A large-scale inoculation identification method for maize rough dwarf resistance
A technology of maize rough shrinkage disease and identification method, which is applied in the fields of horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, etc., can solve the problems such as the tendency of expulsion to interfere with the acquisition of the large-scale quantity of S. streus Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] According to the identification method provided by the present invention, the frozen diseased rice plants taken from the hardest-hit areas are used as the source of the virus, and the nymphs of the first generation of SBPH from the field are inoculated, and the 2nd instar SBPH nymphs are transplanted into the seedlings of different corn varieties after feeding the poison for 48 hours. (Xianyu 335, Nongda 108, Denghai 3622, Jinhai 5, and Zhengdan 958) were inoculated in the insect co-incubation box, the inoculation intensity was 7 heads / plant, and the corn seedlings were sown in the insect-proof net room after 15 days of breeding ; In the same period, 1-2 instar non-toxic SBPH nymphs (from the Zhou Tong Laboratory of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences) were used as a comparison example. After 2 days of poisoning, the worms were moved into seedlings of different corn varieties (Xianyu 335, Nongda 108, Denghai 3622, Jinhai 5 and Zhengdan 958) were inoculated in the in...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2 Using this method to identify the incidence of corn rough dwarf disease that occurs naturally in the hardest-hit areas
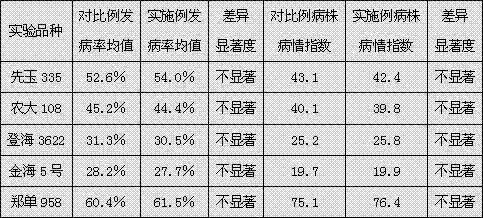
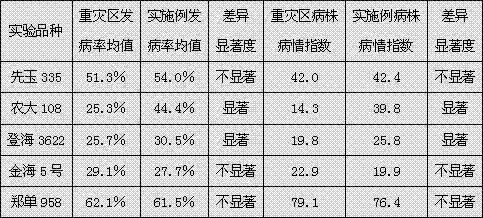
[0041] Adopt the large-scale enhanced inoculation identification method provided by the present invention, according to the ratio of 10 worms / strain, respectively inoculate corn varieties such as Xianyu 335, Nongda 108, Denghai 3622, Jinhai 5 and Zhengdan 958 with poisonous 2nd instar SBPH The nymphs, the statistical results of field-specific symptoms of the above-mentioned corn varieties to be tested and the statistical results of the incidence of corn rough dwarf disease in the hardest-hit areas during the same period are shown in Table 2.
[0042] Table 2 Statistical table of corn varieties to be tested and the incidence of corn rough dwarf naturally occurring in the hardest-hit areas during the same period
[0043]
Embodiment 3
[0045] Example 3 Differential identification of row tropism of different maize varieties
[0046] In order to verify whether the difference in disease resistance between the results of this technical identification speculated in Example 2 and the natural disease identification in the hardest-hit area is caused by the difference in the row-taxis of different corn varieties, we have done the following experiments on the row-taxis identification of different varieties .
[0047] The corn varieties such as Xianyu 335, Nongda 108, Denghai 3622, Jinhai 5 and Zhengdan 958 were sown on seedling trays respectively, and different corn varieties were sown in the same tray, with 10 plants for each variety in the same tray. A total of 10 trays were planted to replicate. Sow seeds at the first-generation SBPH adult initiation stage and inoculate SBPH at the one-leaf-one-core stage of corn. The seedling trays are placed in a quiet greenhouse for cultivation. The cultivation temperature is c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com