwarf resistance
A technology of wheat bush dwarf disease and identification method, which is applied in the field of large-scale quantitative and enhanced inoculation identification of wheat bush dwarf disease resistance, and achieves the effect of overcoming large-scale quantity acquisition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
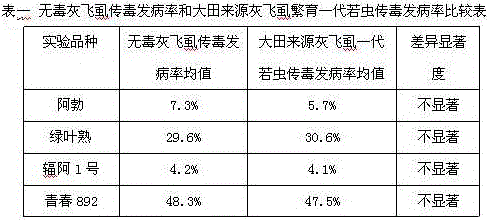
[0035] In June 2013, the frozen wheat diseased strains collected from the hardest-hit areas were used as the virus source, and this method was used for inoculation identification. During the same period, 1-2 instar non-toxic SBPH nymphs were used as controls, and other treatments were the same. The feeding time was set at 48 hours, and the inoculation intensity was 10 heads / plant. After the symptoms were manifested, the incidence of Cong'ao disease points was investigated.
[0036]
[0037] From the above examples and comparative examples, it can be seen that there is no significant difference in the incidence of bush dwarf disease of the four wheat varieties transmitted by field-sourced SBPH and non-toxic SBPH, indicating that the use of field-sourced SBPH to spread wheat Bush dwarf virus is not disturbed by heteroviruses carried by genetics.
[0038] At present, in the identification of wheat bush dwarf disease, the natural identification method cannot overcome the interf...
Embodiment 2
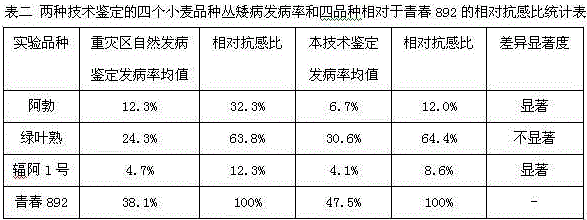
[0040] In 2013, four wheat varieties were identified by this method, and the four wheat varieties were also identified by the natural disease identification method in the severely affected areas of wheat bush dwarf disease, and the incidence of bush dwarf disease was calculated and the relative resistance of other varieties relative to Qingqing 892 was calculated. Compare.
[0041]
[0042] By comparing the incidence of wheat bush dwarf disease identified by this method with that of natural occurrence in the hardest-hit area, and the relative resistance-sensitivity ratio performance relative to Qingqing 892, it can be found that the results of different varieties of wheat identified by this technology are compared with the relative resistance of natural-onset identification in the hardest-hit area. The ratios are not the same, and the individual varieties have significant differences, which may be caused by the differences in row tendency among wheat varieties.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com